化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (3): 801-814.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20231331
王娟1,2( ), 李秀明1,2, 邵炜涛1,2, 丁续1,2, 霍莹3, 付连超3, 白云宇1,2, 李迪1,2
), 李秀明1,2, 邵炜涛1,2, 丁续1,2, 霍莹3, 付连超3, 白云宇1,2, 李迪1,2
收稿日期:2023-12-13
修回日期:2024-01-11
出版日期:2024-03-25
发布日期:2024-05-11
通讯作者:
王娟
作者简介:王娟(1977—),女,博士,副教授,wangjuan@cup.edu.cn
Juan WANG1,2( ), Xiuming LI1,2, Weitao SHAO1,2, Xu DING1,2, Ying HUO3, Lianchao FU3, Yunyu BAI1,2, Di LI1,2
), Xiuming LI1,2, Weitao SHAO1,2, Xu DING1,2, Ying HUO3, Lianchao FU3, Yunyu BAI1,2, Di LI1,2
Received:2023-12-13
Revised:2024-01-11
Online:2024-03-25
Published:2024-05-11
Contact:
Juan WANG
摘要:
采用Euler-Euler双流体模型对安装不同数量的水平多孔板的鼓泡塔内气液两相流动及传质特性进行数值模拟研究,并探究了不同表观气速条件对鼓泡塔内气含率、气泡直径分布和气液传质系数的影响。结果表明,不同数量的多孔板和不同位置的多孔板都会影响气含率的分布;随着多孔板的数目增加,鼓泡塔液相上方区域的气含率增加,但影响区域有限;安装多孔板后,鼓泡塔内径向位置的平均气含率变化明显,出现“M”形状的分布。不同表观气速下,未安装多孔板的鼓泡塔内直径为1~2 mm的微小气泡占比超过30%;安装多孔板后,微小气泡占比明显增加;气液传质系数在中心区域(径向无量纲为-0.5~0.5)较为平缓,波动不大。最后将模拟计算得到的气液体积传质系数与Akita的关联式计算值进行比较,本文计算结果略高。
中图分类号:
王娟, 李秀明, 邵炜涛, 丁续, 霍莹, 付连超, 白云宇, 李迪. 多孔板鼓泡塔流动与传质特性数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 801-814.
Juan WANG, Xiuming LI, Weitao SHAO, Xu DING, Ying HUO, Lianchao FU, Yunyu BAI, Di LI. Numerical simulation of flow and mass transfer characteristics in porous plate bubbling column reactor[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 801-814.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| D/mm | 149 |
| H/mm | 1616 |
| H1/mm | 160 |
| H2/mm | 420 |
| H3/mm | 680 |
| H4/mm | 940 |
| H5/mm | 1130 |
| H6/mm | 8 |
表1 模型建立数据汇总
Table 1 Model establishment data summary
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| D/mm | 149 |
| H/mm | 1616 |
| H1/mm | 160 |
| H2/mm | 420 |
| H3/mm | 680 |
| H4/mm | 940 |
| H5/mm | 1130 |
| H6/mm | 8 |
| Object | Density/(kg/m³) | Viscosity/(Pa·s) |
|---|---|---|
| water | 1000 | 0.00178 |
| oxygen | 1.492 | 0.000019 |
表2 氧气与水的物性参数
Table 2 Physical parameters of oxygen and water
| Object | Density/(kg/m³) | Viscosity/(Pa·s) |
|---|---|---|
| water | 1000 | 0.00178 |
| oxygen | 1.492 | 0.000019 |
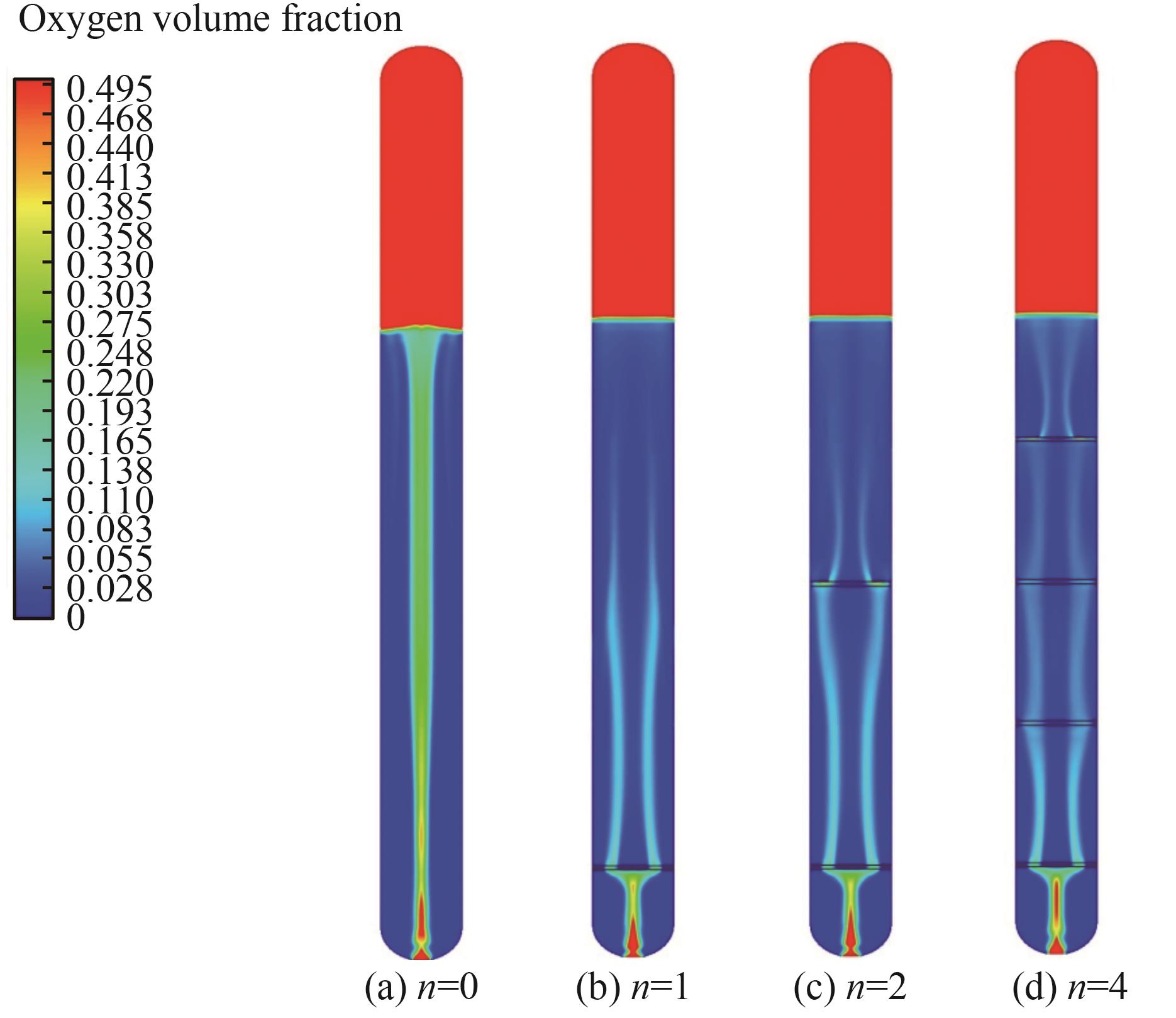
图6 安装不同数量多孔板的鼓泡塔纵截面气含率分布
Fig.6 Distribution of gas holdup in longitudinal section of perforated plates bubbling column reactors with different numbers
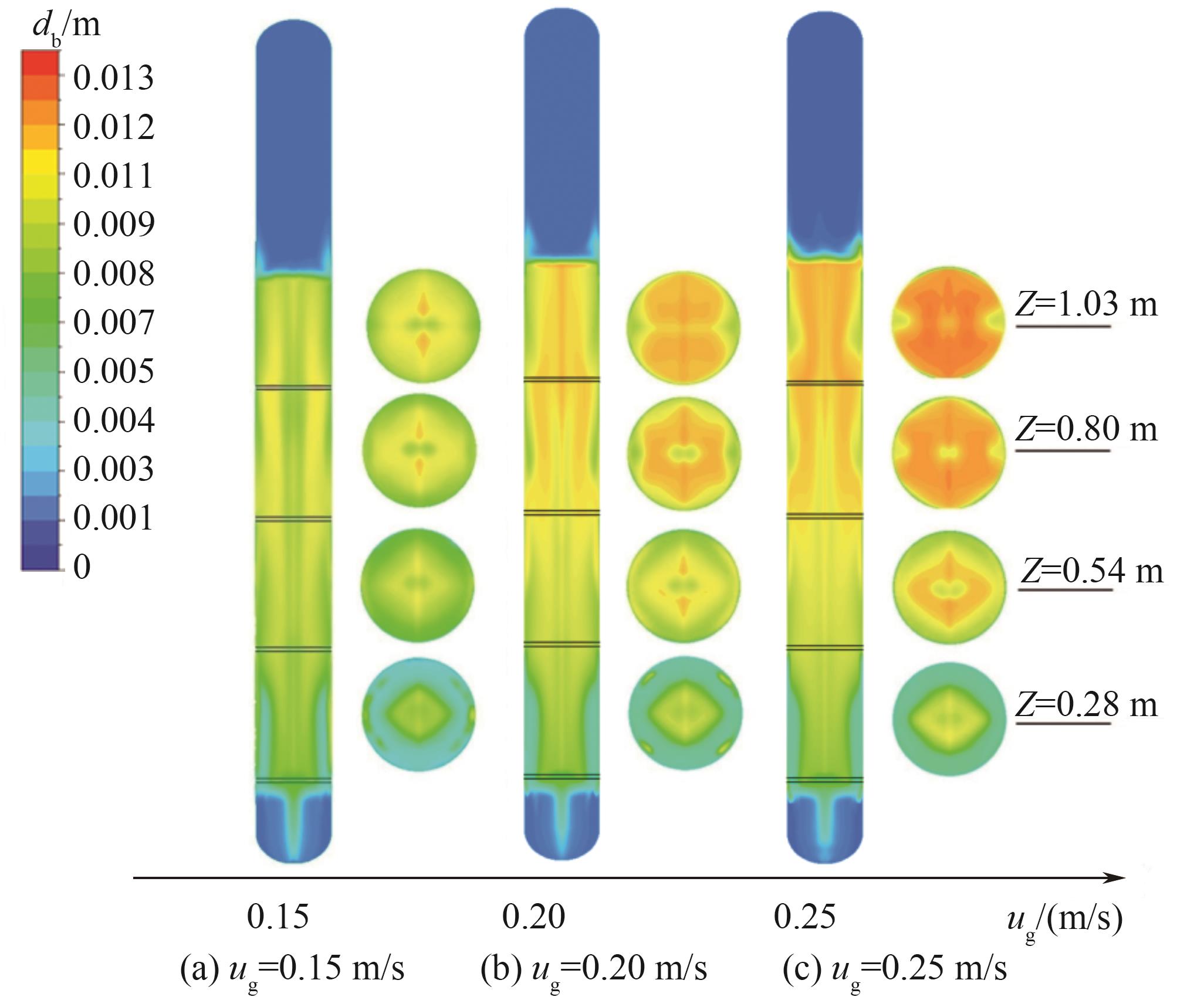
图9 不同表观气速下安装4块多孔板的鼓泡塔内气泡尺寸分布情况
Fig.9 Bubble size distribution in four porous plates bubbling column reactors installed at different superficial gas velocities
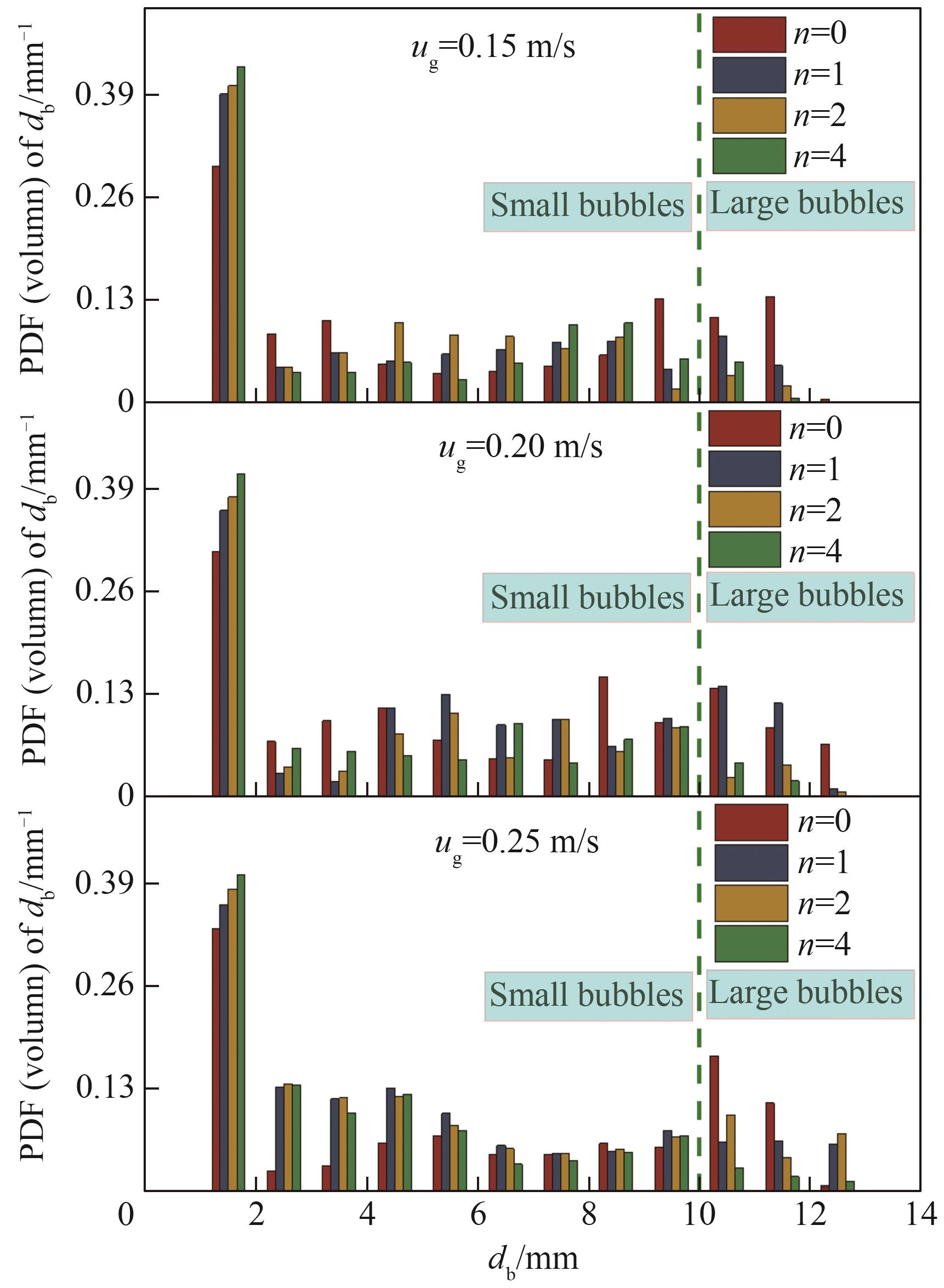
图10 不同表观气速和安装不同数量多孔板的鼓泡塔内气泡直径概率密度分布
Fig.10 Probability density distribution of bubble diameter in bubbling column reactors with different superficial gas velocities and different number of perforated plates

图11 表观气速0.25 m/s时不同向多孔板数量下鼓泡塔内平均气泡直径概率径分布
Fig.11 Probability radial distribution function of average bubble diameter in the bubbling column reactors with different number of perforated plates at the superficial gas velocity of 0.25 m/s
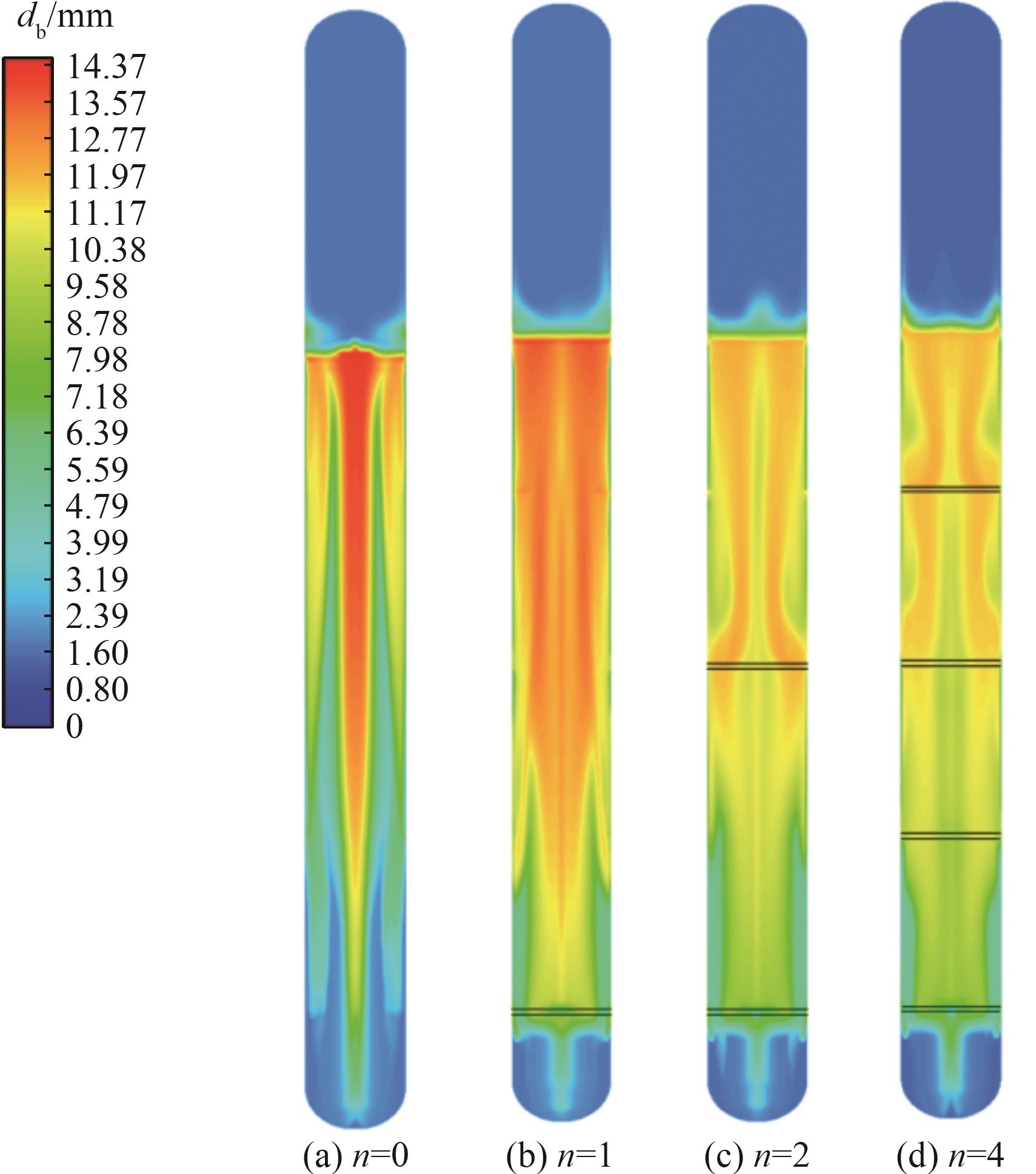
图13 ug=0.25 m/s时安装不同位置的多孔板鼓泡塔内气泡直径分布情况
Fig.13 Distribution of bubble diameter in porous plates bubbling column reactors installed at different positions at ug=0.25 m/s
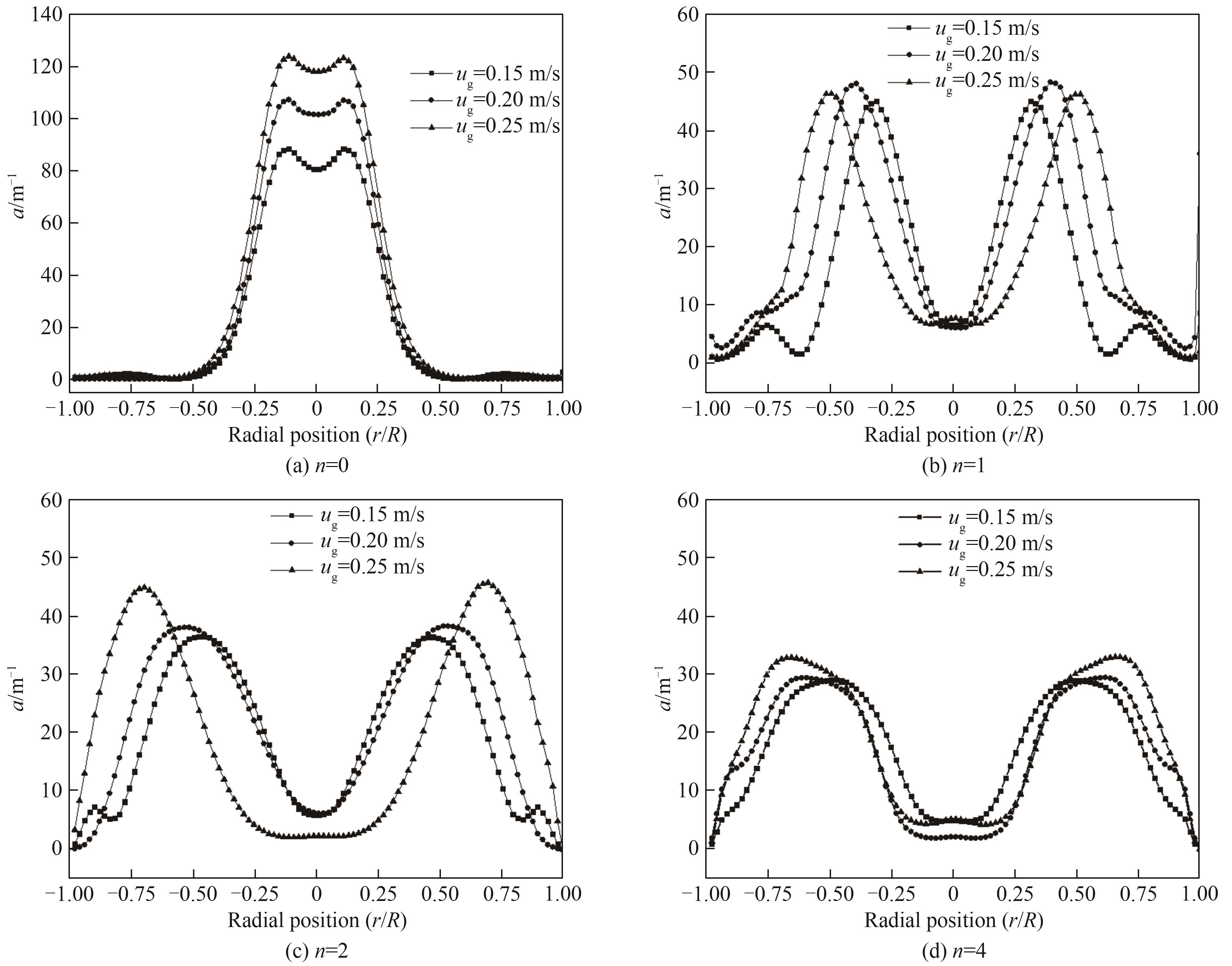
图14 不同表观气速与安装不同数量多孔板下鼓泡塔内H/D=4截面处气液界面面积
Fig.14 The gas-liquid interface area at the H/D=4 cross-section in the bubbling column reactor under different superficial gas velocities and installation of different numbers of porous plates
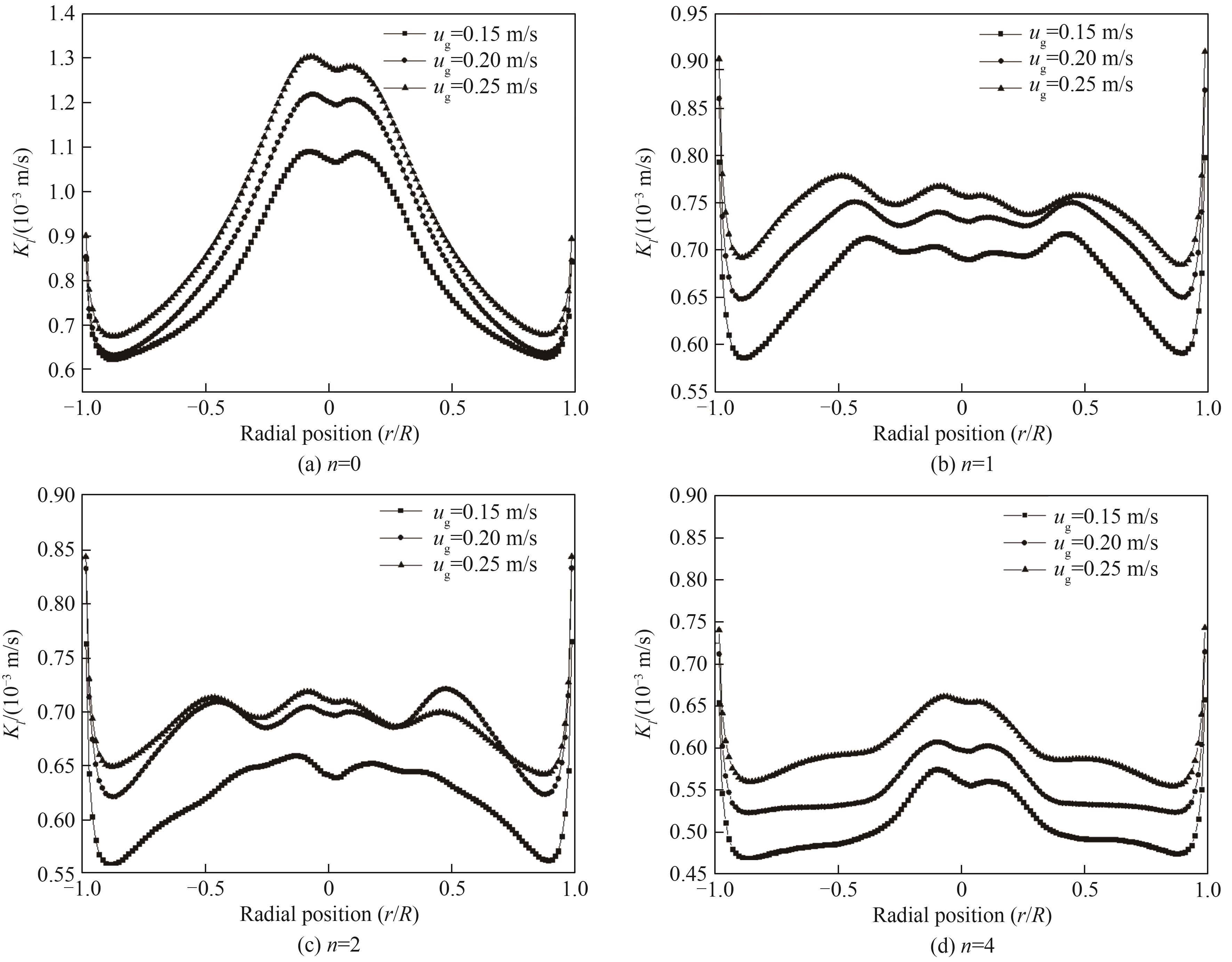
图15 不同表观气速与安装不同数量多孔板下鼓泡塔内平均气液传质系数径向分布
Fig.15 Radial distribution function of average gas-liquid mass transfer coefficient in bubbling column reactors with different superficial gas velocities and different number of perforated plates
| 1 | Mohammadzade Fard S, Farsi M, Rahimpour M R. Optimization of ethylene dimerization in a bubble column reactor based on coupling kinetic and equilibrium models[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2021, 174: 357-364. |
| 2 | Muharam Y, Putri A D. Simulation of hydrotreating of vegetable oil in a slurry bubble column reactor for green diesel production[J]. International Journal of Technology, 2018, 9(6): 1168. |
| 3 | Shaikh A, Al-Dahhan M. Scale-up of bubble column reactors: a review of current state-of-the-art[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(24): 8091-8108. |
| 4 | 李光, 杨晓钢, 戴干策. 鼓泡塔反应器气液两相流CFD数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2008, 59(8): 1958-1965. |
| Li G, Yang X G, Dai G C. CFD simulation of gas-liquid flow in bubble column[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2008, 59(8): 1958-1965. | |
| 5 | 薄守石, 武俊庭, 孙兰义. 流体物性对悬浮床加氢环流反应器的影响[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2013, 44(8): 59-62. |
| Bo S S, Wu J T, Sun L Y. Numerical simulation of effect of physical properties on loop reactor of slurry bed[J]. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals, 2013, 44(8): 59-62. | |
| 6 | Chen P, Duduković M P, Sanyal J. Three-dimensional simulation of bubble column flows with bubble coalescence and breakup[J]. AIChE Journal, 2005, 51(3): 696-712. |
| 7 | van Baten J M, Krishna R. Eulerian simulation strategy for scaling up a bubble column slurry reactor for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2004, 43(16): 4483-4493. |
| 8 | Möller F, Lau Y M, Seiler T, et al. A study on the influence of the tube layout on sub-channel hydrodynamics in a bubble column with internals[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 179: 265-283. |
| 9 | Jhawar A K, Prakash A. Bubble column with internals: effects on hydrodynamics and local heat transfer[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2014, 92(1): 25-33. |
| 10 | Besagni G, Inzoli F. Influence of internals on counter-current bubble column hydrodynamics: holdup, flow regime transition and local flow properties[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 145: 162-180. |
| 11 | Huang Z L, Shuai Y, Ren C J, et al. Effects of internal structures on mass transfer performance of jet bubbling reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2022, 175: 108936. |
| 12 | Guo X F, Chen C X. Simulating the impacts of internals on gas-liquid hydrodynamics of bubble column[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 174: 311-325. |
| 13 | Deshpande S S, Kar K, Pressler J, et al. Mass transfer estimation for bubble column scale up[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 205: 350-357. |
| 14 | Zhang H H, Guo K Y, Wang Y L, et al. Numerical simulations of the effect of liquid viscosity on gas-liquid mass transfer of a bubble column with a CFD-PBM coupled model[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 161: 120229. |
| 15 | Lau R, Peng W, Velazquez-Vargas L G, et al. Gas-liquid mass transfer in high-pressure bubble columns[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2004, 43(5): 1302-1311. |
| 16 | Bando Y, Chaya M, Hamano S I, et al. Effect of liquid height on flow characteristics in bubble column using highly viscous liquid[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 2003, 36(5): 523-529. |
| 17 | Akita K, Yoshida F. Gas holdup and volumetric mass transfer coefficient in bubble columns. Effects of liquid properties[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 1973, 12(1): 76-80. |
| 18 | An M, Guan X P, Yang N, et al. Effects of internals on fluid dynamics and reactions in pilot-scale slurry bubble column reactors: a CFD study for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2018, 132: 194-207. |
| 19 | Xing C T, Wang T F, Wang J F. Experimental study and numerical simulation with a coupled CFD-PBM model of the effect of liquid viscosity in a bubble column[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 95: 313-322. |
| 20 | Ramírez-Muñoz J, Gama-Goicochea A, Salinas-Rodríguez E. Drag force on interacting spherical bubbles rising in-line at large Reynolds number[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2011, 37(8): 983-986. |
| 21 | Yan P, Jin H B, He G X, et al. CFD simulation of hydrodynamics in a high-pressure bubble column using three optimized drag models of bubble swarm[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 199: 137-155. |
| 22 | Lane C D, Parisien V, Macchi A, et al. Investigation of bubble swarm drag at elevated pressure in a contaminated system[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 152: 381-391. |
| 23 | Guan X P, Yang N. CFD simulation of pilot-scale bubble columns with internals: influence of interfacial forces[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2017, 126: 109-122. |
| 24 | Chai X, Otic I, Cheng X. A new drag force model for the wake acceleration effect and its application to simulation of bubbly flow[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2015, 80: 24-36. |
| 25 | Roghair I, Lau Y M, Deen N G, et al. On the drag force of bubbles in bubble swarms at intermediate and high Reynolds numbers[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(14): 3204-3211. |
| 26 | Roghair I, Van Sint Annaland M, Kuipers H J A M. Drag force and clustering in bubble swarms[J]. AIChE Journal, 2013, 59(5): 1791-1800. |
| 27 | Yang G Y, Guo K Y, Wang T F. Numerical simulation of the bubble column at elevated pressure with a CFD-PBM coupled model[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 170: 251-262. |
| 28 | Tomiyama A, Kataoka I, Zun I, et al. Drag coefficients of single bubbles under normal and micro gravity conditions[J]. JSME International Journal Series B, 1998, 41(2): 472-479. |
| 29 | Kumar S, Ramkrishna D. On the solution of population balance equations by discrettization (1): A fixed pivot technique[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1996, 51(8): 1311-1332. |
| 30 | Luo H. Coalescence, breakup and liquid circulation in bubble column reactors[D]. Trondheim: The Norwegian Institute of Technology, 1993. |
| 31 | Luo H A, Svendsen H F. Theoretical model for drop and bubble breakup in turbulent dispersions[J]. AIChE Journal, 1996, 42(5): 1225-1233. |
| 32 | Smith P L, van Winkle M. Discharge cofficients through perforated plates at Reynolds numbers of 400 to 3000[J]. AIChE Journal, 1958, 4(3): 266-268. |
| 33 | 谢明辉. 多层搅拌式生物反应器内溶液流变性质对流场特性影响的研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2013. |
| Xie M H. Study of the effect of the rheology properties on flow fields in stirred bioreactors with multiple impellers[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2013. | |
| 34 | Ranganathan P, Sivaraman S. Investigations on hydrodynamics and mass transfer in gas-liquid stirred reactor using computational fluid dynamics[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(14): 3108-3124. |
| 35 | Moraveji M K, Sajjadi B, Jafarkhani M, et al. Experimental investigation and CFD simulation of turbulence effect on hydrodynamic and mass transfer in a packed bed airlift internal loop reactor[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2011, 38(4): 518-524. |
| 36 | Kerdouss F, Bannari A, Proulx P, et al. Two-phase mass transfer coefficient prediction in stirred vessel with a CFD model[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2008, 32(8): 1943-1955. |
| 37 | 贾翔飞, 钱嘉澍, 吴幼青, 等. 鼓泡塔反应器中两相流动CFD-PBM耦合数值模拟[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 47(1): 1-10. |
| Jia X F, Qian J S, Wu Y Q, et al. CFD-PBM coupled numerical simulation of two phase flow in bubble column reactor[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology, 2021, 47(1): 1-10. |
| [1] | 韩东, 高宁宁, 唐新德, 龚升高, 夏良树. 适用欧拉-拉格朗日方法模拟气液泡状流的气泡破碎模型[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 553-565. |
| [2] | 崔怡洲, 李成祥, 翟霖晓, 刘束玉, 石孝刚, 高金森, 蓝兴英. 亚毫米气泡和常规尺寸气泡气液两相流流动与传质特性对比[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 197-210. |
| [3] | 李乃良, 陈聚凯, 韩骏楷, 赵庆杰, 张一帆. 静态及摇摆条件下弹状流壁面切应力实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(12): 4852-4862. |
| [4] | 禹言芳, 刘桓辰, 孟辉波, 刘励图, 李毓, 吴剑华. Lightnin静态混合器内气泡分散流体动力学特性实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3565-3575. |
| [5] | 王凯玥, 马永丽, 李琛, 刘明言. 气液固微型流化床的气液传质系数[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3529-3540. |
| [6] | 张文龙,宁尚雷,靳海波,马磊,何广湘,杨索和,郭晓燕,张荣月. 鼓泡塔内空气-醋酸体系流体力学参数的CFD-PBM耦合模型数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2589-2602. |
| [7] | 施炜斌, 龙姗姗, 杨晓钢, 蔡心悦. 计及气泡诱导与剪切湍流的气泡破碎、湍流相间扩散及传质模型[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2573-2588. |
| [8] | 姜佳彤, 胡斌, 王如竹, 刘华, 张治平, 李宏波. R1233zd(E)高温热泵用卧式冷凝器的换热动态模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(S1): 98-105. |
| [9] | 张文龙, 侯燕, 靳海波, 马磊, 何广湘, 杨索和, 郭晓燕, 张荣月. 加温加压下CFD-PBM耦合模型空气-水两相流数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4594-4606. |
| [10] | 赵雨萌, 王亦飞, 彭昕, 位宗瑶, 于广锁, 王辅臣. 洗涤冷却室垂直环隙空间内液相流动结构的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(8): 4039-4046. |
| [11] | 高颂,徐燕燕,李继香,叶爽,黄伟光. 基于TFM-PBM耦合模型的离心泵内微气泡破碎合并的模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 5082-5093. |
| [12] | 杨光,王沫然. 共轴反转型生物反应器内流场数值模拟与性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 5188-5199. |
| [13] | 陈宏霞, 肖红洋, 孙源, 刘霖. 微柱表面液滴定壁温沸腾实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(9): 3363-3369. |
| [14] | 张华海, 王铁峰. CFD-PBM耦合模型模拟气液鼓泡床的通用性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(2): 487-495. |
| [15] | 刘英杰, 祝京旭. 气泡驱动液固流化床内二元颗粒的流化行为[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(1): 91-98. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号