CIESC Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (7): 3212-3221.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220084
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ping OUYANG( ),Rui ZHANG,Jian ZHOU,Haiyan LIU,Zhichang LIU,Chunming XU,Xianghai MENG(
),Rui ZHANG,Jian ZHOU,Haiyan LIU,Zhichang LIU,Chunming XU,Xianghai MENG( )
)
Received:2022-01-14
Revised:2022-03-27
Online:2022-08-01
Published:2022-07-05
Contact:
Xianghai MENG
通讯作者:
孟祥海
作者简介:欧阳萍(1992—),女,博士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Ping OUYANG, Rui ZHANG, Jian ZHOU, Haiyan LIU, Zhichang LIU, Chunming XU, Xianghai MENG. Electrochemical behavior and copper electrodeposition mechanism of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3212-3221.
欧阳萍, 张睿, 周剑, 刘海燕, 刘植昌, 徐春明, 孟祥海. 铜铝双金属复合离子液体的电化学行为及电沉积铜机理[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3212-3221.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
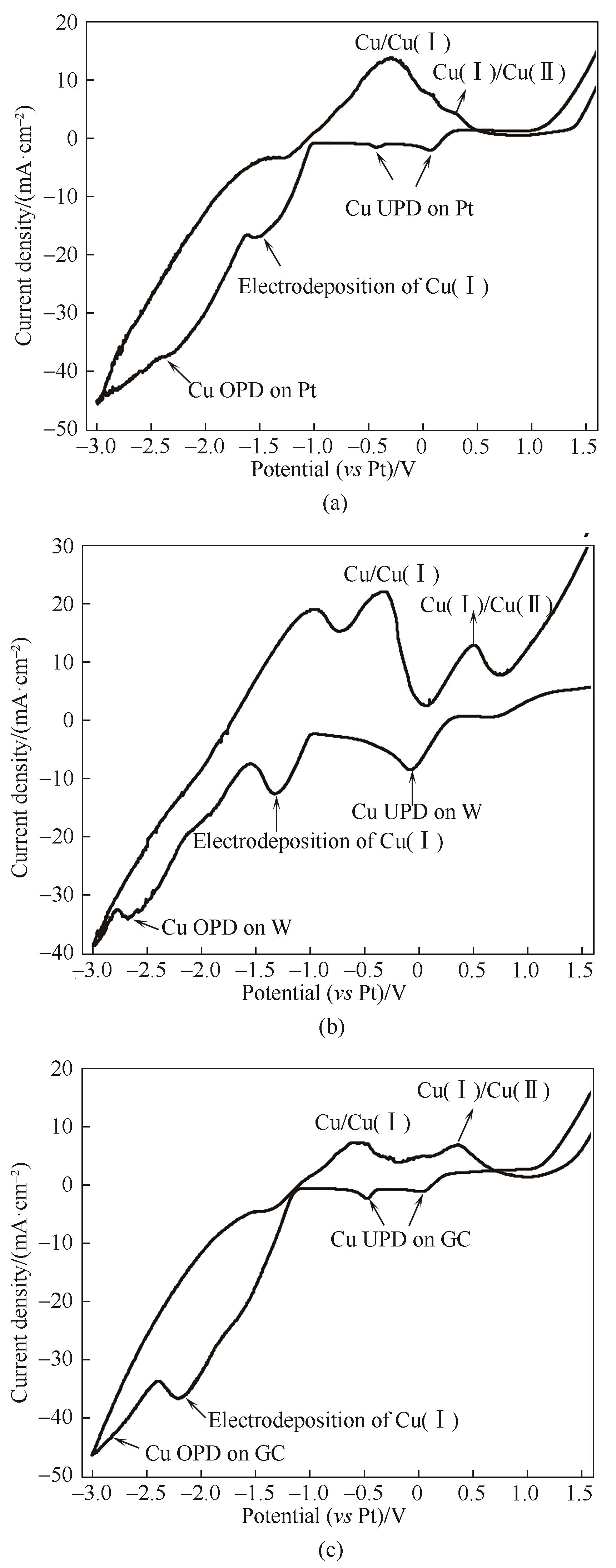
Fig.1 Cyclic voltammograms of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid on Pt electrode (a), W electrode (b) and glass carbon electrode (c) with the scanning rate of 100 mV?s-1
| Electrode | Cu UPD/V | Electrodeposition of Cu(Ⅰ)/V | Cu→ Cu(Ⅰ)/V | Cu(Ⅰ)→Cu(Ⅱ)/V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | 0.07,-0.43 | -1.55 | -0.30 | 0.29 |
| W | -0.08 | -1.32 | -0.31 | 0.54 |
| GC | 0.04,-0.47 | -2.21 | -0.52 | 0.36 |
Table 1 Cyclic voltametric data of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid on different working electrodes
| Electrode | Cu UPD/V | Electrodeposition of Cu(Ⅰ)/V | Cu→ Cu(Ⅰ)/V | Cu(Ⅰ)→Cu(Ⅱ)/V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | 0.07,-0.43 | -1.55 | -0.30 | 0.29 |
| W | -0.08 | -1.32 | -0.31 | 0.54 |
| GC | 0.04,-0.47 | -2.21 | -0.52 | 0.36 |
| v/(mV?s-1) | E | E | Ia1/(mA?cm-2) | E | E | Ia2/(mA?cm-2) | ∣Ic2/Ia2∣ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 12.81 | -0.31 | -0.54 | 21.98 | 0.57 |
| 200 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 14.95 | -0.23 | -0.49 | 26.50 | 0.58 |
| 300 | 0.58 | 0.44 | 17.51 | -0.12 | -0.42 | 31.68 | 0.64 |
| 400 | 0.67 | 0.52 | 19.52 | -0.09 | -0.37 | 34.68 | 0.65 |
| 500 | 0.70 | 0.54 | 21.54 | -0.02 | -0.35 | 38.25 | 0.66 |
| 600 | 0.80 | 0.62 | 23.91 | 0.05 | -0.32 | 41.72 | 0.69 |
| average | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.63 |
Table 2 Data of oxidation peaks of CV curves of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid on W electrode under different scanning rates
| v/(mV?s-1) | E | E | Ia1/(mA?cm-2) | E | E | Ia2/(mA?cm-2) | ∣Ic2/Ia2∣ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 12.81 | -0.31 | -0.54 | 21.98 | 0.57 |
| 200 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 14.95 | -0.23 | -0.49 | 26.50 | 0.58 |
| 300 | 0.58 | 0.44 | 17.51 | -0.12 | -0.42 | 31.68 | 0.64 |
| 400 | 0.67 | 0.52 | 19.52 | -0.09 | -0.37 | 34.68 | 0.65 |
| 500 | 0.70 | 0.54 | 21.54 | -0.02 | -0.35 | 38.25 | 0.66 |
| 600 | 0.80 | 0.62 | 23.91 | 0.05 | -0.32 | 41.72 | 0.69 |
| average | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.63 |
| v/(mV?s-1) | E | E | Ic1/(mA?cm-2) | E | E | Ic2/(mA?cm-2) | αc2 | D0/(10-6cm2?s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | -0.08 | 0.11 | -8.53 | -1.32 | -1.17 | -12.44 | 0.31 | 2.41 |
| 200 | -0.17 | 0.05 | -13.32 | -1.37 | -1.24 | -15.44 | 0.37 | 1.86 |
| 300 | -0.33 | -0.08 | -19.21 | -1.44 | -1.29 | -20.17 | 0.33 | 2.11 |
| 400 | -0.41 | -0.12 | -21.74 | -1.50 | -1.34 | -22.42 | 0.30 | 1.96 |
| 500 | -0.43 | -0.14 | -24.85 | -1.55 | -1.38 | -25.41 | 0.28 | 2.01 |
| 600 | -0.47 | -0.17 | -27.20 | -1.63 | -1.42 | -28.60 | 0.23 | 2.12 |
| average | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.30 | 2.08 |
Table 3 Data of reduction peaks of CV curves of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid on W electrode under different scanning rates
| v/(mV?s-1) | E | E | Ic1/(mA?cm-2) | E | E | Ic2/(mA?cm-2) | αc2 | D0/(10-6cm2?s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | -0.08 | 0.11 | -8.53 | -1.32 | -1.17 | -12.44 | 0.31 | 2.41 |
| 200 | -0.17 | 0.05 | -13.32 | -1.37 | -1.24 | -15.44 | 0.37 | 1.86 |
| 300 | -0.33 | -0.08 | -19.21 | -1.44 | -1.29 | -20.17 | 0.33 | 2.11 |
| 400 | -0.41 | -0.12 | -21.74 | -1.50 | -1.34 | -22.42 | 0.30 | 1.96 |
| 500 | -0.43 | -0.14 | -24.85 | -1.55 | -1.38 | -25.41 | 0.28 | 2.01 |
| 600 | -0.47 | -0.17 | -27.20 | -1.63 | -1.42 | -28.60 | 0.23 | 2.12 |
| average | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.30 | 2.08 |
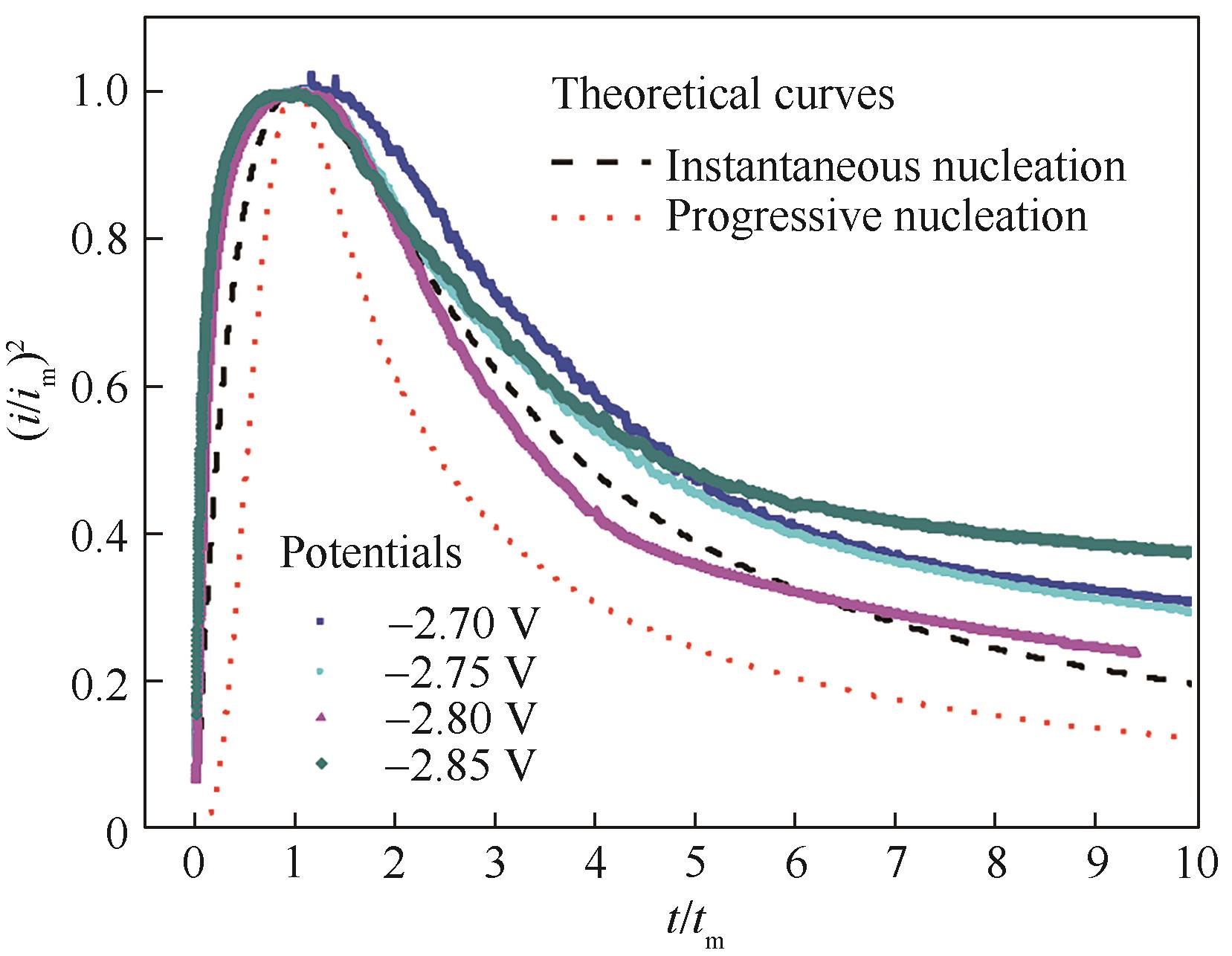
Fig.5 Comparison of the dimensionless experimental current-time transient of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid with the theoretical curves for instantaneous nucleation and progressive nucleation
| Potential/V | Time/h | Charge/C |
|---|---|---|
| -2.60 | 0.5 | 40.1 |
| -2.60 | 1.0 | 39.1 |
| -2.60 | 1.5 | 37.7 |
| -2.60 | 2.0 | 38.4 |
| -2.60 | 2.5 | 37.0 |
| -2.60 | 3.0 | 37.4 |
| -2.60 | 3.5 | 34.1 |
| -2.60 | 4.0 | 33.9 |
| -2.60 | 4.5 | 34.1 |
| -2.60 | 5.0 | 33.7 |
| -2.60 | 5.5 | 33.9 |
| -2.60 | 6.0 | 32.7 |
| -2.60 | 6.5 | 32.0 |
| -2.60 | 7.0 | 32.5 |
| -2.60 | 7.5 | 32.4 |
| -2.60 | 8.0 | 31.7 |
Table 4 Charge for different time during long-term electrodeposition of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid
| Potential/V | Time/h | Charge/C |
|---|---|---|
| -2.60 | 0.5 | 40.1 |
| -2.60 | 1.0 | 39.1 |
| -2.60 | 1.5 | 37.7 |
| -2.60 | 2.0 | 38.4 |
| -2.60 | 2.5 | 37.0 |
| -2.60 | 3.0 | 37.4 |
| -2.60 | 3.5 | 34.1 |
| -2.60 | 4.0 | 33.9 |
| -2.60 | 4.5 | 34.1 |
| -2.60 | 5.0 | 33.7 |
| -2.60 | 5.5 | 33.9 |
| -2.60 | 6.0 | 32.7 |
| -2.60 | 6.5 | 32.0 |
| -2.60 | 7.0 | 32.5 |
| -2.60 | 7.5 | 32.4 |
| -2.60 | 8.0 | 31.7 |
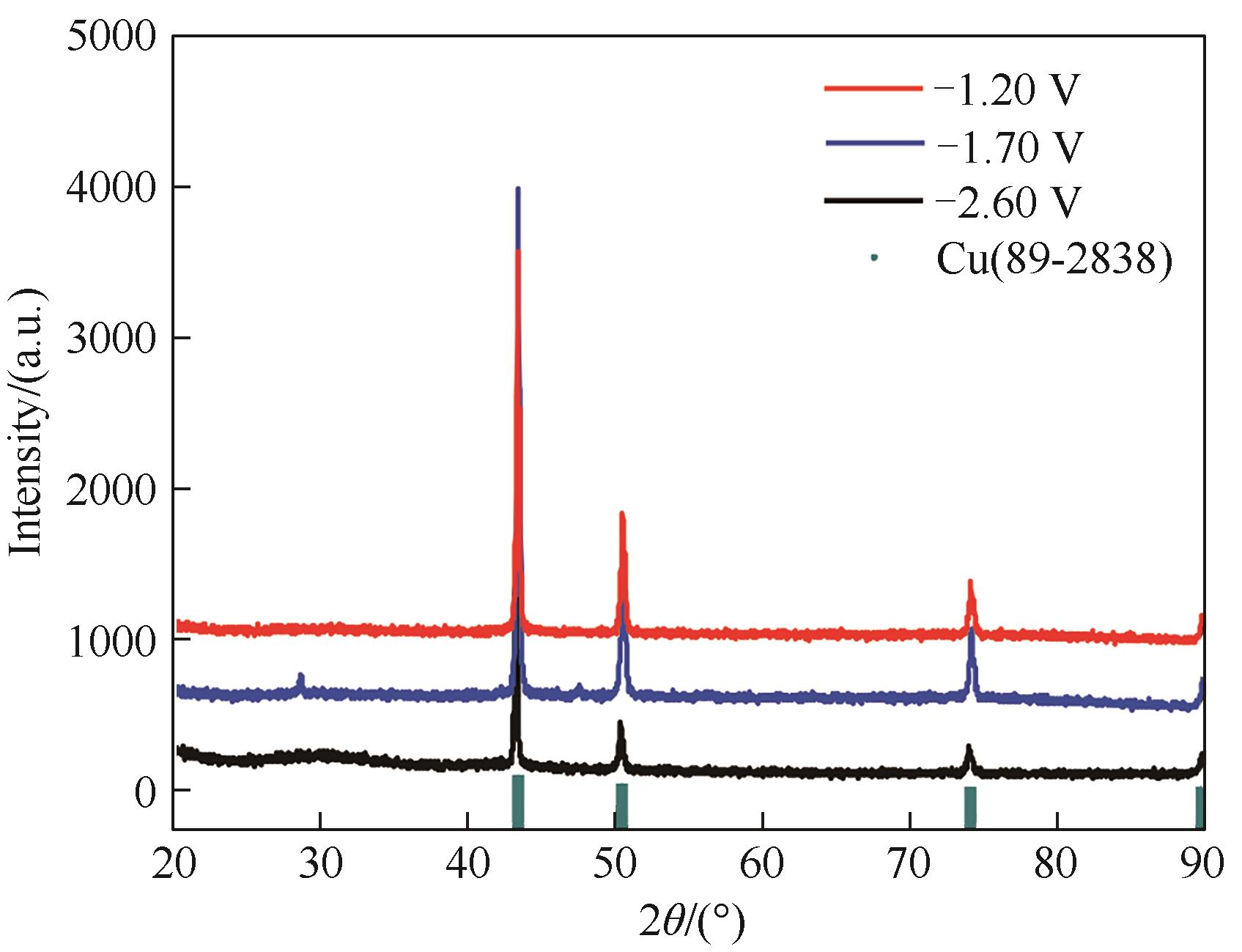
Fig.9 XRD patterns of cathodic electrodeposits from Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid on the silver electrode at the potentials of -1.20, -1.70 and -2.60 V (vs. Pt)
| 1 | Andricacos P C, Uzoh C, Dukovic J O, et al. Damascene copper electroplating for chip interconnections[J]. IBM Journal of Research and Development, 1998, 42(5): 567-574. |
| 2 | Andricacos P C. Copper on-chip interconnections: a breakthrough in electrodeposition to make better chips[J]. The Electrochemical Society Interface, 1999, 8(1): 32-37. |
| 3 | 王鸿建. 电镀工艺学[M]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 1995: 96-110. |
| Wang H J. Electroplating Technology[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 1995: 96-110. | |
| 4 | 陈范才. 现代电镀技术[M]. 北京:中国纺织出版社, 2009: 155-164. |
| Chen F C. Modern Electroplating Technology[M]. Beijing: China Textile & Apparel Press, 2009: 155-164. | |
| 5 | 余德超, 谈定生. 电镀铜技术在电子材料中的应用[J]. 电镀与涂饰, 2007, 26(2): 43-47. |
| Yu D C, Tan D S. Applications of copper plating technology to electronic materials[J]. Electroplating & Finishing, 2007, 26(2): 43-47. | |
| 6 | Welton T. Room-temperature ionic liquids: solvents for synthesis and catalysis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1999, 99(8): 2071-2084. |
| 7 | Ispas A, Bund A. Electrodeposition in ionic liquids[J]. The Electrochemical Society Interface, 2014, 23(1): 47-51. |
| 8 | Nanjundiah C, Osteryoung R A. Electrochemical studies of Cu(Ⅰ) and Cu(Ⅱ) in an aluminum chloride‐N‐(n‐butyl)pyridinium chloride ionic liquid[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1983, 130(6): 1312-1318. |
| 9 | Hussey C L, King L A, Carpio R A. The electrochemistry of copper in a room temperature acidic chloroaluminate melt[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1979, 126(6): 1029-1034. |
| 10 | Chen P Y, Sun I W. Electrochemical study of copper in a basic 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate room temperature molten salt[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1999, 45(3): 441-450. |
| 11 | Shakeela K, Dithya A S, Rao C J, et al. Electrochemical behaviour of Cu(Ⅰ)/Cu(Ⅱ) redox couple in 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquid[J]. Journal of Chemical Sciences, 2015, 127(1): 133-140. |
| 12 | Kitada A, Yanase K, Ichii T, et al. Potentiostatic Cu-Zn alloying for polymer metallization using medium-low temperature ionic liquid baths[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2013, 160(9): D417-D421. |
| 13 | 刘海, 徐存英, 唐杰, 等. ChCl-urea-ZnO-Cu2O低共熔溶剂电镀铜锌合金[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(10): 4402-4408. |
| Liu H, Xu C Y, Tang J, et al. Electroplating of Zn-Cu alloys in ChCl-urea-ZnO-Cu2O deep eutectic solvents[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(10): 4402-4408. | |
| 14 | Sun J, Ming T Y, Qian H X, et al. Electrochemical behaviors and electrodeposition of single-phase Cu-Sn alloy coating in[BMIM]Cl[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 297: 87-93. |
| 15 | Chen P Y, Deng M J, Zhuang D X. Electrochemical codeposition of copper and manganese from room-temperature n-butyl-n-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ionic liquid[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2009, 54(27): 6935-6940. |
| 16 | Wang S H, Guo X, Yang H Y W, et al. Electrodeposition mechanism and characterization of Ni-Cu alloy coatings from a eutectic-based ionic liquid[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 288: 530-536. |
| 17 | Tierney B J, Pitner W R, Mitchell J A, et al. Electrodeposition of copper and copper‐aluminum alloys from a room‐temperature chloroaluminate molten salt[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1998, 145(9): 3110-3116. |
| 18 | Assaker I B, Dhahbi M. Electrochemical study and electrodeposition of copper in the hydrophobic tri-n-octylmethylammonium chloride ionic liquid media[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2011, 161(1): 13-18. |
| 19 | 孙杰, 明庭云, 钱慧璇, 等. BMIMPF6离子液体中铜沉积的电化学行为[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(7): 1497-1502. |
| Sun J, Ming T Y, Qian H X, et al. Electrochemical behavior of copper electrodeposition in BMIMPF6 ionic liquid[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1497-1502. | |
| 20 | Kore R, Berton P, Kelley S P, et al. Group IIIA halometallate ionic liquids: speciation and applications in catalysis[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(10): 7014-7028. |
| 21 | Brown L C, Hogg J M, Swadźba-kwaśny M. Lewis acidic ionic liquids[J]. Topics in Current Chemistry (Cham), 2017, 375(5): 78. |
| 22 | 孟祥海, 张睿, 刘海燕, 等. 复合离子液体碳四烷基化技术开发与应用[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2018, 48(4): 387-396. |
| Meng X H, Zhang R, Liu H Y, et al. Development and application of composite ionic liquid catalyzed isobutane alkylation technology[J]. Scientia Sinica(Chimica), 2018, 48(4): 387-396. | |
| 23 | 刘植昌, 张睿, 刘鹰, 等. 复合离子液体催化碳四烷基化反应性的研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2006, 34(3): 328-331. |
| Liu Z C, Zhang R, Liu Y, et al. Study on isobutane alkylation catalyzed by composite ionic liquid[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2006, 34(3): 328-331. | |
| 24 | 韩晔华, 欧阳萍, 张艳芬, 等. 基于实时直接分析质谱技术的氯铝酸及其复合离子液体分析[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2020, 50(6): 720-728. |
| Han Y H, Ouyang P, Zhang Y F, et al. Comprehensive analysis of chloroaluminate and composite ionic liquids using direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry[J]. Scientia Sinica(Chimica), 2020, 50(6): 720-728. | |
| 25 | Saravanan G, Mohan S. Nucleation of copper on mild steel in copper chloride (CuCl2·2H2O)-1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride [EMIM]Cl-ethylene glycol (EG) ionic liquid[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2013, 37(8): 2564-2567. |
| 26 | Wang S X, Pei Q F, Xu C Y, et al. Effects of cuprous ion on electrodeposition of aluminum from AlCl3-BMIC ionic liquid[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2021, 168(1): 012502 |
| 27 | Chen P Y, Sun I W. Electrochemistry of copper in 1-methyl-3-ethylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate room temperature molten salts[J]. ECS Proceedings Volumes, 1998(1): 55-65. |
| 28 | Zhang Y N, Zhang R, Wu L, et al. Solubilities, structures, and speciations of bimetallic composite ionic liquids: X-ray absorption fine structure and density functional theory calculations[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(20): 7535-7544. |
| 29 | Li Q B, Jiang J Y, Li G F, et al. The electrochemical stability of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2016, 59(5): 571-577. |
| 30 | Endres F, Schweizer A. The electrodeposition of copper on Au(111) and on HOPG from the 66/34 mol% aluminium chloride/1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride room temperature molten salt: an EC-STM study[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2000, 2(23): 5455-5462. |
| 31 | Suneesh P V, Satheesh Babu T G, Ramachandran T. Electrodeposition of aluminium and aluminium-copper alloys from a room temperature ionic liquid electrolyte containing aluminium chloride and triethylamine hydrochloride[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2013, 20(9): 909-916. |
| 32 | Sebastián P, Vallés E, Gómez E. Copper electrodeposition in a deep eutectic solvent. First stages analysis considering Cu(Ⅰ) stabilization in chloride media[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 123: 285-295. |
| 33 | Abbott A P, El Ttaib K, Frisch G, et al. Electrodeposition of copper composites from deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2009, 11(21): 4269-4277. |
| 34 | Scharifker B, Hills G. Theoretical and experimental studies of multiple nucleation[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1983, 28(7): 879-889. |
| 35 | Gunawardena G, Hills G, Montenegro I, et al. Electrochemical nucleation(I): General considerations[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 1982, 138(2): 225-239. |
| 36 | 陈国华, 王光信. 电化学方法应用[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社, 2003: 2-5. |
| Chen G H, Wang G X. Application of Electrochemical Methods[M]. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2003: 2-5. |
| [1] | Runmiao GAO, Mengjie SONG, Enyuan GAO, Long ZHANG, Xuan ZHANG, Keke SHAO, Zekang ZHEN, Zhengyong JIANG. Review on greenhouse gas reduction related to refrigerants in cold chain [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 1-7. |
| [2] | Xiaoxiong FAN, Lifang HAO, Chuigang FAN, Songgeng LI. Study on the catalytic denitrification performance of low-temperature NH3-SCR over LaMnO3/biochar catalyst [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [3] | Baiyu YANG, Yue KOU, Juntao JIANG, Yali ZHAN, Qinghong WANG, Chunmao CHEN. Chemical conversion of dissolved organic matter in petrochemical spent caustic along a wet air oxidation pretreatment process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3912-3920. |
| [4] | Xuejin YANG, Jintao YANG, Ping NING, Fang WANG, Xiaoshuang SONG, Lijuan JIA, Jiayu FENG. Research progress in dry purification technology of highly toxic gas PH3 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3742-3755. |
| [5] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [6] | Song HE, Qiaomai LIU, Guangshuo XIE, Simin WANG, Juan XIAO. Two-phase flow simulation and surrogate-assisted optimization of gas film drag reduction in high-concentration coal-water slurry pipeline [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3766-3774. |
| [7] | Linzheng WANG, Yubing LU, Ruizhi ZHANG, Yonghao LUO. Analysis on thermal oxidation characteristics of VOCs based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [8] | Jintong LI, Shun QIU, Wenshou SUN. Oxalic acid and UV enhanced arsenic leaching from coal in flue gas desulfurization by coal slurry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3522-3532. |
| [9] | Kaixuan LI, Wei TAN, Manyu ZHANG, Zhihao XU, Xuyu WANG, Hongbing JI. Design of cobalt-nitrogen-carbon/activated carbon rich in zero valent cobalt active site and application of catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3342-3352. |
| [10] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [11] | Yuming TU, Gaoyan SHAO, Jianjie CHEN, Feng LIU, Shichao TIAN, Zhiyong ZHOU, Zhongqi REN. Advances in the design, synthesis and application of calcium-based catalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2717-2734. |
| [12] | Qiyu ZHANG, Lijun GAO, Yuhang SU, Xiaobo MA, Yicheng WANG, Yating ZHANG, Chao HU. Recent advances in carbon-based catalysts for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [13] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [14] | Yuying GUO, Jiaqiang JING, Wanni HUANG, Ping ZHANG, Jie SUN, Yu ZHU, Junxuan FENG, Hongjiang LU. Water-lubricated drag reduction and pressure drop model modification for heavy oil pipeline [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2898-2907. |
| [15] | Bin LI, Zhenghu XU, Shuang JIANG, Tianyong ZHANG. Clean and efficient synthesis of accelerator CBS by hydrogen peroxide catalytic oxidation method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2919-2925. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||