CIESC Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (S1): 398-405.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210441
• Catalysis, kinetics and reactors • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Xiaobing1,2( ),LI Jiajia1,2,LI Yining1,YANG Hongyue1,2,LI Xiaosong2,LIU Jinglin2
),LI Jiajia1,2,LI Yining1,YANG Hongyue1,2,LI Xiaosong2,LIU Jinglin2
Received:2021-04-06
Revised:2021-04-20
Online:2021-06-20
Published:2021-06-20
Contact:
ZHU Xiaobing
朱晓兵1,2( ),李佳佳1,2,李怡宁1,杨洪月1,2,李小松2,刘景林2
),李佳佳1,2,李怡宁1,杨洪月1,2,李小松2,刘景林2
通讯作者:
朱晓兵
作者简介:朱晓兵(1977—),男,博士,副教授,基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHU Xiaobing, LI Jiajia, LI Yining, YANG Hongyue, LI Xiaosong, LIU Jinglin. Oxygen evolution reaction over manganese oxides and the electrode-solution interface[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(S1): 398-405.
朱晓兵, 李佳佳, 李怡宁, 杨洪月, 李小松, 刘景林. 氧化锰电催化析氧反应及其电极界面特性[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(S1): 398-405.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig.1 Oxygen evolution over MnOx (pM, cM)[I/C=1, 231 μg/cm2, with double layer coating, 1 mol/L KOH, t0,x, is =(0.659 s, 63.8 μA) for pM, (2.749 s, 65.6 μA) for cM]

Fig.2 Oxygen evolution over MnOx (pM, cM) [I/C=4, 693 μg/cm2, with double layer coating, t0,x, is =(7.97 s, 4.86 μA) for pM, (6.72 s, 32.7 μA) for cM]

Fig.3 Oxygen evolution over MnOx (cM), TiO2 (cT)[I/C=0.2, 231 μg/cm2, I/C=0.3, 693 μgcat/cm2 with single layer coating, with t0,x,is=(8.84 s, 13.5 μA) for cM, (2.02 s, 1.5 μA) for cT, respectively. The scan rate for cT is 50 mV/s]

Fig.4 Oxygen evolution over MnOx (pM) at various I/C=1, 2, 4, loading of 231 μg/cm2, with double layer coating, with t0,x, is =(8.4 s, 1.86 μA) for I/C=1, (9.8s, 1.26 μA) for I/C=2, (7.37 s, 3.29 μA) for I/C=4
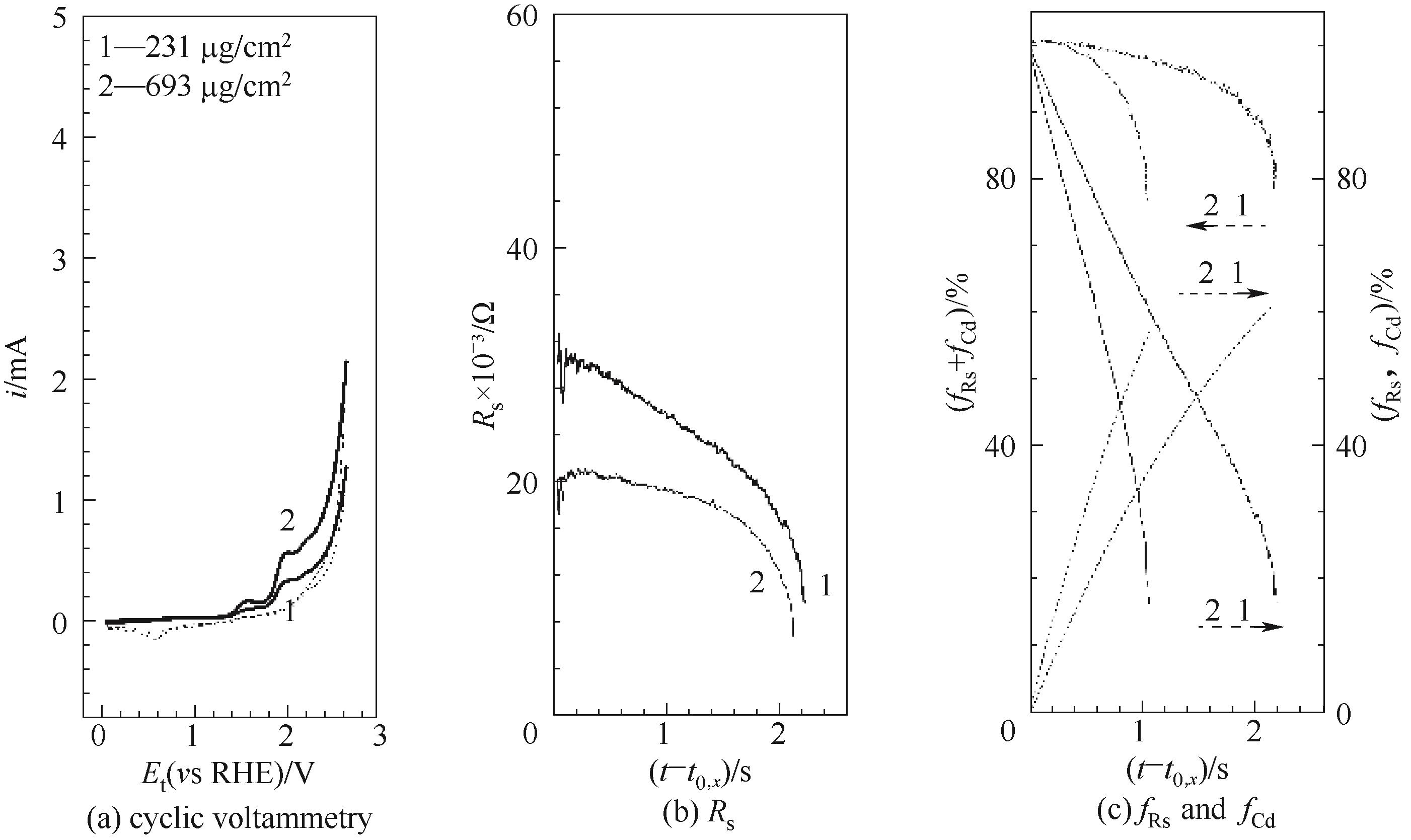
Fig.5 Oxygen evolution over MnOx (pM) at various loadings=231, 693 μg/cm2, at I/C=4, with double layer coating, t0,x, is =(7.37 s, 3.29 μA) for 231 μg/cm2, (7.97 s, 4.86 μA) for 693 μg/cm2; Curve 2, the same as curve 1 in Fig.2
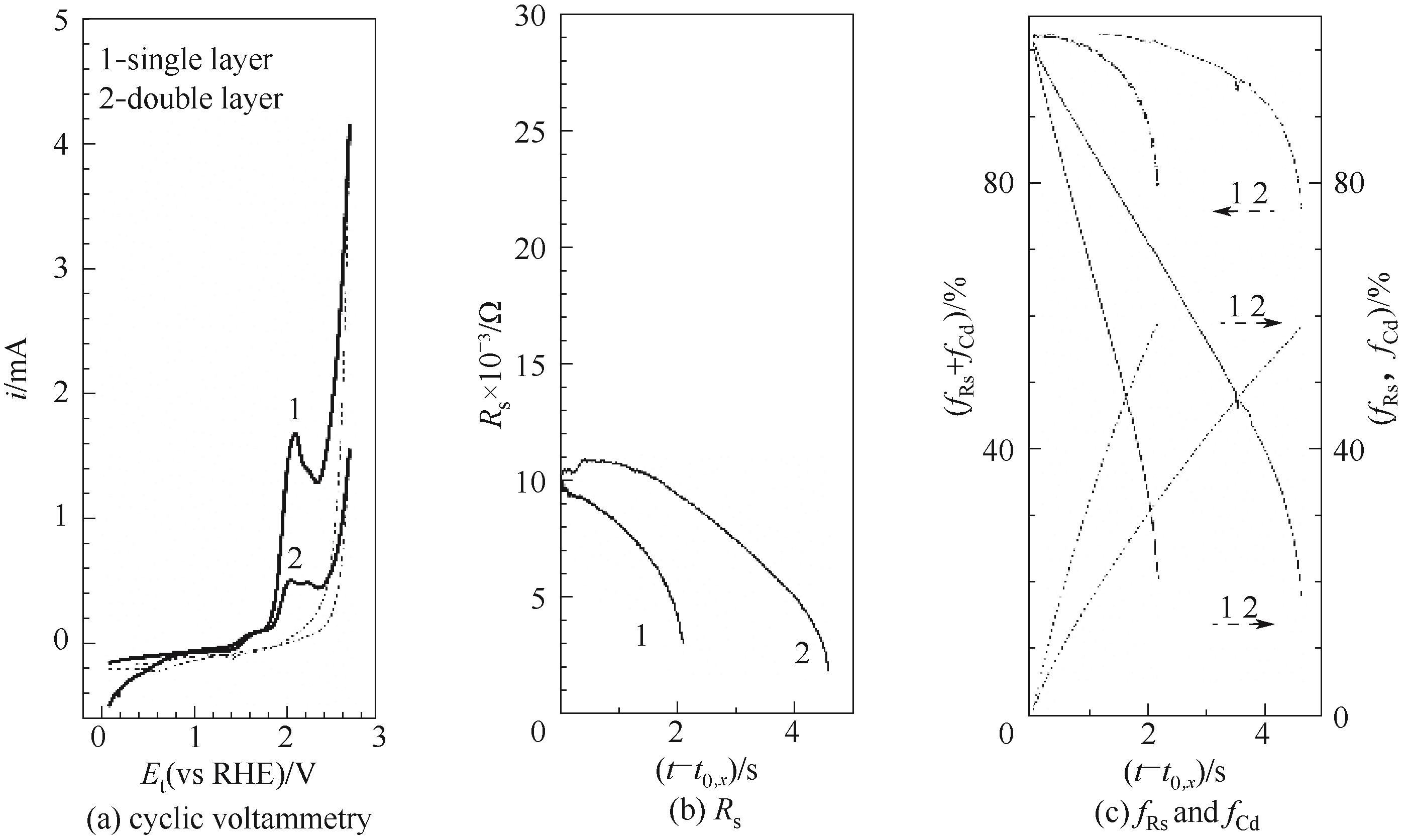
Fig.6 Oxygen evolution over MnOx (cM) withsingle layer or double layer coating, at I/C=0.2, 231 μg/cm2, t0,x, is =(8.84 s, 13.5 μA) for single layer, (7.43 s, 58.2 μA) for double layer; Curve 1, the same as curve 2 in Fig. 3
| Catalyst | Onset potential /V | b①/ (mV/dec) | Starting Tafel (E, i)②/(V, mA) | i③/ mA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pM | 0.85 | 140 | 0.90 | 0.17 | 4.97 |
| cM | 1.03 | 302 | 1.08 | 0.15 | 0.37 |
Table 1 Electrode parameters of MnOx (pM, cM)(sourced from Fig.1(a))
| Catalyst | Onset potential /V | b①/ (mV/dec) | Starting Tafel (E, i)②/(V, mA) | i③/ mA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pM | 0.85 | 140 | 0.90 | 0.17 | 4.97 |
| cM | 1.03 | 302 | 1.08 | 0.15 | 0.37 |
| 1 | Rosen M A, Koohi-Fayegh S. The prospects for hydrogen as an energy carrier: an overview of hydrogen energy and hydrogen energy systems[J]. Energy, Ecology and Environment, 2016, 1(1): 10-29. |
| 2 | Chi J, Yu H M. Water electrolysis based on renewable energy for hydrogen production[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2018, 39(3): 390-394. |
| 3 | Guo Y J, Li G D, Zhou J B, et al. Comparison between hydrogen production by alkaline water electrolysis and hydrogen production by PEM electrolysis[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2019, 371: 042022. |
| 4 | Kim J S, Kim B, Kim H, et al. Recent progress on multimetal oxide catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(11): 1702774. |
| 5 | Millet P, Mbemba N, Grigoriev S A, et al. Electrochemical performances of PEM water electrolysis cells and perspectives[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(6): 4134-4142. |
| 6 | Suen N T, Hung S F, Quan Q, et al. Electrocatalysis for the oxygen evolution reaction: recent development and future perspectives[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(2): 337-365. |
| 7 | Shi Z P, Wang X, Ge J J, et al. Fundamental understanding of the acidic oxygen evolution reaction: mechanism study and state-of-the-art catalysts[J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(25): 13249-13275. |
| 8 | Sun W, Zhou Z H, Zaman W Q, et al. Rational manipulation of IrO2 lattice strain on α-MnO2 nanorods as a highly efficient water-splitting catalyst[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(48): 41855-41862. |
| 9 | Browne M P, Nolan H, Duesberg G S, et al. Low-overpotential high-activity mixed manganese and ruthenium oxide electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline media[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(4): 2408-2415. |
| 10 | Browne M P, Nolan H, Twamley B, et al. Thermally prepared Mn2O3/RuO2/Ru thin films as highly active catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline media[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2016, 3(11): 1847-1855. |
| 11 | Oakton E, Lebedev D, Povia M, et al. IrO2-TiO2: a high-surface-area, active, and stable electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(4): 2346-2352. |
| 12 | Hu W, Chen S L, Xia Q H. IrO2/Nb-TiO2 electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction in acidic medium[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(13): 6967-6976. |
| 13 | Mazúr P, Polonský J, Paidar M, et al. Non-conductive TiO2 as the anode catalyst support for PEM water electrolysis[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(17): 12081-12088. |
| 14 | Etzi Coller Pascuzzi M, Goryachev A, Hofmann J P, et al. Mn promotion of rutile TiO2-RuO2 anodes for water oxidation in acidic media[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 261: 118225. |
| 15 | Tolstoy V P, Vladimirova N I, Gulina L B. Formation of ordered honeycomb-like structures of manganese oxide 2D nanocrystals with the birnessite-like structure and their electrocatalytic properties during oxygen evolution reaction upon water splitting in an alkaline medium[J]. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(26): 22203-22208. |
| 16 | Chen S, Huang H, Jiang P, et al. Mn-doped RuO2 nanocrystals as highly active electrocatalysts for enhanced oxygen evolution in acidic media[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(2): 1152-1160. |
| 17 | Ma Z, Zhang Y, Liu S Z, et al. Reaction mechanism for oxygen evolution on RuO2, IrO2, and RuO2@IrO2 core-shell nanocatalysts[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 819: 296-305. |
| 18 | Ferreira K N, Iverson T M, Maghlaoui K, et al. Architecture of the photosynthetic oxygen-evolving center[J]. Science, 2004, 303(5665): 1831-1838. |
| 19 | Zhang S Y, Li X S, Liu J L, et al. Plasmochemical approach to template-free synthesis of highly crystalline mesoporous TiO2 within milliseconds[J]. ChemNanoMat, 2019, 5(4): 403-406. |
| 20 | Lian H Y, Liu J L, Li X S, et al. Plasma chain catalytic reforming of methanol for on-board hydrogen production[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 369: 245-252. |
| 21 | Li K, Liu J L, Li X S, et al. Warm plasma catalytic reforming of biogas in a heat-insulated reactor: dramatic energy efficiency and catalyst auto-reduction[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 288: 671-679. |
| 22 | Zhu B, Li X S, Liu J L, et al. In-situ regeneration of Au nanocatalysts by atmospheric-pressure air plasma: significant contribution of water vapor[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 179: 69-77. |
| 23 | Lee S J, Pyun S I, Lee S K, et al. Fundamentals of rotating disc and ring-disc electrode techniques and their applications to study of the oxygen reduction mechanism at Pt/C electrode for fuel cells[J]. Israel Journal of Chemistry, 2008, 48(3/4): 215-228. |
| 24 | Lopez-Haro M, Guétaz L, Printemps T, et al. Three-dimensional analysis of Nafion layers in fuel cell electrodes[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 5229. |
| 25 | Li G F, Yang D L, Abel Chuang P Y. Defining nafion ionomer roles for enhancing alkaline oxygen evolution electrocatalysis[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(12): 11688-11698. |
| 26 | Zhang X Y, Ding Y H. Thickness-dependent structural and transport behaviors in the platinum-Nafion interface: a molecular dynamics investigation[J]. RSC Adv., 2014, 4(83): 44214-44222. |
| 27 | Weber A Z, Newman J. Modeling transport in polymer-electrolyte fuel cells[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104(10): 4679-4726. |
| 28 | Bard A J, Faulkner L R. Electrochemical Methods : Fundamentals And Applications [M]. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley, 2001. |
| 29 | Zhu X, Li J, Liu M, et al. Mesoporous TiO2 electrocatalysts synthesized by gliding arc plasma for oxygen evolution reaction [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2021(submitted). |
| 30 | Boddy P J. Oxygen evolution on semiconducting TiO2[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1968, 115(2): 199. |
| 31 | Li A L, Ooka H, Bonnet N, et al. Stable potential windows for long-term electrocatalysis by manganese oxides under acidic conditions[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(15): 5054-5058. |
| [1] | Xin YANG, Xiao PENG, Kairu XUE, Mengwei SU, Yan WU. Preparation of molecularly imprinted-TiO2 and its properties of photoelectrocatalytic degradation of solubilized PHE [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3564-3571. |
| [2] | Juan ZHAO, Mengcheng WU, Jinglei LEI, Lingjie LI. One-step hydrothermal method toward preparation of Ni3S2@Mo2S3 high-efficient catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction in water electrolysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1575-1584. |
| [3] | Yuxian XIE, Tao LIU, Sheng SU, Lijun LIU, Yuxiu ZHONG, Zhiwei MA, Kai XU, Yi WANG, Song HU, Jun XIANG. Influence of oxygen content in industrial kiln flue gas on NH3-SCR denitration reaction of vanadium-titanium catalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4410-4418. |
| [4] | Yuting SHI, Lin HUANGFU, Changming LI, Yue WANG, Shiqiu GAO, Xiaoguang SAN, Zhennan HAN, Jian YU. Preparation and pilot-scale test of V2O5-MoO3/TiO2 catalytic filter bag [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(11): 5598-5606. |
| [5] | Jiahuan MA, Weiwei YANG, Yu BAI, Kening SUN. Research progress of two-dimensional metal organic frameworks and their derivatives for electrocatalytic water splitting [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(9): 4006-4030. |
| [6] | Ling ZHANG, Hongmei CHEN, Zidong WEI. Recent advance in transition metal oxide-based materials for oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(9): 3876-3904. |
| [7] | Wenjun LIANG, Yuxue ZHU, Xiujuan SHI, Huipin SUN, Sida REN. Effect of Ce doping on catalytic chlorobenzene performance of Ru/TiO2 catalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(8): 3585-3593. |
| [8] | Yanqing XU, Wenfei LI, Mengyao WU, Jiangnan SHEN. Preparation of self-assembled graphene oxide / nano TiO2 composite nanofiltration membrane for inkjet printing dye [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(3): 1352-1361. |
| [9] | Na WU, Yihui DONG, Xiaoyan JI, Chang an HUANGFU, Xiaohua LU. Interaction between proteins and roughness-regulated TiO2 nanotube arrays [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(2): 831-842. |
| [10] | YUAN Hefeng,MA Zizai,WANG Shumin,LI Jinping,WANG Xiaoguang. Engineering oxygen vacancy-rich Co3O4 nanowire as high-efficiency and durable bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall alkaline water splitting [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(12): 5831-5841. |
| [11] | Hailing GAO,Bin XU,Yuexiang GAO,Yueming ZHU,Songhe ZHANG,Yimin ZHANG. Removal of ammonium ions in wastewater by electrosorption with TiO2 modified graphene electrode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(11): 5309-5319. |
| [12] | Yao WANG,Yiyun TANG. Advances in single-atom catalysts for oxygen electrodes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(10): 4409-4428. |
| [13] | Xiangyang LI, Yang LI, Lijun JIN, He YANG, Dechao WANG, Haoquan HU. Removal of Hg0 from simulated flue gas by MnOx modified activated carbon [J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(8): 3078-3085. |
| [14] | Zishuai WANG,Yaoqiang WANG,Gang XIAO,Haijia SU. Photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) by magnetic nanomaterial Fe3O4@TiO2 under visible light [J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(10): 4062-4071. |
| [15] | GENG Lili, YANG Kaixu, ZHANG Nuowei, CHEN Binghui. Synergetic effect of Ru and Cu on catalytic wet oxidation of ammonia-wastewater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(9): 3869-3878. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||