CIESC Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (6): 2259-2268.DOI: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20181497
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chuanjie ZHENG( ),Changdong SHENG(
),Changdong SHENG( )
)
Received:2018-12-21
Revised:2019-03-05
Online:2019-06-05
Published:2019-06-05
Contact:
Changdong SHENG
通讯作者:
盛昌栋
作者简介:<named-content content-type="corresp-name">郑传杰</named-content>(1994—),男,硕士研究生,<email>920343372@qq.com</email>
基金资助:CLC Number:
Chuanjie ZHENG, Changdong SHENG. Modeling and reaction kinetics study on K capture by adsorbents in high temperature flue gas[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(6): 2259-2268.
郑传杰, 盛昌栋. 高温烟气中吸附剂捕集K的模型及其反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(6): 2259-2268.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://hgxb.cip.com.cn/EN/10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20181497
| 高岭土 | 煤灰 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KOH | K2CO3 | KCl | K2SO4 | KOH | KCl | K2SO4 | |
| k 0×10-8/(m3 gas/((m3 pore)·s)) | 3.8 | 3.8 | 2.3 | 1.57 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.094 |
| E/(kJ/mol) | 25.08 | 25.08 | 25.08 | 25.08 | 25.08 | 25.08 | 25.08 |
Table 1 Kinetic parameters of kaolin and coal fly ash adsorbing different K-containing gas species
| 高岭土 | 煤灰 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KOH | K2CO3 | KCl | K2SO4 | KOH | KCl | K2SO4 | |
| k 0×10-8/(m3 gas/((m3 pore)·s)) | 3.8 | 3.8 | 2.3 | 1.57 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.094 |
| E/(kJ/mol) | 25.08 | 25.08 | 25.08 | 25.08 | 25.08 | 25.08 | 25.08 |
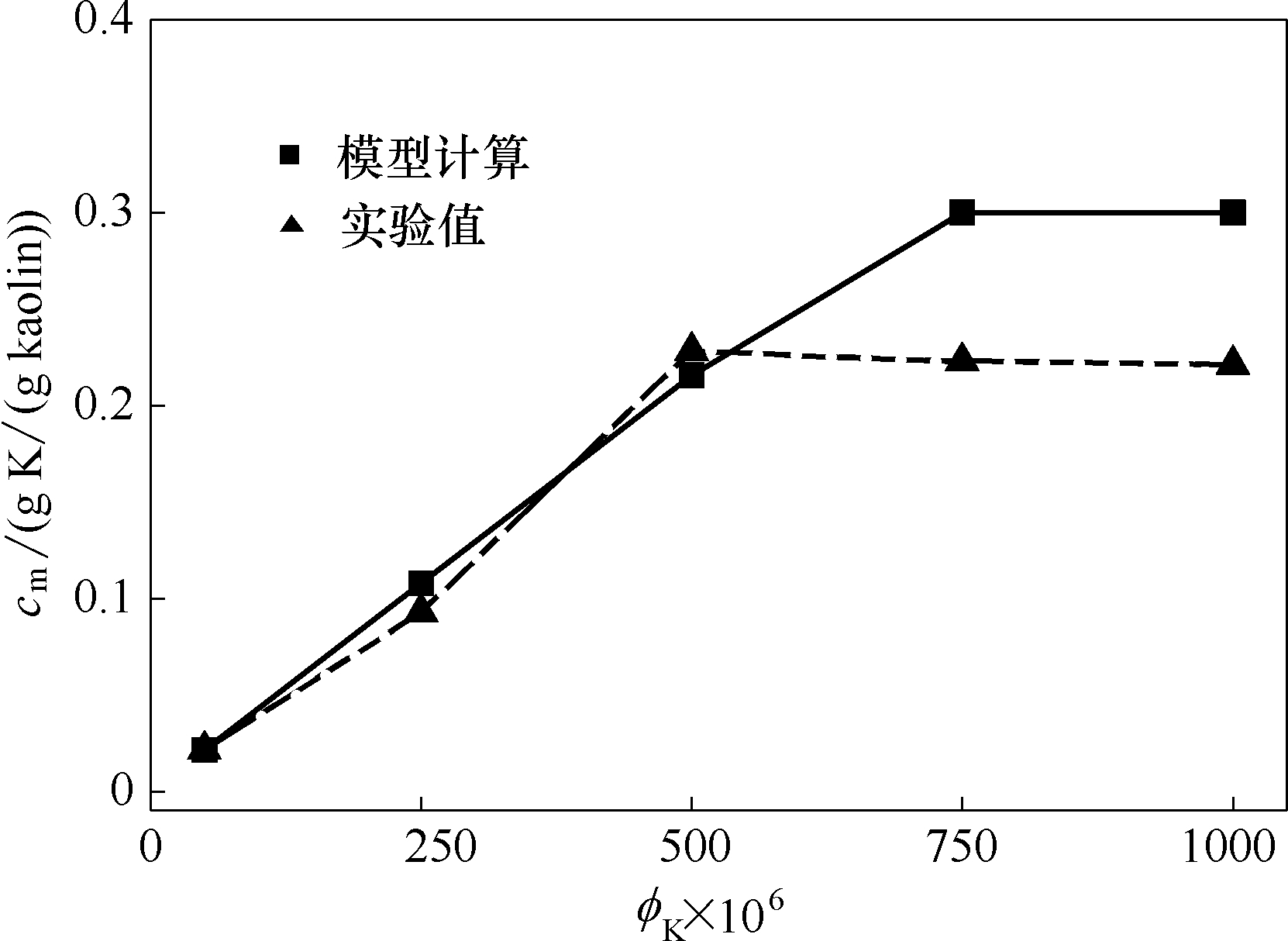
Fig.2 Comparison of model calculated and experiment measured K capture by kaolin at different initial KOH concentrations (at temperature of 1373 K and residence time of 1.2 s)
| 含K成分 | ? K×106 | 烟气温度T/K | 停留时间t/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| K2CO3 | 50 | 1373 | 1.2 |
| 250 | 1373 | 1.2 | |
| 500 | 1073、1173、1373、1573 | 1.2 | |
| 750 | 1373 | 1.2 | |
| 1000 | 1373 | 1.2 | |
| KCl | 50 | 1573 | 1.0 |
| 250 | 1573 | 1.0 | |
| 500 | 1073、1173、1373、1573 | 1.2(1573 K时1.0) | |
| 750 | 1573 | 1.0 | |
| 1000 | 1573 | 1.0 | |
| K2SO4 | 50 | 1373 | 1.2 |
| 250 | 1373 | 1.2 | |
| 500 | 1073、1173、1373、1573 | 1.2 | |
| 750 | 1373 | 1.2 |
Table 2 Model calculating conditions for kaolin adsorbing K2CO3, KCl and K2SO4
| 含K成分 | ? K×106 | 烟气温度T/K | 停留时间t/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| K2CO3 | 50 | 1373 | 1.2 |
| 250 | 1373 | 1.2 | |
| 500 | 1073、1173、1373、1573 | 1.2 | |
| 750 | 1373 | 1.2 | |
| 1000 | 1373 | 1.2 | |
| KCl | 50 | 1573 | 1.0 |
| 250 | 1573 | 1.0 | |
| 500 | 1073、1173、1373、1573 | 1.2(1573 K时1.0) | |
| 750 | 1573 | 1.0 | |
| 1000 | 1573 | 1.0 | |
| K2SO4 | 50 | 1373 | 1.2 |
| 250 | 1373 | 1.2 | |
| 500 | 1073、1173、1373、1573 | 1.2 | |
| 750 | 1373 | 1.2 |
| 平均粒径/μm | BET表面积/(m2/g) | 含量/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO3 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | ||
| 10.2 | 8.04 | 0.52 | 37.98 | 42.61 | 6.68 | 5.08 | 1.31 | 0.59 | 1.69 | 1.18 | 2.36 |
Table 3 Physical and chemical properties of coal fly ash[31]
| 平均粒径/μm | BET表面积/(m2/g) | 含量/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO3 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | ||
| 10.2 | 8.04 | 0.52 | 37.98 | 42.61 | 6.68 | 5.08 | 1.31 | 0.59 | 1.69 | 1.18 | 2.36 |
| 1 | 斯俊平 . 燃煤过程中钠对焦特性及细颗粒物控制的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2014. |
| Si J P . Effects of sodium on char characteristics and fine particulate matters control during coal combustion[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2014. | |
| 2 | 黄忠友 . 试析生物质发电发展现状及前景[J]. 科技风, 2019, (2): 185. |
| Huang Z Y . Analysis of current situation and prospect of biomass power generation[J]. Technology Wind, 2019, (2): 185. | |
| 3 | 徐林林 . 高岭土对高钠煤燃烧过程中碱金属的脱除效果研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2015. |
| Xu L L . Effect of kaolin on removal of alkali metals during combustion of high sodium coal[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2015. | |
| 4 | Mcnallan M J , Yurek G J , Elliott J F . The formation of inorganic particulates by homogeneous nucleation in gases produced by the combustion of coal[J]. Combustion & Flame, 1981, 42(81): 45-60. |
| 5 | 兰泽全, 曹欣玉, 周俊虎, 等 . 锅炉受热面沾污结渣的危害及其防治措施[J]. 电站系统工程, 2003, 19(1): 31-33. |
| Lan Z Q , Cao X Y , Zhou J H , et al . Hazards and prevention measures of fouling and slagging on heating surfaces of boilers[J]. Power Plant System Engineering, 2003, 19(1): 31-33. | |
| 6 | 董雪玲 . 大气可吸入颗粒物对环境和人体健康的危害[J]. 资源·产业, 2004, (5): 52-55. |
| Dong X L . Hazards of inhalable particulates to environment and human health[J]. Resources·Industry, 2004, (5): 52-55. | |
| 7 | Zhan Z , Fry A R , Wendt J O L . Relationship between submicron ash aerosol characteristics and ash deposit compositions and formation rates during air- and oxy-coal combustion[J]. Fuel, 2016, 181: 1214-1223. |
| 8 | Waindich A , Müller M . Alkali removal at 1400℃ under gasification conditions[J]. Fuel, 2014, 116: 889-893. |
| 9 | Gibbs A R , Pooley F D . Analysis and interpretation of inorganic mineral particles in "lung" tissues[J]. Thorax, 1996, 51(3): 327-334. |
| 10 | 周科 . 燃煤细微颗粒物生成特性与炉内控制的研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2011. |
| Zhou K . Study on the generation characteristics and control of fine particles in coal combustion[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2011. | |
| 11 | 温昶, 徐明厚, 于敦喜, 等 . 煤粉O2/CO2燃烧时PM2. 5及其Fe、S的生成特性[J]. 化工学报, 2011, 62(4): 1062-1069. |
| Wen C , Xu M H , Yu D X , et al . Formation characteristics of PM2. 5 including Fe, S during O2/CO2 combustion of pulverized coal[J]. CIESC Journal, 2011, 62(4): 1062-1069. | |
| 12 | Quann R J , Sarofim A F . Vaporization of refractory oxides during pulverized coal combustion[J]. Symposium on Combustion, 1982, 19(1): 1429-1440. |
| 13 | Si J P , Liu X W , Xu M H , et al . Effect of kaolin additive on PM2. 5, reduction during pulverized coal combustion: importance of sodium and its occurrence in coal[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 114(2): 434-444. |
| 14 | Yan L , Gupta R P , Wall T F . The implication of mineral coalescence behaviour on ash formation and ash deposition during pulverised coal combustion[J]. Fuel, 2001, 80(9): 1333-1340. |
| 15 | 徐明厚, 于敦喜, 刘小伟 . 燃煤可吸入颗粒物的形成与排放[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009. |
| Xu M H , Yu D X , Liu X W . Formation and Emission of Inhalable Particles from Coal Combustion[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009. | |
| 16 | 刘建忠, 张光学, 周俊虎, 等 . 燃煤细灰的形成及微观形态特征[J]. 化工学报, 2006, 57(12): 2976-2980. |
| Liu J Z , Zhang G X , Zhou J H , et al . Formation and micromorphology characteristics of fine particles generated during coal combustion [J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering(China), 2006, 57(12): 2976-2980. | |
| 17 | 刘勇, 赵汶, 刘瑞, 等 . 化学团聚促进电除尘脱除PM2. 5的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(9): 3609-3616. |
| Liu Y , Zhao W , Liu R , et al . Improving removal of PM2.5 by electrostatic precipitator with chemical agglomeration[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(9): 3609-3616. | |
| 18 | Quann R J . Ash vaporization under simulated pulverized coal combustion conditions[D]. Massachusetts: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1982. |
| 19 | Li Y , Raj G A , Wall T . Fragmentation behavior of pyrite and calcite during high-temperature processing and mathematical simulation[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2001, 15(2): 389-394. |
| 20 | Quann R J , Neville M , Janghorbani M , et al . Mineral matter and trace-element vaporization in a laboratory-pulverized coal combustion system[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1982, 16(11): 776. |
| 21 | Helble J J . Mechanisms of ash particle formation and growth during pulverized coal combustion[D]. Massachusetts: MIT Library in America, 1987. |
| 22 | 孙伟, 刘小伟, 徐义书, 等 . 两种改性高岭土减排超细颗粒物的对比分析[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(4): 1179-1185. |
| Xun W , Liu X W , Xu Y S , et al . Contrastive analysis of reducing ultrafine particulate matters emission by two modified kaolin[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(4): 1179-1185. | |
| 23 | Mwabe P O , Wendt J O L . Mechanisms governing trace sodium capture by kaolinite in a downflow combustor[J]. Symposium on Combustion, 1996, 26(2): 2447-2453. |
| 24 | Wang G L , Jensen P A , Wu H , et al . Potassium capture by kaolin (1): KOH[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(2): 1851-1862. |
| 25 | Schürmann H , Unterberger S , Hein K R , et al . The influence of fuel additives on the behaviour of gaseous alkali-metal compounds during pulverised coal combustion[J]. Faraday Discussions, 2001, 119(119): 433-444. |
| 26 | Gale T , Wendt J L . Mechanisms and models describing sodium and lead scavenging by a kaolinite aerosol at high temperatures[J]. Aerosol Science & Technology, 2003, 37(11): 865-876. |
| 27 | Wang G L , Jensen P A , Wu H , et al . Potassium capture by kaolin (2): K2CO3, KCl, and K2SO4 [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(3): 3566-3578. |
| 28 | Damoe A J , Wu H , Frandsen F J , et al . Impact of coal fly ash addition on combustion aerosols (PM2. 5) from full-scale suspension-firing of pulverized wood[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(5): 3217-3223. |
| 29 | Scandrett L A , Clift R . The thermodynamics of alkali removal from coal derived gases[J]. Journal of the Institute of Energy, 1984, 57 (433): 391-397. |
| 30 | Li Y , Li J , Jin Y , et al . Study on alkali-metal vapor removal for high-temperature cleaning of coal gas[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2005, 19(4): 1606-1610. |
| 31 | Wang G L . Potassium capture by kaolin and coal fly ash[D]. Kongens Lyngby: Technical University of Denmark, 2018. |
| [1] | Cheng CHENG, Zhongdi DUAN, Haoran SUN, Haitao HU, Hongxiang XUE. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of surface microstructure effect on crystallization fouling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [2] | Xuejin YANG, Jintao YANG, Ping NING, Fang WANG, Xiaoshuang SONG, Lijuan JIA, Jiayu FENG. Research progress in dry purification technology of highly toxic gas PH3 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3742-3755. |
| [3] | Linzheng WANG, Yubing LU, Ruizhi ZHANG, Yonghao LUO. Analysis on thermal oxidation characteristics of VOCs based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [4] | Guoze CHEN, Dong WEI, Qian GUO, Zhiping XIANG. Optimal power point optimization method for aluminum-air batteries under load tracking condition [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3533-3542. |
| [5] | Bingchun SHENG, Jianguo YU, Sen LIN. Study on lithium resource separation from underground brine with high concentration of sodium by aluminum-based lithium adsorbent [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3375-3385. |
| [6] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [7] | Jipeng ZHOU, Wenjun HE, Tao LI. Reaction engineering calculation of deactivation kinetics for ethylene catalytic oxidation over irregular-shaped catalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2416-2426. |
| [8] | Guangyu WANG, Kai ZHANG, Kaihua ZHANG, Dongke ZHANG. Heat and mass transfer and energy consumption for microwave drying of coal slime [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2382-2390. |
| [9] | Zhaoguang CHEN, Yuxiang JIA, Meng WANG. Modeling neutralization dialysis desalination driven by low concentration waste acid and its validation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [10] | Quanbi ZHANG, Yijin YANG, Xujing GUO. Catalytic degradation of dissolved organic matter in rifampicin pharmaceutical wastewater by Fenton oxidation process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2217-2227. |
| [11] | Chuanbao XIAO, Linyang LI, Wufeng LIU, Nianbing ZHONG, Quanhua XIE, Dengjie ZHONG, Haixing CHANG. Effective removal of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by coupling photocatalysis with ion exchange adsorption [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1587-1597. |
| [12] | Laiming LUO, Jin ZHANG, Zhibin GUO, Haining WANG, Shanfu LU, Yan XIANG. Simulation and experiment of high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells stack in the 1—5 kW range [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1724-1734. |
| [13] | Simin YI, Yali MA, Weiqiang LIU, Jinshuai ZHANG, Yan YUE, Qiang ZHENG, Songyan JIA, Xue LI. Study on ammonia evaporation and hydration kinetics of microcrystalline magnesite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1578-1586. |
| [14] | Jin YU, Binbin YU, Xinsheng JIANG. Study on quantification methodology and analysis of chemical effects of combustion control based on fictitious species [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1303-1312. |
| [15] | Lingxin ZU, Rongting HU, Xin LI, Yudao CHEN, Guanglin CHEN. Carbon release products and denitrification bioavailability from chemical components of woody biomass [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1332-1342. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||