化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (11): 5309-5319.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200092
皋海岭1,2( ),徐斌1(
),徐斌1( ),高月香1,朱月明1,张松贺2,张毅敏1
),高月香1,朱月明1,张松贺2,张毅敏1
收稿日期:2020-01-20
修回日期:2020-06-12
出版日期:2020-11-05
发布日期:2020-11-05
通讯作者:
徐斌
作者简介:皋海岭(1995—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Hailing GAO1,2( ),Bin XU1(
),Bin XU1( ),Yuexiang GAO1,Yueming ZHU1,Songhe ZHANG2,Yimin ZHANG1
),Yuexiang GAO1,Yueming ZHU1,Songhe ZHANG2,Yimin ZHANG1
Received:2020-01-20
Revised:2020-06-12
Online:2020-11-05
Published:2020-11-05
Contact:
Bin XU
摘要:
通过水热法制备得到TiO2改性石墨烯复合材料(RGO/TiO2),考察了其形貌结构和电化学性能。将其组装成电极,对比未改性石墨烯(RGO)电极和RGO/TiO2电极的电吸附NH4+性能。重点考察外加电压、循环流速、初始浓度等工艺参数对RGO/TiO2电极电吸附NH4+的影响,并对其电吸附NH4+特性和对模拟实际含NH4+废水深度脱NH4+效果进行研究。结果表明:RGO/TiO2复合材料具有三维孔洞结构,比表面积为382.08 m2·g-1,比电容量在扫速为0.01 V·s-1时达到325.80 F·g-1,优于RGO材料。RGO/TiO2电极的初次电吸附量较RGO电极提升了28.3%,循环再生吸附10次后,RGO/TiO2电极的NH4+吸附量仅降低了5.87%,循环再生吸附性能优于RGO电极。外加电压2.0 V、循环流速35 ml·min-1和NH4+初始浓度1.0 mmol·L-1为RGO/TiO2电极的最佳NH4+电吸附条件。RGO和RGO/TiO2电极电吸附NH4+过程符合准一级动力学模型和Freundlich等温吸附模型,电吸附NH4+为非均匀表面的多层吸附行为,以物理吸附为主。RGO/TiO2电极4级串联时对模拟实际含NH4+炼油净化水的去除率达到86.84%。
中图分类号:
皋海岭,徐斌,高月香,朱月明,张松贺,张毅敏. TiO2改性石墨烯电极电吸附去除污水中NH4+[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 5309-5319.
Hailing GAO,Bin XU,Yuexiang GAO,Yueming ZHU,Songhe ZHANG,Yimin ZHANG. Removal of ammonium ions in wastewater by electrosorption with TiO2 modified graphene electrode[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(11): 5309-5319.
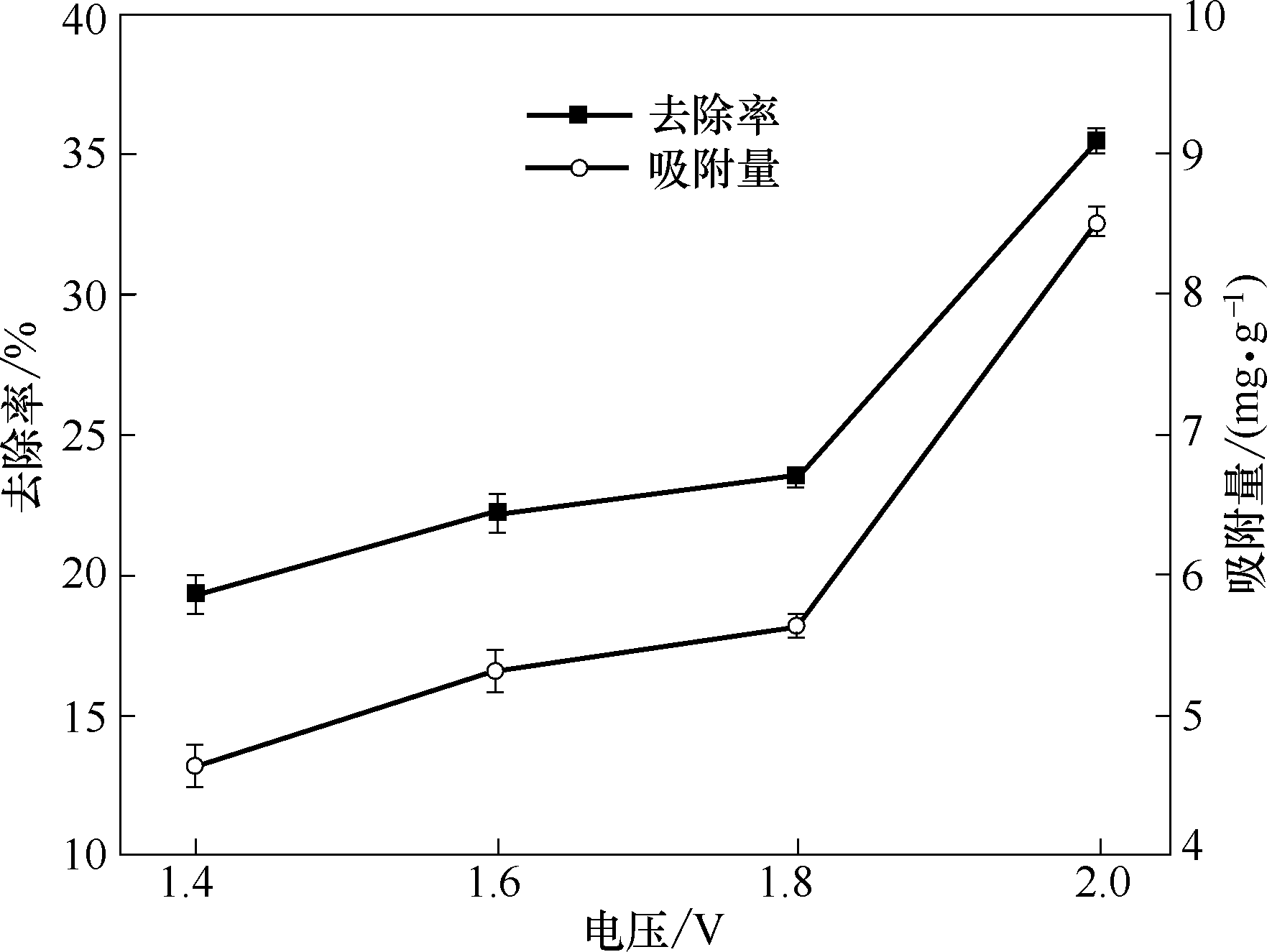
图10 外加电压对RGO/TiO2电极电吸附NH4+的去除率和吸附量的影响
Fig.10 Effect of applied voltage on removal efficiency and electrosorption capacity of NH4+ by RGO/TiO2 electrode
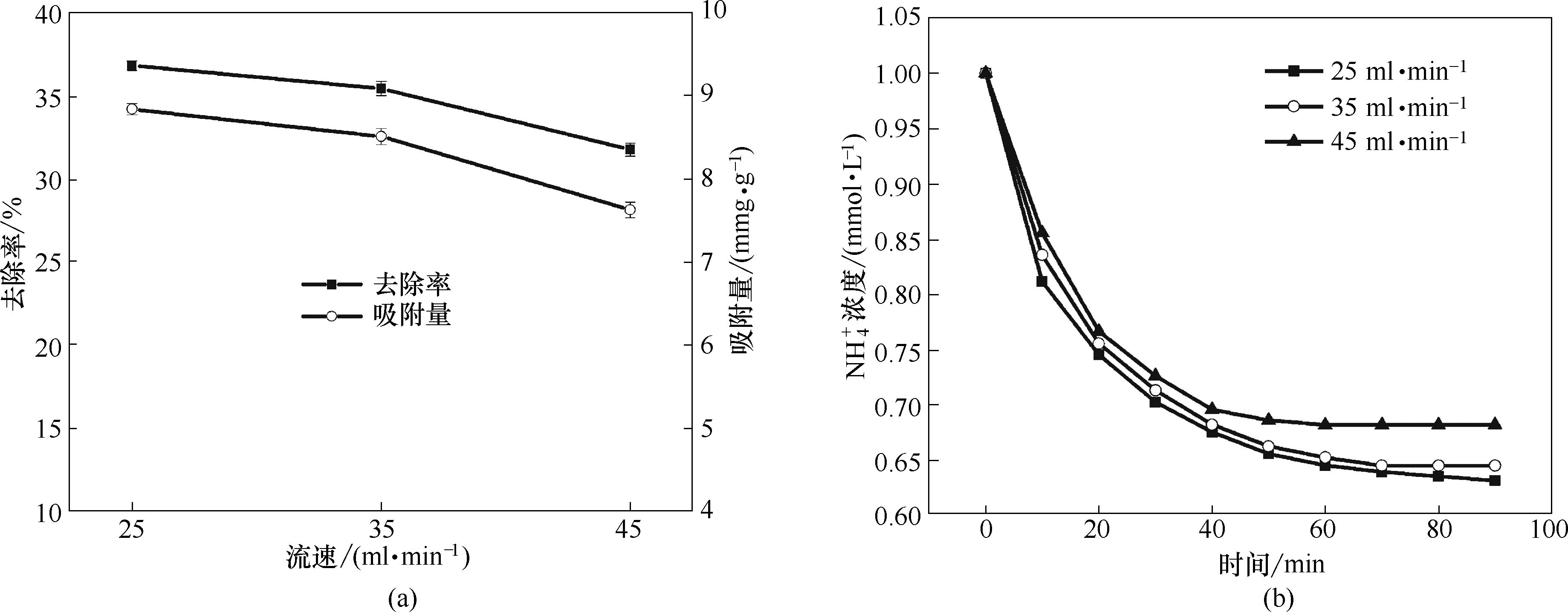
图11 循环流速对RGO/TiO2电极去除NH4+的去除率和吸附量的影响 (a);不同循环流速下RGO/TiO2电极电吸附NH4+的浓度变化 (b)
Fig.11 Effect of circulating velocity on removal efficiency and electrosorption capacity of NH4+ by RGO/TiO2 electrode (a); Electrosorption concentration changes of NH4+ by RGO/TiO2 electrode under different circulating velocities (b)

图12 初始浓度对RGO/TiO2 电极电吸附NH4+的去除率和吸附量的影响
Fig.12 Effect of initial concentration on removal efficiency and electrosorption capacity of NH4+ by RGO/TiO2 electrode
| 样品 | KF | 1/n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGO | 7.545 | 0.436 | 0.995 |
| RGO/TiO2 | 9.914 | 0.332 | 0.998 |
表1 RGO和RGO/TiO2电极电吸附NH4+的Freundlich模型拟合结果
Table 1 Fitting results of Freundlich models for NH4+ removal by RGO and RGO/TiO2 electrodes
| 样品 | KF | 1/n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGO | 7.545 | 0.436 | 0.995 |
| RGO/TiO2 | 9.914 | 0.332 | 0.998 |
| 电压/V | RGO | RGO/TiO2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | qe/ (mg·g-1) | R2 | K1 | qe/ (mg·g-1) | R2 | |
| 1.4 | 0.249 | 3.70 | 0.999 | 0.138 | 4.62 | 0.998 |
| 1.6 | 0.160 | 4.67 | 0.998 | 0.107 | 5.21 | 0.991 |
| 1.8 | 0.174 | 5.00 | 0.995 | 0.101 | 5.56 | 0.994 |
| 2.0 | 0.107 | 6.51 | 0.993 | 0.053 | 8.61 | 0.996 |
表2 RGO和RGO/TiO2电极电吸附NH4+准一级动力学模型拟合结果
Table 2 Fitting results of quasi-first-order kinetic model for NH4+ removal by RGO and RGO/TiO2 electrodes
| 电压/V | RGO | RGO/TiO2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | qe/ (mg·g-1) | R2 | K1 | qe/ (mg·g-1) | R2 | |
| 1.4 | 0.249 | 3.70 | 0.999 | 0.138 | 4.62 | 0.998 |
| 1.6 | 0.160 | 4.67 | 0.998 | 0.107 | 5.21 | 0.991 |
| 1.8 | 0.174 | 5.00 | 0.995 | 0.101 | 5.56 | 0.994 |
| 2.0 | 0.107 | 6.51 | 0.993 | 0.053 | 8.61 | 0.996 |
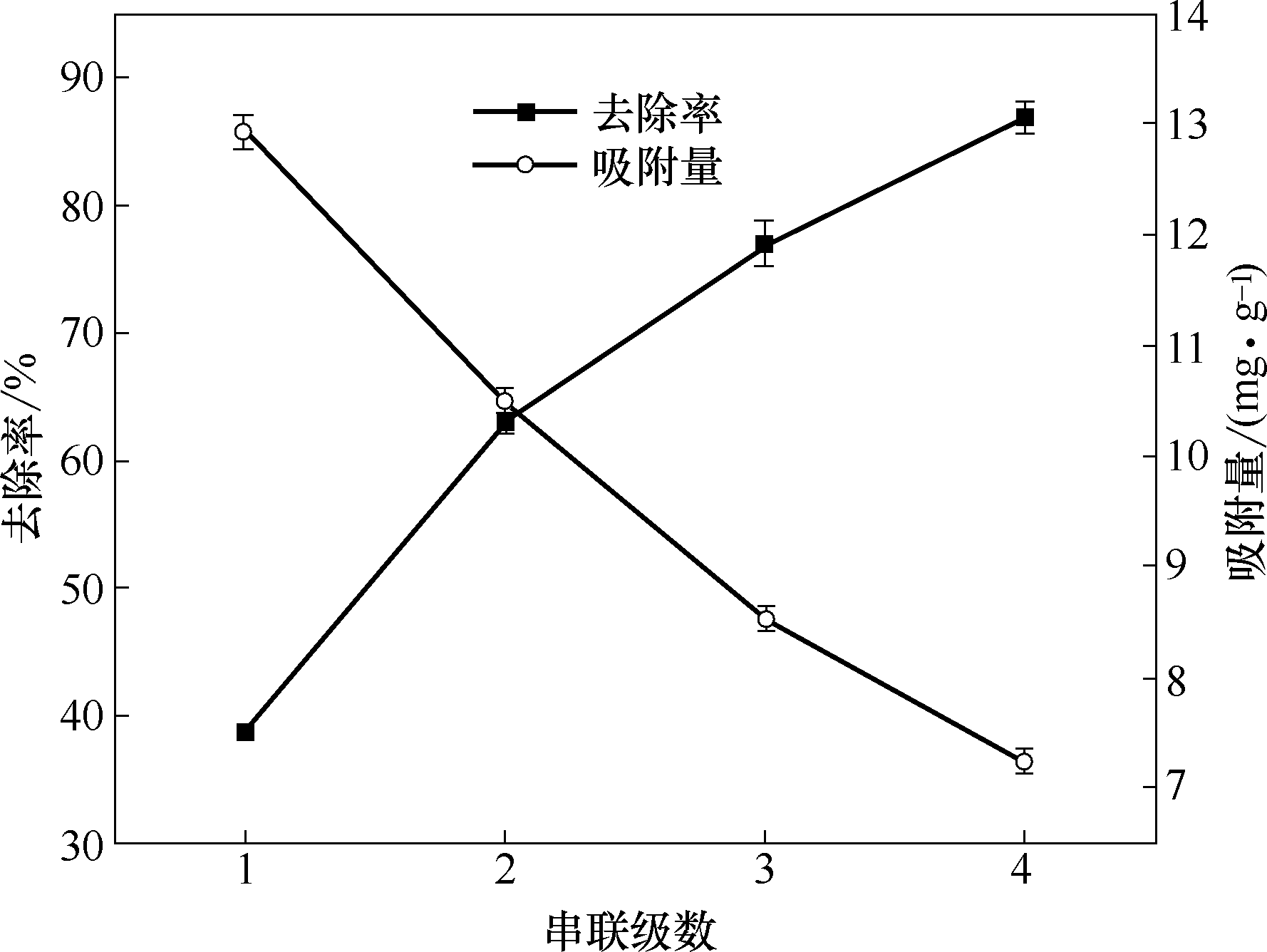
图15 RGO/TiO2电极电吸附模拟实际含NH4+炼油净化水的处理效果
Fig.15 Effect of electrosorption treatment of simulated actual NH4+ refining purified water by RGO/TiO2 electrode
| 1 | Güerena D, Lahman J, Hanley K, et al. Nitrogen dynamics following field application of biochar in a temperate North American maize-based production system[J]. Plant and Soil, 2013, 365(1/2): 239-254. |
| 2 | Buss S R, Herbert A W, Morgan P, et al. A review of ammonium attenuation in soil and groundwater[J]. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology, 2004, 37(4): 347-359. |
| 3 | Bouwer H. Agricultural contamination: problems and solutions[J]. Water Environment and Technology, 1989, 1(2): 292-297. |
| 4 | El-Deen A G, Choi J H, Kim C S, et al. TiO2 nanorod-intercalated reduced graphene oxide as high performance electrode material for membrane capacitive deionization[J]. Desalination, 2015, 361(1): 53-64. |
| 5 | 刘琳, 李莹, 鄂涛, 等. 球状纳米二氧化钛/石墨烯复合材料的合成及导电性能[J]. 材料工程, 2019, 47(8): 97-102. |
| Liu L, Li Y, E T, et al. Synthesis and electrical conductivity of spherical nano-TiO2/graphene composites[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2019, 47(8): 97-102. | |
| 6 | Hu X B, Yu Y, Hou W M, et al. Effects of particle size and ph value on the hydrophilicity of graphene oxide[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 273(19): 118-121. |
| 7 | 施周, 杨文浩, 杨灵芳, 等. 等离子改性CNT/TiO2电极吸附去除水中苯酚的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(9): 2664-2669. |
| Shi Z, Yang W H, Yang L F, et al. Electrosorption of phenol in aqueous solution using a plasma-activated CNT/TiO2 electrode[J]. China Environment Science, 2015, 35(9): 2664-2669. | |
| 8 | 李海红, 杨洁, 郭雅妮, 等. Al2O3/ACF复合电极材料的制备及性能表征[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(11): 4703-4709. |
| Li H H, Yang J, Guo Y N, et al. Preparation and properties characterization of Al2O3/ACF composite electrode materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(11): 4703-4709. | |
| 9 | Fan C S, Tseng S C, Li K C, et al. Electro-removal of arsenic(Ⅲ) and arsenic(Ⅴ) from aqueous solutions by capacitive deionization[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 312(15): 208-215. |
| 10 | 胡瑞兵. 介孔RGO/TiO2复合材料的制备及其对盐酸四环素光催化活性研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2018. |
| Hu R B. Preparation and photocatalytic activity for tetracycline hydrochloride of mesoporous RGO/TiO2 composite[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2018. | |
| 11 | Zhou Y H, Liu C J, Li Y, et al. Platinum nanoparticles supported on noncovalent functionalized graphene as cathode catalysts for aluminum-air batteries[J]. Advanced Materilas Research, 2013, 800(1): 526-530. |
| 12 | 王瑶, 吉庆华, 李永峰, 等. 石墨烯凝胶电极的制备及电吸附Pb2 +的性能[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(9): 3747-3754. |
| Wang Y, Ji Q H, Li Y F, et al. Preparation and Pb2+ electrosorption characteristics of graphere hydrogels electrode[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(9): 3747-3754. | |
| 13 | Wang D, Zhou Z H, Yang H, et al. Preparation of TiO2 loaded with crystalline nano-Ag by a one-step low-temperature hydrothermal method[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(32): 16306-16311. |
| 14 | Chen Q, Zhou M, Zhang Z M, et al. Preparation of TiO2 nanotubes/reduced graphene oxide binary nanocomposites enhanced photocatalytic properties[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2017, 28(13): 9416-9422. |
| 15 | Liu L, Luo C, Xiong J, et al. Reduced graphene oxide (rGO) decorated TiO2, microspheres for visible-light photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ)[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 690(8): 771-776. |
| 16 | 张朕. 膜电容去离子技术去除废水中无机态氮的研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2017. |
| Zhang Z. Study on the removal of inorganic nitrogen from wastewater by membrane capacitive deionization[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2017. | |
| 17 | 金肇岩, 胡筱敏, 孙通, 等. 脉冲电吸附技术深度脱氮及分子动力学模拟[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(7): 2871-2879. |
| Jin Z Y, Hu X M, Sun T, et al. Capacitive deionization using a pulse power supply for depth denitrogenation and molecular dynamics simulation[J]. China Environment Science, 2019, 39(7): 2871-2879. | |
| 18 | 徐乐乐. 多孔炭材料的制备及其电容法脱盐性能研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2015. |
| Xu L L. Study on preparation and capacitive desalination performance of porous carbon materials[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2015. | |
| 19 | 施周, 靳兆祺, 邓林, 等. CNT/PANI电极吸附去除水中Cu2+的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(12): 3650-3656. |
| Shi Z, Jin Z Q, Deng L, et al. Electrosorption of Cu2+ in aqueous solution using CNT/PANI electrodes[J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(12): 3650-3656. | |
| 20 | 周贵忠, 王兆丰, 王绚, 等. 石墨-活性炭纤维复合电极电吸附处理含盐废水的研究[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(5): 1832-1837. |
| Zhou G Z, Wang Z F, Wang X, et al. Research on treatment of high salt wastewater by the graphite and activated carbon fiber composite electrodes[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(5): 1832-1837. | |
| 21 | 赵研. 强化电容去离子脱盐的实验与机理研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2015. |
| Zhao Y. Performance and mechanism of improvement to desalination with capacitive deionization[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2015. | |
| 22 | Wimalasiri Y, Mossad M, Zou L. Thermodynamics and kinetics of adsorption of ammonium ions by graphene laminate electrodes in capacitive deionization[J]. Desalination, 2015, 357(11): 178-188. |
| 23 | 石胜启, 王越, 徐世昌, 等. 石墨带电极电容性脱盐试验研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2013, 39(1): 29-32. |
| Shi S Q, Wang Y, Xu S C, et al. Experimental study on capacitive deionization of graphite ribbon electrode[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2013, 39(1): 29-32. | |
| 24 | Liu P Y, Wang H, Yan T T, et al. Grafting sulfonic and amine functional groups on 3D graphene for improved capacitive deionization[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(14): 5303-5313. |
| 25 | Liu J, Li W Y, Liu Y G, et al. Titanium(Ⅳ) hydrate based on chitosan template for defluoridation from aqueous solution[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 293(12): 46-54. |
| 26 | Chao Y H, Zhu W S, Wu X Y, et al. Application of graphene-like layered molybdenum disulfide and its excellent adsorption behavior for doxycycline antibiotic[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 243(12): 60-67. |
| 27 | 孟晗. 氧化石墨烯复合材料的制备及其对铅离子的吸附性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2017. |
| Meng H. Study on the preparation of graphere oxide composite and adsorption performances for Pb(Ⅱ) ions[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2017. | |
| 28 | 刘方园, 胡承志, 李永峰, 等. MnO2/CFP复合电极的制备及电吸附Pb2 +特性的研究[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(2): 552-558. |
| Liu F Y, Hu C Z, Li Y F, et al. Preparation and Pb2+ electrosorption characteristics of MnO2 /CFP composite electrode[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(2): 552-558. |
| [1] | 胡兴枝, 张皓焱, 庄境坤, 范雨晴, 张开银, 向军. 嵌有超小CeO2纳米粒子的碳纳米纤维的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [2] | 杨欣, 彭啸, 薛凯茹, 苏梦威, 吴燕. 分子印迹-TiO2光电催化降解增溶PHE废水性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3564-3571. |
| [3] | 葛加丽, 管图祥, 邱新民, 吴健, 沈丽明, 暴宁钟. 垂直多孔碳包覆的FeF3正极的构筑及储锂性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [4] | 张澳, 罗英武. 低模量、高弹性、高剥离强度丙烯酸酯压敏胶[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3079-3092. |
| [5] | 王杰, 丘晓琳, 赵烨, 刘鑫洋, 韩忠强, 许雍, 蒋文瀚. 聚电解质静电沉积改性PHBV抗氧化膜的制备与性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [6] | 蔡斌, 张效林, 罗倩, 党江涛, 左栗源, 刘欣梅. 导电薄膜材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2308-2321. |
| [7] | 崔张宁, 胡紫璇, 吴雷, 周军, 叶干, 刘田田, 张秋利, 宋永辉. 可降解纤维素基材料的耐水性能研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2296-2307. |
| [8] | 李振, 张博, 王丽伟. PEG-EG固-固相变材料的制备和性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2680-2688. |
| [9] | 陈韶云, 徐东, 陈龙, 张禹, 张远方, 尤庆亮, 胡成龙, 陈建. 单层聚苯胺微球阵列结构的制备及其吸附性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2228-2238. |
| [10] | 代佳琳, 毕唯东, 雍玉梅, 陈文强, 莫晗旸, 孙兵, 杨超. 热物性对混合型CPCMs固液相变特性影响模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1914-1927. |
| [11] | 顾浩, 张福建, 刘珍, 周文轩, 张鹏, 张忠强. 力电耦合作用下多孔石墨烯膜时间维度的脱盐性能及机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2067-2074. |
| [12] | 刘瑞琪, 周栖桐, 张悦, 贺莹, 高静, 马丽. 基于金纳米颗粒修饰二氧化硅纳米花的生物传感器构建及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1247-1259. |
| [13] | 徐东, 田杜, 陈龙, 张禹, 尤庆亮, 胡成龙, 陈韶云, 陈建. 聚苯胺/二氧化锰/聚吡咯复合纳米球的制备及其电化学储能性[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1379-1389. |
| [14] | 陈瑞哲, 程磊磊, 顾菁, 袁浩然, 陈勇. 纤维增强树脂复合材料化学回收技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 981-994. |
| [15] | 余后川, 任腾, 张宁, 姜晓滨, 代岩, 张晓鹏, 鲍军江, 贺高红. 二维氧化石墨烯膜离子选择性传递调控的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 303-312. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号