CIESC Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (9): 4768-4774.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210125
• Separation engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yijing WEN1( ),Bo ZHANG1,Xiaofei CHEN1,Siyang ZHAO1,Xin ZHOU1(
),Bo ZHANG1,Xiaofei CHEN1,Siyang ZHAO1,Xin ZHOU1( ),Yan HUANG1,2(
),Yan HUANG1,2( ),Zhong LI1
),Zhong LI1
Received:2021-01-19
Revised:2021-03-24
Online:2021-09-05
Published:2021-09-05
Contact:
Xin ZHOU,Yan HUANG
温怡静1( ),张博1,陈晓霏1,赵思洋1,周欣1(
),张博1,陈晓霏1,赵思洋1,周欣1( ),黄艳1,2(
),黄艳1,2( ),李忠1
),李忠1
通讯作者:
周欣,黄艳
作者简介:温怡静(1998—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Yijing WEN, Bo ZHANG, Xiaofei CHEN, Siyang ZHAO, Xin ZHOU, Yan HUANG, Zhong LI. Selectivity reversion mechanism of porous carbon for ethane-ethylene separation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(9): 4768-4774.
温怡静, 张博, 陈晓霏, 赵思洋, 周欣, 黄艳, 李忠. 多孔炭吸附剂的乙烯-乙烷选择性反转机制[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4768-4774.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
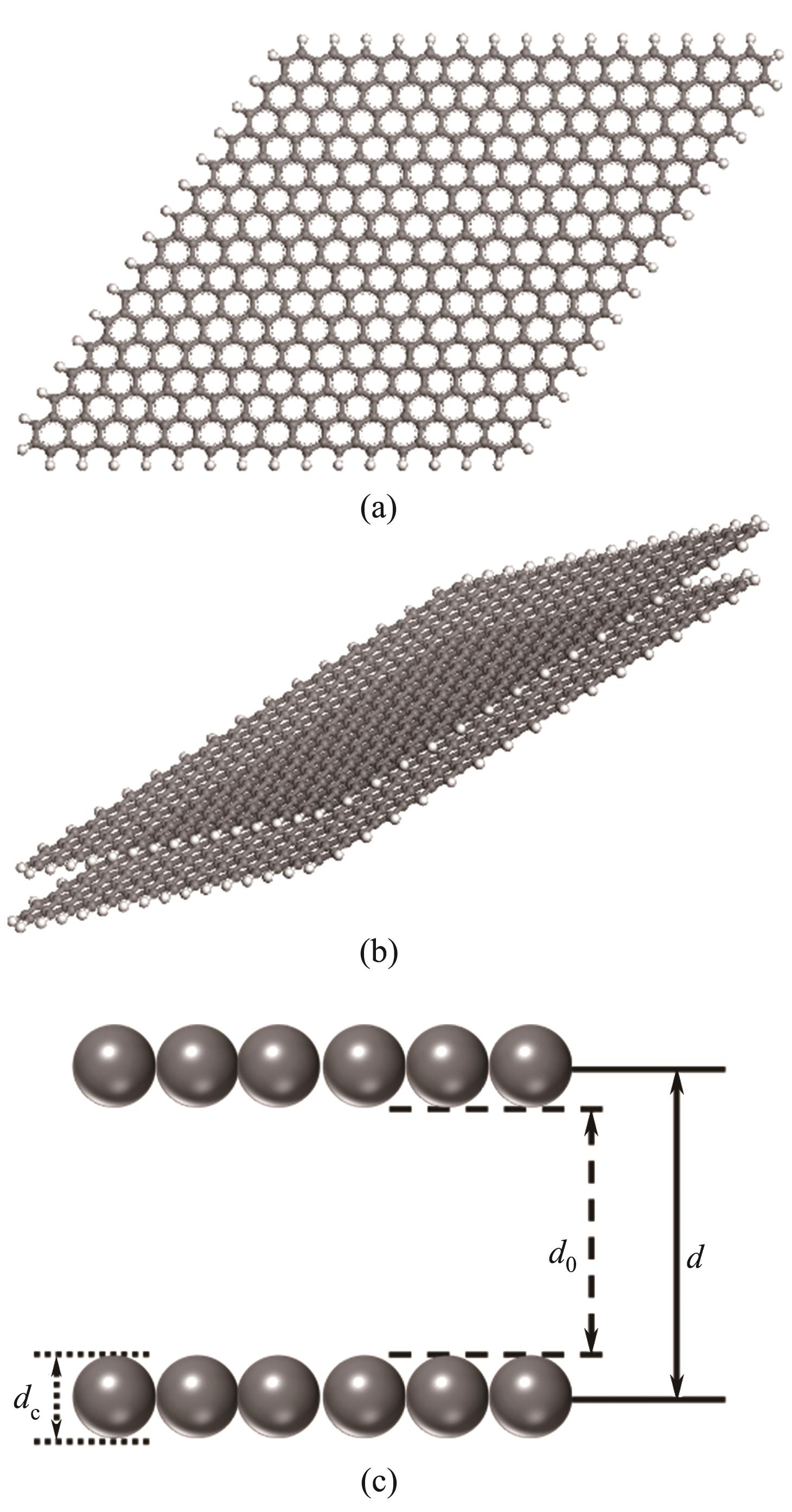
Fig.1 Molecular models of graphitic carbon layer C510H62(a); Slit pore C510H62×2 (b); Schematic diagram of aperture (Gray and white balls represent carbon and hydrogen atoms, respectively)(c)
| 吸附质 | 动力学直径[ | 最小分子笼尺寸 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x/? | y/? | z/? | ||
| 乙烯 | 4.16 | 5.09 | 4.35 | 3.98 |
| 乙烷 | 4.44 | 5.11 | 4.34 | 4.58 |
Table 1 Kinetic diameter and molecular cage size of ethylene and ethane
| 吸附质 | 动力学直径[ | 最小分子笼尺寸 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x/? | y/? | z/? | ||
| 乙烯 | 4.16 | 5.09 | 4.35 | 3.98 |
| 乙烷 | 4.44 | 5.11 | 4.34 | 4.58 |

Fig.3 Exothermic adsorption enthalpies of ethylene, ethane on the surface of graphitic carbon(a); Adsorption configuration of ethylene(b) and ethane (c) on the surface of graphitic carbon
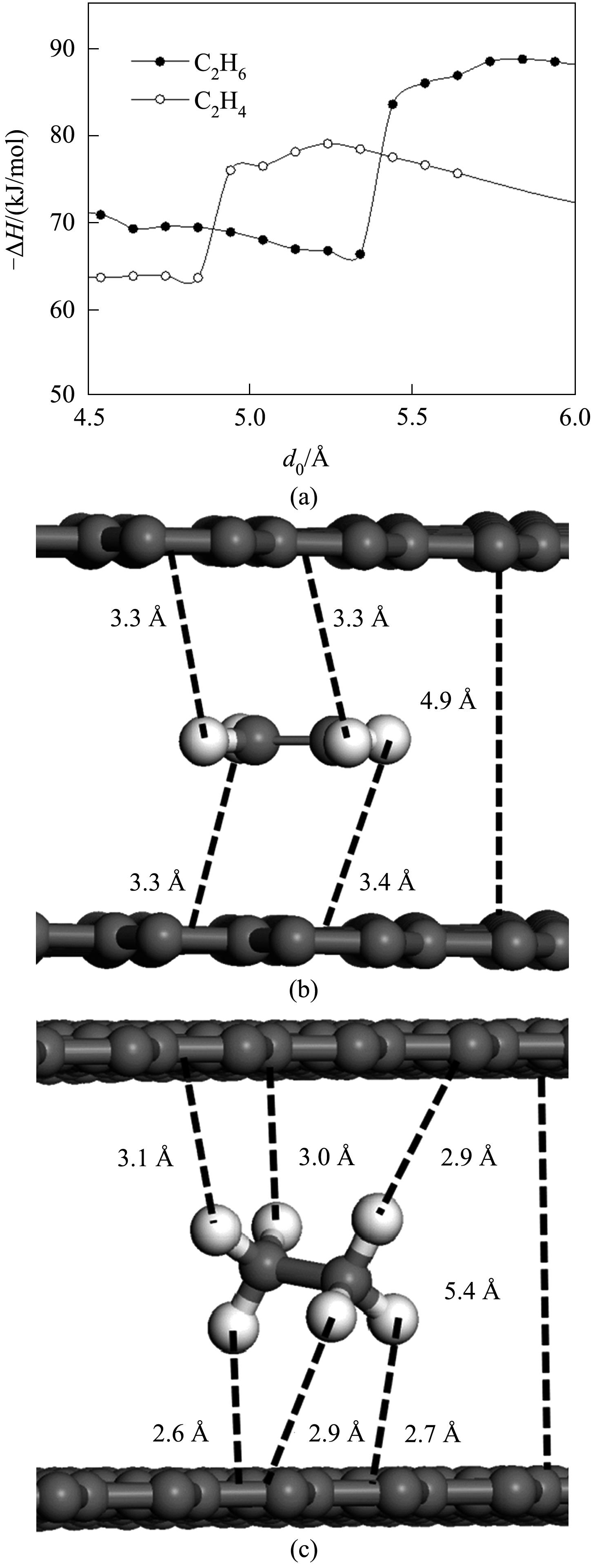
Fig.4 Exothermic adsorption enthalpies of ethylene and ethane changes with the size of slit pore(a); The adsorption configuration of ethylene (b) and ethane(c) in the pore when selectivity reversion occurs
| 1 | Lin R B, Wu H, Li L B, et al. Boosting ethane/ethylene separation within isoreticular ultramicroporous metal-organic frameworks[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(40): 12940-12946. |
| 2 | Yang L F, Cui X L, Ding Q, et al. Polycatenated molecular cage-based propane trap for propylene purification with recorded selectivity[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(2): 2525-2530. |
| 3 | Ren T, Patel M, Blok K. Olefins from conventional and heavy feedstocks: energy use in steam cracking and alternative processes[J]. Energy, 2006, 31(4): 425-451. |
| 4 | Sholl D S, Lively R P. Seven chemical separations to change the world[J]. Nature, 2016, 532(7600): 435-437. |
| 5 | 陈润道, 郑芳, 郭立东, 等. 稀有气体Xe/Kr吸附分离研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 14-26. |
| Chen R D, Zheng F, Guo L D, et al. Advancements in adsorption separation of Xe/Kr noble gases[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 14-26. | |
| 6 | 陈邦林. 反转吸附选择性可助金属有机框架纯化烯烃[J]. 化学进展, 2017, 29(8): 811-813. |
| Chen B L. Reversing adsorption selectivity helps MOFs purifying alkenes[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2017, 29(8): 811-813. | |
| 7 | Li L B, Lin R B, Krishna R, et al. Ethane/ethylene separation in a metal-organic framework with iron-peroxo sites[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6413): 443-446. |
| 8 | 刘普旭, 贺朝辉, 李立博, 等. 高稳定双金属MOF材料用于低浓度乙烷的高效分离[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(9): 4211-4218. |
| Liu P X, He C H, Li L B, et al. Stable mixed metal-organic framework for efficient C2H6/C2H4 separation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(9): 4211-4218. | |
| 9 | Tang Y N, Wang S, Zhou X, et al. Room temperature synthesis of Cu(Qc)2 and its application for ethane capture from light hydrocarbons[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 213: 115355. |
| 10 | Wang S, Zhang Y F, Tang Y N, et al. Propane-selective design of zirconium-based MOFs for propylene purification[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 219: 115604. |
| 11 | Solanki V A, Borah B. In-silico identification of adsorbent for separation of ethane/ethylene mixture[J]. Journal of Molecular Modeling, 2020, 26(12): 1-16. |
| 12 | He C H, Wang Y, Chen Y, et al. Microregulation of pore channels in covalent-organic frameworks used for the selective and efficient separation of ethane[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(47): 52819-52825. |
| 13 | Ding Q, Zhang Z, Yu C, et al. Exploiting equilibrium-kinetic synergetic effect for separation of ethylene and ethane in a microporous metal-organic framework[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(15): eaaz4322. |
| 14 | Wang X J, Wu Y, Zhou X, et al. Novel C-PDA adsorbents with high uptake and preferential adsorption of ethane over ethylene[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 155: 338-347. |
| 15 | Ma C, Wang X J, Wang X, et al. Novel glucose-based adsorbents (Glc-As) with preferential adsorption of ethane over ethylene and high capacity[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 172: 612-621. |
| 16 | Liang W W, Wu Y, Xiao H Y, et al. Ethane-selective carbon composites CPDA@A-ACs with high uptake and its enhanced ethane/ethylene adsorption selectivity[J]. AIChE Journal, 2018, 64(9): 3390-3399. |
| 17 | Liang W W, Xiao H Y, Lv D, et al. Novel asphalt-based carbon adsorbents with super-high adsorption capacity and excellent selectivity for separation for light hydrocarbons[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 190: 60-67. |
| 18 | Liang W W, Liu Z W, Peng J J, et al. Enhanced CO2 adsorption and CO2/N2/CH4 selectivity of novel carbon composites CPDA@A-Cs[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(1): 493-502. |
| 19 | Saha D, Toof B, Krishna R, et al. Separation of ethane-ethylene and propane-propylene by Ag(Ⅰ) doped and sulfurized microporous carbon[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 299: 110099. |
| 20 | Wang X J, Wu Y, Peng J J, et al. Novel glucosamine-based carbon adsorbents with high capacity and its enhanced mechanism of preferential adsorption of C2H6 over C2H4[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 358: 1114-1125. |
| 21 | Rappe A K, Casewit C J, Colwell K S, et al. UFF, a full periodic table force field for molecular mechanics and molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1992, 114(25): 10024-10035. |
| 22 | Rappe A K, Goddard W A. Charge equilibration for molecular dynamics simulations[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1991, 95(8): 3358-3363. |
| 23 | Adamo C, Barone V. Toward reliable density functional methods without adjustable parameters: the PBE0 model[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1999, 110(13): 6158-6170. |
| 24 | Weigend F, Ahlrichs R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: design and assessment of accuracy[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2005, 7(18): 3297-3305. |
| 25 | Mehio N, Dai S, Jiang D E. Quantum mechanical basis for kinetic diameters of small gaseous molecules[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2014, 118(6): 1150-1154. |
| 26 | Lu T, Chen F W. Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2012, 33(5): 580-592. |
| 27 | Lu T, Chen F W. Quantitative analysis of molecular surface based on improved Marching Tetrahedra algorithm[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, 2012, 38: 314-323. |
| 28 | Metropolis N, Rosenbluth A W, Rosenbluth M N, et al. Equation of state calculations by fast computing machines[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1953, 21(6): 1087-1092. |
| 29 | Tang R L, Dai Q B, Liang W W, et al. Synthesis of novel particle rice-based carbon materials and its excellent CH4/N2 adsorption selectivity for methane enrichment from low-rank natural gas[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 384: 123388. |
| 30 | Breck D W. Zeolite Molecular Sieves[M]. New York: Wiley, 1974: 634. |
| 31 | Li J R, Kuppler R J, Zhou H C. Selective gas adsorption and separation in metal-organic frameworks[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(5): 1477. |
| 32 | Zhang Y F, Xiao H Y, Zhou X, et al. Selective adsorption performances of UiO-67 for separation of light hydrocarbons C1, C2, and C3[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(30): 8689-8696. |
| 33 | Bao Z B, Alnemrat S, Yu L, et al. Adsorption of ethane, ethylene, propane, and propylene on a magnesium-based metal-organic framework[J]. Langmuir, 2011, 27(22): 13554-13562. |
| 34 | Bachman J E, Kapelewski M T, Reed D A, et al. M2(m-dobdc) (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) metal-organic frameworks as highly selective, high-capacity adsorbents for olefin/paraffin separations[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(43): 15363-15370. |
| [1] | Yaxin ZHAO, Xueqin ZHANG, Rongzhu WANG, Guo SUN, Shanjing YAO, Dongqiang LIN. Removal of monoclonal antibody aggregates with ion exchange chromatography by flow-through mode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3879-3887. |
| [2] | Minghao SONG, Fei ZHAO, Shuqing LIU, Guoxuan LI, Sheng YANG, Zhigang LEI. Multi-scale simulation and study of volatile phenols removal from simulated oil by ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3654-3664. |
| [3] | Jianbo HU, Hongchao LIU, Qi HU, Meiying HUANG, Xianyu SONG, Shuangliang ZHAO. Molecular dynamics simulation insight into translocation behavior of organic cage across the cellular membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3756-3765. |
| [4] | Jiajia ZHAO, Shixiang TIAN, Peng LI, Honggao XIE. Microscopic mechanism of SiO2-H2O nanofluids to enhance the wettability of coal dust [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3931-3945. |
| [5] | Shuang LIU, Linzhou ZHANG, Zhiming XU, Suoqi ZHAO. Study on molecular level composition correlation of viscosity of residual oil and its components [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3226-3241. |
| [6] | Yan GAO, Peng WU, Chao SHANG, Zejun HU, Xiaodong CHEN. Preparation of magnetic agarose microspheres based on a two-fluid nozzle and their protein adsorption properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3457-3471. |
| [7] | Linzheng WANG, Yubing LU, Ruizhi ZHANG, Yonghao LUO. Analysis on thermal oxidation characteristics of VOCs based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [8] | Lei XING, Chunyu MIAO, Minghu JIANG, Lixin ZHAO, Xinya LI. Optimal design and performance analysis of downhole micro gas-liquid hydrocyclone [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3394-3406. |
| [9] | Jiayi ZHANG, Jiali HE, Jiangpeng XIE, Jian WANG, Yu ZHAO, Dongqiang ZHANG. Research progress of pervaporation technology for N-methylpyrrolidone recovery in lithium battery production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3203-3215. |
| [10] | Bingchun SHENG, Jianguo YU, Sen LIN. Study on lithium resource separation from underground brine with high concentration of sodium by aluminum-based lithium adsorbent [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3375-3385. |
| [11] | Ruihang ZHANG, Pan CAO, Feng YANG, Kun LI, Peng XIAO, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Changyu SUN, Guangjin CHEN. Analysis of key parameters affecting product purity of natural gas ethane recovery process via ZIF-8 nanofluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [12] | Ming DONG, Jinliang XU, Guanglin LIU. Molecular dynamics study on heterogeneous characteristics of supercritical water [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2836-2847. |
| [13] | Zhaolun WEN, Peirui LI, Zhonglin ZHANG, Xiao DU, Qiwang HOU, Yegang LIU, Xiaogang HAO, Guoqing GUAN. Design and optimization of cryogenic air separation process with dividing wall column based on self-heat regeneration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2988-2998. |
| [14] | Jie WANG, Xiaolin QIU, Ye ZHAO, Xinyang LIU, Zhongqiang HAN, Yong XU, Wenhan JIANG. Preparation and properties of polyelectrolyte electrostatic deposition modified PHBV antioxidant films [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [15] | Ji CHEN, Ze HONG, Zhao LEI, Qiang LING, Zhigang ZHAO, Chenhui PENG, Ping CUI. Study on coke dissolution loss reaction and its mechanism based on molecular dynamics simulations [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2935-2946. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||