CIESC Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (8): 3891-3906.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210020
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zi'ang XU( ),Lei WAN,Kai LIU,Baoguo WANG(
),Lei WAN,Kai LIU,Baoguo WANG( )
)
Received:2021-01-08
Revised:2021-03-13
Online:2021-08-05
Published:2021-08-05
Contact:
Baoguo WANG
通讯作者:
王保国
作者简介:徐子昂(1996—),男,博士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Zi'ang XU, Lei WAN, Kai LIU, Baoguo WANG. Recent progress of molecular design for highly stable alkaline anion exchange membranes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(8): 3891-3906.
徐子昂, 万磊, 刘凯, 王保国. 高稳定碱性离子膜分子设计研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(8): 3891-3906.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig.2 Annual journal article publications included by Web of Science from 2006 to 2020. Keywords: (a) “Anion Exchange Membrane” & “Fuel Cell”;(b)“Anion Exchange Membrane” & “Water Electrolysis”. The total number of articles for 2018—2020 is statistics until October 2020
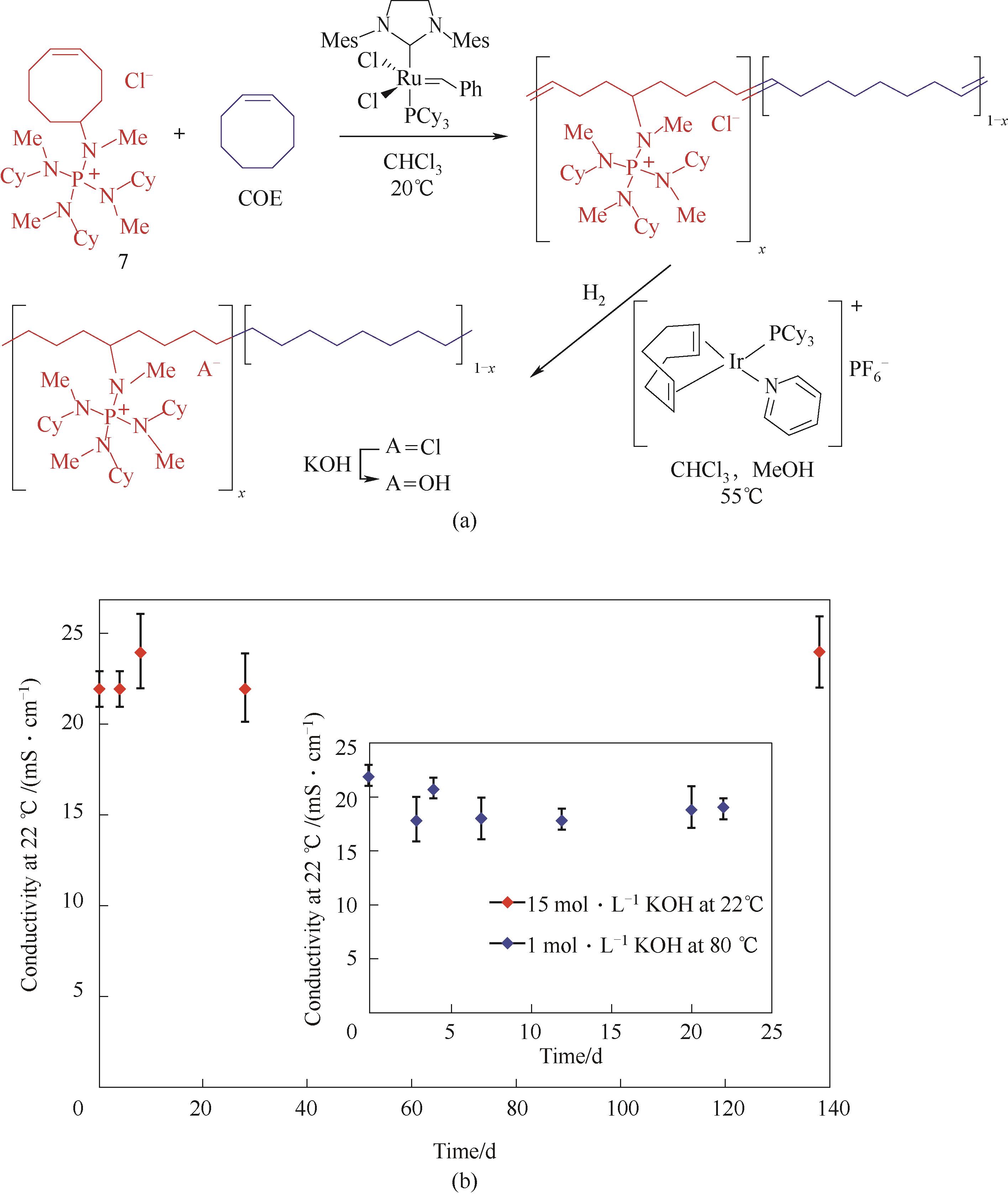
Fig.5 AAEM-17 based on ring opening metathesis polymerization[30](a) synthesis route;(b) stability test based on conductivity variety according to time
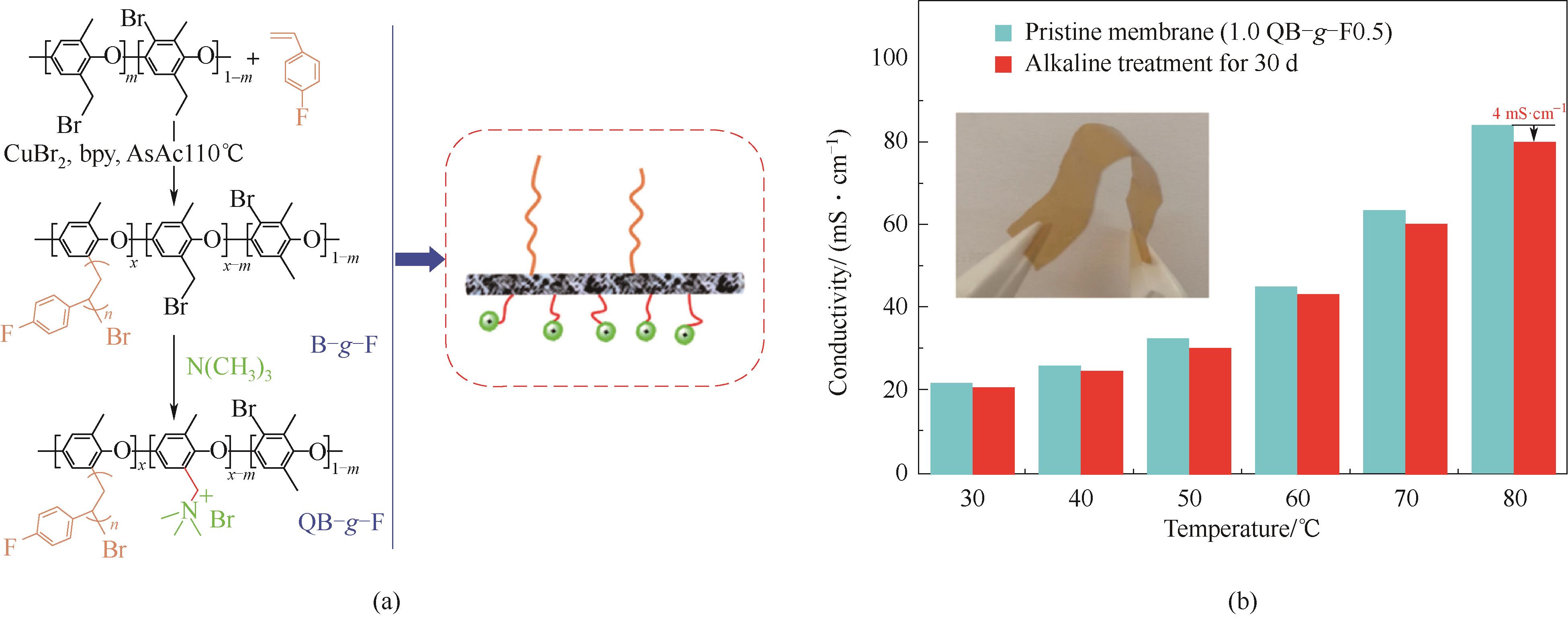
Fig.6 Chemical stable QB-g-F based on side chain engineering[40](a) synthesis route & chemical structure;(b) stability test based on conductivity variety according to time under 2 mol·L-1 OH-, 60℃
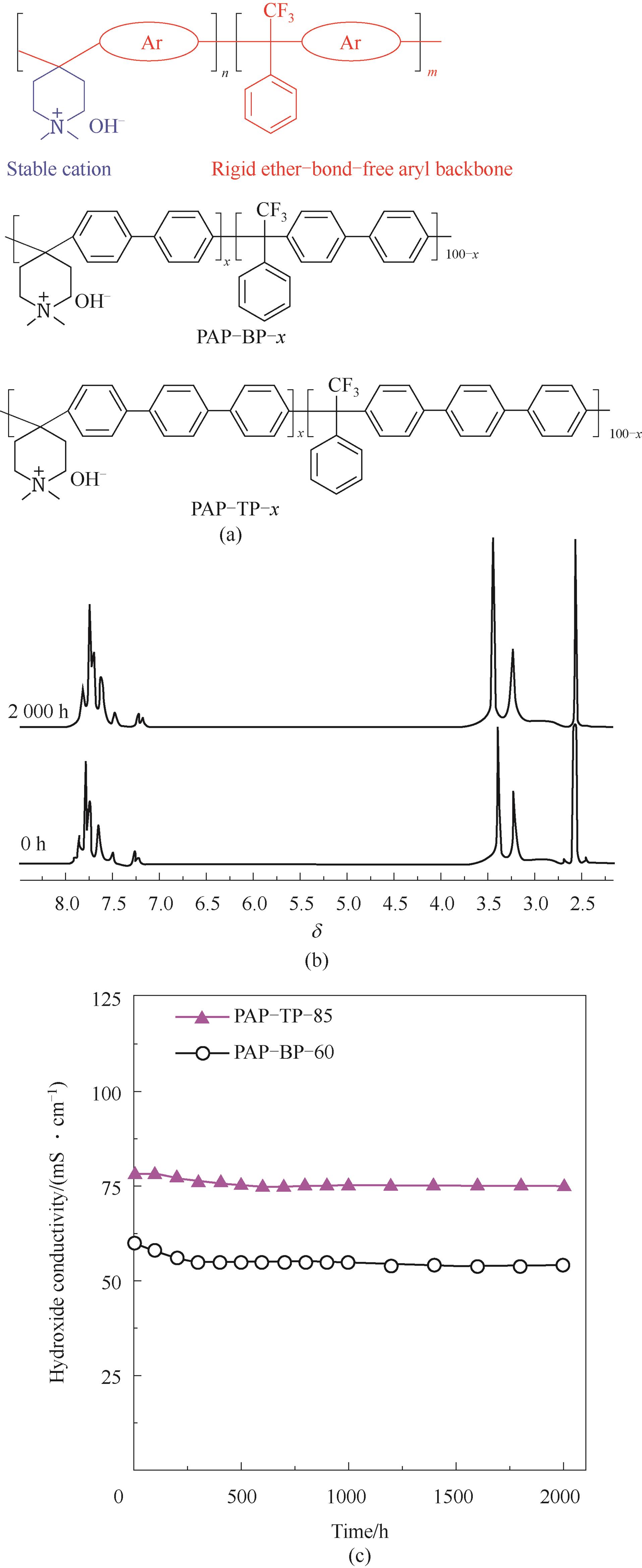
Fig.7 PAP-BP-x & PAP-TP-x with poly-aryl backbone prepared by superacid catalysis[46](a) structure of polymer; (b) alkaline durability based on NMR change; (c) conductivity variety according to time under 1 mol·L-1 KOH, 100℃
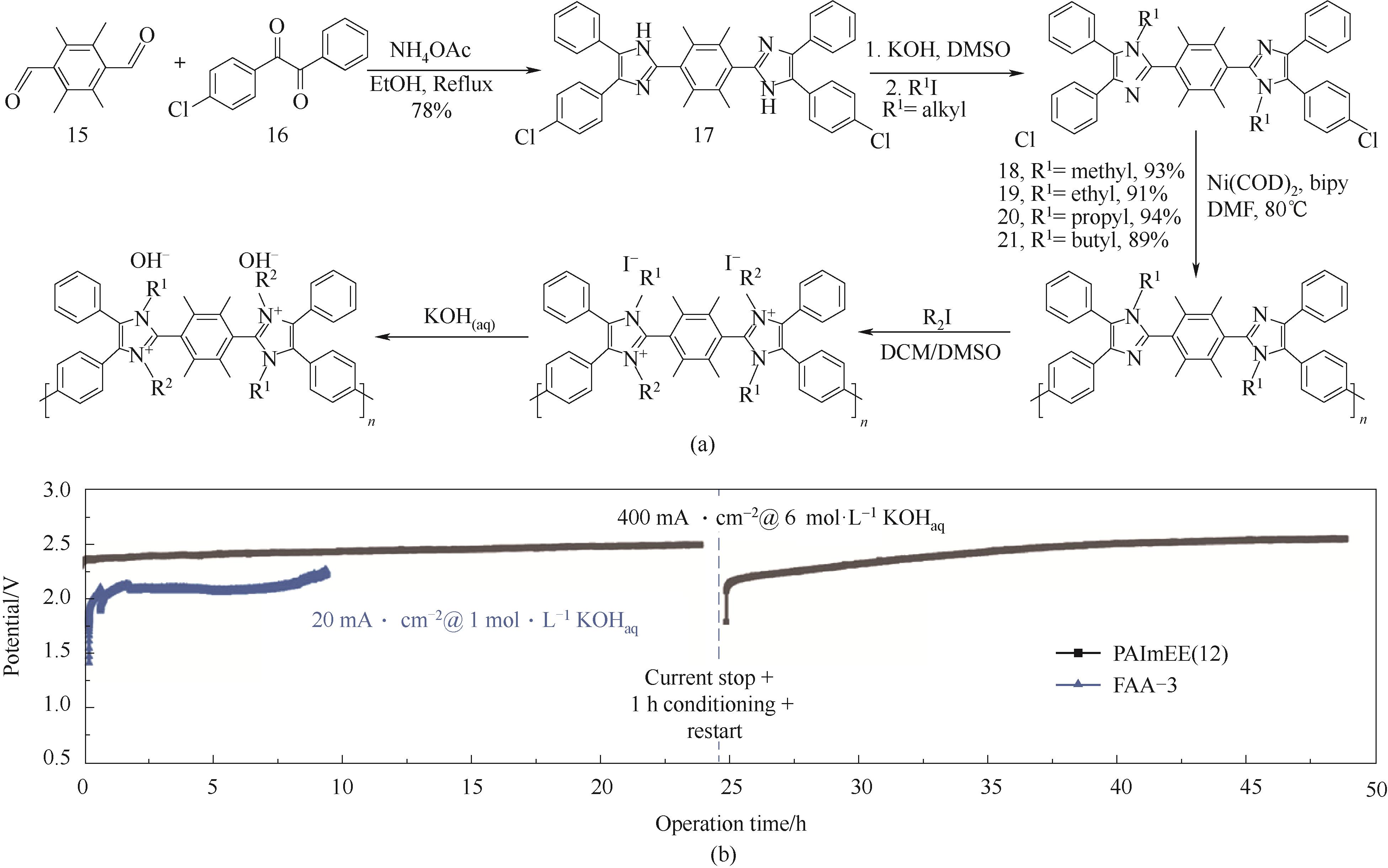
Fig.8 Yamamoto coupling polymerization for poly-aryl backbone PAImXY[48](a) synthesis route; (b) water electrolysis stability test under 6 mol·L-1 KOH
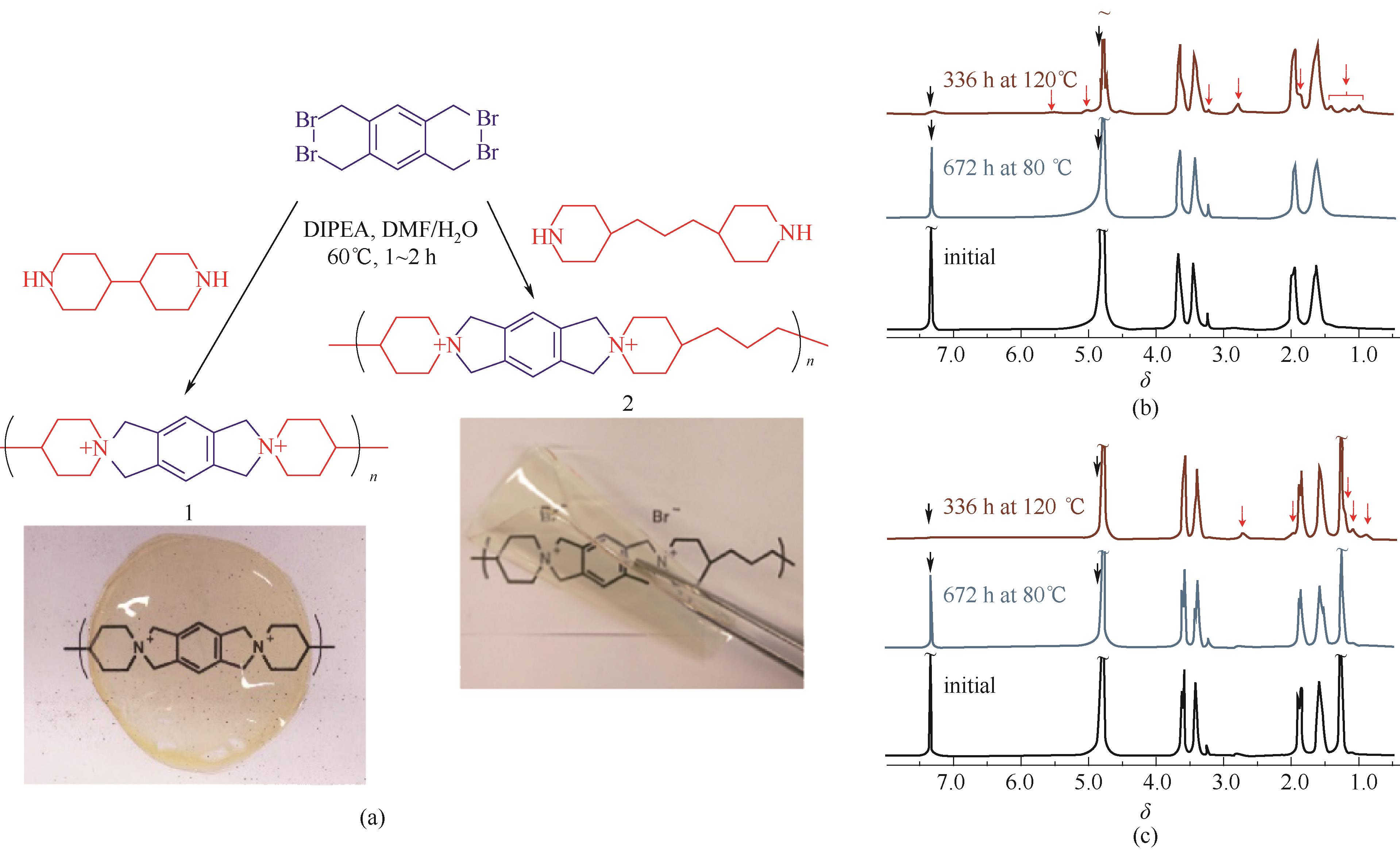
Fig.12 Spiro-ionenes AEMs based on N?spirocyclic quaternary ammonium group[60](a) chemical structure & photographs of AEM; (b),(c) alkaline stability under different condition monitored by NMR

Fig.14 Pyrazolium cross-linked PXm-Tn for OH- transportation highway[67](a) chemical structure & synthesis route; (b) chemical stability test based on conductivity variety under 1 mol·L-1 KOH, 80℃; (c) AEMFC durability test
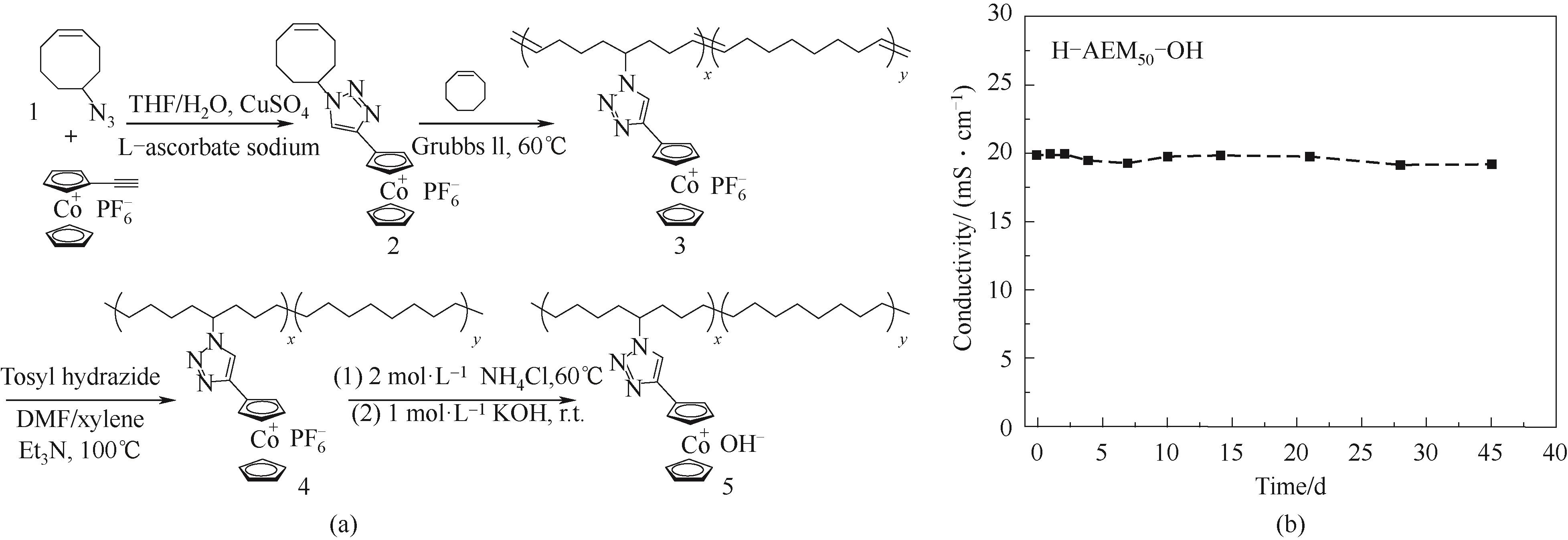
Fig.15 H-AEM-OH based on cobaltocenium center[32](a) chemical structure & synthesis route; (b) chemical stability test based on conductivity variety under 1 mol·L-1 KOH, 80℃
| 类别 | 阳离子 基团 | AEMs名称 | 聚合物主链 | IEC/ (mmol·g-1) | 电导率/(mS·cm-1) | 稳定性 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非芳香型季铵盐 | DBACO型 | CL-QDPEEKOH | 聚醚醚酮 | 1.2 | 51(55℃) | 50%电导率保持(2 mol·L-1 KOH, 60℃,120 h) | [ |
| 奎宁型 | PDPF-Qui | 超酸催化聚芳基 | 1.99 | 100(80℃) | 91.2%电导率保持(5 mol·L-1 NaOH,90℃,168 h) | [ | |
| 哌啶型 | PAP-TP | 超酸催化聚芳基 | 2.37 | 193(95℃) | 97%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 KOH,100℃,2000 h) | [ | |
| 吡咯型 | PyrPIB | 超酸催化聚芳基 | 1.79 | 49.08(80℃) | 64.8%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 NaOH,80℃,1050 h) | [ | |
| 螺环型 | Spiro-ionenes | 螺环-阳离子聚合物 | 4 | 120(90℃)(与聚苯并咪唑共混后) | NMR谱图无变化(1 mol·L-1 KOH,80℃,1800 h) | [ | |
| 芳香型季铵盐 | 胍型 | M-PAES-TMG | 含氟聚芳醚 | 1.03 | 36(80℃) | 63.9%电导率保持(0.5 mol·L-1 NaOH,80℃, 382 h) | [ |
| 咪唑型 | Syne-IM PPO | 聚苯醚 | 1.60 | 34(80℃) | 95%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 KOH,80℃,48 h) | [ | |
| 吡唑型 | PXm-Tn | 全交联聚芳基 | 0.91 | 111.6(80℃) | 76%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 KOH, 80℃,720 h) | [ | |
季 盐 盐 | 氨基 季 | AAEM-17 | 聚烯烃 | 0.67±0.1 | 22±1(22℃) | 81.8%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 KOH,80℃,22 d) | [ |
芳基 季 | TPQPOH | 聚醚砜 | 1.09 | 27(20℃) | 100%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 KOH,80℃,48 h) | [ | |
| 金属盐 | 二茂钴型 | H-AEM-OH | 聚烯烃 | 1.86 | 90(90℃) | 95%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 NaOH, 1个月) | [ |
配位 金属型 | DCPD AEMs | 聚烯烃 | 1.4 | 28.6(30℃) | 7%质量损失(1 mol·L-1 NaOH,80℃,24 h) | [ |
Table 1 Conductivity and alkali resistance of AEMs with different cationic groups
| 类别 | 阳离子 基团 | AEMs名称 | 聚合物主链 | IEC/ (mmol·g-1) | 电导率/(mS·cm-1) | 稳定性 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非芳香型季铵盐 | DBACO型 | CL-QDPEEKOH | 聚醚醚酮 | 1.2 | 51(55℃) | 50%电导率保持(2 mol·L-1 KOH, 60℃,120 h) | [ |
| 奎宁型 | PDPF-Qui | 超酸催化聚芳基 | 1.99 | 100(80℃) | 91.2%电导率保持(5 mol·L-1 NaOH,90℃,168 h) | [ | |
| 哌啶型 | PAP-TP | 超酸催化聚芳基 | 2.37 | 193(95℃) | 97%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 KOH,100℃,2000 h) | [ | |
| 吡咯型 | PyrPIB | 超酸催化聚芳基 | 1.79 | 49.08(80℃) | 64.8%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 NaOH,80℃,1050 h) | [ | |
| 螺环型 | Spiro-ionenes | 螺环-阳离子聚合物 | 4 | 120(90℃)(与聚苯并咪唑共混后) | NMR谱图无变化(1 mol·L-1 KOH,80℃,1800 h) | [ | |
| 芳香型季铵盐 | 胍型 | M-PAES-TMG | 含氟聚芳醚 | 1.03 | 36(80℃) | 63.9%电导率保持(0.5 mol·L-1 NaOH,80℃, 382 h) | [ |
| 咪唑型 | Syne-IM PPO | 聚苯醚 | 1.60 | 34(80℃) | 95%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 KOH,80℃,48 h) | [ | |
| 吡唑型 | PXm-Tn | 全交联聚芳基 | 0.91 | 111.6(80℃) | 76%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 KOH, 80℃,720 h) | [ | |
季 盐 盐 | 氨基 季 | AAEM-17 | 聚烯烃 | 0.67±0.1 | 22±1(22℃) | 81.8%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 KOH,80℃,22 d) | [ |
芳基 季 | TPQPOH | 聚醚砜 | 1.09 | 27(20℃) | 100%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 KOH,80℃,48 h) | [ | |
| 金属盐 | 二茂钴型 | H-AEM-OH | 聚烯烃 | 1.86 | 90(90℃) | 95%电导率保持(1 mol·L-1 NaOH, 1个月) | [ |
配位 金属型 | DCPD AEMs | 聚烯烃 | 1.4 | 28.6(30℃) | 7%质量损失(1 mol·L-1 NaOH,80℃,24 h) | [ |
| 13 | 王培灿, 雷青, 刘帅, 等. 电解水制氢MoS2催化剂研究与氢能技术展望[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(1): 278-290. |
| Wang P C, Lei Q, Liu S, et al. MoS2-based electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution and the prospect of hydrogen energy technology[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(1): 278-290. | |
| 14 | Lee W H, Kim Y S, Bae C. Robust hydroxide ion conducting poly(biphenyl alkylene)s for alkaline fuel cell membranes[J]. ACS Macro Letters, 2015, 4(8): 814-818. |
| 15 | You W, Noonan K J T, Coates G W. Alkaline-stable anion exchange membranes: a review of synthetic approaches[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2020, 100: 101-177. |
| 16 | Marino M G, Kreuer K D. Alkaline stability of quaternary ammonium cations for alkaline fuel cell membranes and ionic liquids[J]. ChemSusChem, 2015, 8(3): 513-523. |
| 17 | Hu J, Zhang C X, Cong J, et al. Plasma-grafted alkaline anion-exchange membranes based on polyvinyl chloride for potential application in direct alcohol fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(10): 4483-4490. |
| 18 | Ran J, Wu L, Lin X C, et al. Synthesis of soluble copolymers bearing ionic graft for alkaline anion exchange membrane[J]. RSC Advances, 2012, 2(10): 4250-4257. |
| 19 | Olsson J S, Pham T H, Jannasch P. Functionalizing polystyrene with N-alicyclic piperidine-based cations via Friedel–Crafts alkylation for highly alkali-stable anion-exchange membranes[J]. Macromolecules, 2020, 53(12):4722-4732. |
| 20 | Danks T N, Slade R C T, Varcoe J R. Comparison of PVDF- and FEP-based radiation-grafted alkaline anion-exchange membranes for use in low temperature portable DMFCs[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2002, 12(12): 3371-3373. |
| 21 | Fang J, Yang Y X, Lu X H, et al. Cross-linked, ETFE-derived and radiation grafted membranes for anion exchange membrane fuel cell applications[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(1): 594-602. |
| 22 | Willdorf-Cohen S, Mondal A N, Dekel D R, et al. Chemical stability of poly(phenylene oxide)-based ionomers in an anion exchange-membrane fuel cell environment[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(44): 22234-22239. |
| 23 | Liu M Y, Wang Z, Mei J, et al. A facile functionalized routine for the synthesis of imidazolium-based anion-exchange membrane with excellent alkaline stability[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016, 505: 138-147. |
| 1 | Varcoe J R, Atanassov P, Dekel D R, et al. Anion-exchange membranes in electrochemical energy systems[J]. Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, 7(10): 3135-3191. |
| 2 | Ran J, Wu L, Ru Y F, et al. Anion exchange membranes (AEMs) based on poly(2, 6-dimethyl-1, 4-phenylene oxide) (PPO) and its derivatives[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2015, 6(32): 5809-5826. |
| 3 | Strathmann H. Electrodialysis, a mature technology with a multitude of new applications[J]. Desalination, 2010, 264(3): 268-288. |
| 4 | Ran J, Wu L, He Y B, et al. Ion exchange membranes: new developments and applications[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 522: 267-291. |
| 5 | Strathmann H, Grabowski A, Eigenberger G. Ion-exchange membranes in the chemical process industry[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(31): 10364-10379. |
| 6 | Varcoe J R, Slade R C T. Prospects for alkaline anion-exchange membranes in low temperature fuel cells[J]. Fuel Cells, 2005, 5(2): 187-200. |
| 24 | Kim D J, Lee B N, Nam S Y. Synthesis and characterization of PEEK containing imidazole for anion exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(37): 23759-23767. |
| 25 | Jeon J Y, Park S, Han J, et al. Synthesis of aromatic anion exchange membranes by Friedel–Crafts bromoalkylation and cross-linking of polystyrene block copolymers[J]. Macromolecules, 2019, 52(5): 2139-2147. |
| 26 | Chen X L, Xiu Q W, En N H, et al. Quaternized triblock polymer anion exchange membranes with enhanced alkaline stability[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 541: 358-366. |
| 27 | Varcoe J R, Slade R C T, Lam How Yee E, et al. Poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene)-derived radiation-grafted anion-exchange membrane with properties specifically tailored for application in metal-cation-free alkaline polymer electrolyte fuel cells[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2007, 19(10): 2686-2693. |
| 28 | Zhang M, Shan C R, Liu L, et al. Facilitating anion transport in polyolefin-based anion exchange membranes via bulky side chains[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(35): 23321-23330. |
| 29 | Zhu L, Peng X, Shang S L, et al. High performance anion exchange membrane fuel cells enabled by fluoropoly(olefin) membranes[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(26): 1902059. |
| 7 | Ursua A, Gandia L M, Sanchis P. Hydrogen production from water electrolysis: current status and future trends[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100(2): 410-426. |
| 8 | Hickner M A, Ghassemi H, Kim Y S, et al. Alternative polymer systems for proton exchange membranes (PEMs)[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104(10): 4587-4612. |
| 9 | Siracusano S, Baglio V, Briguglio N, et al. An electrochemical study of a PEM stack for water electrolysis[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(2): 1939-1946. |
| 10 | Varcoe J R, Slade R C T, Lam How Yee E. An alkaline polymer electrochemical interface: a breakthrough in application of alkaline anion-exchange membranes in fuel cells[J]. Chemical Communications, 2006, (13): 1428-1429. |
| 11 | Leng Y J, Chen G, Mendoza A J, et al. Solid-state water electrolysis with an alkaline membrane[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(22): 9054-9057. |
| 12 | 万磊, 赖忆铭, 王保国. 离子交换膜界面结构对膜电极性能影响的研究进展[J]. 膜科学与技术, 2019, 39(4): 132-141, 147. |
| 30 | Noonan K J, Hugar K M, Kostalik H A, et al. Phosphonium-functionalized polyethylene: a new class of base-stable alkaline anion exchange membranes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(44): 18161-18164. |
| 31 | Kostalik H A, Clark T J, Robertson N J, et al. Solvent processable tetraalkylammonium-functionalized polyethylene for use as an alkaline anion exchange membrane[J]. Macromolecules, 2010, 43(17): 7147-7150. |
| 12 | Wan L, Lai Y M, Wang B G. Recent progress in patterning ion exchange membrane interface for membrane electrode assembly[J]. Membrane Science and Technology, 2019, 39(4): 132-141, 147. |
| 32 | Zhu T, Xu S C, Rahman A, et al. Cationic metallo-polyelectrolytes for robust alkaline anion-exchange membranes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(9): 2388-2392. |
| 33 | Zha Y P, Disabb-Miller M L, Johnson Z D, et al. Metal-cation-based anion exchange membranes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(10): 4493-4496. |
| 34 | Li Y F, Liu Y, Savage A M, et al. Polyethylene-based block copolymers for anion exchange membranes[J]. Macromolecules, 2015, 48(18): 6523-6533. |
| 35 | Gu F L, Dong H L, Li Y Y, et al. Base stable pyrrolidinium cations for alkaline anion exchange membrane applications[J]. Macromolecules, 2014, 47(19): 6740-6747. |
| 36 | Nuñez S A, Hickner M A. Quantitative 1H NMR analysis of chemical stabilities in anion-exchange membranes[J]. ACS Macro Letters, 2013, 2(1): 49-52. |
| 37 | Zhang S L, Wu C M, Xu T W, et al. Synthesis and characterizations of anion exchange organic-inorganic hybrid materials based on poly(2, 6-dimethyl-1, 4-phenylene oxide) (PPO)[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2005, 178(7): 2292-2300. |
| 38 | Xu T W, Liu Z M, Li Y, et al. Preparation and characterization of Type Ⅱ anion exchange membranes from poly(2, 6-dimethyl-1, 4-phenylene oxide) (PPO)[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2008, 320(1/2): 232-239. |
| 39 | Mohanty A D, Tignor S E, Krause J A, et al. Systematic alkaline stability study of polymer backbones for anion exchange membrane applications[J]. Macromolecules, 2016, 49(9): 3361-3372. |
| 40 | Ran J, Ding L, Yu D B, et al. A novel strategy to construct highly conductive and stabilized anionic channels by fluorocarbon grafted polymers[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 549: 631-637. |
| 41 | Dang H S, Weiber E A, Jannasch P. Poly(phenylene oxide) functionalized with quaternary ammonium groups via flexible alkyl spacers for high-performance anion exchange membranes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(10): 5280-5284. |
| 42 | Cruz A R, Zolotukhin M G, Morales S L, et al. Use of 4-piperidones in one-pot syntheses of novel, high-molecular-weight linear and virtually 100%-hyperbranched polymers[J]. Chemical Communications, 2009, (29): 4408-4410. |
| 43 | Cruz A R, Hernandez M C G, Guzmán-Gutiérrez M T, et al. Precision synthesis of narrow polydispersity, ultrahigh molecular weight linear aromatic polymers by A2 + B2 nonstoichiometric step-selective polymerization[J]. Macromolecules, 2012, 45(17): 6774-6780. |
| 44 | Chen N J, Hu C, Wang H H, et al. Poly(alkyl-terphenyl piperidinium) ionomers and membranes with an outstanding alkaline-membrane fuel-cell performance of 2.58 W·cm-2[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(14): 7710-7718. |
| 45 | Olsson J S, Pham T H, Jannasch P. Poly(arylene piperidinium) hydroxide ion exchange membranes: synthesis, alkaline stability, and conductivity[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(2): 1702758. |
| 46 | Wang J H, Zhao Y, Setzler B P, et al. Poly(aryl piperidinium) membranes and ionomers for hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4(5): 392-398. |
| 47 | Miyanishi S, Yamaguchi T. Highly durable spirobifluorene-based aromatic anion conducting polymer for a solid ionomer of alkaline fuel cells and water electrolysis cells[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(5): 2219-2224. |
| 48 | Fan J T, Willdorf-Cohen S, Schibli E M, et al. Poly(bis-arylimidazoliums) possessing high hydroxide ion exchange capacity and high alkaline stability[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 2306. |
| 49 | Wright A G, Weissbach T, Holdcroft S. Poly(phenylene) and m-terphenyl as powerful protecting groups for the preparation of stable organic hydroxides[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(15): 4818-4821. |
| 50 | Luo T, Abdu S, Wessling M. Selectivity of ion exchange membranes: a review[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 555: 429-454. |
| 51 | Merle G, Wessling M, Nijmeijer K. Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: a review[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 377(1/2): 1-35. |
| 52 | Lu W T, Zhang G, Li J, et al. Polybenzimidazole-crosslinked poly(vinylbenzyl chloride) with quaternary 1, 4-diazabicyclo (2.2.2) octane groups as high-performance anion exchange membrane for fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 296: 204-214. |
| 53 | Wang X, Li M Q, Golding B T, et al. A polytetrafluoroethylene-quaternary 1, 4-diazabicyclo-[2.2.2]-octane polysulfone composite membrane for alkaline anion exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(16): 10022-10026. |
| 54 | Wang J J, He G H, Wu X M, et al. Crosslinked poly (ether ether ketone) hydroxide exchange membranes with improved conductivity[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 459: 86-95. |
| 55 | Das G, Park B J, Yoon H H. A bionanocomposite based on 1, 4-diazabicyclo-[2.2.2]-octane cellulose nanofiber cross-linked-quaternary polysulfone as an anion conducting membrane[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(40): 15554-15564. |
| 56 | Allushi A, Pham T H, Olsson J S, et al. Ether-free polyfluorenes tethered with quinuclidinium cations as hydroxide exchange membranes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(47): 27164-27174. |
| 57 | Strasser D J, Graziano B J, Knauss D M. Base stable poly(diallylpiperidinium hydroxide) multiblock copolymers for anion exchange membranes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(20): 9627-9640. |
| 58 | Olsson J S, Pham T H, Jannasch P. Poly(N,N-diallylazacycloalkane)s for anion-exchange membranes functionalized with N-spirocyclic quaternary ammonium cations[J]. Macromolecules, 2017, 50(7): 2784-2793. |
| 59 | Zhang S, Zhu X L, Jin C H. Development of a high-performance anion exchange membrane using poly(isatin biphenylene) with flexible heterocyclic quaternary ammonium cations for alkaline fuel cells[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(12): 6883-6893. |
| 60 | Pham T H, Olsson J S, Jannasch P. N-spirocyclic quaternary ammonium ionenes for anion-exchange membranes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(8): 2888-2891. |
| 61 | Xiao L, Zhang H, Jana T, et al. Synthesis and characterization of pyridine-based polybenzimidazoles for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell applications[J]. Fuel Cells, 2005, 5(2): 287-295. |
| 62 | Li W, Fang J, Lv M, et al. Novel anion exchange membranes based on polymerizable imidazolium salt for alkaline fuel cell applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(30): 11340. |
| 63 | Lin B C, Dong H L, Li Y Y, et al. Alkaline stable C2-substituted imidazolium-based anion-exchange membranes[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2013, 25(9): 1858-1867. |
| 64 | Wang J H, Gu S, Kaspar R B, et al. Stabilizing the imidazolium cation in hydroxide-exchange membranes for fuel cells[J]. ChemSusChem, 2013, 6(11): 2079-2082. |
| 65 | Zhu Y, He Y, Ge X, et al. A benzyltetramethylimidazolium-based membrane with exceptional alkaline stability in fuel cells: role of its structure in alkaline stability[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(2):527-534 |
| 66 | Hugar K M, Kostalik H A, Coates G W. Imidazolium cations with exceptional alkaline stability: a systematic study of structure-stability relationships[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(27): 8730-8737. |
| 67 | Kim Y, Wang Y, France-Lanord A, et al. Ionic highways from covalent assembly in highly conducting and stable anion exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(45): 18152-18159. |
| 68 | Ye Y S, Stokes K K, Beyer F L, et al. Development of phosphonium-based bicarbonate anion exchange polymer membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 443: 93-99. |
| 69 | Gu S, Cai R, Luo T, et al. A soluble and highly conductive ionomer for high-performance hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(35): 6499-6502. |
| 70 | Barnes A, Du Y F, Zhang W X, et al. Phosphonium-containing block copolymer anion exchange membranes: effect of quaternization level on bulk and surface morphologies at hydrated and dehydrated states[J]. Macromolecules, 2019, 52(16): 6097-6106. |
| 71 | Tang H Y, Li D F, Li N W, et al. Anion conductive poly(2, 6-dimethyl phenylene oxide)s with clicked bulky quaternary phosphonium groups[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 558: 9-16. |
| 72 | Zhang B Z, Kaspar R B, Gu S, et al. A new alkali-stable phosphonium cation based on fundamental understanding of degradation mechanisms[J]. ChemSusChem, 2016, 9(17): 2374-2379. |
| 73 | Kwasny M T, Zhu L, Hickner M A, et al. Thermodynamics of counterion release is critical for anion exchange membrane conductivity[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(25): 7961-7969. |
| 74 | Zhu T, Sha Y, Firouzjaie H A, et al. Rational synthesis of metallo-cations toward redox-and alkaline-stable metallo-polyelectrolytes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(2): 1083-1089. |
| 75 | Kim D S, Labouriau A, Guiver M D, et al. Guanidinium-functionalized anion exchange polymer electrolytes via activated fluorophenyl-amine reaction[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2011, 23(17): 3795-3797. |
| [1] | Congqi HUANG, Yimei WU, Jianye CHEN, Shuangquan SHAO. Simulation study of thermal management system of alkaline water electrolysis device for hydrogen production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. |
| [2] | Yitong LI, Hang GUO, Hao CHEN, Fang YE. Study on operating conditions of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform catalyst distributions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [3] | Laiming LUO, Jin ZHANG, Zhibin GUO, Haining WANG, Shanfu LU, Yan XIANG. Simulation and experiment of high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells stack in the 1—5 kW range [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1724-1734. |
| [4] | Zhiguang QIAN, Yue FAN, Shixue WANG, Like YUE, Jinshan WANG, Yu ZHU. Effect of purging conditions on the impedance relaxation phenomenon and low temperature start-up of PEMFC [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1286-1293. |
| [5] | Xiang GUO, Jinshuo QIAO, Zhenhua WANG, Wang SUN, Kening SUN. Progress of structure for carbon-fueled solid oxide fuel cells [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 290-302. |
| [6] | Jiawang YONG, Qianqian ZHAO, Nenglian FENG. Fault diagnosis of proton exchange membrane fuel cell based on nonlinear dynamic model [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 3983-3993. |
| [7] | Wanchen ZHANG, Xiaoyang CHEN, Qiuqiu LYU, Qin ZHONG, Tenglong ZHU. Performance and durability of cobalt doped SrTi0.3Fe0.7O3-δ anode SOFC fueled with by-product gas from chemical industry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4079-4086. |
| [8] | Jian SHAO, Junzong FENG, Fengqi LIU, Yonggang JIANG, Liangjun LI, Jian FENG. Research progress on structural modulation and functionalized preparation of phenolic resin-based carbon microspheres [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 3787-3801. |
| [9] | Huihuang FANG, Jinxing CHENG, Yu LUO, Chongqi CHEN, Chen ZHOU, Lilong JIANG. Recent progress on ammonia oxidation catalysts at anode and their performances in low-temperature direct ammonia alkaline exchange membrane fuel cells [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 3802-3814. |
| [10] | Tong ZHANG, Yang YANG, Dingding YE, Rong CHEN, Xun ZHU, Qiang LIAO. Effect of catalyst distribution on the performance characteristics of microfluidic fuel cell with flow-through anode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4156-4162. |
| [11] | Chengyi AI, Jinshuo QIAO, Zhenhuan WANG, Wang SUN, Kening SUN. Investigation on PrBaFe2O6-δ anode material with in-situ FeNi nanoparticle in direct carbon solid oxide fuel cell [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3708-3719. |
| [12] | Lin WEI, Jian GUO, Zihao LIAO, Dafalla Ahmed Mohmed, Fangming JIANG. Influence of air flow rate on the performance of air cooled hydrogen fuel cell stack [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3222-3231. |
| [13] | Hongrui ZHANG, Tian ZHANG, Xizi LONG, Xianning LI. Degradation characteristics of Cu-EDTA by coupling of photocatalysis and microbial fuel cell [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(5): 2149-2157. |
| [14] | Wenhuai LI, Wei ZHOU. Analysis of influencing factors and design strategies of high oxygen ion conductivity perovskite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1455-1471. |
| [15] | Keqing ZHENG, Ya SUN, Yangtian YAN, Li LI, Jun YANG. Numerical simulation of novel SOFC interconnector with thermoelectric co-enhancement [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(12): 5572-5580. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||