化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (12): 6680-6695.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250672
收稿日期:2025-06-23
修回日期:2025-08-27
出版日期:2025-12-31
发布日期:2026-01-23
通讯作者:
郭惠霞
作者简介:杨田(1999—),男,硕士研究生,2466684520@qq.com
基金资助:
Tian YANG1,2( ), Huixia GUO1,2(
), Huixia GUO1,2( ), Mengci SUN1,2
), Mengci SUN1,2
Received:2025-06-23
Revised:2025-08-27
Online:2025-12-31
Published:2026-01-23
Contact:
Huixia GUO
摘要:
由盐酸四环素(TC-HCl)扩散引起的水体污染已严重危害人类健康和环境。采用溶胶-凝胶-燃烧法制备了不同CeO2含量的CoFe2O4/CeO2复合材料,并将其作为过氧单硫酸盐(PMS)活化剂促进四环素(TC-HCl)的降解。结果表明,在CoFe2O4/CeO2/PMS体系中,对10 mg/L的TC-HCl在40 min内降解率可达91.94%,同时在较宽的pH(3~9)区间内对TC-HCl有较好的去除效果。利用活性物种捕捉实验、电子顺磁共振波谱和高价金属探针分析确定了自由基(
中图分类号:
杨田, 郭惠霞, 孙梦慈. CoFe2O4/CeO2复合材料活化PMS降解盐酸四环素[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6680-6695.
Tian YANG, Huixia GUO, Mengci SUN. The CoFe2O4/CeO2 composite material activates PMS to degrade tetracycline hydrochloride[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6680-6695.
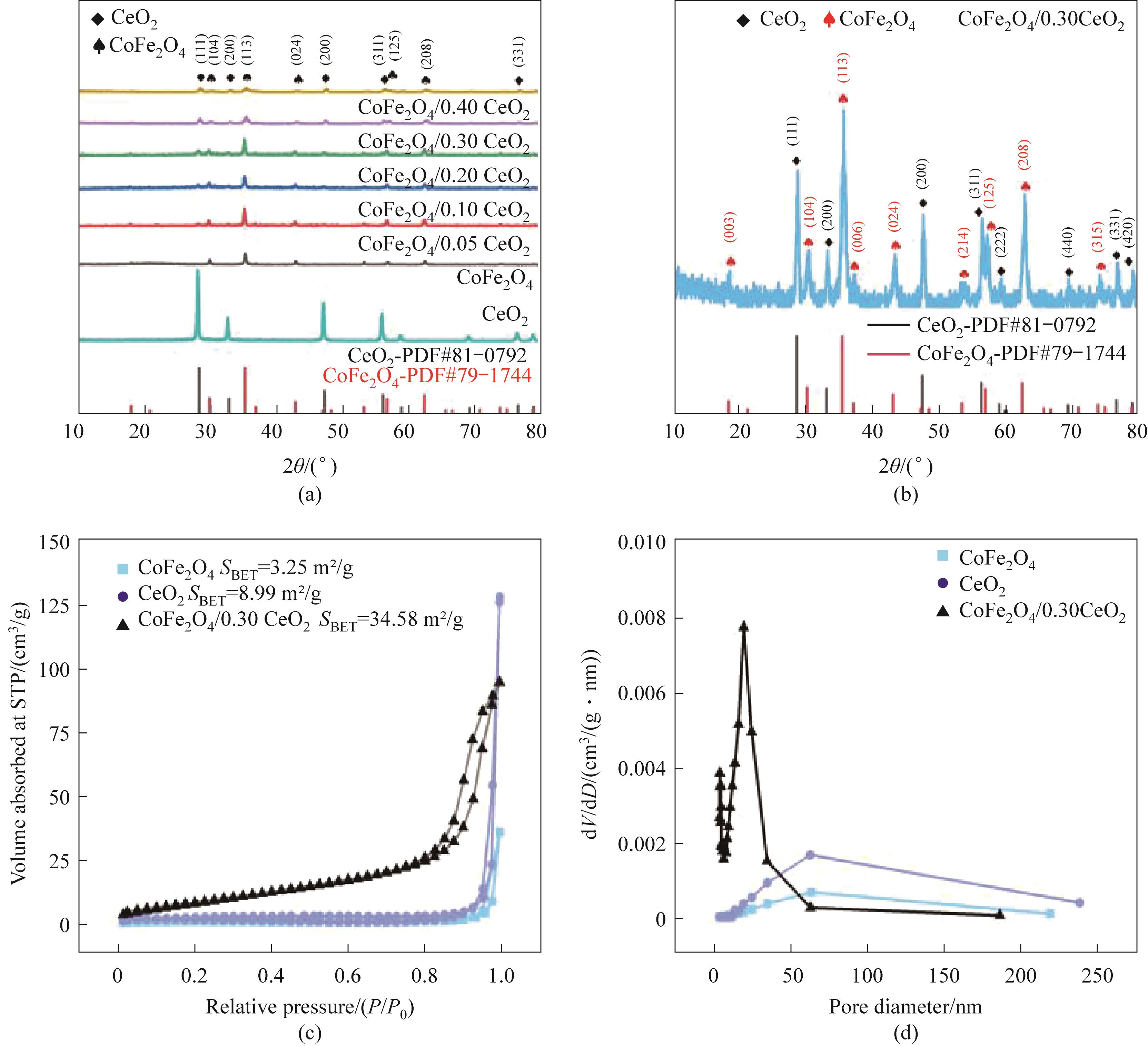
图2 所制样品的XRD谱图(a,b); CoFe2O4、CeO2和CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2的N2吸附-脱附等温线(c)和孔径分布图(d)
Fig.2 XRD patterns of the prepared samples (a,b); N2 adsorption-desorption isotherm (c) and aperture distribution map(d) of CoFe2O4, CeO2 and CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2/g) | 孔体积/(cm3/g) | 平均孔径/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CoFe2O4 | 3.25±0.02 | 0.06 | 62.78 |
| CeO2 | 8.99±0.02 | 0.20 | 61.23 |
| CoFe2O4/0.3CeO2 | 34.58±0.02 | 0.15 | 18.86 |
表1 CoFe2O4、CeO2和CoFe2O4/0.3CeO2的比表面积、孔体积和平均孔径
Table 1 Specific surface area, pore volume and average pore diameter of CoFe2O4, CeO2 and CoFe2O4/0.3CeO2
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2/g) | 孔体积/(cm3/g) | 平均孔径/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CoFe2O4 | 3.25±0.02 | 0.06 | 62.78 |
| CeO2 | 8.99±0.02 | 0.20 | 61.23 |
| CoFe2O4/0.3CeO2 | 34.58±0.02 | 0.15 | 18.86 |
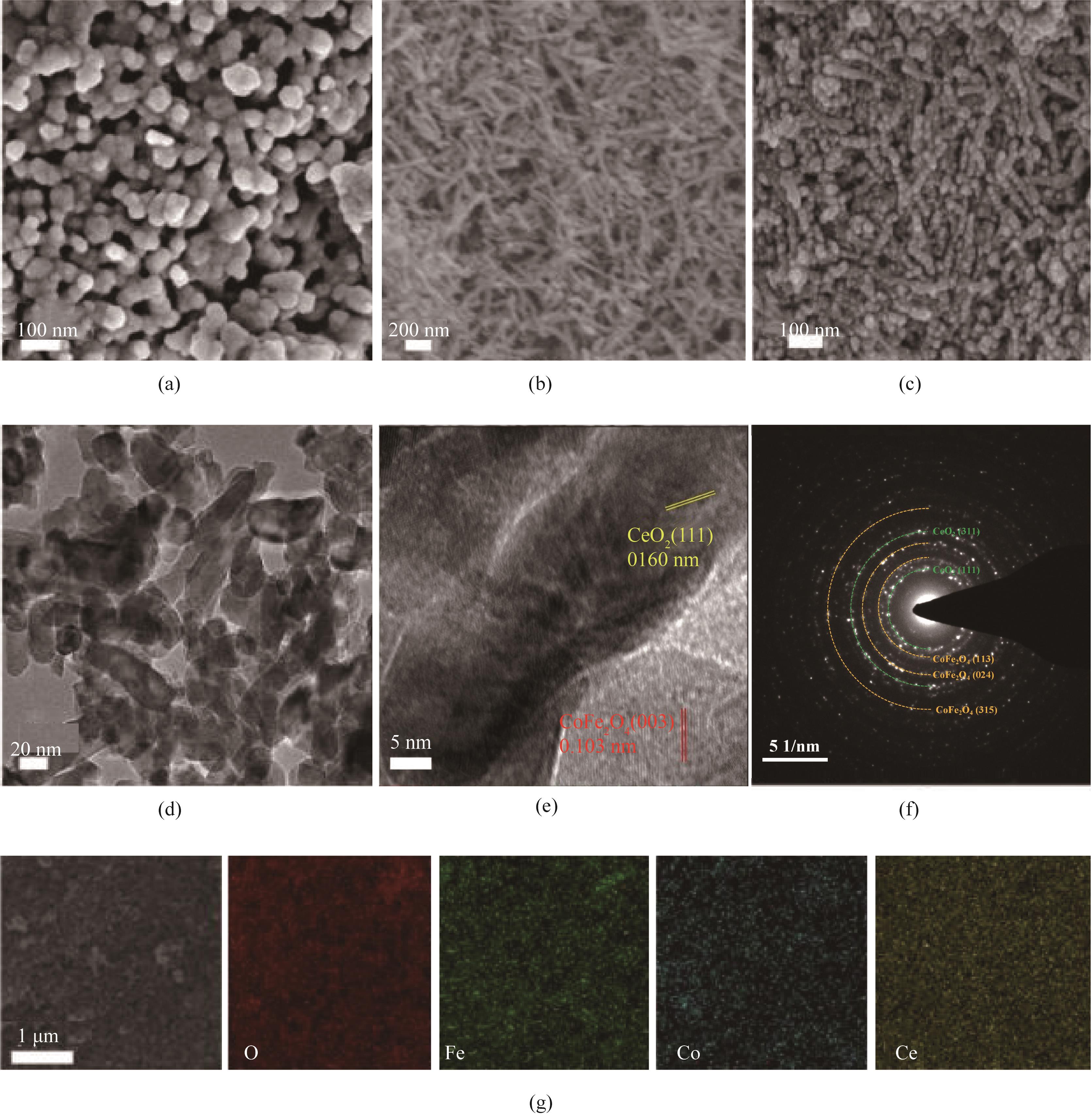
图3 CoFe2O4(a),CeO2(b),CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2(c)的SEM图;CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2的TEM图(d),HRTEM图(e),SAED图(f)和EDS图(g)
Fig.3 SEM of CoFe2O4 (a), CeO2 (b), CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2 (c); TEM (d), HRTEM (e), SAED (f) and EDS (g) of CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2
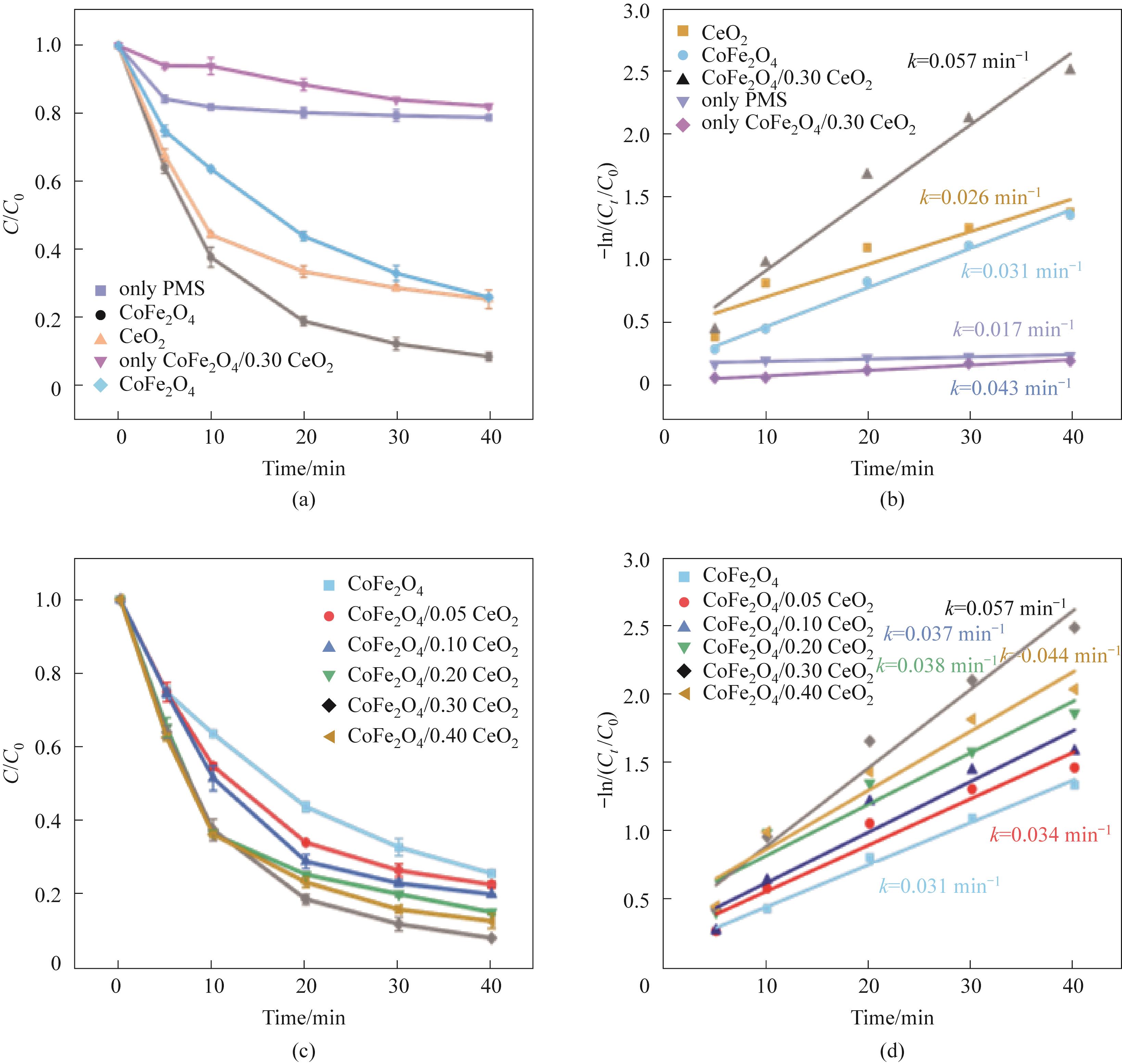
图4 不同体系对TC-HCl的影响(a);不同CeO2复合量对TC-HCl降解效率的影响(c);(a)、(c)相应的拟一级动力学模型[(b),(d)](实验条件:Ccat=0.25 g/L,CPMS=0.30 mmol/L,CTC-HCl=10 mg/L,T=303 K)
Fig.4 Influence of different systems on TC-HCl (a); The effect of different CeO2 complex amount on TC-HCl degradation efficiency (c); (a), (c) Corresponding pseudo-first-order kinetic model [(b),(d)] (experimental conditions: Ccat=0.25 g/L, CPMS=0.30 mmol/L, CTC-HCl=10 mg/L, T=303 K)
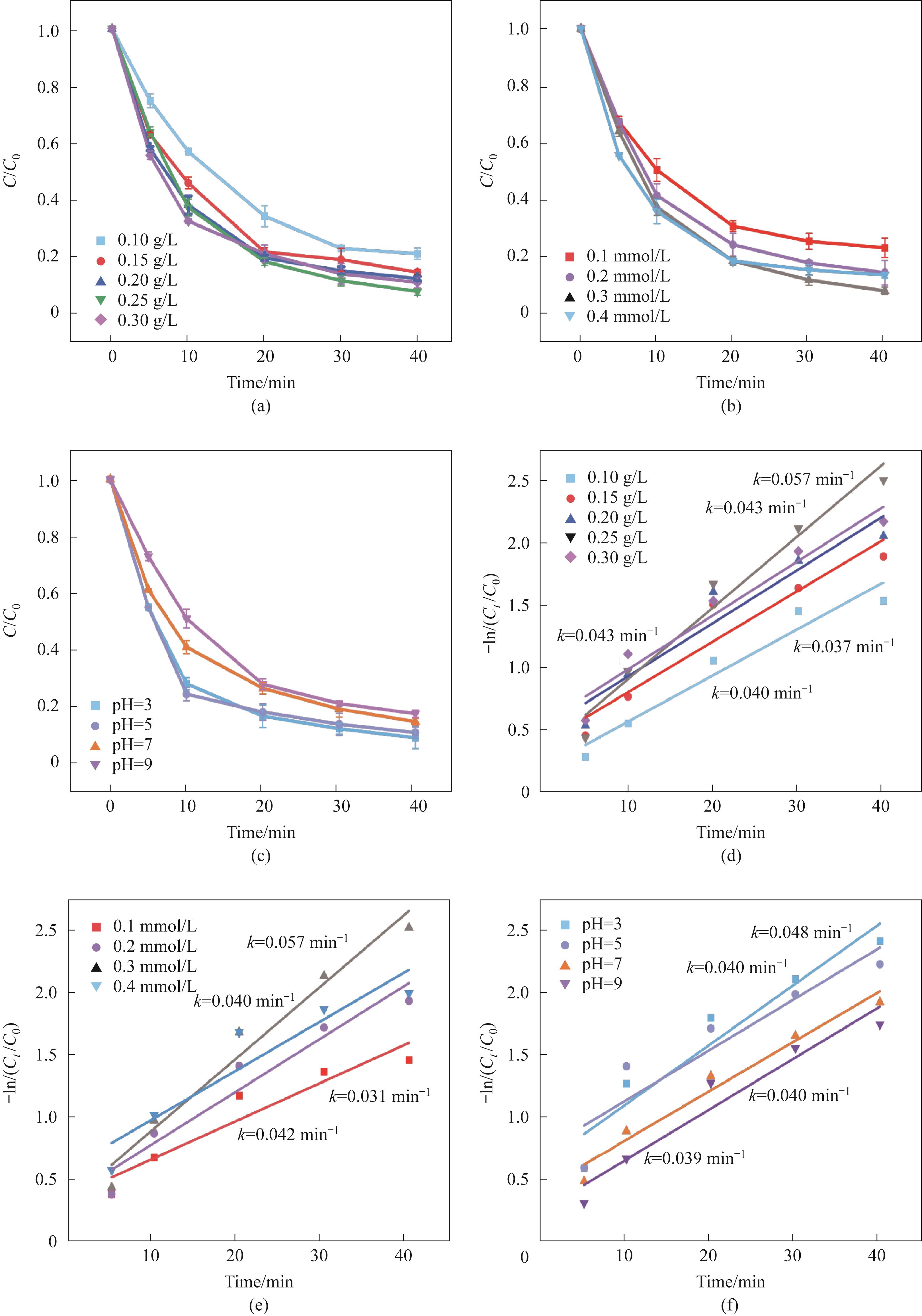
图5 催化剂添加量(a);PMS添加量(b);初始pH(c)对催化性能的影响;(a)~(c)对应催化剂体系的拟一级动力学模型(d~f)(实验条件:Ccat=0.25 g/L,CPMS=0.30 mmol/L,CTC-HCl=10 mg/L,T=303 K)
Fig.5 The influence of catalyst addition amount (a), PMS addition amount (b), and initial pH (c) on catalytic performance; (d)—(f) The pseudo-first-order kinetic model of the catalyst corresponding to (a—c)(experimental conditions: Ccat=0.25 g/L, CPMS=0.30 mmol/L, CTC-HCl=10 mg/L, T=303 K)
| 催化剂 | 工作内容 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|
| ZrO2 / MnFe2O4 | ZrO2/ MnFe2O4 -10 = 0.20 g/L,PDS = 6.0 mmol/L,pH = 7.1,TC=20 mg/L,120 min后TC降解效率达到85.2% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/高岭石 | CFO/K-40%= 0.50 g/L,H2O2 = 1.0 ml,pH = 4,TC=30 mg/L,30 min内降解效率可达84.82% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/氮化碳 | CFO/CN = 0.5 g/L,PMS = 1.0 mmol/L,TC=44.4 mg/L,10 min后TC降解效率达到86% | [ |
| CoFe2O4@MoS2 | CoFe2O4/MoS2 = 0.20 g/L,PDS =0.5 mmol/L,pH = 7,TC=10 mg/L,30 min后TC降解效率达到93% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/二氧化硅 | CFO/MCM-41 = 0.20 g/L,PDS =0.15 mmol/L,pH = 7,SMX=10 mg/L,30 min后TC降解效率达到90.39% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/CeO2 | CoFe2O4/CeO2 = 0.25 g/L,PMS =0.15 mmol/L,TC-HCl=10 mg/L,40 min后TC-HCl降解效率达到91.94% | 本文 |
表2 相似工作的结果总结
Table 2 Summarized the results of similar work
| 催化剂 | 工作内容 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|
| ZrO2 / MnFe2O4 | ZrO2/ MnFe2O4 -10 = 0.20 g/L,PDS = 6.0 mmol/L,pH = 7.1,TC=20 mg/L,120 min后TC降解效率达到85.2% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/高岭石 | CFO/K-40%= 0.50 g/L,H2O2 = 1.0 ml,pH = 4,TC=30 mg/L,30 min内降解效率可达84.82% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/氮化碳 | CFO/CN = 0.5 g/L,PMS = 1.0 mmol/L,TC=44.4 mg/L,10 min后TC降解效率达到86% | [ |
| CoFe2O4@MoS2 | CoFe2O4/MoS2 = 0.20 g/L,PDS =0.5 mmol/L,pH = 7,TC=10 mg/L,30 min后TC降解效率达到93% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/二氧化硅 | CFO/MCM-41 = 0.20 g/L,PDS =0.15 mmol/L,pH = 7,SMX=10 mg/L,30 min后TC降解效率达到90.39% | [ |
| CoFe2O4/CeO2 | CoFe2O4/CeO2 = 0.25 g/L,PMS =0.15 mmol/L,TC-HCl=10 mg/L,40 min后TC-HCl降解效率达到91.94% | 本文 |
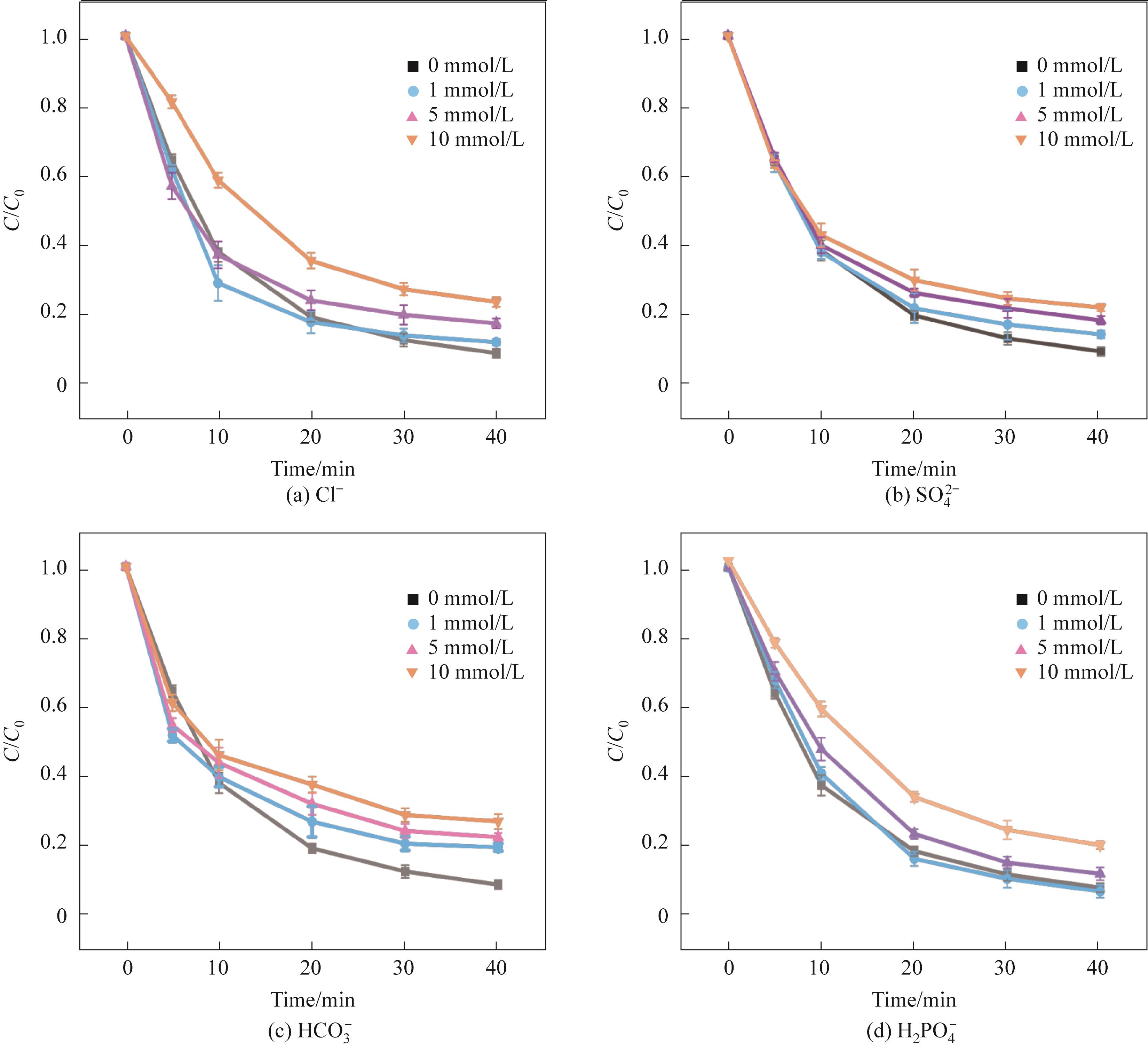
图6 不同浓度无机阴离子对TC-HCl降解的影响(实验条件:Ccat=0.25 g/L,CPMS=0.30 mmol/L,CTC-HCl=10 mg/L,T=303 K)
Fig.6 Effects of different concentrations of inorganic anions on TC-HCl degradation(Experimental conditions: Ccat=0.25 g/L, CPMS=0.30 mmol/L, CTC-HCl=10 mg/L, T=303 K)
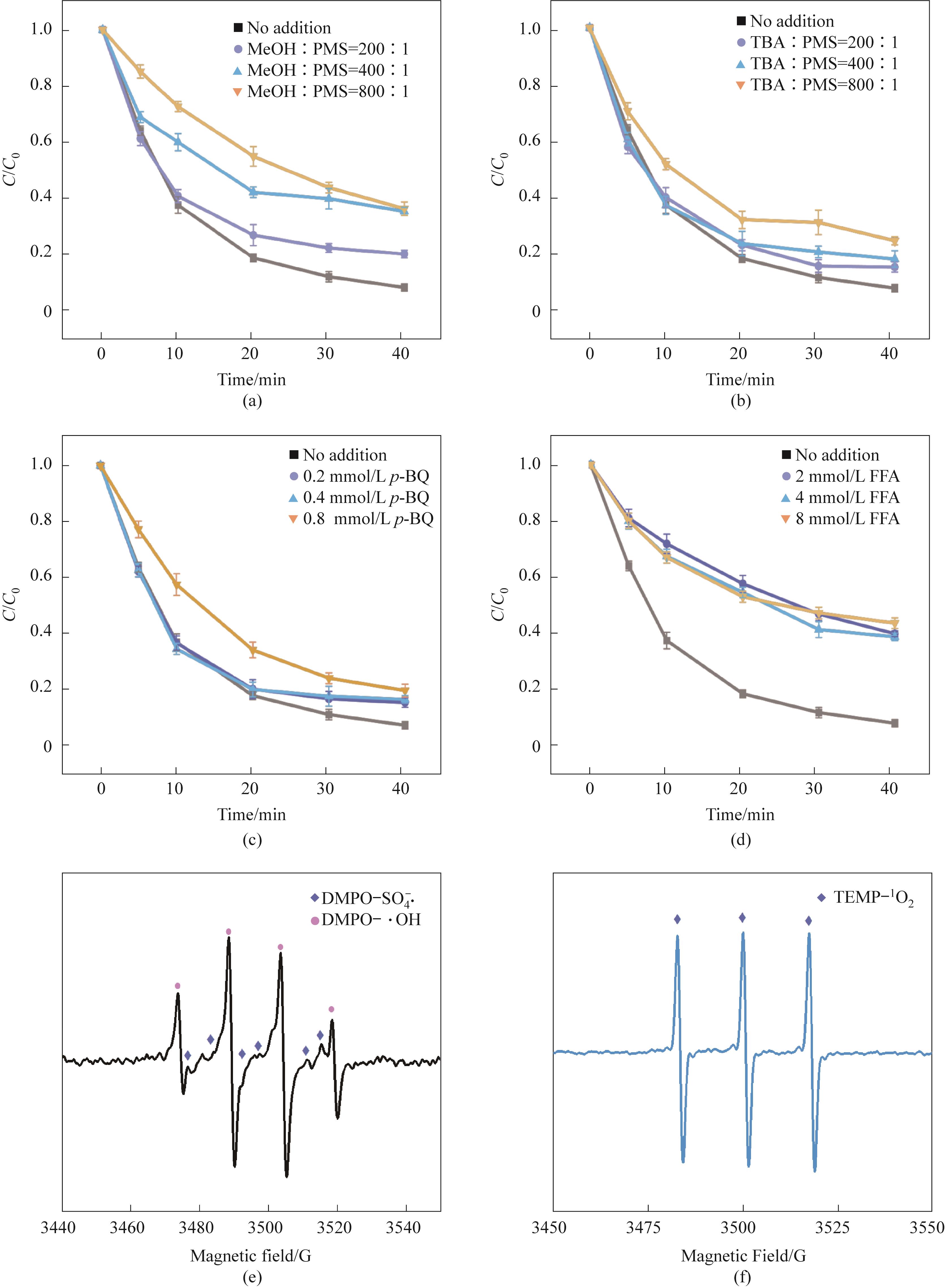
图7 不同浓度的清除剂对CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2/PMS体系去除TC-HCl的影响(a)~(d); DMPO捕获的EPR谱图显示SO4-·、·OH(e); TEMP捕获1O2 EPR谱图(f)(实验条件:Ccat=0.25 g/L,CPMS=0.30 mmol/L,CTC-HCl=10 mg/L,T=303 K)
Fig.7 Effects of different concentrations of scavengers on the removal of TC-HCl in CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2/PMS system(a)—(d); EPR spectra captured by DMPO showed SO4-·, ·OH(e); (f) TEMP captures EPR spectrum (Experimental conditions:Ccat=0.25 g/L, CPMS=0.30 mmol/L, CTC-HCl=10 mg/L, T=303 K)
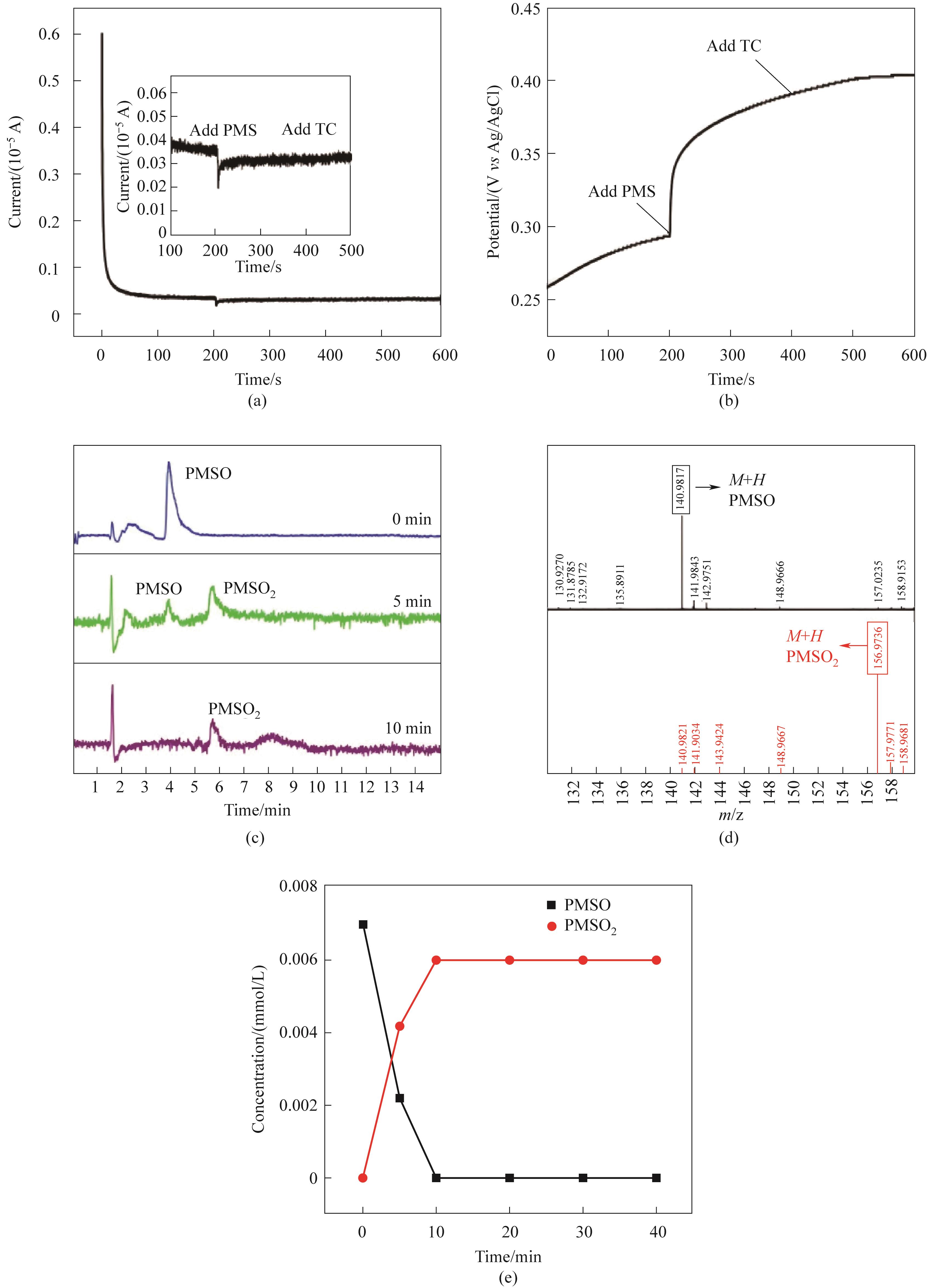
图9 CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2/PMS体系的i-t曲线(a), OCP曲线(b), 降解PMSO生成PMSO2反应过程液质图(c), PMSO和PMSO2的二级质谱图(d),对PMSO的降解和PMSO2的生成曲线(e)(实验条件:Ccat=0.25 g/L,CPMS=0.30 mmol/L,CTC-HCl=10 mg/L,T=303 K)
Fig.9 The i-t curve(a); OCP curve(b) of CoFe2O4/0.30CeO2/PMS system LC-MS chromatogram of the degradation of PMSO to generate PMSO2(c); The secondary mass spectra of PMSO and PMSO2 (d); The curves of the degradation of PMSO and the generation of PMSO2 (e)(Experimental conditions:Ccat=0.25 g/L, CPMS=0.30 mmol/L, CTC-HCl=10 mg/L, T=303 K)
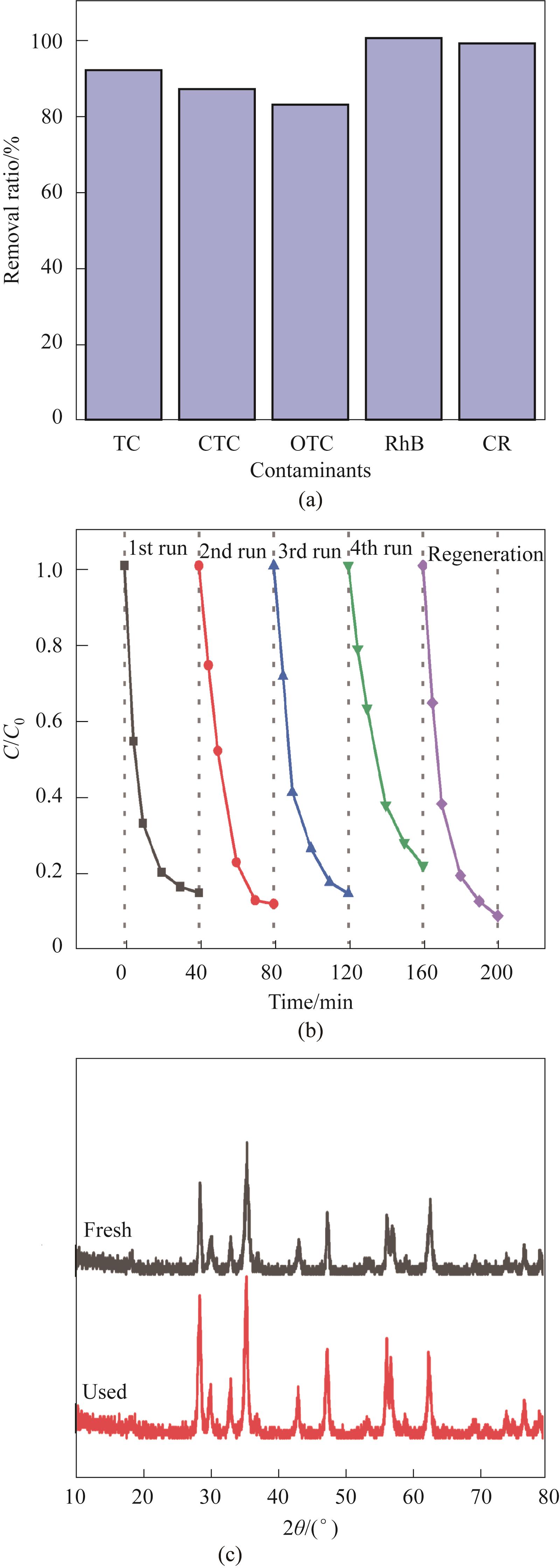
图13 催化剂对其他污染物的降解性能(a);循环试验(b);使用前后的XRD(c)(实验条件:Ccat=0.25 g/L,CPMS=0.30 mmol/L,CTC-HCl=10 mg/L,T=303 K)
Fig.13 Degradability of other pollutants(a); Cyclic experiment (b); Before and after the use of XRD (c) (Experimental conditions: Ccat=0.25 g/L, CPMS=0.30 mmol/L, CTC-HCl=10 mg/L, T=303 K)
| [1] | Zhou M Y, Liu K, Peng Q, et al. Long-acting CoAl2O4 spinel catalyst developed on activated alumina pellets by facile synthesis to activate peroxymonosulfate: controllable cobalt leaching and environmental adaptability[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 310: 114702. |
| [2] | Peng Y T, Tang H M, Yao B, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) by spinel ferrite and their composites in degradation of organic pollutants: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 414: 128800. |
| [3] | Wang Y H, Sun Y L, Wang R Y, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate with cobalt embedded in layered δ-MnO2 for degradation of dimethyl phthalate: mechanisms, degradation pathway, and DFT calculation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 451: 130901. |
| [4] | Zhu K X, Jin C Z, Zhao C X, et al. Modulation synthesis of multi-shelled cobalt-iron oxides as efficient catalysts for peroxymonosulfate-mediated organics degradation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 359: 1537-1549. |
| [5] | Luo J M, Bo S F, Qin Y N, et al. Transforming goat manure into surface-loaded cobalt/biochar as PMS activator for highly efficient ciprofloxacin degradation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 395: 125063. |
| [6] | Pi Y Q, Gao H Q, Cao Y D, et al. Cobalt ferrite supported on carbon nitride matrix prepared using waste battery materials as a peroxymonosulfate activator for the degradation of levofloxacin hydrochloride[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 379: 122377. |
| [7] | Wang Y, Gao C Y, Zhang Y Z, et al. Bimetal-organic framework derived CoFe/NC porous hybrid nanorods as high-performance persulfate activators for bisphenol A degradation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 421: 127800. |
| [8] | Pan Y J, Meng F Y, Bai J X, et al. Highly efficient peroxymonosulfate activation by CoFe2O4@attapulgite-biochar composites: degradation properties and mechanism insights[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(3): 112579. |
| [9] | Guo Z Y, Jin H Y, Sun H Y, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by novel magnetically recyclable CoFe2O4/MXene quantum dots composites for rapid degradation of tetracycline: synergistic performance and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 370: 122398. |
| [10] | Zhu Z H, Yang X, He J, et al. Deciphering the structural origin for the remarkable CO oxidation activities of the CuO-based catalysts with diverse morphological CeO2 supports[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(6): 114385. |
| [11] | Geng Y, Jin K, Mei J, et al. CeO2 grafted with different heteropoly acids for selective catalytic reduction of NO x with NH3 [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 382: 121032. |
| [12] | Deng R Y, He Q, Yang D X, et al. Enhanced synergistic performance of nano-Fe0-CeO2 composites for the degradation of diclofenac in DBD plasma[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 406: 126884. |
| [13] | Zhang L J, Wang N, Wang F Y, et al. Robust high-entropy spinel oxides for peroxymonosulfate activation: stabilization effect and enhancement mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 488: 150826. |
| [14] | Ren T F, Yang S Y, Wu S, et al. High-energy ball milling enhancing the reactivity of microscale zero-valent aluminum toward the activation of persulfate and the degradation of trichloroethylene[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 374: 100-111. |
| [15] | Huang W Q, Xiao S, Zhong H, et al. Activation of persulfates by carbonaceous materials: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 418: 129297. |
| [16] | Li X, Qin Y, Jia Y, et al. Preparation and application of Fe/biochar (Fe-BC) catalysts in wastewater treatment: a review[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 274: 129766. |
| [17] | Wu Y W, Chen X T, Han Y, et al. Highly efficient utilization of nano-Fe(0) embedded in mesoporous carbon for activation of peroxydisulfate[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(15): 9081-9090. |
| [18] | Niu L J, Zhang G M, Xian G, et al. Tetracycline degradation by persulfate activated with magnetic γ - F e 2 O 3 / C e O 2 catalyst: performance, activation mechanism and degradation pathway[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 259: 118156. |
| [19] | Liu Z M, Gao Z M, Wu Q. Activation of persulfate by magnetic zirconium-doped manganese ferrite for efficient degradation of tetracycline[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 423: 130283. |
| [20] | Li J M, Li S Y, Cao Z, et al. Heterostructure CoFe2O4/kaolinite composite for efficient degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride through synergetic photo-Fenton reaction[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2023, 244: 107102. |
| [21] | Pan B, Chen W, Zhou L X, et al. CoFe2O4/carbon nitride Z-scheme heterojunction photocatalytic PMS activation for efficient tetracycline degradation: accelerated electron transfer[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2024, 191: 2522-2532. |
| [22] | Peng X M, Yang Z H, Hu F P, et al. Mechanistic investigation of rapid catalytic degradation of tetracycline using CoFe2O4@MoS2 by activation of peroxymonosulfate[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 287: 120525. |
| [23] | Gao P, Fan X H, Su Y N, et al. Efficient peroxymonosulfate activation for sulfamethoxazole degradation by CoFe2O4 decorated mesoporous silica through a simple one-step grinding-calcination method[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2025, 13(3): 116890. |
| [24] | Dong X B, Ren B X, Sun Z M, et al. Monodispersed CuFe2O4 nanoparticles anchored on natural kaolinite as highly efficient peroxymonosulfate catalyst for bisphenol A degradation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 253: 206-217. |
| [25] | Wang S, Long J R, Jiang T, et al. Magnetic Fe3O4/CeO2/g-C3N4 composites with a visible-light response as a high efficiency Fenton photocatalyst to synergistically degrade tetracycline[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 278: 119609. |
| [26] | Zhao D S, Fan W L, Wang Z H, et al. Sustainable cycling and mechanism of C o ( Ⅱ ) / C o ( Ⅳ ) / C o ( Ⅲ ) with S(Ⅳ) highly triggered by C o ( Ⅳ ) in E / C o ( Ⅱ ) / S ( Ⅳ ) for enhanced removal of reactive brilliant red X-3B[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 343: 126997. |
| [27] | Wang Z, Jiang J, Pang S Y, et al. Is sulfate radical really generated from peroxydisulfate activated by iron ( Ⅱ ) for environmental decontamination?[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(19): 11276-11284. |
| [28] | Wang Z, Qiu W, Pang S Y, et al. Further understanding the involvement of F e ( Ⅳ ) in peroxydisulfate and peroxymonosulfate activation by F e ( Ⅱ ) for oxidative water treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 371: 842-847. |
| [29] | Zong Y, Zhang H, Zhang X M, et al. High-valent cobalt-oxo species triggers hydroxyl radical for collaborative environmental decontamination[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 300: 120722. |
| [30] | Zhang H, Luo M F, Zhou P, et al. Enhanced ferrate(Ⅵ) oxidation of sulfamethoxazole in water by CaO2: the role of Fe(Ⅳ) and Fe(Ⅴ)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 425: 128045. |
| [31] | Si Q S, Guo W Q, Wang H Z, et al. Difunctional carbon quantum dots/g-C3N4 with in-plane electron buffer for intense tetracycline degradation under visible light: tight adsorption and smooth electron transfer[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 299: 120694. |
| [32] | Zhao Z D, Zhou W J, Lin D H, et al. Construction of dual active sites on diatomic metal (FeCo-N/C-x) catalysts for enhanced Fenton-like catalysis[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 309: 121256. |
| [1] | 赵维, 邢文乐, 韩朝旭, 袁兴中, 蒋龙波. g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化降解水中有机污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769. |
| [2] | 张晓晨, 鲁中山, 郭腾, 桂恒, 宋红兵, 肖盟. 一株端羟基聚丁二烯降解菌的筛选及降解机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4205-4216. |
| [3] | 廖兵, 祝鑫宇, 黄倩倩, 胥雯, 寇梦瑶, 郭娜. 盐酸羟胺强化芬顿体系在近中性条件下去除2,4-DCP的性能及机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4273-4283. |
| [4] | 吴雷, 胡紫璇, 高渊, 刘长波, 曹虎生, 刘田田, 朱瑞玉, 周军. 微波联合生物炭活化过硫酸盐氧化修复多环芳烃污染土壤研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3659-3670. |
| [5] | 赵清萍, 张敏, 赵辉, 王刚, 邱永福. 乙烯氢甲酯化合成丙酸甲酯的氢键作用机制及反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2701-2713. |
| [6] | 何军, 李勇, 赵楠, 何孝军. 碳负载硒掺杂硫化钴在锂硫电池中的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2995-3008. |
| [7] | 高越, 李丁, 高玉苗. 有机污染场地土壤催化氧化修复技术研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1297-1304. |
| [8] | 陈仲卿, 刘家旭, 王艳语, 井红权, 侯翠红, 屈凌波. K-B-Al体系对磷矿熔融特性及玻璃结构的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1323-1333. |
| [9] | 宫政, 高秀鲁, 赵玲, 胡冬冬. 超临界CO2发泡PBAT/PLA复合材料及其形状记忆性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 888-896. |
| [10] | 郭琛龙, 彭正奇, 姜冰雪, 吴正凯, 王德良, 王青月, 郑杰元, Ho Lim Khak, 史胜斌, 杨轩, 刘平伟, 王文俊. 退役PET高值回用的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 532-542. |
| [11] | 王煜晨, 王万宗, 张鑫, 郭茂强, 周晓明, 盛利志. 高负载梓树豆荚壳衍生多孔碳材料的电化学性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6748-6760. |
| [12] | 尹胜强, 钟湘宇, 龚漫雨, 李露, 刘远征, 周寿斌, 肖俊兵, 刘昌会, 贾传坤. 活化桃胶碳基复合相变材料性能表征及导热增强研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6614-6625. |
| [13] | 彭郅众, 郎学磊, 房强, 井慧芳, 钟达忠, 李晋平, 赵强. Ag-Sn间电子结构调控在酸性环境中实现1 A/cm2下高效CO2还原[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6376-6386. |
| [14] | 邱家齐, 杨仲卿, 张志刚, 甘海龙, 霍春秀, 窦志帅, 冉景煜. Mn/Ce共掺杂强化氧物种转化与稀薄甲烷催化燃烧机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5604-5616. |
| [15] | 韩霜, 王秋月, 刘泽贤, 仲兆祥, 邢卫红. PVDF/LFTCO(LaFe0.55Ti0.2Co0.25O3)催化膜类光芬顿降解盐酸四环素[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5290-5299. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号