CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (12): 5027-5037.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20231144
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mengqi PENG1( ), Tao ZHANG1,2(
), Tao ZHANG1,2( ), Maosheng LI1, Zhengrong SHI1,2, Jingyong CAI1,2
), Maosheng LI1, Zhengrong SHI1,2, Jingyong CAI1,2
Received:2023-11-07
Revised:2023-12-08
Online:2024-02-19
Published:2023-12-25
Contact:
Tao ZHANG
彭梦琦1( ), 张涛1,2(
), 张涛1,2( ), 李茂胜1, 施正荣1,2, 蔡靖雍1,2
), 李茂胜1, 施正荣1,2, 蔡靖雍1,2
通讯作者:
张涛
作者简介:彭梦琦(1999—),男,硕士研究生,memgqipeng@mail.shiep.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Mengqi PENG, Tao ZHANG, Maosheng LI, Zhengrong SHI, Jingyong CAI. Study on preparation and thermoelectric regulation performance of water-ZnO nanofluids for spectral-beam splitting[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(12): 5027-5037.
彭梦琦, 张涛, 李茂胜, 施正荣, 蔡靖雍. 光谱分频水基ZnO纳米流体制备及其热电性能调控[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(12): 5027-5037.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 试剂/仪器 | 厂家 | 型号/规格 |
|---|---|---|
| ZnO | 阿拉丁 | 50 nm |
| 分散剂 | 阿拉丁 | — |
| 去离子水 | — | — |
| 磁力搅拌器 | 群安仪器 | HS5S |
| 超声处理仪 | 力辰科技 | LC-JY92-IIDN |
| 分光光度计 | 岛津 | 3700i DUV |
Table 1 Information of instruments and chemical reagents
| 试剂/仪器 | 厂家 | 型号/规格 |
|---|---|---|
| ZnO | 阿拉丁 | 50 nm |
| 分散剂 | 阿拉丁 | — |
| 去离子水 | — | — |
| 磁力搅拌器 | 群安仪器 | HS5S |
| 超声处理仪 | 力辰科技 | LC-JY92-IIDN |
| 分光光度计 | 岛津 | 3700i DUV |
| 时间 | 实验结果 | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h |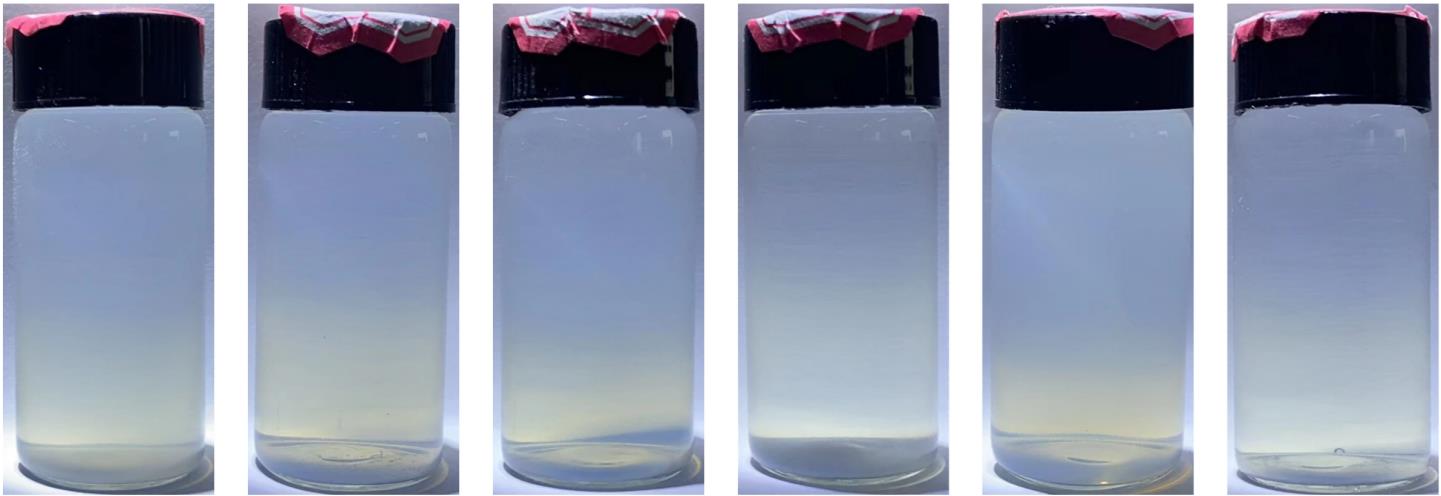  | 均未出现沉淀 | |
| 48 h |  | SDS出现沉淀 |  |
| 72 h |  | CTAB出现沉淀 | 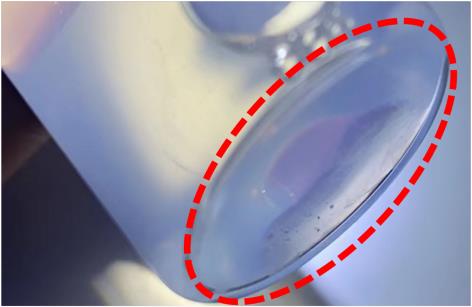 |
| 96 h |  | 乙二醇,SDBS出现沉淀 | 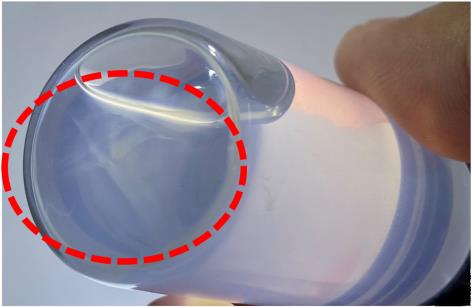  |
| 144 h |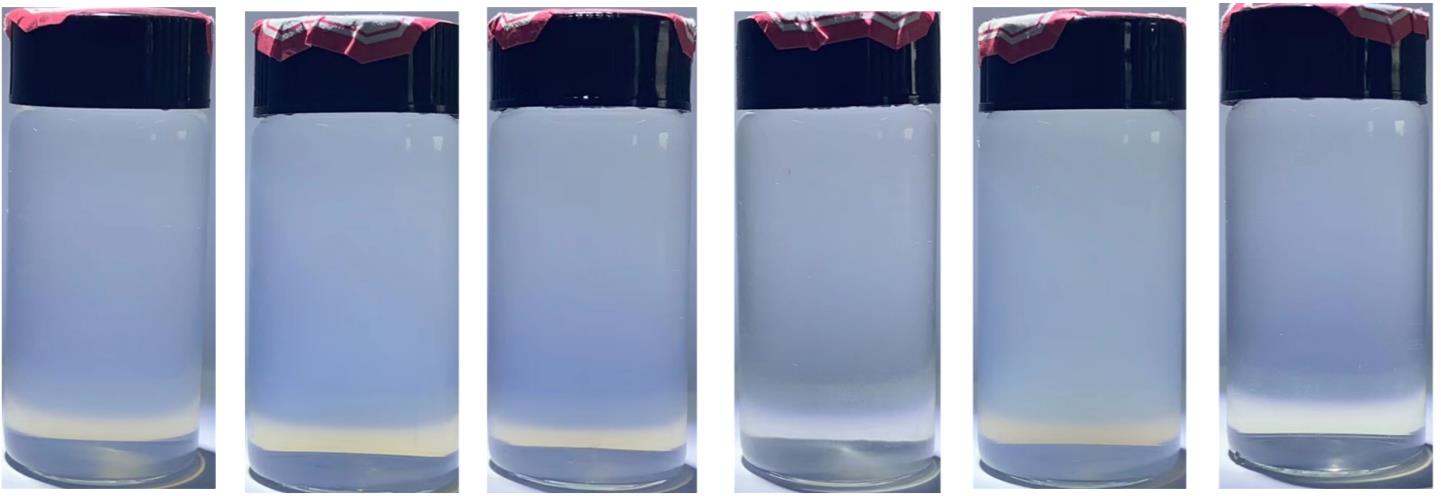  | GA出现沉淀 | 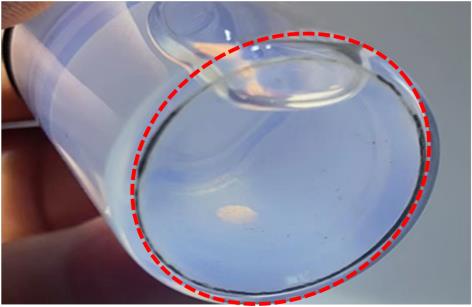 |
| 360 h |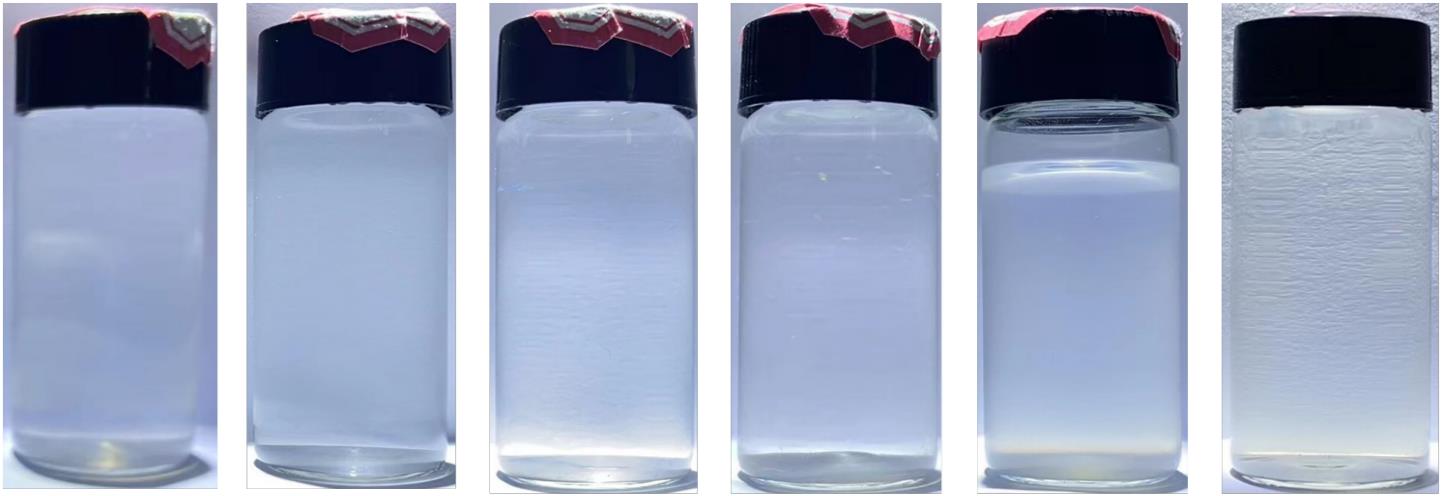  | 仅SHMP未出现沉淀 |  |
Table 2 Experimental results of sedimentation of water-ZnO nanofluids with different dispersants and glycol-ZnO nanofluid without dispersant
| 时间 | 实验结果 | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h |  | 均未出现沉淀 | |
| 48 h |  | SDS出现沉淀 |  |
| 72 h |  | CTAB出现沉淀 |  |
| 96 h |  | 乙二醇,SDBS出现沉淀 |   |
| 144 h |  | GA出现沉淀 |  |
| 360 h |  | 仅SHMP未出现沉淀 |  |
| 1 | 樊苗苗, 夏小康, 顾涛, 等. 太阳能光伏光热/催化净化复合技术的研究进展[J]. 太阳能学报, 2023, 44(7): 96-106. |
| Fan M M, Xia X K, Gu T, et al. Research progress on solar photovoltaic/thermal-catalytic/purification comperhensive technology[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2023, 44(7): 96-106. | |
| 2 | 孙亮亮, 袁艳平, 胡文举, 等. 热水型PV/T组件结构参数的敏感性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(S2): 235-239. |
| Sun L L, Yuan Y P, Hu W J, et al. Sensitivity analysis of configuration parameters of water-type PV/T module[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(S2): 235-239. | |
| 3 | Du M, Tang G H, Wang T M. Exergy analysis of a hybrid PV/T system based on plasmonic nanofluids and silica aerogel glazing[J]. Solar Energy, 2019, 183: 501-511. |
| 4 | Hassani S, Saidur R, Mekhilef S, et al. Environmental and exergy benefit of nanofluid-based hybrid PV/T systems[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2016, 123: 431-444. |
| 5 | Said Z, Arora S, Farooq S, et al. Recent advances on improved optical, thermal, and radiative characteristics of plasmonic nanofluids: academic insights and perspectives[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2022, 236: 111504. |
| 6 | Kameya Y, Hanamura K. Enhancement of solar radiation absorption using nanoparticle suspension[J]. Solar Energy, 2011, 85(2): 299-307. |
| 7 | Hjerrild N E, Mesgari S, Crisostomo F, et al. Hybrid PV/T enhancement using selectively absorbing Ag-SiO2/carbon nanofluids[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2016, 147: 281-287. |
| 8 | An W, Wu J R, Zhu T, et al. Experimental investigation of a concentrating PV/T collector with Cu9S5 nanofluid spectral splitting filter[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 184: 197-206. |
| 9 | Zhang C X, Shen C, Wei S, et al. Flexible management of heat/electricity of novel PV/T systems with spectrum regulation by Ag nanofluids[J]. Energy, 2021, 221: 119903. |
| 10 | Ni J, Li J, An W, et al. Performance analysis of nanofluid-based spectral splitting PV/T system in combined heating and power application[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 129: 1160-1170. |
| 11 | Sharma R, Chauhan P, Sharma A K, et al. Characterization of ZnO/nanofluid for improving heat transfer in thermal systems[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2022, 62: 1904-1908. |
| 12 | Sohani A, Shahverdian M H, Sayyaadi H, et al. Selecting the best nanofluid type for a photovoltaic thermal (PV/T) system based on reliability, efficiency, energy, economic, and environmental criteria[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2021, 124: 351-358. |
| 13 | Xu Y, Li X Y. A study of the structure optimization of silicon-based solar cells[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2015, 713/714/715: 1234-1238. |
| 14 | Jiao Y, Xing M B, Estellé P. Efficient utilization of hybrid photovoltaic/thermal solar systems by nanofluid-based spectral beam splitting: a review[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2024, 265: 112648. |
| 15 | Liang H X, Wang F Q, Yang L W, et al. Progress in full spectrum solar energy utilization by spectral beam splitting hybrid PV/T system[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 141: 110785. |
| 16 | Liang H X, Wang F Q, Zhang D, et al. Experimental investigation of cost-effective ZnO nanofluid based spectral splitting CPV/T system[J]. Energy, 2020, 194: 116913. |
| 17 | Meraje W C, Huang C C, Barman J, et al. Design and experimental study of a Fresnel lens-based concentrated photovoltaic thermal system integrated with nanofluid spectral splitter[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 258: 115455. |
| 18 | Zhu Q Z, Cui Y, Mu L J, et al. Characterization of thermal radiative properties of nanofluids for selective absorption of solar radiation[J]. International Journal of Thermophysics, 2013, 34: 2307-2321. |
| 19 | 韩晓飞. 基于太阳光谱分频利用的纳米流体特性及实验研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古工业大学, 2020. |
| Han X F. The characteristics and experimental study of the nanofluid based on solar spectrum beam splitting utilization[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University of Technology, 2020. | |
| 20 | 刘昌会, 刘红莉, 张天键, 等. 基于尿素/氯化胆碱低共熔溶剂体系纳米流体制备及其热物性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1333-1341. |
| Liu C H, Liu H L, Zhang T J, et al. Preparation and thermal physical properties of nanofluids based on a urea/choline chloride deep eutectic solvent system[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(3): 1333-1341. | |
| 21 | 郭文杰, 翟玉玲, 陈文哲, 等. Al2O3-CuO/水混合纳米流体对流传热性能及热经济性分析[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(5): 2315-2324. |
| Guo W J, Zhai Y L, Chen W Z, et al. Analysis of convective heat transfer and thermo-economic performance of Al2O3-CuO/water hybrid nanofluids[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(5): 2315-2324. | |
| 22 | Alktranee M, Shehab M A, Németh Z, et al. Experimental study for improving photovoltaic thermal system performance using hybrid titanium oxide-copper oxide nanofluid[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2023, 16(9): 105102. |
| 23 | 雷刚, 范襄, 王凯, 等. 太阳电池在不同光谱下电性能的分析与换算方法[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42(7): 179-184. |
| Lei G, Fan X, Wang K, et al. Analysis and conversion method for electrical performance of solar cells at different solar spectra[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42(7): 179-184. | |
| 24 | 王婷婷, 戴妙妙, 卞志华, 等. 光谱响应测试在太阳能电池中的应用[J]. 日用电器, 2014(9): 73-75. |
| Wang T T, Dai M M, Bian Z H, et al. The application of spectral response test in solar cells[J]. Electrical Appliances, 2014(9): 73-75. | |
| 25 | Otanicar T, Chowdhury I, Phelan P E, et al. Parametric analysis of a coupled photovoltaic/thermal concentrating solar collector for electricity generation[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 108(11): 114907. |
| 26 | Libra M, Petrík T, Poulek V, et al. Changes in the efficiency of photovoltaic energy conversion in temperature range with extreme limits[J]. IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics, 2021, 11(6): 1479-1484. |
| 27 | 赵晓波. Ag和Ag@SiO2纳米流体的太阳能分频特性优化及其在PV/T系统中的性能研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2022. |
| Zhao X B. Study on solar spectral splitting characteristics optimization of Ag and Ag@SiO2 nanofluid and its Performance in PV/T system [D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2022. | |
| 28 | 陈晓彬, 韩新月, 孙耀, 等. 分频型光伏光热系统中丙二醇基Ag/CoSO4纳米流体的性能研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42(5): 168-173. |
| Chen X B, Han X Y, Sun Y, et al. Study on propylene glycol based Ag/CoSO4 nanofluid splitter for spectrum-splitting PV/T system[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42(5): 168-173. | |
| 29 | Han X Y, Zhao X B, Huang J, et al. Optical properties optimization of plasmonic nanofluid to enhance the performance of spectral splitting photovoltaic/thermal systems[J]. Renewable Energy, 2022, 188: 573-587. |
| 30 | 刘艳峰, 李荟婷, 王登甲, 等. 太阳能集热系统过热影响因素分析[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42(3): 463-468. |
| Liu Y F, Li H T, Wang D J, et al. Factor analysis of overheating in solar collector system[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42(3): 463-468. | |
| 31 | Kong L H, Sun J L, Bao Y Y. Preparation, characterization and tribological mechanism of nanofluids[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(21): 12599-12609. |
| 32 | 刘冉, 夏国栋, 杜墨. 三角形微通道内纳米流体流动与换热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(12): 4936-4943. |
| Liu R, Xia G D, Du M. Characteristics of convective heat transfer in triangular microchannel heat sink using different nanofluids[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(12): 4936-4943. | |
| 33 | 郑新建, 马建中, 鲍艳. 纳米TiO2在水中的分散与改性研究[J]. 涂料工业, 2010, 40(10): 15-18, 23. |
| Zheng X J, Ma J Z, Bao Y. Research on the dispersion and modification of nano TiO2 in aqueous solution[J]. Paint & Coatings Industry, 2010, 40(10): 15-18, 23. |
| [1] | Zhanyu YE, He SHAN, Zhenyuan XU. Performance simulation of paper folding-like evaporator for solar evaporation systems [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 132-140. |
| [2] | He JIANG, Junfei YUAN, Lin WANG, Guyu XING. Experimental study on the effect of flow sharing cavity structure on phase change flow characteristics in microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [3] | Jiajia ZHAO, Shixiang TIAN, Peng LI, Honggao XIE. Microscopic mechanism of SiO2-H2O nanofluids to enhance the wettability of coal dust [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3931-3945. |
| [4] | Cong QI, Zi DING, Jie YU, Maoqing TANG, Lin LIANG. Study on solar thermoelectric power generation characteristics based on selective absorption nanofilm [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3921-3930. |
| [5] | Lingding MENG, Ruqing CHONG, Feixue SUN, Zihui MENG, Wenfang LIU. Immobilization of carbonic anhydrase on modified polyethylene membrane and silica [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3472-3484. |
| [6] | Yu FU, Xingchong LIU, Hanyu WANG, Haimin LI, Yafei NI, Wenjing ZOU, Yue LEI, Yongshan PENG. Research on F3EACl modification layer for improving performance of perovskite solar cells [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3554-3563. |
| [7] | Yuyuan ZHENG, Zhiwei GE, Xiangyu HAN, Liang WANG, Haisheng CHEN. Progress and prospect of medium and high temperature thermochemical energy storage of calcium-based materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3171-3192. |
| [8] | Wentao WU, Liangyong CHU, Lingjie ZHANG, Weimin TAN, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. High-efficient preparation of cardanol-based self-healing microcapsules [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3103-3115. |
| [9] | Zhilong WANG, Ye YANG, Zhenzhen ZHAO, Tao TIAN, Tong ZHAO, Yahui CUI. Influence of mixing time and sequence on the dispersion properties of the cathode slurry of lithium-ion battery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3127-3138. |
| [10] | Lei MAO, Guanzhang LIU, Hang YUAN, Guangya ZHANG. Efficient preparation of carbon anhydrase nanoparticles capable of capturing CO2 and their characteristics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [11] | Feng ZHU, Kailin CHEN, Xiaofeng HUANG, Yinzhu BAO, Wenbin LI, Jiaxin LIU, Weiqiang WU, Wangwei GAO. Performance study of KOH modified carbide slag for removal of carbonyl sulfide [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2668-2679. |
| [12] | Bin CAI, Xiaolin ZHANG, Qian LUO, Jiangtao DANG, Liyuan ZUO, Xinmei LIU. Research progress of conductive thin film materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2308-2321. |
| [13] | Wenchao XU, Zhigao SUN, Cuimin LI, Juan LI, Haifeng HUANG. Effect of surfactant E-1310 on the formation of HCFC-141b hydrate under static conditions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2179-2185. |
| [14] | Zijian WANG, Ming KE, Jiahan LI, Shuting LI, Jinru SUN, Yanbing TONG, Zhiping ZHAO, Jiaying LIU, Lu REN. Progress in preparation and application of short b-axis ZSM-5 molecular sieve [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1457-1473. |
| [15] | Runzhu LIU, Tiantian CHU, Xiaoa ZHANG, Chengzhong WANG, Junying ZHANG. Synthesis and properties of phenylene-containing α,ω-hydroxy-terminated fluorosilicone polymers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1360-1369. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||