化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (12): 5578-5588.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200539
杨润农1( ),余林1(
),余林1( ),赵向云2,杨晓波1,2(
),赵向云2,杨晓波1,2( ),高梓寒1,傅广赢3,姜久兴3,练纬琳2,刘武源1,2,范群1,2
),高梓寒1,傅广赢3,姜久兴3,练纬琳2,刘武源1,2,范群1,2
收稿日期:2020-05-09
修回日期:2020-07-08
出版日期:2020-12-05
发布日期:2020-12-05
通讯作者:
余林,杨晓波
作者简介:杨润农(1989—),女,博士研究生,基金资助:
YANG Runnong1( ),YU Lin1(
),YU Lin1( ),ZHAO Xiangyun2,YANG Xiaobo1,2(
),ZHAO Xiangyun2,YANG Xiaobo1,2( ),GAO Zihan1,FU Guangying3,JIANG Jiuxing3,LIAN Weilin2,LIU Wuyuan1,2,FAN Qun1,2
),GAO Zihan1,FU Guangying3,JIANG Jiuxing3,LIAN Weilin2,LIU Wuyuan1,2,FAN Qun1,2
Received:2020-05-09
Revised:2020-07-08
Online:2020-12-05
Published:2020-12-05
Contact:
YU Lin,YANG Xiaobo
摘要:
氮氧化物(NOx)是大气中的一种主要污染物。采用具有菱沸石结构(CHA)的铜基分子筛作为催化剂,通过选择性催化还原(SCR)技术可有效去除NOx。采用一种经济环保的制备方法,在不使用模板剂的条件下水热合成一种具有结构缺陷的低硅铝比CHA型分子筛(Phi,Si/Al=4.7)。结果表明,经Cu离子交换制备的Cu/Phi具有最丰富的表面酸性与孤立态Cu2+,表现出较好的低温活性、较宽的工作温度窗口以及良好的水热稳定性。Na或Mg的存在降低了Cu/Phi的表面酸性及孤立态Cu2+的含量,水热老化后的Na,Cu/Phi和Mg,Cu/Phi均呈现出不同程度的骨架坍塌,相应导致了催化剂失活。
中图分类号:
杨润农,余林,赵向云,杨晓波,高梓寒,傅广赢,姜久兴,练纬琳,刘武源,范群. 无模板法合成的Phi分子筛在NO选择性催化还原中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(12): 5578-5588.
YANG Runnong,YU Lin,ZHAO Xiangyun,YANG Xiaobo,GAO Zihan,FU Guangying,JIANG Jiuxing,LIAN Weilin,LIU Wuyuan,FAN Qun. Phi zeolite synthesized by template-free method for selective catalytic reduction of NO[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(12): 5578-5588.
| Catalyst① | Cu content /% | M② content /% | Effect on catalytic activity | Effect on hydrothermal stability | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-Na-SSZ-13(4) | ~2.5 | <1.7 | slightly enhanced | positive | [ |
| 1.7—3.4 | negative | negative | |||
| Cu-Li/Na-SSZ-13(6) | 1.0 | 0.4/1.8 | positive | positive | [ |
| Cu-K/Cs-SSZ-13(6) | 0.9/0.6 | 4.2/15.0 | negative | negative | [ |
| Cu-Na-SSZ-13(9) | 1.0 | 1.5 | slightly enhanced | — | [ |
| 2.0—4.0 | 1.5 | negative | negative | ||
| Cu-Na-SSZ-13 | 1.7—3.9 | <0.8 | positive | positive | [ |
| 4.3—5.3 | 2.5—3.7 | negative | negative | ||
| Cu-Ba-BEA(25) | — | 2.0 | no influence | positive | [ |
| Cu-Na-ZSM-5 | 2.4—3.5 | 0.04—0.6 | positive | — | [ |
| Cu-Na-SSZ-13(12) | — | 1.2—3.5 | negative | negative | [ |
| Cu-Na-SSZ-13 | — | 0.7—3.5 | negative | negative | [ |
| Cu-Na-SAPO-34 | ~2.0 | 0.4—1.8 | negative | — | [ |
| Cu-K/Na/Ca/Mg-SAPO-18 | ~2.1 | ~0.5 | negative | negative | [ |
| ~1.0 | negative | negative | |||
| Cu-K/Mg/Ca/Na-SSZ-39 | ~2.3 | 3.9/2.2/3.1/3.0 | negative | negative | [ |
表1 碱/碱土金属对不同分子筛催化剂的影响
Table 1 Effect of alkali/alkaline earth metals on different zeolite catalysts
| Catalyst① | Cu content /% | M② content /% | Effect on catalytic activity | Effect on hydrothermal stability | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-Na-SSZ-13(4) | ~2.5 | <1.7 | slightly enhanced | positive | [ |
| 1.7—3.4 | negative | negative | |||
| Cu-Li/Na-SSZ-13(6) | 1.0 | 0.4/1.8 | positive | positive | [ |
| Cu-K/Cs-SSZ-13(6) | 0.9/0.6 | 4.2/15.0 | negative | negative | [ |
| Cu-Na-SSZ-13(9) | 1.0 | 1.5 | slightly enhanced | — | [ |
| 2.0—4.0 | 1.5 | negative | negative | ||
| Cu-Na-SSZ-13 | 1.7—3.9 | <0.8 | positive | positive | [ |
| 4.3—5.3 | 2.5—3.7 | negative | negative | ||
| Cu-Ba-BEA(25) | — | 2.0 | no influence | positive | [ |
| Cu-Na-ZSM-5 | 2.4—3.5 | 0.04—0.6 | positive | — | [ |
| Cu-Na-SSZ-13(12) | — | 1.2—3.5 | negative | negative | [ |
| Cu-Na-SSZ-13 | — | 0.7—3.5 | negative | negative | [ |
| Cu-Na-SAPO-34 | ~2.0 | 0.4—1.8 | negative | — | [ |
| Cu-K/Na/Ca/Mg-SAPO-18 | ~2.1 | ~0.5 | negative | negative | [ |
| ~1.0 | negative | negative | |||
| Cu-K/Mg/Ca/Na-SSZ-39 | ~2.3 | 3.9/2.2/3.1/3.0 | negative | negative | [ |
| Sample | Mass content/% | Atomic ratio② | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Na | Mg | Si/Al | Cu/Al | M③/Al | |
| Cu/SSZ-13 | 3.16①/2.29② | — | — | 10.9 | 0.36 | — |
| Cu/Phi | 4.41①/3.58② | — | — | 4.65 | 0.24 | — |
| Na,Cu/Phi | 4.83①/4.07② | 0.81①/0.80② | — | 4.81 | 0.26 | 0.14 |
| Mg,Cu/Phi | 4.07①/3.04② | — | 1.53①/1.10② | 4.71 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
表2 催化剂中各元素含量分析
Table 2 Element contents in catalysts
| Sample | Mass content/% | Atomic ratio② | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Na | Mg | Si/Al | Cu/Al | M③/Al | |
| Cu/SSZ-13 | 3.16①/2.29② | — | — | 10.9 | 0.36 | — |
| Cu/Phi | 4.41①/3.58② | — | — | 4.65 | 0.24 | — |
| Na,Cu/Phi | 4.83①/4.07② | 0.81①/0.80② | — | 4.81 | 0.26 | 0.14 |
| Mg,Cu/Phi | 4.07①/3.04② | — | 1.53①/1.10② | 4.71 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
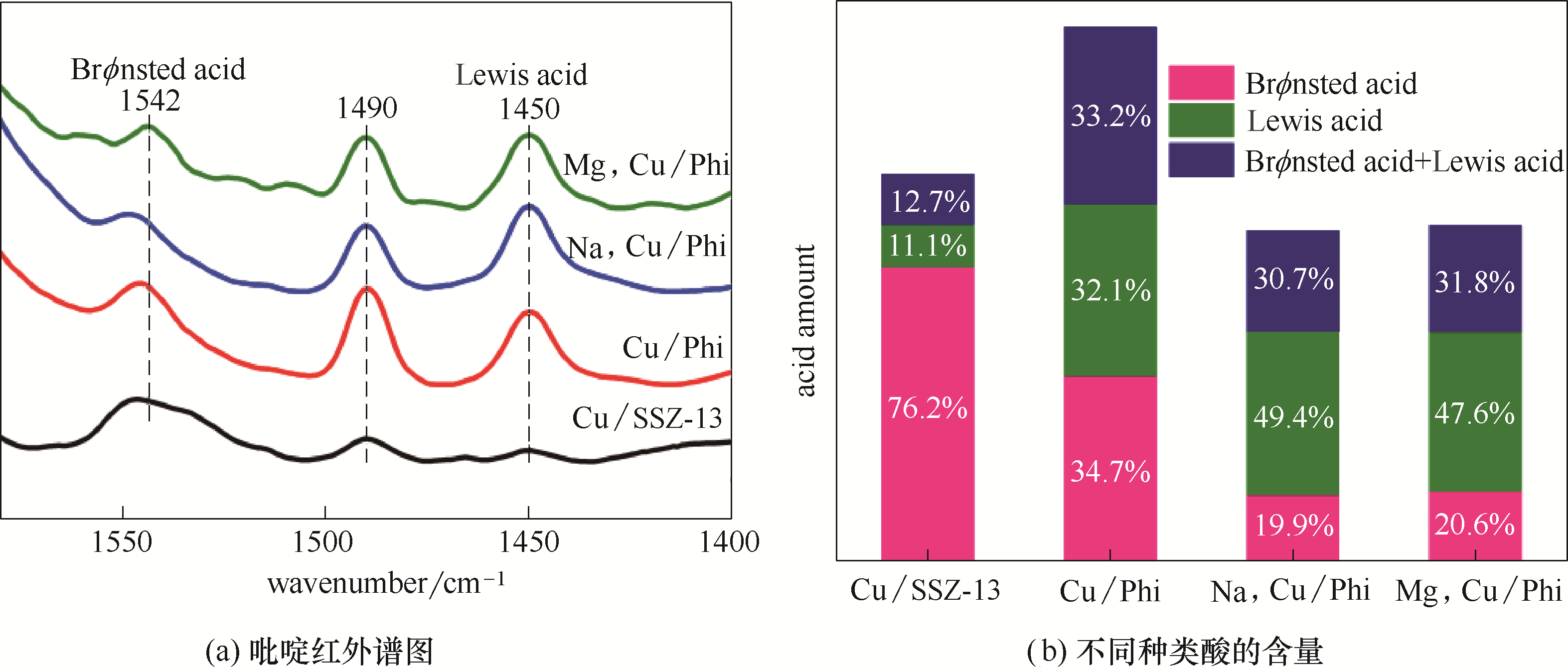
图4 不同催化剂的吡啶红外谱图和相应的不同种类酸的含量
Fig.4 FTIR spectra of pyridine adsorption for different catalysts and the corresponding amounts of acid sites with different natures
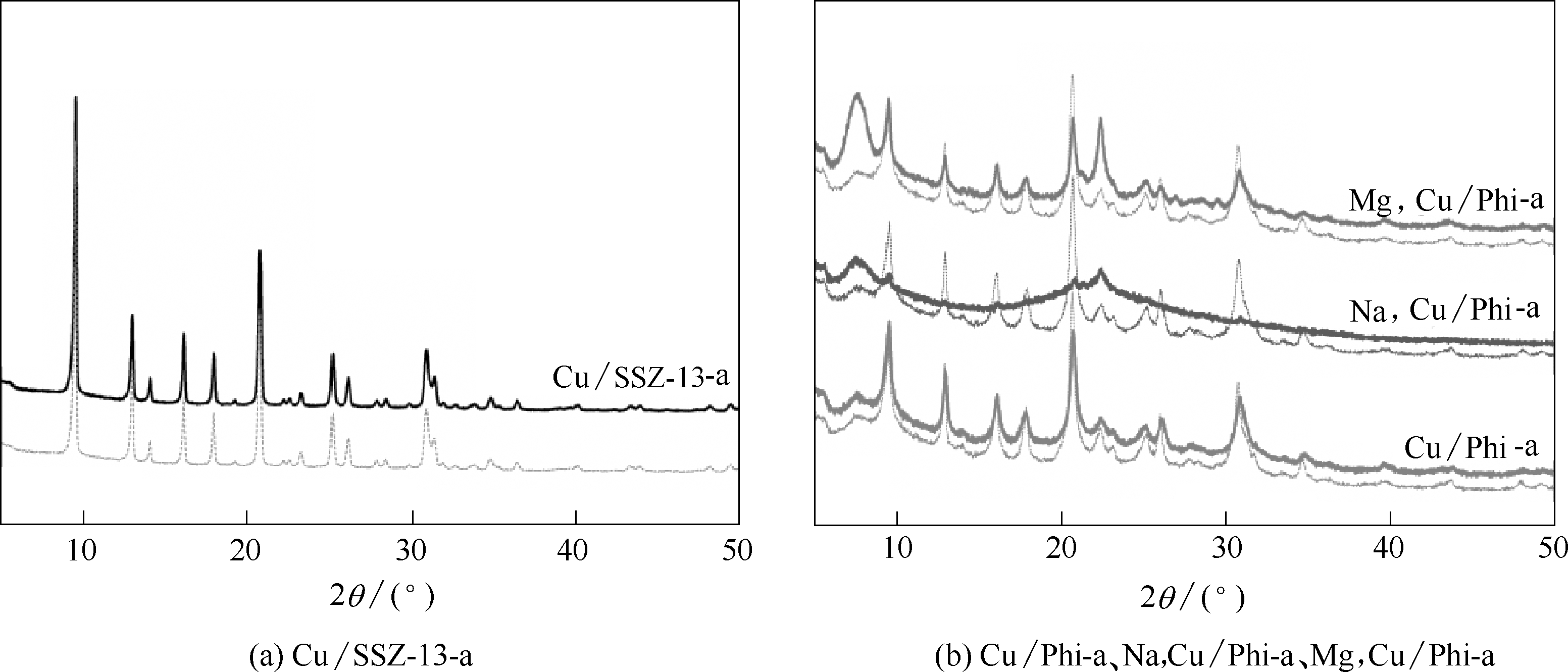
图7 水热老化催化剂的XRD谱图(虚线表示老化前催化剂的XRD谱图)
Fig.7 XRD patterns of hydrothermal aged catalysts (XRD patterns of corresponding fresh catalysts are shown as dashed lines)
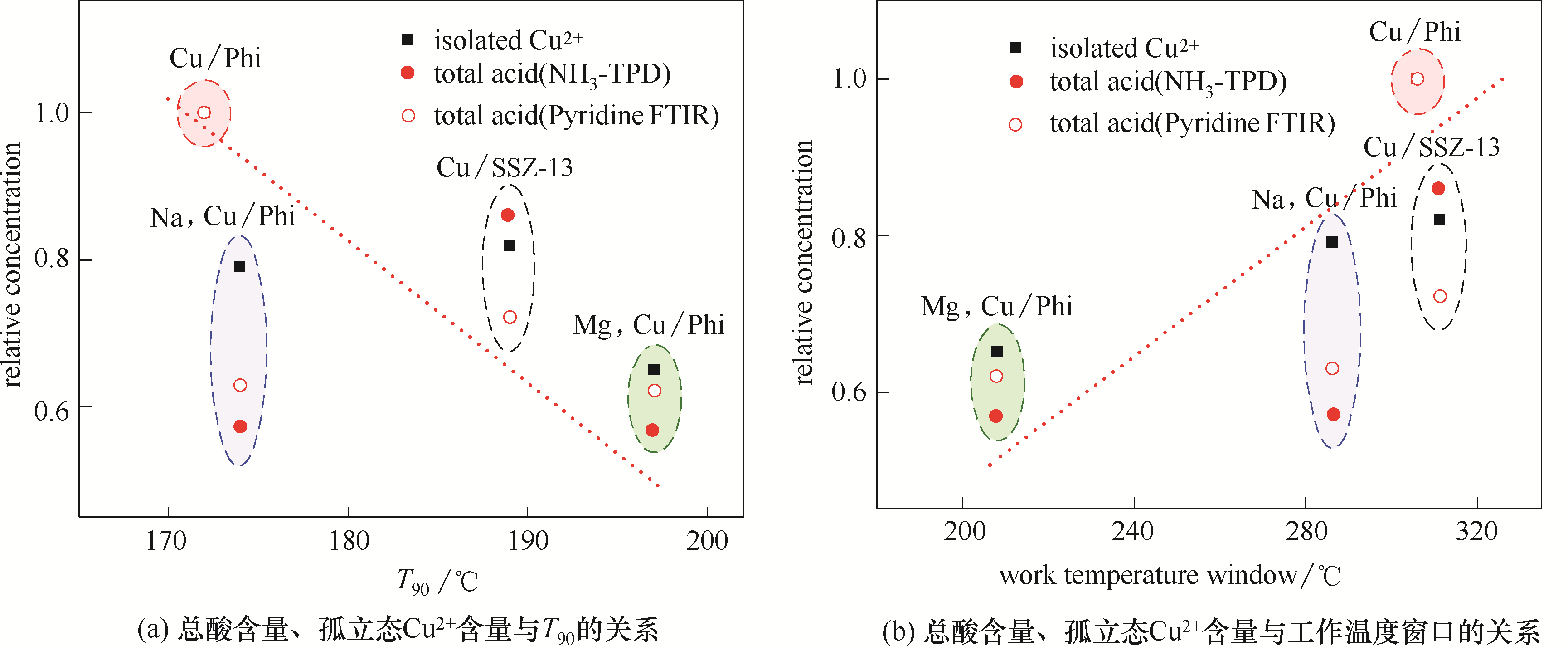
图9 不同催化剂的总酸含量、孤立态Cu2+含量与T90及工作温度窗口间的关系
Fig.9 Relationships among total acid amount, isolated Cu2+ amount and T90 or work temperature window for different catalysts
| 1 | 秦萱, 尹德嘉,余丽泽,等. 硅铝比对Cu/SSZ-13的SCR活性位影响规律研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(2): 591-599. |
| Qin X, Yin D J, Yu L Z, et al. Effect of Si/Al ratio on the SCR active sites of Cu/SSZ-13[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(2): 591-599. | |
| 2 | 高岩. 选择性催化还原脱硝催化剂的实验与机理研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2013. |
| Gao Y. Experiment and mechanism analysis on selective catalytic reduction deNOx catalyst[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2013. | |
| 3 | Roy S, Baiker A. NOx storage-reduction catalysis: from mechanism and materials properties to storage-reduction performance[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2009, 109(9): 4054-4091. |
| 4 | Hong Z, Wang Z, Liu X B. Catalytic oxidation of nitric oxide (NO) over different catalysts: an overview[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2017, 7: 3440. |
| 5 | 左建良. 氮氧化物低温选择性催化还原锰基催化剂研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2014. |
| Zuo J L. Study on Mn-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2014. | |
| 6 | 郭星萌. 船用柴油机尾气后处理系统的优化设计[D]. 贵阳: 贵州民族大学, 2019. |
| Guo X M. Optimization design and policy simulation of marine diesel engine post-processing system[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Minzu University, 2019. | |
| 7 | 翁端, 王蕾, 吴晓东, 等. 铜基小孔分子筛柴油车尾气脱硝催化材料研究进展[J]. 科技导报, 2013, 31(24): 68-73. |
| Weng D, Wang L, Wu X D, et al. Progress for Cu-based small pore molecular sieves as disel De-NOx catalysts[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2013, 32(24): 68-73. | |
| 8 | 张秋林, 徐海迪,邱春天,等. Cu-ZSM-5的NH3选择性催化还原NO性能及其稳态动力学[J]. 物理化学学报, 2012, 28(5): 1230-1236. |
| Zhang Q L, Xu H D, Qiu C T, et al. Catalytic performance and steady-state kinetics of Cu-ZSM-5 for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2012, 28(5): 1230-1236. | |
| 9 | 汪宗御, 邝海浪, 张继锋, 等. 基于 DOC+SCR 的船用柴油机尾气污染物脱除实验[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(7): 3249-3256. |
| Wang Z Y, Kuang H L, Zhang J F, et al. Removal of marine diesel engine exhaust pollutants with DOC+SCR technologies[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(7): 3249-3256. | |
| 10 | Hu H, Cai S X, Li H R, et al. Mechanistic aspects of deNOx processing over TiO2 supported Co-Mn oxide catalysts: structure-activity relationships and in situ DRIFTs analysis[J]. ASC Catalysis, 2015, 5: 6069-6077. |
| 11 | 刘建华, 杨晓博, 张琛, 等. Fe2O3对V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂表面性质及其性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(4): 1287-1293. |
| Liu J H, Yang X B, Zhang C, et al. Effect of Fe2O3 on surface properties and activities of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(4): 1287-1293. | |
| 12 | Wang Z Y, Guo R T, Shi X, et al. The enhanced performance of Sb-modified Cu/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 475: 334-341. |
| 13 | 郭凤, 余剑, Tran Tuyet-Suong, 等. 溶胶-凝胶原位合成钒钨钛催化剂及NH3-SCR性能[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(7): 3747-3754. |
| Guo F, Yu J, Tran T S, et al. In situ preparation of mesoporous V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst by sol-gel method and its performance for NH3-SCR reaction[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(7): 3747-3754. | |
| 14 | 宿文康. Cu/CHA分子筛选择性催化还原柴油车尾气NOx的机理研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2016. |
| Su W K. Fundamental research on SCR of NOx by NH3 over Cu/CHA zeolite for diesel vehicle emission control[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2016. | |
| 15 | Prodinger S, Derewinski M A, Wang Y L, et al. Sub-micron Cu/SSZ-13: synthesis and application as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 201: 461-469. |
| 16 | Ye Y Z, Shen F, Wang H N, et al. SSZ-13-supported manganese oxide catalysts for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3[J]. Journal of Chemical Sciences, 2017, 129(6): 765-774. |
| 17 | Wang C, Wang J, Wang J Q, et al. The role of impregnated sodium ions in Cu/SSZ-13 NH3-SCR catalysts[J]. Catalysts, 2018, 8(12): 593. |
| 18 | Gao F, Szanyi J. On the hydrothermal stability of Cu/SSZ-13 SCR catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2018, 560: 185-194. |
| 19 | Godiksen A, Stappen F N, Vennestrøm P N R, et al. Coordination environment of copper sites in Cu-CHA zeolite investigated by electron paramagnetic resonance[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(40): 23126-23138. |
| 20 | Janssens T V W, Falsig H, Lundegaard L F, et al. A consistent reaction scheme for the selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with ammonia[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(5): 2832-2845. |
| 21 | Zhao Z C, Yu R, Zhao R R, et al. Cu-exchanged Al-rich SSZ-13 zeolite from organotemplate-free synthesis as NH3-SCR catalyst: effects of Na+ ions on the activity and hydrothermal stability[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 217: 421-428. |
| 22 | Gao F, Wang Y L, Washton N M, et al. Effects of alkali and alkaline earth cocations on the activity and hydrothermal stability of Cu/SSZ-13 NH3-SCR catalysts[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(11): 6780-6791. |
| 23 | Wang C, Yan W J, Wang Z X, et al. The role of alkali metal ions on hydrothermal stability of Cu/SSZ-13 NH3-SCR catalysts[J]. Catalysis Today, 2020, 355: 482-492. |
| 24 | Ming S, Pang L, Fan C, et al. Chemical deactivation of Cu-SAPO-18 deNO catalyst caused by basic inorganic contaminants in diesel exhaust[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 40(4): 590-599. |
| 25 | Cui Y R, Wang Y L, Walter E D, et al. Influences of Na+ co-cation on the structure and performance of Cu/SSZ-13 selective catalytic reduction catalysts[J]. Catalysis Today, 2020, 339: 233-240. |
| 26 | Xie L J, Liu F D, Shi X Y, et al. Effects of post-treatment method and Na co-cation on the hydrothermal stability of Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 179: 206-212. |
| 27 | Lin Q J, Liu J Y, Liu S, et al. Barium-promoted hydrothermal stability of monolithic Cu/BEA catalyst for NH3-SCR[J]. Dalton Trans, 2018, 47(42): 15038-15048. |
| 28 | Sultana A, Nanba T, Haneda M, et al. Influence of co-cations on the formation of Cu+ species in Cu/ZSM-5 and its effect on selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2010, 101(1/2): 61-67. |
| 29 | Wang C, Wang C, Wang J, et al. Effects of Na+ on Cu/SAPO-34 for ammonia selective catalytic reduction[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 70: 20-28. |
| 30 | Zhu N, Shan W P, Shan Y L, et al. Effects of alkali and alkaline earth metals on Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 388: 124250. |
| 31 | Yang X B, Zhao X Y, Xiao J M, et al. High silica zeolite Phi, a CHA type zeolite with ABC-D6R stacking faults[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017, 248: 129-138. |
| 32 | 刘小青, 李时卉, 孙梦婷, 等. MnOx/SAPO-11催化剂的制备、表征及其低温NH3-SCR活性[J]. 物理化学学报, 2016, 32(5): 1236-1246. |
| Liu X Q, Li S H, Sun M T, et al. Preparation, characterization and low-temperature NH3-SCR activity of MnOx/SAPO-11 catalysts[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2016, 32(5): 1236-1246. | |
| 33 | 郝腾. SO2对Cu/SAPO-34催化剂NH3-SCR性能的影响[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2014. |
| He T. The effect of SO2 poisoning on the NH3-SCR performance over Cu/SAPO-34 catalysts[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2014. | |
| 34 | Niu C, Shi X Y, Liu F D, et al. High hydrothermal stability of Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts for the NH3-SCR of NOx[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 294: 254-263. |
| 35 | Wang Q Y, Liu Z L, Zou H B, et al. Effect of calcinations temperature of Cu/Ti-PILCs for selective catalytic reduction of NO by propylene[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 396/397/398: 776-781. |
| 36 | Bendrich M, Scheuer A, Hayes R E, et al. Unified mechanistic model for standard SCR, fast SCR, and NO2 SCR over a copper chabazite catalyst[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 222: 76-87. |
| 37 | Zhang D, Yang R T. NH3-SCR of NO over one-pot Cu-SAPO-34 catalyst: performance enhancement by doping Fe and MnCe and insight into N2O formation[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2017, 543: 247-256. |
| [1] | 杨学金, 杨金涛, 宁平, 王访, 宋晓双, 贾丽娟, 冯嘉予. 剧毒气体PH3的干法净化技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3742-3755. |
| [2] | 陈杰, 林永胜, 肖恺, 杨臣, 邱挺. 胆碱基碱性离子液体催化合成仲丁醇性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [3] | 李艺彤, 郭航, 陈浩, 叶芳. 催化剂非均匀分布的质子交换膜燃料电池操作条件研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [4] | 杨欣, 彭啸, 薛凯茹, 苏梦威, 吴燕. 分子印迹-TiO2光电催化降解增溶PHE废水性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3564-3571. |
| [5] | 杨菲菲, 赵世熙, 周维, 倪中海. Sn掺杂的In2O3催化CO2选择性加氢制甲醇[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| [6] | 李凯旋, 谭伟, 张曼玉, 徐志豪, 王旭裕, 纪红兵. 富含零价钴活性位点的钴氮碳/活性炭设计及甲醛催化氧化应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3342-3352. |
| [7] | 李盼, 马俊洋, 陈志豪, 王丽, 郭耘. Ru/α-MnO2催化剂形貌对NH3-SCO反应性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2908-2918. |
| [8] | 涂玉明, 邵高燕, 陈健杰, 刘凤, 田世超, 周智勇, 任钟旗. 钙基催化剂的设计合成及应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2717-2734. |
| [9] | 张琦钰, 高利军, 苏宇航, 马晓博, 王翊丞, 张亚婷, 胡超. 碳基催化材料在电化学还原二氧化碳中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [10] | 余娅洁, 李静茹, 周树锋, 李清彪, 詹国武. 基于天然生物模板构建纳米材料及集成催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2735-2752. |
| [11] | 周继鹏, 何文军, 李涛. 异形催化剂上乙烯催化氧化失活动力学反应工程计算[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2416-2426. |
| [12] | 张希庆, 王琰婷, 徐彦红, 常淑玲, 孙婷婷, 薛定, 张立红. Mg量影响的纳米片负载Pt-In催化异丁烷脱氢性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2427-2435. |
| [13] | 张谭, 刘光, 李晋平, 孙予罕. Ru基氮还原电催化剂性能调控策略[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [14] | 韩奎奎, 谭湘龙, 李金芝, 杨婷, 张春, 张永汾, 刘洪全, 于中伟, 顾学红. 四通道中空纤维MFI分子筛膜用于二甲苯异构体分离[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2468-2476. |
| [15] | 王辰, 史秀锋, 武鲜凤, 魏方佳, 张昊虹, 车寅, 吴旭. 氧化还原法制备Mn3O4催化剂及其甲苯催化氧化性能与机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2447-2457. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号