CIESC Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (2): 1078-1088.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201095
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Yiqin( ),XU Yu,ZHOU Jinghong(
),XU Yu,ZHOU Jinghong( ),SUI Zhijun,ZHOU Xinggui
),SUI Zhijun,ZHOU Xinggui
Received:2020-08-03
Revised:2020-09-11
Online:2021-02-05
Published:2021-02-05
Contact:
ZHOU Jinghong
通讯作者:
周静红
作者简介:陈怡沁(1995—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
CHEN Yiqin, XU Yu, ZHOU Jinghong, SUI Zhijun, ZHOU Xinggui. Heterogeneous modeling and internal mass transfer mechanism of lithium-ion batteries: effect of particle size distribution[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(2): 1078-1088.
陈怡沁, 许于, 周静红, 隋志军, 周兴贵. 锂离子电池异构建模及内部传质机理探究:粒径分布的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 1078-1088.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig.1 Geometry schematic of lithium ion battery with positive electrode of single-sized particles (a); Geometry schematic of lithium ion battery with positive electrode of bimodel-sized particles (b)
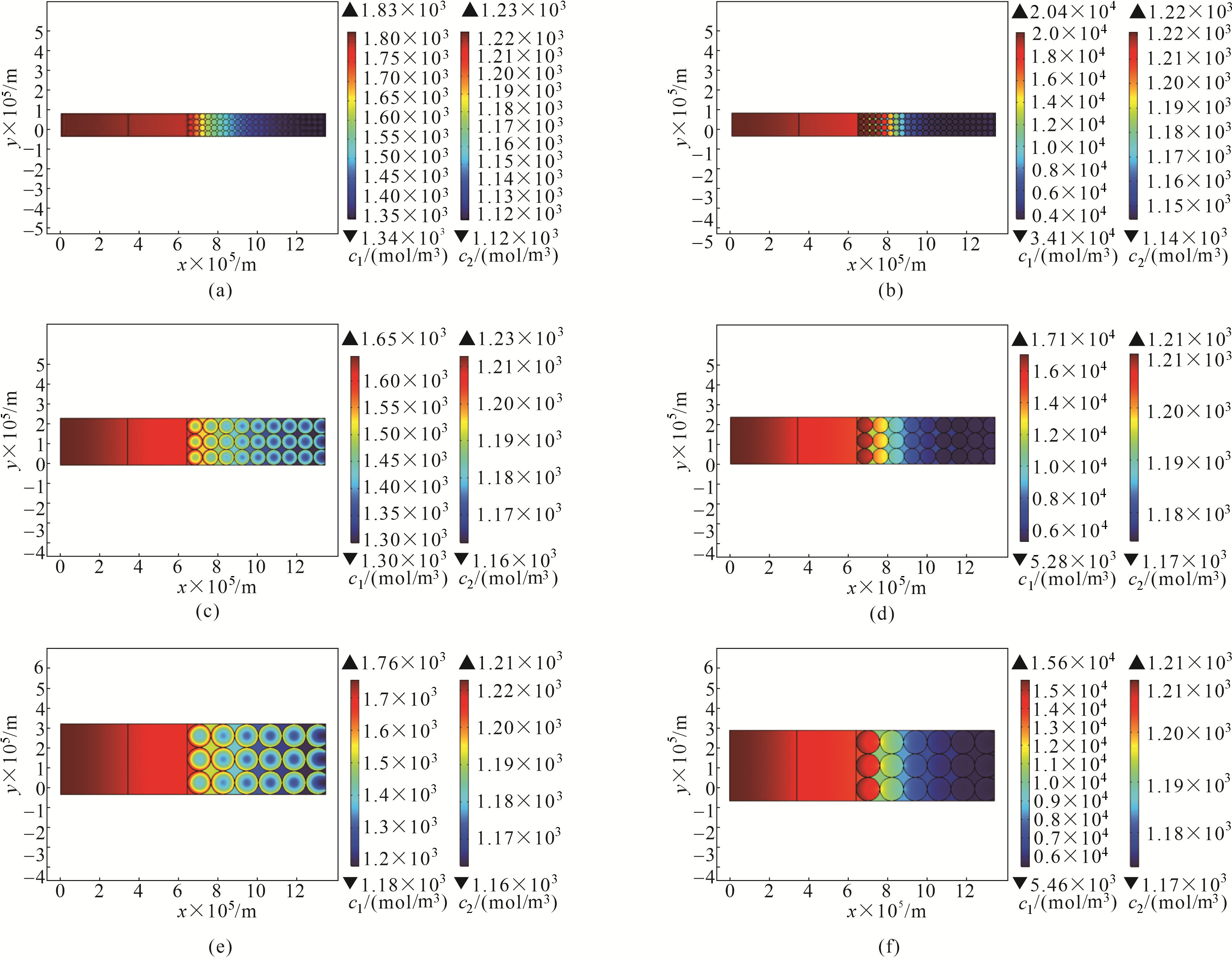
Fig.5 The concentration distribution of lithium ion in the electrolyte and metal lithium in active particles for lithium-ion battery with single-sized particles(a) Rp = 1.5 μm, discharge time is 300 s; (b) Rp = 1.5 μm, discharge time is 3000 s; (c) Rp = 4.0 μm, discharge time is 300 s; (d) Rp = 4.0 μm, discharge time is 3000 s; (e) Rp = 6.0 μm, discharge time is 300 s; (f) Rp = 6.0 μm, discharge time is 3000 s

Fig. 8 The concentration distribution of lithium ion in the electrolyte and metal lithium in active material particles for the lithium-ion battery with bimodel-sized particles(a) (1.5&4.0) μm, discharge time is 300 s; (b) (1.5&4.0) μm, discharge time is 3000 s; (c) (1.5&6.0) μm, discharge time is 300 s; (d) (1.5&6.0) μm, discharge time is 3000 s; (e) (4.0&6.0) μm, discharge time is 300 s; (f) (4.0&6.0) μm, discharge time is 3000 s
| Rp/μm | c1/(mol/m3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Δ | ||
| 单粒径 | 1.5 | 20445.0 | 3411.8 | 17033.2 |
| 4.0 | 17066.0 | 5275.8 | 11790.2 | |
| 6.0 | 15565.0 | 5454.4 | 10110.6 | |
| 双粒径 | 1.5&4.0 | 15064.0 | 6273.8 | 8790.2 |
| 1.5&6.0 | 19848.0 | 5153.1 | 14694.9 | |
| 4.0&6.0 | 14854.0 | 5519.5 | 9334.5 | |
Table 1 The maximum and minimum concentration of the metal lithium in the positive electrode with single-sized particles and bimodel-sized particles when discharging for 500 s under 1 C discharge rate
| Rp/μm | c1/(mol/m3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Δ | ||
| 单粒径 | 1.5 | 20445.0 | 3411.8 | 17033.2 |
| 4.0 | 17066.0 | 5275.8 | 11790.2 | |
| 6.0 | 15565.0 | 5454.4 | 10110.6 | |
| 双粒径 | 1.5&4.0 | 15064.0 | 6273.8 | 8790.2 |
| 1.5&6.0 | 19848.0 | 5153.1 | 14694.9 | |
| 4.0&6.0 | 14854.0 | 5519.5 | 9334.5 | |
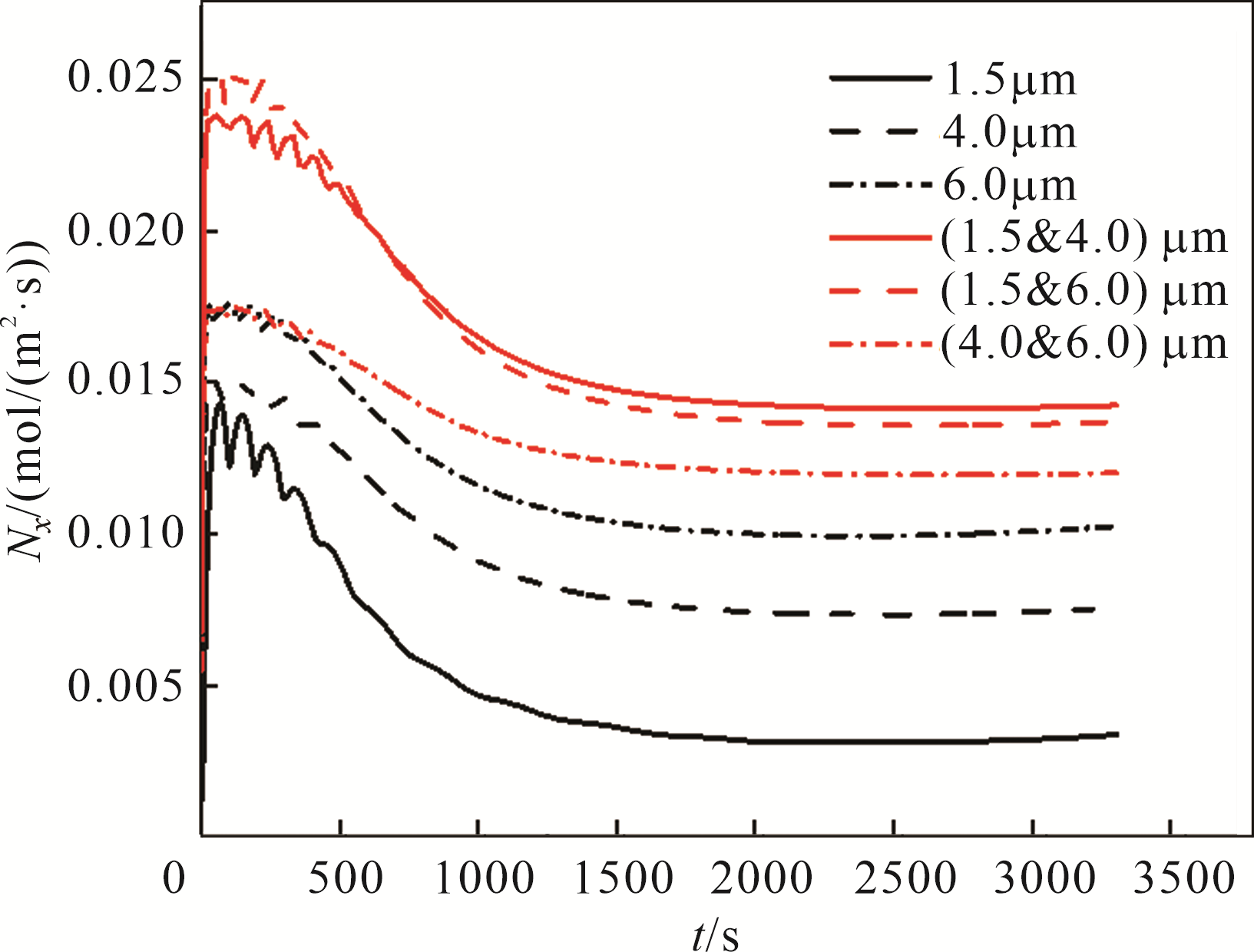
Fig.9 The lithium ion flux during discharge time inside the positive electrode with single-sized particles and bimodel-sized particles(x=100 μm) under 1 C discharge rate
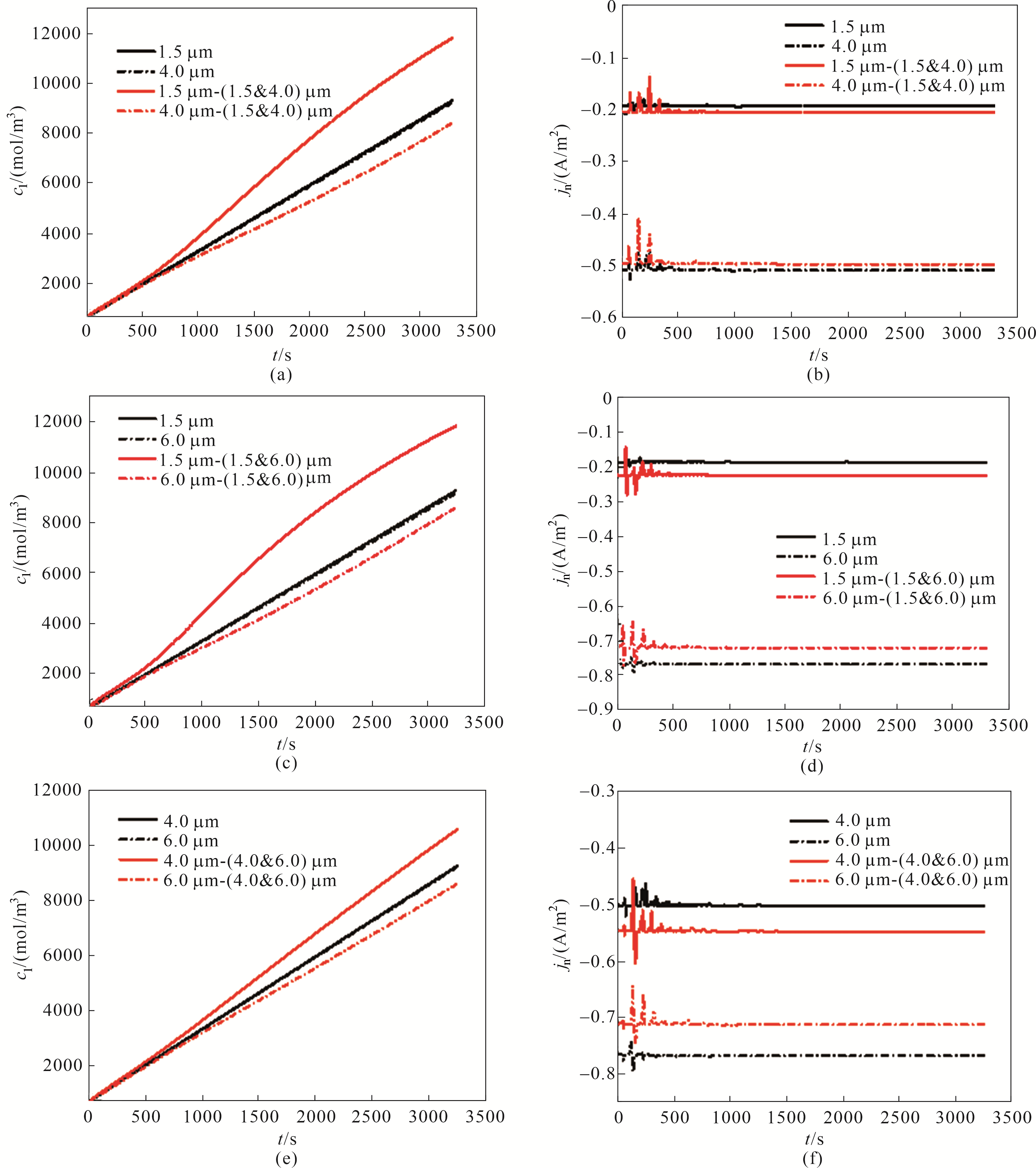
Fig.10 The average solid lithium concentration [(a),(c),(e)] and surface current density [(b),(d),(f)] of the large and small particles in the positive electrode of the lithium ion battery with single-sized and bimodal-sized particles during the discharge time under 1 C discharge rate
| 1 | Feng X, Ouyang M, Liu X, et al. Thermal runaway mechanism of lithium ion battery for electric vehicles: a review[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 10: 246-267. |
| 2 | Zhang W J. Structure and performance of LiFePO4 cathode materials: a review[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(6): 2962-2970. |
| 3 | 杨杰, 王婷, 杜春雨, 等. 锂离子电池模型研究综述[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(1): 58-64. |
| Yang J, Wang T, Du C Y, et al. Overview of the modeling of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(1): 58-64. | |
| 4 | Jokar A, Rajabloo B, Désilets M, et al. Review of simplified pseudo-two-dimensional models of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 327: 44-55. |
| 5 | Doyle M, Fuller T F, Newman J. Modeling of galvanostatic charge and discharge of the lithium/polymer/insertion cell[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1993, 140(6): 1526-1533. |
| 6 | Doyle M, Newman J. The use of mathematical modeling in the design of lithium/polymer battery systems[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1995, 40(13/14): 2191-2196. |
| 7 | Yu S, Kim S, Kim T Y, et al. Transportation properties in nanosized LiFePO4 positive electrodes and their effects on the cell performance[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2013, 43(3): 253-262. |
| 8 | Heubner C, Schneider M, Michaelis A. Diffusion-limited C-rate: a fundamental principle quantifying the intrinsic limits of Li-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(2): 1902523. |
| 9 | 许于, 陈怡沁, 周静红, 等. LiFePO4锂离子电池的数值模拟:正极材料颗粒粒径的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(2): 821-830. |
| Xu Y, Chen Y Q, Zhou J H, et al. Numerical simulation of lithium-ion battery with LiFePO4 as cathode material: effect of particle size[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(2): 821-830. | |
| 10 | Chen L, Chen Z, Liu S, et al. Effects of particle size distribution on compacted density of lithium iron phosphate 18650 battery[J]. Journal of Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage, 2018, 15(4): 041011. |
| 11 | Zhang Y, Wang Z B, Nie M, et al. A simple method for industrialization to enhance the tap density of LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 cathode material for high-specific volumetric energy lithium-ion batteries[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(70): 65941-65949. |
| 12 | Hong J, Wei W, He G. Optimizing the particle-size distribution and tap density of LiFePO4/C composites containing excess lithium[J]. Ionics, 2019, 25(5): 2035-2039. |
| 13 | Yu S, Chung Y, Song M S, et al. Investigation of design parameter effects on high current performance of lithium-ion cells with LiFePO4/graphite electrodes[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2012, 42(6): 443-453. |
| 14 | Röder F, Sonntag S, Schröder D, et al. Simulating the impact of particle size distribution on the performance of graphite electrodes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Technology, 2016, 4(12): 1588-1597. |
| 15 | Goldin G M, Colclasure A M, Wiedemann A H, et al. Three-dimensional particle-resolved models of Li-ion batteries to assist the evaluation of empirical parameters in one-dimensional models[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 64: 118-129. |
| 16 | Kikukawa H, Honkura K, Koyama M. Influence of inter-particle resistance between active materials on the discharge characteristics of the positive electrode of lithium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 278: 385-395. |
| 17 | Awarke A, Lauer S, Wittler M, et al. Quantifying the effects of strains on the conductivity and porosity of LiFePO4 based Li-ion composite cathodes using a multi-scale approach[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2011, 50(3): 871-879. |
| 18 | 郭孝东, 钟本和, 唐艳, 等. 一次粒径和二次粒径对LiFePO4性能的影响[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2013, 27(5): 884-888. |
| Guo X D, Zhong B H, Tang Y, et al. The influence of primary particle size and secondary particle size on performances of LiFePO4[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2013, 27(5): 884-888. | |
| 19 | Ye Y, Shi Y, Tay A A O. Electro-thermal cycle life model for lithium iron phosphate battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 217: 509-518. |
| 20 | Shirazi A H N, Azadi Kakavand M R, Rabczuk T. Numerical study of composite electrode's particle size effect on the electrochemical and heat generation of a Li-ion battery[J]. Journal of Nanotechnology in Engineering and Medicine, 2015, 6(4): 041003. |
| 21 | Liu H, Strobridge F C, Borkiewicz O J, et al. Capturing metastable structures during high-rate cycling of LiFePO4 nanoparticle electrodes[J]. Science, 2014, 344(6191): 1252817. |
| 22 | Sheu S P, Yao C Y, Chen J M, et al. Influence of the LiCoO2 particle size on the performance of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1997, 68: 533-535. |
| 23 | 施柳柳. 以LiFePO4为正极材料的电极制备工艺研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2018: 20-33. |
| Shi L L. Optimization of preparation process of LiFePO4 cathode[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2018: 20-33. | |
| 24 | Li Y, Meyer S, Lim J, et al. Effects of particle size, electronic connectivity, and incoherent nanoscale domains on the sequence of lithiation in LiFePO4 porous electrodes[J]. Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(42): 6591-6597. |
| 25 | Lee K, Kum D. The impact of inhomogeneous particle size distribution on Li-ion cell performance under galvanostatic and transient loads[C]// Asia-Pacific IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo. Busan, South Korea. IEEE, 2016: 454-459. |
| [1] | Fei KANG, Weiguang LYU, Feng JU, Zhi SUN. Research on discharge path and evaluation of spent lithium-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3903-3911. |
| [2] | Yue YANG, Dan ZHANG, Jugan ZHENG, Maoping TU, Qingzhong YANG. Experimental study on flash and mixing evaporation of aqueous NaCl solution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3279-3291. |
| [3] | Guoze CHEN, Dong WEI, Qian GUO, Zhiping XIANG. Optimal power point optimization method for aluminum-air batteries under load tracking condition [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3533-3542. |
| [4] | Zhilong WANG, Ye YANG, Zhenzhen ZHAO, Tao TIAN, Tong ZHAO, Yahui CUI. Influence of mixing time and sequence on the dispersion properties of the cathode slurry of lithium-ion battery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3127-3138. |
| [5] | Zhaoguang CHEN, Yuxiang JIA, Meng WANG. Modeling neutralization dialysis desalination driven by low concentration waste acid and its validation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [6] | Laiming LUO, Jin ZHANG, Zhibin GUO, Haining WANG, Shanfu LU, Yan XIANG. Simulation and experiment of high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells stack in the 1—5 kW range [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1724-1734. |
| [7] | Ruiheng WANG, Pinjing HE, Fan LYU, Hua ZHANG. Parameter comparison and optimization of three solid-liquid separation methods for washed air pollution control residues from municipal solid waste incinerators [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1712-1723. |
| [8] | Weijiang CHENG, Heqi WANG, Xiang GAO, Na LI, Sainan MA. Research progress on film-forming electrolyte additives for Si-based lithium-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 571-584. |
| [9] | Jianglong DU, Wenqi YANG, Kai HUANG, Cheng LIAN, Honglai LIU. Heat dissipation performance of the module combined CPCM with air cooling for lithium-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 674-689. |
| [10] | Tongpeng LU, Xiaolin PAN, Hongfei WU, Yu LI, Haiyan YU. Effect of organic flocculant on settling performance of iron-bearing minerals and its adsorption mechanism [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4122-4132. |
| [11] | Lei ZHONG, Xueqing QIU, Wenli ZHANG. Advances in lignin-derived carbon anodes for alkali metal ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3369-3380. |
| [12] | Yifang DONG, Yingying YU, Xuegong HU, Gang PEI. Electric field effect on wetting and capillary flow characteristics in vertical microgrooves [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 2952-2961. |
| [13] | Ziyi CHI, Chengwei LIU, Yuling ZHANG, Xuegang LI, Wende XIAO. Reactor simulation and optimization for CO oxidative coupling to dimethyl oxalate reactions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(11): 4974-4986. |
| [14] | Juntao DAI, Li LIU, Shuai LIU, Hanyang GU, Ke WANG. Investigation of bubble behaviors in gas-liquid two-phase flow in helically coiled tube based on wire mesh sensor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4377-4388. |
| [15] | Huiyan WANG, Yiqin CHEN, Jinghong ZHOU, Yueqiang CAO, Xinggui ZHOU. Numerical simulation of cathode coating of lithium-ion battery for porosity optimization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(1): 376-383. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||