CIESC Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (10): 4021-4031.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190421
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Haotian LU( ),Yiqin CHEN,Jinghong ZHOU(
),Yiqin CHEN,Jinghong ZHOU( ),Zhijun SUI,Xinggui ZHOU
),Zhijun SUI,Xinggui ZHOU
Received:2019-04-23
Revised:2019-06-11
Online:2019-10-05
Published:2019-10-05
Contact:
Jinghong ZHOU
通讯作者:
周静红
作者简介:鲁浩天(1993—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Haotian LU, Yiqin CHEN, Jinghong ZHOU, Zhijun SUI, Xinggui ZHOU. Simulation and optimization of electrochemical double layer capacitors: effects of ion size and diffusion coefficient[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(10): 4021-4031.
鲁浩天, 陈怡沁, 周静红, 隋志军, 周兴贵. 电化学双电层电容器动态模拟:离子尺寸及扩散系数的优化[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(10): 4021-4031.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| minimum value of imposed potential/V | -0.5 |
| maximum value of imposed potential/V | 0.5 |
| scan rate of cyclic voltammetry/(V·s-1) | 10,102,104,105 |
| cycle number | 6 |
| local temperature/K | 298.5 |
| bulk electrolyte concentration/(mol·L-1) | 1.0 |
| solvated ion size/nm | 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 |
| diffuse layer thickness/μm | 200 |
| ion valency | 1 |
| initial diffusion coefficient of ions in electrolyte/(m2·s-1)[ | 3.17×10-10 |
| dielectric constant of electrolyte within diffuse layer[ | 61.4 |
| dielectric constant of electrolyte within Stern layer | 6.5 |
Table 1 Parameters for elctric double capacitor dynamic state model simulation
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| minimum value of imposed potential/V | -0.5 |
| maximum value of imposed potential/V | 0.5 |
| scan rate of cyclic voltammetry/(V·s-1) | 10,102,104,105 |
| cycle number | 6 |
| local temperature/K | 298.5 |
| bulk electrolyte concentration/(mol·L-1) | 1.0 |
| solvated ion size/nm | 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 |
| diffuse layer thickness/μm | 200 |
| ion valency | 1 |
| initial diffusion coefficient of ions in electrolyte/(m2·s-1)[ | 3.17×10-10 |
| dielectric constant of electrolyte within diffuse layer[ | 61.4 |
| dielectric constant of electrolyte within Stern layer | 6.5 |
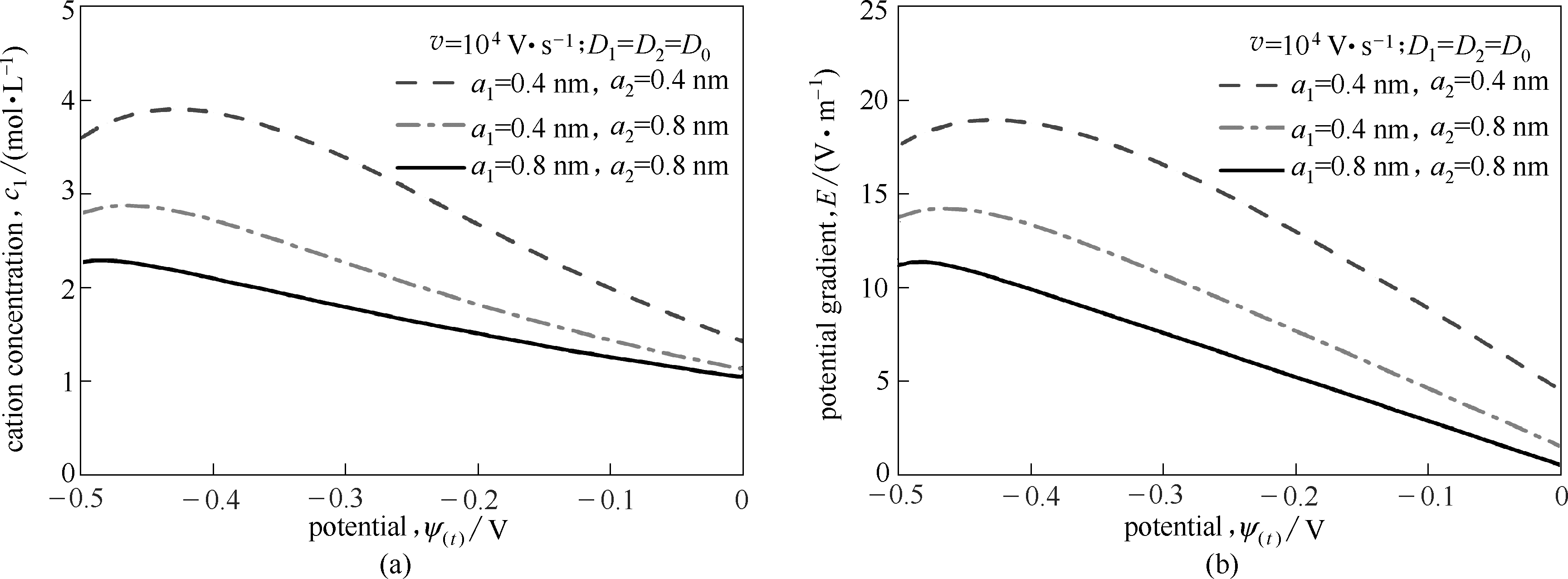
Fig.8 Cation concentration and potential gradient at interface of Stern and diffusion layer with linear sweep potential for different solvated ion diameters
| 1 | Thounthong P , Raël S , Davat B . Energy management of fuel cell/battery/supercapacitor hybrid power source for vehicle applications[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 193(1): 376-385. |
| 2 | Conway B E . Transition from “supercapacitor” to “battery” behavior in electrochemical energy storage[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1991, 138(6): 1539-1548. |
| 3 | Wang Y , Song Y , Xia Y . Electrochemical capacitors: mechanism, materials, systems, characterization and applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016, 45(21): 5925-5950. |
| 4 | Zhong C , Deng Y , Hu W , et al . A review of electrolyte materials and compositions for electrochemical supercapacitors[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(21): 7484-7539. |
| 5 | Chmiola J , Yushin G , Gogotsi Y , et al . Anomalous increase in carbon at pore sizes less than 1 nanometer[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5794): 1760-1763. |
| 6 | Sun G , Song W , Liu X , et al . Capacitive matching of pore size and ion size in the negative and positive electrodes for supercapacitors[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(25): 9248-9256. |
| 7 | Izadi-Najafabadi A , Yasuda S , Kobashi K , et al . Extracting the full potential of single-walled carbon nanotubes as durable supercapacitor electrodes operable at 4 V with high power and energy density[J]. Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(35): E235-E241. |
| 8 | Saito M , Kawaharasaki S , Ito K , et al . Strategies for fast ion transport in electrochemical capacitor electrolytes from diffusion coefficients, ionic conductivity, viscosity, density and interaction energies based on HSAB theory[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(24): 14528-14535. |
| 9 | Largeot C , Portet C , Chmiola J , et al . Relation between the ion size and pore size for an electric double-layer capacitor[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(9): 2730-2731. |
| 10 | 武长城, 吴宝军, 段建, 等 . 电解质离子尺寸对超级电容器电化学性能的影响[J]. 天津工业大学学报, 2019, 38(1): 39-44. |
| Wu C C , Wu B J , Duan J , et al . Influence of size of electrolyte ion on the electrochemical performanceof supercapacitor[J]. Journal of Tianjin Polytechnic University, 2019, 38(1): 39-44. | |
| 11 | Simon P , Gogotsi Y . Materials for electrochemical capacitors[J]. Nature Materials, 2008, 7(11): 845-854. |
| 12 | Izadi-Najafabadi A , Futaba D N , Iijima S , et al . Ion diffusion and electrochemical capacitance in aligned and packed single-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(51): 18017-18019. |
| 13 | 鲁浩天, 周静红, 叶光华, 等 . 电化学电容器连续模型的建立与研究进展[J]. 电化学, 2018, 24(5): 517-528. |
| Lu H T , Zhou J H , Ye G H , et al . Recent advances in continuous models of electrochemical supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry, 2018, 24(5): 517-528. | |
| 14 | Wang H , Pilon L . Physical interpretation of cyclic voltammetry for measuring electric double layer capacitances[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 64: 130-139. |
| 15 | Gouy M . Sur la constitution de la charge électrique à la surface d'un électrolyte[J]. Journal de Physique Théorique et Appliquée, 1910, 9(1): 457-468. |
| 16 | Chapman D L . A contribution to the theory of electrocapillarity[J]. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science, 1913, 25(148): 475-481. |
| 17 | Adamczyk Z , Belouschek P , Lorenz D . Electrostatic interactions of bodies bearing thin double-layers (Ⅰ): General formulation[J]. Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für Physikalische Chemie, 1990, 94(12): 1483-1492. |
| 18 | Kilic M S , Bazant M Z , Ajdari A . Steric effects in the dynamics of electrolytes at large applied voltages (Ⅰ): Double-layer charging[J]. Physical Review E, 2007, 75(2): 021502. |
| 19 | Zhang L L , Zhou R , Zhao X S . Graphene-based materials as supercapacitor electrodes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2010, 20(29): 5983-5992. |
| 20 | Senapati S , Chandra A . Dielectric constant of water confined in a nanocavity[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2001, 105(22): 5106-5109. |
| 21 | Hantel M M , Weingarth D , Kötz R . Parameters determining dimensional changes of porous carbons during capacitive charging[J]. Carbon, 2014, 69: 275-286. |
| 22 | Sullivan J M , Hanson D C , Keller R . Diffusion coefficients in propylene carbonate, dimethyl formamide, acetonitrile, and methyl formate[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1970, 117(6): 779-780. |
| 23 | Kovacs H , Kowalewski J , Maliniak A , et al . Multinuclear relaxation and NMR self-diffusion study of the molecular dynamics in acetonitrile-chloroform liquid mixtures[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1989, 93(2): 962-969. |
| 24 | Kalugin O N , Chaban V V , Loskutov V V , et al . Uniform diffusion of acetonitrile inside carbon nanotubes favors supercapacitor performance[J]. Nano Letters, 2008, 8(8): 2126-2130. |
| 25 | Nishikawa K , Fukunaka Y , Sakka T , et al . Measurement of LiClO4 diffusion coefficient in propylene carbonate by moirá pattern[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2006, 153(5): A830-A834. |
| 26 | Wang H , Varghese J , Pilon L . Simulation of electric double layer capacitors with mesoporous electrodes: effects of orphology and electrolyte permittivity[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(17): 6189-6197. |
| 27 | Daniels I N , Wang Z , Laird B B . Dielectric properties of organic solvents in an electric field[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(2): 1025-1031. |
| 28 | Pech D , Brunet M , Durou H , et al . Ultrahigh-power micrometre-sized supercapacitors based on onion-like carbon[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2010, 5(9): 651-654. |
| 29 | Cohen H , Cooley J . The numerical solution of the time-dependent Nernst-Planck equations[J]. Biophysical Journal, 1965, 5(2): 145-162. |
| 30 | Conway B E . Electrochemical Supercapacitors: Scientific Fundamentals and Technological Applications[M]. Springer Science & Business Media, 2013. |
| 31 | Wang H , Pilon L . Accurate simulations of electric double layer capacitance of ultramicroelectrodes[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(33): 16711-16719. |
| 32 | Qu Q T , Wang B , Yang L C , et al . Study on electrochemical performance of activated carbon in aqueous Li2SO4, Na2SO4 and K2SO4 electrolytes[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2008, 10(10): 1652-1655. |
| 33 | Lee H Y , Goodenough J B . Supercapacitor behavior with KCl electrolyte[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1999, 144(1): 220-223. |
| 34 | Reddy R N , Reddy R G . Sol-gel MnO2 as an electrode material for electrochemical capacitors[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 124(1): 330-337. |
| 35 | Bazant M Z , Kilic M S , Storey B D , et al . Towards an understanding of induced-charge electrokinetics at large applied voltages in concentrated solutions[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2009, 152(1/2): 48-88. |
| 36 | Jiang D E , Wu J . Unusual effects of solvent polarity on capacitance for organic electrolytes in a nanoporous electrode[J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(10): 5545-5550. |
| 37 | Chae W S , Gough D V , Ham S K , et al . Effect of ordered intermediate porosity on ion transport in hierarchically nanoporous electrodes[J]. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2012, 4(8): 3973-3979. |
| [1] | Zhewen CHEN, Junjie WEI, Yuming ZHANG. System integration and energy conversion mechanism of the power technology with integrated supercritical water gasification of coal and SOFC [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3888-3902. |
| [2] | Cong QI, Zi DING, Jie YU, Maoqing TANG, Lin LIANG. Study on solar thermoelectric power generation characteristics based on selective absorption nanofilm [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3921-3930. |
| [3] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [4] | Zhaolun WEN, Peirui LI, Zhonglin ZHANG, Xiao DU, Qiwang HOU, Yegang LIU, Xiaogang HAO, Guoqing GUAN. Design and optimization of cryogenic air separation process with dividing wall column based on self-heat regeneration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2988-2998. |
| [5] | Weiming SHAO, Wenxue HAN, Wei SONG, Yong YANG, Can CHEN, Dongya ZHAO. Dynamic soft sensor modeling method based on distributed Bayesian hidden Markov regression [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2495-2502. |
| [6] | Jinbo JIANG, Xin PENG, Wenxuan XU, Rixiu MEN, Chang LIU, Xudong PENG. Study on leakage characteristics and parameter influence of pump-out spiral groove oil-gas seal [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2538-2554. |
| [7] | Shanghao LIU, Shengkun JIA, Yiqing LUO, Xigang YUAN. Optimization of ternary-distillation sequence based on gradient boosting decision tree [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2075-2087. |
| [8] | Bimao ZHOU, Shisen XU, Xiaoxiao WANG, Gang LIU, Xiaoyu LI, Yongqiang REN, Houzhang TAN. Effect of burner bias angle on distribution characteristics of gasifier slag layer [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1939-1949. |
| [9] | Wenxuan XU, Jinbo JIANG, Xin PENG, Rixiu MEN, Chang LIU, Xudong PENG. Comparative study on leakage and film-forming characteristics of oil-gas seal with three-typical groove in a wide speed range [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1660-1679. |
| [10] | Jiyuan LI, Jinwang LI, Liuwei ZHOU. Heat transfer performance of cold plates with different turbulence structures [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1474-1488. |
| [11] | Junxian CHEN, Zhongli JI, Yu ZHAO, Qian ZHANG, Yan ZHOU, Meng LIU, Zhen LIU. Study on online detection method of particulate matter in natural gas pipeline based on microwave technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1042-1053. |
| [12] | Xin LI, Shaojuan ZENG, Kuilin PENG, Lei YUAN, Xiangping ZHANG. Research progress and tendency of CO2 electrocatalytic reduction to syngas [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 313-329. |
| [13] | Jinjia WEI, Lei LIU, Xiaoping YANG. Research progress of loop heat pipes for heat dissipation of high-heat-flux electronic devices [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 60-73. |
| [14] | Wangxin GE, Yihua ZHU, Hongliang JIANG, Chunzhong LI. Research progress on electrolytes for carbon dioxide electroreduction [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3433-3447. |
| [15] | Bin LI, Wenming SONG, Kunlong YANG, Shuang JIANG, Tianyong ZHANG. Molecular engineering research progress of active materials for aqueous organic flow batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 2806-2818. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||