CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (8): 3753-3771.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250058
• Reviews and monographs • Next Articles
Yufeng WANG1( ), Xiaoxue LUO1(
), Xiaoxue LUO1( ), Hongliang FAN1, Baijing WU1, Cunpu LI1,2(
), Hongliang FAN1, Baijing WU1, Cunpu LI1,2( ), Zidong WEI1,2(
), Zidong WEI1,2( )
)
Received:2025-01-14
Revised:2025-03-11
Online:2025-09-17
Published:2025-08-25
Contact:
Cunpu LI, Zidong WEI
王御风1( ), 罗小雪1(
), 罗小雪1( ), 范鸿亮1, 吴白婧1, 李存璞1,2(
), 范鸿亮1, 吴白婧1, 李存璞1,2( ), 魏子栋1,2(
), 魏子栋1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
李存璞,魏子栋
作者简介:王御风(2000—),男,硕士研究生,30406870@qq.com基金资助:CLC Number:
Yufeng WANG, Xiaoxue LUO, Hongliang FAN, Baijing WU, Cunpu LI, Zidong WEI. Green organic electrosynthesis coupled with water electrolysis to produce hydrogen—overview of electrode interface regulation strategies[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3753-3771.
王御风, 罗小雪, 范鸿亮, 吴白婧, 李存璞, 魏子栋. 耦合电解水制氢的绿色有机电合成——电极界面调控策略综述[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3753-3771.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
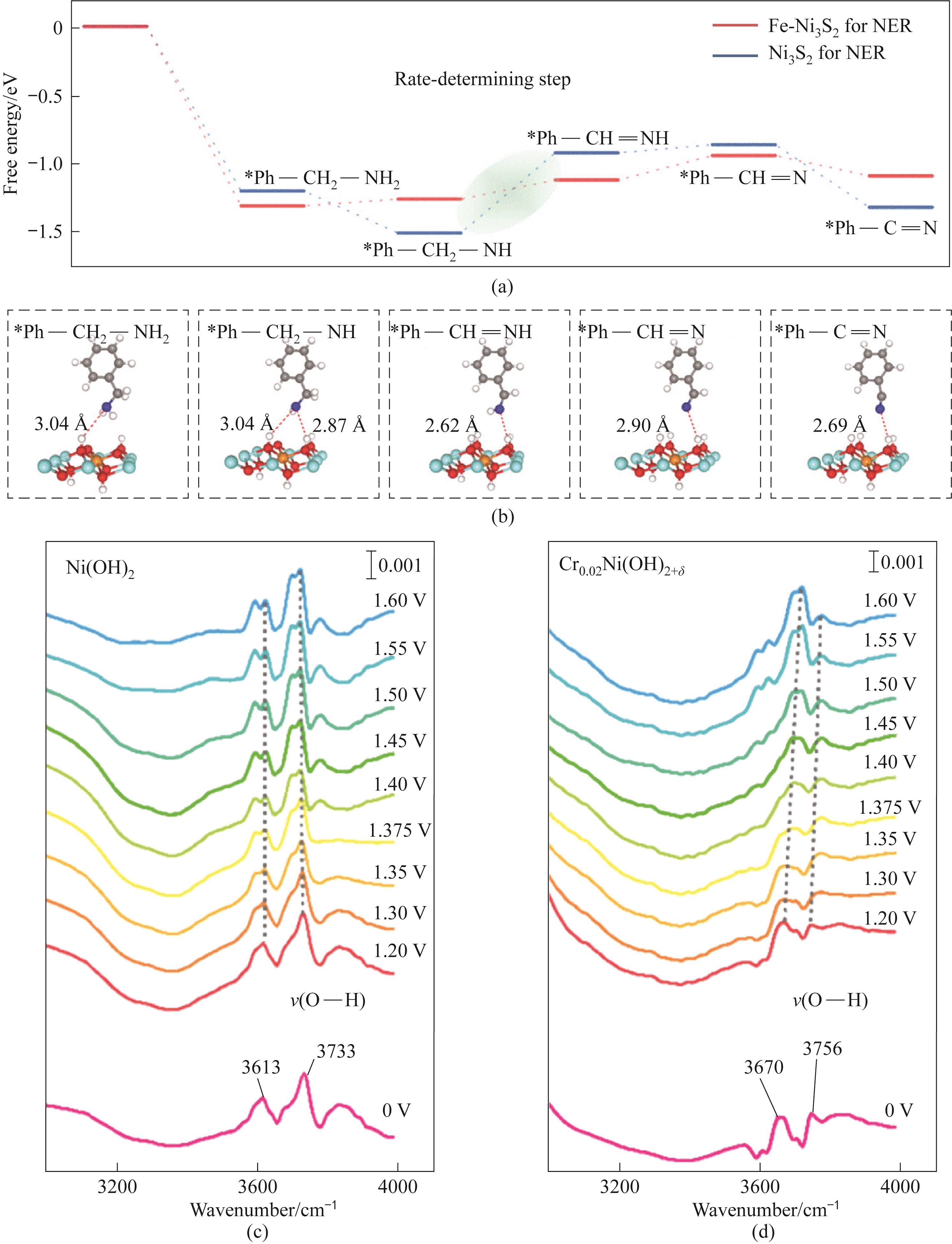
Fig.2 (a) Reaction pathways of BA electro oxidation after Fe-Ni3S2 and Ni3S2 self reconstruction; (b) BA electro oxidation adsorption intermediate structure; In situ ATR-FTIR spectra of (c) Ni (OH)2 and (d) Cr0.02Ni (OH)2+δ at different potentials[51-52]

Fig.3 (a) S-NiCo LDH LSV curve; High resolution XPS spectra of (b) Co 2p and (c) Mn 2p for Mn-Co-S/NF and Mn Co/NF; (d) S 2p high-resolution XPS spectra of Mn-Co-S/NF; (e) DFT calculation of the free energy distribution of HzOR on the surfaces of Co3N and PW-Co3N[53-55]
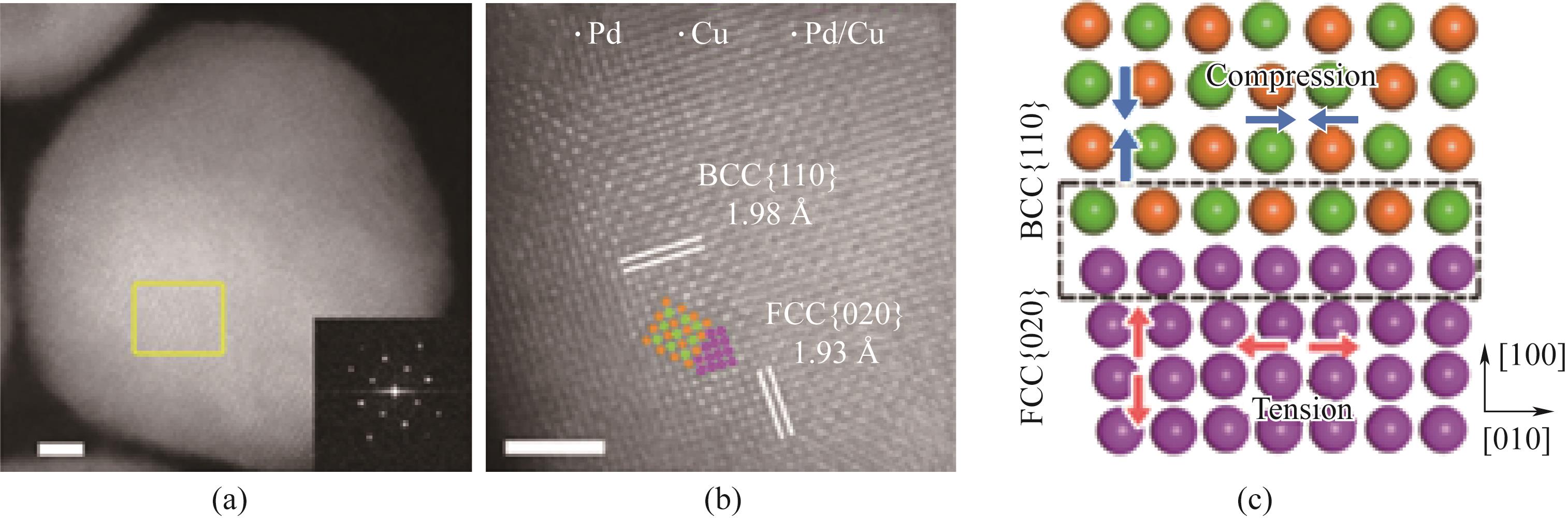
Fig.4 (a) Aberration corrected HAADF-STEM image of DP PdCu (DP: biphasic) along the BCC [001] region axis; (b) The atomic arrangement of the selected rectangular region in Fig.(a); (c) Simulated atomic model of the interface between BCC [110] and FCC [020] planes[56]
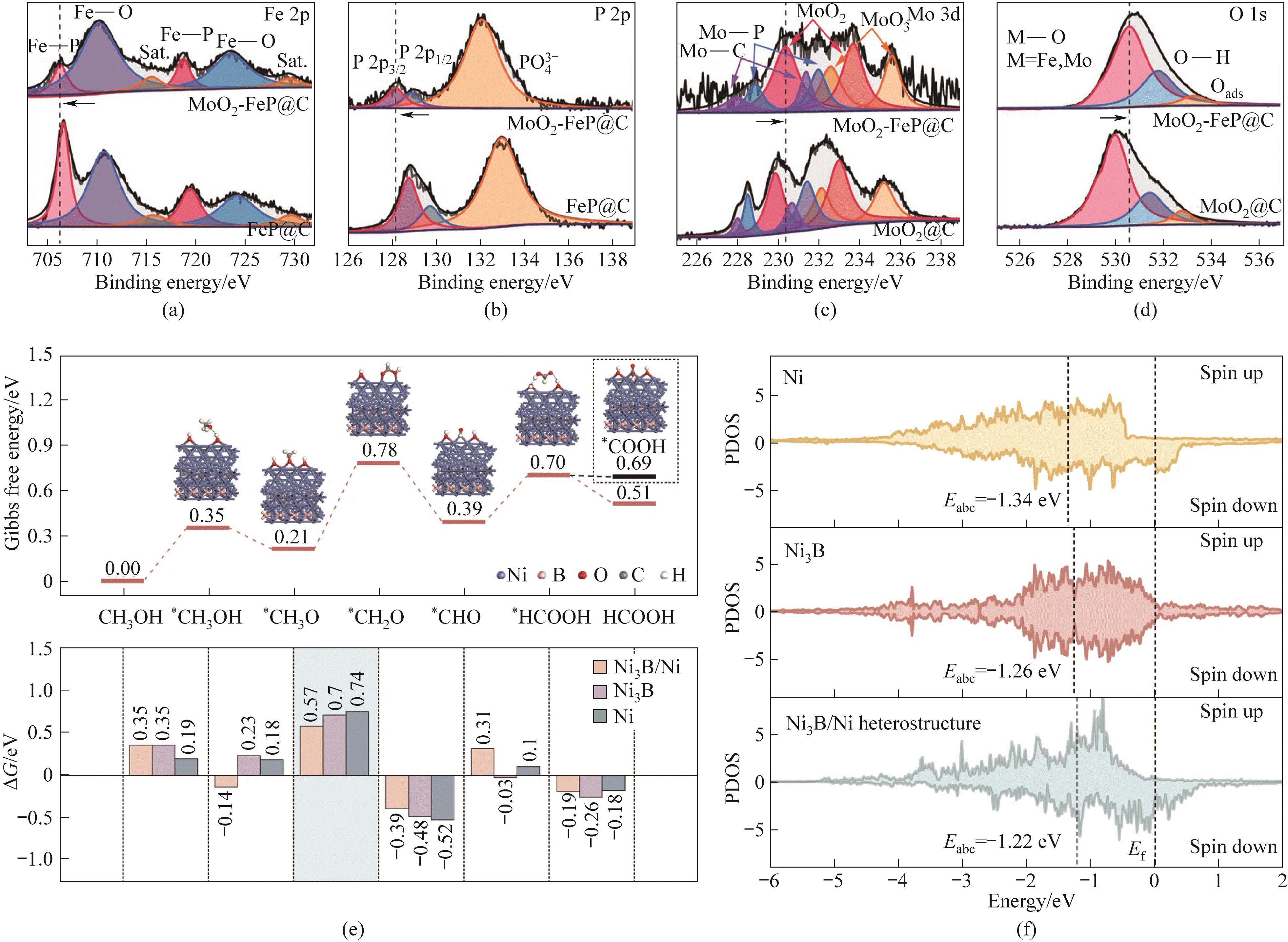
Fig.5 MoO2-FeP@C and FeP@C XPS spectra of (a) Fe 2p, (b) P 2p, (c) Mo 3d, (d) O 1s; (e) MOR Gibbs free energy diagram on Ni3B/Ni heterostructure (top) and Gibbs free energy variation between steps on different surfaces (bottom); (f) Partial density of states (PDOS) of the d-projection DOS of Ni3B (001)/Ni (111) heterostructures and Ni active sites in Ni3B and Ni[59,61]
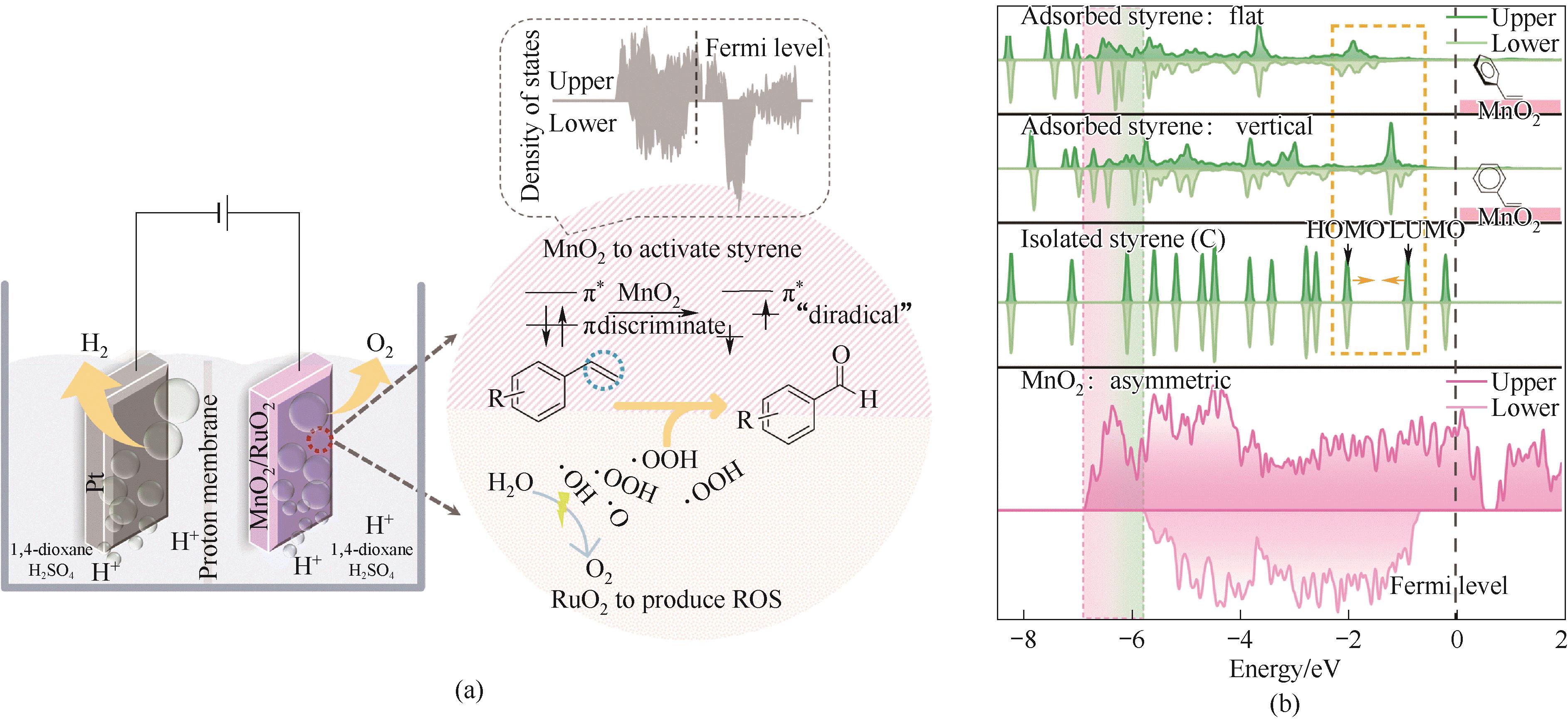
Fig.6 (a) Schematic diagram of MnO2 and RuO2 used for activating styrene vinyl and generating ROS; (b) The total DOS of MnO2 (131) before and after adsorption, as well as the partial electronic density of states of styrene[66]

Fig.7 (a)In situ EIS spectra with substrate 50 mmol/L HMF added; (b) In situ EIS spectra without 50 mmol/L HMF substrate addition; (c) The electrode internal oxidation resistance (Rp) of Vo-Co3O4 and Co3O4; (d) The electrode interface reaction resistance (Rct) of Vo-Co3O4 and Co3O4
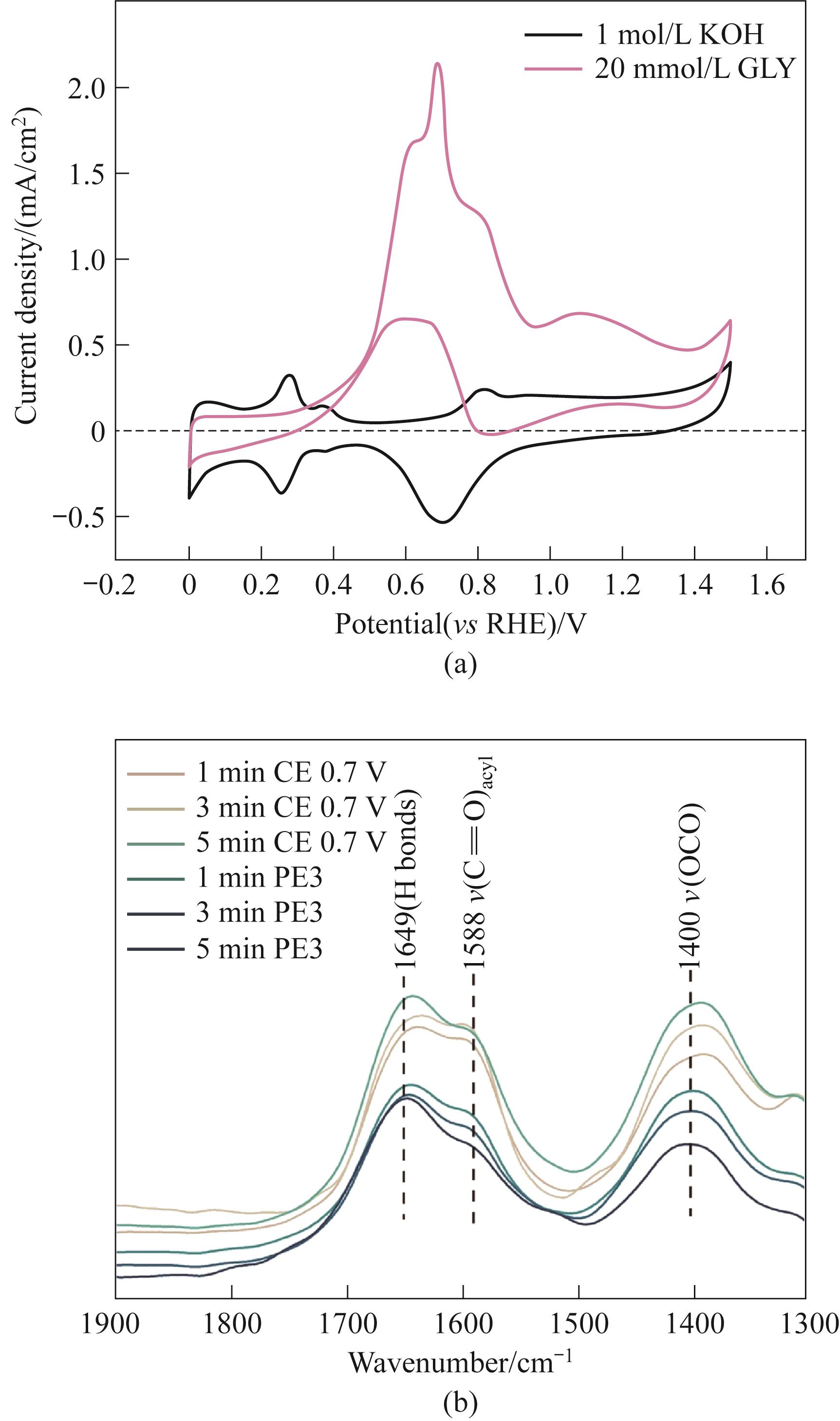
Fig.9 (a) CV curves of Pt@G in electrolytes with and without GLY (glycerol); (b) In situ FTIR spectroscopy of Pt@G with PE3 (pulse electrolysis) and CE (constant potential electrolysis) at different time under 0.7 V[74]
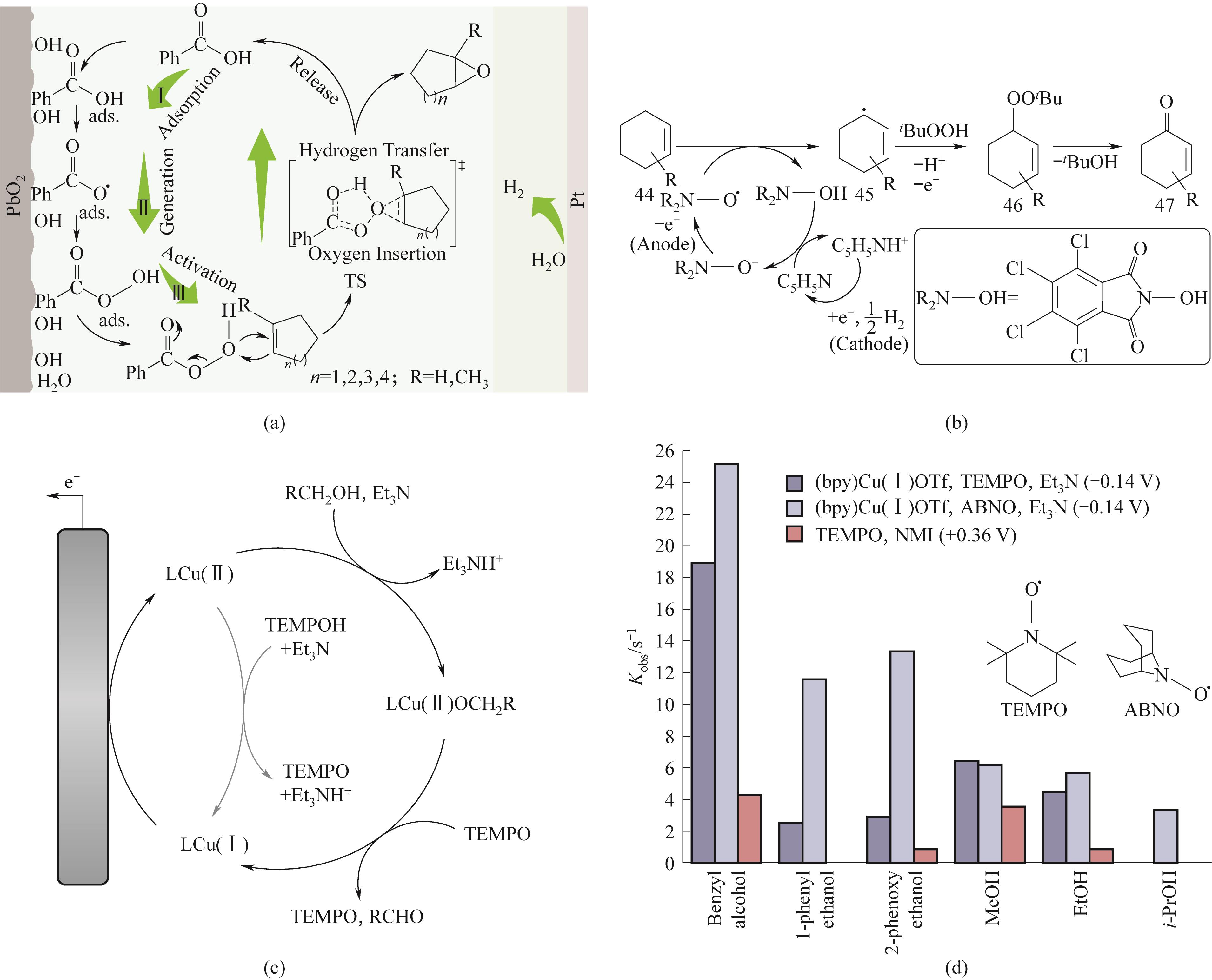
Fig.10 (a)Schematic diagram of the mechanism for achieving sustainable epoxidation of olefins by using carboxylic acid as a recyclable peroxide mediator; (b) Schematic diagram of the reaction mechanism of Cl4NHPI as a dehydrogenation agent; (c) Schematic diagram of the reaction mechanism of (bpy)Cu/TEMPO co-catalyst system; (d) Relative catalytic activity of three different catalyst systems with six different benzyl, aliphatic, primary, and secondary alcohols[80,82-83]
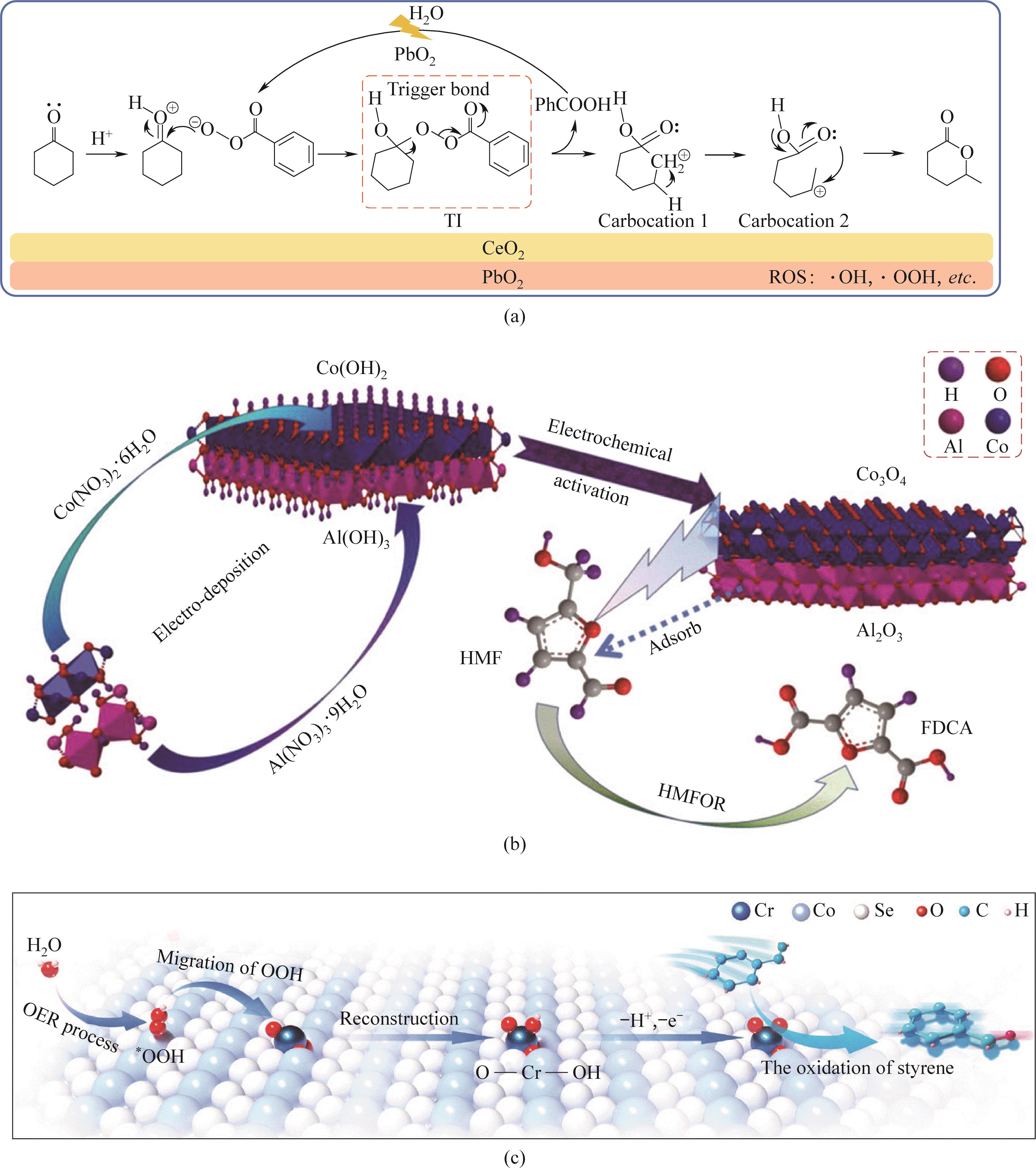
Fig.11 (a)Schematic diagram of the mechanism of Baeyer-Villiger reaction using CeO2@PbO2@Ti electrode; (b) Schematic diagram of Al(OH)3/Co(OH)2 synthesis and electrochemical system of HMFOR; (c) A schematic diagram illustrating the reaction pathway of a series reaction[88-90]
| [1] | Tang W S, Zhang L N, Qiu T Y, et al. Efficient conversion of biomass to formic acid coupled with low energy consumption hydrogen production from water electrolysis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(30): e202305843. |
| [2] | Wang J Y, Yang J B, Feng Y, et al. Comparative experimental study of alkaline and proton exchange membrane water electrolysis for green hydrogen production[J]. Applied Energy, 2025, 379: 124936. |
| [3] | Liu M, Yao Z D, Gu J, et al. Issues and opportunities facing hydrolytic hydrogen production materials[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 461: 141918. |
| [4] | Volta A. On the electricity excited by the mere contact of conducting substances of different kinds[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, 1800, 90: 403-431. |
| [5] | Faraday H M. Experimental researches in electricity. First series[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, 1837, 18(121): 125-162. |
| [6] | Faraday M. Siebente reihe von experimental-untersuchungen über elektricität[J]. Annalen der Physik, 1834, 109(31/32/33/34): 481-520. |
| [7] | Kolbe H. Beobachtungen über die oxydirende Wirkung des Sauerstoffs, wenn derselbe mit Hülfe einer elektrischen Säule entwickelt wird[J]. Journal Für Praktische Chemie, 1847, 41(1): 137-139. |
| [8] | Heyrovský J. Electrolysis with a dropping mercury cathode(part Ⅰ): Deposition of alkali and alkaline earth[J]. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science, 1923, 45(266): 303-315. |
| [9] | Baizer M M. Electrolytic reductive coupling[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1964, 111(2): 215. |
| [10] | Baizer M M. Recent developments in organic synthesis by electrolysis[J]. Tetrahedron, 1984, 40(6): 935-969. |
| [11] | Simons J H. Production of fluorocarbons(Ⅰ): The generalized procedure and its use with nitrogen compounds[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1949, 95: 47-67. |
| [12] | Steckhan E. Organic syntheses with electrochemically regenerable redox systems[C]//Electrochemistry Ⅰ. Berlin, Heidelbery: Springer, 1987: 1-69. |
| [13] | Steckhan E. Indirect electroorganic syntheses: a modern chapter of organic electrochemistry[new synthetic methods(59)][J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 1986, 25(8): 683-701. |
| [14] | Yoshida J I, Murata T, Isoe S. Electrochemical oxidation of organosilicon compounds(Ⅰ): Oxidative cleavage of carbon-silicon bond in allylsilanes and benzylsilanes[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 1986, 27(29): 3373-3376. |
| [15] | Hammer B, Norskov J K. Why gold is the noblest of all the metals[J]. Nature, 1995, 376(6537): 238-240. |
| [16] | Grabowski G, Lewkowski J, Skowroński R. The electrochemical oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural with the nickel oxide/hydroxide electrode[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1991, 36(13): 1995. |
| [17] | Gandeepan P, Finger L H, Meyer T H, et al. 3d metallaelectrocatalysis for resource economical syntheses[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(13): 4254-4272. |
| [18] | Zhu C J, Ang N W J, Meyer T H, et al. Organic electrochemistry: molecular syntheses with potential[J]. ACS Central Science, 2021, 7(3): 415-431. |
| [19] | Jiao K J, Xing Y K, Yang Q L, et al. Site-selective C—H functionalization via synergistic use of electrochemistry and transition metal catalysis[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2020, 53(2): 300-310. |
| [20] | Yuan Y, Lei A W. Electrochemical oxidative cross-coupling with hydrogen evolution reactions[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2019, 52(12): 3309-3324. |
| [21] | Xia T, Yang J R, Ren Q H, et al. Promoting alcohols electrooxidation coupled with hydrogen production via asymmetric pulse potential strategy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2025, 64(9): e202420992. |
| [22] | 谢文富, 邵明飞, 段雪. 电解水制氢之提效降本[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2021, 52(10): 18-24. |
| Xie W F, Shao M F, Duan X. Boosting efficiency and reducing cost of hydrogen production from electrochemical water splittinng[J]. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals, 2021, 52(10): 18-24. | |
| [23] | 夏天, 栗振华, 邵明飞, 等. 电解水制氢耦合有机物氧化研究进展[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2024, 55(1): 42-51. |
| Xia T, Li Z H, Shao M F, et al. Research progress in electrocatalytic organic oxidation coupled with hydrogen production[J]. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals, 2024, 55(1): 42-51. | |
| [24] | Li J, Duan H H. Recent progress in energy-saving hydrogen production by coupling with value-added anodic reactions[J]. Chem, 2024, 10(10): 3008-3039. |
| [25] | Li J C, Ma Y Q, Mu X G, et al. Recent advances and perspectives on coupled water electrolysis for energy-saving hydrogen production[J]. Advanced Science, 2025, 12(7): e2411964. |
| [26] | Barlocco I, Cipriano L A, Di Liberto G, et al. Does the oxygen evolution reaction follow the classical OH*, O*, OOH* path on single atom catalysts?[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2023, 417: 351-359. |
| [27] | Lee T H, Lee S A, Park H, et al. Understanding the enhancement of the catalytic properties of goethite by transition metal doping: critical role of O* formation energy relative to OH* and OOH*[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3(2): 1634-1643. |
| [28] | Xu X M, Zhang Y M, Chen Y, et al. Revealing *OOH key intermediates and regulating H2O2 photoactivation by surface relaxation of Fenton-like catalysts[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2022, 119(36): e2205562119. |
| [29] | Fan L, Wang D, Ma K, et al. Recent advances in hydrogen production from hybrid water electrolysis through alternative oxidation reactions[J]. ChemCatChem, 2024, 16(5): e202301332. |
| [30] | Garlyyev B, Xue S, Fichtner J, et al. Prospects of value-added chemicals and hydrogen via electrolysis[J]. ChemSusChem, 2020, 13(10): 2513-2521. |
| [31] | Deng C, Toe C Y, Li X, et al. Earth-abundant metal-based electrocatalysts promoted anodic reaction in hybrid water electrolysis for efficient hydrogen production: recent progress and perspectives[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(25): 2201047. |
| [32] | Vadivel N, Murthy A P. Recent developments in membrane-free hybrid water electrolysis for low-cost hydrogen production along with value-added products[J]. Small, 2024, 20(52): e2407845. |
| [33] | Wei Z D, Huang X, Duan H H, et al. Electrochemical synthesis in company with hydrogen production via renewable energy: opportunities and challenges[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2024, 58: 1-6. |
| [34] | 向阳, 黄寻, 魏子栋. 电催化有机合成反应的活性和选择性调控研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(8): 4005-4014. |
| Xiang Y, Huang X, Wei Z D. Recent progresses in the activity and selectivity improvement of electrocatalytic organic synthesis[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(8): 4005-4014. | |
| [35] | Ren J T, Chen L, Wang H Y, et al. Water electrolysis for hydrogen production: from hybrid systems to self-powered/catalyzed devices[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(1): 49-113. |
| [36] | Cheng J, Xiang Y, Huang X, et al. Reducing energy costs during hydrogen production from water electrolysis by coupling small molecule oxidation: from molecular catalysis to industrial exploration[J]. Precision Chemistry, 2024, 2(9): 447-470. |
| [37] | Zhang J F, Shen Y, Wu Z L, et al. Efficient alkaline-free electrooxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid using electrochemically-charged Ni x Co1- x (OH)2 as a redox mediator[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2025, 64(13): e202423109. |
| [38] | Wang D, Lu X Y, Xu H Y, et al. Selective synthesis of formyl-2-furancarboxylic acid via enhanced adsorption of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural on composite catalysts[J]. ChemCatChem, 2024, 16(18): e202400449. |
| [39] | Li Y H, Alorku K, Shen C, et al. In-situ redispersion of Ni@C catalyst boosts 5-hydroxymethylfurfural electrooxidation by increasing Ni4+ sites[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2024, 357: 124250. |
| [40] | Pan X, Sun L Z, Zhou Z Y, et al. Positive electronic nickel active site enhances N—H/C—H bonds breaking for electrooxidation of amines to nitriles coupling with hydrogen production[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(23): 2400374. |
| [41] | Chen L, Yin Z H, Cui J Y, et al. Unlocking lattice oxygen on selenide-derived NiCoOOH for amine electrooxidation and efficient hydrogen production[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(39): 27090-27099. |
| [42] | Sun L Z, Pan X, Xie Y N, et al. Accelerated dynamic reconstruction in metal-organic frameworks with ligand defects for selective electrooxidation of amines to azos coupling with hydrogen production[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(21): e202402176. |
| [43] | Liu G H, Nie T Q, Wang H J, et al. Size sensitivity of supported palladium species on layered double hydroxides for the electro-oxidation dehydrogenation of hydrazine: from nanoparticles to nanoclusters and single atoms[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(17): 10711-10717. |
| [44] | Zhu L B, Huang J, Meng G, et al. Active site recovery and N—N bond breakage during hydrazine oxidation boosting the electrochemical hydrogen production[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 1997. |
| [45] | Zhu Y, Chen Y X, Feng Y F, et al. Constructing Ru—O—TM bridge in NiFe-LDH enables high current hydrazine-assisted H2 production[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(30): e2401694. |
| [46] | Sun H C, Luo Z E, Chen M P, et al. Manipulating trimetal catalytic activities for efficient urea electrooxidation-coupled hydrogen production at ampere-level current densities[J]. ACS Nano, 2024, 18(52): 35654-35670. |
| [47] | Zhan G M, Hu L F, Li H, et al. Highly selective urea electrooxidation coupled with efficient hydrogen evolution[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 5918. |
| [48] | Xiong H C, Yu P P, Chen K D, et al. Urea synthesis via electrocatalytic oxidative coupling of CO with NH3 on Pt[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2024, 7(7): 785-795. |
| [49] | Yu Y H, Chen Q R, Li J, et al. Progress in the development of heteroatom-doped nickel phosphates for electrocatalytic water splitting[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 607: 1091-1102. |
| [50] | Xiao J H, Duan C P, Song J L, et al. Research progress of single-atomic series catalysts for anodic coupled electrolysis of water and small molecules[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 500: 157208. |
| [51] | Sun L Z, Zhou Z Y, Xie Y N, et al. Surface self-reconstruction of Fe-Ni3S2 electrocatalyst for value-generating nitrile evolution reaction to drive efficient hydrogen production[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(33): 2301884. |
| [52] | Qin H Y, Ye Y K, Lin G L, et al. Regulating the electrochemical microenvironment of Ni(OH)2 by Cr doping for highly efficient methanol electrooxidation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2024, 14(21): 16234-16244. |
| [53] | Xiao C Q, Cheng L, Wang Y T, et al. Low full-cell voltage driven high-current-density selective paired formate electrosynthesis[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(3): 1329-1335. |
| [54] | Fang Y, Dai C F, Liu X Y, et al. Sulfur-doped manganese-cobalt hydroxide with promoted surface reconstruction for glycerol electrooxidation assisted hydrogen production[J]. Nano Energy, 2024, 127: 109754. |
| [55] | Liu Y, Zhang J H, Li Y P, et al. Manipulating dehydrogenation kinetics through dual-doping Co3N electrode enables highly efficient hydrazine oxidation assisting self-powered H2 production[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1853. |
| [56] | Geng J R, Zhu Z, Ni Y X, et al. Biaxial strained dual-phase palladium-copper bimetal boosts formic acid electrooxidation[J]. Nano Research, 2022, 15(1): 280-284. |
| [57] | Chen Y J, Pei J J, Chen Z, et al. Pt atomic layers with tensile strain and rich defects boost ethanol electrooxidation[J]. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(18): 7563-7571. |
| [58] | Feng C, Lv M Y, Shao J X, et al. Lattice strain engineering of Ni2P enables efficient catalytic hydrazine oxidation-assisted hydrogen production[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(42): 2305598. |
| [59] | Yang G C, Jiao Y Q, Yan H J, et al. Interfacial engineering of MoO2-FeP heterojunction for highly efficient hydrogen evolution coupled with biomass electrooxidation[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(17): e2000455. |
| [60] | Wu J, Wang K, Yu T Q, et al. Amorphous-crystalline heterostructure: efficient catalyst for biomass oxidation coupled with hydrogen evolution[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2024, 655: 676-684. |
| [61] | Qi Y B, Zhang Y, Yang L, et al. Insights into the activity of nickel boride/nickel heterostructures for efficient methanol electrooxidation[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 4602. |
| [62] | Li Y, Jiao Y Q, Yan H J, et al. Mo-Ni-based heterojunction with fine-customized d-band centers for hydrogen production coupled with benzylamine electrooxidation in low alkaline medium[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(39): e202306640. |
| [63] | Lu Y X, Liu T Y, Huang Y C, et al. Integrated catalytic sites for highly efficient electrochemical oxidation of the aldehyde and hydroxyl groups in 5-hydroxymethylfurfural[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(7): 4242-4251. |
| [64] | Song Y J, Li Z H, Fan K, et al. Ultrathin layered double hydroxides nanosheets array towards efficient electrooxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural coupled with hydrogen generation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 299: 120669. |
| [65] | Yang C, Shang S S, Li X Y. Oxygen-vacancy-enriched substrate-less SnO x /La-Sb anode for high-performance electrocatalytic oxidation of antibiotics in wastewater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 436: 129212. |
| [66] | Luo X X, Tang X X, Ni J T, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of styrene to benzaldehyde by discrimination of spin-paired π electrons[J]. Chemical Science, 2023, 14(7): 1679-1686. |
| [67] | Zeng Z W, Wu S T, Huang X, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of furfural on NiMoP/NF: boosting current density with enhanced adsorption of oxygenates[J]. Small, 2024, 20(4): e2305462. |
| [68] | Jin K, Maalouf J H, Lazouski N, et al. Epoxidation of cyclooctene using water as the oxygen atom source at manganese oxide electrocatalysts[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(15): 6413-6418. |
| [69] | Gao L F, Liu Z B, Ma J L, et al. NiSe@NiO x core-shell nanowires as a non-precious electrocatalyst for upgrading 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 261: 118235. |
| [70] | Lu Y X, Liu T Y, Dong C L, et al. Tailoring competitive adsorption sites by oxygen-vacancy on cobalt oxides to enhance the electrooxidation of biomass[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(2): e2107185. |
| [71] | Han S Y, Wang C H, Shi Y M, et al. Membrane-free selective oxidation of thioethers with water over a nickel phosphide nanocube electrode[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2021, 2(6): 100462. |
| [72] | Wu B J, Li J R, Luo X X, et al. A round-trip journey of electrons: electron catalyzed direct fixation of N2 to azos[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2025, 68: 386-393. |
| [73] | Xia Z C, Ma C Y, Fan Y, et al. Vacancy optimized coordination on nickel oxide for selective electrocatalytic oxidation of glycerol[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2024, 14(3): 1930-1938. |
| [74] | Chen W, Zhang L, Xu L T, et al. Pulse potential mediated selectivity for the electrocatalytic oxidation of glycerol to glyceric acid[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 2420. |
| [75] | Boudjelel M, Zhong J, Ballerini L, et al. Electrochemical generation of aryl radicals from organoboron reagents enabled by pulsed electrosynthesis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(31): e202406203. |
| [76] | Atkins A P, Chaturvedi A K, Tate J A, et al. Pulsed electrolysis: enhancing primary benzylic C(sp3)—H nucleophilic fluorination[J]. Organic Chemistry Frontiers, 2024, 11(3): 802-808. |
| [77] | Zeng L, Yang Q H, Wang J X, et al. Programmed alternating current optimization of Cu-catalyzed C—H bond transformations[J]. Science, 2024, 385(6705): 216-223. |
| [78] | Wan Q Q, Chen K X, Dong X, et al. Elucidating the underlying reactivities of alternating current electrosynthesis by time-resolved mapping of short-lived reactive intermediates[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(40): e202306460. |
| [79] | Lee B, Naito H, Nagao D M, et al. Alternating-current electrolysis for the production of phenol from benzene[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(28): 6961-6965. |
| [80] | Luo X X, Wu B J, Li J R, et al. Benzoic acid: electrode-regenerated molecular catalyst to boost cycloolefin epoxidation[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(37): 20665-20671. |
| [81] | Hoque M A, Jiang T X, Poole D L, et al. Manganese-mediated electrochemical oxidation of thioethers to sulfoxides using water as the source of oxygen atoms[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(31): 21960-21967. |
| [82] | Horn E J, Rosen B R, Chen Y, et al. Scalable and sustainable electrochemical allylic C—H oxidation[J]. Nature, 2016, 533(7601): 77-81. |
| [83] | Badalyan A, Stahl S S. Cooperative electrocatalytic alcohol oxidation with electron-proton-transfer mediators[J]. Nature, 2016, 535(7612): 406-410. |
| [84] | Rafiee M, Alherech M, Karlen S D, et al. Electrochemical aminoxyl-mediated oxidation of primary alcohols in lignin to carboxylic acids: polymer modification and depolymerization[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(38): 15266-15276. |
| [85] | McLoughlin E A, Armstrong K C, Waymouth R M. Electrochemically regenerable hydrogen atom acceptors: mediators in electrocatalytic alcohol oxidation reactions[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(19): 11654-11662. |
| [86] | Sun Y X, Li X S, Yang M, et al. Highly selective electrocatalytic oxidation of benzyl C—H using water as safe and sustainable oxygen source[J]. Green Chemistry, 2020, 22(21): 7543-7551. |
| [87] | Behera S, Ganguly S, Loha C, et al. Critical role of interface design in acceleration of overall water splitting and hybrid electrolysis process: state of the art and perspectives[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2023, 37(11): 7603-7633. |
| [88] | Luo X X, Wang Y F, Wu B J, et al. A stepwise electrochemical baeyer-villiger oxidation with water as the oxygen source[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2024, 15(42): 10435-10441. |
| [89] | Dai H L, Huang Y F, Bai H Y, et al. Adsorption-activation bifunctional center of Al/CO-base catalyst for boosting 5-hydroxymethylfurfural oxidation[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(43): 2402789. |
| [90] | Dang K, Dong H L, Wang L G, et al. Boosting electrochemical styrene transformation via tandem water oxidation over a single-atom Cr1/CoSe2 catalyst[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(27): e2200302. |
| [91] | Li Z H, Li X F, Zhou H, et al. Electrocatalytic synthesis of adipic acid coupled with H2 production enhanced by a ligand modification strategy[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 5009. |
| [92] | Li L, Zhang Z Y, Chen H T, et al. Promoting electrocatalytic alcohols oxidation coupled with H2 production via ligand intercalation strategy[J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16(4): 4596-4602. |
| [1] | Jiaxin LUO, Yan YUAN. Research progress of piezoelectric materials in solid-state metal secondary batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3822-3833. |
| [2] | Yitong ZHOU, Mingxi ZHOU, Ruochen LIU, Shuang YE, Weiguang HUANG. Technical and economic analysis on hydrogen based direct reduction steelmaking co-driven by photovoltaic and power grid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4318-4330. |
| [3] | Xiayu FAN, Jianchen SUN, Keying LI, Xinya YAO, Hui SHANG. Machine learning drives system optimization of liquid organic hydrogen storage technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [4] | Ning YANG, Haonan LI, Xiao LIN, Stella GEORGIADOU, Wen-Feng LIN. Application of plastic-derived carbon@CoMoO4 composites as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction in water electrolysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [5] | Xinran LI, Longjiao CHANG, Shaohua LUO, Yongbing LI, Ruifen YANG, Zenglei HOU, Jie ZOU. Modification mechanism of Ho doped NCM622 induced local electron remodeling to inhibit cationic mixing [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3733-3741. |
| [6] | Lixiao WU, Xixi YAN, Suna ZHANG, Yiming XU, Jiaying QIAN, Yongmin QIAO, Lijun WANG. The preparation of phosphorus-doped microcrystalline graphite and its electrochemical performance as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3615-3625. |
| [7] | Ziheng WANG, Wenhuai LI, Wei ZHOU. Application of patterned electrodes in solid oxide fuel cell [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3153-3171. |
| [8] | Peiqiang CHEN, Qun ZHENG, Yuting JIANG, Chunhua XIONG, Jinmao CHEN, Xudong WANG, Long HUANG, Man RUAN, Wanli XU. Effects of electrolyte flow rate and current density on the output performance of seawater-activated batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3235-3245. |
| [9] | Jiaxiang CHEN, Wei ZHOU, Xuewei ZHANG, Lijie WANG, Yuming HUANG, Yang YU, Miaoting SUN, Wanjing LI, Junshu YUAN, Hongbo ZHANG, Xiaoxiao MENG, Jihui GAO, Guangbo ZHAO. Simulation study on the hydrogen production performance of a two-dimensional PEMWE model under pulsed voltage [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3521-3530. |
| [10] | Guoqing SUN, Haibo LI, Zhiyang DING, Wenhui GUO, Hao XU, Yanxia ZHAO. Research progress of silicon based anode materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3197-3211. |
| [11] | Tianhao WU, Tingwei YE, Yan LIN, Zhen HUANG. In-situ hydrogen supplementation of biomass chemical looping gasification to produce syngas with controllable H2/CO [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3498-3508. |
| [12] | Pengwei LIAO, Qinghui LIU, An PAN, Jiayue WANG, Xiaogui FU, Siyu YANG, Hao YU. Wind power hydrogen production systems considering uncertainty: multi-time scale operation strategy [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2743-2754. |
| [13] | Fenhong SONG, Wenguang WANG, Liang GUO, Jing FAN. Modulation of TiO2 by C-element modified g-C3N4 and photocatalytic hydrogen production performance of composites [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2983-2994. |
| [14] | Haiyan JI, Jiayin LIU, Haijun WU, Jinglin HE, Ziheng JIN, Dianhang WEI, Xia JIANG. Research progress on the application of low-temperature plasma in biomass gasification to produce hydrogen [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2419-2433. |
| [15] | Chang ZHANG, Qiang XIE, Yutong SHA, Bingjie WANG, Dingcheng LIANG, Jinchang LIU. Preparation of bamboo char with low ash and silicon content and electrochemical properties of its derived hard carbon [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 3073-3083. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||