CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (4): 1256-1269.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20231215
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mingze SUN( ), Helai HUANG(
), Helai HUANG( ), Zhiqiang NIU(
), Zhiqiang NIU( )
)
Received:2023-11-22
Revised:2024-03-11
Online:2024-06-06
Published:2024-04-25
Contact:
Zhiqiang NIU
通讯作者:
牛志强
作者简介:孙铭泽(1998—),男,博士研究生,smz20@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn基金资助:CLC Number:
Mingze SUN, Helai HUANG, Zhiqiang NIU. Pt-based oxygen reduction reaction catalysts: from single crystal electrode to nanostructured extended surface[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1256-1269.
孙铭泽, 黄鹤来, 牛志强. 铂基氧还原催化剂:从单晶电极到拓展表面纳米材料[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1256-1269.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
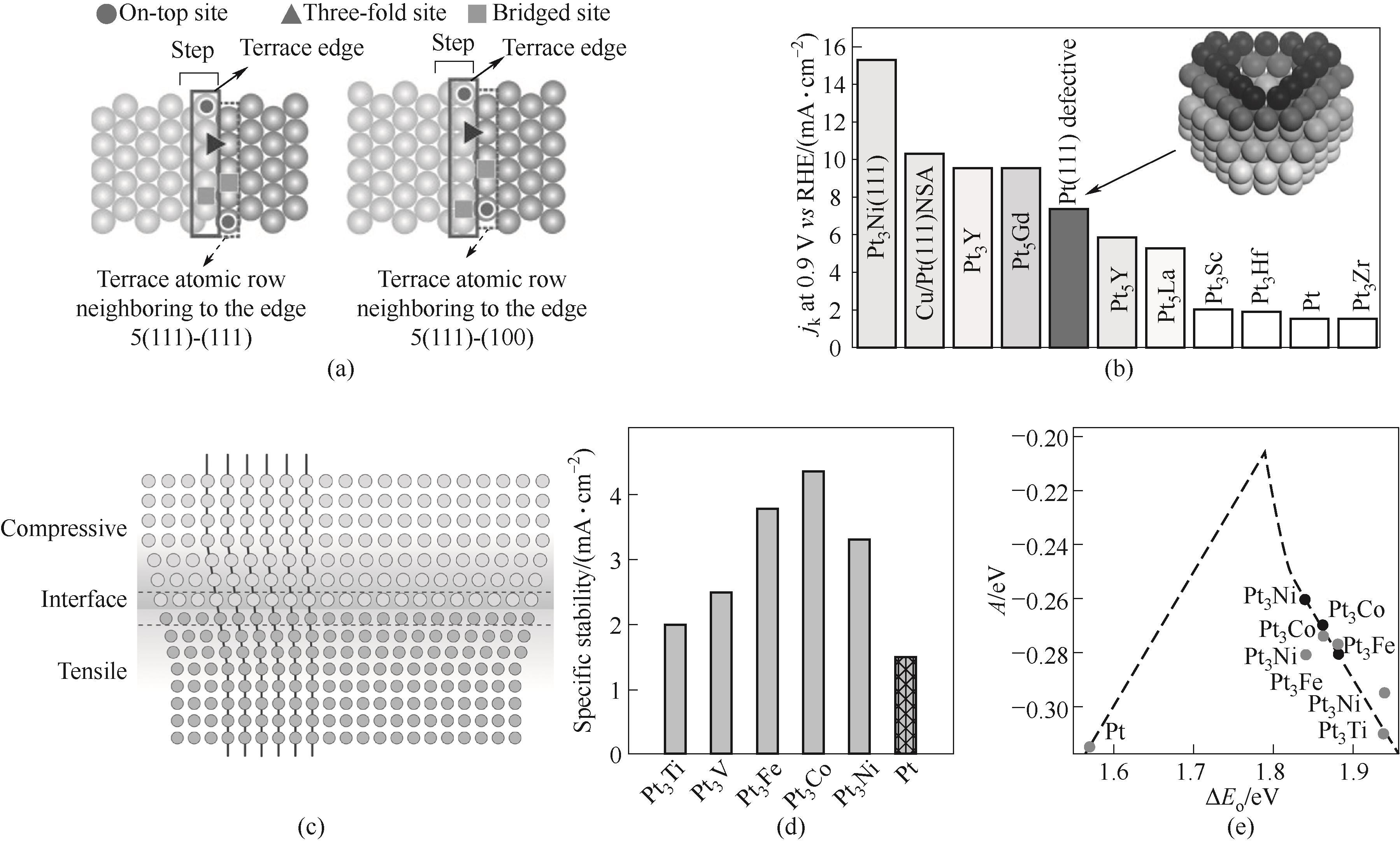
Fig.2 Origin of the increase of ORR activity by step sites (a)[39]; Increase of ORR activities for defective Pt(111) cavity (b)[40]; Schematic illustration of strain effect (c)[44]; Specific activity (d) as well as theory calculation (e) of Pt and Pt3M electrodes[45]
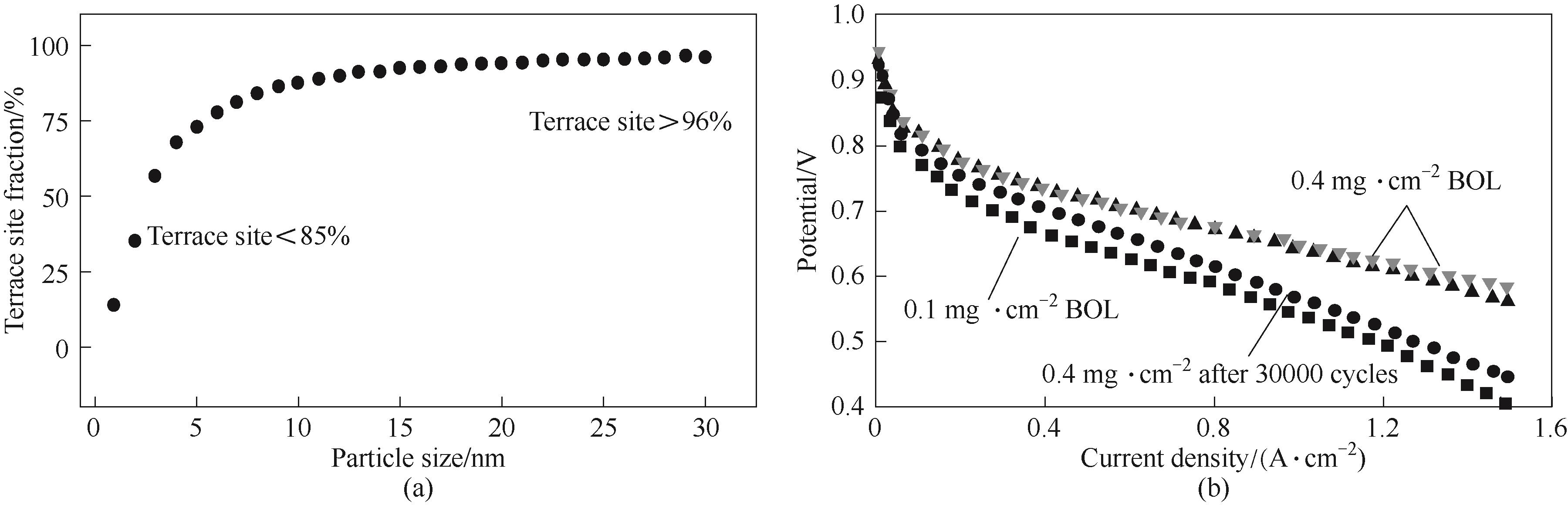
Fig.3 Relationship between particle size and terrace site fraction (a)[71]; Influence of low Pt loading for ORR activity especially at high current density (b)[72]
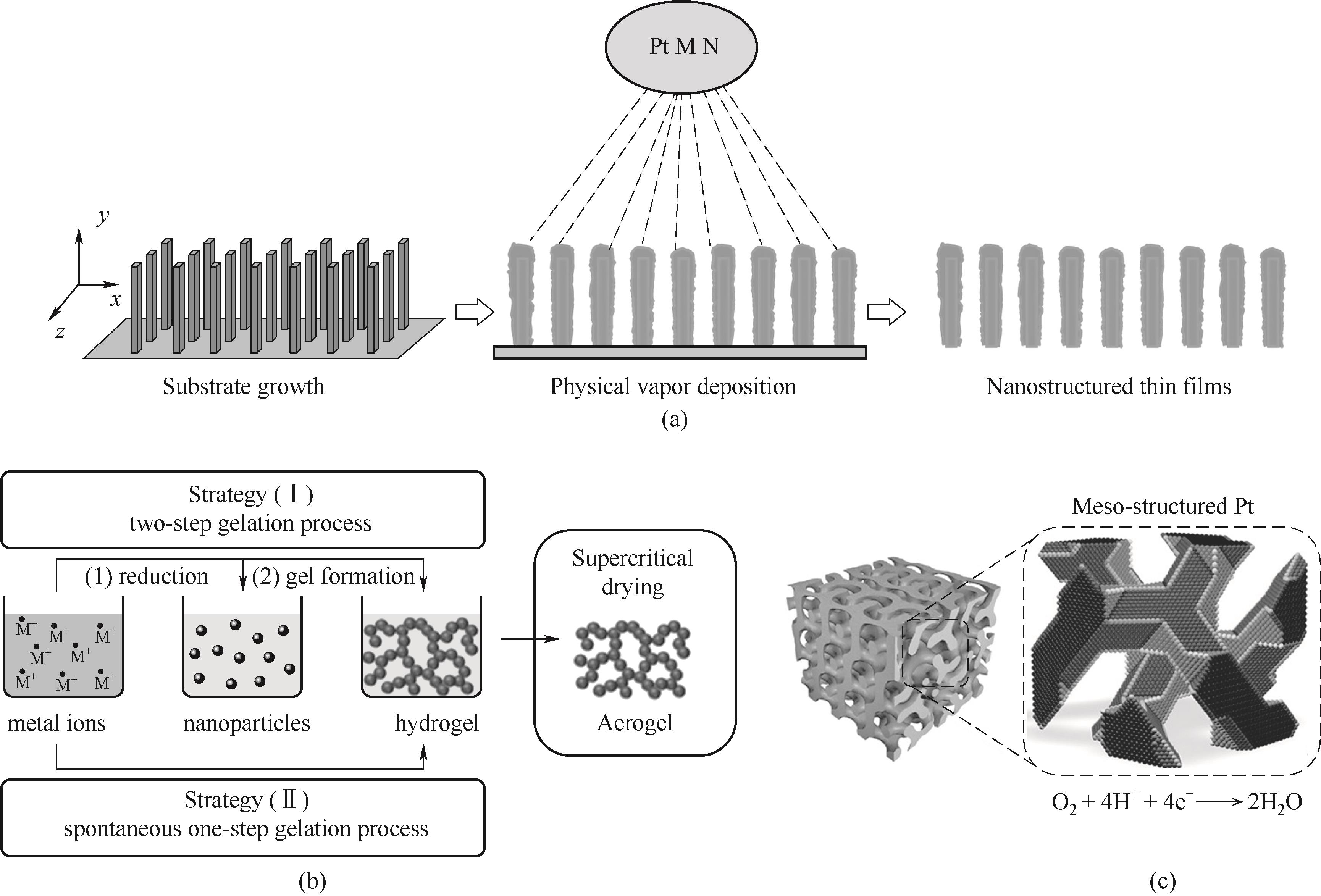
Fig.2 Schematic illustration of the preperation and structure of NSTF catalyst (a)[84]; Schematic illustration of the synthesis of aerogel (b)[85]; Schematic illustration of the synthesis of meso-structured Pt (c)[89]
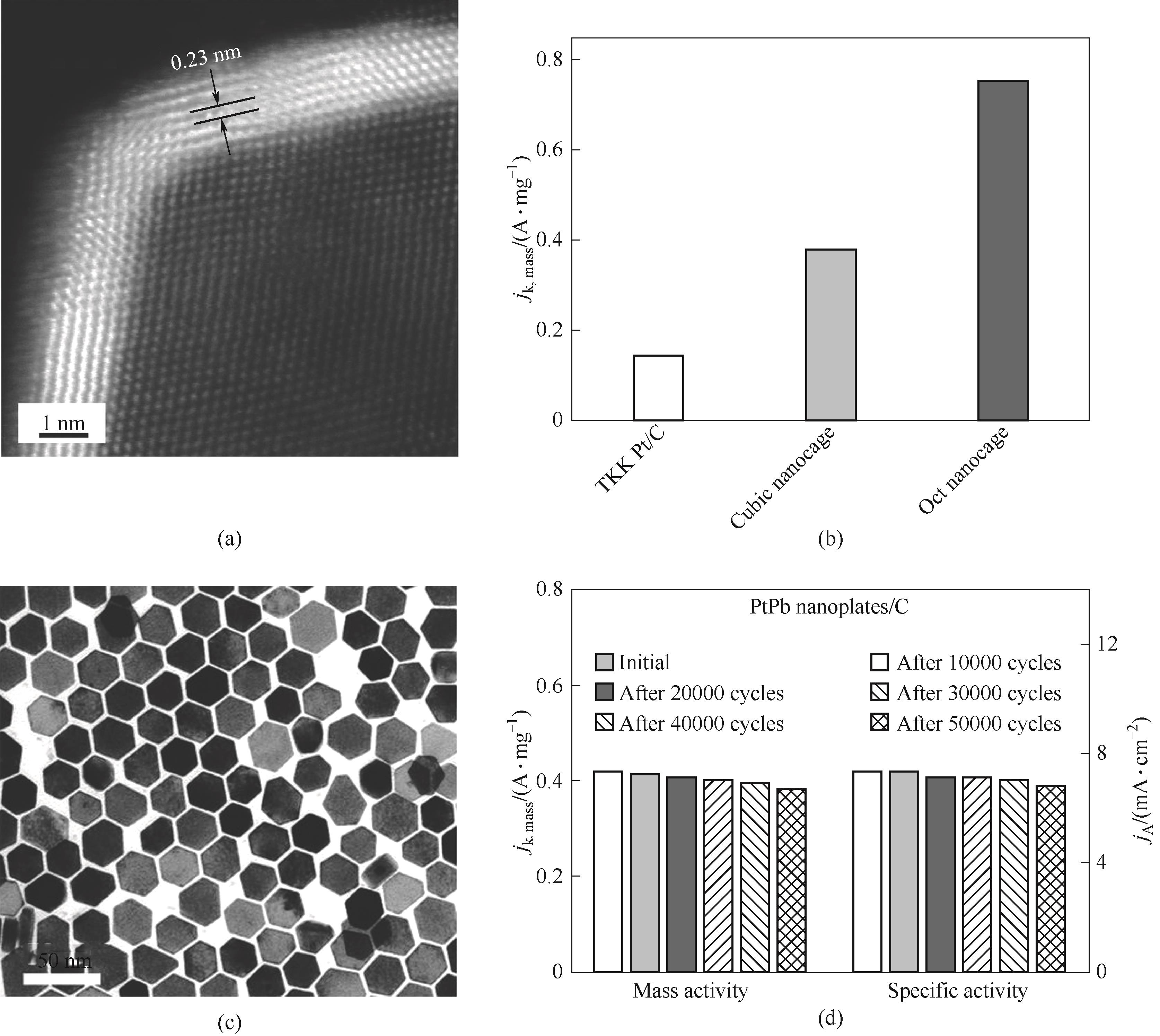
Fig.5 HAADF-STEM image of an individual octahedral nanocage (a); Specific activities and mass activities at 0.9 V (RHE) of octahedral nanocages, cubic nanocages, and TKK Pt/C (b)[96]; TEM image of PtPb/Pt hexagonal nanoplates (c); Specific activities and mass activities of hexagonal nanoplates after stability test (d)[97]

Fig.6 Schematic illustration of the synthesis of extended PtCuNi catalyst (a); Representative HAADF-STEM image of Cu@PtNi core-shell nanowire (b); EDS elemental mapping of Cu@PtNi core-shell nanowire (c); Specific activities and mass activities at 0.9 V (RHE) of extended PtCuNiAu, extended PtCuNi, PtCuNi NPs and commercial Pt/C (d); H2-air fuel cell polarization and power density plots of commercial Pt/C and extended PtCuNi (e)[102]
| 1 | Hassan Q, Sameen A Z, Salman H M, et al. Hydrogen energy future: advancements in storage technologies and implications for sustainability[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 72: 108404. |
| 2 | Pathak P K, Yadav A K, Padmanaban S. Transition toward emission-free energy systems by 2050: potential role of hydrogen[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(26): 9921-9927. |
| 3 | Abe J O, Popoola A P I, Ajenifuja E, et al. Hydrogen energy, economy and storage: review and recommendation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(29): 15072-15086. |
| 4 | Yusaf T, Faisal Mahamude A S, Kadirgama K, et al. Sustainable hydrogen energy in aviation—a narrative review[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 52: 1026-1045. |
| 5 | Dyantyi N, Parsons A, Bujlo P, et al. Behavioural study of PEMFC during start-up/shutdown cycling for aeronautic applications[J]. Materials for Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 2019, 8(1): 4. |
| 6 | Wang X Y, Zhu J Z, Han M F. Industrial development status and prospects of the marine fuel cell: a review[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11(2): 238. |
| 7 | Zhan Z P. Current status and future development of fuel cell ships in China[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2022, 2160(1): 012061. |
| 8 | Debe M K. Electrocatalyst approaches and challenges for automotive fuel cells[J]. Nature, 2012, 486: 43-51. |
| 9 | Zhu X Y, Gui P P, Zhang X X, et al. Multi-objective optimization of a hybrid energy system integrated with solar-wind-PEMFC and energy storage[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 72: 108562. |
| 10 | Shao M H, Chang Q W, Dodelet J P, et al. Recent advances in electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(6): 3594-3657. |
| 11 | Hu X Y, Yang B Z, Ke S R, et al. Review and perspectives of carbon-supported platinum-based catalysts for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2023, 37(16): 11532-11566. |
| 12 | Zhang X, Xie Y, Wang L. Progress and prospect of Pt-based catalysts for electrocatalytic hydrogen oxidation reactions[J]. Nano Research, 2024, 17(3): 960-981. |
| 13 | James B, Huya-Kouadio J, Houchins C, et al. DOE Hydrogen and Fuel Cells Program. Heavy-Duty Fuel Cell System Cost - 2022[EB/OL]. Dimitrios Papageorgopoulos and Sunita Satyapal (DOE), 2023[2024-04-10]. |
| 14 | Duan Z Y, Wang G F. Comparison of reaction energetics for oxygen reduction reactions on Pt(100), Pt(111), Pt/Ni(100), and Pt/Ni(111) surfaces: a first-principles study[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(12): 6284-6292. |
| 15 | Dong J C, Zhang X G, Briega-Martos V, et al. In situ Raman spectroscopic evidence for oxygen reduction reaction intermediates at platinum single-crystal surfaces[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4: 60-67. |
| 16 | Wang T, Zhang Y R, Huang B T, et al. Enhancing oxygen reduction electrocatalysis by tuning interfacial hydrogen bonds[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2021, 4: 753-762. |
| 17 | Chen C H, Meadows K E, Cuharuc A, et al. High resolution mapping of oxygen reduction reaction kinetics at polycrystalline platinum electrodes[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(34): 18545-18552. |
| 18 | Temmel S E, Fabbri E, Pergolesi D, et al. Investigating the role of strain toward the oxygen reduction activity on model thin film Pt catalysts[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(11): 7566-7576. |
| 19 | Ahluwalia R K, Wang X, Lajunen A, et al. Kinetics of oxygen reduction reaction on nanostructured thin-film platinum alloy catalyst[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 215: 77-88. |
| 20 | Zhang J M, Yang H B, Zhou D J, et al. Adsorption energy in oxygen electrocatalysis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2022, 122(23): 17028-17072. |
| 21 | Zhao J Y, Lian J X, Zhao Z, et al. A review of In-situ techniques for probing active sites and mechanisms of electrocatalytic oxygen reduction reactions[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 15(1): 19. |
| 22 | Tang C, Chen L, Li H J, et al. Tailoring acidic oxygen reduction selectivity on single-atom catalysts via modification of first and second coordination spheres[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(20): 7819-7827. |
| 23 | Huang H L, Sun M Z, Li M, et al. Recent advances in single-atom catalysts for electrocatalytic synthesis of hydrogen peroxide[J]. Green Energy and Resources, 2023, 1(3): 100031. |
| 24 | Zhang Y X, Zhang S B, Huang H L, et al. General synthesis of a diatomic catalyst library via a macrocyclic precursor-mediated approach[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(8): 4819-4827. |
| 25 | Sun M Z, Gong S Y, Zhang Y-X, et al. A perspective on the PGM-free metal-nitrogen-carbon catalysts for PEMFC[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 67: 250-254. |
| 26 | Zhang S B, Wu Y F, Zhang Y X, et al. Dual-atom catalysts: controllable synthesis and electrocatalytic applications[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2021, 64(11): 1908-1922. |
| 27 | Viswanathan V, Hansen H A, Rossmeisl J, et al. Universality in oxygen reduction electrocatalysis on metal surfaces[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2012, 2(8): 1654-1660. |
| 28 | Xie C L, Niu Z Q, Kim D, et al. Surface and interface control in nanoparticle catalysis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(2): 1184-1249. |
| 29 | Gao G P, Waclawik E R, Du A J. Computational screening of two-dimensional coordination polymers as efficient catalysts for oxygen evolution and reduction reaction[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2017, 352: 579-585. |
| 30 | Calle-Vallejo F, Krabbe A, García-Lastra J M. How covalence breaks adsorption-energy scaling relations and solvation restores them[J]. Chemical Science, 2017, 8(1): 124-130. |
| 31 | Tritsaris G A, Greeley J, Rossmeisl J, et al. Atomic-scale modeling of particle size effects for the oxygen reduction reaction on Pt[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2011, 141(7): 909-913. |
| 32 | Hammer B, Nørskov J K. Why gold is the noblest of all the metals[J]. Nature, 1995, 376: 238-240. |
| 33 | Hammer B, Nørskov J K. Theoretical Surface Science and Catalysis—Calculations and Concepts[M]//Advances in Catalysis. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2000: 71-129. |
| 34 | Nilsson A, Pettersson L G M, Hammer B, et al. The electronic structure effect in heterogeneous catalysis[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2005, 100(3): 111-114. |
| 35 | Zhu X J, Guo Q S, Sun Y F, et al. Optimising surface d charge of AuPd nanoalloy catalysts for enhanced catalytic activity[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1428. |
| 36 | Kitchin J R, Nørskov J K, Barteau M A, et al. Modification of the surface electronic and chemical properties of Pt(111) by subsurface 3d transition metals[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2004, 120(21): 10240-10246. |
| 37 | Marković N M, Adžić R R, Cahan B D, et al. Structural effects in electrocatalysis: oxygen reduction on platinum low index single-crystal surfaces in perchloric acid solutions[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 1994, 377(1/2): 249-259. |
| 38 | Marković N M, Gasteiger H A, Ross P N. Oxygen reduction on platinum low-index single-crystal surfaces in sulfuric acid solution: rotating ring-Pt(hkl) disk studies[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1995, 99(11): 3411-3415. |
| 39 | Hoshi N, Nakamura M, Hitotsuyanagi A. Active sites for the oxygen reduction reaction on the high index planes of Pt[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 112: 899-904. |
| 40 | Calle-Vallejo F, Tymoczko J, Colic V, et al. Finding optimal surface sites on heterogeneous catalysts by counting nearest neighbors[J]. Science, 2015, 350(6257): 185-189. |
| 41 | Calle-Vallejo F, Martínez J I, García-Lastra J M, et al. Fast prediction of adsorption properties for platinum nanocatalysts with generalized coordination numbers[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(32): 8316-8319. |
| 42 | Calle-Vallejo F, Pohl M D, Reinisch D, et al. Why conclusions from platinum model surfaces do not necessarily lead to enhanced nanoparticle catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Chemical Science, 2017, 8(3): 2283-2289. |
| 43 | Calle-Vallejo F, Bandarenka A S. Enabling generalized coordination numbers to describe strain effects[J]. ChemSusChem, 2018, 11(11): 1824-1828. |
| 44 | Luo M C, Guo S J. Strain-controlled electrocatalysis on multimetallic nanomaterials[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2(11): 17059. |
| 45 | Stamenkovic V, Mun B S, Mayrhofer K J J, et al. Changing the activity of electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction by tuning the surface electronic structure[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2006, 118(18): 2963-2967. |
| 46 | Strasser P, Koh S, Anniyev T, et al. Lattice-strain control of the activity in dealloyed core-shell fuel cell catalysts[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2010, 2: 454-460. |
| 47 | Wang Z C, Chen S H, Wu W, et al. Tailored lattice compressive strain of Pt-skins by the L12-Pt3M intermetallic core for highly efficient oxygen reduction[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(36): e2301310. |
| 48 | Yang W H, Zou L L, Huang Q H, et al. Lattice contracted ordered intermetallic core-shell PtCo@Pt nanoparticles: synthesis, structure and origin for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(6): H331-H337. |
| 49 | Stephens I E L, Bondarenko A S, Perez-Alonso F J, et al. Tuning the activity of Pt(111) for oxygen electroreduction by subsurface alloying[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(14): 5485-5491. |
| 50 | Hernandez-Fernandez P, Masini F, McCarthy D N, et al. Mass-selected nanoparticles of Pt x Y as model catalysts for oxygen electroreduction[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2014, 6: 732-738. |
| 51 | Escudero-Escribano M, Malacrida P, Hansen M H, et al. Tuning the activity of Pt alloy electrocatalysts by means of the lanthanide contraction[J]. Science, 2016, 352(6281): 73-76. |
| 52 | Li J, Li L, Wang M J, et al. Alloys with Pt-skin or Pt-rich surface for electrocatalysis[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2018, 20: 60-67. |
| 53 | van der Vliet D F, Wang C, Li D G, et al. Unique electrochemical adsorption properties of Pt-skin surfaces[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(13): 3139-3142. |
| 54 | Wang C, Chi M F, Li D G, et al. Design and synthesis of bimetallic electrocatalyst with multilayered Pt-skin surfaces[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(36): 14396-14403. |
| 55 | Stamenkovic V R, Mun B S, Mayrhofer K J J, et al. Effect of surface composition on electronic structure, stability, and electrocatalytic properties of Pt-transition metal alloys: Pt-skin versus Pt-skeleton surfaces[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128(27): 8813-8819. |
| 56 | Wang G W, Huang B, Xiao L, et al. Pt skin on AuCu intermetallic substrate: a strategy to maximize Pt utilization for fuel cells[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(27): 9643-9649. |
| 57 | Stamenkovic V R, Fowler B, Mun B S, et al. Improved oxygen reduction activity on Pt3Ni(111) via increased surface site availability[J]. Science, 2007, 315(5811): 493-497. |
| 58 | Huang X Q, Zhao Z P, Cao L, et al. High-performance transition metal-doped Pt3Ni octahedra for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Science, 2015, 348(6240): 1230-1234. |
| 59 | Wang S J, Sheng T, Yuan Q. Low-Pt octahedral PtCuCo nanoalloys: “one stone, four birds” for oxygen reduction and methanol oxidation reactions[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2023, 62(29): 11581-11588. |
| 60 | Kong F P, Ren Z H, Norouzi Banis M, et al. Active and stable Pt-Ni alloy octahedra catalyst for oxygen reduction via near-surface atomical engineering[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(7): 4205-4214. |
| 61 | Luo Y Y, Lou W H, Feng H Y, et al. Ultra-small nanoparticles of Pd-Pt-Ni alloy octahedra with high lattice strain for efficient oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Catalysts, 2023, 13(1): 97. |
| 62 | 常丰瑞, 黄俭标, 马建新, 等. PEMFC用Pt纳米线阴极催化剂的制备及在电堆中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(10): 3891-3898. |
| Chang F R, Huang J B, Ma J X, et al. Preparation of Pt nanowires as cathode catalyst for PEMFC and its application in stack[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(10): 3891-3898. | |
| 63 | Inaba M, Zana A, Quinson J, et al. The oxygen reduction reaction on Pt: why particle size and interparticle distance matter[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(12): 7144-7153. |
| 64 | Gan J, Luo W, Chen W Y, et al. Mechanistic understanding of size-dependent oxygen reduction activity and selectivity over Pt/CNT nanocatalysts[J]. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2019, 2019(27): 3210-3217. |
| 65 | van Helden P, Ciobîca I M, Coetzer R L J. The size-dependent site composition of FCC cobalt nanocrystals[J]. Catalysis Today, 2016, 261: 48-59. |
| 66 | Kodama K, Nagai T, Kuwaki A, et al. Challenges in applying highly active Pt-based nanostructured catalysts for oxygen reduction reactions to fuel cell vehicles[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2021, 16: 140-147. |
| 67 | Yuan Y, Yan N, Dyson P J. Advances in the rational design of rhodium nanoparticle catalysts: control via manipulation of the nanoparticle core and stabilizer[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2012, 2(6): 1057-1069. |
| 68 | Fan L H, Deng H, Zhang Y G, et al. Towards ultralow platinum loading proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(4): 1466-1479. |
| 69 | Patil V, Reshmi P V, Prajna S, et al. Degradation mechanisms in PEM fuel cells: a brief review[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, DOI:10.1016/j.matpr.2023.03.603 . |
| 70 | Miao Z P, Li S Z, Priest C, et al. Effective approaches for designing stable M-N x /C oxygen-reduction catalysts for proton-exchange-membrane fuel cells[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(52): e2200595. |
| 71 | Sun M Z, Gong S Y, Li Z W, et al. Terrace-rich ultrathin PtCu surface on earth-abundant metal for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(19): 19421-19430. |
| 72 | Greszler T A, Caulk D, Sinha P. The impact of platinum loading on oxygen transport resistance[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(12): F831-F840. |
| 73 | Zhao Z P, Chen C L, Liu Z Y, et al. Pt-based nanocrystal for electrocatalytic oxygen reduction[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(31): e1808115. |
| 74 | Kongkanand A, Mathias M F. The priority and challenge of high-power performance of low-platinum proton-exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2016, 7(7): 1127-1137. |
| 75 | Pan L J, Ott S, Dionigi F, et al. Current challenges related to the deployment of shape-controlled Pt alloy oxygen reduction reaction nanocatalysts into low Pt-loaded cathode layers of proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2019, 18: 61-71. |
| 76 | Cao F, Ding R, Rui Z Y, et al. Advances in low Pt loading membrane electrode assembly for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(2): 773. |
| 77 | Zaman S, Douka A I, Noureen L, et al. Oxygen reduction performance measurements: discrepancies against benchmarks[J]. Battery Energy, 2023, 2(3): 20220060. |
| 78 | Zaman S, Tian X L, Xia B Y. Bridging oxygen reduction performance gaps in half and full cells: challenges and perspectives[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2023, 7(20): 4605-4612. |
| 79 | Li J R, Liu M X, Liu X, et al. The recent progress of oxygen reduction electrocatalysts used at fuel cell level[J]. Small Methods, 2024, 8(3): e2301249. |
| 80 | Luo M C, Guo S J. Multimetallic electrocatalyst stabilized by atomic ordering[J]. Joule, 2019, 3(1): 9-10. |
| 81 | Liu J Y, Liu S Y, Yan F Z, et al. Ultrathin nanotube structure for mass-efficient and durable oxygen reduction reaction catalysts in PEM fuel cells[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(41): 19106-19114. |
| 82 | Li J L, Liu H Y, Zhang W Q, et al. In-situ preparation of low Pt loading multi rhombic-pyramidal Pt-Pd catalyst layer for high-performance proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 556: 232445. |
| 83 | van der Vliet D, Wang C, Debe M, et al. Platinum-alloy nanostructured thin film catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(24): 8695-8699. |
| 84 | van der Vliet D F, Wang C, Tripkovic D, et al. Mesostructured thin films as electrocatalysts with tunable composition and surface morphology[J]. Nature Materials, 2012, 11: 1051-1058. |
| 85 | Liu W, Herrmann A K, Bigall N C, et al. Noble metal aerogels-synthesis, characterization, and application as electrocatalysts[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2015, 48(2): 154-162. |
| 86 | Liu W, Rodriguez P, Borchardt L, et al. Bimetallic aerogels: high-performance electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(37): 9849-9852. |
| 87 | Liu W, Herrmann A K, Geiger D, et al. High-performance electrocatalysis on palladium aerogels[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(23): 5743-5747. |
| 88 | Hwang C K, Kim J M, Hwang S, et al. Porous strained Pt nanostructured thin-film electrocatalysts via dealloying for PEM fuel cells[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2020, 7(2): 1901326. |
| 89 | Kibsgaard J, Gorlin Y, Chen Z B, et al. Meso-structured platinum thin films: active and stable electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(18): 7758-7765. |
| 90 | Beermann V, Gocyla M, Willinger E, et al. Rh-doped Pt-Ni octahedral nanoparticles: understanding the correlation between elemental distribution, oxygen reduction reaction, and shape stability[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(3): 1719-1725. |
| 91 | Meier J C, Galeano C, Katsounaros I, et al. Design criteria for stable Pt/C fuel cell catalysts[J]. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, 2014, 5: 44-67. |
| 92 | Mayrhofer K J J, Blizanac B B, Arenz M, et al. The impact of geometric and surface electronic properties of Pt-catalysts on the particle size effect in electrocatalysis[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005, 109(30): 14433-14440. |
| 93 | Han B H, Carlton C E, Kongkanand A, et al. Record activity and stability of dealloyed bimetallic catalysts for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2015, 8(1): 258-266. |
| 94 | Marković N M, Ross P N. Surface science studies of model fuel cell electrocatalysts[J]. Surface Science Reports, 2002, 45(4): 117-229. |
| 95 | Todoroki N, Kato T, Hayashi T, et al. Pt-Ni nanoparticle-stacking thin film: highly active electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(4): 2209-2212. |
| 96 | Zhang L, Roling L T, Wang X, et al. Platinum-based nanocages with subnanometer-thick walls and well-defined, controllable facets[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6246): 412-416. |
| 97 | Bu L Z, Zhang N, Guo S J, et al. Biaxially strained PtPb/Pt core/shell nanoplate boosts oxygen reduction catalysis[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6318): 1410-1414. |
| 98 | Xie M H, Lyu Z H, Chen R H, et al. Pt-Co@Pt octahedral nanocrystals: enhancing their activity and durability toward oxygen reduction with an intermetallic core and an ultrathin shell[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(22): 8509-8518. |
| 99 | Li Z, Ji S F, Liu Y W, et al. Well-defined materials for heterogeneous catalysis: from nanoparticles to isolated single-atom sites[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(2): 623-682. |
| 100 | Gong S Y, Zhang Y X, Niu Z Q. Recent advances in earth-abundant core/noble-metal shell nanoparticles for electrocatalysis[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(19): 10886-10904. |
| 101 | Ding H, Wang P, Su C J, et al. Epitaxial growth of ultrathin highly crystalline Pt-Ni nanostructure on a metal carbide template for efficient oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(12): e2109188. |
| 102 | Gong S Y, Sun M Z, Lee Y Y, et al. Bulk-like Pt(100)-oriented ultrathin surface: combining the merits of single crystals and nanoparticles to boost oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(4): 2214516. |
| [1] | Yu HAN, Le ZHOU, Xin ZHANG, Yong LUO, Baochang SUN, Haikui ZOU, Jianfeng CHEN. Preparation of high adhesion Pd/SiO2/NF monolithic catalyst and its hydrogenation performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1533-1542. |
| [2] | Ang LI, Zhenyu ZHAO, Hong LI, Xin GAO. Microwave induced construction of highly dispersed Pd/FeP catalysts and their electrocatalytic performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1594-1606. |
| [3] | Yunxuan LI, Xinyue LIU, Xi CHEN, Wen LIU, Mingyue ZHOU, Xingying LAN. Energy storage technologies based on solid-liquid redox-targeting reactions: materials, devices, and kinetics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1222-1240. |
| [4] | Yiwei FAN, Wei LIU, Yingying LI, Peixia WANG, Jisong ZHANG. Research progress on catalytic dehydrogenation of dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole as liquid organic hydrogen carrier [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1198-1208. |
| [5] | Binbin FENG, Mingjia LU, Zhihong HUANG, Yiwen CHANG, Zhiming CUI. Application and optimization of carbon supports in proton exchange membrane fuel cells [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1469-1484. |
| [6] | Xudong JIA, Bolong YANG, Qian CHENG, Xueli LI, Zhonghua XIANG. Preparation of high-efficiency iron-cobalt bimetallic site oxygen reduction electrocatalysts by step-by-step metal loading method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1578-1593. |
| [7] | Xi WU, Bo SUN, Yindong LIU, Chuanlei QI, Kaiyi CHEN, Luhai WANG, Chong XU, Yongfeng LI. Research progress in preparation technology of pitch-based carbon anode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1270-1283. |
| [8] | Jin ZHANG, Zhibin GUO, Laiming LUO, Shanfu LU, Yan XIANG. Design and performance of 5 kW reforming methanol high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1697-1704. |
| [9] | Pei WANG, Ruiming DUAN, Guangru ZHANG, Wanqin JIN. Modeling and simulation analysis of solar driven membrane separation biomethane hydrogen production process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 967-973. |
| [10] | Na PAN, Chang TIAN, Lankun HUAI, Yuyu LIU, Fenfen ZHANG, Xiaomei GAO, Wei LIU, Liangguo YAN, Yanxia ZHAO. Synthesis and application of polymerized Al-Ti based flocculant [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 1009-1018. |
| [11] | Lingxian ZHANG, Bin LIU, Lin DENG, Yuhang REN. PEMFC fault diagnosis based on improved TSO optimized Xception [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 945-955. |
| [12] | Zhipeng LIU, Changying ZHAO, Rui WU, Zhihao ZHANG. Experimental study of gas-liquid flow visualization in gradient porous transport layers based on hydrogen production by water electrolysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 520-530. |
| [13] | Hong CHEN, Kun JIANG, Tingjiang TANG, Yiyuan HUANG, Bin CHI, Shijun LIAO. Research on membrane electrode assembly consistency of high-power proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 637-646. |
| [14] | Xin ZHANG, Yu XUE, Yixing MA, Xueqian WANG, Langlang WANG, Nifei XIE, Yi CHEN, Xiaoxia ZHOU. Purification mechanism of hydrogen cyanide by corona discharge and dielectric barrier discharge [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 675-684. |
| [15] | Yuhua YIN, Can FANG, Qingfeng YI, Guang LI. Impact of different carbon conductive agents on performance of iron-air battery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 685-694. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||