CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (1): 197-210.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230782
• Fluid dynamics and transport phenomena • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yizhou CUI( ), Chengxiang LI, Linxiao ZHAI, Shuyu LIU, Xiaogang SHI, Jinsen GAO, Xingying LAN(
), Chengxiang LI, Linxiao ZHAI, Shuyu LIU, Xiaogang SHI, Jinsen GAO, Xingying LAN( )
)
Received:2023-08-01
Revised:2023-09-11
Online:2024-03-11
Published:2024-01-25
Contact:
Xingying LAN
崔怡洲( ), 李成祥, 翟霖晓, 刘束玉, 石孝刚, 高金森, 蓝兴英(
), 李成祥, 翟霖晓, 刘束玉, 石孝刚, 高金森, 蓝兴英( )
)
通讯作者:
蓝兴英
作者简介:崔怡洲(1994—),男,博士研究生,cuiyizhou_cup@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yizhou CUI, Chengxiang LI, Linxiao ZHAI, Shuyu LIU, Xiaogang SHI, Jinsen GAO, Xingying LAN. Comparative study on the flow and mass transfer characteristics of sub-millimeter bubbles and conventional bubbles in gas-liquid two-phase flow[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 197-210.
崔怡洲, 李成祥, 翟霖晓, 刘束玉, 石孝刚, 高金森, 蓝兴英. 亚毫米气泡和常规尺寸气泡气液两相流流动与传质特性对比[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 197-210.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 对比方式 | 实验编号 | 表观气速/(m/s) | 表观液速/(m/s) | 鼓泡塔入口处液相CO2浓度/(mol/L) | d32/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基准 | Exp.1 | 0.03226 | 0.04247 | 0.0384 | 0.312 |
| 对比方 | Exp.2 | 0.06717 | 0.04247 | 0 | 7.77 |
| 对比方 | Exp.3 | 0.03226 | 0.04247 | 0.0384 | 8.12 |
Table 1 Summary of the operating conditions of the mass transfer experiments
| 对比方式 | 实验编号 | 表观气速/(m/s) | 表观液速/(m/s) | 鼓泡塔入口处液相CO2浓度/(mol/L) | d32/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基准 | Exp.1 | 0.03226 | 0.04247 | 0.0384 | 0.312 |
| 对比方 | Exp.2 | 0.06717 | 0.04247 | 0 | 7.77 |
| 对比方 | Exp.3 | 0.03226 | 0.04247 | 0.0384 | 8.12 |
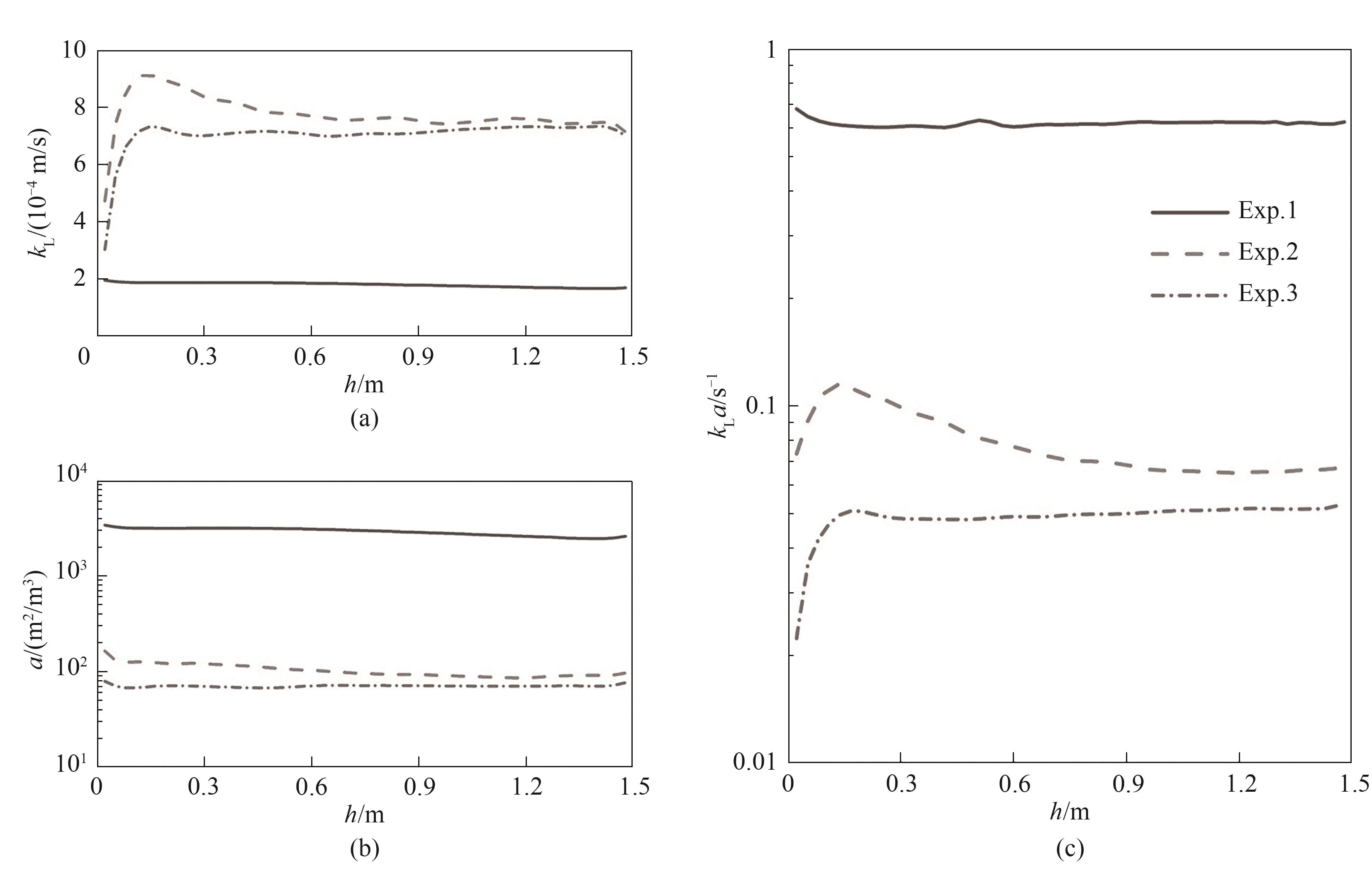
Fig.16 Comparison of liquid side mass transfer coefficient, gas-liquid interfacial area, and volumetric mass transfer coefficient between sub-millimeter bubbles and millimeter bubbles
| 1 | Martín M, Galan M A, Cerro R L, et al. Shape oscillating bubbles: hydrodynamics and mass transfer—a review[J]. Bubble Science Engineering and Technology, 2011, 3(2): 48-63. |
| 2 | International Organization for Standardization. Fine bubble technology—general principles for usage and measurement of fine bubbles(part 1): Terminology: [S]. Switzerland, 2017. |
| 3 | 邓超, 杨丽, 陈海军, 等. 微纳米气泡发生装置及其应用的研究进展[J]. 石油化工, 2014, 43(10): 1206-1213. |
| Deng C, Yang L, Chen H J, et al. Progresses in research and application of micro-nano bubble generating device[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2014, 43(10): 1206-1213. | |
| 4 | Parmar R, Majumder S K. Microbubble generation and microbubble-aided transport process intensification—a state-of-the-art report[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification, 2013, 64: 79-97. |
| 5 | Muroyama K, Imai K, Oka Y, et al. Mass transfer properties in a bubble column associated with micro-bubble dispersions[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 100: 464-473. |
| 6 | Muroyama K, Oka Y, Fujiki R. Transport properties of micro-bubbles in a bubble column[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 2012, 45(9): 666-671. |
| 7 | Kalaga D V, Ansari M, Turney D E, et al. Scale-up of a downflow bubble column: experimental investigations[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 386: 121447. |
| 8 | 张志炳. 微界面传质强化技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2020: 379-426. |
| Zhang Z B. Microinterfacial Mass Transfer Intensification[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2020: 379-426. | |
| 9 | Li J J, Song Y C, Yin J L, et al. Investigation on the effect of geometrical parameters on the performance of a Venturi type bubble generator[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2017, 325: 90-96. |
| 10 | Tsuge H. Fundamental of microbubbles and nanobubbles[J]. Bulletin of the Society of Sea Water Science Japan, 2010, 64: 4-10. |
| 11 | Kim Y B, Lee H S, Francis L, et al. Innovative swirling flow-type microbubble generator for multi-stage DCMD desalination system: focus on the two-phase flow pattern, bubble size distribution, and its effect on MD performance[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 588: 117197. |
| 12 | Rehman F, Medley G J D, Bandulasena H, et al. Fluidic oscillator-mediated microbubble generation to provide cost effective mass transfer and mixing efficiency to the wastewater treatment plants[J]. Environmental Research, 2015, 137: 32-39. |
| 13 | Tian H Z, Pi S F, Feng Y C, et al. One-dimensional drift-flux model of gas holdup in fine-bubble jet reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 386: 121222. |
| 14 | Weber J, Agblevor F A. Microbubble fermentation of Trichoderma reesei for cellulase production[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2005, 40(2): 669-676. |
| 15 | Wang X Y, Shuai Y, Zhou X R, et al. Performance comparison of swirl-Venturi bubble generator and conventional Venturi bubble generator[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification, 2020, 154: 108022. |
| 16 | 丁国栋, 陈家庆, 王春升, 等. 轴向旋流式微气泡发生器的结构设计与数值模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2018, 18(5): 934-941. |
| Ding G D, Chen J Q, Wang C S, et al. Structural design and numerical simulation of axial-swirling type micro-bubble generator[J]. Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2018, 18(5): 934-941. | |
| 17 | Han Y, Liu Y F, Hong J, et al. Large scale preparation of microbubbles by multi-channel ceramic membranes: hydrodynamics and mass transfer characteristics[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2017, 95(11): 2176-2185. |
| 18 | Liu Y, Han Y, Li X L, et al. Controlling microbubbles in alcohol solutions by using a multi-channel ceramic membrane distributor[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2018, 93: 2456-2463. |
| 19 | Liu Y, Han Y, Li X L, et al. Efficient control of microbubble properties by alcohol shear flows in ceramic membrane channels[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2018, 41(1): 168-174. |
| 20 | Wang Z C, Guo K, Liu H, et al. Effects of bubble size on the gas-liquid mass transfer of bubble swarms with Sauter mean diameters of 0.38—4.88 mm in a co-current upflow bubble column[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2020, 95(11): 2853-2867. |
| 21 | Zeng W, Jia C, Luo H X, et al. Microbubble-dominated mass transfer intensification in the process of ammonia-based flue gas desulfurization[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(44): 19781-19792. |
| 22 | Li C X, Cui Y Z, Shi X G, et al. Numerical simulation on the terminal rise velocity and mass transfer rate of single sub-millimeter bubbles[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 246: 116963. |
| 23 | 李成祥, 崔怡洲, 石孝刚, 等. 表面活性物质影响下单个自由上升微气泡传质过程的直接数值模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021, 21(8): 877-886. |
| Li C X, Cui Y Z, Shi X G, et al. Direct numerical simulation of mass transfer process of single free rising microbubbles under the influence of surface active materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2021, 21(8): 877-886. | |
| 24 | Cui Y Z, Li C X, Zhang W L, et al. A deep learning-based image processing method for bubble detection, segmentation, and shape reconstruction in high gas holdup sub-millimeter bubbly flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 449: 137859. |
| 25 | Ansari M, Turney D E, Yakobov R, et al. Chemical hydrodynamics of a downward microbubble flow for intensification of gas-fed bioreactors[J]. AIChE Journal, 2018, 64(4): 1399-1411. |
| 26 | 安钢, 孙波, 安以弘, 等. 不同类型鼓泡塔气液并流时液相轴向扩散系数[J]. 过程工程学报, 2010, 10(6): 1048-1053. |
| An G, Sun B, An Y H, et al. Liquid phase axial diffusion coefficients of gas-liquid concurrent flow in different types of bubbling column[J]. Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2010, 10(6): 1048-1053. | |
| 27 | Li C X, Cui Y Z, Zhai L X, et al. Study on drag coefficient for sub-millimeter bubbles in gas-liquid bubbly flow: experiments and CFD simulations[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.147236 . |
| 28 | Tomiyama A. Struggle with computational bubble dynamics[J]. Multiphase Science and Technology, 1998, 10: 369-405. |
| 29 | Jajuee B, Margaritis A, Karamanev D, et al. Application of surface-renewal-stretch model for interface mass transfer[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2006, 61: 3917-3929. |
| 30 | Chen J Q, Brooks C S. Experiments and CFD simulation of mass transfer and hydrodynamics in a cylindrical bubble column[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 234: 116435. |
| 31 | 黄子宾. 鼓泡塔内液相多尺度循环流动结构的研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2011. |
| Huang Z B. Study on liquid multiscale circulation structure in a bubble column[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2011. |
| [1] | Ruohan ZHAO, Mengmeng HUANG, Chunying ZHU, Taotao FU, Xiqun GAO, Youguang MA. Flow and mass transfer study of CO2 absorption by nanofluid in T-shaped microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 221-230. |
| [2] | Junnan WANG, Chengxiang HE, Zhongdong WANG, Chunying ZHU, Youguang MA, Taotao FU. Numerical simulation of homogeneous mixing in T-junction micromixers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 242-254. |
| [3] | Yao ZHOU, Xiaoping YANG, Yicheng NI, Jiping LIU, Jinjia WEI, Junjie YAN. Numerical simulation of two-phase steam ejector applied in novel loop heat pipe [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 268-278. |
| [4] | Yijiang WANG, Li SUN, Menghan LIU, Jinhong YANG, Guoyuan WANG. Optimization on parameter of plate-fin-and-tube air cooler in mines based on response surface method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 279-291. |
| [5] | Bidan ZHAO, Yiyang DAI, Junwu WANG, Yongmin ZHANG. CFD-DEM-IBM simulation on force characteristic on inclined-surface baffles in fluidized beds [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 255-267. |
| [6] | Zhanyu YE, He SHAN, Zhenyuan XU. Performance simulation of paper folding-like evaporator for solar evaporation systems [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 132-140. |
| [7] | Yifei ZHANG, Fangchen LIU, Shuangxing ZHANG, Wenjing DU. Performance analysis of printed circuit heat exchanger for supercritical carbon dioxide [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [8] | Zhiguo WANG, Meng XUE, Yushuang DONG, Tianzhen ZHANG, Xiaokai QIN, Qiang HAN. Numerical simulation and analysis of geothermal rock mass heat flow coupling based on fracture roughness characterization method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 223-234. |
| [9] | Jiahao SONG, Wen WANG. Study on coupling operation characteristics of Stirling engine and high temperature heat pipe [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 287-294. |
| [10] | Siyu ZHANG, Yonggao YIN, Pengqi JIA, Wei YE. Study on seasonal thermal energy storage characteristics of double U-shaped buried pipe group [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 295-301. |
| [11] | Jingwei CHAO, Jiaxing XU, Tingxian LI. Investigation on the heating performance of the tube-free-evaporation based sorption thermal battery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 302-310. |
| [12] | Yitong LI, Hang GUO, Hao CHEN, Fang YE. Study on operating conditions of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform catalyst distributions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [13] | Song HE, Qiaomai LIU, Guangshuo XIE, Simin WANG, Juan XIAO. Two-phase flow simulation and surrogate-assisted optimization of gas film drag reduction in high-concentration coal-water slurry pipeline [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3766-3774. |
| [14] | Lei XING, Chunyu MIAO, Minghu JIANG, Lixin ZHAO, Xinya LI. Optimal design and performance analysis of downhole micro gas-liquid hydrocyclone [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3394-3406. |
| [15] | Chen HAN, Youmin SITU, Bin ZHU, Jianliang XU, Xiaolei GUO, Haifeng LIU. Study of reaction and flow characteristics in multi-nozzle pulverized coal gasifier with co-processing of wastewater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||