CIESC Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (8): 3529-3540.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220166
• Fluid dynamics and transport phenomena • Previous Articles Next Articles
Kaiyue WANG1( ), Yongli MA1(
), Yongli MA1( ), Chen LI1, Mingyan LIU1,2
), Chen LI1, Mingyan LIU1,2
Received:2022-02-07
Revised:2022-07-22
Online:2022-09-06
Published:2022-08-05
Contact:
Yongli MA
通讯作者:
马永丽
作者简介:王凯玥(1997—),女,硕士研究生,wangky97@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Kaiyue WANG, Yongli MA, Chen LI, Mingyan LIU. Gas-liquid mass transfer coefficients in the gas-liquid-solid micro-fluidized beds[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3529-3540.
王凯玥, 马永丽, 李琛, 刘明言. 气液固微型流化床的气液传质系数[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3529-3540.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
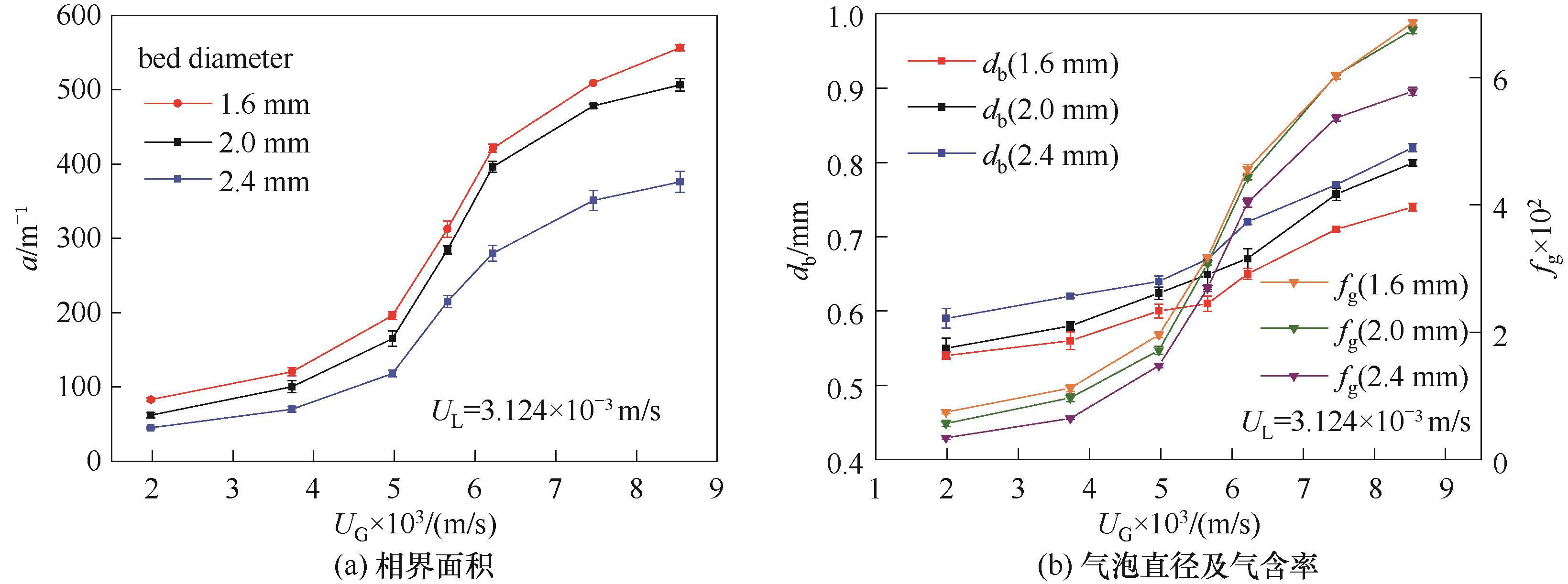
Fig.5 Changes of gas-liquid phase interface area, bubble diameter and gas holdup with superficial gas velocity in gas-liquid-solid micro-fluidized bed

Fig.16 Liquid-phase mass transfer coefficients of gas-liquid-solid micro-fluidized bed with different particle sizes when superficial gas velocity changes
| 1 | Fan L S. Gas-Liquid-Solid Fluidization Engineering[M]. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1989. |
| 2 | Kashid M N, Kiwi-Minsker L. Microstructured reactors for multiphase reactions: state of the art[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(14): 6465-6485. |
| 3 | Ye C B, Chen G W, Yuan Q. Process characteristics of CO2 absorption by aqueous monoethanolamine in a microchannel reactor[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2012, 20(1): 111-119. |
| 4 | Li Y J, Liu M Y, Li X N. Minimum fluidization velocity in gas-liquid-solid minifluidized beds[J]. AIChE Journal, 2016, 62(6): 1940-1957. |
| 5 | Li Y J, Liu M Y, Li X N. Single bubble behavior in gas-liquid-solid mini-fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 286: 497-507. |
| 6 | Li Y J, Liu M Y, Li X N. Flow regimes in gas-liquid-solid mini-fluidized beds with single gas orifice[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 333: 293-303. |
| 7 | Li X N, Liu M Y, Li Y J. Bed expansion and multi-bubble behavior of gas-liquid-solid micro-fluidized beds in sub-millimeter capillary[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 328: 1122-1138. |
| 8 | Li X N, Liu M Y, Ma Y L, et al. Experiments and meso-scale modeling of phase holdups and bubble behavior in gas-liquid-solid mini-fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 192: 725-738. |
| 9 | Wang X Y, Liu M Y, Yang Z G. Coupled model based on radiation transfer and reaction kinetics of gas-liquid-solid photocatalytic mini-fluidized bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2018, 134: 172-185. |
| 10 | Dong T T, Liu M Y, Li X N, et al. Catalytic oxidation of crotonaldehyde to crotonic acid in a gas-liquid-solid mini-fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 352: 32-41. |
| 11 | Yao C Q, Zhu K, Liu Y Y, et al. Intensified CO2 absorption in a microchannel reactor under elevated pressures[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 319: 179-190. |
| 12 | Zhu C Y, Guo H, Chu C Y, et al. Gas-liquid distribution and mass transfer of CO2 absorption into sodium glycinate aqueous solution in parallel multi-channel microreactor[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 157: 119943. |
| 13 | Zhang S Z, Zhu C Y, Feng H S, et al. Intensification of gas-liquid two-phase flow and mass transfer in microchannels by sudden expansions[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 229: 116040. |
| 14 | Conlisk A T, McFerran J, Zheng Z, et al. Mass transfer and flow in electrically charged micro- and nanochannels[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2002, 74(9): 2139-2150. |
| 15 | Zhang Y B. Efficient multiscale calculation results for microchannel mass transfer[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11: 10023. |
| 16 | Dong T T, Ma Y L, Liu M Y. Gas-liquid mass transfer in the gas-liquid-solid mini fluidized beds[J]. Particuology, 2022, 69: 22-30. |
| 17 | Zahid Saima. 液-固微型流化床中的颗粒-液体间传质[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2019. |
| Saima Z. Mass transfer between solid particle and liquid flow in the liquid-solid mini-fluidized bed[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2019. | |
| 18 | 郝玲, 郑朝振, 章俊, 等. CO2吸收模型中容积传质系数的确定[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2012, 11(2): 98-101. |
| Hao L, Zheng C Z, Zhang J, et al. Determination of volumetric mass transfer coefficient for CO2 absorption model experiment[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2012, 11(2): 98-101. | |
| 19 | 刘燕, 张廷安, 赵洪亮, 等. CO2微细气泡在NaOH溶液中吸收速率研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2009, 9(S1): 185-188. |
| Liu Y, Zhang T A, Zhao H L, et al. Study on absorption of CO2 bubble disintegration in NaOH solution[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2009, 9(S1): 185-188. | |
| 20 | Inada S, Watanabe A. Effect of gas liquid properties on the absorption rate of CO2 into NaOH solution[J]. Tetsu-to-Hagane, 1976, 62(7): 807-816. |
| 21 | Takemura F, Yabe A. Gas dissolution process of spherical rising gas bubbles[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1998, 53(15): 2691-2699. |
| 22 | Motarjemi M, Jameson G J. Mass transfer from very small bubbles—the optimum bubble size for aeration[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1978, 33(11): 1415-1423. |
| 23 | Lee J S, Jin H R, Lim H, et al. Interfacial area and liquid-side and overall mass transfer coefficients in a three-phase circulating fluidized bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 100: 203-211. |
| 24 | Dani A, Guiraud P, Cockx A. Local measurement of oxygen transfer around a single bubble by planar laser-induced fluorescence[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(24): 7245-7252. |
| 25 | Bischof F, Sommerfeld M, Durst F. The determination of mass transfer rates from individual small bubbles[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1991, 46(12): 3115-3121. |
| 26 | Doroodchi E, Peng Z B, Sathe M, et al. Fluidisation and packed bed behaviour in capillary tubes[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 223: 131-136. |
| 27 | Tang C, Liu M Y, Li Y J. Experimental investigation of hydrodynamics of liquid-solid mini-fluidized beds[J]. Particuology, 2016, 27: 102-109. |
| [1] | He JIANG, Junfei YUAN, Lin WANG, Guyu XING. Experimental study on the effect of flow sharing cavity structure on phase change flow characteristics in microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [2] | Jiaqi YUAN, Zheng LIU, Rui HUANG, Lefu ZHANG, Denghui HE. Investigation on energy conversion characteristics of vortex pump under bubble inflow [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3807-3820. |
| [3] | Yan GAO, Peng WU, Chao SHANG, Zejun HU, Xiaodong CHEN. Preparation of magnetic agarose microspheres based on a two-fluid nozzle and their protein adsorption properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3457-3471. |
| [4] | Lei XING, Chunyu MIAO, Minghu JIANG, Lixin ZHAO, Xinya LI. Optimal design and performance analysis of downhole micro gas-liquid hydrocyclone [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3394-3406. |
| [5] | Jinming GAO, Yujiao GUO, Chenglin E, Chunxi LU. Study on the separation characteristics of a downstream gas-liquid vortex separator in a closed hood [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2957-2966. |
| [6] | Qichao LIU, Yunlong ZHOU, Cong CHEN. Analysis and calculation of void fraction of gas-liquid two-phase flow in vertical riser under fluctuating vibration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2391-2403. |
| [7] | Yuanyuan ZHANG, Jiangyuan QU, Xinxin SU, Jing YANG, Kai ZHANG. Gas-liquid mass transfer and reaction characteristics of SNCR denitration in CFB coal-fired unit [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2404-2415. |
| [8] | Jinbo JIANG, Xin PENG, Wenxuan XU, Rixiu MEN, Chang LIU, Xudong PENG. Study on leakage characteristics and parameter influence of pump-out spiral groove oil-gas seal [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2538-2554. |
| [9] | Xin DONG, Yongrui SHAN, Yinuo LIU, Ying FENG, Jianwei ZHANG. Numerical simulation of bubble plume vortex characteristics for non-Newtonian fluids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1950-1964. |
| [10] | Wenxuan XU, Jinbo JIANG, Xin PENG, Rixiu MEN, Chang LIU, Xudong PENG. Comparative study on leakage and film-forming characteristics of oil-gas seal with three-typical groove in a wide speed range [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1660-1679. |
| [11] | Wanyuan HE, Yiyu CHEN, Chunying ZHU, Taotao FU, Xiqun GAO, Youguang MA. Study on gas-liquid mass transfer characteristics in microchannel with array bulges [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 690-697. |
| [12] | Jianzhao BAI, Zixuan GUO, Dewu WANG, Yan LIU, Ruojin WANG, Meng TANG, Shaofeng ZHANG. Effect of roll on pressure drop in concurrent gas-liquid columns with tridimensional rotational flow sieve tray [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 707-720. |
| [13] | Lin SHENG, Yu CHANG, Jian DENG, Guangsheng LUO. Formation and flow characteristics of ordered bubble swarm in a step T-junction microchannel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 416-427. |
| [14] | Tong ZHANG, Yang YANG, Dingding YE, Rong CHEN, Xun ZHU, Qiang LIAO. Effect of catalyst distribution on the performance characteristics of microfluidic fuel cell with flow-through anode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4156-4162. |
| [15] | Qiaoling SU, Junfeng WANG, Wei ZHANG, Shuiqing ZHAN, Tianyi WU. Experimental study on polarization motion characteristics of bubbles in a low conductivity working medium [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 3861-3869. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||