化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (3): 1297-1304.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240860
收稿日期:2024-07-29
修回日期:2024-09-18
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-03-28
通讯作者:
高玉苗
作者简介:高越(1993—),女,博士,工程师,gaoyue@bcig.cn
基金资助:
Yue GAO1( ), Ding LI1,2, Yumiao GAO1(
), Ding LI1,2, Yumiao GAO1( )
)
Received:2024-07-29
Revised:2024-09-18
Online:2025-03-25
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Yumiao GAO
摘要:
本文针对有机污染土壤,开发了一种多元催化氧化技术。以过硫酸钠和双氧水作为氧化剂,Fe2+和Cu2+作为过渡金属活化剂,同时以抗坏血酸作为络合剂,形成均相液体修复药剂。在50℃的反应条件下耦合紫外光照处理,形成过渡金属离子、热、光三元活化体系。其中Cu2+的添加有效促进了Fe3+向Fe2+的还原过程,抗坏血酸的加入有效调节Fe2+的持续活化作用。本氧化体系中主要依靠活性自由基
中图分类号:
高越, 李丁, 高玉苗. 有机污染场地土壤催化氧化修复技术研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1297-1304.
Yue GAO, Ding LI, Yumiao GAO. Study on catalytic oxidation remediation technology of organic polluted site soil[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1297-1304.
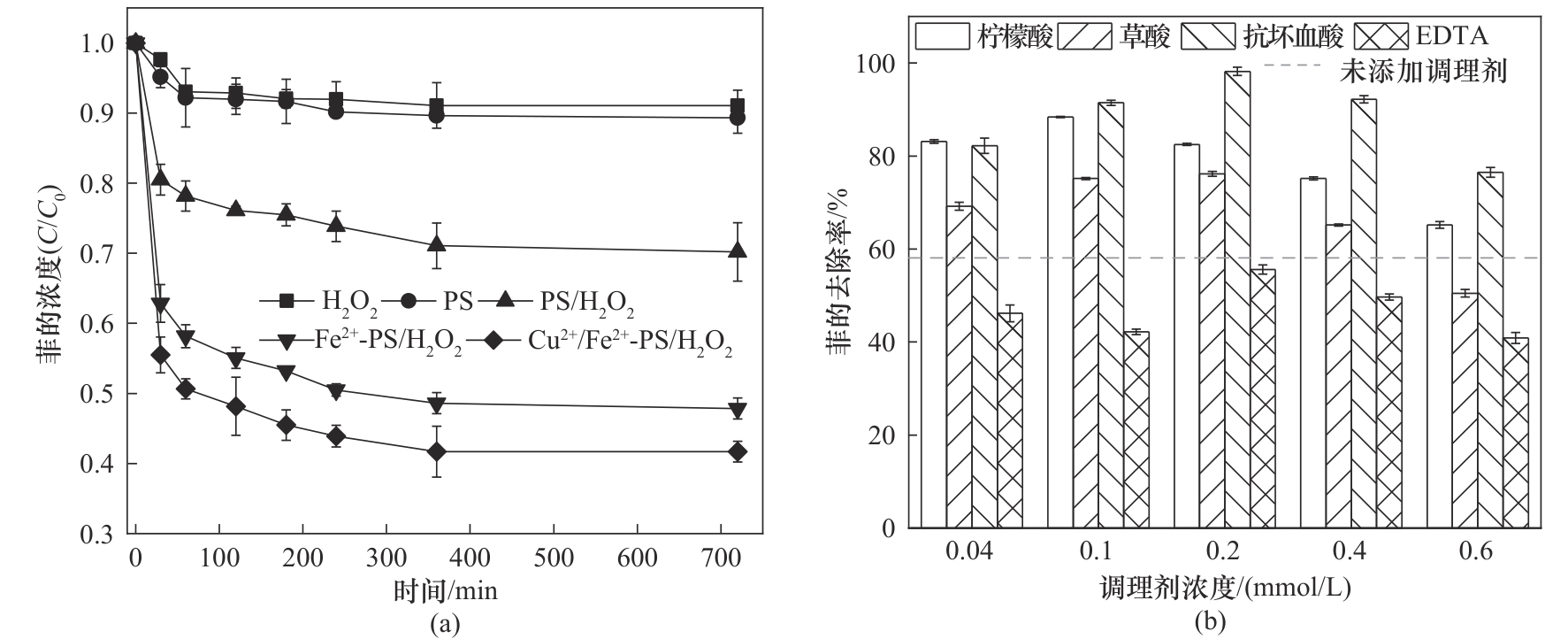
图1 (a)不同氧化体系对水中菲的影响;(b)络合剂对Fe2+/Cu2+活化PS/H2O2体系的影响([PS] 1.6 mmol/L;[H2O2] 0.4 mmol/L; [Fe2+] 0.3 mmol/L;[Cu2+] 0.1 mmol/L;反应时间 720 min;25℃)
Fig.1 (a) The effects of different oxidative system on phenanthrene; (b) The effect of chelating agents on Cu2+/Fe2+-PS/H2O2 system ([PS] 1.6 mmol/L; [H2O2] 0.4 mmol/L; [Fe2+] 0.3 mmol/L; [Cu2+] 0.1 mmol/L; reaction time 720 min; 25℃)
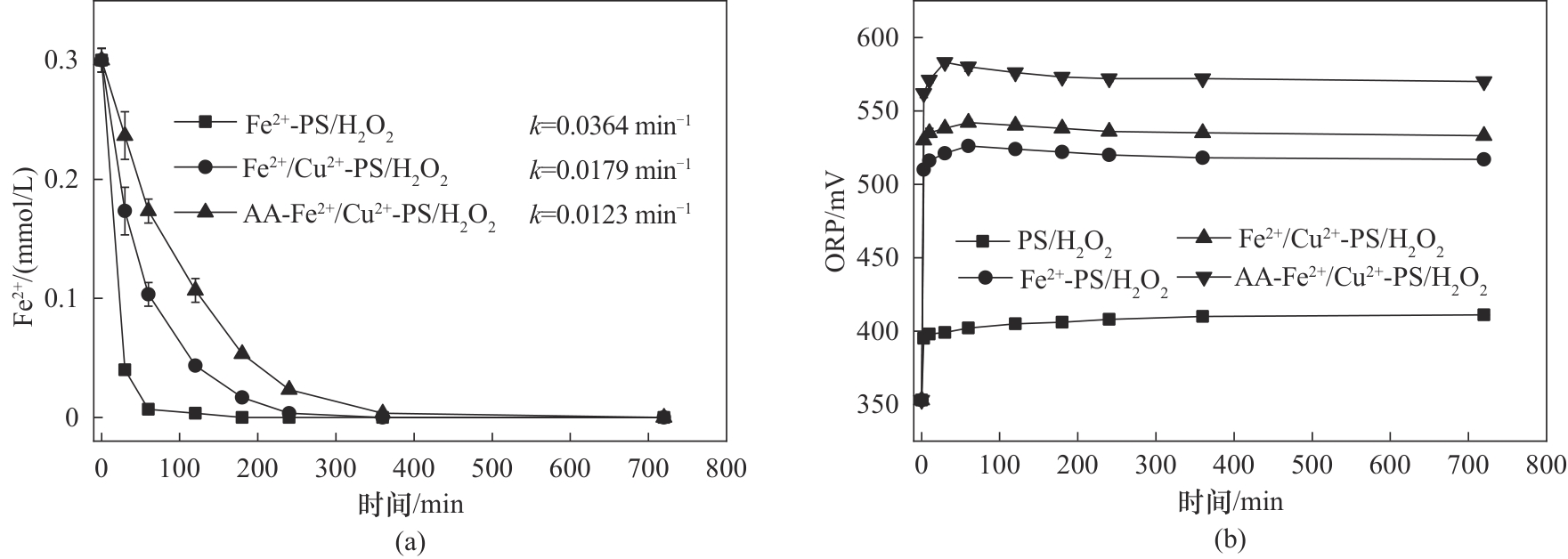
图2 (a)不同氧化体系氧化过程中Fe2+含量;(b)不同氧化体系氧化过程中ORP变化([PS] 1.6 mmol/L;[H2O2] 0.4 mmol/L;[Fe2+] 0.3 mmol/L;[Cu2+] 0.1 mmol/L;[AA] 0.2 mmol/L;25℃)
Fig.2 (a) The variation of Fe2+ content in different oxidation system during the oxidation process; (b) The variation of ORP value in different oxidation system during the oxidation process ([PS] 1.6 mmol/L; [H2O2] 0.4 mmol/L; [Fe2+] 0.3 mmol/L; [Cu2+] 0.1 mmol/L; [AA] 0.2 mmol/L; 25℃)
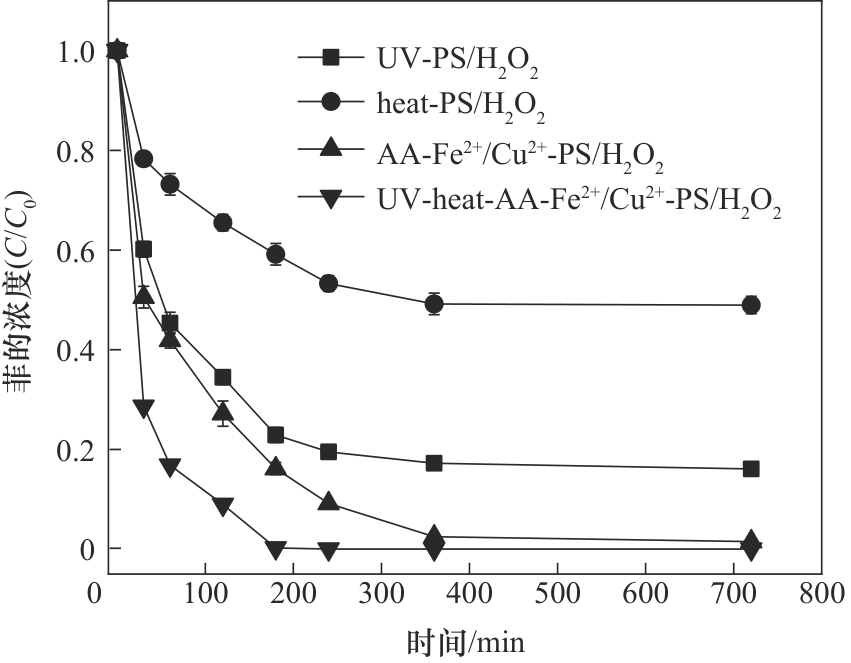
图3 不同活化方式对氧化体系对菲降解的影响([PS] 1.6 mmol/L; [H2O2] 0.4 mmol/L; [Fe2+] 0.3 mmol/L; [Cu2+]0.1 mmol/L; [AA] 0.2 mmol/L; [heat] 50℃; [λUV] 254 nm; 25℃)
Fig.3 The effects of different activation methods on the phenanthrene removal ([PS] 1.6 mmol/L; [H2O2] 0.4 mmol/L; [Fe2+] 0.3 mmol/L; [Cu2+] 0.1 mmol/L; [AA] 0.2 mmol/L; [heat] 50℃; [λUV] 254 nm; 25℃)
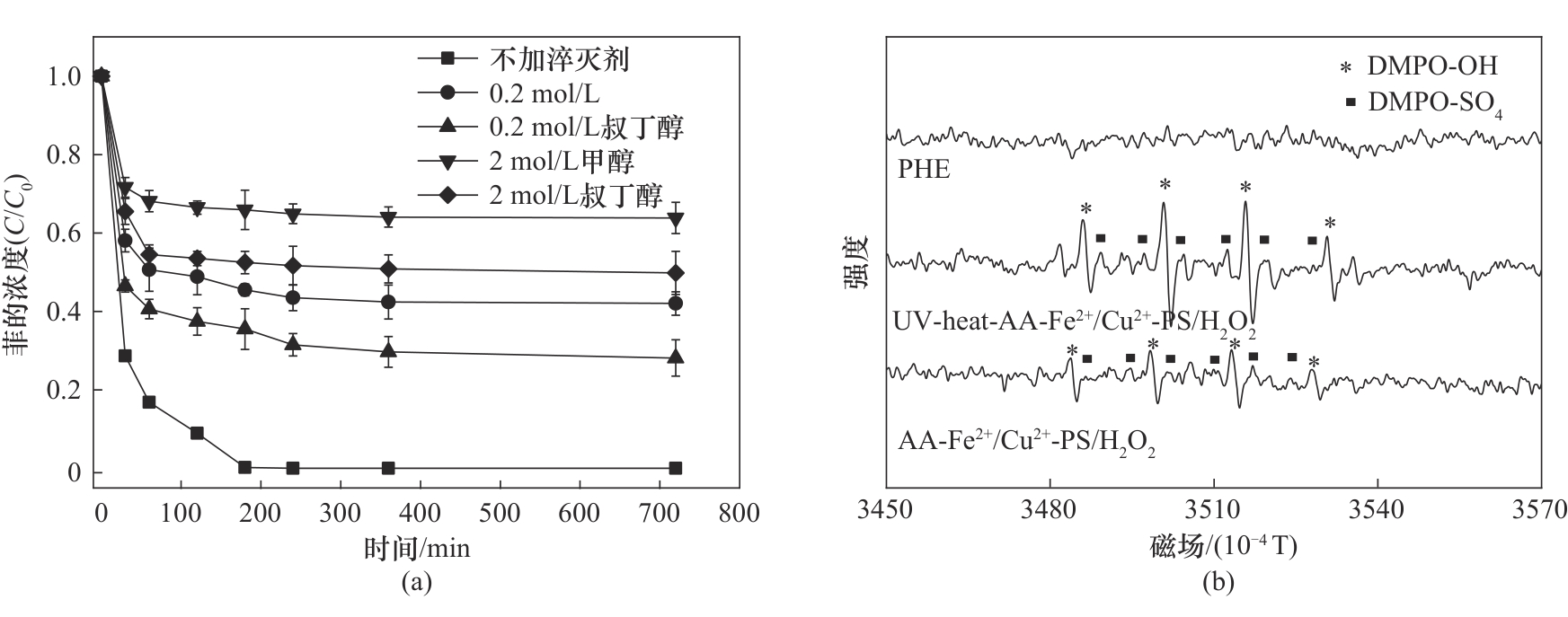
图4 (a)淬灭剂对UV-heat-AA-Fe2+/Cu2+-PS/H2O2体系去除菲的影响;(b)不同氧化体系的EPR波谱图([PS] 1.6 mmol/L; [H2O2] 0.4 mmol/L; [Fe2+] 0.3 mmol/L; [Cu2+] 0.1 mmol/L; [AA] 0.2 mmol/L; [heat] 50℃; [λUV] 254 nm; [DMPO] 0.15 mol/L; 25℃)
Fig.4 (a) The effect of free radical quencher in UV-heat-AA-Fe2+/Cu2+-PS/H2O2 system on the phenanthrene removal;(b) The EPR spectrum of different systems ([PS] 1.6 mmol/L; [H2O2] 0.4 mmol/L; [Fe2+] 0.3 mmol/L; [Cu2+] 0.1 mmol/L; [AA] 0.2 mmol/L; [heat] 50℃; [λUV] 254 nm; [DMPO] 0.15 mol/L; 25℃)
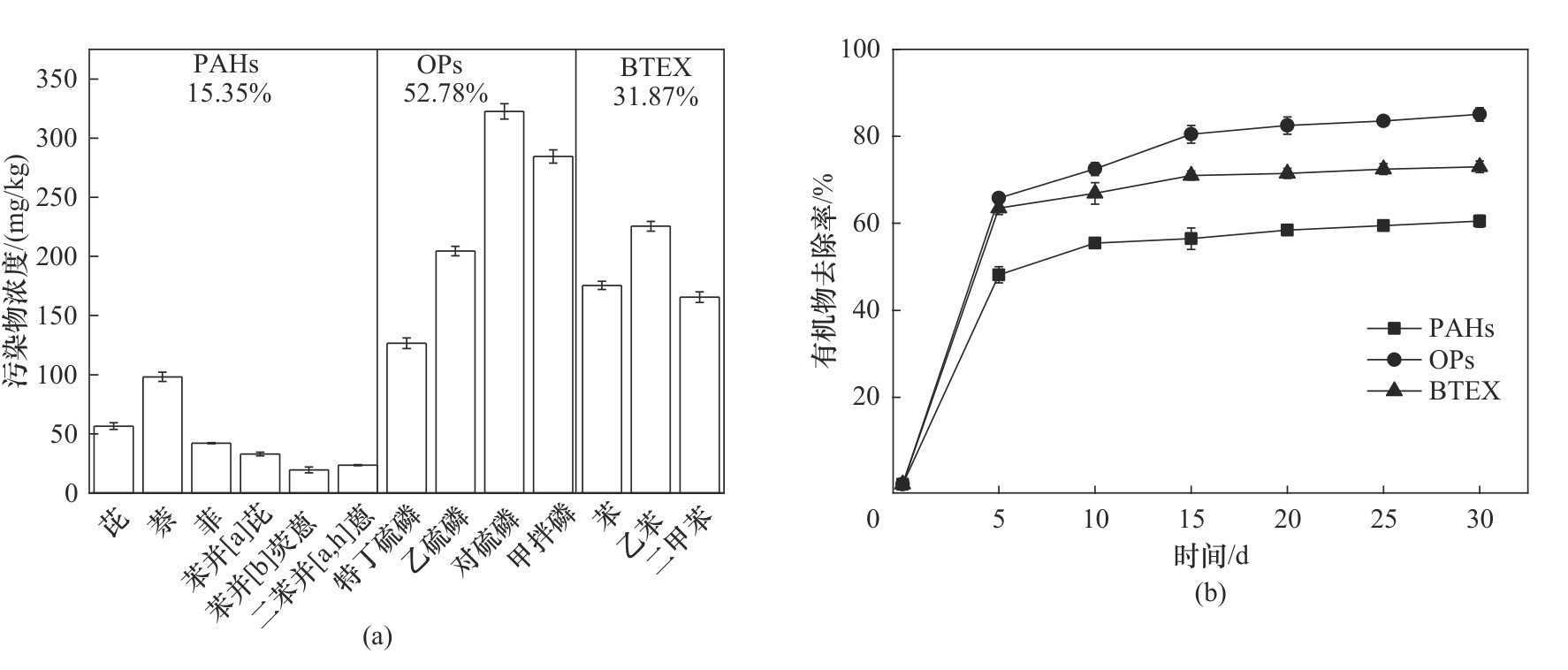
图5 (a)某农药污染场地土壤各污染物浓度;(b)UV-heat-AA-Fe2+/Cu2+-PS/H2O2体系去除土壤中有机物去除率([PS]0.4 mol/L; [H2O2] 0.1 mol/L; [Fe2+] 75 mmol/L; [Cu2+] 25 mmol/L; [AA] 50 mmol/L; [heat] 50℃;[λUV] 254 nm;
Fig.5 (a) Concentrations of soil pollutants in a site contaminated with pesticide;(b) Curve of organic matters removal rate in soil by UV-heat-AA-Fe2+/Cu2+-PS/H2O2 system ([PS] 0.4 mol/L; [H2O2] 0.1 mol/L; [Fe2+] 75 mmol/L; [Cu2+] 25 mmol/L; [AA] 50 mmol/L; [heat] 50℃; [λUV] 254 nm)
| 28 | Zhou L, Zheng W, Ji Y F, et al. Ferrous-activated persulfate oxidation of arsenic (Ⅲ) and diuron in aquatic system[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 263: 422-430. |
| 29 | Yan D Y S, Lo I M C. Removal effectiveness and mechanisms of naphthalene and heavy metals from artificially contaminated soil by iron chelate-activated persulfate[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 178: 15-22. |
| 30 | Han D H, Wan J Q, Ma Y W, et al. Enhanced decolorization of Orange G in a Fe (Ⅱ)-EDDS activated persulfate process by accelerating the regeneration of ferrous iron with hydroxylamine[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 256: 316-323. |
| 31 | Liang C J, Liang C P, Chen C C. pH dependence of persulfate activation by EDTA/Fe (Ⅲ) for degradation of trichloroethylene[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2009, 106(3/4): 173-182. |
| 32 | Neta P, Huie R E, Ross A B. Rate constants for reactions of inorganic radicals in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1988, 17(3): 1027-1284. |
| 33 | Timmins G S, Liu K J, Bechara E J, et al. Trapping of free radicals with direct in vivo EPR detection: a comparison of 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide and 5-diethoxyphosphoryl-5-methyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide as spin traps for HO· and S O 4 · - [J]. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 1999, 27(3/4): 329-333. |
| 34 | Matafonova G, Batoev V. Recent advances in application of UV light-emitting diodes for degrading organic pollutants in water through advanced oxidation processes: a review[J]. Water Research, 2018, 132: 177-189. |
| 1 | Cao J P, Xie S Q, Cheng Z B, et al. Impacts of sampling-tube loss on quantitative analysis of gaseous semi-volatile organic compounds (SVOCs) using an SPME-based active sampler[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 301: 134780. |
| 2 | Weber J B, Miller C T. Organic chemical movement over and through soil[M]//Reactions and Movement of Organic Chemicals in soils. Madison: Wiley-Blackwell, 2015: 305-334. |
| 3 | Zhou Z, Liu X T, Sun K, et al. Persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for organic-contaminated soil remediation: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 372: 836-851. |
| 4 | Rivas F J. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons sorbed on soils: a short review of chemical oxidation based treatments[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 138(2): 234-251. |
| 5 | Lemaire J, Buès M, Kabeche T, et al. Oxidant selection to treat an aged PAH contaminated soil by in situ chemical oxidation[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2013, 1(4): 1261-1268. |
| 6 | Wang J L, Wang S Z. Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334: 1502-1517. |
| 7 | Matzek L W, Carter K E. Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: a review[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 151: 178-188. |
| 8 | Dombrowski P M, Kakarla P, Caldicott W, et al. Technology review and evaluation of different chemical oxidation conditions on treatability of PFAS[J]. Remediation Journal, 2018, 28(2): 135-150. |
| 9 | Yang F, Wang B B, Su H, et al. Thermal-induced surface defective Co/Fe-Co planar hybrid composite nanosheet with enhanced catalytic activity in the Fenton-like reaction[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2017, 1(10): 2065-2077. |
| 10 | Lin K Y A, Chen Y C, Lin T, et al. Lanthanum cobaltite perovskite supported on zirconia as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for activating Ozone in water[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 497: 325-332. |
| 11 | Fasnabi P A, Madhu G, Soloman P A. Removal of acetamiprid from wastewater by Fenton and photo-Fenton processes-optimization by response surface methodology and kinetics[J]. CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water, 2016, 44(6): 728-737. |
| 12 | Jiang Y, Ran J B, Mao K, et al. Recent progress in Fenton/Fenton-like reactions for the removal of antibiotics in aqueous environments[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 236: 113464. |
| 13 | Kim C, Ahn J Y, Kim T Y, et al. Activation of persulfate by nanosized zero-valent iron (NZVI): mechanisms and transformation products of NZVI[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(6): 3625-3633. |
| 14 | Jian H X, Yang F, Gao Y, et al. Efficient removal of pyrene by biochar supported iron oxide in heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction via radicals and high-valent iron-oxo species[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 265: 118518. |
| 15 | Al-Shamsi M A, Thomson N R. Treatment of organic compounds by activated persulfate using nanoscale zerovalent iron[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(38): 13564-13571. |
| 16 | Bokare A D, Choi W. Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 275: 121-135. |
| 17 | Yu S X, Gu X G, Lu S G, et al. Degradation of phenanthrene in aqueous solution by a persulfate/percarbonate system activated with CA chelated-Fe(Ⅱ)[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 333: 122-131. |
| 18 | Sun H W, Xie G H, He D, et al. Ascorbic acid promoted magnetite Fenton degradation of alachlor: mechanistic insights and kinetic modeling[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 267: 118383. |
| 19 | Fang G D, Liu C, Gao J, et al. Manipulation of persistent free radicals in biochar to activate persulfate for contaminant degradation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(9): 5645-5653. |
| 20 | Gao Y, Yang F, Jian H X, et al. Pyrene degradation in an aqueous system using ferrous citrate complex activated persulfate over a wide pH range[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(6): 106733. |
| 21 | dos Santos A J, Brillas E, Cabot P L, et al. Simultaneous persulfate activation by electrogenerated H2O2 and anodic oxidation at a boron-doped diamond anode for the treatment of dye solutions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 747: 141541. |
| 22 | Yuan X, Pham A N, Xing G W, et al. Effects of pH, chloride, and bicarbonate on Cu(Ⅰ) oxidation kinetics at circumneutral pH[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(3): 1527-1535. |
| 23 | Velosa A C, Nascimento C A O. Evaluation of sulfathiazole degradation by persulfate in Milli-Q water and in effluent of a sewage treatment plant[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2017, 24(7): 6270-6277. |
| 24 | Moffett J W, Zika R G. Reaction kinetics of hydrogen peroxide with copper and iron in seawater[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1987, 21(8): 804-810. |
| 25 | Pardo F, Rosas J M, Santos A, et al. Remediation of a biodiesel blend-contaminated soil with activated persulfate by different sources of iron[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2015, 226(2): 17. |
| 26 | Do S H, Kwon Y J, Kong S H. Effect of metal oxides on the reactivity of persulfate/Fe (Ⅱ) in the remediation of diesel-contaminated soil and sand[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 182(1/2/3): 933-936. |
| 27 | Rastogi A, Al-Abed S R, Dionysiou D D. Effect of inorganic, synthetic and naturally occurring chelating agents on Fe (Ⅱ) mediated advanced oxidation of chlorophenols[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43: 684-694. |
| [1] | 杨猛, 丁晓倩, 余涛, 刘畅, 汤成龙, 黄佐华. 甲烷/氧化亚氮绿色推进剂自着火特性实验及动力学[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1221-1229. |
| [2] | 齐珂, 王迪, 谢喆, 陈东升, 周云龙, 孙灵芳. 考虑多物理场耦合特性的固体氧化物燃料电池瞬态特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1264-1274. |
| [3] | 马钟琛, 魏子杰, 朱明涛, 叶恒棣, 郭学益, 谭磊. 一步氧化法制备锰酸锂正极材料用电池级四氧化三锰[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1363-1374. |
| [4] | 张履胜, 王治红, 柳青, 李雪雯, 谭仁敏. 液-液相变吸收剂捕集二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 933-950. |
| [5] | 伏遥, 邵应娟, 钟文琪. TiO2掺杂钙基材料加压碳酸化循环储热性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1180-1190. |
| [6] | 李中青, 王志远, 栾小建, 梁四凯, 王凯. 电沉积-低氧分压法制备MnO涂层及其抑制石脑油热裂解结焦性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1050-1063. |
| [7] | 彭子林, 周蕾, 邓庆航, 叶光华, 周兴贵. 包含偏硅酸影响的3D NAND磷酸湿法刻蚀动力学[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 645-653. |
| [8] | 杨晋宁, 王卫凡, 徐冬, 刘毅, 翁小涵, 原野, 王志. 工业烟道气碳捕集膜技术放大研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 504-518. |
| [9] | 肖志华, 房浩楠, 郑方植, 孙冬, 陶丽达, 李永峰, 徐春明, 马新龙. NaCl辅助构筑高性能沥青基硬炭负极材料[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 846-857. |
| [10] | 张泽雨, 王平, 戴凯论, 钱伟佳, Roy Subhajit, 帅瑞洋, Ferrante Antonio. 轴向双级氨/甲烷湍流预混火焰燃烧特性及NO生成[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 835-845. |
| [11] | 姚佳逸, 张东辉, 唐忠利, 李文彬. 基于二级双回流的变压吸附捕碳工艺研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 744-754. |
| [12] | 宫政, 高秀鲁, 赵玲, 胡冬冬. 超临界CO2发泡PBAT/PLA复合材料及其形状记忆性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 888-896. |
| [13] | 吴雨轩, 常诚, 顾雪萍, 冯连芳, 张才亮. 面向立体异构的丁二烯乳液聚合过程模型化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 879-887. |
| [14] | 李文宝, 胡锦鹏, 杜淼, 潘鹏举, 单国荣. 强韧P(SBMA-co-AAc)/SiO2复合水凝胶海洋防污减阻涂层[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 787-796. |
| [15] | 贾艳萍, 马艳菊, 管文昕, 杨彬, 张健, 张兰河. 响应面法优化Fe0/H2O2体系降解染料废水的工艺条件及机理[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 348-362. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号