CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (3): 1346-1352.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240913
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Sanlong WANG( ), Yuelin WANG, Yu CAO(
), Yuelin WANG, Yu CAO( )
)
Received:2024-08-12
Revised:2024-10-21
Online:2025-03-28
Published:2025-03-25
Contact:
Yu CAO
通讯作者:
曹宇
作者简介:王三龙(1992—),男,博士,讲师,20233209@neepu.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Sanlong WANG, Yuelin WANG, Yu CAO. Research on the performance of inorganic perovskite solar cells based on phase heterojunction[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1346-1352.
王三龙, 王跃霖, 曹宇. 基于相异质结的高效无机钙钛矿太阳能电池的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1346-1352.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
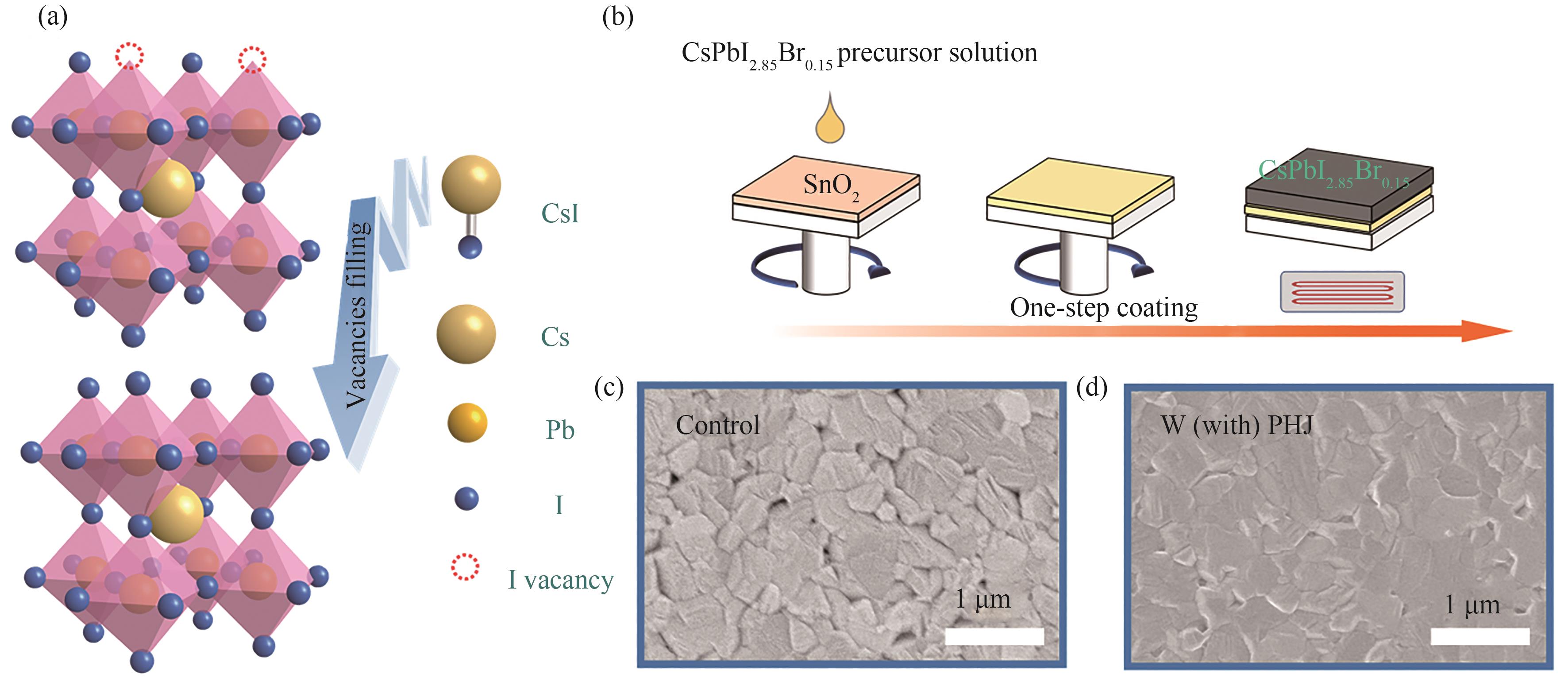
Fig.1 Mechanism and morphology characterization of PHJ: (a) Schematic diagram of the action mechanism of PHJ; (b) Flow chart for the preparation of inorganic perovskite films; SEM images of (c) Control and (d) PHJ inorganic perovskite films
| 1 | Zhao K, Liu Q Q, Yao L B, et al. peri-Fused polyaromatic molecular contacts for perovskite solar cells[J]. Nature, 2024, 632(8024): 301-306. |
| 2 | Paik M J, Kim Y Y, Kim J,et al. Ultrafine SnO2 colloids with enhanced interface quality for high-efficiency perovskite solar cells[J]. Joule, 2024, 8(7): 2073-2086. |
| 3 | Li M H, Jiao B X, Peng Y C, et al. High-efficiency perovskite solar cells with improved interfacial charge extraction by bridging molecules[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(38): e2406532. |
| 4 | Zhu Z J, Yuan S J, Mao K T, et al. Low-temperature atomic layer deposition of hole transport layers for enhanced performance and scalability in textured perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024,14(42): 2402365. |
| 5 | Wang G L, Duan W Y, Lian Q, et al. Reducing voltage loss via dipole tuning for electron-transport in efficient and stable perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(40): 2401029. |
| 6 | Liu Z L, Xiong Z J, Yang S F, et al. Strained heterojunction enables high-performance, fully textured perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells[J]. Joule, 2024, 8(10): 2834-2850. |
| 7 | Li C, Li Y H, Chen Y, et al. Enhancing efficiency of industrially-compatible monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells with dually-mixed self-assembled monolayers[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024: 2407805. |
| 8 | Jin Y B, Feng H P, Fang Z, et al. Efficient and stable monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells enabled by contact-resistance-tunable indium tin oxide interlayer[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(35): e2404010. |
| 9 | Wang S L, Wang P Y, Shi B, et al. Inorganic perovskite surface reconfiguration for stable inverted solar cells with 20.38% efficiency and its application in tandem devices[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(28): e2300581. |
| 10 | Wang S L, Wang P Y, Chen B B, et al. Suppressed recombination for monolithic inorganic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells with an approximate efficiency of 23%[J]. eScience, 2022, 2(3): 339-346. |
| 11 | Ji R, Zhang Z B, Hofstetter Y J, et al. Perovskite phase heterojunction solar cells[J]. Nature Energy, 2022, 7: 1170-1179. |
| 12 | Wang S, Li M H, Zhang Y Y, et al. Surface n-type band bending for stable inverted CsPbI3 perovskite solar cells with over 20% efficiency[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(6): 2572-2578. |
| 13 | Gu X J, Xiang W C, Tian Q W, et al. Rational surface-defect control via designed passivation for high-efficiency inorganic perovskite solar cells[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Edition), 2021, 60(43): 23164-23170. |
| 14 | Yoon S M, Min H, Kim J B, et al. Surface engineering of ambient-air-processed cesium lead triiodide layers for efficient solar cells[J]. Joule, 2021, 5(1): 183-196. |
| 15 | Zhang H, Tian Q W, Xiang W C, et al. Tailored cysteine-derived molecular structures toward efficient and stable inorganic perovskite solar cells[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(31): e2301140. |
| 16 | Tan S, Shi J J, Yu B C, et al. Inorganic ammonium halide additive strategy for highly efficient and stable CsPbI3 perovskite solar cells[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(21): 2010813. |
| 17 | Xu T F, Xiang W C, Kubicki D J, et al. Simultaneous lattice engineering and defect control via cadmium incorporation for high-performance inorganic perovskite solar cells[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(36): e2204486. |
| 18 | Wang Z T, Tian Q W, Zhang H, et al. Managing multiple halide-related defects for efficient and stable inorganic perovskite solar cells[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Edition), 2023, 62(30): e202305815. |
| 19 | Yu G H, Jiang K J, Gu W M, et al. Vacuum-assisted thermal annealing of CsPbI3 for highly stable and efficient inorganic perovskite solar cells[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Edition), 2022,61(27): e202203778. |
| 20 | Wang S L, Sun H R, Wang P Y, et al. Small molecule regulatory strategy for inorganic perovskite solar cells with 368mV of VOC deficit and its application in tandem devices[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(26): 2400151. |
| 21 | Sun N N, Fu S, Li Y, et al. Tailoring crystallization dynamics of CsPbI3 for scalable production of efficient inorganic perovskite solar cells[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 34 (6): 2309894. |
| 22 | Zhang S A, Zhang L, Tian Q W, et al. Spontaneous construction of multidimensional heterostructure enables enhanced hole extraction for inorganic perovskite solar cells to exceed 20% efficiency[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(1): 2103007. |
| 23 | Huang J, Wang H, Chen C Y, et al. Ionic bilateral passivator carboxyethylisothiuronium chloride for CsPbI3- x Br x perovskite solar cells with PCE 20.9% and superior stability[J]. Materials Today, 2023, 67: 46-56. |
| 24 | Tan S, Yu B C, Cui Y Q, et al. Temperature-reliable low-dimensional perovskites passivated black-phase CsPbI3 toward stable and efficient photovoltaics[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Edition), 2022, 61(23): e202201300. |
| 25 | Wang P Y, Zhang X W, Zhou Y Q, et al. Solvent-controlled growth of inorganic perovskite films in dry environment for efficient and stable solar cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 2225. |
| 26 | Yao Z, Xu Z, Zhao W G, et al. Enhanced efficiency of inorganic CsPbI3- x Br x perovskite solar cell via self-regulation of antisite defects[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(23): 2100403. |
| 27 | Yang Y, Chen R H, Wu J D, et al. Bilateral chemical linking at NiOx buried interface enables efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells and modules[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Edition), 2024, 63(36): e202409689. |
| 28 | Zhao Q Q, Zhang B Q, Hui W, et al. Oxygen vacancy mediation in SnO2 electron transport layers enables efficient, stable, and scalable perovskite solar cells[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146 (28): 19108-19117. |
| 29 | Yan N, Cao Y, Dai Z H, et al. Heterogeneous seed-assisted FAPbI3 crystallization for efficient inverted perovskite solar cells[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(14): 5070-5079. |
| 30 | Shi X Y, Liu T X, Dou Y J, et al. Air-processed perovskite solar cells with >25% efficiency and high stability enabled by crystallization modulation and holistic passivation[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(31): e2402785. |
| 31 | Liu T R, Zhao X M, Zhong X J, et al. Improved absorber phase stability, performance, and lifetime in inorganic perovskite solar cells with alkyltrimethoxysilane strain-release layers at the perovskite/TiO2 interface[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2022, 7(10): 3531-3538. |
| 32 | Wu W W, Xiong H, Deng J H, et al. Rotatable skeleton for the alleviation of thermally accumulated defects in inorganic perovskite solar cells[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2023, 8(5): 2284-2291. |
| 33 | Wang S L, Qi S S, Sun H R, et al. Nanoscale local contacts enable inverted inorganic perovskite solar cells with 20.8% efficiency[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Edition), 2024, 63(19): e202400018. |
| [1] | Guipei XU, Qian SUN, Jiewen LAI, Yifeng LU, Huifang DI, Hui HUANG, Zhenbing WANG. Research progress on failure mechanism of electrochemical double layer capacitors [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 951-962. |
| [2] | Yao FU, Yingjuan SHAO, Wenqi ZHONG. Experimental study on cyclic heat storage performance of TiO2-doped calcium based materials under pressurized carbonation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1180-1190. |
| [3] | Heng ZHANG, Dianlu KUI, Hong CHANG, Zhigang ZHAN. Effect of mechanical stress on the interfacial transport properties of gas diffusion layers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 637-644. |
| [4] | Lingya YUAN, Ying ZHANG. The growth of PV sector in China and its implications for the resource and environmental sustainability [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 14-24. |
| [5] | Xinyue WANG, Xiaohu XU, Haiyang ZHANG, Chunhua YIN. Study on encapsulation and properties vitamin A acetate/cyclodextrin [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 321-328. |
| [6] | Huanjuan ZHAO, Yingxin BAO, Kang YU, Jing LIU, Xinming QIAN. Quantitative experimental study on detonation instability of multi-component [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 339-348. |
| [7] | Dan PENG, Junjie LU, Wenjing NI, Yuan YANG, Jinglun WANG. Research progress of functional electrolyte for high-voltage LiCoO2 battery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3028-3040. |
| [8] | Lei ZUO, Junfeng WANG, Jian GAO, Daorui WANG. Electric field-regulating combustion behavior of biodiesel droplet [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2983-2990. |
| [9] | Haoyu WANG, Yang YANG, Wenjie JING, Bin YANG, Yu TANG, Yi LIU. Study on characteristics of gas-liquid spiral annular flow under action by different swirlers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2744-2755. |
| [10] | Jing LI, Fangfang ZHANG, Shuaishuai WANG, Jianhua XU, Pengyuan ZHANG. Effect of cavity structure on flammability limit of n-butane partially premixed flame [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(5): 2081-2090. |
| [11] | Zhouyang SHEN, Kang XUE, Qing LIU, Chengxiang SHI, Jijun ZOU, Xiangwen ZHANG, Lun PAN. Research progress on endothermic nanofluid fuels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1167-1182. |
| [12] | Haoqi CHEN, Bohui SHI, Qi PENG, Qi KANG, Shangfei SONG, Haiyuan YAO, Haihong CHEN, Haihao WU, Jing GONG. Phase equilibrium calculation of acid/alcohol hydrocarbon and water system based on stability analysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 789-800. |
| [13] | Shihao LI, Zhenhua WU, Zhanfeng ZHAO, Hong WU, Dong YANG, Jiafu SHI, Zhongyi JIANG. Electron transfer, proton transfer and molecule transfer in chemical processes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 1052-1064. |
| [14] | Bangjun GUO, Linan JIA, Xi ZHANG. A review of NCM cathode and interface characteristics in all-solid-state lithium-ion battery with sulfide electrolytes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 743-759. |
| [15] | Pei WANG, Ruiming DUAN, Guangru ZHANG, Wanqin JIN. Modeling and simulation analysis of solar driven membrane separation biomethane hydrogen production process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 967-973. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||