化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (8): 3193-3202.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230441
吕龙义1( ), 及文博1, 韩沐达1, 李伟光2, 高文芳1(
), 及文博1, 韩沐达1, 李伟光2, 高文芳1( ), 刘晓阳1(
), 刘晓阳1( ), 孙丽1, 王鹏飞1, 任芝军1, 张光明1
), 孙丽1, 王鹏飞1, 任芝军1, 张光明1
收稿日期:2023-05-05
修回日期:2023-07-14
出版日期:2023-08-25
发布日期:2023-10-18
通讯作者:
高文芳,刘晓阳
作者简介:吕龙义(1989—),男,博士研究生,副教授,lvlongyi@hebut.edu.cn
基金资助:
Longyi LYU1( ), Wenbo JI1, Muda HAN1, Weiguang LI2, Wenfang GAO1(
), Wenbo JI1, Muda HAN1, Weiguang LI2, Wenfang GAO1( ), Xiaoyang LIU1(
), Xiaoyang LIU1( ), Li SUN1, Pengfei WANG1, Zhijun REN1, Guangming ZHANG1
), Li SUN1, Pengfei WANG1, Zhijun REN1, Guangming ZHANG1
Received:2023-05-05
Revised:2023-07-14
Online:2023-08-25
Published:2023-10-18
Contact:
Wenfang GAO, Xiaoyang LIU
摘要:
随着工农业发展,越来越多的卤代污染物被排放到环境中。鉴于卤代污染物高毒性及强稳定性的特点,如何高效地去除环境中卤代污染物成为国内外学者关注的焦点。厌氧生物处理因为其绿色高效的特点,近年来常被用于去除环境中的卤代污染物,其中微生物胞外电子传递是影响脱氯效率的重要因素。铁基导电材料比表面积大,导电性强,而且能够提高脱卤相关菌的微生物活性,可强化胞外电子传递过程,加速厌氧脱卤效率的同时提高甲烷产量。本文综述了铁基导电材料强化厌氧脱卤的研究现状,重点对铁基导电材料促进电子转移机制进行了论述。探讨了目前铁基导电材料相关研究存在的问题,并对铁基材料促进厌氧脱卤的研究方向进行了展望。
中图分类号:
吕龙义, 及文博, 韩沐达, 李伟光, 高文芳, 刘晓阳, 孙丽, 王鹏飞, 任芝军, 张光明. 铁基导电材料强化厌氧去除卤代有机污染物:研究进展及未来展望[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3193-3202.
Longyi LYU, Wenbo JI, Muda HAN, Weiguang LI, Wenfang GAO, Xiaoyang LIU, Li SUN, Pengfei WANG, Zhijun REN, Guangming ZHANG. Enhanced anaerobic removal of halogenated organic pollutants by iron-based conductive materials: research progress and future perspectives[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3193-3202.
| 卤代污染物 | 英文名称 | 分子式 | 应用领域 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 二氯乙烷 | dichloroethane | C2H4Cl2 | 工业溶剂、橡胶、杀虫剂 |
| 三氯乙烯 | trichloroethylene | C2HCl3 | 杀虫剂、香料、电子元件清洗剂 |
| 四溴化碳 | tetrabromomethane | CBr4 | 麻醉剂、制冷剂、染料中间体 |
| 五氯酚 | pentachlorophenol | C6HCl5O | 杀菌剂、合成塑料 |
| 2,4,6-三氯酚 | 2,4,6-trichlorophenol | C6H3Cl3O | 杀菌剂、防腐剂 |
| 2,4-二氯酚 | 2,4-dichlorophenol | C6H4Cl2O | 工业溶剂、杀虫剂、杀菌剂 |
| 四溴双酚A | tetrabromobisphenol A | C15H12Br4O2 | 阻燃剂 |
| 十溴二苯醚 | decabromodiphenyl oxide | C12Br10O | 阻燃剂 |
| 四氟乙烯 | tetrafluoroethene | C2F4 | 耐热塑料、灭火剂 |
| 氟化氢钠 | sodium hydrogen difluoride | NaHF2 | 食品添加剂、防腐剂 |
表1 常见的卤代污染物及其应用领域
Table 1 Common halogenated pollutants and their application fields
| 卤代污染物 | 英文名称 | 分子式 | 应用领域 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 二氯乙烷 | dichloroethane | C2H4Cl2 | 工业溶剂、橡胶、杀虫剂 |
| 三氯乙烯 | trichloroethylene | C2HCl3 | 杀虫剂、香料、电子元件清洗剂 |
| 四溴化碳 | tetrabromomethane | CBr4 | 麻醉剂、制冷剂、染料中间体 |
| 五氯酚 | pentachlorophenol | C6HCl5O | 杀菌剂、合成塑料 |
| 2,4,6-三氯酚 | 2,4,6-trichlorophenol | C6H3Cl3O | 杀菌剂、防腐剂 |
| 2,4-二氯酚 | 2,4-dichlorophenol | C6H4Cl2O | 工业溶剂、杀虫剂、杀菌剂 |
| 四溴双酚A | tetrabromobisphenol A | C15H12Br4O2 | 阻燃剂 |
| 十溴二苯醚 | decabromodiphenyl oxide | C12Br10O | 阻燃剂 |
| 四氟乙烯 | tetrafluoroethene | C2F4 | 耐热塑料、灭火剂 |
| 氟化氢钠 | sodium hydrogen difluoride | NaHF2 | 食品添加剂、防腐剂 |
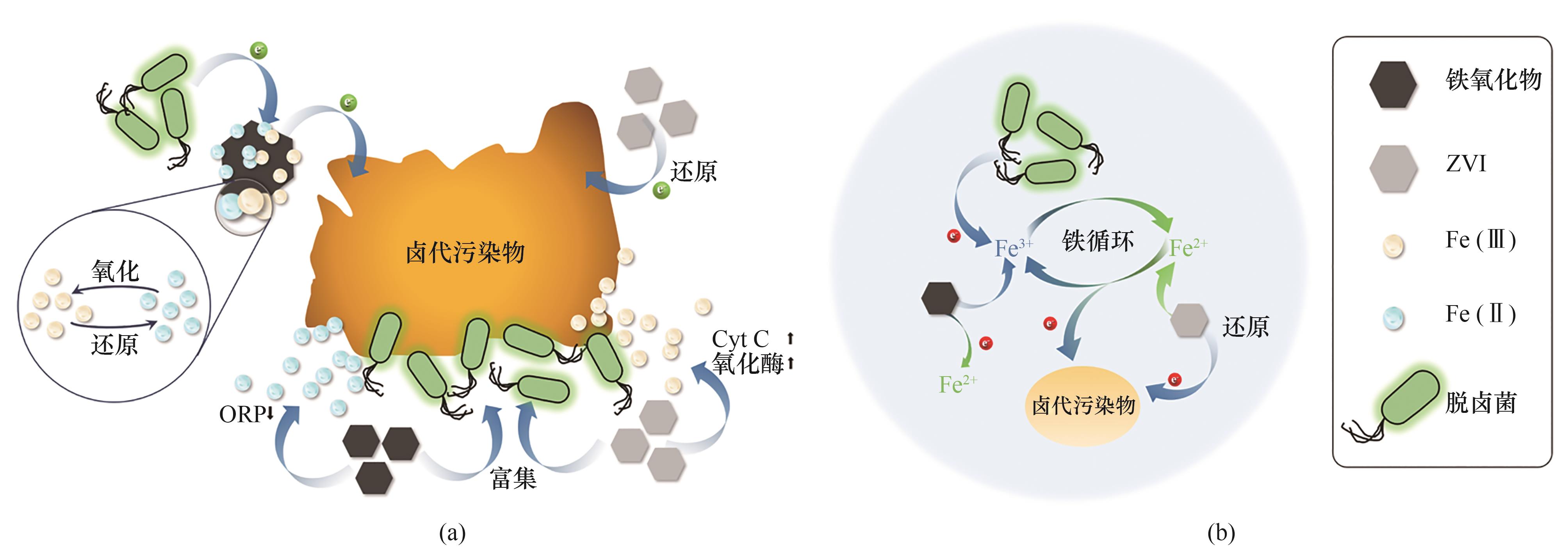
图1 铁基材料强化厌氧去除卤代污染物的机制(a);脱卤过程中铁的价态变化及电子的传递方向(b)
Fig.1 Mechanism of enhanced anaerobic removal of halogenated pollutants by iron-based materials (a); Valence change of iron and electron transfer direction during dehalogenation (b)
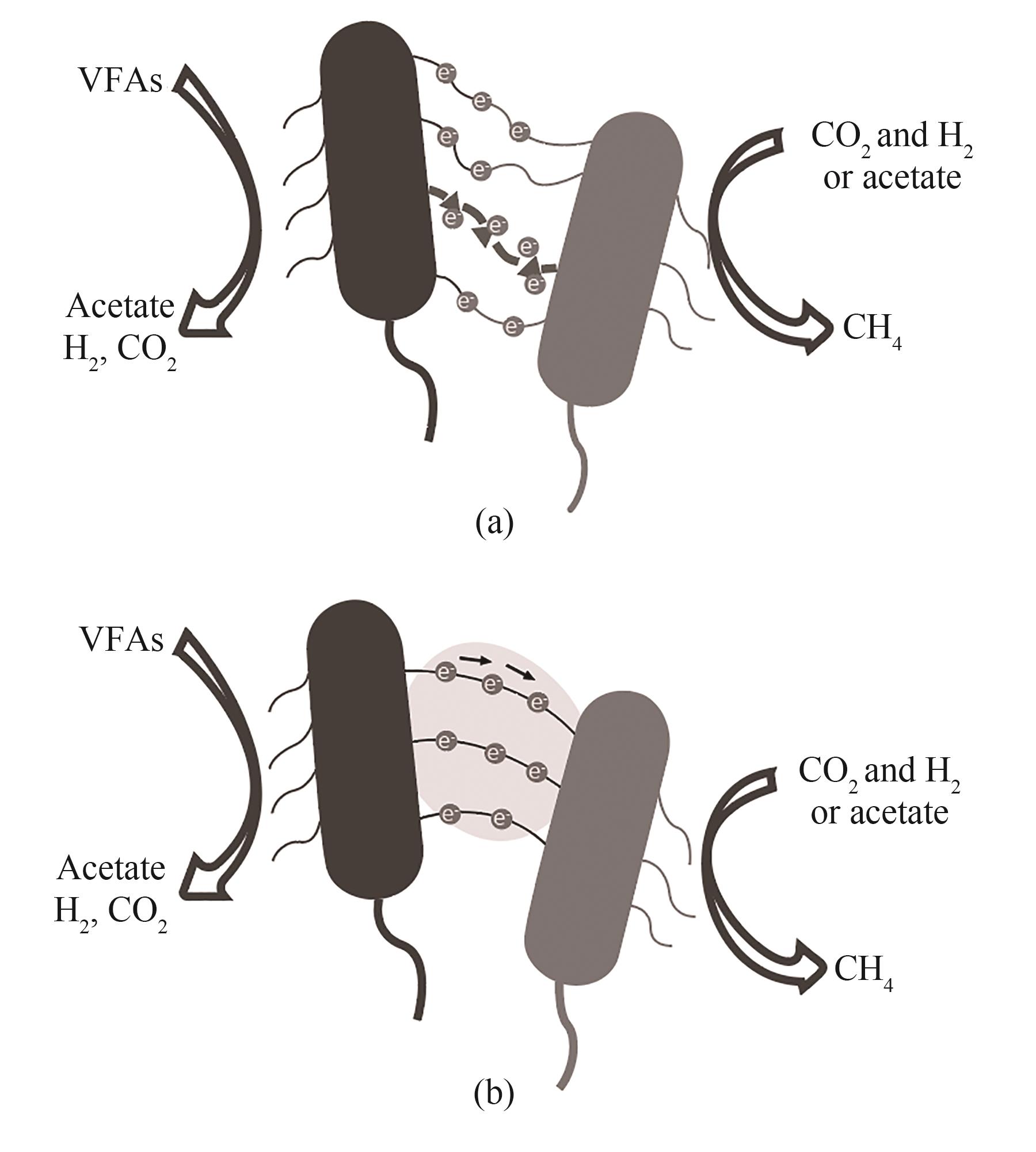
图2 互营细菌通过导电菌毛和细胞色素进行DIET (a);利用导电材料进行DIET (b)
Fig.2 DIET by mutualistic bacteria via conductive pili and cytochrome (a); DIET using conductive materials (b)
| 1 | Maqsood Q, Sumrin A, Waseem R, et al. Bioengineered microbial strains for detoxification of toxic environmental pollutants[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 227: 115665. |
| 2 | 王晶晶, 李秀颖, 宋玉芳, 等. 环境因子对厌氧微生物脱卤的影响研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2022, 49(10): 4357-4381. |
| Wang J J, Li X Y, Song Y F, et al. Research progress on the influence of environmental factors on dehalogenation by anaerobic microorganisms[J]. Microbiology China, 2022, 49(10): 4357-4381. | |
| 3 | Du Y, Lv X T, Wu Q Y, et al. Formation and control of disinfection byproducts and toxicity during reclaimed water chlorination: a review [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 58: 51-63. |
| 4 | Rusyn I, Chiu W A, Lash L H, et al. Trichloroethylene: mechanistic, epidemiologic and other supporting evidence of carcinogenic hazard[J]. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2014, 141(1): 55-68. |
| 5 | She Y Z, Wu J P, Zhang Y, et al. Bioaccumulation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and several alternative halogenated flame retardants in a small herbivorous food chain[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 174: 164-170. |
| 6 | 张杰, 陆雅海. 互营氧化产甲烷微生物种间电子传递研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2015, 42(5): 920-927. |
| Zhang J, Lu Y H. A review of interspecies electron transfer in syntrophic-methanogenic associations[J]. Microbiology China, 2015, 42(5): 920-927 | |
| 7 | Yu J L, Xiao K, Xu H, et al. Spectroscopic fingerprints profiling the polysaccharide/protein/humic architecture of stratified extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in activated sludge[J]. Water Research, 2023, 235: 119866. |
| 8 | Gahlot P, Ahmed B, Tiwari S B, et al. Conductive material engineered direct interspecies electron transfer (DIET) in anaerobic digestion: mechanism and application[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2020, 20: 101056. |
| 9 | Mun H, Ri C, Liu Q L, et al. Ball-milled PET plastic char as an electron shuttle accelerated anaerobic degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in water environment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 885: 163740. |
| 10 | Zhao Z Q, Li Y, Quan X, et al. Towards engineering application: potential mechanism for enhancing anaerobic digestion of complex organic waste with different types of conductive materials[J]. Water Research, 2017, 115: 266-277. |
| 11 | Ren Z J, Ma P Y, Lv L Y, et al. Application of exogenous redox mediators in anaerobic biological wastewater treatment: a critical review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 372: 133527. |
| 12 | Yin Q D, Wu G X. Advances in direct interspecies electron transfer and conductive materials: electron flux, organic degradation and microbial interaction[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(8): 107443. |
| 13 | Zhao W X, Yang H Z, He S F, et al. A review of biochar in anaerobic digestion to improve biogas production: performances, mechanisms and economic assessments[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 341: 125797. |
| 14 | Lan H X, Ji L Y, Li K, et al. Mediated anaerobic system performance, co-metabolizing flora and electron transfer by graphene oxide supported zero-valent iron composite[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(2): 109631. |
| 15 | Xu Y G, Wang M W, Yu Q L, et al. Enhancing methanogenesis from anaerobic digestion of propionate with addition of Fe oxides supported on conductive carbon cloth[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 302: 122796. |
| 16 | Ye J, Hu A D, Ren G P, et al. Enhancing sludge methanogenesis with improved redox activity of extracellular polymeric substances by hematite in red mud[J]. Water Research, 2018, 134: 54-62. |
| 17 | Wu L, Patton S D, Liu H Z. Mechanisms of oxidative removal of 1,4-dioxane via free chlorine rapidly mixing into monochloramine: implications on water treatment and reuse[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 440: 129760. |
| 18 | Hu Z T, Hu S H, Hong P Y, et al. Impact of electrochemically generated iron on the performance of an anaerobic wastewater treatment process[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 875: 162628. |
| 19 | 刘翠英, 王宇, 马煜春. 铁氧化物与丙酸对土壤中六氯苯厌氧降解影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(3): 1073-1080. |
| Liu C Y, Wang Y, Ma Y C. Effect of iron oxide and propionic acid on anaerobic degradation of hexachlorobenzene in soil[J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(3): 1073-1080. | |
| 20 | 孔殿超, 周跃飞, 陈天虎, 等. 针铁矿、磁铁矿和石膏对2,4-二氯苯酚厌氧降解的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(7): 2875-2882. |
| Kong D C, Zhou Y F, Chen T H, et al. Effects of goethite, magnetite and gypsum on the anaerobic degradation of 2, 4-dichlorophenol[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(7): 2875-2882. | |
| 21 | Leitão P, Aulenta F, Rossetti S, et al. Impact of magnetite nanoparticles on the syntrophic dechlorination of 1,2-dichloroethane[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 624: 17-23. |
| 22 | Aulenta F, Fazi S, Majone M, et al. Electrically conductive magnetite particles enhance the kinetics and steer the composition of anaerobic TCE-dechlorinating cultures[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2014, 49(12): 2235-2240. |
| 23 | 周洪波, 陈坚. 五氯苯酚对厌氧颗粒污泥微生物的毒性作用[J]. 中南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2002(5): 469-472. |
| Zhou H B, Chen J. Toxicity of pentachlorophenol to microorganisms of anaerobic granular sludge[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology (Natural Science), 2002, 33(5): 469-472. | |
| 24 | Li Q, Chen Z S, Wang H H, et al. Removal of organic compounds by nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 792: 148546. |
| 25 | Li J H, Yang L X, Li J Q, et al. Anchoring nZVI on metal-organic framework for removal of uranium(Ⅵ) from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2019, 269: 16-23. |
| 26 | Qiu M Q, Wang M, Zhao Q Z, et al. XANES and EXAFS investigation of uranium incorporation on nZVI in the presence of phosphate[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 201: 764-771. |
| 27 | Wang Y, Jiang W, Tang Y Q, et al. Biochar-supported sulfurized nanoscale zero-valent iron facilitates extensive dechlorination and rapid removal of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol in aqueous solution[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 332: 138835. |
| 28 | Dominguez C M, Romero A, Fernandez J, et al. In situ chemical reduction of chlorinated organic compounds from lindane production wastes by zero valent iron microparticles[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2018, 26: 146-155. |
| 29 | Chen X Q, Bai C H, Li Z L, et al. Directional bioelectrochemical dechlorination of trichloroethene to valuable ethylene by introduction poly-3-hydroxybutyrate as a slow release carbon source[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 455: 140737. |
| 30 | 廖娣劼, 杨琦, 李俊錡. 零价铁降解4-氯硝基苯动力学研究[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(2): 469-475. |
| Liao D J, Yang Q, Lee C. Kinetic study of 4-chloronitrobenzene degradation by zero-valent iron[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(2): 469-475. | |
| 31 | Yang X M, Zhang C, Liu F, et al. Diversity in the species and fate of chlorine during TCE reduction by two nZVI with non-identical anaerobic corrosion mechanism[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 230: 230-238. |
| 32 | Shih Y H, Chou H L, Peng Y H, et al. Synergistic effect of microscale zerovalent iron particles combined with anaerobic sludges on the degradation of decabromodiphenyl ether[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 108: 14-20. |
| 33 | Peng Y H, Chen Y J, Chang M, et al. The effect of zerovalent iron on the microbial degradation of hexabromocyclododecane[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 200: 419-426. |
| 34 | Chen Z Z, Tang X J, Qiao W J, et al. Nanoscale zero-valent iron reduction coupled with anaerobic dechlorination to degrade hexachlorocyclohexane isomers in historically contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 400: 123298. |
| 35 | 范利花, 李辉, 林匡飞, 等. 零价铁-厌氧活性污泥耦合降解三氯乙烷和二𫫇烷复合污染[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 42(1): 72-78. |
| Fan L H, Li H, Lin K F, et al. Degradation of trichloroethane and dioxane co-contamination via a ZVI-anaerobic microbe combined system[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 42(1): 72-78. | |
| 36 | Pan Y, Leung P Y, Li Y Y, et al. Enhancement effect of nanoscale zero-valent iron addition on microbial degradation of BDE-209 in contaminated mangrove sediment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 781: 146702. |
| 37 | 姚春洪, 韦志鹏, 车林轩, 等. 导电材料强化厌氧生物处理过程的研究进展[J]. 水处理技术, 2022, 48(8): 23-28. |
| Yao C H, Wei Z P, Che L X, et al. Research progress of conductive materials in enhancing anaerobic biological treatment process[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2022, 48(8): 23-28. | |
| 38 | Wang Y Q, Wang H W, Chen H B, et al. Zero-valent iron effectively enhances valuable products generated from wastewater containing 2-bromo-4,6-dinitroaniline during hydrolysis acidification process: performance and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 445: 130515. |
| 39 | Zhu X M, Wang X, Li N, et al. Bioelectrochemical system for dehalogenation: a review[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 293: 118519. |
| 40 | Corsino S F, Capodici M, Torregrossa M, et al. Physical properties and extracellular polymeric substances pattern of aerobic granular sludge treating hypersaline wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 229: 152-159. |
| 41 | Lin H H, Sun S C, Lin Z P, et al. Bio-carrier-enhanced aerobic granulation: effects on the extracellular polymeric substances production and microorganism community[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 280: 130756. |
| 42 | Ghotekar S, Pansambal S, Bilal M, et al. Environmentally friendly synthesis of Cr2O3 nanoparticles: characterization, applications and future perspective ─ a review[J]. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 2021, 3: 100089. |
| 43 | Lu J, Chang J, Lee D. Adding carbon-based materials on anaerobic digestion performance: a mini-review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 300: 122696. |
| 44 | Jiang Q, Zheng Z Y, Zhang Y, et al. Key properties identification of biochar material in anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge for enhancement of methane production[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(3): 109850. |
| 45 | Kilduff J E, Karanfil T. Trichloroethylene adsorption by activated carbon preloaded with humic substances: effects of solution chemistry[J]. Water Research, 2002, 36(7): 1685-1698. |
| 46 | Zhang L Q, Chen Z K, Zhu S S, et al. Effects of biochar on anaerobic treatment systems: some perspectives[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 367: 128226. |
| 47 | Lyu H H, Tang J C, Shen B X, et al. Development of a novel chem-bio hybrid process using biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite and Corynebacterium variabile HRJ4 for enhanced trichloroethylene dechlorination[J]. Water Research, 2018, 147: 132-141. |
| 48 | 吉昌铃, 孟梁, 邓欢, 等. 纳米零价铁-聚乳酸-生物炭复合材料协同微生物去除水中1,1,1-三氯乙烷[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(8): 1909-1917. |
| Ji C L, Meng L, Deng H, et al. 1, 1, 1-Trichloroethane removal from water by nano-zero valent iron-polylactic acid-biochar composite coupled with microorganism[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2019, 13(8): 1909-1917. | |
| 49 | Dong H R, Deng J M, Xie Y K, et al. Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar for Cr(Ⅵ) removal from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 332: 79-86. |
| 50 | Dong H R, He Q, Zeng G M, et al. Chromate removal by surface-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron: effect of different surface coatings and water chemistry[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 471: 7-13. |
| 51 | Xie Y K, Dong H R, Zeng G M, et al. The interactions between nanoscale zero-valent iron and microbes in the subsurface environment: a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 321: 390-407. |
| 52 | Dong H, Zhang C, Hou K, et al. Removal of trichloroethylene by biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous solution[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 188: 188-196. |
| 53 | Li J J, Li C X, Li Y L, et al. Elucidation of high removal efficiency of dichlorophen wastewater in anaerobic treatment system with iron/carbon mediator[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 330: 129854. |
| 54 | Lu Y, Zhang S J, Liu Q, et al. Nitrobenzene reduction promoted by the integration of carbon nanotubes and Geobacter sulfurreducens [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2023, 325: 121444. |
| 55 | Xu J, Lv X S, Li J D, et al. Simultaneous adsorption and dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol by Pd/Fe nanoparticles with multi-walled carbon nanotube support[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 225/226: 36-45. |
| 56 | Stankovich S, Dikin D A, Piner R D, et al. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide[J]. Carbon, 2007, 45(7): 1558-1565. |
| 57 | Sahu R S, Li D L, Doong R A. Unveiling the hydrodechlorination of trichloroethylene by reduced graphene oxide supported bimetallic Fe/Ni nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334: 30-40. |
| 58 | 陆海楠, 理鹏, 郭琳, 等. 改性生物炭负载零价铁对土壤中三氯乙烯的去除及微生物响应[J]. 环境科学, DOI: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202207273 . |
| Lu H N, Li P, Guo L, et al. Effects of modified biochar-supported zero-valent iron on the removal of trichloroethylene and responses of microbial community in soil[J]. Environmental Science, DOI: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202207273 . | |
| 59 | Zhao Z Q, Li Y, Zhang Y B, et al. Sparking anaerobic digestion: promoting direct interspecies electron transfer to enhance methane production[J]. iScience, 2020, 23(12): 101794.. |
| 60 | Zhao Z Q, Zhang Y B, Li Y, et al. Potentially shifting from interspecies hydrogen transfer to direct interspecies electron transfer for syntrophic metabolism to resist acidic impact with conductive carbon cloth[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 313: 10-18. |
| 61 | Wang Z K, Liu Q H, Yang Z M. Nano magnetite-loaded biochar boosted methanogenesis through shifting microbial community composition and modulating electron transfer[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 861: 160597. |
| 62 | 武讨龙, 张胜江, 刘津洋, 等. 双金属有机框架材料的研究进展[J]. 无机盐工业, 2023, 55(6): 8-17. |
| Wu T L, Zhang S J, Liu J Y, et al. Research progress of bimetallic-organic frameworks materials[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2023, 55(6): 8-17. | |
| 63 | 尚海涛, 李智灵, 杨琦, 等. 负载型纳米Pd/Fe对挥发性氯代烃的去除[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(2): 313-320. |
| Shang H T, Li Z L, Yang Q, et al. Removal of volatile chlorinated hydrocarbons in water by supported nanoscale Pd/Fe particles[J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(2): 313-320. | |
| 64 | Lin X Q, Li Z L, Zhu Y Y, et al. Palladium/iron nanoparticles stimulate tetrabromobisphenol a microbial reductive debromination and further mineralization in sediment[J]. Environment International, 2020, 135: 105353. |
| 65 | Su J, Chen H, Wang J, et al. Enhanced dechlorination of carbon tetrachloride by Ni-doped zero-valent iron nanoparticles @ magnetic Fe3O4 (Ni4/Fe@Fe3O4) nanocomposites[J]. Colloids and Surfaces a: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 623: 126691. |
| 66 | Ma Y Y, Wang Y Y, Lv X F, et al. Insight into the mode of action of Pd-doped zero-valent iron nanoparticles@graphene (Pd/FePs@G) toward carbon tetrachloride dechlorination reaction in aqueous solution[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2018, 560: 84-93. |
| 67 | Gong L, Qi J L, Lv N, et al. Mechanistic role of nitrate anion in TCE dechlorination by ball milled ZVI and sulfidated ZVI: experimental investigation and theoretical analysis[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123844. |
| 68 | Ri C, Li F X, Mun H, et al. Ball-milled Fe0/FeS2 enhanced interaction of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 with anaerobic microbial community: impact on 2,4-dichloronitrobenzene reduction and methane yield[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 452: 139086. |
| 69 | Dai C B, Yang L B, Wang J, et al. Enhancing anaerobic digestion of pharmaceutical industries wastewater with the composite addition of zero valent iron (ZVI) and granular activated carbon (GAC)[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 346: 126566. |
| 70 | Kang H, Lee S, Lim T, et al. Effect of microbial community structure in inoculum on the stimulation of direct interspecies electron transfer for methanogenesis[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 332: 125100. |
| 71 | Park J H, Park J H, Seong H J, et al. Metagenomic insight into methanogenic reactors promoting direct interspecies electron transfer via granular activated carbon[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 259: 414-422. |
| 72 | Vilela R, Saia F T, Gregoracci G B, et al. Hydrogen production in reactors: the influence of organic loading rate, inoculum and support material[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(50): 27259-27271. |
| 73 | Zhuang H, Zhu H, Zhang J, et al. Enhanced 2,4,6-trichlorophenol anaerobic degradation by Fe3O4 supported on water hyacinth biochar for triggering direct interspecies electron transfer and its use in coal gasification wastewater treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 296: 122306. |
| 74 | Castilho T G, Rodrigues J A D, García J, et al. Recent advances and perspectives in the use of conductive materials to improve anaerobic wastewater treatment: a systematic review approached[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2022, 50: 103193. |
| 75 | 朱剑锋, 王艳琼, 王红武. 铁氧化物促进微生物直接种间电子传递的机理及其研究现状[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(6): 1856-1868. |
| Zhu J F, Wang Y Q, Wang H W. A review on enhancement of direct interspecies electron transfer induced by iron oxides and its mechanism[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(6): 1856-1868. | |
| 76 | Lovley D R. Electrically conductive pili: biological function and potential applications in electronics[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2017, 4(1): 190-198. |
| 77 | 蒋海明, 王路路, 李侠. 微生物种间直接电子传递方式耦合产甲烷研究进展[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2019, 33(6): 1303-1313. |
| Jiang H M, Wang L L, Li X. Research progress on coupling methane production by direct electron transfer between microbial species[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2019, 33(6): 1303-1313. | |
| 78 | He S F, Feng L K, Zhao W X, et al. Composition and molecular structure analysis of hydrophilic/hydrophobic extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) with impacts on sludge dewaterability[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 462: 142234. |
| 79 | Xiao Y, Zhao F. Electrochemical roles of extracellular polymeric substances in biofilms[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2017, 4(1): 206-211. |
| 80 | Gao Y J, Cai T, Yin J, et al. Insights into biodegradation behaviors of methanolic wastewater in up-flow anaerobic sludge bed (UASB) reactor coupled with in-situ bioelectrocatalysis[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 376: 128835. |
| 81 | Yan W W, Sun F Q, Liu J B, et al. Enhanced anaerobic phenol degradation by conductive materials via EPS and microbial community alteration[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 352: 1-9. |
| [1] | 杨百玉, 寇悦, 姜峻韬, 詹亚力, 王庆宏, 陈春茂. 炼化碱渣湿式氧化预处理过程DOM的化学转化特征[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3912-3920. |
| [2] | 段重达, 姚小伟, 朱家华, 孙静, 胡南, 李广悦. 环境因素对克雷白氏杆菌诱导碳酸钙沉淀的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3543-3553. |
| [3] | 屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [4] | 朱理想, 罗默也, 张晓东, 龙涛, 余冉. 醌指纹法指示三氯乙烯污染土功能微生物活性应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2647-2654. |
| [5] | 张建华, 陈萌萌, 孙雅雯, 彭永臻. 部分短程硝化同步除磷耦合Anammox实现生活污水高效脱氮除磷[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2147-2156. |
| [6] | 胡香凝, 尹渊博, 袁辰, 是赟, 刘翠伟, 胡其会, 杨文, 李玉星. 成品油在土壤中运移可视化的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1827-1835. |
| [7] | 王思琪, 顾天宇, 陈献富, 王通, 李佳, 柯威, 李小锋, 范益群. 陶瓷膜用于杜仲叶提取液澄清的分离特性与膜污染机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1113-1125. |
| [8] | 祖凌鑫, 胡荣庭, 李鑫, 陈余道, 陈广林. 木质生物质化学组分的碳释放产物特征和反硝化利用程度[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1332-1342. |
| [9] | 刘定平, 陈爱桦, 张向阳, 何文浩, 王海. 铝灰半干法水解脱氮研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1294-1302. |
| [10] | 徐银, 蔡洁, 陈露, 彭宇, 刘夫珍, 张晖. 异相可见光催化耦合过硫酸盐活化技术在水污染控制中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 995-1009. |
| [11] | 黄玉龙, 吕凡, 仇俊杰, 章骅, 何品晶. 易腐垃圾厌氧消化沼液理化性质及VOCs分子特征[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1275-1285. |
| [12] | 陈瑞哲, 程磊磊, 顾菁, 袁浩然, 陈勇. 纤维增强树脂复合材料化学回收技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 981-994. |
| [13] | 查坦捷, 杨涵, 秦荷杰, 关小红. 仿生材料的构建及其在水环境化学领域中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 585-598. |
| [14] | 陈晨, 杨倩, 陈云, 张睿, 刘冬. 不同氧浓度下煤挥发分燃烧的化学动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4133-4146. |
| [15] | 许贤伦, 钱旸, 张兴旺, 雷乐成. 高压脉冲介质阻挡放电降解土壤中芘的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4025-4033. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号