CIESC Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (10): 4507-4517.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220531
• Separation engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yujie WANG1,2( ), Shenhui LI2, Zhiping ZHAO2(
), Shenhui LI2, Zhiping ZHAO2( )
)
Received:2022-04-13
Revised:2022-08-08
Online:2022-11-02
Published:2022-10-05
Contact:
Zhiping ZHAO
通讯作者:
赵之平
作者简介:王玉杰(1980—),女,博士,高级工程师,wangyuj.bjhy@sinopec.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yujie WANG, Shenhui LI, Zhiping ZHAO. Molecular simulation study on adsorption and separation of H2/He mixtures by M-MOF-74[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4507-4517.
王玉杰, 李申辉, 赵之平. M-MOF-74吸附分离H2/He混合物的分子模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4507-4517.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 名称 | CSD号 | 孔径/nm | 孔隙率/% | 比表面积/(m2·m-3) | 晶胞参数/nm;(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-MOF-74 | 1863524 | 1.1 | 0.724 | 1943.2 | 2.6×2.6×0.69;90×90×120 |
| Co-MOF-74 | 1494752 | 1.1 | 0.721 | 1818.5 | 2.6×2.6×0.67;90×90×120 |
| Ni-MOF-74 | 1494751 | 1.1 | 0.725 | 1834.4 | 2.6×2.6×0.67;90×90×120 |
| Cu-MOF-74 | — | 1.1 | 0.722 | 1878.8 | 2.6×2.6×0.69;90×90×120 |
| Zn-MOF-74 | 1863522 | 1.1 | 0.723 | 1922.4 | 2.6×2.6×0.69;90×90×120 |
Table 1 Structural features of M-MOF-74
| 名称 | CSD号 | 孔径/nm | 孔隙率/% | 比表面积/(m2·m-3) | 晶胞参数/nm;(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-MOF-74 | 1863524 | 1.1 | 0.724 | 1943.2 | 2.6×2.6×0.69;90×90×120 |
| Co-MOF-74 | 1494752 | 1.1 | 0.721 | 1818.5 | 2.6×2.6×0.67;90×90×120 |
| Ni-MOF-74 | 1494751 | 1.1 | 0.725 | 1834.4 | 2.6×2.6×0.67;90×90×120 |
| Cu-MOF-74 | — | 1.1 | 0.722 | 1878.8 | 2.6×2.6×0.69;90×90×120 |
| Zn-MOF-74 | 1863522 | 1.1 | 0.723 | 1922.4 | 2.6×2.6×0.69;90×90×120 |
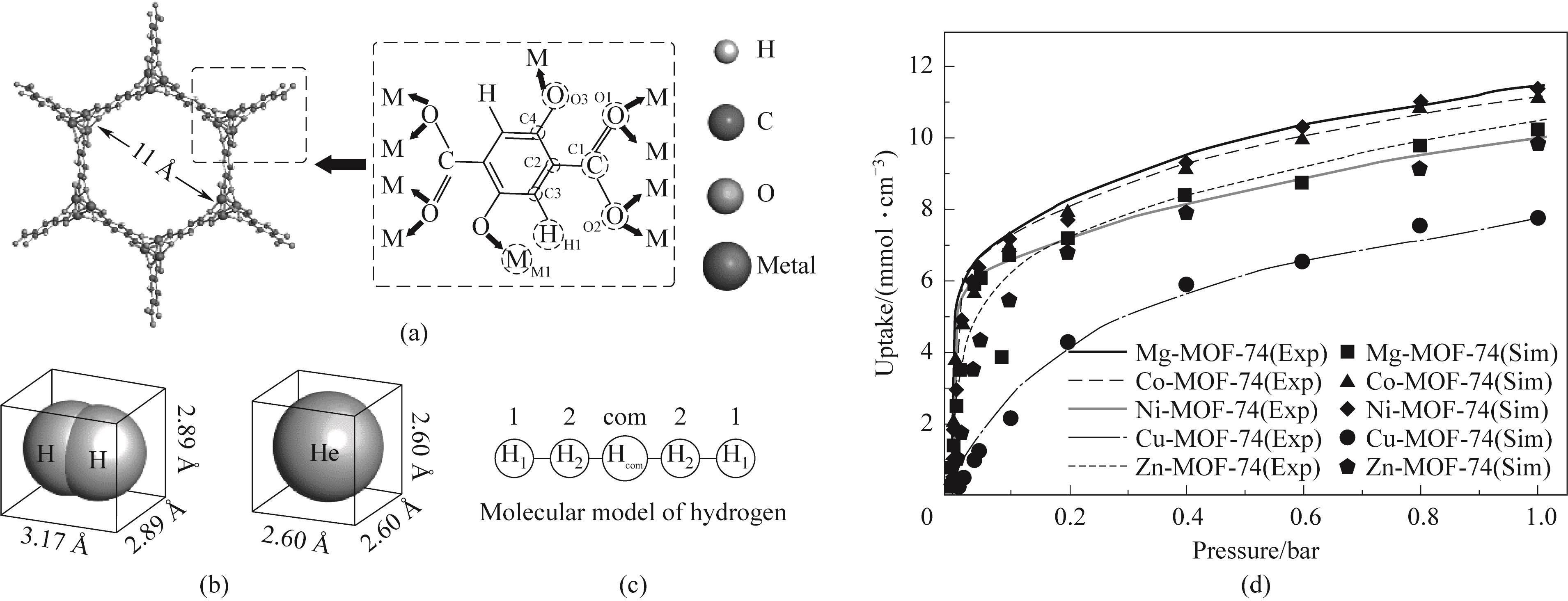
Fig.1 (a) Structure of M-MOF-74; (b) Molecular dimensions of hydrogen and helium; (c) Five-point model of hydrogen; (d) Adsorption isotherms of H2 in M-MOF-74 (where Exp represents the experimentally measured adsorption isotherm, and the data are from Refs. [36-38]; Sim represents the data get from the simulation of this work)
| 名称 | 临界温度/K | 临界压力/bar | 分子动力学直径/nm | 极化率/(10-25 cm3) | 电四极矩/(10-40 C·m-2) | 摩尔质量/(g·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| He | 5.2 | 2.28 | 0.260 | 2.08 | 0 | 4.003 |
| H2 | 33.2 | 13.15 | 0.289 | 7.87 | 2.21 | 2.016 |
Table 2 Physicochemical properties of H2 and He
| 名称 | 临界温度/K | 临界压力/bar | 分子动力学直径/nm | 极化率/(10-25 cm3) | 电四极矩/(10-40 C·m-2) | 摩尔质量/(g·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| He | 5.2 | 2.28 | 0.260 | 2.08 | 0 | 4.003 |
| H2 | 33.2 | 13.15 | 0.289 | 7.87 | 2.21 | 2.016 |
| 名称 | 势陷深度ε/K | 平衡距离σ/nm | 原子电荷q/e | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Co | Ni | Zn | Cu | |||
| Mg | 55.857 | 0.260 | 1.678 | ||||
| Co | 7.045 | 0.255 | 1.420 | ||||
| Ni | 7.545 | 0.252 | 1.501 | ||||
| Zn | 62.399 | 0.246 | 1.492 | ||||
| Cu | 2.516 | 0.311 | 1.128 | ||||
| C1 | 47.856 | 0.347 | 0.93030 | 0.93940 | 0.88260 | 0.87980 | 1.14250 |
| C2 | 47.856 | 0.347 | -0.48150 | -0.52700 | -0.44910 | -0.26750 | -0.53740 |
| C3 | 47.856 | 0.347 | 0.46750 | 0.49000 | 0.44070 | 0.40420 | 0.55200 |
| C4 | 47.856 | 0.347 | -0.38240 | -0.40320 | -0.43910 | -0.37410 | -0.33180 |
| O1 | 48.158 | 0.303 | -0.87140 | -0.79450 | -0.78000 | -0.82960 | -0.76640 |
| O2 | 48.158 | 0.303 | -0.76800 | -0.58940 | -0.66470 | -0.75710 | -0.72140 |
| O3 | 48.158 | 0.303 | -0.80540 | -0.72910 | -0.71650 | -0.77420 | -0.68620 |
Table 3 Force field parameters and atomic charges of M-MOF-74
| 名称 | 势陷深度ε/K | 平衡距离σ/nm | 原子电荷q/e | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Co | Ni | Zn | Cu | |||
| Mg | 55.857 | 0.260 | 1.678 | ||||
| Co | 7.045 | 0.255 | 1.420 | ||||
| Ni | 7.545 | 0.252 | 1.501 | ||||
| Zn | 62.399 | 0.246 | 1.492 | ||||
| Cu | 2.516 | 0.311 | 1.128 | ||||
| C1 | 47.856 | 0.347 | 0.93030 | 0.93940 | 0.88260 | 0.87980 | 1.14250 |
| C2 | 47.856 | 0.347 | -0.48150 | -0.52700 | -0.44910 | -0.26750 | -0.53740 |
| C3 | 47.856 | 0.347 | 0.46750 | 0.49000 | 0.44070 | 0.40420 | 0.55200 |
| C4 | 47.856 | 0.347 | -0.38240 | -0.40320 | -0.43910 | -0.37410 | -0.33180 |
| O1 | 48.158 | 0.303 | -0.87140 | -0.79450 | -0.78000 | -0.82960 | -0.76640 |
| O2 | 48.158 | 0.303 | -0.76800 | -0.58940 | -0.66470 | -0.75710 | -0.72140 |
| O3 | 48.158 | 0.303 | -0.80540 | -0.72910 | -0.71650 | -0.77420 | -0.68620 |
| 文献 | H2吸附热/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mg- MOF-74 | Co- MOF-74 | Ni- MOF-74 | Cu-MOF-74 | Zn-MOF-74 | |
| [ | -10.1 | -10.7 | -12.9 | — | -8.8 |
| [ | -10.3 | — | — | — | — |
| [ | — | — | — | — | -8.8 |
| [ | — | — | — | — | -8.3 |
| 本文 | -10.41 | -10.44 | -11.71 | -8.41 | -9.17 |
Table 4 Comparison of heat of adsorption calculated in this work with experimental values
| 文献 | H2吸附热/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mg- MOF-74 | Co- MOF-74 | Ni- MOF-74 | Cu-MOF-74 | Zn-MOF-74 | |
| [ | -10.1 | -10.7 | -12.9 | — | -8.8 |
| [ | -10.3 | — | — | — | — |
| [ | — | — | — | — | -8.8 |
| [ | — | — | — | — | -8.3 |
| 本文 | -10.41 | -10.44 | -11.71 | -8.41 | -9.17 |

Fig.7 (a) Metal ion adsorption sites and RDG analysis of H2 on M-MOF-74 (Blue represents certain coordination and green represents weak van der Waals interactions), isosurface at 0.2; (b) H2 adsorption sites on the benzene ring on M-MOF-74; (c) Equilibrium distances of H2 and He to M-MOF-74; (d) Binding energy of H2 and He to M-MOF-74
| 1 | 秦胜飞, 李济远. 世界氦气供需现状及发展趋势[J]. 石油知识, 2021(5): 44-45. |
| Qin S F, Li J Y. Current situation and development trend of helium supply and demand in the world [J]. Petroleum Knowledge, 2021(5): 44-45. | |
| 2 | Xiong L, Peng N, Liu L, et al. Helium extraction and nitrogen removal from LNG boil-off gas[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 171: 012003. |
| 3 | 邢国海. 天然气提取氦气技术现状与发展[J]. 天然气工业, 2008, 28(8): 114-116, 149. |
| Xing G H. Status quo and development of the technology on helium gas abstracted from natural gas[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2008, 28(8): 114-116, 149. | |
| 4 | 李均方, 何琳琳, 柴露华. 天然气提氦技术现状及建议[J]. 石油与天然气化工, 2018, 47(4): 41-44. |
| Li J F, He L L, Chai L H. Present situation and suggestion of helium extraction from natural gas[J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil & Gas, 2018, 47(4): 41-44. | |
| 5 | Rufford T E, Chan K I, Huang S H, et al. A review of conventional and emerging process technologies for the recovery of helium from natural gas[J]. Adsorption Science & Technology, 2014, 32(1): 49-72. |
| 6 | Antunes R, B?hml?nder A, Bükki-Deme A, et al. Experimental investigation of the ideal selectivity of MFI-ZSM-5 zeolite-type membranes for a first evaluation of the separation of hydrogen isotopologues from helium[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 212: 767-773. |
| 7 | Simplicio M, Afonso M D, Borisevich O, et al. Permeation of single gases and binary mixtures of hydrogen and helium through a MFI zeolite hollow fibres membrane for application in nuclear fusion[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2014, 122: 199-205. |
| 8 | Favvas E P, Heliopoulos N S, Papageorgiou S K, et al. Helium and hydrogen selective carbon hollow fiber membranes: the effect of pyrolysis isothermal time[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2015, 142: 176-181. |
| 9 | He T, Pachfule P, Wu H, et al. Hydrogen carriers[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2016, 1: 16059. |
| 10 | Wang X S, Ma S Q, Forster P, et al. Enhancing H2 uptake by "close-packing" alignment of open copper sites in metal-organic frameworks[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2008, 120(38): 7373-7376. |
| 11 | Bae Y S, Snurr R Q. Optimal isosteric heat of adsorption for hydrogen storage and delivery using metal-organic frameworks[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2010, 132(1/2): 300-303. |
| 12 | Pham T, Forrest K A, Eckert J, et al. Dramatic effect of the electrostatic parameters on H2 sorption in an M-MOF-74 analogue[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2016, 16(2): 867-874. |
| 13 | Valenzano L, Civalleri B, Chavan S, et al. Computational and experimental studies on the adsorption of CO, N2, and CO2 on Mg-MOF-74[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(25): 11185-11191. |
| 14 | Liu A Q, Peng X, Jin Q B, et al. Adsorption and diffusion of benzene in Mg-MOF-74 with open metal sites[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(4): 4686-4700. |
| 15 | Su X, Bromberg L, Martis V, et al. Postsynthetic functionalization of Mg-MOF-74 with tetraethylenepentamine: structural characterization and enhanced CO2 adsorption[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(12): 11299-11306. |
| 16 | Perry J J, Teich-McGoldrick S L, Meek S T, et al. Noble gas adsorption in metal-organic frameworks containing open metal sites[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(22): 11685-11698. |
| 17 | Qiao Z W, Xu Q S, Jiang J W. High-throughput computational screening of metal-organic framework membranes for upgrading of natural gas[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 551: 47-54. |
| 18 | Tang H J, Jiang J W. In silico screening and design strategies of ethane-selective metal-organic frameworks for ethane/ethylene separation[J]. AIChE Journal, 2021, 67(3): e17025. |
| 19 | Yeo B C, Kim D, Kim H, et al. High-throughput screening to investigate the relationship between the selectivity and working capacity of porous materials for propylene/propane adsorptive separation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(42): 24224-24230. |
| 20 | Moghadam P Z, Li A, Wiggin S B, et al. Development of a Cambridge structural database subset: a collection of metal-organic frameworks for past, present, and future[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(7): 2618-2625. |
| 21 | Chung Y G, Haldoupis E, Bucior B J, et al. Advances, updates, and analytics for the computation-ready, experimental metal-organic framework database: core MOF 2019[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2019, 64(12): 5985-5998. |
| 22 | Willems T F, Rycroft C H, Kazi M, et al. Algorithms and tools for high-throughput geometry-based analysis of crystalline porous materials[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2012, 149(1): 134-141. |
| 23 | Dubbeldam D, Calero S, Ellis D E, et al. RASPA: molecular simulation software for adsorption and diffusion in flexible nanoporous materials[J]. Molecular Simulation, 2016, 42(2): 81-101. |
| 24 | Eggimann B L, Sunnarborg A J, Stern H D, et al. An online parameter and property database for the TraPPE force field[J]. Molecular Simulation, 2014, 40(1/2/3): 101-105. |
| 25 | Belof J L, Stern A C, Space B. An accurate and transferable intermolecular diatomic hydrogen potential for condensed phase simulation[J]. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2008, 4(8): 1332-1337. |
| 26 | Rappe A K, Casewit C J, Colwell K S, et al. UFF, a full periodic table force field for molecular mechanics and molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1992, 114(25): 10024-10035. |
| 27 | Pham T, Forrest K A, Banerjee R, et al. Understanding the H2 sorption trends in the M-MOF-74 series (M = Mg, Ni, Co, Zn)[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(2): 1078-1090. |
| 28 | Souers P C. Hydrogen Properties for Fusion Energy[M]. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1986. |
| 29 | Stogryn D E, Stogryn A P. Molecular multipole moments[J]. Molecular Physics, 1966, 11(4): 371-393. |
| 30 | National Institute of Standards and Technology. NIST Chemistry WebBook, SRD 69 [EB/OL]. 2018-07-15. . |
| 31 | Auerbach S M, Carrado K A, Dutta P K. Handbook of Zeolite Science and Technology[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2003. |
| 32 | Zhou W, Wu H, Yildirim T. Enhanced H2 adsorption in isostructural metal–organic frameworks with open metal sites: strong dependence of the binding strength on metal ions[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(46): 15268-15269. |
| 33 | Sumida K, Brown C M, Herm Z R, et al. Hydrogen storage properties and neutron scattering studies of Mg2(dobdc): a metal-organic framework with open Mg2+ adsorption sites[J]. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 2011, 47(4): 1157-1159. |
| 34 | Liu Y, Kabbour H, Brown C M, et al. Increasing the density of adsorbed hydrogen with coordinatively unsaturated metal centers in metal-organic frameworks[J]. Langmuir: the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids, 2008, 24(9): 4772-4777. |
| 35 | Rowsell J L C, Yaghi O M. Effects of functionalization, catenation, and variation of the metal oxide and organic linking units on the low-pressure hydrogen adsorption properties of metal-organic frameworks[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128(4): 1304-1315. |
| 36 | Dietzel P D, Georgiev P A, Eckert J, et al. Interaction of hydrogen with accessible metal sites in the metal–organic frameworks M2(dhtp) (CPO-27-M; M = Ni, Co, Mg)[J]. Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(27): 4962-4964. |
| 37 | Jesse L C R, Yaghi O M. Effects of functionalization, catenation, and variation of the metal oxide and organic linking units on the low-pressure hydrogen adsorption properties of metal-organic frameworks[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128(4): 1304-1315. |
| 38 | Rosnes M H, Opitz M, Frontzek M, et al. Intriguing differences in hydrogen adsorption in CPO-27 materials induced by metal substitution[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(9): 4827. |
| 39 | Johnson E R, Keinan S, Mori-Sánchez P, et al. Revealing noncovalent interactions[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(18): 6498-6506. |
| 40 | Lu T, Chen F W. Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2012, 33(5): 580-592. |
| 41 | Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics, 1996, 14(1): 33-38. |
| 42 | Liao P Q, Huang N Y, Zhang W X, et al. Controlling guest conformation for efficient purification of butadiene[J]. Science, 2017, 356(6343): 1193-1196. |
| [1] | Minghao SONG, Fei ZHAO, Shuqing LIU, Guoxuan LI, Sheng YANG, Zhigang LEI. Multi-scale simulation and study of volatile phenols removal from simulated oil by ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3654-3664. |
| [2] | Xuejin YANG, Jintao YANG, Ping NING, Fang WANG, Xiaoshuang SONG, Lijuan JIA, Jiayu FENG. Research progress in dry purification technology of highly toxic gas PH3 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3742-3755. |
| [3] | Jianbo HU, Hongchao LIU, Qi HU, Meiying HUANG, Xianyu SONG, Shuangliang ZHAO. Molecular dynamics simulation insight into translocation behavior of organic cage across the cellular membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3756-3765. |
| [4] | Jiajia ZHAO, Shixiang TIAN, Peng LI, Honggao XIE. Microscopic mechanism of SiO2-H2O nanofluids to enhance the wettability of coal dust [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3931-3945. |
| [5] | Bingchun SHENG, Jianguo YU, Sen LIN. Study on lithium resource separation from underground brine with high concentration of sodium by aluminum-based lithium adsorbent [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3375-3385. |
| [6] | Ruihang ZHANG, Pan CAO, Feng YANG, Kun LI, Peng XIAO, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Changyu SUN, Guangjin CHEN. Analysis of key parameters affecting product purity of natural gas ethane recovery process via ZIF-8 nanofluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [7] | Yan GAO, Peng WU, Chao SHANG, Zejun HU, Xiaodong CHEN. Preparation of magnetic agarose microspheres based on a two-fluid nozzle and their protein adsorption properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3457-3471. |
| [8] | Linzheng WANG, Yubing LU, Ruizhi ZHANG, Yonghao LUO. Analysis on thermal oxidation characteristics of VOCs based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [9] | Ji CHEN, Ze HONG, Zhao LEI, Qiang LING, Zhigang ZHAO, Chenhui PENG, Ping CUI. Study on coke dissolution loss reaction and its mechanism based on molecular dynamics simulations [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2935-2946. |
| [10] | Ming DONG, Jinliang XU, Guanglin LIU. Molecular dynamics study on heterogeneous characteristics of supercritical water [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2836-2847. |
| [11] | Jie WANG, Xiaolin QIU, Ye ZHAO, Xinyang LIU, Zhongqiang HAN, Yong XU, Wenhan JIANG. Preparation and properties of polyelectrolyte electrostatic deposition modified PHBV antioxidant films [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [12] | Yuanchao LIU, Xuhao JIANG, Ke SHAO, Yifan XU, Jianbin ZHONG, Zhuan LI. Influence of geometrical dimensions and defects on the thermal transport properties of graphyne nanoribbons [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2708-2716. |
| [13] | Shaoyun CHEN, Dong XU, Long CHEN, Yu ZHANG, Yuanfang ZHANG, Qingliang YOU, Chenglong HU, Jian CHEN. Preparation and adsorption properties of monolayer polyaniline microsphere arrays [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2228-2238. |
| [14] | Hao GU, Fujian ZHANG, Zhen LIU, Wenxuan ZHOU, Peng ZHANG, Zhongqiang ZHANG. Desalination performance and mechanism of porous graphene membrane in temporal dimension under mechanical-electrical coupling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2067-2074. |
| [15] | Caihong LIN, Li WANG, Yu WU, Peng LIU, Jiangfeng YANG, Jinping LI. Effect of alkali cations in zeolites on adsorption and separation of CO2/N2O [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2013-2021. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||