CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (8): 3805-3821.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250289
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiayu FAN1( ), Jianchen SUN1, Keying LI1, Xinya YAO2, Hui SHANG1(
), Jianchen SUN1, Keying LI1, Xinya YAO2, Hui SHANG1( )
)
Received:2025-03-24
Revised:2025-04-06
Online:2025-09-17
Published:2025-08-25
Contact:
Hui SHANG
范夏雨1( ), 孙建辰1, 李可莹1, 姚馨雅2, 商辉1(
), 孙建辰1, 李可莹1, 姚馨雅2, 商辉1( )
)
通讯作者:
商辉
作者简介:范夏雨(1998—),女,博士研究生,fanxiayu2022@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xiayu FAN, Jianchen SUN, Keying LI, Xinya YAO, Hui SHANG. Machine learning drives system optimization of liquid organic hydrogen storage technology[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821.
范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
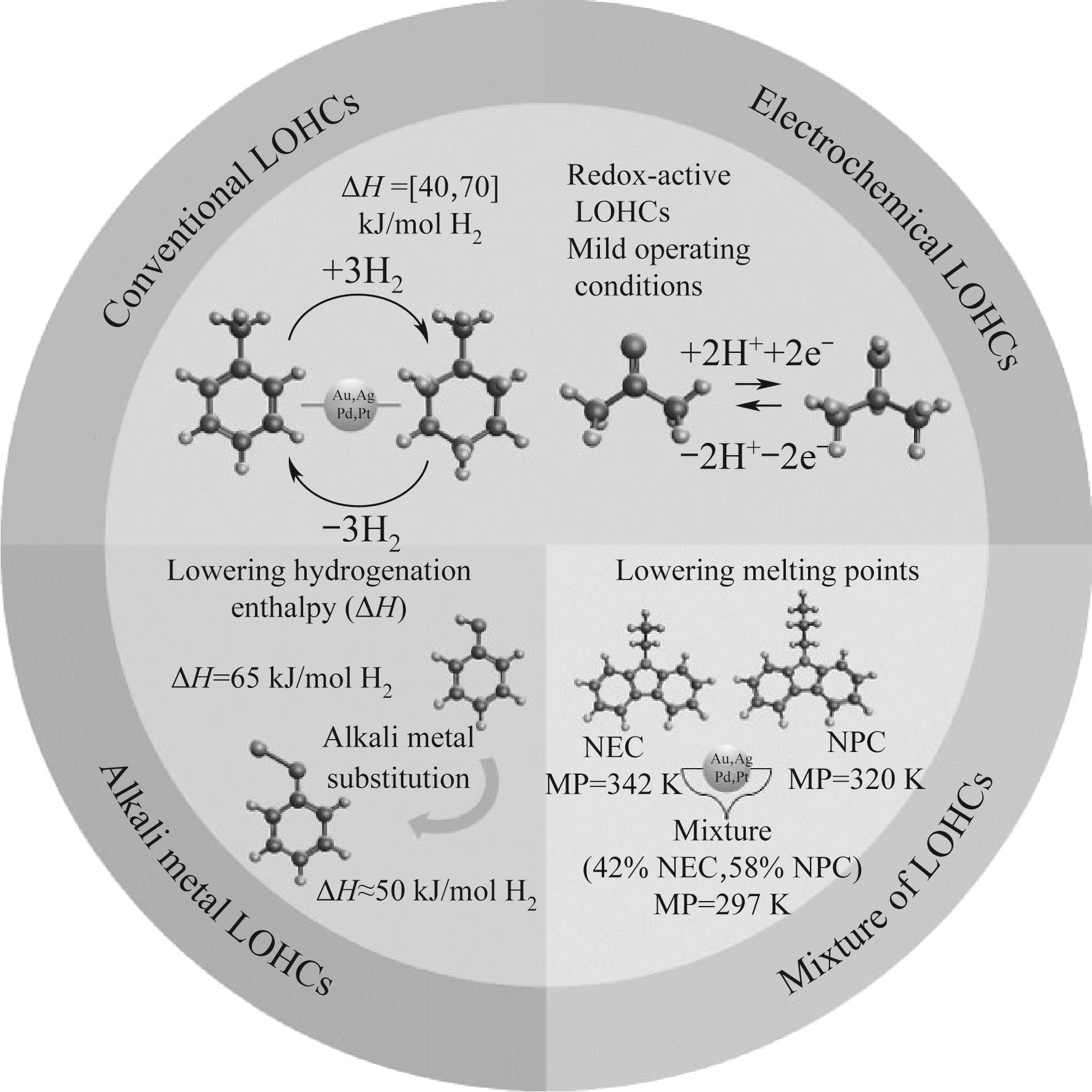
Fig.7 Four categories of LOHCs molecules: conventional, electrochemical, alkali metal and mixtures of LOHCs(MP stands for melting point, ΔH is dehydrogenation enthalpy)[44]
| 储氢体系 | 目标值 | 特征值 | 最优ML模型 | 精度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲酸[ | 甲酸在M@g-C3N4上的吸附能 | M—N键长、电荷转移量、M-g-C3N4内聚能、金属原子d带中心、电负性、电子亲和力、第一电离能、共价半径、荣格半径、d轨道电子数和原子序数等 | GBR模型 | 训练集R2=1,RMSE=0.00 eV;测试集R2=0.92,RMSE=0.07 eV |
| 甲醇 | 筛选催化剂[ | 原子序数、原子量、电负性、电离能、电子亲和能、原子半径、离子半径、氧化态、电子构型、价电子数、金属性、非金属性、电导率、热导率、硬度、熔点、沸点、密度、磁性等 | PMC-IGM模型 | 准确率61%,兰德指数97% |
| Cu/ZnO/Al₂O₃的铜表面积[ | Cu/Zn、Al%、老化时间、老化温度、pH、沉淀剂、煅烧时间、煅烧温度等 | RF分类模型 | 训练集准确率90.0%,测试集准确率94.7% | |
| MCH[ | 脱氢中间体的吸附能 | 配位数、内聚能、电负性以及所有不饱和碳与其最近的金属原子之间的平均键长(d̅C—Pt/M) | GPR模型 | 训练集MAE=0.05 eV,验证集MAE=0.13 eV,测试集MAE=0.12 eV |
| 12H-NECZ[ | 反应的Gibbs自由能 | 各种二维和三维描述符,包括OpenBabel 描述符、库仑矩阵、Bag of bonds、Fractional buried volumes等 | 深度神经网络 | — |
Table 1 Comprehensive cases of ML assisting catalyst design
| 储氢体系 | 目标值 | 特征值 | 最优ML模型 | 精度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲酸[ | 甲酸在M@g-C3N4上的吸附能 | M—N键长、电荷转移量、M-g-C3N4内聚能、金属原子d带中心、电负性、电子亲和力、第一电离能、共价半径、荣格半径、d轨道电子数和原子序数等 | GBR模型 | 训练集R2=1,RMSE=0.00 eV;测试集R2=0.92,RMSE=0.07 eV |
| 甲醇 | 筛选催化剂[ | 原子序数、原子量、电负性、电离能、电子亲和能、原子半径、离子半径、氧化态、电子构型、价电子数、金属性、非金属性、电导率、热导率、硬度、熔点、沸点、密度、磁性等 | PMC-IGM模型 | 准确率61%,兰德指数97% |
| Cu/ZnO/Al₂O₃的铜表面积[ | Cu/Zn、Al%、老化时间、老化温度、pH、沉淀剂、煅烧时间、煅烧温度等 | RF分类模型 | 训练集准确率90.0%,测试集准确率94.7% | |
| MCH[ | 脱氢中间体的吸附能 | 配位数、内聚能、电负性以及所有不饱和碳与其最近的金属原子之间的平均键长(d̅C—Pt/M) | GPR模型 | 训练集MAE=0.05 eV,验证集MAE=0.13 eV,测试集MAE=0.12 eV |
| 12H-NECZ[ | 反应的Gibbs自由能 | 各种二维和三维描述符,包括OpenBabel 描述符、库仑矩阵、Bag of bonds、Fractional buried volumes等 | 深度神经网络 | — |
| 储氢体系 | 目标值 | 特征值 | 最优ML模型 | 精度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲醇 | 产氢速率[ | 反应条件(GHSV、温度、S/C、O2/C、催化剂质量等)、元素以及元素描述符 | DTR模型 | R2=0.99762 MSE=2.8150×10-7 MAE=4.6309×10-5 |
| 技术性能:氢气产率 | 反应器数量、操作温度、氢气渗透率、膜面积、吹扫气流量、S/C 反应器成本、压缩机成本、人工成本、反应物成本、天然气成本、电力成本 | DTR | RMSE=0.00132 | |
| 环境性能:二氧化碳排放率 | SVR、DTR、GPR | 均能较好地拟合数据 | ||
| 经济性能:单位氢气生产成本[ | GPR | |||
| CH3OH转化率和H2产率[ | 进料气体温度、S/C和Reynolds数等 | 基于反向传播网络的神经网络(NN)模型 | H₂产率和CH₃OH转化率的预测误差分别为0.206%和1.004% | |
| 甲酸[ | 甲酸转化率 | 温度、时间、甲酸浓度、催化剂尺寸、催化剂质量、甲酸钠浓度和溶液体积等 | ET模型 | RMSE=3.16,R2=0.97,MAE=0.75 |
| DBT/H18-DBT | DBT储氢能力预测 | 各种反应参数(如底物、催化剂、试剂、添加剂、溶剂、浓度、温度以及反应器类型等) | ① HSP-SVM模型[ ② HSPS-WFML模型[ ③ HSPSML模型[ | ① HV方法准确率97.0% ② 总体准确率96.40%,误分类率3.60% ③ BR和SCG准确率均为98.70% |
| H18-DBT脱氢反应[ | 温度、压力、催化剂用量、搅拌速率和反应物浓度等 | HPPSML模型 | 整体准确率89.80% |
Table 2 Comprehensive cases of ML assisting reaction condition optimization
| 储氢体系 | 目标值 | 特征值 | 最优ML模型 | 精度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲醇 | 产氢速率[ | 反应条件(GHSV、温度、S/C、O2/C、催化剂质量等)、元素以及元素描述符 | DTR模型 | R2=0.99762 MSE=2.8150×10-7 MAE=4.6309×10-5 |
| 技术性能:氢气产率 | 反应器数量、操作温度、氢气渗透率、膜面积、吹扫气流量、S/C 反应器成本、压缩机成本、人工成本、反应物成本、天然气成本、电力成本 | DTR | RMSE=0.00132 | |
| 环境性能:二氧化碳排放率 | SVR、DTR、GPR | 均能较好地拟合数据 | ||
| 经济性能:单位氢气生产成本[ | GPR | |||
| CH3OH转化率和H2产率[ | 进料气体温度、S/C和Reynolds数等 | 基于反向传播网络的神经网络(NN)模型 | H₂产率和CH₃OH转化率的预测误差分别为0.206%和1.004% | |
| 甲酸[ | 甲酸转化率 | 温度、时间、甲酸浓度、催化剂尺寸、催化剂质量、甲酸钠浓度和溶液体积等 | ET模型 | RMSE=3.16,R2=0.97,MAE=0.75 |
| DBT/H18-DBT | DBT储氢能力预测 | 各种反应参数(如底物、催化剂、试剂、添加剂、溶剂、浓度、温度以及反应器类型等) | ① HSP-SVM模型[ ② HSPS-WFML模型[ ③ HSPSML模型[ | ① HV方法准确率97.0% ② 总体准确率96.40%,误分类率3.60% ③ BR和SCG准确率均为98.70% |
| H18-DBT脱氢反应[ | 温度、压力、催化剂用量、搅拌速率和反应物浓度等 | HPPSML模型 | 整体准确率89.80% |
| [1] | Olhoff A, Bataille C. Emissions Gap Report 2024: No more hot air … please! With a massive gap between rhetoric and reality, countries draft new climate commitments[R]. Nairobi: United Nations Environment Programme, 2024. |
| [2] | Kearney A T. 2024 statistical review of world energy[R]. London: Energy Institute, 2024. |
| [3] | Sun J C, Shang H, Miao C, et al. Microwave enhanced hydrogen production from liquid organic hydrogen carriers: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2023, 190: 109432. |
| [4] | 舟丹. 氢能将成为我国深度脱碳的关键选择[J]. 中外能源, 2025, 30(1): 37. |
| Zhou D. Hydrogen energy will become the key choice for deep decarbonization in China[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2025, 30(1): 37. | |
| [5] | 张丝钰, 张宁, 卢静, 等. 绿氢示范项目模式分析与发展展望[J]. 南方能源建设, 2023, 10(3): 89-96. |
| Zhang S Y, Zhang N, Lu J, et al. Analysis and development outlook on the typical modes of green hydrogen projects[J]. Southern Energy Construction, 2023, 10(3): 89-96. | |
| [6] | Hren R, Vujanović A, Van Fan Y, et al. Hydrogen production, storage and transport for renewable energy and chemicals: an environmental footprint assessment[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2023, 173: 113113. |
| [7] | Muhammed N S, Gbadamosi A O, Epelle E I, et al. Hydrogen production, transportation, utilization, and storage: recent advances towards sustainable energy[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 73: 109207. |
| [8] | 刘若璐, 汤海波, 罗凤盈, 等. 液态有机储氢技术应用与展望[J]. 现代化工, 2025, 45(2): 47-51, 56. |
| Liu R L, Tang H B, Luo F Y, et al. Application and prospect of liquid organics hydrogen storage technology[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2025, 45(2): 47-51, 56. | |
| [9] | Chu C Y, Wu K, Luo B B, et al. Hydrogen storage by liquid organic hydrogen carriers: catalyst, renewable carrier, and technology — a review[J]. Carbon Resources Conversion, 2023, 6(4): 334-351. |
| [10] | Munyentwali A, Tan K C, He T. Advancements in the development of liquid organic hydrogen carrier systems and their applications in the hydrogen economy[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2024, 34(5): 825-839. |
| [11] | Gemechu D N, Mohammed A M, Redi M, et al. First principles-based approaches for catalytic activity on the dehydrogenation of liquid organic hydrogen carriers: a review[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(85): 33186-33206. |
| [12] | Ugwu L I, Morgan Y, Ibrahim H. Application of density functional theory and machine learning in heterogenous-based catalytic reactions for hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(4): 2245-2267. |
| [13] | Cao Y J, Wang B J, Fan M H, et al. DFT calculations and machine learning for the study of ethane dehydrogenation on the heteroatom-doped graphene supported Pt SACs[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2025, 305: 121169. |
| [14] | Ding Y, Shang H, Yang C Z, et al. Identifying efficient and inexpensive hydrodesulfurization catalysts through machine learning-assisted analysis of metal-sulfur bonds in transition metal sulfides[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2024, 298: 120337. |
| [15] | Verma A, Wilson N, Joshi K. Solid state hydrogen storage: decoding the path through machine learning[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 50: 1518-1528. |
| [16] | Salehi K, Rahmani M, Atashrouz S. Machine learning assisted predictions for hydrogen storage in metal-organic frameworks[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(85): 33260-33275. |
| [17] | Jia Z P, Lu S, Song P, et al. Machine learning accelerates design of bilayer-modified graphene hydrogen storage materials[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 352: 128229. |
| [18] | Abdul Jameel A G, Al-Muslem A, Ahmad N, et al. Predicting enthalpy of combustion using machine learning[J]. Processes, 2022, 10(11): 2384. |
| [19] | Lu Z L, Wang J W, Wu Y F, et al. Prediction and theoretical investigation of dehydrogenation enthalpy of V-Ti-Cr-Fe alloy using machine learning and density functional theory[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 50: 379-389. |
| [20] | Ali A, Khan M A, Choi H. Supervised machine learning-based prediction of hydrogen storage classes utilizing dibenzyltoluene as an organic carrier[J]. Molecules, 2024, 29(6): 1280. |
| [21] | Zhang X, Zheng Q R, He H Z. Machine-learning-based prediction of hydrogen adsorption capacity at varied temperatures and pressures for MOFs adsorbents[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2022, 138: 104479. |
| [22] | Peng C C, Liu X Y, Long R, et al. Performance optimization of adsorption hydrogen storage system via computation fluid dynamics and machine learning[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2024, 207: 100-109. |
| [23] | Lu Z L, Wang J W, Wu Y F, et al. Predicting hydrogen storage capacity of V-Ti-Cr-Fe alloy via ensemble machine learning[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(81): 34583-34593. |
| [24] | Huang P R, Cai D, Lin H Z, et al. Materials genome engineering-based hydrogen storage materialsdatabase and its applications[J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2022, 52(10): 1863-1870. |
| [25] | Allal Z, Noura H N, Salman O, et al. A review on machine learning applications in hydrogen energy systems[J]. International Journal of Thermofluids, 2025, 26: 101119. |
| [26] | 吴铮, 李全安, 陈晓亚, 等. 机器学习在镁合金应用中的研究进展[J]. 工程科学学报, 2024, 46(10): 1797-1811. |
| Wu Z, Li Q A, Chen X Y, et al. Applications of machine learning on magnesium alloys[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2024, 46(10): 1797-1811. | |
| [27] | 文一如, 付佳, 刘大欢. 基于机器学习的MOFs材料研究进展: 能源气体吸附分离[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1370-1381. |
| Wen Y R, Fu J, Liu D H. Advances in machine learning-based materials research for MOFs: energy gas adsorption separation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1370-1381. | |
| [28] | Zhou P P, Zhou Q W, Xiao X Z, et al. Machine learning in solid-state hydrogen storage materials: challenges and perspectives[J]. Advanced Materials, 2025, 37(6): 2413430. |
| [29] | Gombolay G Y, Gopalan N, Bernasconi A, et al. Review of machine learning and artificial intelligence (ML/AI) for the pediatric neurologist[J]. Pediatric Neurology, 2023, 141: 42-51. |
| [30] | Yang Z, Gao W. Applications of machine learning in alloy catalysts: rational selection and future development of descriptors[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(12): 2106043. |
| [31] | Moosaei H, Ganaie M A, Hladík M, et al. Inverse free reduced universum twin support vector machine for imbalanced data classification[J]. Neural Networks, 2023, 157: 125-135. |
| [32] | Gao W, Xu F, Zhou Z H. Towards convergence rate analysis of random forests for classification[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 313: 103788. |
| [33] | Dong M H, Ma R, Sun G C, et al. Size distribution of pores and their geometric analysis in red mud-based autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) using regression neural network and elastic mechanics[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 359: 129420. |
| [34] | Liu W, Zou P, Jiang D G, et al. Zoning of reservoir water temperature field based on K-means clustering algorithm[J]. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, 2022, 44: 101239. |
| [35] | Chen H R, Li J H, Gao J B, et al. Maximally correlated principal component analysis based on deep parameterization learning[J]. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2019, 13(4): 1-17. |
| [36] | 杨凯博, 钟铭恩, 谭佳威, 等. 基于半监督学习的多场景火灾小规模稀薄烟雾检测[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2025, 59(3): 546-556, 565. |
| Yang K B, Zhong M E, Tan J W, et al. Small-scale sparse smoke detection in multiple fire scenarios based on semi-supervised learning[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2025, 59(3): 546-556, 565. | |
| [37] | 马幼捷, 刘熠铭, 周雪松, 等. 微网储能侧DC-DC变换器的强化学习自抗扰控制策略[J]. 太阳能学报, 2025, 46(3): 63-72. |
| Ma Y J, Liu Y M, Zhou X S, et al. Reinforcement learning active disturbance rejection control strategy for microgrid energy storage side DC-DC converter[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2025, 46(3): 63-72. | |
| [38] | Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, et al. Scikit-Learn: machine learning in python[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12: 2825-2830. |
| [39] | Abadi M, Agarwal A, Barham P, et al. TensorFlow: large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems[J]. arXiv, 2016: 1603.04467. |
| [40] | Fang J H, Xie M, He X Q, et al. Machine learning accelerates the materials discovery[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2022, 33: 104900. |
| [41] | D'Ambra F, Gébel G. Literature review: state-of-the-art hydrogen storage technologies and liquid organic hydrogen carrier (LOHC) development[J]. Science and Technology for Energy Transition, 2023, 78: 32. |
| [42] | Han L, Pei Q J, Tan K C, et al. Photothermal catalytic dehydrogenation of methylcyclohexane at ambient temperature for hydrogen storage[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2025, 102: 163-170. |
| [43] | 李文达, 王凤丽, 赵俊哲, 等. Pt/NiAl层状双金属氢氧化物载体催化剂上十氢萘产氢性能[J]. 石油化工, 2025, 54(2): 151-160. |
| Li W D, Wang F L, Zhao J Z, et al. Hydrogen production performance of decalin over Pt/NiAl layered double hydroxide-based supported catalyst[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2025, 54(2): 151-160. | |
| [44] | Harb H, Elliott S N, Ward L, et al. Accurate dehydrogenation enthalpies dataset for liquid organic hydrogen carriers[J]. Scientific Data, 2025, 12(1): 171. |
| [45] | Paragian K, Li B W, Massino M, et al. A computational workflow to discover novel liquid organic hydrogen carriers and their dehydrogenation routes[J]. Molecular Systems Design & Engineering, 2020, 5(10): 1658-1670. |
| [46] | 刘焕. 甲酸脱氢催化剂的研究进展[J]. 四川化工, 2024, 27(5): 26-30. |
| Liu H. Research progress of formic acid dehydrogenation catalysts[J]. Sichuan Chemical Industry, 2024, 27(5): 26-30. | |
| [47] | Li H M, Gui Y, Zhang J H, et al. Simultaneous alkali/air activation for hierarchical pore development in biochar and its use as catalyst carrier for formic acid dehydrogenation[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2025, 193: 107549. |
| [48] | Berfin Ekin Ü, Coşkuner Filiz B, Açıkalın K, et al. Boron-based hydrogen storage materials for highly selective hydrogenation to liquid organic hydrogen carriers synthesis focus on formic acid[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024: 12.237. |
| [49] | Gao X, Yang Y Y, Yang S, et al. Production of CO-free H2 through aqueous formic acid dehydrogenation over the α-Mo2C/NC catalyst[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 500: 156933. |
| [50] | Zhao X M, Wang L, Pei Y. Single metal atom catalyst supported on g-C3N4 for formic acid dehydrogenation: a combining density functional theory and machine learning study[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(41): 22513-22521. |
| [51] | Lu H, Zhong Y, Jie Y, et al. DFT study on the mechanism of methanol dehydrogenation over Ru x P y surfaces[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2024, 26(42): 26900-26910. |
| [52] | Thirumalesh B S, Asapu D R. State of the art of methanol reforming for hydrogen generation[J]. ChemBioEng Reviews, 2024, 11(3): 543-554. |
| [53] | 廖逸飞, 商辉, 杨捷, 等. 甲醇液相重整制氢研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2024, 44(1): 78-82. |
| Liao Y F, Shang H, Yang J, et al. Advances on hydrogen production through liquid phase methanol reforming[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2024, 44(1): 78-82. | |
| [54] | Liu Y J, Liang Z W, Huang J Z, et al. Screening of steam-reforming catalysts using unsupervised machine learning[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2023, 13(21): 6281-6290. |
| [55] | Saffary S, Rafiee M, Varnoosfaderani M S, et al. Smart paradigm to predict copper surface area of Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst based on synthesis parameters[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2023, 191: 604-616. |
| [56] | Lin C H, Lee B C S, Anjum U, et al. Harnessing physics-inspired machine learning to design nanocluster catalysts for dehydrogenating liquid organic hydrogen carriers[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2025, 371: 125192. |
| [57] | Dong C Y, Gao Z R, Li Y L, et al. Fully exposed palladium cluster catalysts enable hydrogen production from nitrogen heterocycles[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2022, 5: 485-493. |
| [58] | Zhou W H, Li X X, Chen C, et al. Sn modified carbon support PdCo bimetallic oxide for boosting low-temperature dehydrogenation of dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole[J]. Fuel, 2025, 382: 133718. |
| [59] | Permude P, Tang C G, Ahmad A, et al. Effective catalysts for typical liquid organic hydrogen carrier N-ethylcarbazole[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2025, 98: 1492-1509. |
| [60] | Vishwakarma G, Hachmann J. Liquid organic hydrogen carriers: high-throughput screening of homogeneous catalysts[J]. ChemRxiv, 2023: s8pkf. |
| [61] | Liang Z W, Huang J Z, Zhong B Q, et al. Unveiling feature importance in methanol reforming systems through the machine learning[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(32): 14104-14114. |
| [62] | Byun M, Lee H, Choe C, et al. Machine learning based predictive model for methanol steam reforming with technical, environmental, and economic perspectives[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 426: 131639. |
| [63] | Chen W H, Chen Z Y, Hsu S Y, et al. Reactor design of methanol steam reforming by evolutionary computation and hydrogen production maximization by machine learning[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2022, 46(14): 20685-20703. |
| [64] | Tazikeh S, Davoudi A, Zendehboudi S, et al. Predicting hydrogen production from formic acid dehydrogenation using smart connectionist models[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2025, 109: 574-590. |
| [65] | Xu M K, Gao R J, Shi C X, et al. Study on the dehydrogenation of perhydro-dibenzyltoluene catalyzed by Pt/Al2O3 in a fixed bed reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2024, 287: 119754. |
| [66] | Ali A, G U K, Lee H J. Parametric study of the hydrogenation of dibenzyltoluene and its dehydrogenation performance as a liquid organic hydrogen carrier[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2020, 34(7): 3069-3077. |
| [67] | Ali A, Kumar G U, Lee H J. Investigation of hydrogenation of dibenzyltoluene as liquid organic hydrogen carrier[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021, 45: 1123-1127. |
| [68] | Ali A, Rohini A K, Lee H J. Dehydrogenation of perhydro-dibenzyltoluene for hydrogen production in a microchannel reactor[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(48): 20905-20914. |
| [69] | Ali A, Khan M A, Choi H. Hydrogen storage prediction in dibenzyltoluene as liquid organic hydrogen carrier empowered with weighted federated machine learning[J]. Mathematics, 2022, 10(20): 3846. |
| [70] | Ali A, Khan M A, Abbas N, et al. Prediction of hydrogen storage in dibenzyltoluene empowered with machine learning[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 55: 105844. |
| [71] | Ali A, Khan M A, Choi H. Prediction of hydrogen generation from perhydro-dibenzyltoluene empowered with machine learning[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 51: 171-178. |
| [1] | Ziteng YAN, Feilong ZHAN, Guoliang DING. Structural design and effect verification of casing-type distributor used in air-conditioners [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [2] | Biao FENG, Zhao ZHANG, Siqi LI, Bingrui WANG, Hongying WU, Miao SHI, Dan WANG, Suxia MA. Performance of flame retardant for environmentally friendly refrigerant R290 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 462-468. |
| [3] | Siyuan WANG, Guoqiang LIU, Tong XIONG, Gang YAN. Characteristics of non-uniform wind velocity distribution in window air conditioner axial fans and their impact on optimizing condenser circuit optimization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [4] | Ke LI, Haolin XIE, Jian WEN. Multi-objective genetic algorithm optimization for thermal insulation performance of liquid hydrogen tank with multiple vapor-cooled shields [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4217-4227. |
| [5] | Zheng GAO, Hui WANG, Zhiguo QU. Data-driven high-throughput screening of anion-pillared metal-organic frameworks for hydrogen storage [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4259-4272. |
| [6] | Zhihong CHEN, Jiawei WU, Xiaoling LOU, Junxian YUN. Recent advances in machine learning for biomanufacturing of chemicals [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3789-3804. |
| [7] | Yitong ZHOU, Mingxi ZHOU, Ruochen LIU, Shuang YE, Weiguang HUANG. Technical and economic analysis on hydrogen based direct reduction steelmaking co-driven by photovoltaic and power grid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4318-4330. |
| [8] | Ning YANG, Haonan LI, Xiao LIN, Stella GEORGIADOU, Wen-Feng LIN. Application of plastic-derived carbon@CoMoO4 composites as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction in water electrolysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [9] | Yufeng WANG, Xiaoxue LUO, Hongliang FAN, Baijing WU, Cunpu LI, Zidong WEI. Green organic electrosynthesis coupled with water electrolysis to produce hydrogen—overview of electrode interface regulation strategies [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3753-3771. |
| [10] | Xiaolong WU, Xiaohuang HUANG, Yuan XIAO, Linghai SHAN, Jiahui YE, Guomin CUI. Reserve empty node strategy applied to optimization of heat exchanger networks [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3388-3402. |
| [11] | Peng YANG, Wanli YOU, Zhongqian LING, Xianyang ZENG, Yunchao LI, Jiayi LIN, Lijian WANG, Dingkun YUAN. Experimental study on performance of compact three-chamber RTO system for treating waste gas containing ethyl acetate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3585-3595. |
| [12] | Tao WANG, Guangming LI, Qiuxia HU, Jing XU. Optimization of warpage process for two-color injection products based on temporal evolution particle swarm optimization algorithm [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3403-3415. |
| [13] | Tianhao WU, Tingwei YE, Yan LIN, Zhen HUANG. In-situ hydrogen supplementation of biomass chemical looping gasification to produce syngas with controllable H2/CO [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3498-3508. |
| [14] | Jiaxiang CHEN, Wei ZHOU, Xuewei ZHANG, Lijie WANG, Yuming HUANG, Yang YU, Miaoting SUN, Wanjing LI, Junshu YUAN, Hongbo ZHANG, Xiaoxiao MENG, Jihui GAO, Guangbo ZHAO. Simulation study on the hydrogen production performance of a two-dimensional PEMWE model under pulsed voltage [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3521-3530. |
| [15] | Yifei WANG, Jingjie REN, Mingshu BI, Haotian YE. Multi-objective optimization of cyclohexane oxidation process parameters based on inherent safety and economic performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2722-2732. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||