• •
收稿日期:2025-11-03
修回日期:2025-12-24
出版日期:2026-02-02
通讯作者:
刘迎文
作者简介:戴浩(1997—),男,博士研究生,haodai88888@126.com
基金资助:
Hao DAI1,2( ), Yi LIU3, Yingwen LIU1,2(
), Yi LIU3, Yingwen LIU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-11-03
Revised:2025-12-24
Online:2026-02-02
Contact:
Yingwen LIU
摘要:
针对高热通量、高集成度电子设备的散热需求,提出一种基于相变悬浮液射流冲击覆盖多孔介质受热面的强化冷却方案。通过数值方法研究了射流流体和构型、多孔介质孔隙率、孔径以及不同射流速度与悬浮液质量分数对散热性能的影响,并与裸板冷却模式进行了对比。研究发现,相对于水,在相同射流速度下,相变悬浮液在射流冲击裸板模式下的壁面温度升高、传热系数降低。当孔隙率和孔径较小时,倒梯形与三角形射流模式具有更高的平均传热系数;而在孔隙率和孔径较大时,矩形与倒梯形射流模式的平均传热系数更高。在低速、高质量分数条件下,倒梯形射流构型的平均传热系数高于三角形构型;但在高速、低质量分数条件下,三角形构型反而更具优势。这些发现可为利用相变悬浮液的冷却系统设计提供有价值的指导。
中图分类号:
戴浩, 刘燚, 刘迎文. 相变悬浮液射流冲击变形状多孔层覆盖壁面的热分析[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251211.
Hao DAI, Yi LIU, Yingwen LIU. Thermal analysis of phase change suspension jet impinging on wall surface covered with variable-shape porous layer[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251211.
| 物性 | 水 | 相变微胶囊 | 相变悬浮液(cm = 5%) | 相变悬浮液(cm = 10%) | 相变悬浮液(cm = 15%) | 相变悬浮液(cm = 20%) | 钢 | 铜 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ (kg·m-3) | 981.3 | 867.2 | 974.9 | 968.6 | 962.3 | 956.1 | 8030 | 8978 |
| Cp (J·kg-1·K-1) | 4189 | 1899 | 4075 | 3960 | 3846 | 3731 | 502.48 | 381 |
| λ (W·m-1·K-1) | 0.643 | 0.1643 | 0.608 | 0.5744 | 0.5426 | 0.5121 | 16.27 | 387.6 |
| μ (kg·m-1·s-1) | 5.98×10-4 | – | 6.98×10-4 | 8.37×10-4 | 1.04×10-3 | 1.34×10-3 | – | – |
表1 相关材料的热物理性质
Table 1 Thermophysical properties of related materials
| 物性 | 水 | 相变微胶囊 | 相变悬浮液(cm = 5%) | 相变悬浮液(cm = 10%) | 相变悬浮液(cm = 15%) | 相变悬浮液(cm = 20%) | 钢 | 铜 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ (kg·m-3) | 981.3 | 867.2 | 974.9 | 968.6 | 962.3 | 956.1 | 8030 | 8978 |
| Cp (J·kg-1·K-1) | 4189 | 1899 | 4075 | 3960 | 3846 | 3731 | 502.48 | 381 |
| λ (W·m-1·K-1) | 0.643 | 0.1643 | 0.608 | 0.5744 | 0.5426 | 0.5121 | 16.27 | 387.6 |
| μ (kg·m-1·s-1) | 5.98×10-4 | – | 6.98×10-4 | 8.37×10-4 | 1.04×10-3 | 1.34×10-3 | – | – |
| 域名 | 名称 | 方程式 |
|---|---|---|
| 流体域 | 连续性方程 | |
| 动量方程 | ||
| 能量方程 | ||
| 组分方程 | ||
| 湍流动能k方程 | ||
| 湍流耗散率ε方程 | ||
| 多孔域 | 连续性方程 | |
| 动量方程 | ||
| 能量方程 | ||
| 组分方程 | ||
| 固体域 | 能量方程 |
表2 计算域的相关控制方程
Table 2 Related governing equations of the computational domain
| 域名 | 名称 | 方程式 |
|---|---|---|
| 流体域 | 连续性方程 | |
| 动量方程 | ||
| 能量方程 | ||
| 组分方程 | ||
| 湍流动能k方程 | ||
| 湍流耗散率ε方程 | ||
| 多孔域 | 连续性方程 | |
| 动量方程 | ||
| 能量方程 | ||
| 组分方程 | ||
| 固体域 | 能量方程 |
| 网格编号 (n) | 节点数 | ΔTmax (K) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh (I) | 78×47 | 14.09 | 1.08 | 83837.05 | 2.42 |
| Mesh (II) | 128×79 | 13.89 | 0.36 | 86148.97 | 0.27 |
| Mesh (Ⅲ) | 252×163 | 13.92 | 0.14 | 86169.75 | 0.29 |
| Mesh (Ⅳ) | 350×231 | 13.94 | – | 85917.30 | – |
表3 网格独立性测试结果
Table 3 Grid independence test results
| 网格编号 (n) | 节点数 | ΔTmax (K) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh (I) | 78×47 | 14.09 | 1.08 | 83837.05 | 2.42 |
| Mesh (II) | 128×79 | 13.89 | 0.36 | 86148.97 | 0.27 |
| Mesh (Ⅲ) | 252×163 | 13.92 | 0.14 | 86169.75 | 0.29 |
| Mesh (Ⅳ) | 350×231 | 13.94 | – | 85917.30 | – |
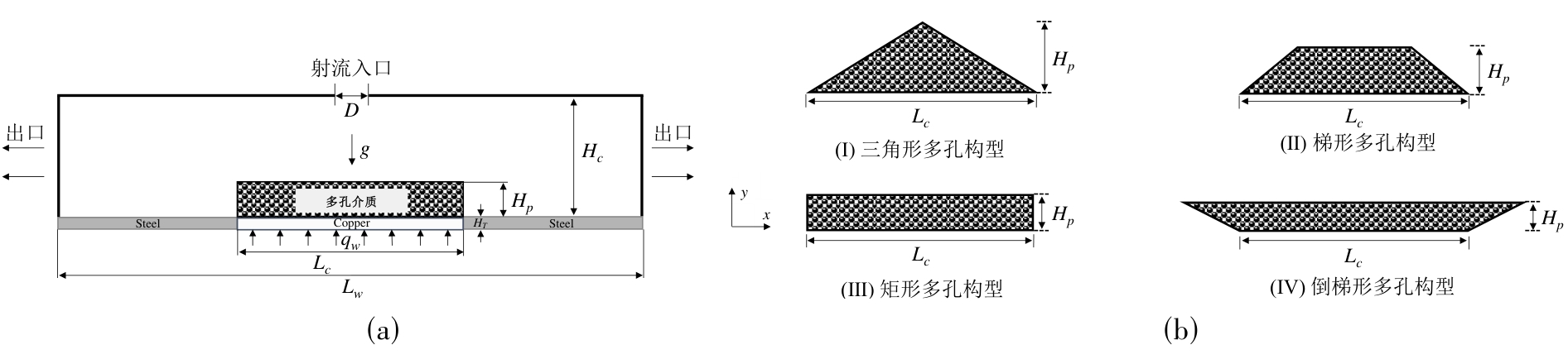
图1 (a) 射流冲击被不同形状多孔介质覆盖的受热面,以及 (b) 多孔介质形状分别为 (Ⅰ) 三角形、(Ⅱ) 梯形、(Ⅲ) 矩形和 (Ⅳ) 倒梯形的不同射流构型的示意图
Fig.1 The schematic diagrams of (a) jet impinging on the heating surface covered by porous media of different shapes, and (b) different jet configurations with porous media shapes of (Ⅰ) triangular, (Ⅱ) trapezoidal, (Ⅲ) rectangular, and (Ⅳ) inverted trapezoidal, respectively
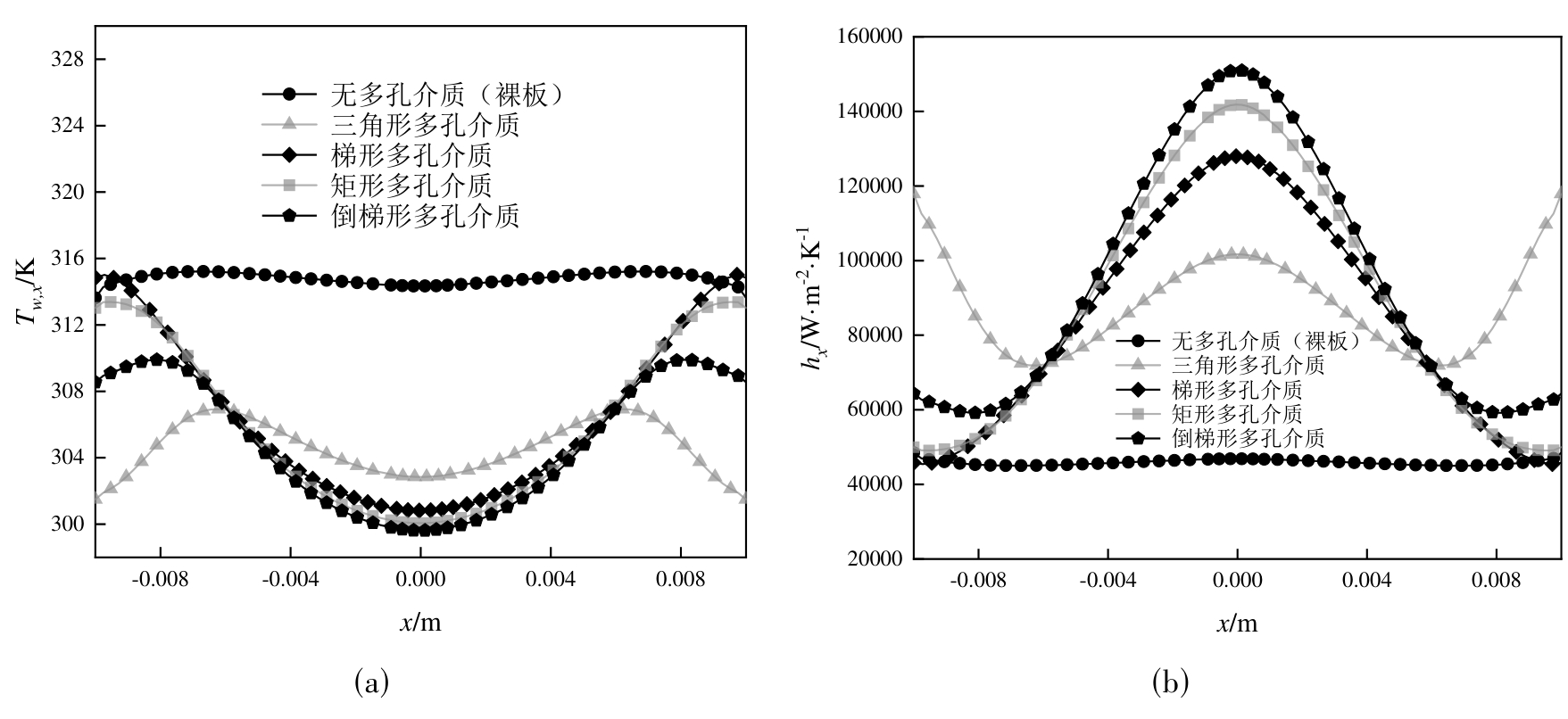
图3 水为工质时不同射流模式下 (a) 局部壁温与 (b) 局部传热系数随x位置的变化
Fig.3 Variation of (a) local wall temperature and (b) local heat transfer coefficient along the x-position under different jet modes with water as the working fluid
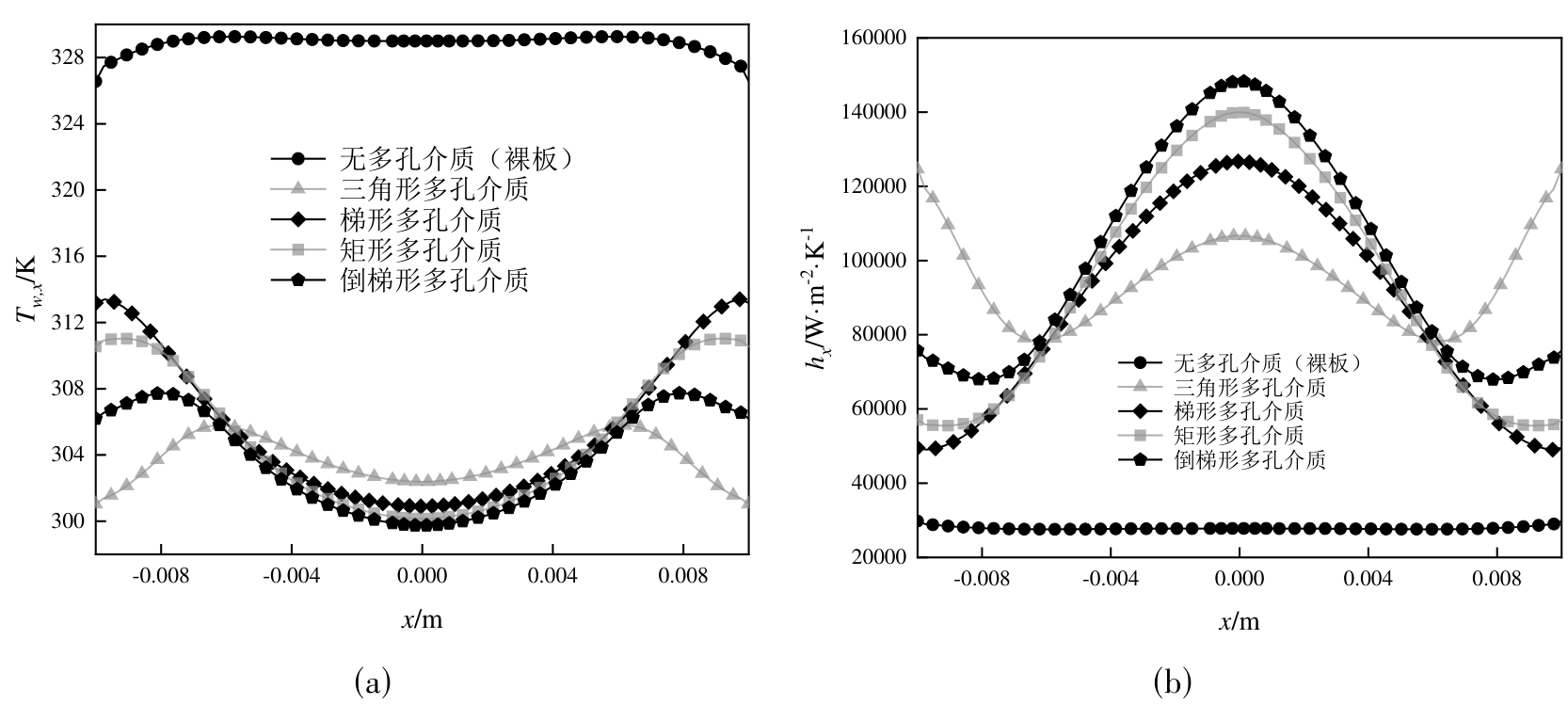
图4 相变悬浮液(cm= 10%)为工质时不同射流模式下 (a) 局部壁温与 (b) 局部传热系数随x位置的变化
Fig. 4 Variation of (a) local wall temperature and (b) local heat transfer coefficient along the x-position under different jet modes with phase change suspension (cm = 10%) as the working fluid
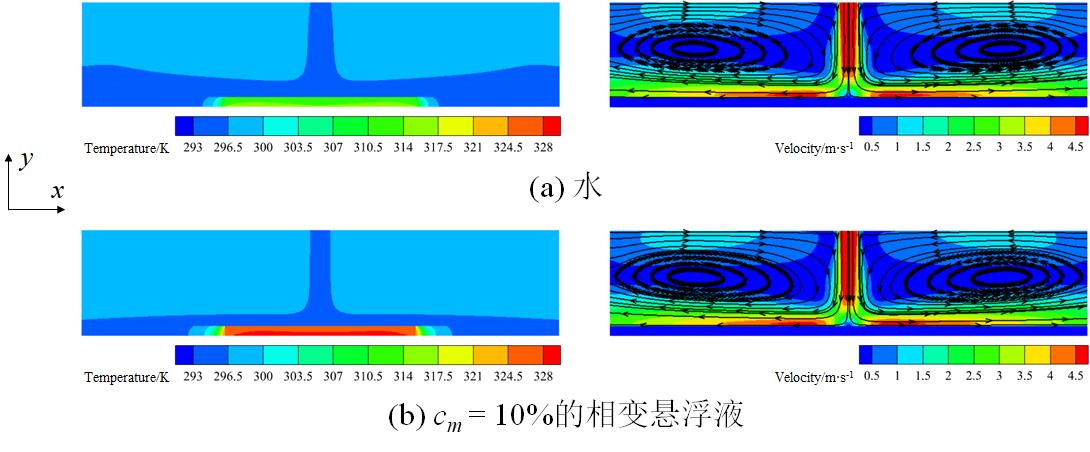
图5 不同工质射流冲击裸板构型时的温度和速度矢量场
Fig.5 Temperature and velocity vector fields during jet impingement of different working fluids on a bare plate configuration
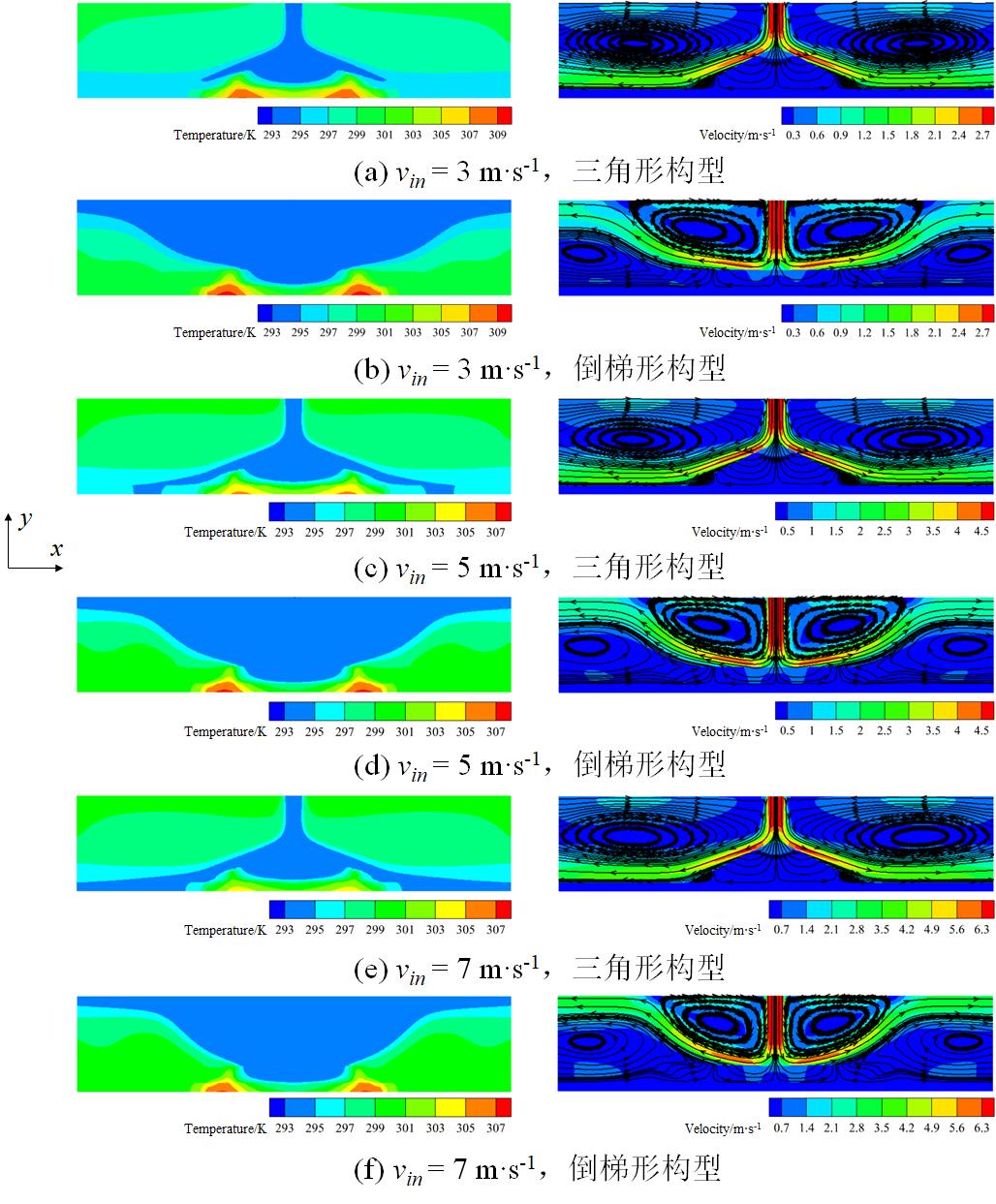
图9 相变悬浮液在不同射流速度下射流冲击三角形和倒梯形构型时的温度和速度矢量场
Fig.9 Temperature and velocity vector fields during jet impingement of phase change suspension on triangular and inverted trapezoidal configurations at varied velocities
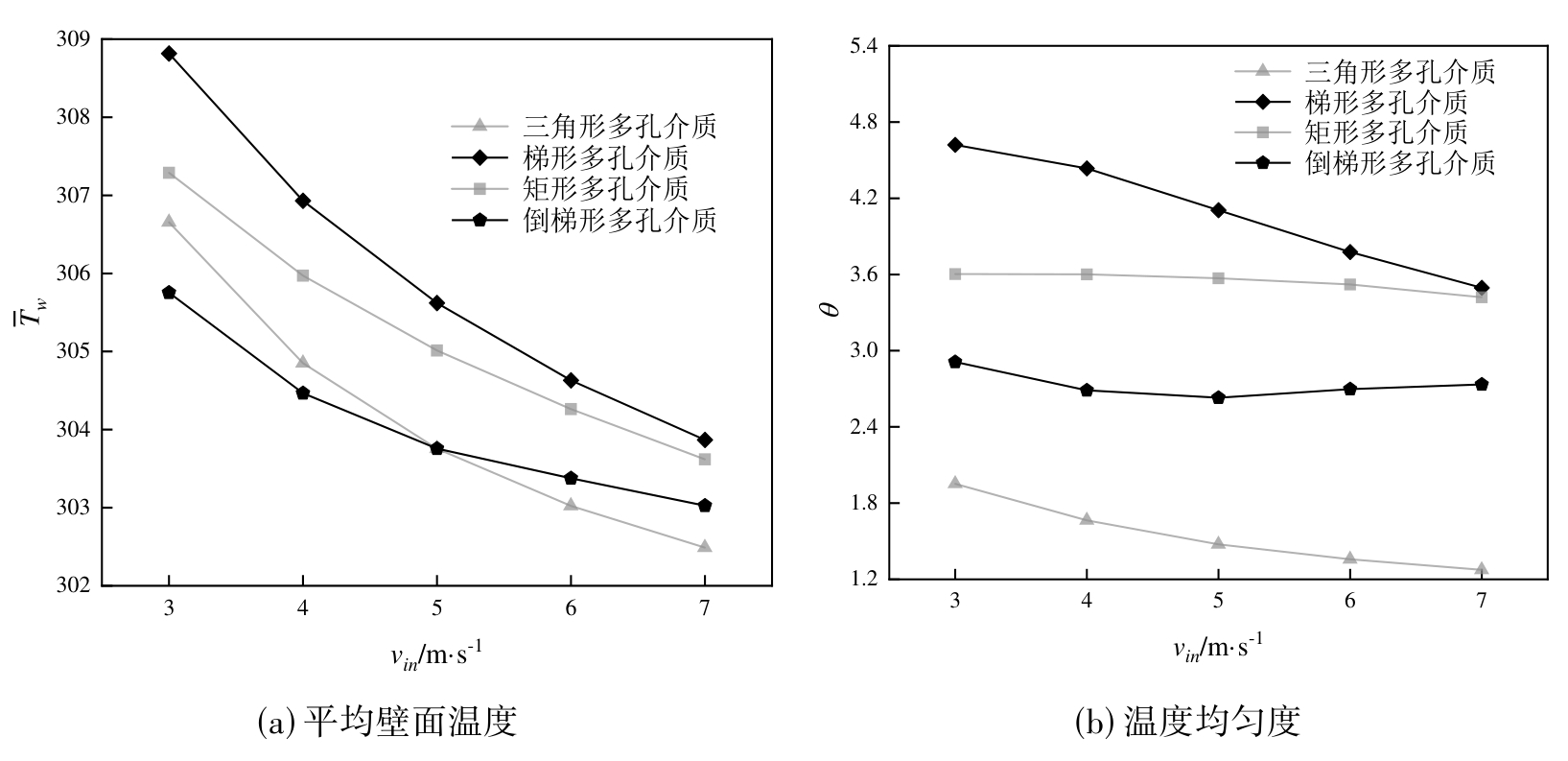
图10 不同射流模式下平均壁面温度和温度均匀度随相变悬浮液射流速度的变化
Fig.10 Variation of average wall temperature and temperature uniformity with jet velocity of phase change suspension under different jet modes
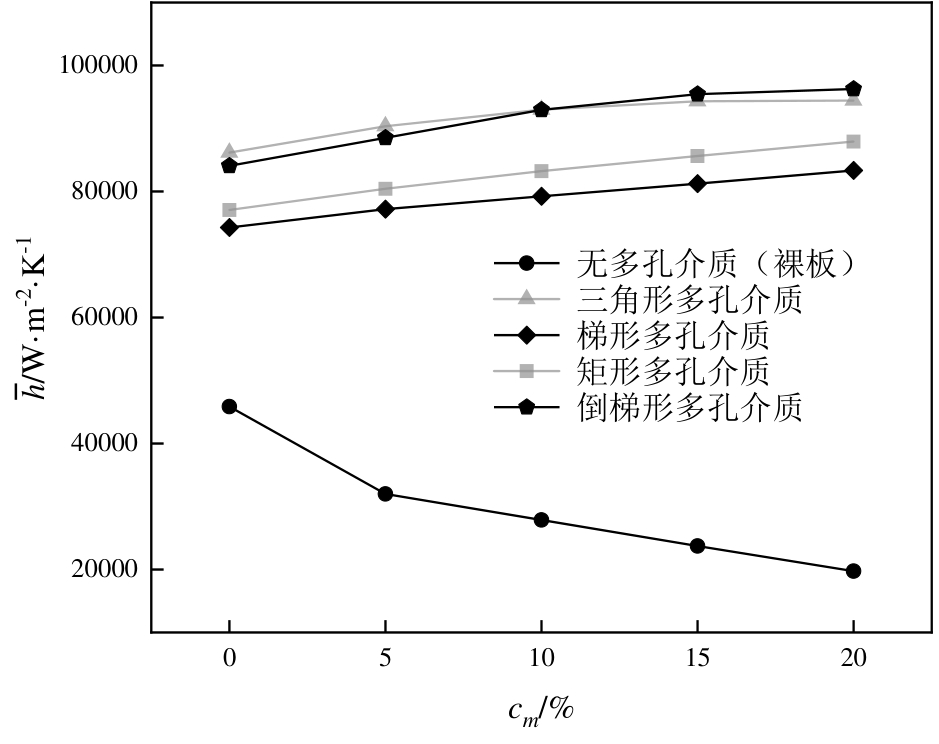
图11 不同射流模式下平均传热系数随相变悬浮液质量分数的变化
Fig.11 Variation of average heat transfer coefficient with mass fraction of phase change suspension under different jet modes
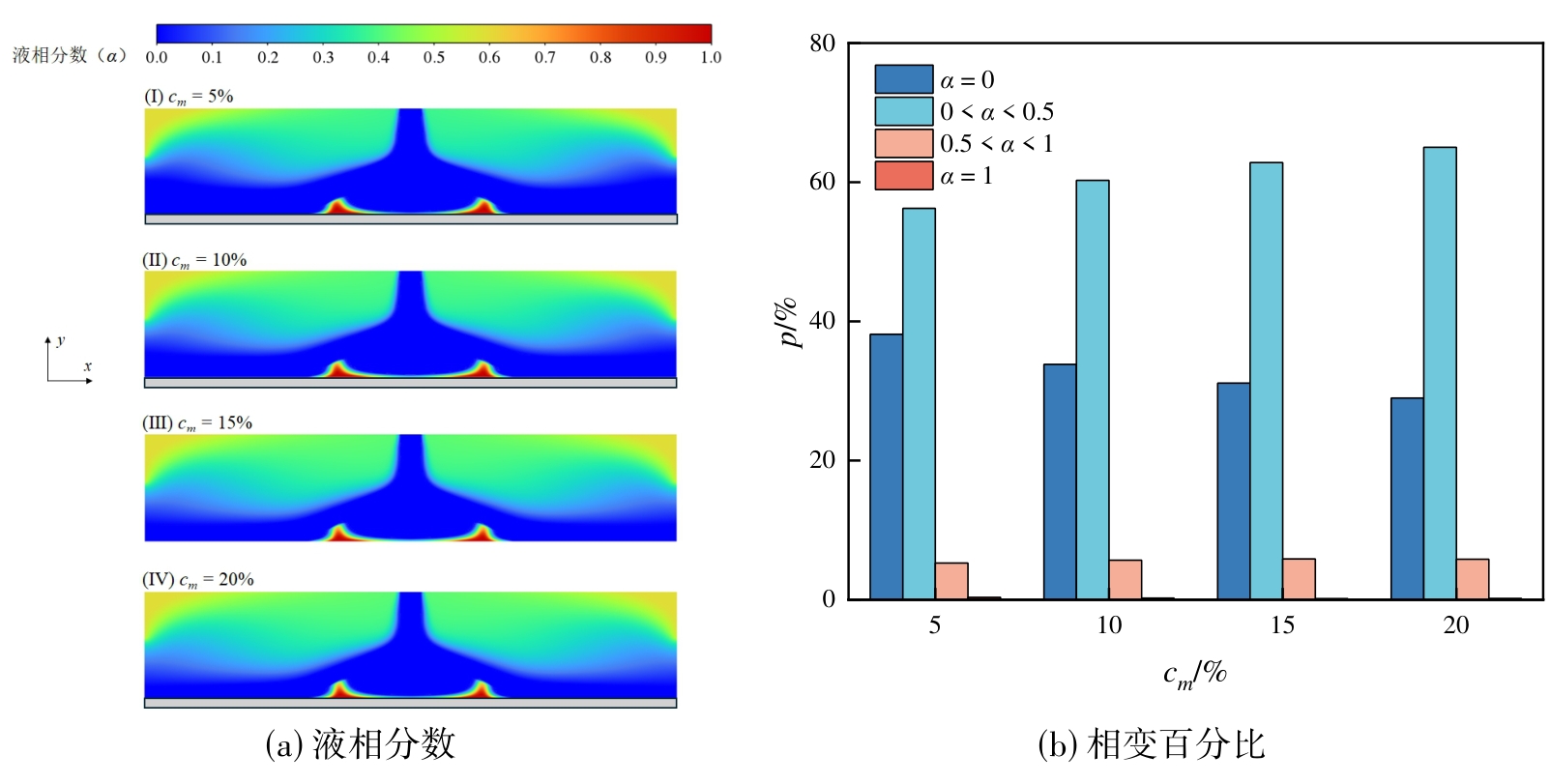
图12 相变悬浮液射流冲击三角形构型时微胶囊中相变材料的液相分数及相变百分比随质量分数的变化
Fig.12 Variation of liquid fraction and phase change percentage of phase change material in microcapsules with mass fraction under jet impingement of phase change suspension on a triangular configuration
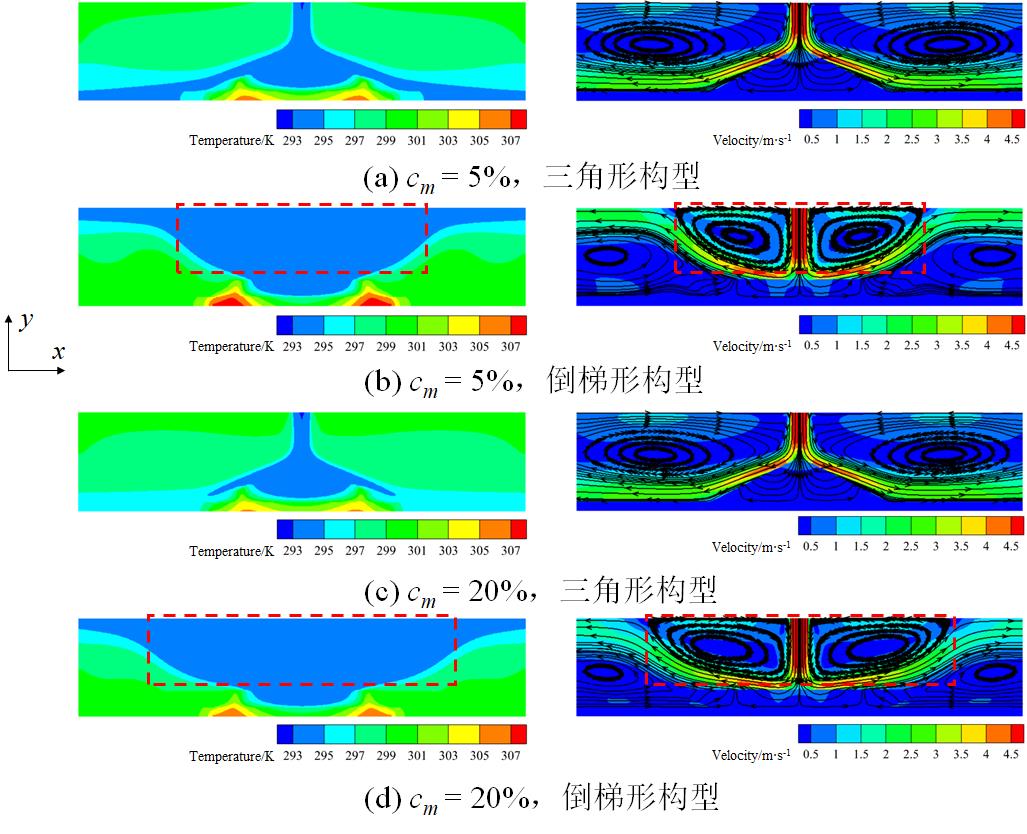
图13 相变悬浮液在不同质量分数下射流冲击三角形和倒梯形构型时的温度和速度矢量场
Fig.13 Temperature and velocity vector fields during jet impingement of phase change suspension on triangular and inverted trapezoidal configurations at different mass fractions
| [8] | de Lemos M J S, Fischer C. Thermal analysis of an impinging jet on a plate with and without a porous layer[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A: Applications, 2008, 54(11): 1022-1041. |
| [9] | 张红军, 邹正平. 多孔介质中受限层流冲击射流的流动与换热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(7): 2033-2044. |
| Zhang H J, Zou Z P. Flow and heat transfer characteristics of confined laminar impinging jet on plate with porous layer[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(7): 2033-2044. | |
| [10] | Yogi K, Krishnan S, Prabhu S V. Experimental investigation on the local heat transfer with an unconfined slot jet impinging on a metal foamed flat plate[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2021, 169: 107065. |
| [11] | 裘腾威, 刘敏, 刘源, 等. 新型多孔铜微通道热沉散热性能实验研究[J]. 热科学与技术, 2020, 19(4): 339-346. |
| Qiu T W, Liu M, Liu Y, et al. Experimental research on heat transfer performance of a novel porous copper micro-channel heat sink[J]. Journal of Thermal Science and Technology, 2020, 19(4): 339-346. | |
| [12] | Kumar C S, Pattamatta A. Assessment of heat transfer enhancement using metallic porous foam configurations in laminar slot jet impingement: an experimental study[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2018, 140(2): 022202. |
| [13] | Dórea F T, de Lemos M J S. Simulation of laminar impinging jet on a porous medium with a thermal non-equilibrium model[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2010, 53(23/24): 5089-5101. |
| [14] | Fu W S, Huang H C. Thermal performances of different shape porous blocks under an impinging jet[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1997, 40(10): 2261-2272. |
| [15] | Saeid N H, Hasan N, Bin Hj Mohd Ali M H. Effect of the metallic foam heat sink shape on the mixed convection jet impingement cooling of a horizontal surface[J]. Journal of Porous Media, 2018, 21(4): 295-309. |
| [16] | Dai H, Wang L, Liu Y, et al. Heat transfer augmentation in a heating surface covered by variable-shape or double-layer porous media subjected to water jet impingement[J]. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2024, 53: 102729. |
| [17] | Sohel Murshed S M, Nieto de Castro C A. A critical review of traditional and emerging techniques and fluids for electronics cooling[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 78: 821-833. |
| [18] | Li Z X, Khaled U, Al-Rashed A A A A, et al. Heat transfer evaluation of a micro heat exchanger cooling with spherical carbon-acetone nanofluid[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 149: 119124. |
| [19] | 方立昌, 李梓龙, 陈博, 等. 基于相变微胶囊悬浮液的芯片阵列冷却特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2455-2464, 2378. |
| Fang L C, Li Z L, Chen B, et al. Study on cooling characteristics of chip array based on microencapsulated phase change material slurry[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2455-2464, 2378. | |
| [20] | 钟小龙, 刘东, 胥海伦. 微小管道内相变微胶囊悬浮液换热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(S1): 203-209. |
| Zhong X L, Liu D, Xu H L. Heat transfer characteristics of micro-encapsulated phase change material suspension in mini-tubes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(S1): 203-209. | |
| [21] | Wu W, Bostanci H, Chow L C, et al. Jet impingement and spray cooling using slurry of nanoencapsulated phase change materials[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2011, 54(13/14): 2715-2723. |
| [22] | M S A, Venkatasubbaiah K. Numerical investigation on heat transfer performance of a confined slot jet impingement with different MEPCM-water slurries using two-phase Eulerian–Eulerian model[J]. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2022, 33: 101315. |
| [23] | Seyf H R, Zhou Z, Ma H B, et al. Three dimensional numerical study of heat-transfer enhancement by nano-encapsulated phase change material slurry in microtube heat sinks with tangential impingement[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 56(1/2): 561-573. |
| [24] | Mohib Ur Rehman M, Qu Z G, Fu R P. Three-dimensional numerical study of laminar confined slot jet impingement cooling using slurry of nano-encapsulated phase change material[J]. Journal of Thermal Science, 2016, 25(5): 431-439. |
| [25] | Zhang J J, Zhao R, Li H, et al. Numerical simulation on jet impingement heat transfer with microcapsule phase change material suspension: Single jet and array jet[J]. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 2023, 50: 103449. |
| [26] | Rehman M M U, Qu Z G, Fu R P, et al. Numerical study on free-surface jet impingement cooling with nanoencapsulated phase-change material slurry and nanofluid[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 109: 312-325. |
| [27] | Zhang J J, Yang C H, Jin Z G, et al. Experimental study of jet impingement heat transfer with microencapsulated phase change material slurry[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 188: 116588. |
| [1] | Sarkar S, Gupta R, Roy T, et al. Review of jet impingement cooling of electronic devices: emerging role of surface engineering[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2023, 206: 123888. |
| [2] | 汤振彪, 崔晓钰. 液体阵列射流冲击冷板工质与传热结构研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(7): 3431-3445. |
| Tang Z B, Cui X Y. Research progress on working medium and heat transfer structure of liquid cooling plate with array jet impingement[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(7): 3431-3445. | |
| [3] | 耿丽萍, 许庆功, 郑传波, 等. 多喷嘴带相差射流冲击传热的数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(S1): 240-244. |
| Geng L P, Xu Q G, Zheng C B, et al. Numerical simulations of impinging heat transfer characteristics for multi-pulsating jets with phase difference[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(S1): 240-244. | |
| [4] | 张永海, 魏进家, 孔新. 柱状微结构射流强化换热性能研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2016, 37(9): 1952-1955. |
| Zhang Y H, Wei J J, Kong X. Enhanced heat transfer characteristic of micro-pin-finned surfaces with jet impingement[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2016, 37(9): 1952-1955. | |
| [5] | 汪健生, 王振川, 李美军. 不同工作因数下方波冲击射流的换热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(7): 2428-2435. |
| Wang J S, Wang Z C, Li M J. Heat transfer characteristics of square wave impinging jets with different duty cycles[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(7): 2428-2435. | |
| [6] | Martínez-Filgueira P, Portal-Porras K, Fernandez-Gamiz U, et al. Experimental and numerical modeling of an air jet impingement system[J]. European Journal of Mechanics - B/Fluids, 2022, 94: 228-245. |
| [7] | 王琪, 苗琳, 陈良, 等. 局部高热通量器件射流冲击冷板流动传热特性数值研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2023, 57(2): 90-99. |
| Wang Q, Miao L, Chen L, et al. Numerical study on flow and heat transfer characteristics of jet impinging cold plate for local high heat flux device[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2023, 57(2): 90-99. | |
| [28] | Dai H, Liu Y W. Entropy generation analysis on thermo-hydraulic characteristics of microencapsulated phase change slurry in wavy microchannel with porous fins[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 219: 119440. |
| [29] | 奚坤, 谢志辉. 基于OpenFOAM的多孔介质微通道热沉传热数值分析[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2022, 34(3): 38-43. |
| Xi K, Xie Z H. Numerical analysis of heat transfer in porous media microchannel heat sink based on OpenFOAM[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2022, 34(3): 38-43. | |
| [30] | Hasan M I. Numerical investigation of counter flow microchannel heat exchanger with MEPCM suspension[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2011, 31(6/7): 1068-1075. |
| [31] | Dai H, Chen W, Cheng Q, et al. Analysis of thermo-hydraulic characteristics in the porous-wall microchannel with microencapsulated phase change slurry[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 165: 120634. |
| [32] | Rehman M M U, Ahmad Cheema T, Khan M, et al. Parametric evaluation of a hydrofoil-shaped sidewall rib-employed microchannel heat sink with and without nano-encapsulated phase change material slurry as coolant[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 178: 115514. |
| [33] | Hung T C, Huang Y X, Yan W M. Thermal performance analysis of porous-microchannel heat sinks with different configuration designs[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 66: 235-243. |
| [34] | Dai H, Liu Y W. Hydrothermal analysis of parallel and symmetric microchannels with phase change slurry and porous fin designs[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2024, 203: 109142. |
| [35] | Dai H, Chen W. Numerical investigation of heat transfer in the double-layered minichannel with microencapsulated phase change suspension[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 119: 104918. |
| [36] | Li H, Xiao X Y, Wang Y N, et al. Performance investigation of a battery thermal management system with microencapsulated phase change material suspension[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 180: 115795. |
| [37] | Chen H, Dai H, Liu Y W. Numerical analysis of microencapsulated phase change suspension flow in wavy porous microchannels with different phase differences[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2026, 255: 127856. |
| [38] | Jeng T M, Tzeng S C. Experimental study of forced convection in metallic porous block subject to a confined slot jet[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2007, 46(12): 1242-1250. |
| [1] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [2] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [3] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [4] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [5] | 郭纪超, 徐肖肖, 孙云龙. 基于植物工厂中的CO2浓度气流模拟及优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 237-245. |
| [6] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [7] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [8] | 吴梓航, 徐震原, 游锦方, 潘权稳, 王如竹. 基于吸附式储冷技术的深井钻探设备冷却系统[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 309-317. |
| [9] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [10] | 郭松源, 周晓庆, 缪五兵, 汪彬, 耑锐, 曹庆泰, 陈成成, 杨光, 吴静怡. 火箭上升段含多孔板液氧贮箱增压输运数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [11] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [12] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| [13] | 陈昇, 李子争, 苗超, 白学刚, 李飞, 刘家璇, 李天天, 杨爽, 吕蓉蓉, 王江云. 大尺度密集场景高危氯气非均匀湍流扩散特性三维CFD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4630-4643. |
| [14] | 贾志勇, 沈宪琨, 蓝晓程, 王铁峰. 气体密度对高压流态化影响的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4383-4397. |
| [15] | 解勤勤, 翁俊旗, 林振利, 叶光华, 周兴贵. 固定床反应器中甲醇制芳烃工业催化剂结构影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4487-4498. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号