CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (12): 4804-4814.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240650
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jiefeng HE( ), Zhaohong MIAO, Jian ZHOU(
), Zhaohong MIAO, Jian ZHOU( )
)
Received:2024-06-12
Revised:2024-07-19
Online:2025-01-03
Published:2024-12-25
Contact:
Jian ZHOU
通讯作者:
周健
作者简介:何杰锋(1999—),男,硕士研究生,1964870228@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jiefeng HE, Zhaohong MIAO, Jian ZHOU. Computer simulations on loading and release of antimicrobial peptides by zwitterionic copolymers[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(12): 4804-4814.
何杰锋, 苗朝虹, 周健. 两性离子共聚物负载和释放抗菌肽的计算机模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(12): 4804-4814.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| aij | K | O | M | E | B | P | L | A | D1 | D2 | D3 | W | Na+ | Cl- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 104.9 | |||||||||||||
| O | 113.2 | 104.9 | ||||||||||||
| M | 110.1 | 113.5 | 104.9 | |||||||||||
| E | 112.5 | 110.5 | 106.0 | 104.9 | ||||||||||
| B | 115.3 | 112.5 | 114.8 | — | 104.9 | |||||||||
| P | 106.9 | 111.2 | 112.4 | 108.5 | 110.4 | 104.9 | ||||||||
| L | 112.4 | 117.8 | 110.2 | 107.0 | 121.2 | 107.5 | 104.9 | |||||||
| A | 108.6 | 113.4 | 113.5 | 107.4 | 109.3 | 106.7 | 105.3 | 104.9 | ||||||
| D1 | 129.1 | 122.5 | 118.3 | 118.8 | 136.5 | 119.3 | 113.4 | 119.2 | 104.9 | |||||
| D2 | 122.4 | 119.3 | 112.5 | 111.7 | 126.9 | 109.8 | 111.4 | 114.1 | 105.0 | 104.9 | ||||
| D3 | 114.5 | 116.3 | 116.3 | 109.5 | 119.6 | 107.5 | 107.2 | 110.4 | 108.3 | 109.5 | 104.9 | |||
| W | 124.1 | 128.1 | 127.6 | 114.6 | 105.6 | 124.6 | 138.4 | 117.1 | 166.3 | 148.5 | 141.2 | 104.9 | ||
| Na+ | 124.1 | 128.1 | 127.6 | 114.6 | 105.6 | 124.6 | 138.4 | 117.1 | 166.3 | 148.5 | 141.2 | 104.9 | 104.9 | |
| Cl- | 124.1 | 128.1 | 127.6 | 114.6 | 105.6 | 124.6 | 138.4 | 117.1 | 166.3 | 148.5 | 141.2 | 104.9 | 104.9 | 104.9 |
Table 1 Repulsive parameters aij between different beads
| aij | K | O | M | E | B | P | L | A | D1 | D2 | D3 | W | Na+ | Cl- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 104.9 | |||||||||||||
| O | 113.2 | 104.9 | ||||||||||||
| M | 110.1 | 113.5 | 104.9 | |||||||||||
| E | 112.5 | 110.5 | 106.0 | 104.9 | ||||||||||
| B | 115.3 | 112.5 | 114.8 | — | 104.9 | |||||||||
| P | 106.9 | 111.2 | 112.4 | 108.5 | 110.4 | 104.9 | ||||||||
| L | 112.4 | 117.8 | 110.2 | 107.0 | 121.2 | 107.5 | 104.9 | |||||||
| A | 108.6 | 113.4 | 113.5 | 107.4 | 109.3 | 106.7 | 105.3 | 104.9 | ||||||
| D1 | 129.1 | 122.5 | 118.3 | 118.8 | 136.5 | 119.3 | 113.4 | 119.2 | 104.9 | |||||
| D2 | 122.4 | 119.3 | 112.5 | 111.7 | 126.9 | 109.8 | 111.4 | 114.1 | 105.0 | 104.9 | ||||
| D3 | 114.5 | 116.3 | 116.3 | 109.5 | 119.6 | 107.5 | 107.2 | 110.4 | 108.3 | 109.5 | 104.9 | |||
| W | 124.1 | 128.1 | 127.6 | 114.6 | 105.6 | 124.6 | 138.4 | 117.1 | 166.3 | 148.5 | 141.2 | 104.9 | ||
| Na+ | 124.1 | 128.1 | 127.6 | 114.6 | 105.6 | 124.6 | 138.4 | 117.1 | 166.3 | 148.5 | 141.2 | 104.9 | 104.9 | |
| Cl- | 124.1 | 128.1 | 127.6 | 114.6 | 105.6 | 124.6 | 138.4 | 117.1 | 166.3 | 148.5 | 141.2 | 104.9 | 104.9 | 104.9 |
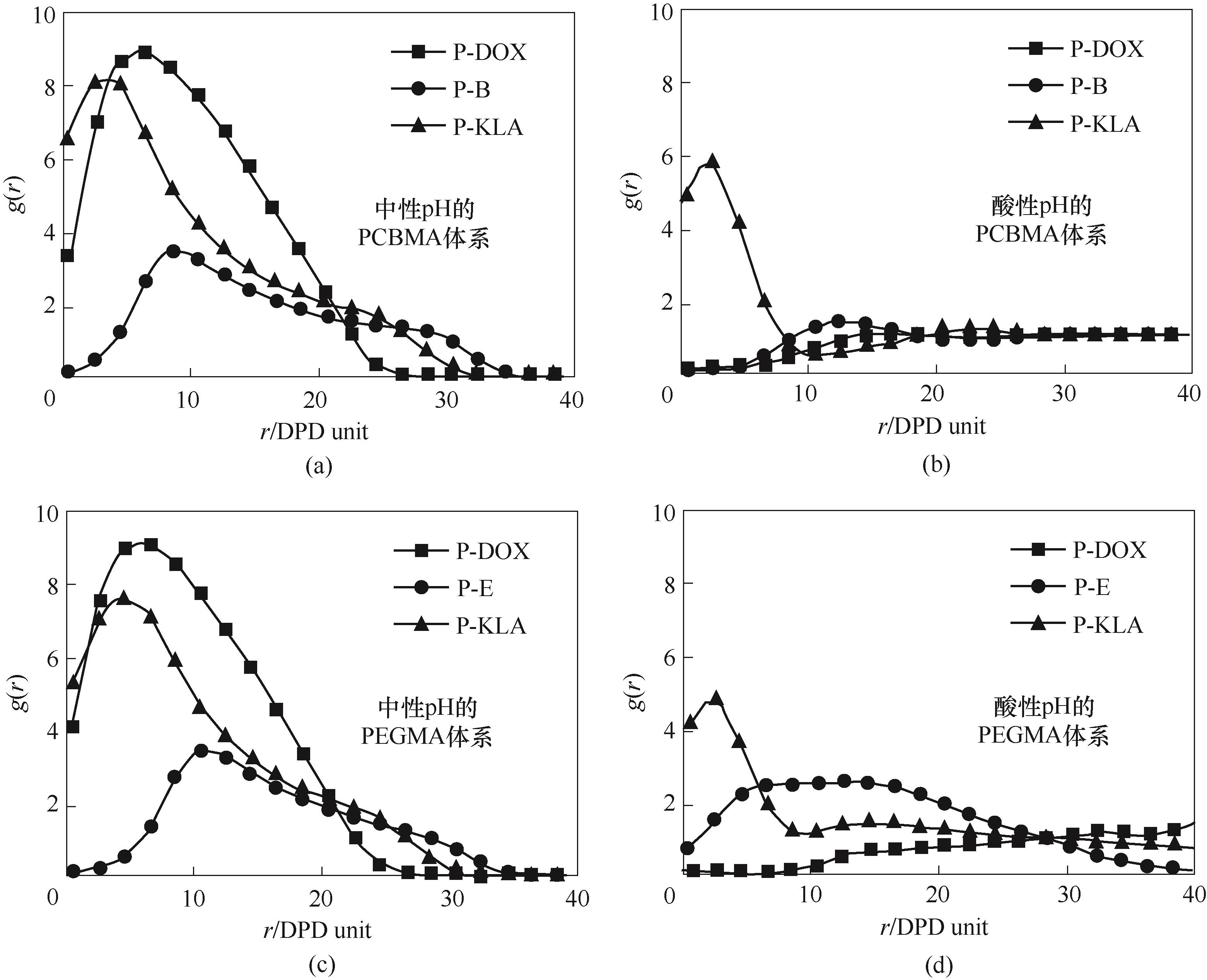
Fig.9 RDF profiles at different pH conditions: (a) PCBMA system at neutral condition; (b) PCBMA system at acidic condition; (c) PEGMA system at neutral condition; (d) PEGMA system at acidic condition
| 1 | Moretta A, Scieuzo C, Petrone A M, et al. Antimicrobial peptides: a new hope in biomedical and pharmaceutical fields[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2021, 11: 668632. |
| 2 | Jenssen H, Hamill P, Hancock R E W. Peptide antimicrobial agents[J]. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 2006, 19(3): 491-511. |
| 3 | Zhang Q Y, Yan Z B, Meng Y M, et al. Antimicrobial peptides: mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential[J]. Military Medical Research, 2021, 8(1): 48. |
| 4 | Tan P, Fu H Y, Ma X. Design, optimization, and nanotechnology of antimicrobial peptides: from exploration to applications[J]. Nano Today, 2021, 39: 101229. |
| 5 | Wang C, Hong T T, Cui P F, et al. Antimicrobial peptides towards clinical application: delivery and formulation[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2021, 175: 113818. |
| 6 | Friede M, Muller S, Briand J P, et al. Induction of immune response against a short synthetic peptide antigen coupled to small neutral liposomes containing monophosphoryl lipid A[J]. Molecular Immunology, 1993, 30(6): 539-547. |
| 7 | van Gent M E, Ali M, Nibbering P H, et al. Current advances in lipid and polymeric antimicrobial peptide delivery systems and coatings for the prevention and treatment of bacterial infections[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2021, 13(11): 1840. |
| 8 | Ghasemiyeh P, Mohammadi-Samani S. Hydrogels as drug delivery systems; pros and cons[J]. Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2019, 5(1): 7-24. |
| 9 | Figueiras A, Domingues C, Jarak I, et al. New advances in biomedical application of polymeric micelles[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2022, 14(8): 1700. |
| 10 | Kumar P, Pletzer D, Haney E F, et al. Aurein-derived antimicrobial peptides formulated with pegylated phospholipid micelles to target methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus skin infections[J]. ACS Infectious Diseases, 2019, 5(3): 443-453. |
| 11 | Knop K, Hoogenboom R, Fischer D, et al. Poly(ethylene glycol) in drug delivery: pros and cons as well as potential alternatives[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(36): 6288-6308. |
| 12 | Li M Z, Zhang W, Li J X, et al. Zwitterionic polymers: addressing the barriers for drug delivery[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2023, 34(11): 108177. |
| 13 | He Y, Hower J, Chen S F, et al. Molecular simulation studies of protein interactions with zwitterionic phosphorylcholine self-assembled monolayers in the presence of water[J]. Langmuir, 2008, 24(18): 10358-10364. |
| 14 | Harijan M, Singh M. Zwitterionic polymers in drug delivery: a review[J]. Journal of Molecular Recognition, 2022, 35(1): e2944. |
| 15 | Dong P, Zhou Y, He W W, et al. A strategy for enhanced antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus by the assembly of alamethicin with a thermo-sensitive polymeric carrier[J]. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(5): 896-899. |
| 16 | Ivanova A, Ivanova K, Tzanov T. Simultaneous ultrasound-assisted hybrid polyzwitterion/antimicrobial peptide nanoparticles synthesis and deposition on silicone urinary catheters for prevention of biofilm-associated infections[J]. Nanomaterials, 2021, 11(11): 3143. |
| 17 | Răileanu M, Lonetti B, Serpentini C L, et al. Encapsulation of a cationic antimicrobial peptide into self-assembled polyion complex nano-objects enhances its antitumor properties[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2022, 1249: 131482. |
| 18 | Wang C H, Feng S L, Qie J K, et al. Polyion complexes of a cationic antimicrobial peptide as a potential systemically administered antibiotic[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2019, 554: 284-291. |
| 19 | Sun J W, Jiang L, Lin Y, et al. Enhanced anticancer efficacy of paclitaxel through multistage tumor-targeting liposomes modified with RGD and KLA peptides[J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2017, 12: 1517-1537. |
| 20 | Lim C, Won W R, Moon J, et al. Co-delivery of d-(KLAKLAK)2 peptide and doxorubicin using a pH-sensitive nanocarrier for synergistic anticancer treatment[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2019, 7(27): 4299-4308. |
| 21 | Wang W, Ye Z, Gao H L, et al. Computational pharmaceutics — a new paradigm of drug delivery[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2021, 338: 119-136. |
| 22 | 苏运祥, 全学波, 闵文凤, 等. PAMAM树状大分子负载和释放阿霉素的耗散粒子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(5): 1757-1766. |
| Su Y X, Quan X B, Min W F, et al. Dissipative particle dynamics simulations on loading and release of doxorubicin by PAMAM dendrimers[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(5): 1757-1766. | |
| 23 | 胡建波, 刘洪超, 胡齐, 等. 有机笼跨细胞膜易位行为的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3756-3765. |
| Hu J B, Liu H C, Hu Q, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation insight into translocation behavior of organic cage across the cellular membrane[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3756-3765. | |
| 24 | Feng Y H, Zhang X P, Zhao Z Q, et al. Dissipative particle dynamics aided design of drug delivery systems: a review[J]. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2020, 17(6): 1778-1799. |
| 25 | Liao M R, Gong H N, Quan X B, et al. Intramembrane nanoaggregates of antimicrobial peptides play a vital role in bacterial killing[J]. Small, 2023, 19(3): e2204428. |
| 26 | Ulmschneider J P, Ulmschneider M B. Molecular dynamics simulations are redefining our view of peptides interacting with biological membranes[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2018, 51(5): 1106-1116. |
| 27 | Asadzadeh H, Moosavi A. Investigation of the interactions between Melittin and the PLGA and PLA polymers: molecular dynamic simulation and binding free energy calculation[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(5): 055318. |
| 28 | Nejabat M, Soltani F, Alibolandi M, et al. Smac peptide and doxorubicin-encapsulated nanoparticles: design, preparation, computational molecular approach and in vitro studies on cancer cells[J]. Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics, 2022, 40(2): 807-819. |
| 29 | Guo W X, Hu L F, Feng Y H, et al. Advances in self-assembling of pH-sensitive polymers: a mini review on dissipative particle dynamics[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2022, 210: 112202. |
| 30 | Chen Z, Huo J H, Hao L X, et al. Multiscale modeling and simulations of responsive polymers[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2019, 23: 21-33. |
| 31 | Wang J H, Han Y F, Xu Z Y, et al. Dissipative particle dynamics simulation: a review on investigating mesoscale properties of polymer systems[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2021, 306(4): e2000724. |
| 32 | Su Y X, Quan X B, Li L B, et al. Computer simulation of DNA condensation by PAMAM dendrimer[J]. Macromolecular Theory and Simulations, 2018, 27(2): e1700070. |
| 33 | Zeng S J, Quan X B, Zhu H L, et al. Computer simulations on a pH-responsive anticancer drug delivery system using zwitterion-grafted polyamidoamine dendrimer unimolecular micelles[J]. Langmuir, 2021, 37(3): 1225-1234. |
| 34 | Miao Z H, Chen Z, Wang L, et al. Dual-responsive zwitterion-modified nanopores: a mesoscopic simulation study[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2022, 10(14): 2740-2749. |
| 35 | Hoogerbrugge P J, Koelman J M V A. Simulating microscopic hydrodynamic phenomena with dissipative particle dynamics[J]. Europhysics Letters, 1992, 19: 155. |
| 36 | Groot R D, Warren P B. Dissipative particle dynamics: bridging the gap between atomistic and mesoscopic simulation[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1997, 107(11): 4423-4435. |
| 37 | Groot R D. Electrostatic interactions in dissipative particle dynamics—simulation of polyelectrolytes and anionic surfactants[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2003, 118(24): 11265-11277. |
| 38 | Wang Y L, Laaksonen A, Lu Z Y. Implementation of non-uniform FFT based Ewald summation in dissipative particle dynamics method[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2013, 235: 666-682. |
| 39 | Groot R D, Madden T J. Dynamic simulation of diblock copolymer microphase separation[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1998, 108(20): 8713-8724. |
| 40 | Wei J C, Liu Y W, Song F. Coarse-grained simulation of the translational and rotational diffusion of globular proteins by dissipative particle dynamics[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2020, 153(23): 234902. |
| 41 | Fan C F, Olafson B D, Blanco M, et al. Application of molecular simulation to derive phase diagrams of binary mixtures[J]. Macromolecules, 1992, 25(14): 3667-3676. |
| 42 | Zhu Y L, Liu H, Li Z W, et al. GALAMOST: GPU-accelerated large-scale molecular simulation toolkit[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2013, 34(25): 2197-2211. |
| 43 | Song X Y, Zhao S L, Fang S W, et al. Mesoscopic simulations of adsorption and association of PEO-PPO-PEO triblock copolymers on a hydrophobic surface: from mushroom hemisphere to rectangle brush[J]. Langmuir, 2016, 32(44): 11375-11385. |
| 44 | Yang S C, Zhu Y L, Qian H J, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of antipolyelectrolyte effect and solubility of polyzwitterions[J]. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities, 2017, 33(2): 261-267. |
| 45 | Ma M K, Ahsan B, Wang J H, et al. Supramolecular crosslinks enable PIC micelles with tuneable salt stability and diverse properties[J]. Soft Matter, 2019, 15(41): 8210-8218. |
| [1] | Qirui GUO, Liyuan REN, Kang CHEN, Xiangyu HUANG, Weihua MA, Leqin XIAO, Weiliang ZHOU. Numerical simulation of static mixing tubes for HTPB propellant slurry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 206-216. |
| [2] | Xinyue WANG, Xiaohu XU, Haiyang ZHANG, Chunhua YIN. Study on encapsulation and properties vitamin A acetate/cyclodextrin [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 321-328. |
| [3] | Shaojun DOU, Liang HAO. Mesoscale simulation of coupled gas charge transfer process in PEMFC catalyst layer [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 3002-3010. |
| [4] | Zheming WU, Biyun ZHANG, Renchao ZHENG. Engineering of nitrilase enantioselectivity for efficient synthesis of brivaracetam [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2633-2643. |
| [5] | Haiyan DU, Kai ZHU, Feng YOU, Jinfeng WANG, Yifan ZHAO, Nan ZHANG, Ying LI. Self-healing anti-freezing ionic hydrogel for strain sensors [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2709-2722. |
| [6] | Hansong QIN, Guoliang LI, Hao YAN, Xiang FENG, Yibin LIU, Xiaobo CHEN, Chaohe YANG. Theoretical study on the adsorption and diffusion behavior of methyl oleate catalytic cracking in hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(5): 1870-1881. |
| [7] | Youming SI, Lingfeng ZHENG, Pengzhong CHEN, Jiangli FAN, Xiaojun PENG. Performance and mechanism of novel antimony oxo cluster photoresist [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1705-1717. |
| [8] | Wenhui ZHANG, Ruyi TANG, Xili CUI, Huabin XING. Fluorine spectrum analysis and structural characterization of Y-type perfluoropolyether carboxylic acid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1718-1723. |
| [9] | Jinpeng ZHAO, Yongmin ZHANG, Bin LAN, Jiewen LUO, Bidan ZHAO, Junwu WANG. Model development and validation of structural two-fluid model for heat transfer in a gas-solid bubbling fluidized bed [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1497-1507. |
| [10] | Kang ZHOU, Jianxin WANG, Hai YU, Chaoliang WEI, Fengqi FAN, Xinhao CHE, Lei ZHANG. Foam rupture properties of mineral base oils based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1668-1678. |
| [11] | Yuwei YANG, Min LI, Zhiying YAO, Qinlin SUN, Yang LIU, Dan GE, Bingbing SUN. Application and prospect of organoids-on-chip in the study of nano-drug delivery systems [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1209-1221. |
| [12] | Dongfei LIU, Fan ZHANG, Zheng LIU, Diannan LU. A review of machine learning potentials and their applications to molecular simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1241-1255. |
| [13] | Zheng ZHANG, Wuqiong WANG, Yajing ZHANG, Kangjun WANG, Yuanhui JI. Research progress in theoretical calculation of pharmaceutical formulation design [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1429-1438. |
| [14] | Fan WU, Xudong PENG, Jinbo JIANG, Xiangkai MENG, Yangyang LIANG. Study on adaptability of molecular dynamics in predicting density and viscosity of natural gas [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 450-462. |
| [15] | Xudong CHEN, Weidong FU, Jinjin LI, Ling ZHAO, Zhenhao XI. Synthesis of amphiphilic polyphosphoester-PTX prodrug and its potential in reduction-responsive drug release [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(12): 4815-4824. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||