CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (S1): 217-229.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241369
• Fluid dynamics and transport phenomena • Previous Articles
Qingtai CAO1( ), Songyuan GUO1, Jianqiang LI2, Zan JIANG2, Bin WANG2, Rui ZHUAN2, Jingyi WU1, Guang YANG1(
), Songyuan GUO1, Jianqiang LI2, Zan JIANG2, Bin WANG2, Rui ZHUAN2, Jingyi WU1, Guang YANG1( )
)
Received:2024-11-27
Revised:2024-12-19
Online:2025-06-26
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
Guang YANG
曹庆泰1( ), 郭松源1, 李建强2, 蒋赞2, 汪彬2, 耑锐2, 吴静怡1, 杨光1(
), 郭松源1, 李建强2, 蒋赞2, 汪彬2, 耑锐2, 吴静怡1, 杨光1( )
)
通讯作者:
杨光
作者简介:曹庆泰(1999—),男,硕士研究生,qingtaicao@sjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Qingtai CAO, Songyuan GUO, Jianqiang LI, Zan JIANG, Bin WANG, Rui ZHUAN, Jingyi WU, Guang YANG. Numerical study on influence of perforated plate on retention performance of liquid oxygen tank under negative gravity[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229.
曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 工况 | 负过载/(m/s2) | 孔板布置情况 | 液面初始化情况 | 填充率/% | 液面坐标描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | -0.20g | 无多孔隔板 | 水平液面,位于正常情况的位置 | 50.18 | z=602 mm |
| 工况1 | -0.20g | 有多孔隔板 | 水平液面,高于孔板中截面30 mm | 52.68 | z=632 mm |
| 工况2 | -0.20g | 有多孔隔板 | 水平液面,低于孔板中截面30 mm | 47.68 | z=572 mm |
| 工况3 | -0.20g | 有多孔隔板 | 液面倾斜10°,液面中心位于孔板中截面上 | 50.18 | z=(tan10°)x + 602 mm |
| 工况4 | -0.03g | 有多孔隔板 | 水平液面,与孔板中截面重合 | 50.18 | z=602 mm |
| 工况5 | -0.10g | 有多孔隔板 | 水平液面,与孔板中截面重合 | 50.18 | z=602 mm |
| 工况6 | -0.20g | 有多孔隔板 | 水平液面,与孔板中截面重合 | 50.18 | z=602 mm |
| 工况7 | -0.40g | 有多孔隔板 | 水平液面,与孔板中截面重合 | 50.18 | z=602 mm |
Table 1 Summary of working conditions
| 工况 | 负过载/(m/s2) | 孔板布置情况 | 液面初始化情况 | 填充率/% | 液面坐标描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | -0.20g | 无多孔隔板 | 水平液面,位于正常情况的位置 | 50.18 | z=602 mm |
| 工况1 | -0.20g | 有多孔隔板 | 水平液面,高于孔板中截面30 mm | 52.68 | z=632 mm |
| 工况2 | -0.20g | 有多孔隔板 | 水平液面,低于孔板中截面30 mm | 47.68 | z=572 mm |
| 工况3 | -0.20g | 有多孔隔板 | 液面倾斜10°,液面中心位于孔板中截面上 | 50.18 | z=(tan10°)x + 602 mm |
| 工况4 | -0.03g | 有多孔隔板 | 水平液面,与孔板中截面重合 | 50.18 | z=602 mm |
| 工况5 | -0.10g | 有多孔隔板 | 水平液面,与孔板中截面重合 | 50.18 | z=602 mm |
| 工况6 | -0.20g | 有多孔隔板 | 水平液面,与孔板中截面重合 | 50.18 | z=602 mm |
| 工况7 | -0.40g | 有多孔隔板 | 水平液面,与孔板中截面重合 | 50.18 | z=602 mm |
| 物性参数 | 液氧 | 氧气 |
|---|---|---|
| 密度/(kg/m3) | 1142.70 | 5.34 |
| 动力黏度/(Pa·s) | 2.032×10-4 | 1.785×10-5 |
Table 2 Physical properties of liquid and gas oxygen
| 物性参数 | 液氧 | 氧气 |
|---|---|---|
| 密度/(kg/m3) | 1142.70 | 5.34 |
| 动力黏度/(Pa·s) | 2.032×10-4 | 1.785×10-5 |
| 网格数量/个 | 质心轴向位置/m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t=0.5 s | t=1.0 s | t=1.5 s | t=2.0 s | t=2.5 s | t=3.0 s | t=3.5 s | |
| 190万 | 0.316329 | 0.316900 | 0.321874 | 0.333099 | 0.347278 | 0.359630 | 0.370671 |
| 244万 | 0.316330 | 0.316864 | 0.321895 | 0.331798 | 0.343617 | 0.359207 | 0.373889 |
| 326万 | 0.316339 | 0.316937 | 0.321092 | 0.328244 | 0.337817 | 0.351348 | 0.361177 |
Table 3 Axial position of center of mass for different number of meshes
| 网格数量/个 | 质心轴向位置/m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t=0.5 s | t=1.0 s | t=1.5 s | t=2.0 s | t=2.5 s | t=3.0 s | t=3.5 s | |
| 190万 | 0.316329 | 0.316900 | 0.321874 | 0.333099 | 0.347278 | 0.359630 | 0.370671 |
| 244万 | 0.316330 | 0.316864 | 0.321895 | 0.331798 | 0.343617 | 0.359207 | 0.373889 |
| 326万 | 0.316339 | 0.316937 | 0.321092 | 0.328244 | 0.337817 | 0.351348 | 0.361177 |
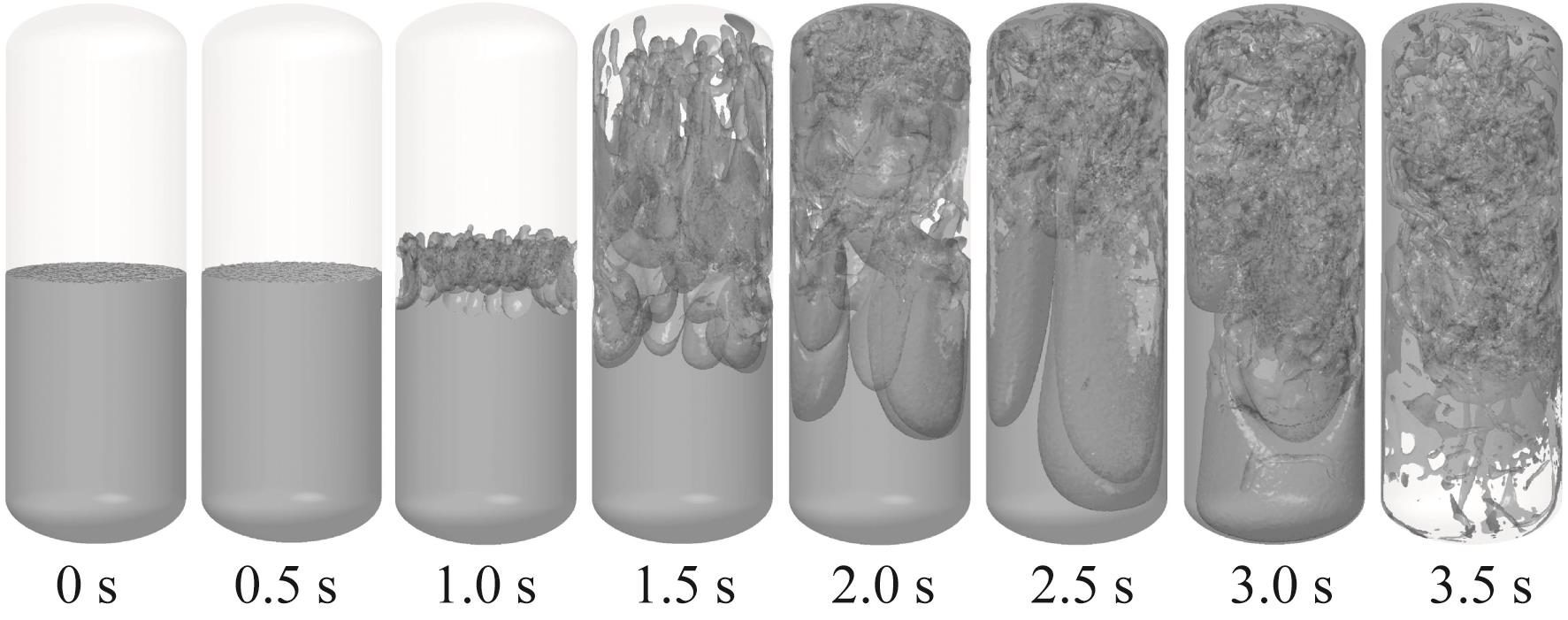
Fig.8 Liquid oxygen flow behavior of control group (no perforated plate, horizontal initial liquid level with 50.18% initial liquid oxygen fill rate, -0.20g)

Fig.9 Liquid oxygen flow behavior in Case 6 (with perforated plate, horizontal initial liquid level with 50.18% initial liquid oxygen fill rate, -0.20g)
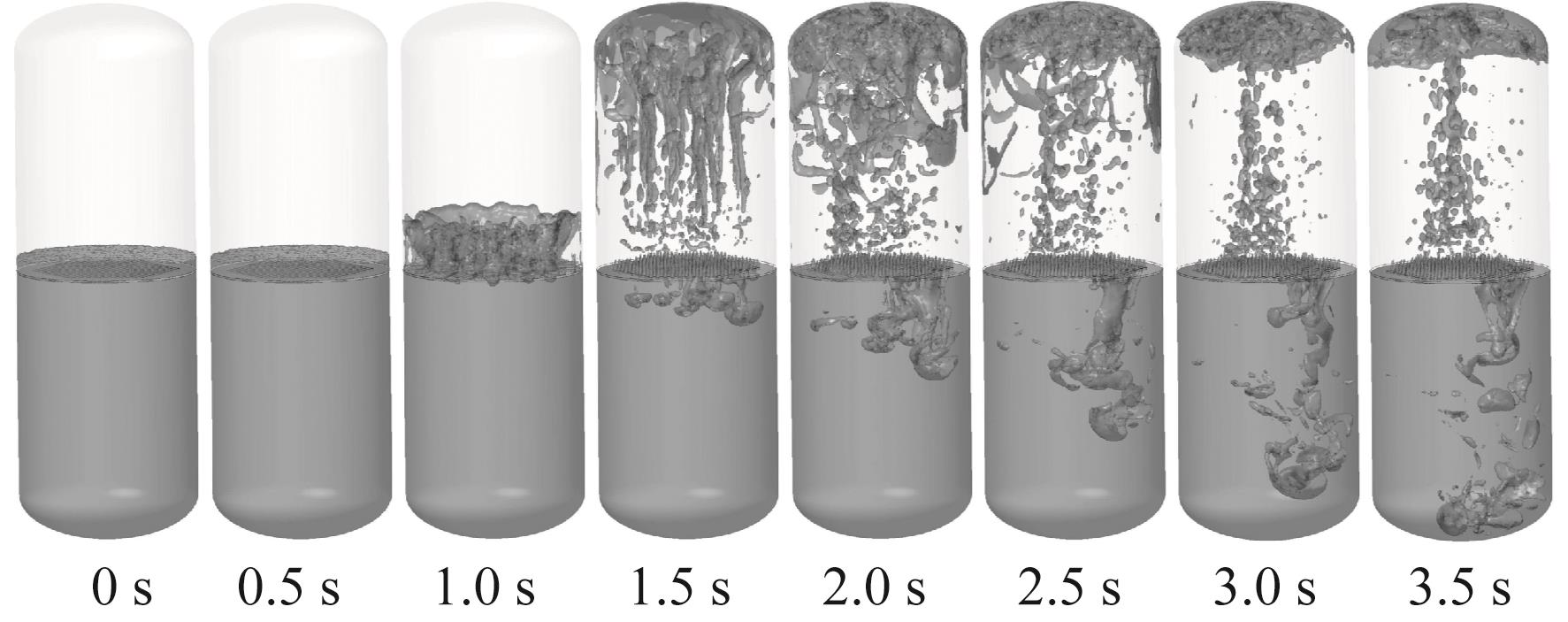
Fig.12 Liquid oxygen flow behavior in Case 1 (with perforated plate, horizontal initial liquid level with 52.68% initial liquid oxygen fill rate, -0.20g)
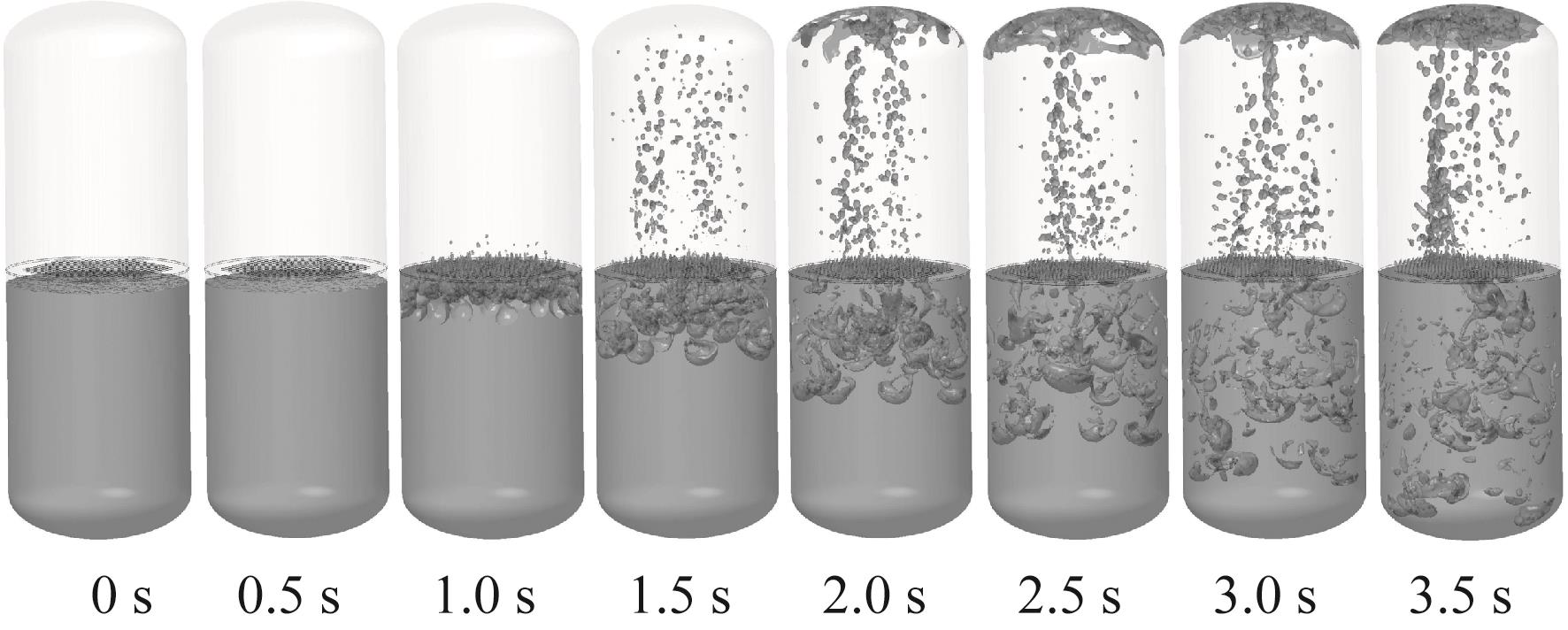
Fig.13 Liquid oxygen flow behavior in Case 2 (with perforated plate, horizontal initial liquid level with 47.68% initial liquid oxygen fill rate, -0.20g)
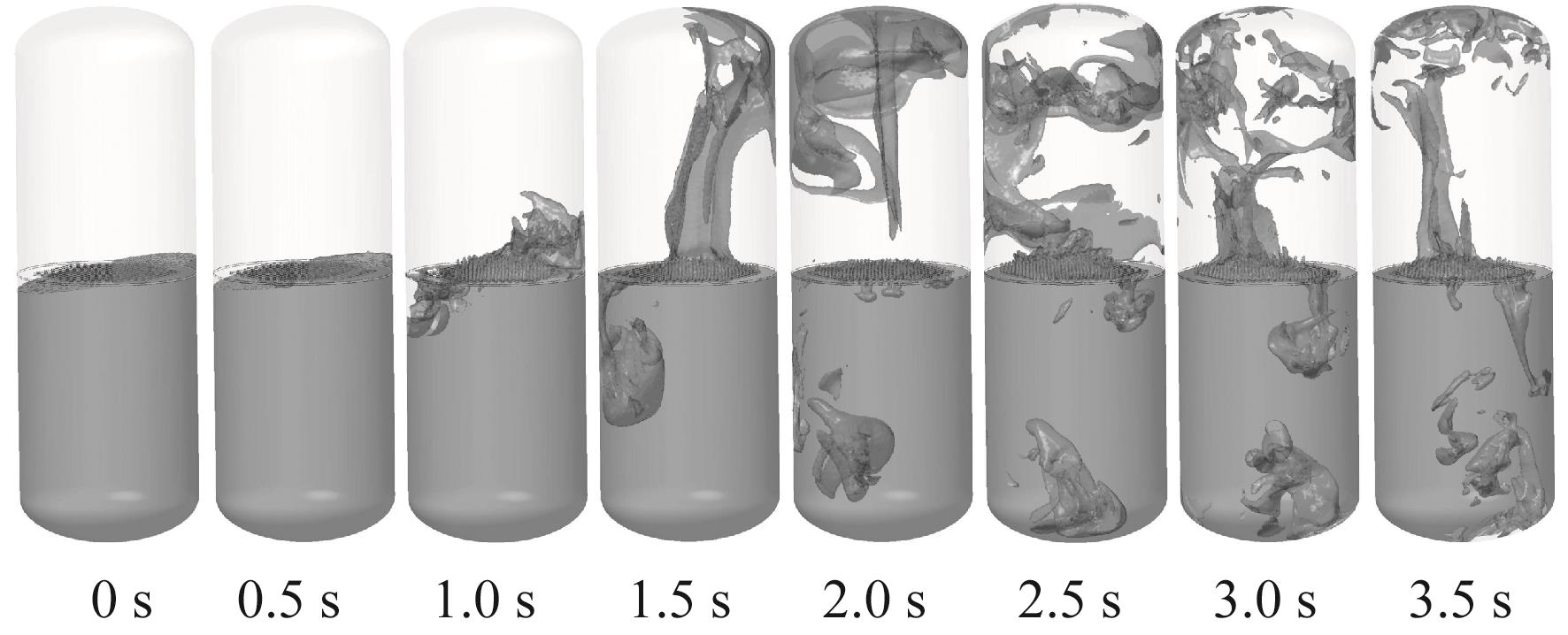

Fig.14 Liquid oxygen flow behavior in Case 3 (with perforated plate, inclined initial liquid level with 50.18% initial liquid oxygen fill rate, -0.20g)
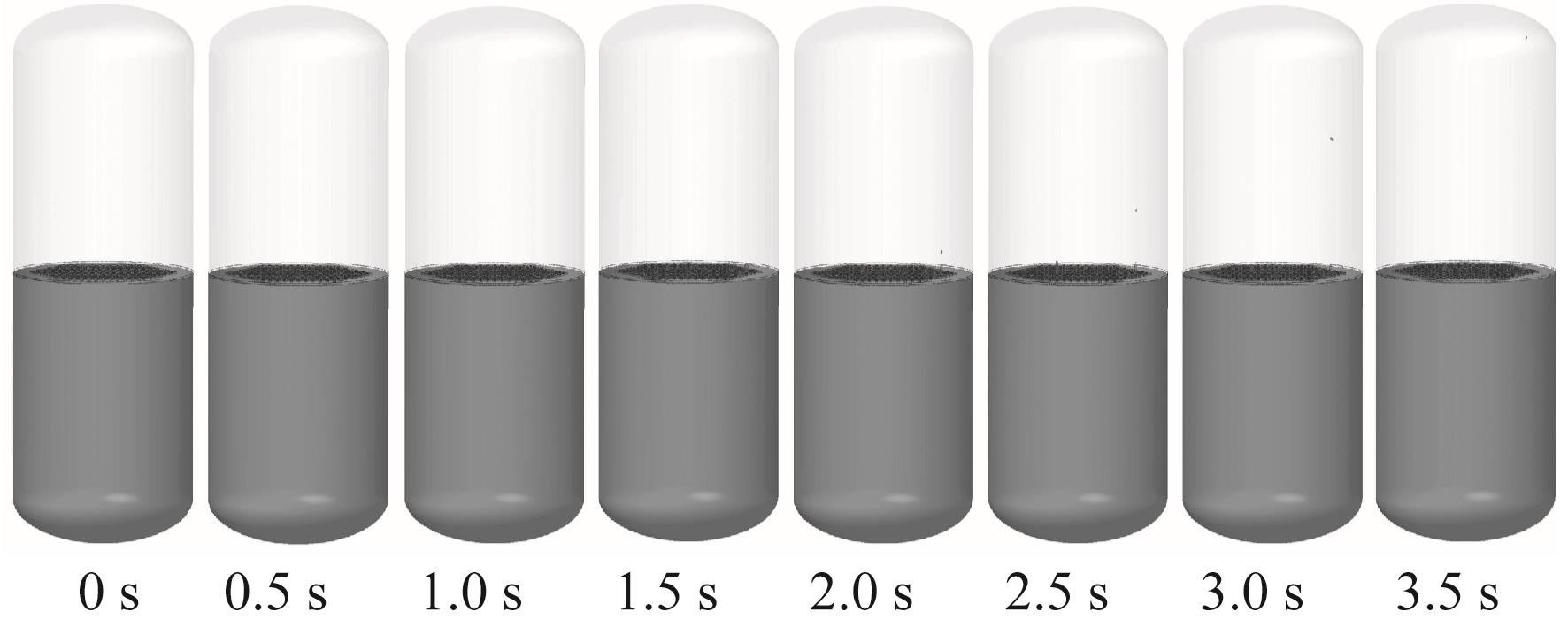

Fig.19 Liquid oxygen flow behavior in Case 4 (with perforated plate, inclined initial liquid level with 50.18% initial liquid oxygen fill rate, -0.03g)
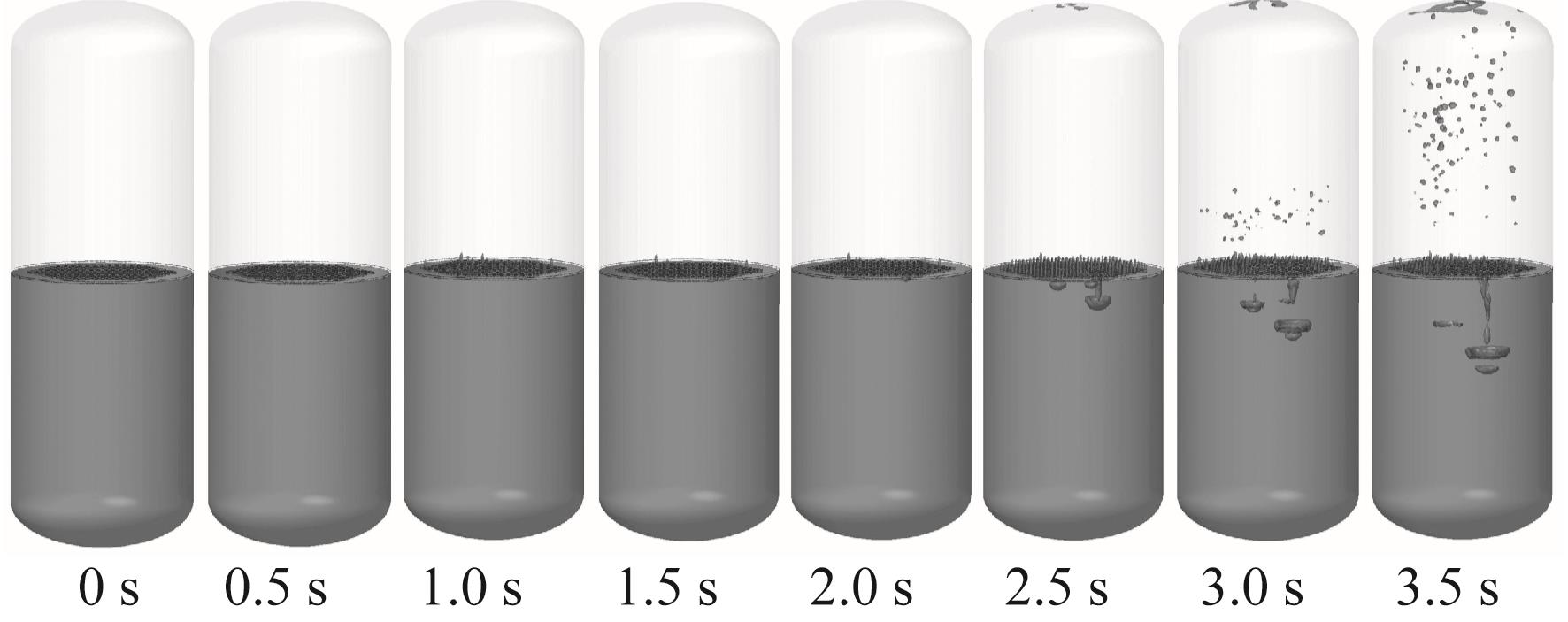
Fig.20 Liquid oxygen flow behavior in Case 5 (with perforated plate, inclined initial liquid level with 50.18% initial liquid oxygen fill rate, -0.10g)
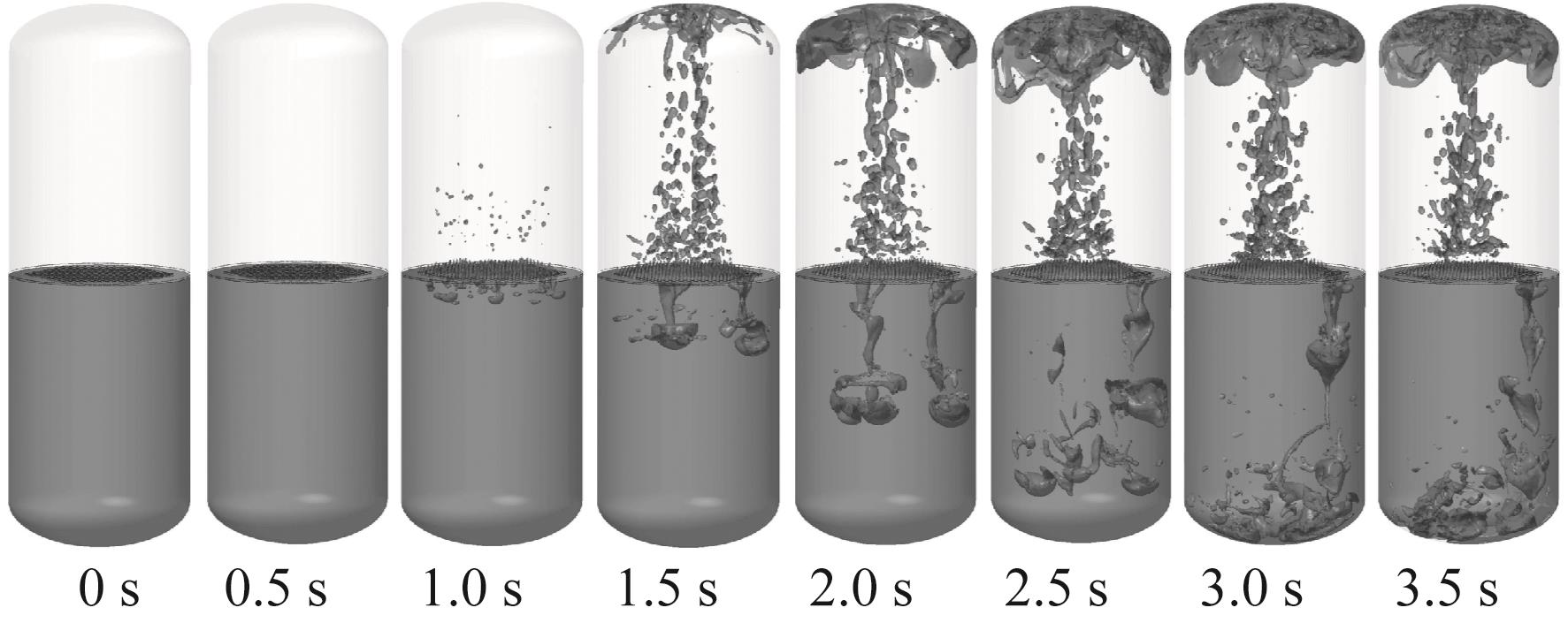

Fig.21 Liquid oxygen flow behavior in Case 7 (with perforated plate, inclined initial liquid level with 50.18% initial liquid oxygen fill rate, -0.40g)
| 负过载 | 质心轴向移动速度/(m/s) |
|---|---|
| -0.03g | 2.05×10-5 |
| -0.10g | 2.11×10-3 |
| -0.20g | 1.75×10-2 |
| -0.40g | 2.97×10-2 |
Table 4 Velocity of axial center of mass movement at the late stage of different negative gravity
| 负过载 | 质心轴向移动速度/(m/s) |
|---|---|
| -0.03g | 2.05×10-5 |
| -0.10g | 2.11×10-3 |
| -0.20g | 1.75×10-2 |
| -0.40g | 2.97×10-2 |
| 1 | 包为民. 可重复使用运载火箭技术发展综述[J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(23): 8-33, 3. |
| Bao W M. A review of reusable launch vehicle technology development[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(23): 8-33, 3. | |
| 2 | 宋征宇, 黄兵, 汪小卫, 等. 重复使用航天运载器的发展及其关键技术[J]. 前瞻科技, 2022, 1(1): 62-74. |
| Song Z Y, Huang B, Wang X W, et al. Development and key technologies of reusable launch vehicle[J]. Science and Technology Foresight, 2022, 1(1): 62-74. | |
| 3 | 容易, 刘辉, 于子文, 等. 可重复使用运载火箭返回段低温流体行为特性[J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(23): 105-116. |
| Rong Y, Liu H, Yu Z W, et al. Behavior of cryogenic propellant in return stage of reusable launch vehicle[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(23): 105-116. | |
| 4 | 高朝辉, 刘宇, 肖肖, 等. 垂直着陆重复使用运载火箭对动力技术的挑战[J]. 火箭推进, 2015, 41(3): 1-6, 45. |
| Gao Z H, Liu Y, Xiao X, et al. Challenge to propulsion technology for vertical landing reusable launch vehicle[J]. Journal of Rocket Propulsion, 2015, 41(3): 1-6, 45. | |
| 5 | Zuo Z Q, Zhu W X, Huang Y H, et al. A review of cryogenic quasi-steady liquid-vapor phase change: theories, models, and state-of-the-art applications[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2023, 205: 123916. |
| 6 | Dodge F T. Fluid management in low gravity[M]//Low-Gravity Fluid Dynamics and Transport Phenomena. Washington D C: AIAA, 1990: 3-14. |
| 7 | 尕永婧, 王浩苏, 张青松, 等. 垂直着陆过程推进剂流动行为特性及影响分析[J]. 深空探测学报, 2021, 8(1): 42-50. |
| Ga Y J, Wang H S, Zhang Q S, et al. Propellant flow characteristics in tank and related impact analysis during the vertical landing stage[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2021, 8(1): 42-50. | |
| 8 | 王晔, 张婉雨, 汪彬, 等. 多孔网幕泡破压力预测模型的建立及实验验证[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(3): 1102-1110. |
| Wang Y, Zhang W Y, Wang B, et al. Analytical model of bubble point pressure for metal wire screens and experimental validation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(3): 1102-1110. | |
| 9 | Hartwig J W. Liquid Acquisition Devices for Advanced In-Space Cryogenic Propulsion Systems[M]. New York: Academic Press, 2016. |
| 10 | Himeno T, Watanabe T, Nonaka S, et al. Numerical and experimental investigation on sloshing in rocket tanks with damping devices[C]//43rd AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit. AIAA, 2007: AIAA2007-5557. |
| 11 | Chen L, Liu J T. Numerical simulation of fluid flow in the vane type tank on orbital refuelling process[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2018, 163: 012085. |
| 12 | 杨唱, 孙冰, 方杰. 航天器贮箱出流过程液体晃动及防晃[J]. 航空动力学报, 2018, 33(12): 3065-3072. |
| Yang C, Sun B, Fang J. Liquid sloshing and anti-sloshing of spacecraft tank during outflow[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2018, 33(12): 3065-3072. | |
| 13 | Ohashi A, Furuichi Y, Haba D C, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on pressure change in cryogenic sloshing with a ring baffle[C]//53rd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference. AIAA, 2017: AIAA2017-4760. |
| 14 | Liu Z, Li C. Influence of slosh baffles on thermodynamic performance in liquid hydrogen tank[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 346: 253-262. |
| 15 | 肖明堃, 黄永华, 吴静怡, 等. 非均匀磁场力作用下微重力液氧气液界面特性[J]. 制冷技术, 2020, 40(6): 1-11. |
| Xiao M K, Huang Y H, Wu J Y, et al. Gas-liquid interface behavior of liquid oxygen in compensated microgravity field with inhomogeneous magnetic force[J]. Chinese Journal of Refrigeration Technology, 2020, 40(6): 1-11. | |
| 16 | Hartwig J W. Propellant management devices for low-gravity fluid management: past, present, and future applications[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2017, 54(4): 808-824. |
| 17 | Liu Z, Yuan K F, Liu Y L, et al. Fluid sloshing thermo-mechanical characteristic in a cryogenic fuel storage tank under different gravity acceleration levels[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(59): 25007-25021. |
| 18 | Berglund M D, Bassett C E, Kelso J M, et al. The boeing delta Ⅳ launch vehicle—pulse-settling approach for second-stage hydrogen propellant management[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2007, 61(1/2/3/4/5/6): 416-424. |
| 19 | Space Exploration Technologies Corporation. SpaceX Demo Flight 2 Flight Review Update[EB/OL]. [2007-06-16]. . |
| 20 | Space Systems Engineering Website. The NEAR Rendezvous Burn Anomaly of December 1998[DS/OL]. [1999-11]. . |
| 21 | Hubert C. Behavior of spinning space vehicles with onboard liquids [R]. Technical Report, 2008: B8030. |
| 22 | Hartwig J, Esser N, Jain S, et al. CFD modeling of bidirectional PMDs inside cryogenic propellant tanks onboard parabolic flights[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2024, 61(1): 296-312. |
| 23 | Varghese A P, Hartwig J W, Lieber S C, et al. Numerical design of a flow restrictor for tanked liquid nitrogen undergoing reduced-gravity flights[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2024, 154: 109539. |
| 24 | Cheng G H, Jing W X, Gao C S. Recovery trajectory planning for the reusable launch vehicle[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 117: 106965. |
| 25 | Hirt C W, Nichols B D. Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1981, 39(1): 201-225. |
| 26 | Morton K W. Numerical Methods for Fluid Dynamics[M]//Baines M J. New York: Academic Press, 1982: 273-486. |
| 27 | Guo S Y, Xiao M K, Xie F, et al. Optimization of helium consumption for feedback pressurization in liquid oxygen tanks[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 230: 125739. |
| 28 | 刘辉, 王亚军, 黄兵, 等. 推进剂重定位过程仿真与分析[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 53(S1): 17-24. |
| Liu H, Wang Y J, Huang B, et al. Simulation and analysis of propellant reorientation process[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2021, 53(S1): 17-24. | |
| 29 | Brackbill J U, Kothe D B, Zemach C. A continuum method for modeling surface tension[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1992, 100(2): 335-354. |
| 30 | 陈虹, 高旭, 王向南, 等. 过冷液氧增压排液过程数值模拟研究[J]. 低温工程, 2023(1): 20-25, 36. |
| Chen H, Gao X, Wang X N, et al. Numerical investigation on pressurization discharge of subcooled liquid oxygen[J]. Cryogenics, 2023(1): 20-25, 36. | |
| 31 | Lemmon E W, Bell I H, Huber M L, et al. NIST Standard Reference Database 23: Reference Fluid Thermodynamic and Transport Properties-REFPROP, Version 10.0 [M]. Gaithersburg, 2018. |
| 32 | Salzman J, Masica W, Lacovic R. Low gravity reorientation in a scale-model Centaur liquid-hydrogen tank[R]. NASA, 1967. |
| [1] | Zixiang ZHAO, Zhongdi DUAN, Haoran SUN, Hongxiang XUE. Numerical modelling of water hammer induced by two phase flow with large temperature difference [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [2] | Hao HUANG, Wen WANG, Longkun HE. Simulation and analysis on precooling process of membrane LNG carriers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [3] | Siyuan WANG, Guoqiang LIU, Tong XIONG, Gang YAN. Characteristics of non-uniform wind velocity distribution in window air conditioner axial fans and their impact on optimizing condenser circuit optimization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [4] | Lu LIU, Kai WAN, Wenyue WANG, Tai WANG, Jiancheng TANG, Shaoheng WANG. Study on orthohydrogen and parahydrogen conversion coupled flow and heat transfer based on helium expansion refrigeration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1513-1522. |
| [5] | Chengcheng XU, Suola SHAO, Wenjian WEI, Xu ZHENG. Research on heating performance of direct-condensation thermal storage aluminum radiant heating panel under multiple working conditions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1545-1558. |
| [6] | Wenlong JIA, Huan XIAO, Xiangyu LENG, Qiaojing HUANG, Chengwei LIU, Xia WU. Experimental and numerical simulation of ultrasonic cavitation microjet cleaning of heavy deposition in crude oil storage tank [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1288-1296. |
| [7] | Chuanchao HE, Jinghong ZHOU, Yueqiang CAO, Yao SHI, Xinggui ZHOU. Bed-particle dual scale coupled simulation on Ag/SiO2 catalyzed hydrogenation of oxalate to methyl glycolate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 654-666. |
| [8] | Yunlong HUANG, Jian XU, Tong LIU, Xintong YUAN, Qiang XU. Experimental study on temperature distribution characteristics and flow measurement of horizontal wells in gas reservoir [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 612-622. |
| [9] | Ke ZHANG, Weijie REN, Mengna WANG, Kaifeng FAN, Liping CHANG, Jiabin LI, Tao MA, Jinping TIAN. Liquid-liquid mixing characteristics of Bunsen reaction products in microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 623-636. |
| [10] | Zeyu ZHANG, Ping WANG, Kailun DAI, Weijia QIAN, Subhajit Roy, Ruiyang SHUAI, Antonio Ferrante. Combustion characteristics and NO production of axially staged premixed NH3/CH4 turbulent swirling flames [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 835-845. |
| [11] | Jiayi YAO, Donghui ZHANG, Zhongli TANG, Wenbin LI. Research on carbon capture by pressure swing adsorption based on two-stage dual reflux [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 744-754. |
| [12] | Shuyue LI, Huan WANG, Shaoqiang ZHOU, Zhihong MAO, Yongmin ZHANG, Junwu WANG, Xiuhua WU. Current status and prospects of research on fluidization characteristics of high-density particles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 466-483. |
| [13] | Xiaoyu DAI, Qiang XU, Chenyu YANG, Xiaobin SU, Liejin GUO. Gas-liquid two-phase pressurization characteristics of multistage mixed-flow multiphase pump [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 554-563. |
| [14] | Jingyu JIA, Deqi KONG, Yuanhui SHEN, Donghui ZHANG, Wenbin LI, Zhongli TANG. Simulation and analysis of ammonia separation process by pressure swing adsorption from synthetic ammonia reactor-off gas [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 718-730. |
| [15] | Qiwo HAN, Yongfeng LIU, Pucheng PEI, Lu ZHANG, Shengzhuo YAO. Analysis of influence of operating temperature on water distribution, proton transport and performance of PEMFC [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 374-384. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||