CIESC Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (6): 2612-2621.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20211519
• Fluid dynamics and transport phenomena • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yilin LIU1( ),Yu LI1(
),Yu LI1( ),Yaxiong YU1,Zheqing HUANG1,Qiang ZHOU1,2,3(
),Yaxiong YU1,Zheqing HUANG1,Qiang ZHOU1,2,3( )
)
Received:2021-10-26
Revised:2022-01-11
Online:2022-06-30
Published:2022-06-05
Contact:
Yu LI,Qiang ZHOU
刘怡琳1( ),李钰1(
),李钰1( ),余亚雄1,黄哲庆1,周强1,2,3(
),余亚雄1,黄哲庆1,周强1,2,3( )
)
通讯作者:
李钰,周强
作者简介:刘怡琳(1997—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Yilin LIU, Yu LI, Yaxiong YU, Zheqing HUANG, Qiang ZHOU. Construction of two parameter mesoscale heat transfer model for gas-solid flow based on resetting temperature method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2612-2621.
刘怡琳, 李钰, 余亚雄, 黄哲庆, 周强. 基于重置温度方法的双参数介尺度气固传热模型构建[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2612-2621.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 颗粒直径 | 7.5×10-5 m |
| 计算域尺寸 | 240dp × 960dp× 6dp |
| 网格尺寸 | 2.5dp × 2.5dp × 3dp |
| 重力加速度 | 9.81 m/s2 |
| 颗粒密度 | 1500 kg/m3 |
| 法向弹性系数 | 5 N/m |
| 恢复系数 | 0.8 |
| 颗粒间碰撞的切向阻尼系数与法向阻尼系数之比 | 0.5 |
| 颗粒间摩擦系数 | 0.5 |
| 颗粒比热容 | 840 J/(kg·K) |
| 颗粒热导率 | 1.4 W/(m·K) |
| 气相密度 | 1.3 kg/m3 |
| 气相黏度 | 1.8×105 Pa·s |
| 气相比热容 | 1010 J/(kg·K) |
| 气相热导率 | 0.02552 W/(m·K) |
| 颗粒弛豫时间 | 0.026 s |
| 整体固含率 | 0.05 |
| 初始固相温度 | 0 K |
| 方法一初始气相温度 | 0.1 K |
| 方法二重置气相温度 | 1000 K |
| 颗粒数目 | 1.3201×105 |
| 曳力模型 | Gidaspow_blend |
Table 1 Parameters and settings
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 颗粒直径 | 7.5×10-5 m |
| 计算域尺寸 | 240dp × 960dp× 6dp |
| 网格尺寸 | 2.5dp × 2.5dp × 3dp |
| 重力加速度 | 9.81 m/s2 |
| 颗粒密度 | 1500 kg/m3 |
| 法向弹性系数 | 5 N/m |
| 恢复系数 | 0.8 |
| 颗粒间碰撞的切向阻尼系数与法向阻尼系数之比 | 0.5 |
| 颗粒间摩擦系数 | 0.5 |
| 颗粒比热容 | 840 J/(kg·K) |
| 颗粒热导率 | 1.4 W/(m·K) |
| 气相密度 | 1.3 kg/m3 |
| 气相黏度 | 1.8×105 Pa·s |
| 气相比热容 | 1010 J/(kg·K) |
| 气相热导率 | 0.02552 W/(m·K) |
| 颗粒弛豫时间 | 0.026 s |
| 整体固含率 | 0.05 |
| 初始固相温度 | 0 K |
| 方法一初始气相温度 | 0.1 K |
| 方法二重置气相温度 | 1000 K |
| 颗粒数目 | 1.3201×105 |
| 曳力模型 | Gidaspow_blend |
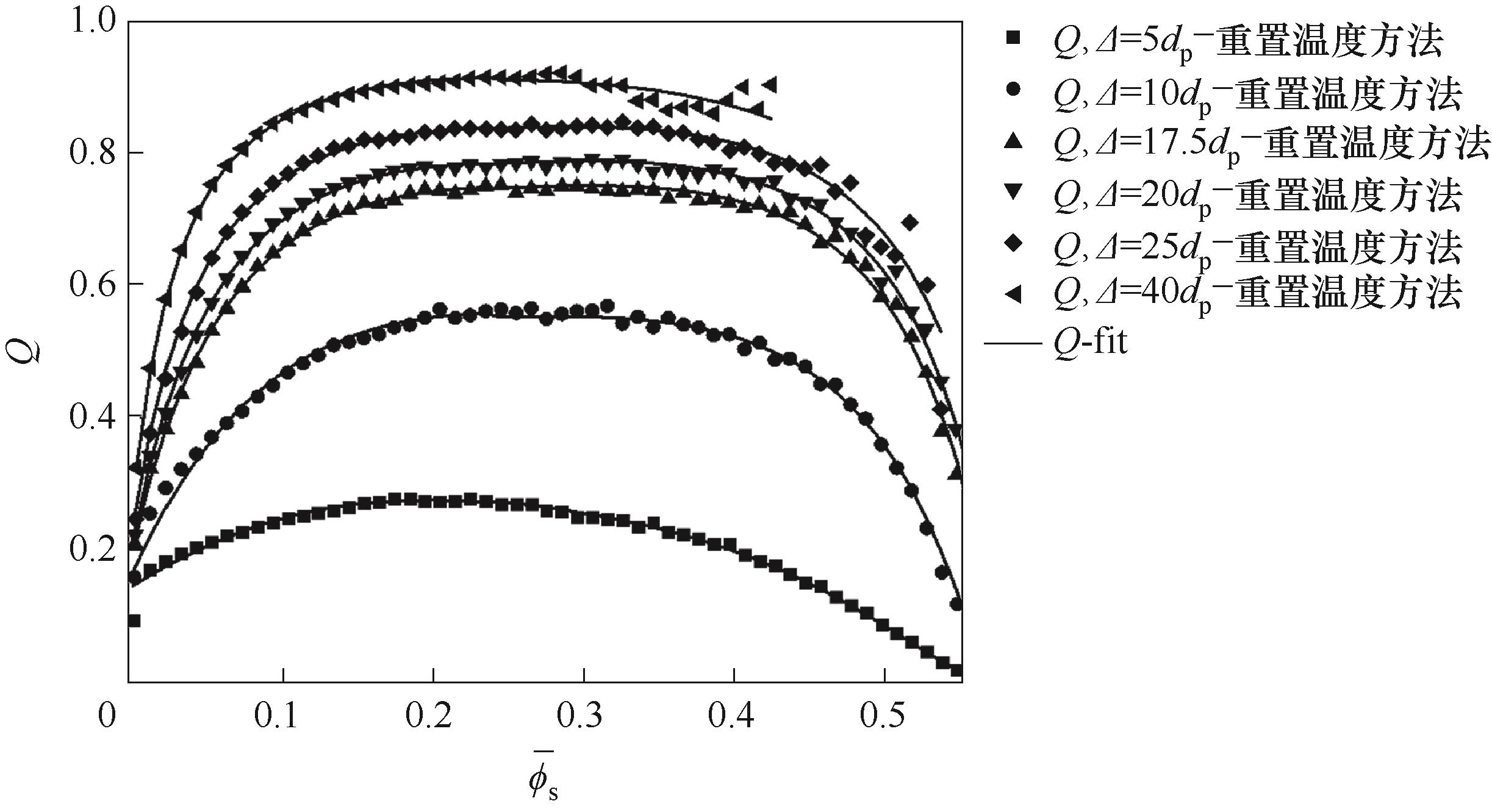
Fig.9 The variation of fitting Q obtained by the mesoscale model and real Q with the filtered solid volume fraction under the resetting temperature method
| 1 | Tavassoli H, Peters E A J F, Kuipers J A M. Direct numerical simulation of non-isothermal flow through dense bidisperse random arrays of spheres[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 314: 291-298. |
| 2 | Agrawal K, Loezos P N, Syamlal M, et al. The role of meso-scale structures in rapid gas–solid flows[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2001, 445: 151-185. |
| 3 | Li J H, Kwauk M. Multiscale nature of complex fluid-particle systems[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2001, 40(20): 4227-4237. |
| 4 | Helland E, Bournot H, Occelli R, et al. Drag reduction and cluster formation in a circulating fluidised bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(1/2): 148-158. |
| 5 | Sundaresan S. Modeling the hydrodynamics of multiphase flow reactors: current status and challenges[J]. AIChE Journal, 2000, 46(6): 1102-1105. |
| 6 | Wang S Y, Yin L J, Lu H L, et al. Numerical analysis of interphase heat and mass transfer of cluster in a circulating fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2009, 189(1): 87-96. |
| 7 | Wang S, Luo K, Hu C S, et al. CFD-DEM simulation of heat transfer in fluidized beds: model verification, validation, and application[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 197: 280-295. |
| 8 | Baltussen M W, Buist K A, Peters E A J F, et al. Multiscale modelling of dense gas-particle flows[J]. Advances in Chemical Engineering, 2018, 53: 1-52. |
| 9 | Igci Y, Andrews A T, Sundaresan S, et al. Filtered two-fluid models for fluidized gas-particle suspensions[J]. AIChE Journal, 2008, 54(6): 1431-1448. |
| 10 | Igci Y, Sundaresan S. Constitutive models for filtered two-fluid models of fluidized gas-particle flows[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(23): 13190-13201. |
| 11 | 王维, 洪坤, 鲁波娜, 等. 流态化模拟: 基于介尺度结构的多尺度CFD[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(1): 95-106. |
| Wang W, Hong K, Lu B N, et al. Fluidized bed simulation: structure-dependent multiscale CFD[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(1): 95-106. | |
| 12 | Cloete J H, Cloete S, Radl S, et al. On the choice of closure complexity in anisotropic drag closures for filtered Two Fluid Models[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 207: 379-396. |
| 13 | Li J, Kwauk M. Particle-Fluid Two-Phase Flow: the Energy-Minimization Multi-Scale Method[M]. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 1994. |
| 14 | Yang N, Wang W, Ge W, et al. Simulation of heterogeneous structure in a circulating fluidized-bed riser by combining the two-fluid model with the EMMS approach[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2004, 43(18): 5548-5561. |
| 15 | Wang W, Li J H. Simulation of gas-solid two-phase flow by a multi-scale CFD approach—extension of the EMMS model to the sub-grid level[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(1/2): 208-231. |
| 16 | Sundaresan S, Ozel A, Kolehmainen J. Toward constitutive models for momentum, species, and energy transport in gas-particle flows[J]. Annual Review of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 2018, 9: 61-81. |
| 17 | Gao X, Li T W, Sarkar A, et al. Development and validation of an enhanced filtered drag model for simulating gas-solid fluidization of Geldart A particles in all flow regimes[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 184: 33-51. |
| 18 | Jiang M, Chen X, Zhou Q. A gas pressure gradient-dependent subgrid drift velocity model for drag prediction in fluidized gas–particle flows[J]. AIChE Journal, 2020, 66(4): e16884. |
| 19 | Dong W G, Wang W, Li J H. A multiscale mass transfer model for gas-solid riser flows(Ⅰ):Sub-grid model and simple tests[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2008, 63(10): 2798-2810. |
| 20 | Hou B L, Li H Z. Relationship between flow structure and transfer coefficients in fast fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 157(2/3): 509-519. |
| 21 | 鲁波娜, 程从礼, 鲁维民, 等. 基于多尺度模型的MIP提升管反应历程数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(6): 1983-1992. |
| Lu B N, Cheng C L, Lu W M, et al. Numerical simulation of reaction process in MIP riser based on multi-scale model[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(6): 1983-1992. | |
| 22 | Shu Z, Wang J W, Zhou Q, et al. Evaluation of multifluid model for heat transfer behavior of binary gas-solid flow in a downer reactor[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 281: 34-48. |
| 23 | Guo L, Capecelatro J. The role of clusters on heat transfer in sedimenting gas-solid flows[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 132: 1217-1230. |
| 24 | Lane W A, Sarkar A, Sundaresan S, et al. Sub-grid models for heat transfer in gas-particle flows with immersed horizontal cylinders[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 151: 7-15. |
| 25 | Lane W A, Ryan E M. Verification, validation, and uncertainty quantification of a sub-grid model for heat transfer in gas-particle flows with immersed horizontal cylinders[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 176: 409-420. |
| 26 | Rauchenzauner S, Schneiderbauer S. A dynamic spatially averaged two-fluid model for heat transport in moderately dense gas-particle flows[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2020, 32(6): 063307. |
| 27 | Agrawal K, Holloway W, Milioli C C, et al. Filtered models for scalar transport in gas-particle flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 95: 291-300. |
| 28 | Huang Z Q, Zhang C, Jiang M, et al. Development of a filtered interphase heat transfer model based on fine-grid simulations of gas–solid flows[J]. AIChE Journal, 2020, 66(1): e16755. |
| 29 | Li Y, Yu Y X, Zhang C, et al. Improved filtered mesoscale interphase heat transfer model[J]. Particuology, 2021, 57: 176-186. |
| 30 | Lei H, Zhu L T, Luo Z H. Study of filtered interphase heat transfer using highly resolved CFD–DEM simulations[J]. AIChE Journal, 2021, 67(4): e17121. |
| 31 | Capecelatro J, Desjardins O, Fox R O. Numerical study of collisional particle dynamics in cluster-induced turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2014, 747: R2. |
| 32 | Ozel A, Kolehmainen J, Radl S, et al. Fluid and particle coarsening of drag force for discrete-parcel approach[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 155: 258-267. |
| 33 | Garg R, Galvin J, Li T W, et al. Open-source MFIX-DEM software for gas-solids flows(Ⅰ): Verification studies[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 220: 122-137. |
| 34 | Hou Q F, Zhou Z Y, Yu A B. Computational study of heat transfer in a bubbling fluidized bed with a horizontal tube[J]. AIChE Journal, 2012, 58(5): 1422-1434. |
| 35 | Gunn D J. Transfer of heat or mass to particles in fixed and fluidised beds[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1978, 21(4): 467-476. |
| 36 | Yu Y X, Li Y, Jiang M, et al. Meso-scale drag model designed for coarse-grid Eulerian-Lagrangian simulation of gas-solid flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 223: 115747. |
| 37 | Ozel A, Gu Y L, Milioli C C, et al. Towards filtered drag force model for non-cohesive and cohesive particle-gas flows[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2017, 29(10): 103308. |
| 38 | Wang J W, van der Hoef M A, Kuipers J A M. Why the two-fluid model fails to predict the bed expansion characteristics of Geldart A particles in gas-fluidized beds: a tentative answer[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(3): 622-625. |
| 39 | Fullmer W D, Hrenya C M. Quantitative assessment of fine-grid kinetic-theory-based predictions of mean-slip in unbounded fluidization[J]. AIChE Journal, 2016, 62(1): 11-17. |
| [1] | Cheng CHENG, Zhongdi DUAN, Haoran SUN, Haitao HU, Hongxiang XUE. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of surface microstructure effect on crystallization fouling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [2] | Shuangxing ZHANG, Fangchen LIU, Yifei ZHANG, Wenjing DU. Experimental study on phase change heat storage and release performance of R-134a pulsating heat pipe [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 165-171. |
| [3] | Yifei ZHANG, Fangchen LIU, Shuangxing ZHANG, Wenjing DU. Performance analysis of printed circuit heat exchanger for supercritical carbon dioxide [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [4] | Aiqiang CHEN, Yanqi DAI, Yue LIU, Bin LIU, Hanming WU. Influence of substrate temperature on HFE7100 droplet evaporation process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 191-197. |
| [5] | Mingxi LIU, Yanpeng WU. Simulation analysis of effect of diameter and length of light pipes on heat transfer [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 206-212. |
| [6] | Zhiguo WANG, Meng XUE, Yushuang DONG, Tianzhen ZHANG, Xiaokai QIN, Qiang HAN. Numerical simulation and analysis of geothermal rock mass heat flow coupling based on fracture roughness characterization method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 223-234. |
| [7] | Cong QI, Zi DING, Jie YU, Maoqing TANG, Lin LIANG. Study on solar thermoelectric power generation characteristics based on selective absorption nanofilm [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3921-3930. |
| [8] | Yitong LI, Hang GUO, Hao CHEN, Fang YE. Study on operating conditions of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform catalyst distributions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [9] | Yubing WANG, Jie LI, Hongbo ZHAN, Guangya ZHU, Dalin ZHANG. Experimental study on flow boiling heat transfer of R134a in mini channel with diamond pin fin array [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3797-3806. |
| [10] | Ke LI, Jian WEN, Biping XIN. Study on influence mechanism of vacuum multi-layer insulation coupled with vapor-cooled shield on self-pressurization process of liquid hydrogen storage tank [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3786-3796. |
| [11] | Tianhua CHEN, Zhaoxuan LIU, Qun HAN, Chengbin ZHANG, Wenming LI. Research progress and influencing factors of the heat transfer enhancement of spray cooling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3149-3170. |
| [12] | Yue YANG, Dan ZHANG, Jugan ZHENG, Maoping TU, Qingzhong YANG. Experimental study on flash and mixing evaporation of aqueous NaCl solution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3279-3291. |
| [13] | Rui HONG, Baoqiang YUAN, Wenjing DU. Analysis on mechanism of heat transfer deterioration of supercritical carbon dioxide in vertical upward tube [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3309-3319. |
| [14] | Ben ZHANG, Songbai WANG, Ziya WEI, Tingting HAO, Xuehu MA, Rongfu WEN. Capillary liquid film condensation and heat transfer enhancement driven by superhydrophilic porous metal structure [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2824-2835. |
| [15] | Hai WANG, Hong LIN, Chen WANG, Haojie XU, Lei ZUO, Junfeng WANG. Investigation of enhanced boiling heat transfer on porous structural surfaces by high voltage electric field [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2869-2879. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||