CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (1): 221-230.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230601
• Fluid dynamics and transport phenomena • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ruohan ZHAO1( ), Mengmeng HUANG1, Chunying ZHU1(
), Mengmeng HUANG1, Chunying ZHU1( ), Taotao FU1, Xiqun GAO2, Youguang MA1
), Taotao FU1, Xiqun GAO2, Youguang MA1
Received:2023-06-20
Revised:2023-08-28
Online:2024-03-11
Published:2024-01-25
Contact:
Chunying ZHU
赵若晗1( ), 黄蒙蒙1, 朱春英1(
), 黄蒙蒙1, 朱春英1( ), 付涛涛1, 高习群2, 马友光1
), 付涛涛1, 高习群2, 马友光1
通讯作者:
朱春英
作者简介:赵若晗(1999—),女,硕士研究生,2021207330@tju.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Ruohan ZHAO, Mengmeng HUANG, Chunying ZHU, Taotao FU, Xiqun GAO, Youguang MA. Flow and mass transfer study of CO2 absorption by nanofluid in T-shaped microchannels[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 221-230.
赵若晗, 黄蒙蒙, 朱春英, 付涛涛, 高习群, 马友光. 缩口T型微通道内纳米流体吸收CO2的流动与传质研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 221-230.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| SiO2浓度/ %(质量) | 流体密度 ρ/(kg·m-3) | 流体黏度 μ/(mPa·s) | 表面张力 σ/(mN·m-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1028.3 | 1.102 | 35.14 |
| 10 | 1059.2 | 1.253 | 33.46 |
| 20 | 1126.5 | 1.689 | 30.91 |
Table 1 Physical properties of silica slurry
| SiO2浓度/ %(质量) | 流体密度 ρ/(kg·m-3) | 流体黏度 μ/(mPa·s) | 表面张力 σ/(mN·m-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1028.3 | 1.102 | 35.14 |
| 10 | 1059.2 | 1.253 | 33.46 |
| 20 | 1126.5 | 1.689 | 30.91 |
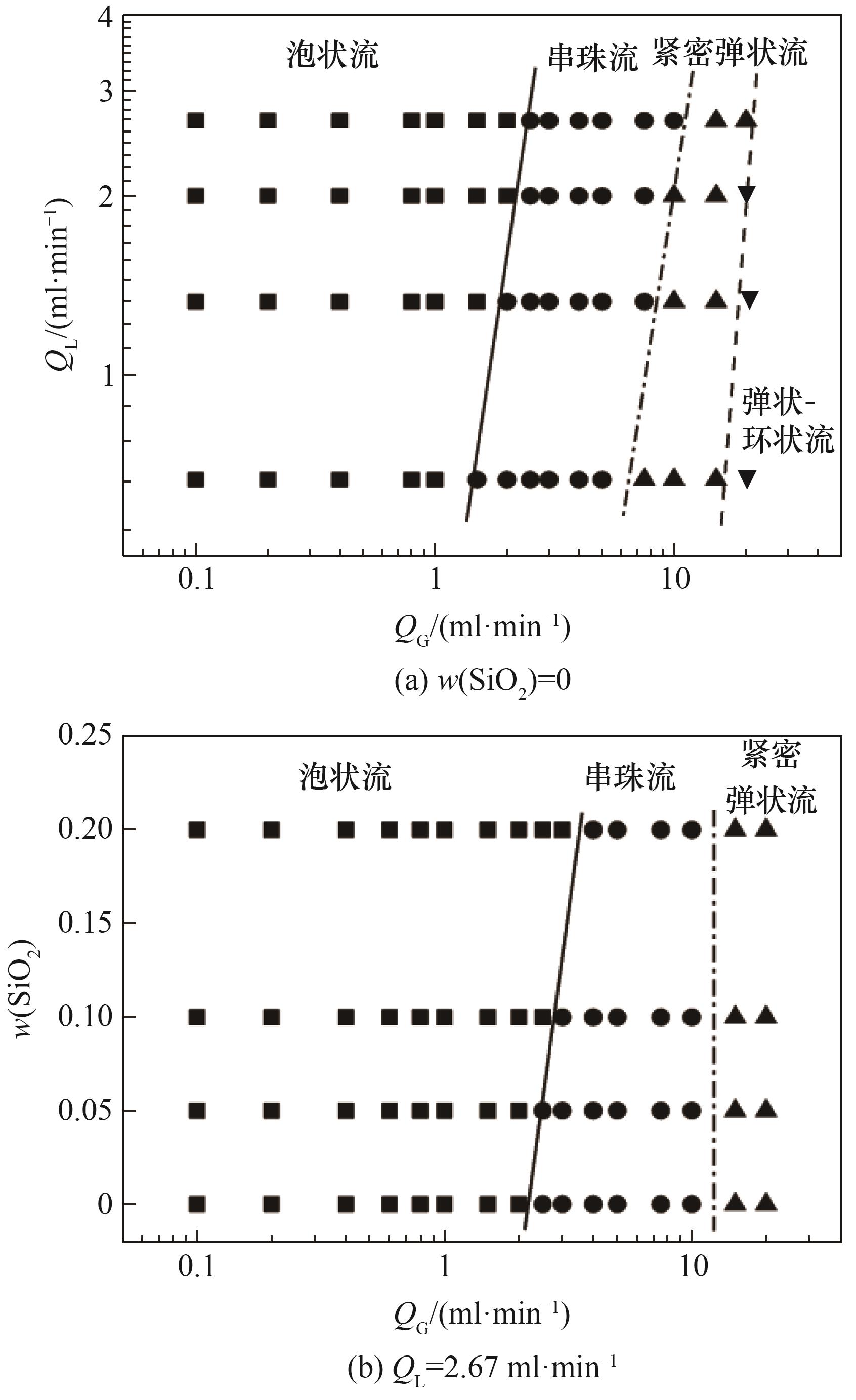
Fig.5 Gas-liquid flow regime in the microchannel■bubbly flow; ●beaded bubble flow;▲compact slug flow; ▼slug-annular flow; —— conversion line between bubbly flow and beaded bubble flow; —·— conversion line between beaded bubble flow and compact slug flow; — — — conversion line between compact slug flow and slug-annular flow
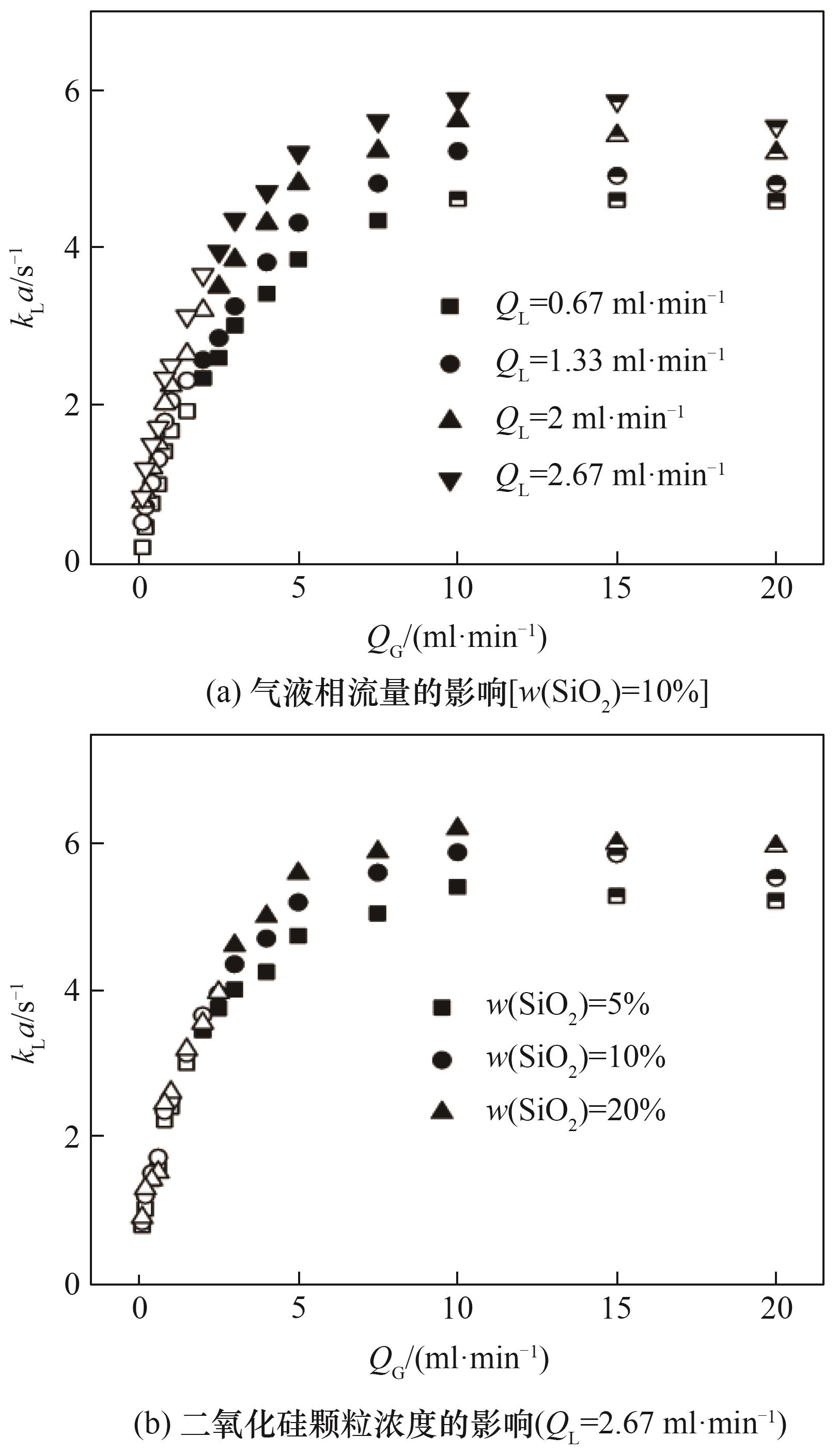
Fig.9 Variation of liquid side volumetric mass transfer coefficient with operating conditions(hollow symbols represent bubbly flow, solid symbols represent beaded bubble flow, and semi-solid symbols represent compact slug flow)
| 1 | Tiwari S C, Bhardwaj A, Nigam K D P, et al. A strategy of development and selection of absorbent for efficient CO2 capture: an overview of properties and performance[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 163: 244-273. |
| 2 | Sheng L, Wang K, Deng J, et al. Gas-liquid microdispersion and microflow for carbon dioxide absorption and utilization: a review[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2023, 40: 100917. |
| 3 | 张雪婷, 胡激江, 赵晶, 等. 高分子量聚丙二醇在微通道反应器中的制备[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1343-1351. |
| Zhang X T, Hu J J, Zhao J, et al. Preparation of high molecular weight polypropylene glycol in microchannel reactor[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1343-1351. | |
| 4 | 尧超群, 陈光文, 袁权. 微通道内气-液两相传质过程行为及其应用[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(10): 3635-3644. |
| Yao C Q, Chen G W, Yuan Q. Mass transfer characteristics of gas-liquid two-phase flow in microchannels and applications[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(10): 3635-3644. | |
| 5 | Huang M M, Zhu C Y, Fu T T, et al. Enhancement of gas-liquid mass transfer by nanofluids in a microchannel under Taylor flow regime[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 176: 121435. |
| 6 | Yao C Q, Zhao Y C, Ma H Y, et al. Two-phase flow and mass transfer in microchannels: a review from local mechanism to global models[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 229: 116017. |
| 7 | 郭戎威, 付涛涛, 朱春英, 等. 微通道内气-液两相流及并行放大的研究进展[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2021, 38(6): 74-86. |
| Guo R W, Fu T T, Zhu C Y, et al. Research progress on gas-liquid two-phase flow and numbering-up strategy in microchannel[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2021, 38(6):74-86. | |
| 8 | Ganapathy H, Shooshtari A, Dessiatoun S, et al. Hydrodynamics and mass transfer performance of a microreactor for enhanced gas separation processes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 266: 258-270. |
| 9 | 何万媛, 陈一宇, 朱春英, 等. 阵列凸起微通道内气液两相传质特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 690-697. |
| He W Y, Chen Y Y, Zhu C Y, et al. Study on gas-liquid mass transfer characteristics in microchannel with array bulges[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 690-697. | |
| 10 | Rzehak R. Modeling of mass-transfer in bubbly flows encompassing different mechanisms[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 151: 139-143. |
| 11 | Sheng L, Chang Y, Wang J J, et al. Remarkable improvement of gas-liquid mass transfer by modifying the structure of conventional T-junction microchannel[J]. AIChE Journal, 2023, 69(7): 18089. |
| 12 | Chen Y C, Sheng L, Deng J, et al. Geometric effect on gas-liquid bubbly flow in capillary-embedded T-junction microchannels[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(12): 4735-4744. |
| 13 | Wang Z H, Ding W B, Fan Y W, et al. Design of improved flow-focusing microchannel with constricted continuous phase inlet and study of fluid flow characteristics[J]. Micromachines, 2022, 13(10): 1776. |
| 14 | Keblinski P, Phillpot S R, Choi S U S, et al. Mechanisms of heat flow in suspensions of nano-sized particles (nanofluids)[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2002, 45(4): 855-863. |
| 15 | Darvanjooghi M H K, Esfahany M N, Esmaeili-Faraj S H. Investigation of the effects of nanoparticle size on CO2 absorption by silica-water nanofluid[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 195: 208-215. |
| 16 | Yu W, Wang T, Park A H A, et al. Review of liquid nano-absorbents for enhanced CO2 capture[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(37): 17137-17156. |
| 17 | Valeh-e-Sheyda P, Afshari A. A detailed screening on the mass transfer modeling of the CO2 absorption utilizing silica nanofluid in a wetted wall column[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 127: 125-132. |
| 18 | Thulasidas T C, Abraham M A, Cerro R L. Bubble-train flow in capillaries of circular and square cross section[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1995, 50(2): 183-199. |
| 19 | Fries D M, Trachsel F, von Rohr P R. Segmented gas-liquid flow characterization in rectangular microchannels[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2008, 34(12): 1108-1118. |
| 20 | Wu Y N, Fu T T, Zhu C Y, et al. Asymmetrical breakup of bubbles at a microfluidic T-junction divergence: feedback effect of bubble collision[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2012, 13(5): 723-733. |
| 21 | van Steijn V, Kleijn C R, Kreutzer M T. Flows around confined bubbles and their importance in triggering pinch-off[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(21): 214501. |
| 22 | Piroird K, Lorenceau É. Capillary flow of oil in a single foam microchannel[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 111(23): 234503. |
| 23 | Cai W F, Zhang J, Zhang X B, et al. Enhancement of CO2 absorption under Taylor flow in the presence of fine particles[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2013, 21(2): 135-143. |
| 24 | Kluytmans J H J, van Wachem B G M, Kuster B F M, et al. Mass transfer in sparged and stirred reactors: influence of carbon particles and electrolyte[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2003, 58(20): 4719-4728. |
| 25 | Vandu C O, Liu H, Krishna R. Mass transfer from Taylor bubbles rising in single capillaries[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2005, 60(22): 6430-6437. |
| 26 | Rettich T R, Battino R, Wilhelm E. Solubility of gases in liquids. ⅩⅥ. Henry’s law coefficients for nitrogen in water at 5 to 50℃[J]. Journal of Solution Chemistry, 1984, 13(5): 335-348. |
| 27 | Abiev R S. Simulation of the slug flow of a gas-liquid system in capillaries[J]. Theoretical Foundations of Chemical Engineering, 2008, 42(2): 105-117. |
| 28 | Abiev R S. Modeling of pressure losses for the slug flow of a gas-liquid mixture in mini- and microchannels[J]. Theoretical Foundations of Chemical Engineering, 2011, 45(2): 156-163. |
| 29 | Kreutzer M T, Kapteijn F, Moulijn J A, et al. Multiphase monolith reactors: chemical reaction engineering of segmented flow in microchannels[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2005, 60(22): 5895-5916. |
| 30 | Sheng L, Chen Y C, Deng J, et al. High-frequency formation of bubble with short length in a capillary embedded step T-junction microdevice[J]. AIChE Journal, 2021, 67(11): 17376. |
| 31 | Wang K, Lu Y C, Xu J H, et al. Generation of micromonodispersed droplets and bubbles in the capillary embedded T-junction microfluidic devices[J]. AIChE Journal, 2011, 57(2): 299-306. |
| 32 | Xu J H, Li S W, Wang Y J, et al. Controllable gas-liquid phase flow patterns and monodisperse microbubbles in a microfluidic T-junction device[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(13): 133506. |
| 33 | Sheng L, Ma L, Chen Y C, et al. A comprehensive study of droplet formation in a capillary embedded step T-junction: from squeezing to jetting[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 427: 132067. |
| 34 | Zhao Y C, Chen G W, Ye C B, et al. Gas-liquid two-phase flow in microchannel at elevated pressure[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 87: 122-132. |
| 35 | Zhu C Y, Lu Y T, Fu T T, et al. Experimental investigation on gas-liquid mass transfer with fast chemical reaction in microchannel[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 114: 83-89. |
| 36 | Ma D F, Zhu C Y, Fu T T, et al. Synergistic effect of functionalized ionic liquid and alkanolamines mixed solution on enhancing the mass transfer of CO2 absorption in microchannel[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 417: 129302. |
| 37 | Korczyk P M, van Steijn V, Blonski S, et al. Accounting for corner flow unifies the understanding of droplet formation in microfluidic channels[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 2528. |
| 38 | Haase S. Characterisation of gas-liquid two-phase flow in minichannels with co-flowing fluid injection inside the channel (Ⅱ): Gas bubble and liquid slug lengths, film thickness, and void fraction within Taylor flow[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2017, 88: 251-269. |
| 39 | Salman W, Gavriilidis A, Angeli P. On the formation of Taylor bubbles in small tubes[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2006, 61(20): 6653-6666. |
| 40 | Abiev R S. Gas-liquid and gas-liquid-solid mass transfer model for Taylor flow in micro (milli) channels: a theoretical approach and experimental proof[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances, 2020, 4: 100065. |
| 41 | Abiev R S, Butler C, Cid E, et al. Mass transfer characteristics and concentration field evolution for gas-liquid Taylor flow in milli channels[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 207: 1331-1340. |
| 42 | Woo M, Tischer S, Deutschmann O, et al. A step toward the numerical simulation of catalytic hydrogenation of nitrobenzene in Taylor flow at practical conditions[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 230: 116132. |
| 43 | Peng Z B, Gai S L, Barma M, et al. Experimental study of gas-liquid-solid flow characteristics in slurry Taylor flow-based multiphase microreactors[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 405: 126646. |
| 44 | Bahmanyar A, Khoobi N, Mozdianfard M R, et al. The influence of nanoparticles on hydrodynamic characteristics and mass transfer performance in a pulsed liquid-liquid extraction column[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2011, 50(11/12): 1198-1206. |
| 45 | Alper E, Wichtendahl B, Deckwer W D. Gas absorption mechanism in catalytic slurry reactors[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1980, 35(1/2): 217-222. |
| 46 | Farzani Tolesorkhi S, Esmaeilzadeh F, Riazi M. Experimental and theoretical investigation of CO2 mass transfer enhancement of silica nanoparticles in water[J]. Petroleum Research, 2018, 3(4): 370-380. |
| 47 | Nagy E, Feczkó T, Koroknai B. Enhancement of oxygen mass transfer rate in the presence of nanosized particles[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(24): 7391-7398. |
| [1] | Yuting ZHENG, Guandong FANG, Mengbo ZHANG, Haomiao ZHANG, Jingdai WANG, Yongrong YANG. Research progress on micro-chemical rectification and separation technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 47-59. |
| [2] | Yating LI, Zhongdong WANG, Yanpeng DONG, Chunying ZHU, Youguang MA, Taotao FU. Research progress of capillary flow in microchannels and its engineering application [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 159-170. |
| [3] | Yizhou CUI, Chengxiang LI, Linxiao ZHAI, Shuyu LIU, Xiaogang SHI, Jinsen GAO, Xingying LAN. Comparative study on the flow and mass transfer characteristics of sub-millimeter bubbles and conventional bubbles in gas-liquid two-phase flow [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 197-210. |
| [4] | Junnan WANG, Chengxiang HE, Zhongdong WANG, Chunying ZHU, Youguang MA, Taotao FU. Numerical simulation of homogeneous mixing in T-junction micromixers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 242-254. |
| [5] | Weigu WEN, Zhihong YUAN, Kai WANG, Guangsheng LUO. Microdispersion droplet optical fiber detection [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 211-220. |
| [6] | He JIANG, Junfei YUAN, Lin WANG, Guyu XING. Experimental study on the effect of flow sharing cavity structure on phase change flow characteristics in microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [7] | Jingwei CHAO, Jiaxing XU, Tingxian LI. Investigation on the heating performance of the tube-free-evaporation based sorption thermal battery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 302-310. |
| [8] | Yitong LI, Hang GUO, Hao CHEN, Fang YE. Study on operating conditions of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform catalyst distributions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [9] | Jiajia ZHAO, Shixiang TIAN, Peng LI, Honggao XIE. Microscopic mechanism of SiO2-H2O nanofluids to enhance the wettability of coal dust [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3931-3945. |
| [10] | Wenzhu LIU, Heming YUN, Baoxue WANG, Mingzhe HU, Chonglong ZHONG. Research on topology optimization of microchannel based on field synergy and entransy dissipation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3329-3341. |
| [11] | Lei MAO, Guanzhang LIU, Hang YUAN, Guangya ZHANG. Efficient preparation of carbon anhydrase nanoparticles capable of capturing CO2 and their characteristics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [12] | Yuanyuan ZHANG, Jiangyuan QU, Xinxin SU, Jing YANG, Kai ZHANG. Gas-liquid mass transfer and reaction characteristics of SNCR denitration in CFB coal-fired unit [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2404-2415. |
| [13] | Hao WANG, Siyang TANG, Shan ZHONG, Bin LIANG. An investigation of the enhancing effect of solid particle surface on the CO2 desorption behavior in chemical sorption process with MEA solution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1539-1548. |
| [14] | Lufan JIA, Yiying WANG, Yuman DONG, Qinyuan LI, Xin XIE, Hao YUAN, Tao MENG. Aqueous two-phase system based adherent droplet microfluidics for enhanced enzymatic reaction [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1239-1246. |
| [15] | Xueting ZHANG, Jijiang HU, Jing ZHAO, Bogeng LI. Preparation of high molecular weight polypropylene glycol in microchannel reactor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1343-1351. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||