• •
收稿日期:2025-04-25
修回日期:2025-06-08
出版日期:2025-06-27
通讯作者:
兰文杰,李少伟
作者简介:兰文杰(1986—),女,博士,副教授,lanwj@cup.edu.cn
基金资助:
Wenjie LAN1( ), Shan JING2, Juntao YUAN1, Shaowei LI2,3(
), Shan JING2, Juntao YUAN1, Shaowei LI2,3( )
)
Received:2025-04-25
Revised:2025-06-08
Online:2025-06-27
Contact:
Wenjie LAN, Shaowei LI
摘要:
脉冲萃取柱是乏燃料后处理过程中重要的液-液萃取设备。本文利用计算流体力学(CFD)方法对中试规模环形折流板脉冲萃取柱(APDDC)内的水力学性能进行了模拟与研究。首先,针对有机相连续和水相连续两种不同工艺过程中分散相对折流板的浸润性差异,发展了近板区等效液滴尺寸模型,分别建立了适用于两种工艺流程的欧拉—欧拉两相流模拟方法,模拟结果与实验测量结果符合良好。而后,对萃取柱内的流场、分散相分布以及分散相返混情况进行了研究,并建立了分散相板上富集度和返流率的关联式。
中图分类号:
兰文杰, 景山, 袁俊涛, 李少伟. 中试规模环形折流板脉冲萃取柱内液—液两相流数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250440.
Wenjie LAN, Shan JING, Juntao YUAN, Shaowei LI. Simulation of liquid-liquid two-phase flow in a pilot-plant scale annular pulsed disc and doughnut extraction column[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250440.
| 溶液 | 硝酸浓度 (mol/L) | 密度ρ (kg/m3) | 黏度μ(Pa·s) | 两相之间的界面张力γ(N/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30%TBP-煤油溶液(平衡后) | 0.55 | 828.3 | 0.00197 | 0.00959 |
| 3 mol/L硝酸水溶液(平衡后) | 2.45 | 1058.2 | 0.00103 |
表1 体系物性参数
Table 1 Physical properties of the systems
| 溶液 | 硝酸浓度 (mol/L) | 密度ρ (kg/m3) | 黏度μ(Pa·s) | 两相之间的界面张力γ(N/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30%TBP-煤油溶液(平衡后) | 0.55 | 828.3 | 0.00197 | 0.00959 |
| 3 mol/L硝酸水溶液(平衡后) | 2.45 | 1058.2 | 0.00103 |
| 编号 | 柱径D (mm) | 环隙宽度L (mm) | 圆盘直径Dd (mm) | 圆环内径Da (mm) | 板间距h (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 175 | 50 | 158 | 107 | 38 |
| C2 | 215 | 70 | 192 | 122 | 48 |
| C3 | 255 | 90 | 227 | 139 | 58 |
表2 环形折流板脉冲萃取柱的几何结构参数
Table 2 Geometric parameters of APDDCs
| 编号 | 柱径D (mm) | 环隙宽度L (mm) | 圆盘直径Dd (mm) | 圆环内径Da (mm) | 板间距h (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 175 | 50 | 158 | 107 | 38 |
| C2 | 215 | 70 | 192 | 122 | 48 |
| C3 | 255 | 90 | 227 | 139 | 58 |
| 方法 | 网格尺寸 | 计算域总网格数 | 分散相存留分数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 模拟计算 | 2.5 mm | 39080 | 0.122 |
| 模拟计算 | 2 mm | 75296 | 0.121 |
| 模拟计算 | 1.5 mm | 153719 | 0.122 |
| 实验 | / | / | 0.12 |
表3 不同网格密度条件下的存留分数模拟结果
Table 3 Simulation results of volume fraction under different mesh density conditions
| 方法 | 网格尺寸 | 计算域总网格数 | 分散相存留分数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 模拟计算 | 2.5 mm | 39080 | 0.122 |
| 模拟计算 | 2 mm | 75296 | 0.121 |
| 模拟计算 | 1.5 mm | 153719 | 0.122 |
| 实验 | / | / | 0.12 |
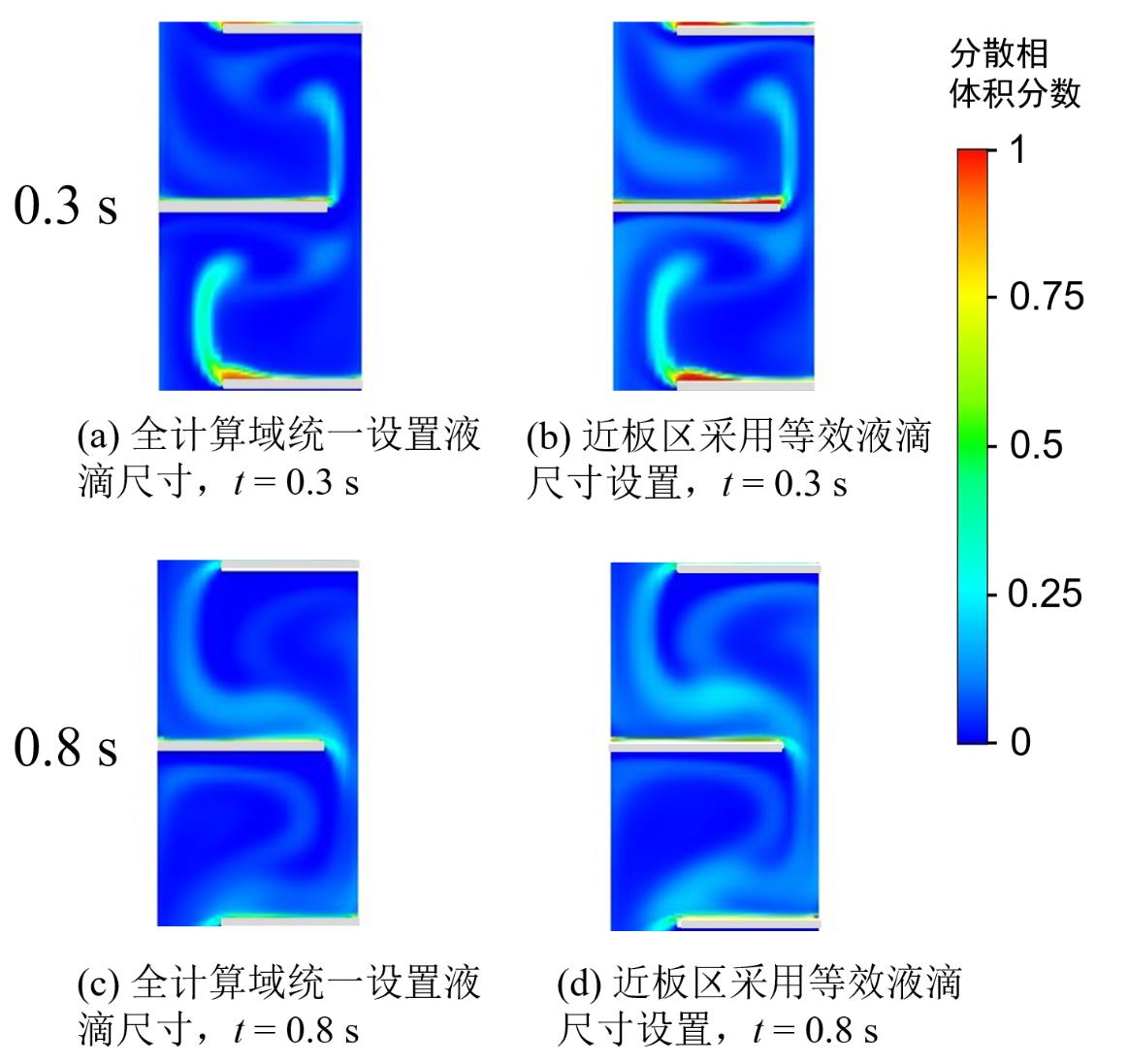
图5 有机相连续工艺过程中分散相体积分数分布注:(C1柱, F = 250 L/(dm2·h), Ra = 0.63, Af = 9.4 mm/s,以达到稳态后某一脉冲周期的起始时间为0 s)
Fig. 5 Distribution of dispersed phase volume fraction in continuous organic phase process.(Column C1, F = 250 L/(dm2·h), Ra = 0.63, Af = 9.4 mm/s. The starting time of a certain pulse period is set as 0 s after the steady state is reached.)
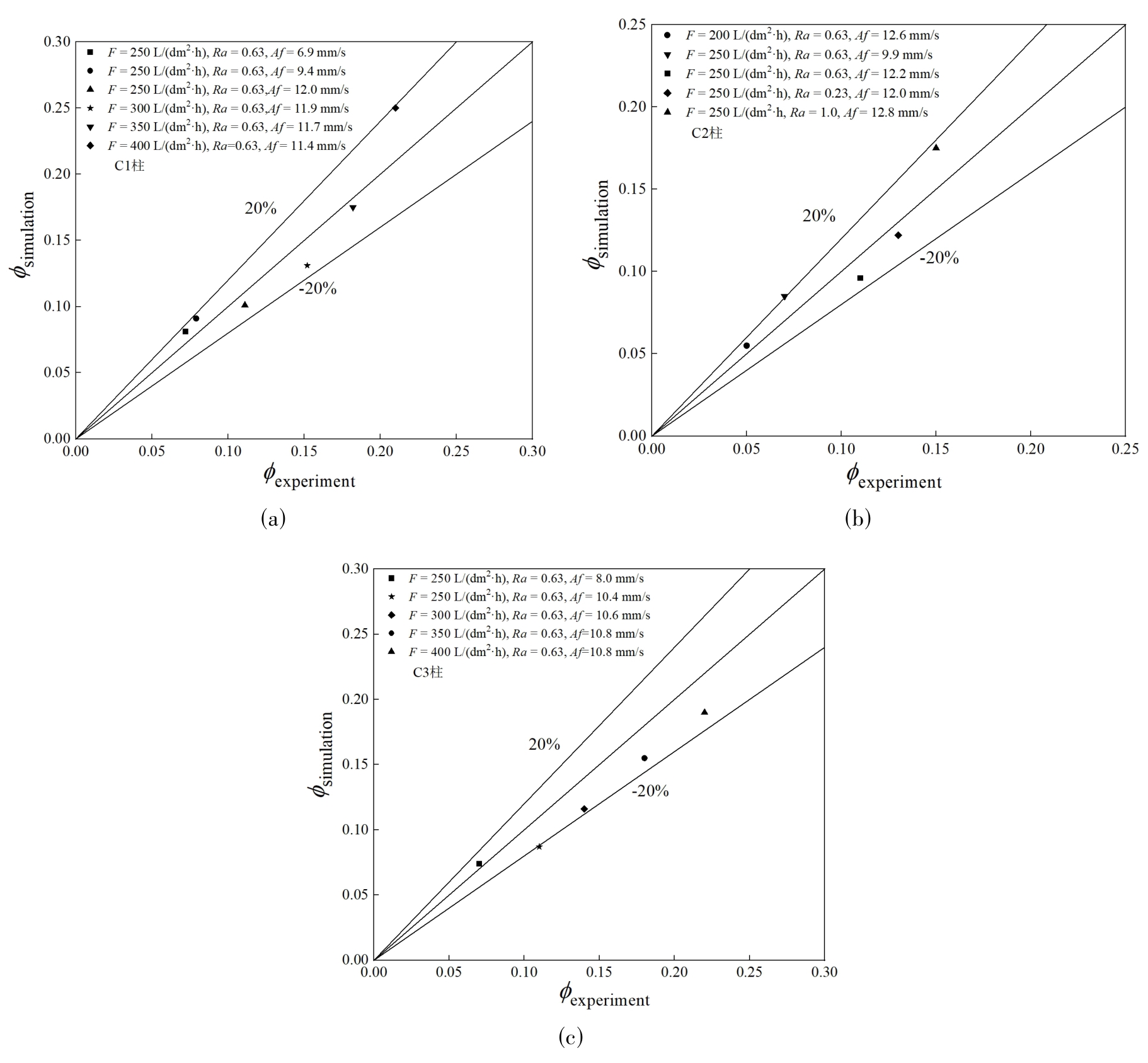
图6 近板区等效液滴尺寸算法下,有机相连续工艺过程中分散相存留分数模拟与实验结果对比
Fig. 6 Comparison of the simulated and experimental holdup in continuous organic phase process when the equivalent droplet size is applied in the near plate area.
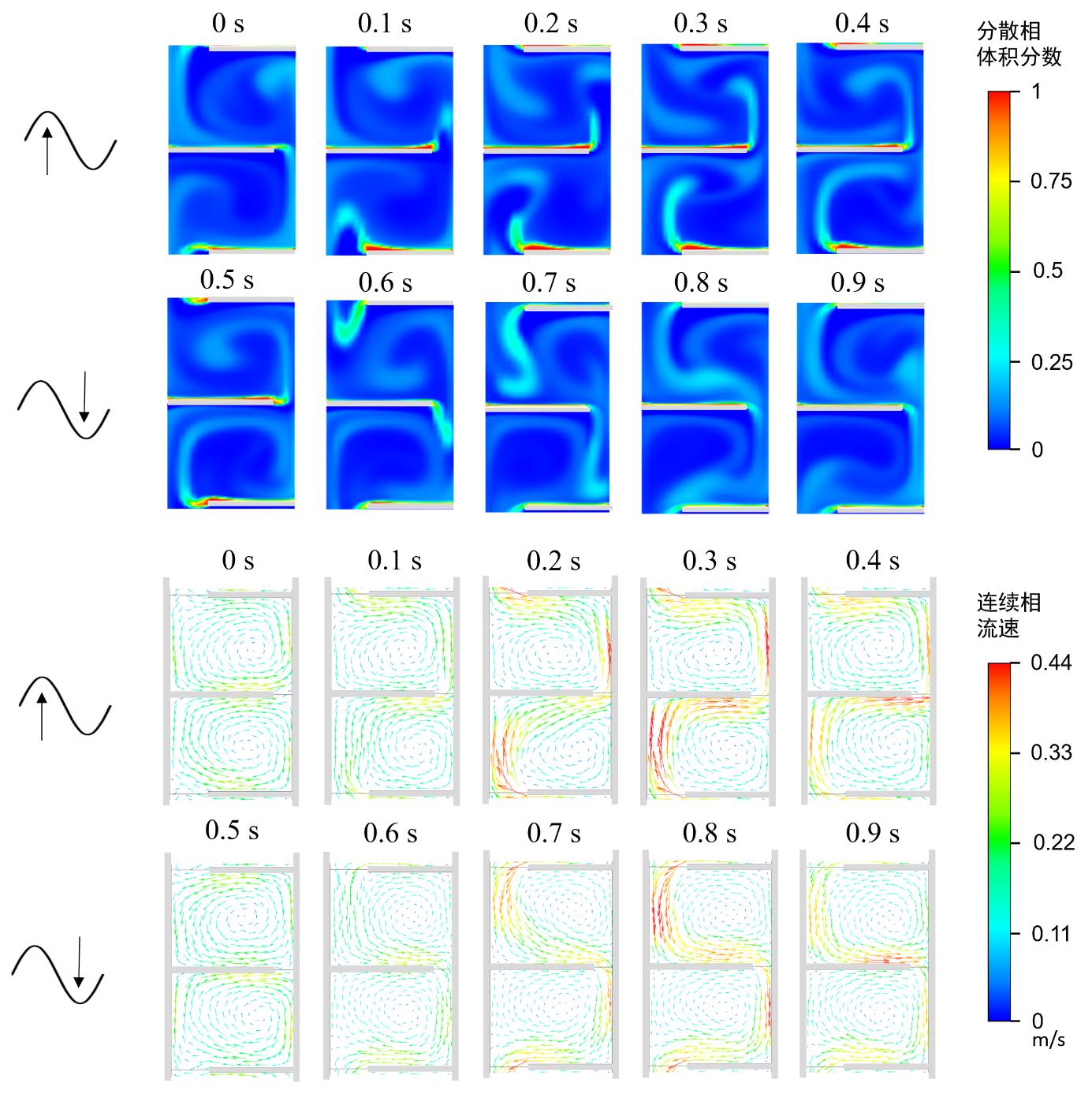
图8 有机相连续工艺过程中一个脉冲周期内萃取柱中的分散相体积分数分布和连续相流速分布注:(C1柱, F = 250 L/(dm2·h), Ra = 0.63, Af = 9.4 mm/s,以达到稳态后某一脉冲周期的起始时间为0 s)
Fig. 8 Dispersed phase volume fraction profile and continuous phase velocity vector in one pulsation cycle in continuous organic phase process. (Column C1, F = 250 L/(dm2·h), Ra = 0.63, Af = 9.4 mm/s. The starting time of a certain pulse period is set as 0 s after the steady state is reached.)
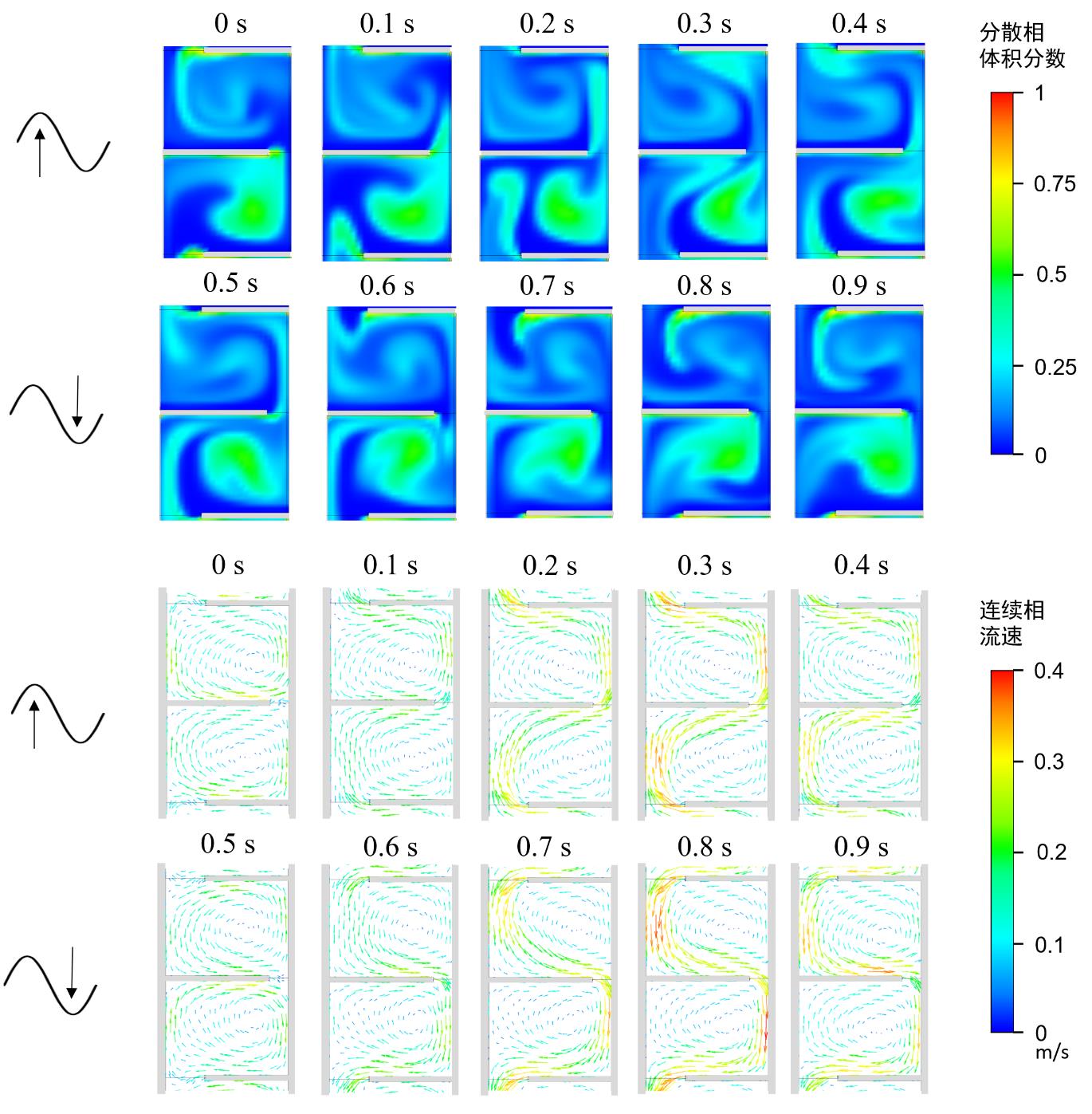
图9 水相连续工艺过程中一个脉冲周期内萃取柱中的分散相体积分数分布和连续相流速分布注:(C1柱, F = 250 L/(dm2·h), Ra = 0.91, Af = 7 mm/s,以达到稳态后某一脉冲周期的起始时间为0 s)
Fig. 9 Dispersed phase volume fraction profile and continuous phase velocity vector in one pulsation cycle in continuous aqueous phase process. (Column C1, F = 250 L/(dm2·h), Ra = 0.91, Af = 7 mm/s. The starting time of a certain pulse period is set as 0 s after the steady state is reached.)
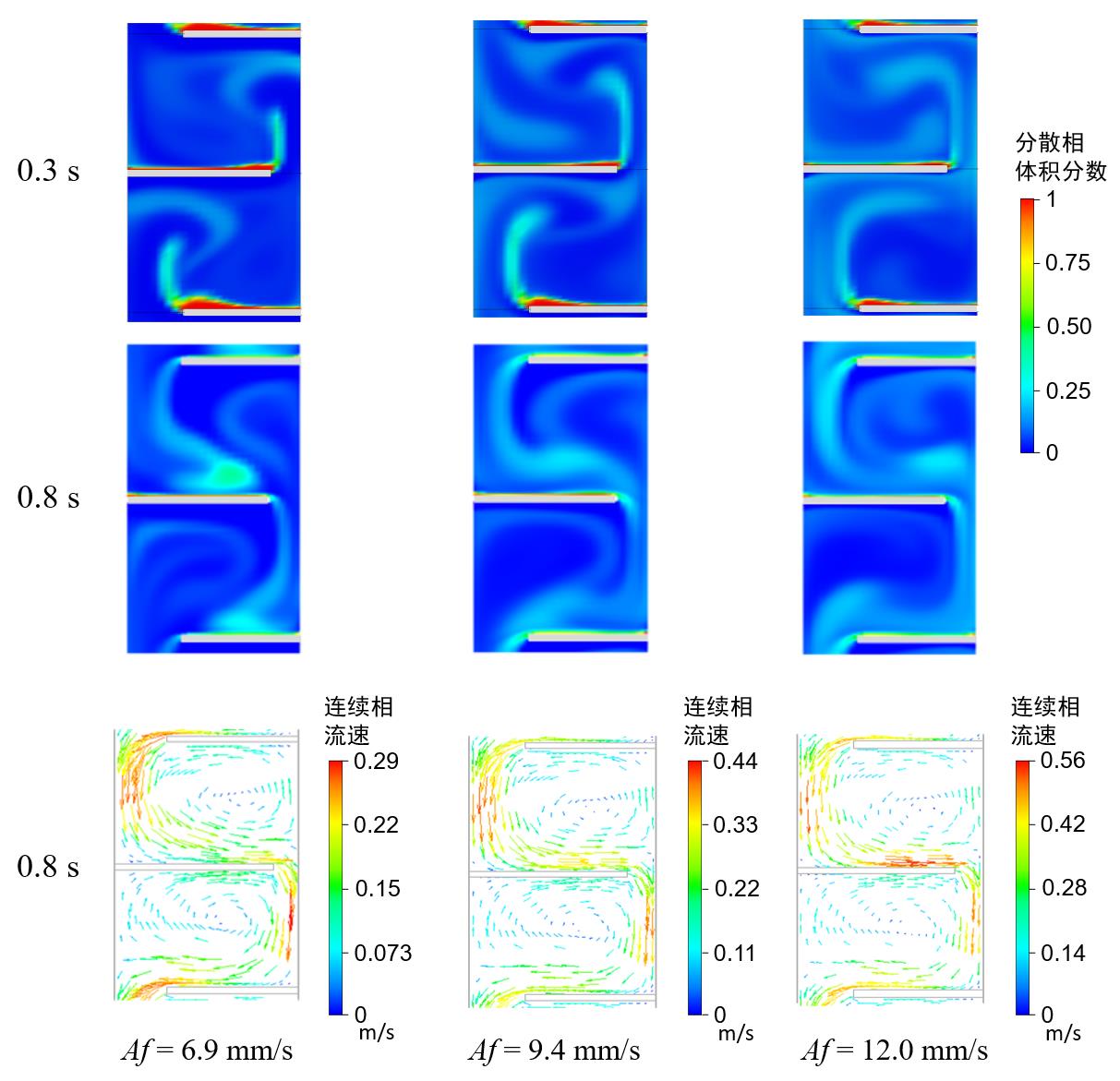
图10 脉冲强度对分散相体积分数分布和连续相流速的影响(有机相连续工艺过程, C1柱, F = 250 L/(dm2·h), Ra = 0.63,以达到稳态后某一脉冲周期的起始时间为0 s)
Fig. 10 The influence of pulsation intensity on the dispersed phase volume fraction profile and continuous phase velocity (Continuous organic phase process, Column C1, F = 250 L/(dm2·h), Ra = 0.63. The starting time of a certain pulse period is set as 0 s after the steady state is reached.)
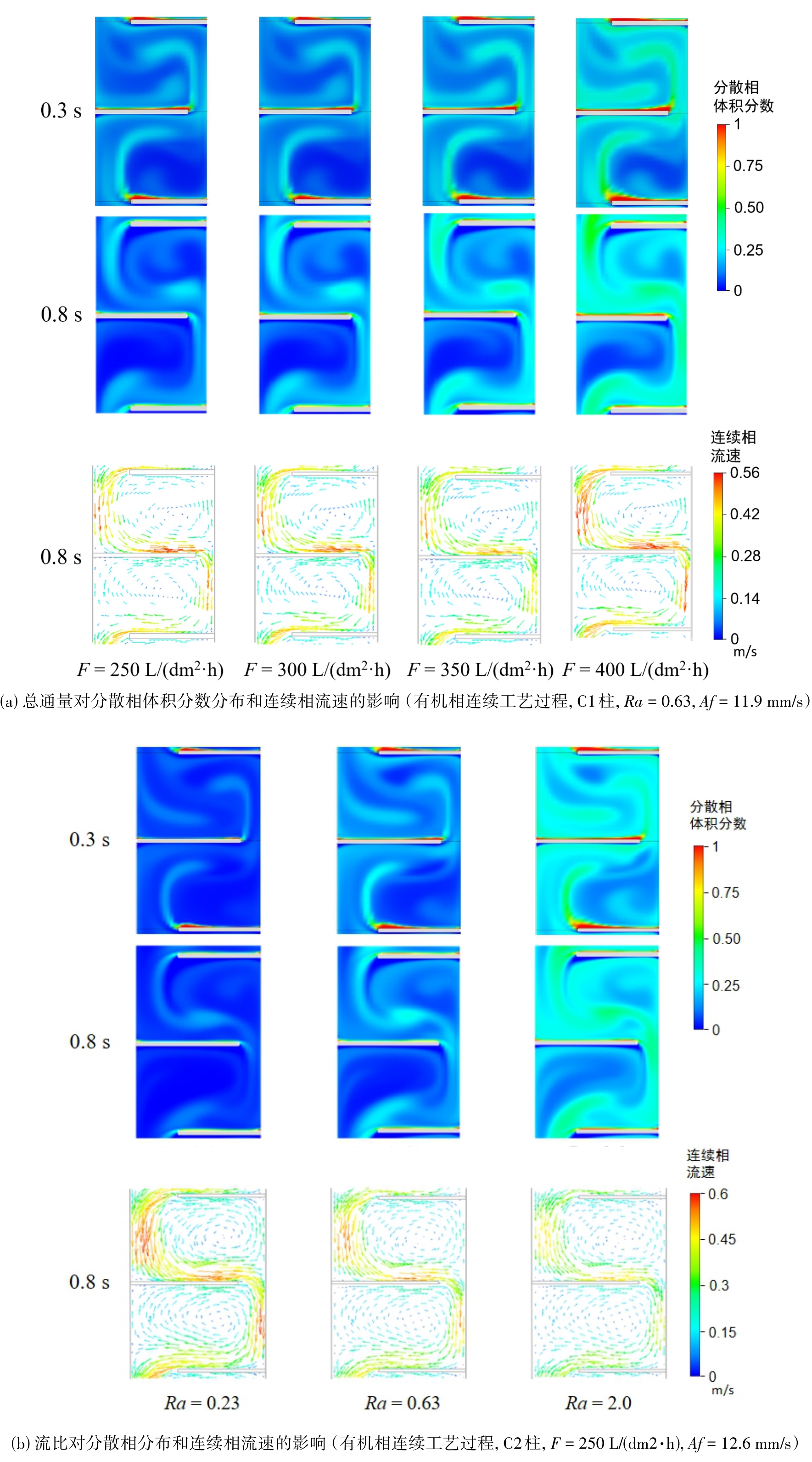
图11 总通量和流比对分散相体积分数分布和连续相流速的影响(以达到稳态后某一脉冲周期的起始时间为0 s)
Fig. 11 The influence of total flow throughput and flow ratio on the dispersed phase volume fraction profile and continuous phase velocity. (The starting time of a certain pulse period is set as 0 s after the steady state is reached.)
| 1 | Van Delden M L, Kuipers N J M, de Haan A B. Extraction of caprolactam with toluene in a pulsed disc and doughnut column—part I: recommendation of a model for hydraulic characteristics[J]. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 2006, 24(4): 499-517. |
| 2 | Sarkar S, Sen N, Singh K K, et al. Effect of operating and geometric parameters on dispersed phase holdup in Pulsed Disc and Doughnut and Pulsed Sieve Plate Columns: a comparative study[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification, 2017, 118: 131-142. |
| 3 | Sen N, Sarkar S, Singh K K, et al. Regime transition and holdup in pulsed sieve-plate and pulsed disc-and-doughnut columns: a comparative study[J]. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 2018, 36 (1): 66–83. |
| 4 | Torab-mostaedi M, Ghaemi A, Asadollahzadeh M. Flooding and drop size in a pulsed disc and doughnut extraction column[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2011, 89 (12A): 2742-2751. |
| 5 | Khooshechin S, Safdari J, Moosavian M A, et al. Applying forward mixing model in an L-shape pulsed packed extraction column to investigate the influence of drop size distribution on mass transfer[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2019, 145: 279-287. |
| 6 | Jeong G H, Kim C. A study on the flow characteristics in a pulsed doughnut-disc type plate extraction column[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1984, 1(2): 111-117. |
| 7 | Van Delden M L, Vos G S, Kuipers N J M, et al. Extraction of caprolactam with toluene in a pulsed disc and doughnut column—part II: experimental evaluation of the hydraulic characteristics[J]. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 2006, 24(4): 519-538. |
| 8 | Van Delden M L, Vos G S, Kuipers N J M, et al. Extraction of caprolactam with an alternative benign solvent in a pulsed disc and doughnut column[J]. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 2007, 25(5): 639-664. |
| 9 | Torab-Mostaedi M, Jalilvand H, Outokesh M. Dispersed phase holdup in a pulsed disc and doughnut extraction column[J]. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2011, 28(2): 313-323. |
| 10 | Li W, Wang Y, Mumford K A, et al. Prediction of holdup and drop size distribution in a disc-doughnut pulsed column with tenova kinetics internals for the water-Alamine 336 system[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2018, 181: 82-90. |
| 11 | Kumar A, Hartland S. A unified correlation for the prediction of dispersed-phase hold-up in liquid-liquid extraction columns [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1995, 34(11): 3925-3940. |
| 12 | Jahya A B, Stevens G W, PRATT H R C. Pulsed disc-and-doughnut column performance[J]. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 2009, 27(1): 63-82. |
| 13 | Kumar R, Sivakumar D, Kumar S, et al. Modeling of hydrodynamics in a 25 mm ϕ pulsed disk and doughnut column[J]. ISRN Chemical Engineering, 2013, 2013: 547489. |
| 14 | Kumar A, Hartland S. Unified correlations for the prediction of drop size in liquid–liquid extraction columns[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1996, 35(8): 2682-2695. |
| 15 | Wang B, Ma S, Zhou H, et al. A CFD-PBM-ANN framework to simulate the liquid–liquid two-phase flow in a pulsed column. AIChE Journal, 2025, 71(1): e18612. |
| 16 | Wang B, Zhou H, Yu X, et al. CFD-PBM coupled with dynamic interfacial tension model for simulating liquid-liquid two-phase flow and interphase mass transfer in a pulsed column. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2025, 64(10), 5656-5670. |
| 17 | Tu Y Q, Chen H, Sun Y Z, et al. High-efficient CFD-based framework for the comprehensive hydrodynamic evaluation of pulsed extraction columns[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 236: 116540. |
| 18 | Sarkar S, Singh K K, Shenoy K T. CFD modeling of pulsed disc and doughnut column: Prediction of axial dispersion in pulsatile liquid-liquid two-phase flow[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(33): 15307-15320. |
| 19 | Sarkar S, Singh K K, Shenoy K T. Two-phase CFD modeling of pulsed disc and doughnut column: prediction of dispersed phase holdup[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 209: 608-622. |
| 20 | Charton S, Duhamet J, Borda G, et al. Axial dispersion in pulsed disk and doughnut columns: a unified law[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2012, 75(6): 468-477. |
| 21 | Sen N, Singh K K, Patwardhan A W, et al. CFD simulations of pulsed sieve plate column: axial dispersion in single-phase flow[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2015, 50(16): 2485-2495. |
| 22 | 曹鑫, 侯媛媛, 刘继连, 等. 乏燃料湿法后处理中脉冲萃取柱的设计选型[J]. 产业与科技论坛, 2020, 19(3): 43-45. |
| Cao X, Hou Y Y, Liu J L, et al. Design and selection of pulse extraction column in wet reprocessing of spent fuel[J]. Industrial & Science Tribune, 2020, 19(3): 43-45. | |
| 23 | Liu J Q, Li S W, Jing S. Hydraulic performance of an annular pulsed disc-and-doughnut column[J]. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 2015, 33(4): 385-406. |
| 24 | Liu J Q, Li S W, Jing S. Scale-up study on the performance of annular pulsed disc-and-doughnut columns[J]. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 2016, 34(5): 485-501. |
| 25 | Liu J Q, Li S W, Wang Y Y, et al. Extraction of uranium nitrate with 30% (v/v) tributyl phosphate in kerosene in an pilot annular pulsed disc-and-doughnut column-part I: hydraulic performance[J]. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 2017, 35(1):19-34. |
| 26 | Liu J Q, Li S W, Wang Y Y, et al. Extraction of uranium nitrate with 30% (v/v) tributyl phosphate in kerosene in a pilot annular pulsed disc-and-doughnut column-part II: axial mixing and mass transfer performance[J]. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 2017, 35(3): 187-198. |
| 27 | Sarkar S, Singh K K, Shenoy K T. Axial dispersion and pressure drop for single-phase flow in annular pulsed disc and doughnut columns: a CFD study[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2018, 106: 335-344. |
| 28 | Ishii M, Zuber N. Drag coefficient and relative velocity in bubbly, droplet or particulate flows[J]. AIChE Journal, 1979, 25(5): 843-855. |
| 29 | Nabli M A, Guiraud P, Gourdon C. Numerical experimentation: a tool to calculate the axial dispersion coefficient in discs and doughnuts pulsed solvent extraction columns[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1997, 52(14): 2353-2368. |
| 30 | Fang Q, Jing D, Zhou H, et al. Population balance of droplets in a pulsed disc and doughnut column with wettable internals[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 161: 274-287. |
| [1] | 郭纪超, 徐肖肖, 孙云龙. 基于植物工厂中的CO2浓度气流模拟及优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 237-245. |
| [2] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [3] | 孔俊龙, 毕扬, 赵耀, 代彦军. 储能电池直冷热管理系统的模拟实验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 289-296. |
| [4] | 马爱华, 赵帅, 王林, 常明慧. 太阳能吸收制冷循环动态特性仿真方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 318-325. |
| [5] | 吴成云, 孙浩然. 民用飞机空调系统性能仿真与燃油代偿损失研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 351-359. |
| [6] | 李卫, 陈浩, 柯钢, 黄孝胜, 李成娇, 郭航, 叶芳. 高原环境适应性试验室模拟平台新风系统仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 360-369. |
| [7] | 密晓光, 孙国刚, 程昊, 张晓慧. 印刷电路板式天然气冷却器性能仿真模型和验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 426-434. |
| [8] | 黄灏, 王文, 李沛昀. 三角转子膨胀机串联运行特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 435-443. |
| [9] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [10] | 郭松源, 周晓庆, 缪五兵, 汪彬, 耑锐, 曹庆泰, 陈成成, 杨光, 吴静怡. 火箭上升段含多孔板液氧贮箱增压输运数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [11] | 张文锋, 郭玮, 张新玉, 曹昊敏, 丁国良. 铝管铝翅片换热器模型开发及软件实现[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 84-92. |
| [12] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [13] | 刘豪, 王林, 丁昊, 耿嘉怡. R1150+R1234ze(E)二元体系223.15~253.15 K汽液相平衡研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 1-8. |
| [14] | 燕子腾, 詹飞龙, 丁国良. 空调用套管式分流器结构设计及分流效果验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [15] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号