化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (10): 3437-3451.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240147
收稿日期:2024-01-31
修回日期:2024-04-20
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
贺缨
作者简介:朱子厚(1999—),男,硕士研究生,3325519805@qq.com
基金资助:
Zihou ZHU( ), Feng PAN, Pengfei ZHAO, Ying HE(
), Feng PAN, Pengfei ZHAO, Ying HE( )
)
Received:2024-01-31
Revised:2024-04-20
Online:2024-10-25
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Ying HE
摘要:
不同材质的加热表面因其热物性参数存在差异,在沸腾过程中会表现出不同的热响应特性,对气泡成核、生长脱离也有一定影响。为深入探究加热表面热物性对单气泡沸腾过程中加热表面热响应与气泡动力学行为之间相互作用的影响机理,基于开源软件OpenFOAM,通过对微液层内传热传质过程进行分析,建立了包含传热、相变和流动的流-热耦合模拟框架。首先对铜、铝和硅表面上不同尺寸的汽化核心进行了单气泡沸腾模拟,结果表明,随着导热性能的提升,加热表面过热度下降,气泡等待周期缩短,同时随着汽化核心尺寸的减小,加热表面热物性对气泡等待周期的影响逐渐减弱。另外,对于覆有石墨烯涂层的铜表面,石墨烯涂层的存在增强了沸腾表面热量的横向扩散,由于基底材料向上传递热量的速度慢,同时加热表面因液层蒸发带走热量多,导致汽化核心处过热度恢复较慢,出现了更低的表面过热度和更长的气泡等待周期。
中图分类号:
朱子厚, 潘丰, 赵鹏飞, 贺缨. 加热表面材质对核态沸腾换热影响的流-热耦合数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3437-3451.
Zihou ZHU, Feng PAN, Pengfei ZHAO, Ying HE. Fluid-thermal coupling numerical study on effect of heater surface materials on nucleate boiling heat transfer[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3437-3451.
| 材质 | 密度 ρs/(kg/m3) | 热导率 λs/(W/(m·K)) | 比热容 cp,s/(J/(kg·K)) | 热扩散率 DT/(m2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 铜 | 8930 | 393 | 386 | 1.140×10-4 |
| 铝 | 2690 | 247 | 900 | 1.020×10-4 |
| 硅 | 2340 | 110 | 750 | 6.268×10-5 |
表1 不同材质的热物性参数
Table 1 Thermophysical parameters of different materials
| 材质 | 密度 ρs/(kg/m3) | 热导率 λs/(W/(m·K)) | 比热容 cp,s/(J/(kg·K)) | 热扩散率 DT/(m2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 铜 | 8930 | 393 | 386 | 1.140×10-4 |
| 铝 | 2690 | 247 | 900 | 1.020×10-4 |
| 硅 | 2340 | 110 | 750 | 6.268×10-5 |
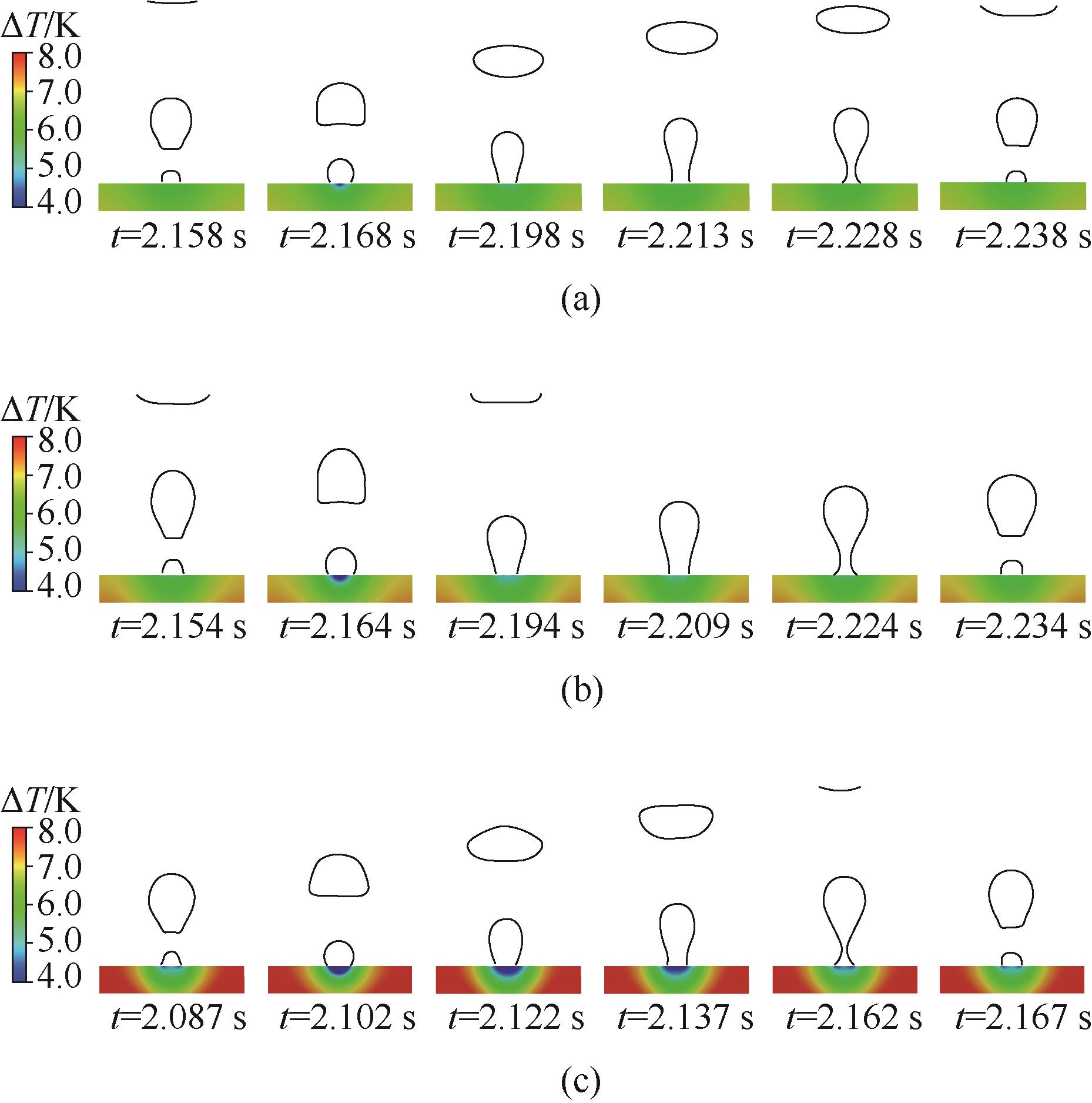
图6 铜(a)、铝(b)和硅(c)加热器表面上一个周期内的气泡生长过程及加热器内部的过热度云图
Fig.6 Bubble growth process on surface of copper (a), aluminum (b), and silicon (c) heaters within one cycle and cloud map of superheat inside heater
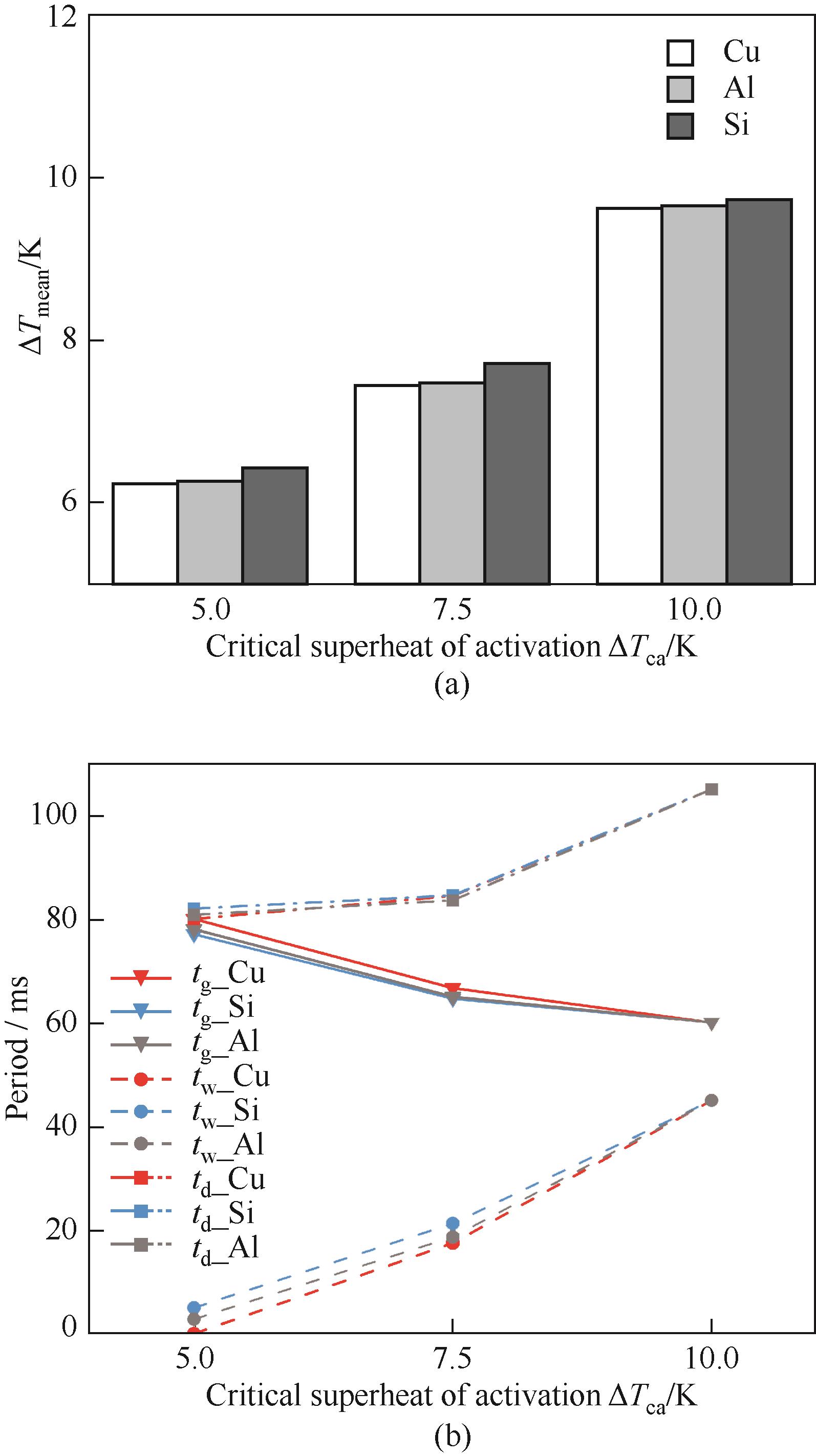
图8 (a)铜、铝和硅表面平均过热度对比;(b)气泡生长时间、等待时间和脱离周期的对比
Fig.8 (a) Average superheat on copper, aluminum, and silicon surfaces; (b) Bubble growth time, waiting time, and detachment period
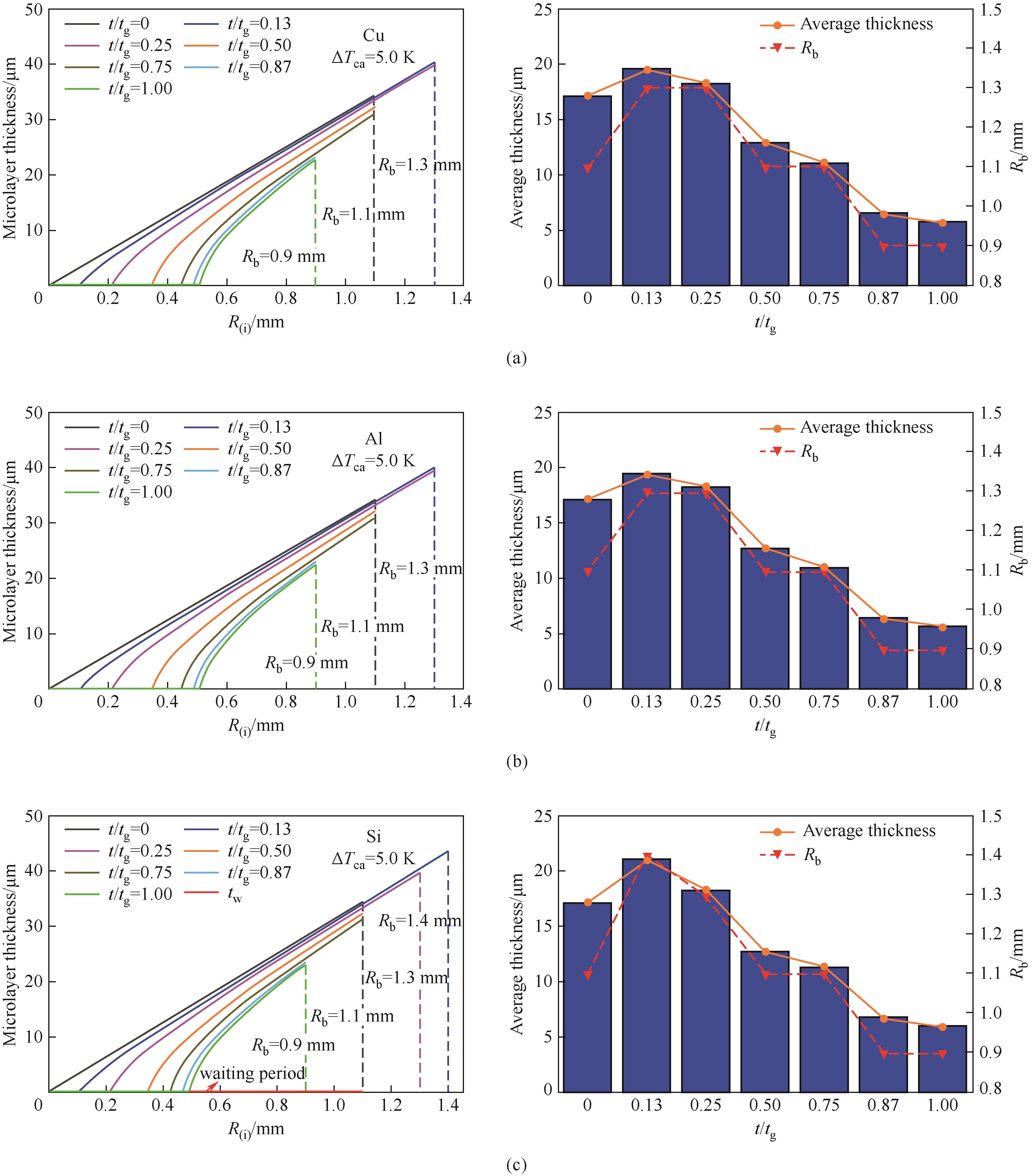
图9 铜(a)、铝(b)和硅(c)加热表面上气泡生长过程中微液层分布的动态变化及微液层平均厚度随时间的变化
Fig.9 Distribution and average thickness of microlayer on copper (a), aluminum (b), and silicon (c) heater surfaces
| 材质 | 密度 ρs/(kg/m3) | 热导率 λs/(W/(m·K)) | 比热容 cp.s/(J/(kg·K)) | 热扩散率 DT/(m2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 石墨烯 | 2300 | 1584 | 710 | 9.70×10-4 |
表2 石墨烯的热物性参数
Table 2 Thermophysical parameters of graphene
| 材质 | 密度 ρs/(kg/m3) | 热导率 λs/(W/(m·K)) | 比热容 cp.s/(J/(kg·K)) | 热扩散率 DT/(m2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 石墨烯 | 2300 | 1584 | 710 | 9.70×10-4 |
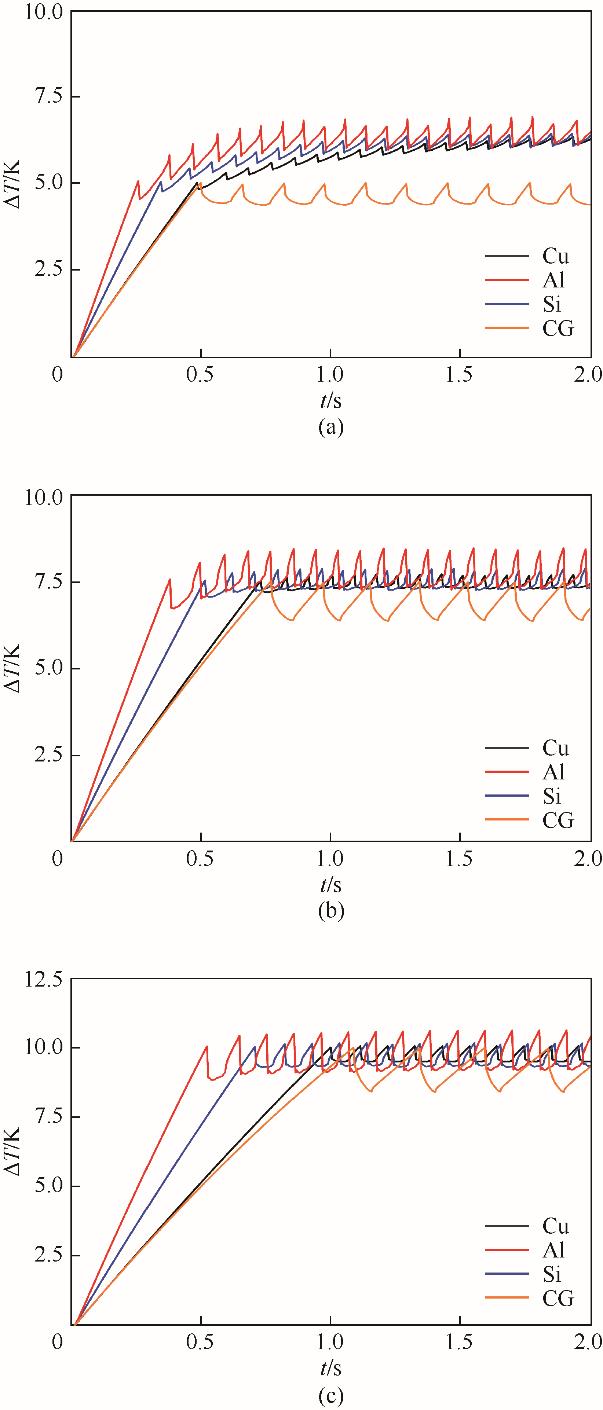
图13 临界活化过热度为5.0 K(a)、7.5 K(b)和10.0 K(c)时加热表面平均过热度随时间的变化
Fig.13 Variation of average superheat over time when critical activation superheat is 5.0 K (a), 7.5 K (b), and 10.0 K (c)
| 孔穴临界活化过热度/K | 平均过热度差距/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CG | Cu | Al | |
| 5.0 | 28.37% | 3.18% | 2.62% |
| 7.5 | 10.47% | 3.12% | 2.55% |
| 10.0 | 5.95% | 1.38% | 0.53% |
表3 不同加热表面平均过热度的差距
Table 3 Differences in average superheat on heater surfaces
| 孔穴临界活化过热度/K | 平均过热度差距/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CG | Cu | Al | |
| 5.0 | 28.37% | 3.18% | 2.62% |
| 7.5 | 10.47% | 3.12% | 2.55% |
| 10.0 | 5.95% | 1.38% | 0.53% |
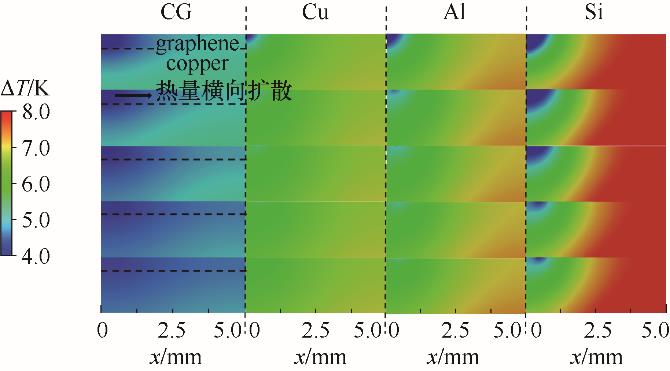
图19 覆有石墨烯涂层的铜表面以及铜、铝和硅表面上沸腾过程中加热器内部的瞬时热响应
Fig.19 Instantaneous thermal response inside heater during boiling process on copper-graphene surface, copper surface, aluminum surface and silicon surface
| 1 | Goel P, Nayak A K, Kulkarni P P, et al. Experimental study on bubble departure characteristics in subcooled nucleate pool boiling[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2017, 89: 163-176. |
| 2 | Abbassi W, Besbes S, Ben Aissia H, et al. Study of the rise of a single/multiple bubbles in quiescent liquids using the VOF method[J]. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 2019, 41(6): 272. |
| 3 | Cooper M G. The microlayer and bubble growth in nucleate pool boiling[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1969, 12(8): 915-933. |
| 4 | Das A K, Das P K, Saha P. Heat transfer during pool boiling based on evaporation from micro and macrolayer[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2006, 49(19/20): 3487-3499. |
| 5 | Hänsch S, Walker S. Microlayer formation and depletion beneath growing steam bubbles[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2019, 111: 241-263. |
| 6 | Jung S, Kim H. An experimental method to simultaneously measure the dynamics and heat transfer associated with a single bubble during nucleate boiling on a horizontal surface[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 73: 365-375. |
| 7 | Bongarala M, Hu H, Weibel J A, et al. Microlayer evaporation governs heat transfer enhancement during pool boiling from microstructured surfaces[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2022, 120(22): 221602. |
| 8 | Urbano A, Tanguy S, Colin C. Direct numerical simulation of nucleate boiling in zero gravity conditions[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 143: 118521. |
| 9 | Chen Z H, Utaka Y. On heat transfer and evaporation characteristics in the growth process of a bubble with microlayer structure during nucleate boiling[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 81: 750-759. |
| 10 | Zou A, Singh D P, Maroo S C. Early evaporation of microlayer for boiling heat transfer enhancement[J]. Langmuir, 2016, 32(42): 10808-10814. |
| 11 | 潘丰, 王超杰, 母立众, 等. 池沸腾孤立气泡生长过程中微液层蒸发影响的实验和模拟耦合分析[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(5): 2514-2527. |
| Pan F, Wang C J, Mu L Z, et al. Analysis of the influence of microlayer evaporation on single-bubble pool boiling by coupling the experimental observations and numerical simulations[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(5): 2514-2527. | |
| 12 | Zhang L, Li Z D, Li K, et al. Influence of transient thermal response of solid wall on bubble dynamics in pool boiling[J]. The Journal of Computational Multiphase Flows, 2014, 6(4): 361-375. |
| 13 | Zhang L, Li Z D, Li K, et al. Influence of heater thermal capacity on bubble dynamics and heat transfer in nucleate pool boiling[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 88: 118-126. |
| 14 | 黄潇立, 陈泽亮, 桂南, 等. 石墨烯强化沸腾传热研究进展及应用综述[J]. 清华大学学报 (自然科学版), 2022, 62(10): 1681-1690. |
| Huang X L, Chen Z L, Gui N, et al. Review of graphene enhanced boiling heat transfer[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2022, 62(10): 1681-1690. | |
| 15 | 王雪鉴, 袁朝飞, 赵亚楠, 等. 铜表面-氧化石墨烯纳米涂层池沸腾换热特性实验[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2024, 58(5): 1033-1039. |
| Wang X J, Yuan C F, Zhao Y N, et al. Experimental study on pool boiling heat transfer characteristics of graphite oxide nano coating on copper surface[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2024, 58(5): 1033-1039. | |
| 16 | Ahn H S, Kim J M, Kim J M, et al. Boiling characteristics on the reduced graphene oxide films[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2015, 60: 361-366. |
| 17 | Ahn H S, Kim J M, Kim T, et al. Enhanced heat transfer is dependent on thickness of graphene films: the heat dissipation during boiling[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6276. |
| 18 | 张伟, 牛志愿, 李亚, 等. 石墨烯/镍复合微结构表面的池沸腾传热特性[J]. 化工进展, 2018, 37(10): 3759-3764. |
| Zhang W, Niu Z Y, Li Y, et al. Pool boiling heat transfer characteristics on graphene/nickel composite microstructures[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2018, 37(10): 3759-3764. | |
| 19 | Jaikumar A, Gupta A, Kandlikar S G, et al. Scale effects of graphene and graphene oxide coatings on pool boiling enhancement mechanisms[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 109: 357-366. |
| 20 | Huang X L, Chen Z L, Gui N, et al. Pool boiling experiment characteristics on the pure copper surface[J]. Experimental and Computational Multiphase Flow, 2023, 5(2): 192-198. |
| 21 | 徐济鋆. 沸腾传热和气液两相流[M]. 2版. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2001: 241-271. |
| Xu J J. Boiling Heat Transfer and Two-phase Flow [M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Atomic Press, 2001: 241-271. | |
| 22 | Utaka Y, Kashiwabara Y, Ozaki M. Microlayer structure in nucleate boiling of water and ethanol at atmospheric pressure[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 57(1): 222-230. |
| 23 | He Y, Shoji M, Maruyama S. Numerical study of high heat flux pool boiling heat transfer[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2001, 44(12): 2357-2373. |
| 24 | Sato Y, Niceno B. A depletable micro-layer model for nucleate pool boiling[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2015, 300: 20-52. |
| 25 | Utaka Y, Hu K, Chen Z H, et al. Measurement of contribution of microlayer evaporation applying the microlayer volume change during nucleate pool boiling for water and ethanol[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 125: 243-247. |
| 26 | Koizumi Y, Shōji M, Monde M, et al. Boiling: Research and Advances[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2017. |
| 27 | Pan F, Mu L Z, He Y, et al. A thermal-hydrodynamic coupling method for simulating the interplay between bubble departure and wall temperature variation in nucleate boiling[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2021, 33(2): 243-258. |
| 28 | 潘丰. 汽化核心对核态沸腾换热影响的流-热耦合研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2021. |
| Pan F. Thermal-hydrodynamic study on the interplay of nucleation sites and heat transfer characteristics of nucleate boiling[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2021. | |
| 29 | Zhao P F, Zhu Z H, Jamali J A, et al. Experimental study of single-bubble dynamics and microlayer characteristics in pool boiling on different wettability surfaces[C]//Proceedings of 7th ASME International Conference of Micro/Nanoscale Heat and Mass Transfer. Nottingham, UK, 2024. |
| 30 | Jiang Y Y, Osada H, Inagaki M, et al. Dynamic modeling on bubble growth, detachment and heat transfer for hybrid-scheme computations of nucleate boiling[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 56(1/2): 640-652. |
| 31 | Allred T P, Weibel J A, Garimella S V. The effect of dynamic wetting behavior on boiling heat transfer mechanisms during bubble growth and departure[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 184: 122276. |
| 32 | Aktinol E, Dhir V K. Numerical simulation of nucleate boiling phenomenon coupled with thermal response of the solid[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2012, 24(4): 255-265. |
| 33 | Li Z D, Zhang L, Zhao J F, et al. Numerical simulation of bubble dynamics and heat transfer with transient thermal response of solid wall during pool boiling of FC-72[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 84: 409-418. |
| [1] | 赵璐璐, 唐二军, 邢旭腾, 刘少杰, 褚晓萌, 呼娜, 张泽. POSS改性氧化石墨烯对涂层防腐和疏水性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1977-1986. |
| [2] | 李文宁, 陆敏, 殷俞. 钴高度分散于还原氧化石墨烯用于高级氧化降解有机污染物[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3793-3803. |
| [3] | 葛加丽, 管图祥, 邱新民, 吴健, 沈丽明, 暴宁钟. 垂直多孔碳包覆的FeF3正极的构筑及储锂性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [4] | 顾浩, 张福建, 刘珍, 周文轩, 张鹏, 张忠强. 力电耦合作用下多孔石墨烯膜时间维度的脱盐性能及机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2067-2074. |
| [5] | 陈佩佩, 汪秋英, 肖泽卿, 周思佳, 张小亮. 石墨烯量子点复合膜的调控制备:前体的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(12): 5006-5015. |
| [6] | 余后川, 任腾, 张宁, 姜晓滨, 代岩, 张晓鹏, 鲍军江, 贺高红. 二维氧化石墨烯膜离子选择性传递调控的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 303-312. |
| [7] | 黄凯, 王思洁, 苏海萍, 练成, 刘洪来. 石墨烯层间距调控抑制锂枝晶生长的第一性原理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3501-3510. |
| [8] | 韩双, 张楠, 王慧, 张璇, 杨金栾, 张蔓琳, 张志超. 金霉素分子印迹电化学传感器的制备与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3758-3767. |
| [9] | 刘洪超, 陈苏航, 段先力, 吴凡, 徐小飞, 宋先雨, 赵双良, 刘洪来. Janus石墨烯量子点在生物膜中的输运行为:分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2835-2843. |
| [10] | 李智超, 郑瑜, 张润楠, 姜忠义. 高通量抗污染氧化石墨烯膜研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2370-2380. |
| [11] | 张苗, 杨洪海, 尹勇, 徐悦, 沈俊杰, 卢心诚, 施伟刚, 王军. 氧化石墨烯/水脉动热管的启动及传热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(3): 1136-1146. |
| [12] | 陈雪梅, 王彤, 高玉箔, 彭鼎程, 罗雨婷. 利用激光诱导石墨烯实现高效太阳能界面蒸发[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5648-5659. |
| [13] | 徐欢, 柯律, 张生辉, 张子林, 韩广东, 崔金声, 唐道远, 黄东辉, 高杰峰, 何新建. GO表面原位生长CNTs改善聚丙烯导热复合材料分散与界面形态[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5150-5157. |
| [14] | 韩威, 詹俊, 石红, 赵东, 蔡少君, 彭湘红, 肖标, 高宇. 氮和硫双掺杂石墨烯量子点的合成及其性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(S1): 530-538. |
| [15] | 马生贵, 田博文, 周雨薇, 陈琳, 江霞, 高涛. 氮掺杂Stone-Wales缺陷石墨烯吸附H2S的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4496-4503. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号