• •
收稿日期:2025-09-26
修回日期:2025-12-02
出版日期:2025-12-03
通讯作者:
曹景沛
作者简介:王鸿燕(1994—),女,博士,副教授,hongyanwang@cumt.edu.cn; hongyanwang@tju.edu.cn
基金资助:
Hongyan WANG( ), Xinru WANG, Changrui TAN, Xiaoyu QIAO, Jingpei CAO(
), Xinru WANG, Changrui TAN, Xiaoyu QIAO, Jingpei CAO( )
)
Received:2025-09-26
Revised:2025-12-02
Online:2025-12-03
Contact:
Jingpei CAO
摘要:
萘油作为煤焦油在210-230 oC区间的馏出物,富含萘及甲基萘等双环芳烃,经催化加氢提质可制备密度>0.85 g/cm3的煤基多环烷烃高密度燃料。通过调控HZSM-5分子筛的硅铝比与Pd负载策略,系统研究了金属分散度、电子态与酸性位点的协同机制对萘加氢路径的影响。采用直接还原法成功制备出高分散Pd/HZ5催化剂,表征结果表明其Pd平均粒径为3.58 nm,显著小于传统焙烧-还原法制备的催化剂(8.24 nm),且形成了具有缺电子特性的Pd物种。适中的载体酸性不仅促进反应物吸附活化,还通过金属-载体相互作用优化Pd电子结构。在240°C、2 MPa的温和条件下,Pd/HZ5-50催化剂萘加氢转化率达94.5%。动力学研究显示其表观活化能为105 kJ/mol,表现出优异的反应活性。
中图分类号:
王鸿燕, 王心如, 谭长锐, 乔晓宇, 曹景沛. Pd/HZ5催化剂金属-酸位点匹配机制及萘加氢性能[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251094.
Hongyan WANG, Xinru WANG, Changrui TAN, Xiaoyu QIAO, Jingpei CAO. Metal-acid site matching mechanism and catalytic performance of naphthalene hydrogenation in Pd/HZ5[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251094.
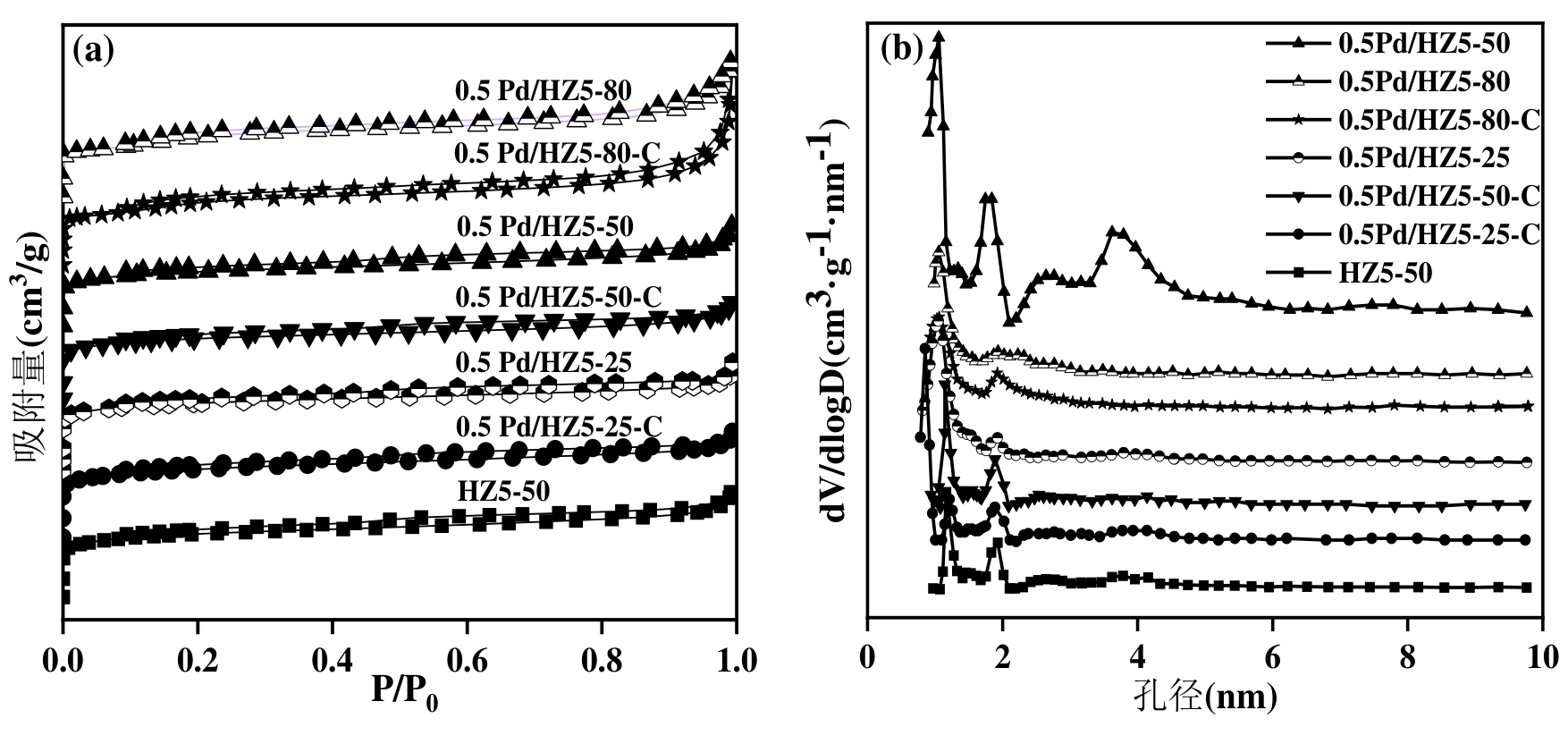
图2 不同硅铝比的HZ5催化剂(a)N2吸附-脱附等温线及(b)孔径分布图
Figure 2 (a) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distribution of HZ5 catalysts with different SiO2/Al2O3 ratios
| 样品 | SBET (m2/g) | Sext (m2/g) | Smic (m2/g) | Vtotal (cm3/g) | Vmic (cm3/g) | Dava (nm) | Pda (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ5-50 | 353 | 63 | 290 | 0.223 | 0.131 | 2.53 | - |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-25-C | 384 | 58 | 327 | 0.227 | 0.146 | 2.37 | - |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-25 | 360 | 53 | 307 | 0.223 | 0.137 | 2.48 | 0.43 |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50-C | 336 | 54 | 282 | 0.206 | 0.128 | 2.45 | 0.40 |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50 | 334 | 59 | 275 | 0.223 | 0.125 | 2.68 | 0.45 |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-80-C | 325 | 59 | 266 | 0.388 | 0.137 | 4.77 | - |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-80 | 334 | 49 | 286 | 0.289 | 0.142 | 3.45 | 0.58 |
表1 不同硅铝比的HZ5催化剂的孔结构特性
Table 1 Pore textural properties of HZ5 catalysts with different SiO2/Al2O3 ratios
| 样品 | SBET (m2/g) | Sext (m2/g) | Smic (m2/g) | Vtotal (cm3/g) | Vmic (cm3/g) | Dava (nm) | Pda (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ5-50 | 353 | 63 | 290 | 0.223 | 0.131 | 2.53 | - |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-25-C | 384 | 58 | 327 | 0.227 | 0.146 | 2.37 | - |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-25 | 360 | 53 | 307 | 0.223 | 0.137 | 2.48 | 0.43 |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50-C | 336 | 54 | 282 | 0.206 | 0.128 | 2.45 | 0.40 |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50 | 334 | 59 | 275 | 0.223 | 0.125 | 2.68 | 0.45 |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-80-C | 325 | 59 | 266 | 0.388 | 0.137 | 4.77 | - |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-80 | 334 | 49 | 286 | 0.289 | 0.142 | 3.45 | 0.58 |
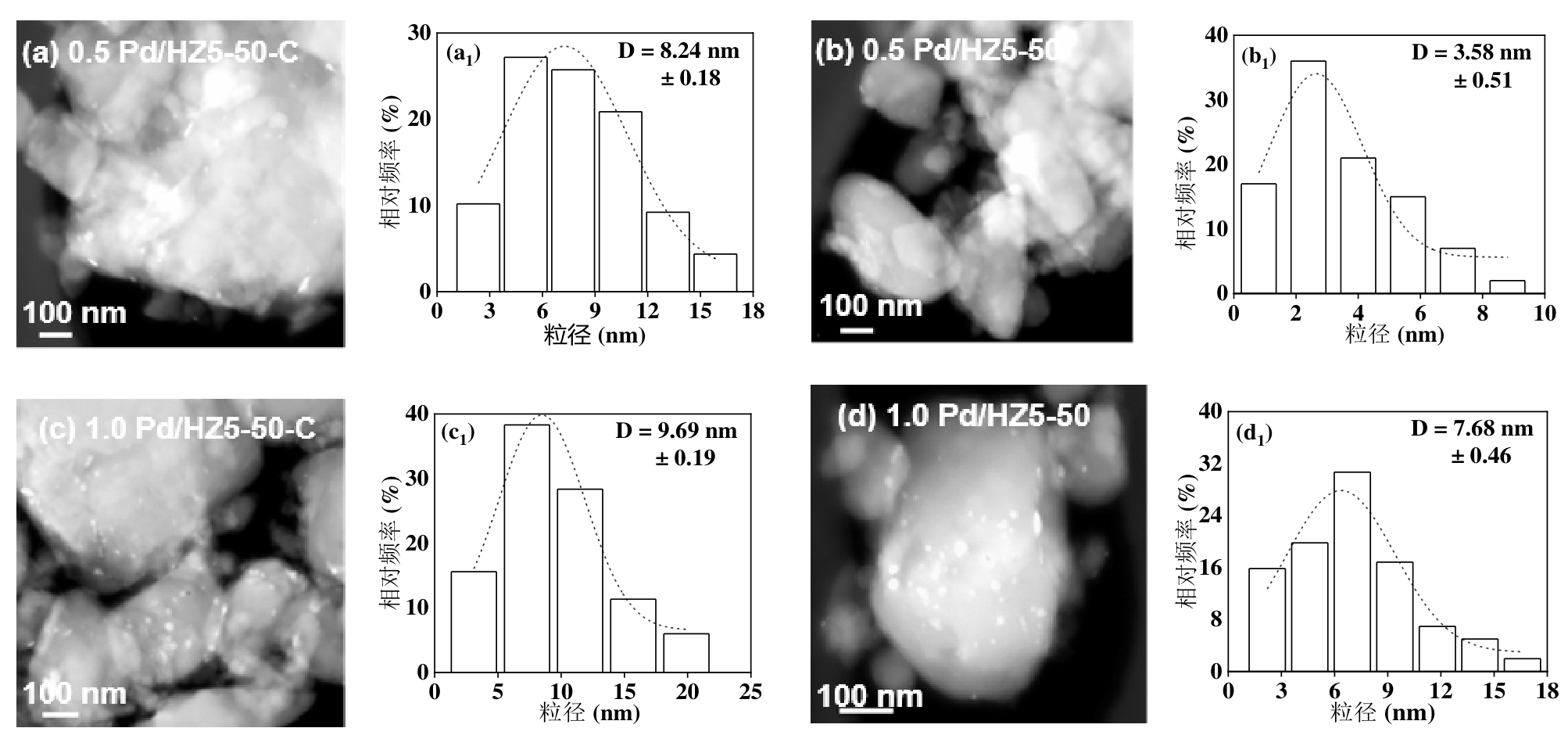
图5 负载量为0.5-1.0 Pd/HZ5-50催化剂的TEM及粒径分布图(a-a1)1.0 Pd/HZ5-50-C、(b-b1)0.5 Pd/HZ5-50、(c-c1)1.0 Pd/HZ5-50和(d-d1)1.0 Pd/HZ5-50
Figure 5 TEM and particle size distribution of a series of Pd/HZ5-50 catalysts with loadings of 0.5-1.0 wt%: (a-a1) 0.5Pd/HZ5-50-C, (b-b1) 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50, (c-c1) 1.0Pd/HZ5-50-C and (d-d1) 1.0 Pd/HZ5-50
| 样品 | NH3-TPD 酸量/ (mmol g-1) | Py-FTIR B/L酸比值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 °C | 350 °C | ||||
| L酸量 | B酸量 | 总酸量 | B/L | B/L | |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-25 | 5.34 | 1.97 | 7.31 | 7.98 | 7.46 |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50-C | 0.91 | 0.75 | 1.66 | 5.64 | 6.51 |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50 | 1.70 | 2.39 | 4.09 | 5.61 | 6.36 |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-80 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 1.55 | 2.62 |
表2 不同硅铝比Pd/HZ5-50催化剂的酸性质
Table 2 Acidity properties of a series of Pd/HZ5-50 catalysts with different SiO2/Al2O3 ratios
| 样品 | NH3-TPD 酸量/ (mmol g-1) | Py-FTIR B/L酸比值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 °C | 350 °C | ||||
| L酸量 | B酸量 | 总酸量 | B/L | B/L | |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-25 | 5.34 | 1.97 | 7.31 | 7.98 | 7.46 |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50-C | 0.91 | 0.75 | 1.66 | 5.64 | 6.51 |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50 | 1.70 | 2.39 | 4.09 | 5.61 | 6.36 |
| 0.5 Pd/HZ5-80 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 1.55 | 2.62 |
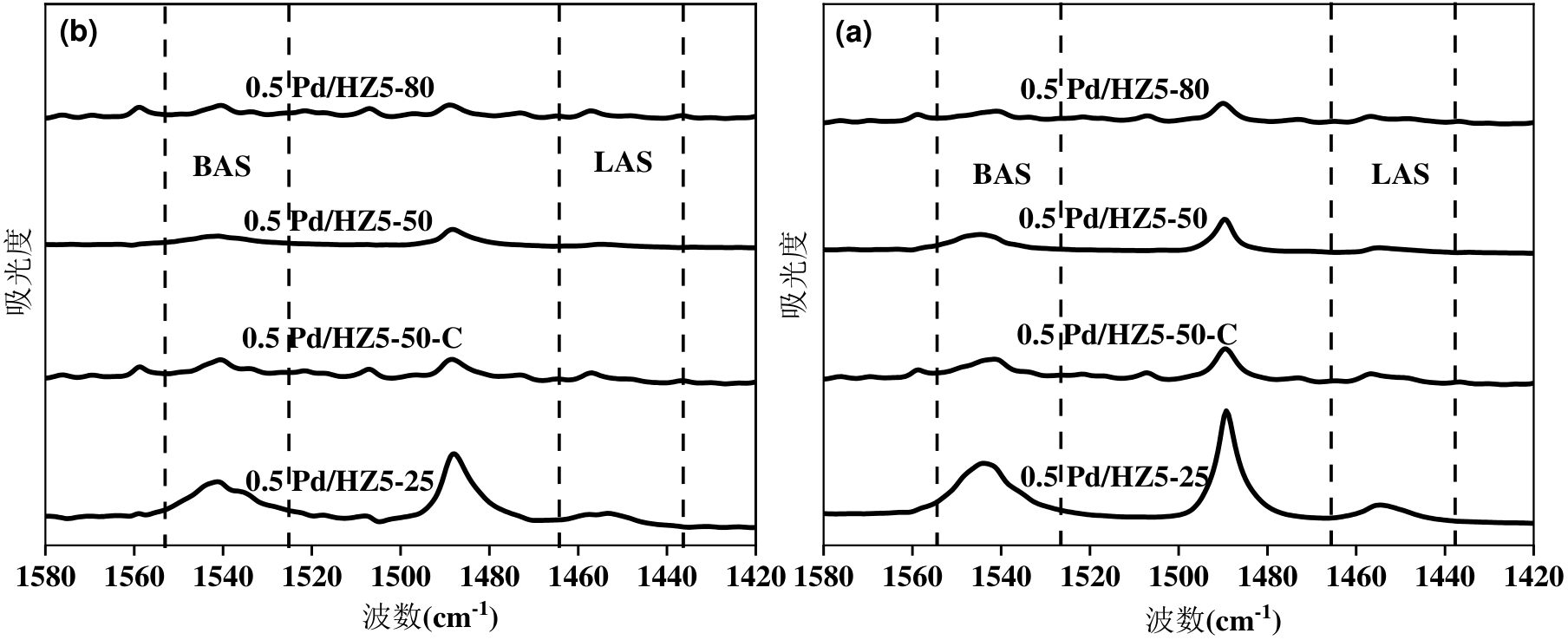
图7 不同硅铝比Pd/HZ5-50催化剂的Py-FTIR图:(a)200 °C;(b)350 °C
Figure 7 Py-FTIR patterns of a series of Pd/HZ5-50 catalysts with different SiO2/Al2O3 ratios: (a) 200 °C; (b) 350 °C
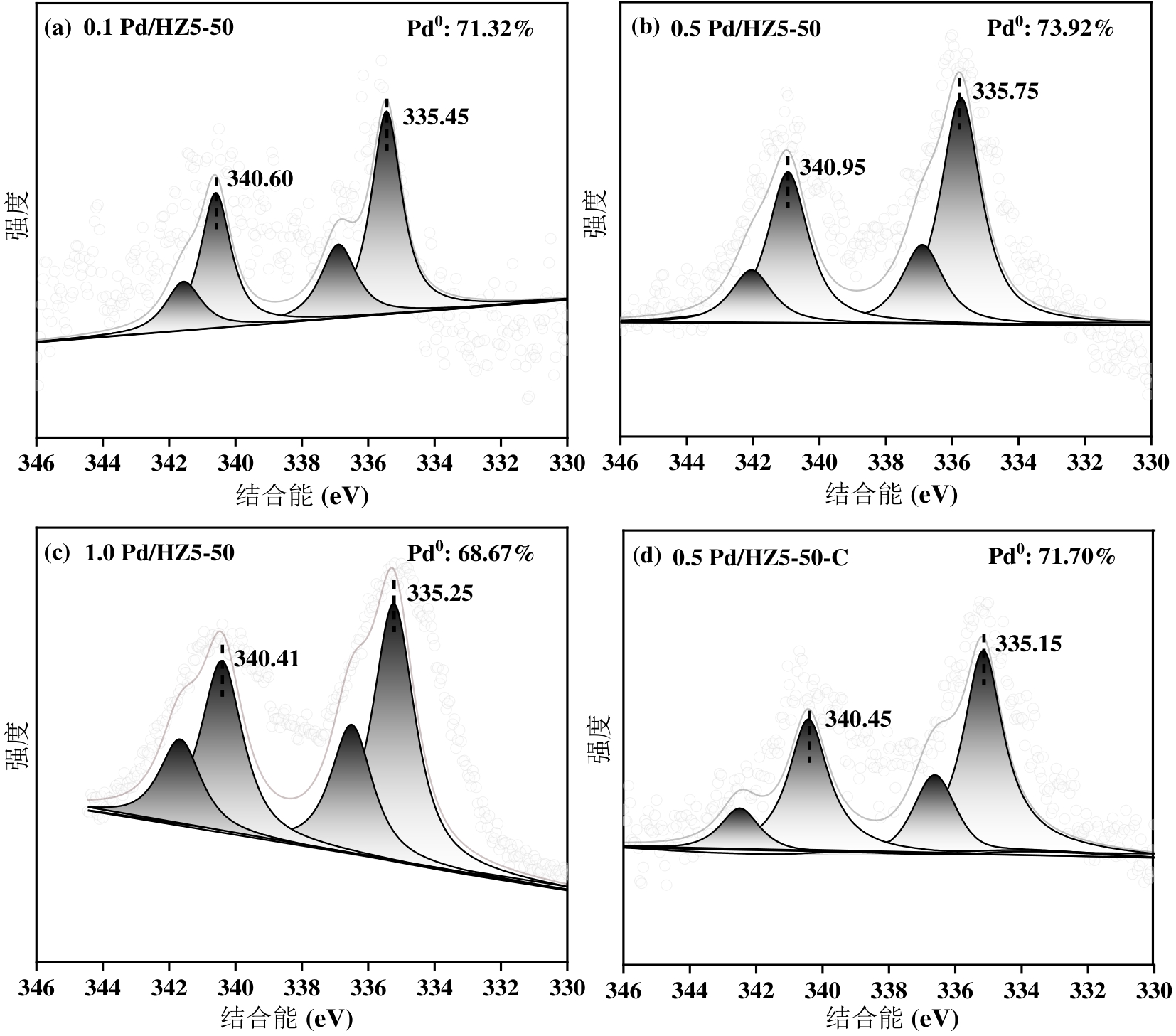
图8 不同负载量的Pd/HZ5-50催化剂的Pd 3d XPS能谱:(a)0.1 Pd/HZ5-50、(b)0.5 Pd/HZ5-50、(c)1.0 Pd/HZ5-50、注:(d)0.5 Pd/HZ5-50-C(c) 1.0 Pd/HZ5-50 and (d) 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50-C
Figure 8 Pd 3d spectra of a series of Pd/HZ5-50 catalysts with different loadings: (a) 0.1 Pd/HZ5-50, (b) 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50,
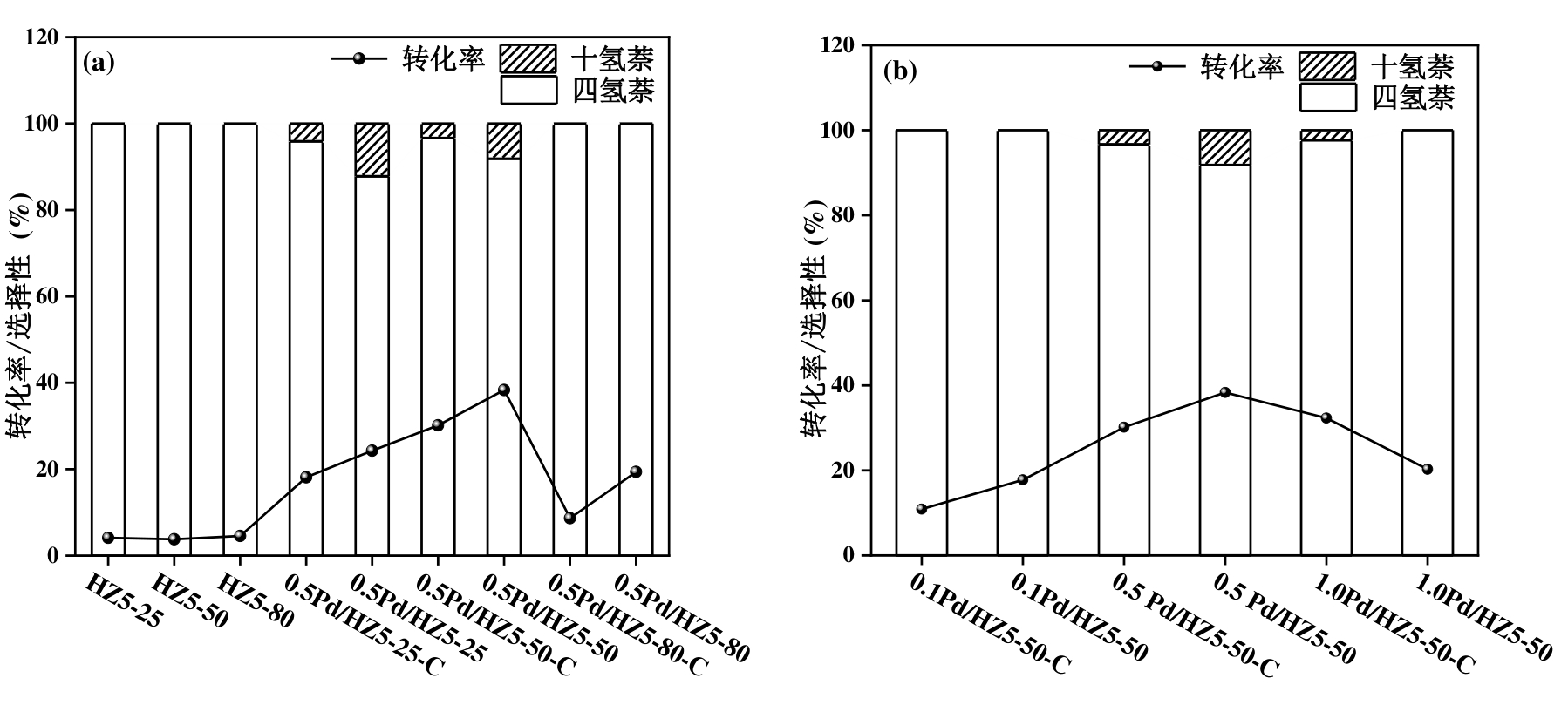
图10 萘加氢反应活性对比:a)不同硅铝比的HZ5-x、0.5 Pd/HZ5-x-C和0.5 Pd/HZ5-x催化剂;b)不同金属负载量的Pd/HZ5-x-C和Pd/HZ5-x催化剂。反应条件:100 mg萘,50 mg催化剂,20 mL溶剂,1 h,200 oC,2 MPa H2(初始)
Figure 10 Comparison of naphthalene hydrogenation activity: (a) HZ5-x supports with different SiO2/Al2O3 ratios, 0.5 Pd/HZ5-x-C, and 0.5 Pd/HZ5-x catalysts; (b) Pd/HZ5-x-C and Pd/HZ5-x catalysts with different metal loadings. Reaction conditions: 100 mg naphthalene, 50 mg catalyst, 20 mL solvent, 1 h, 200 °C, 2 MPa H2 (initial pressure).
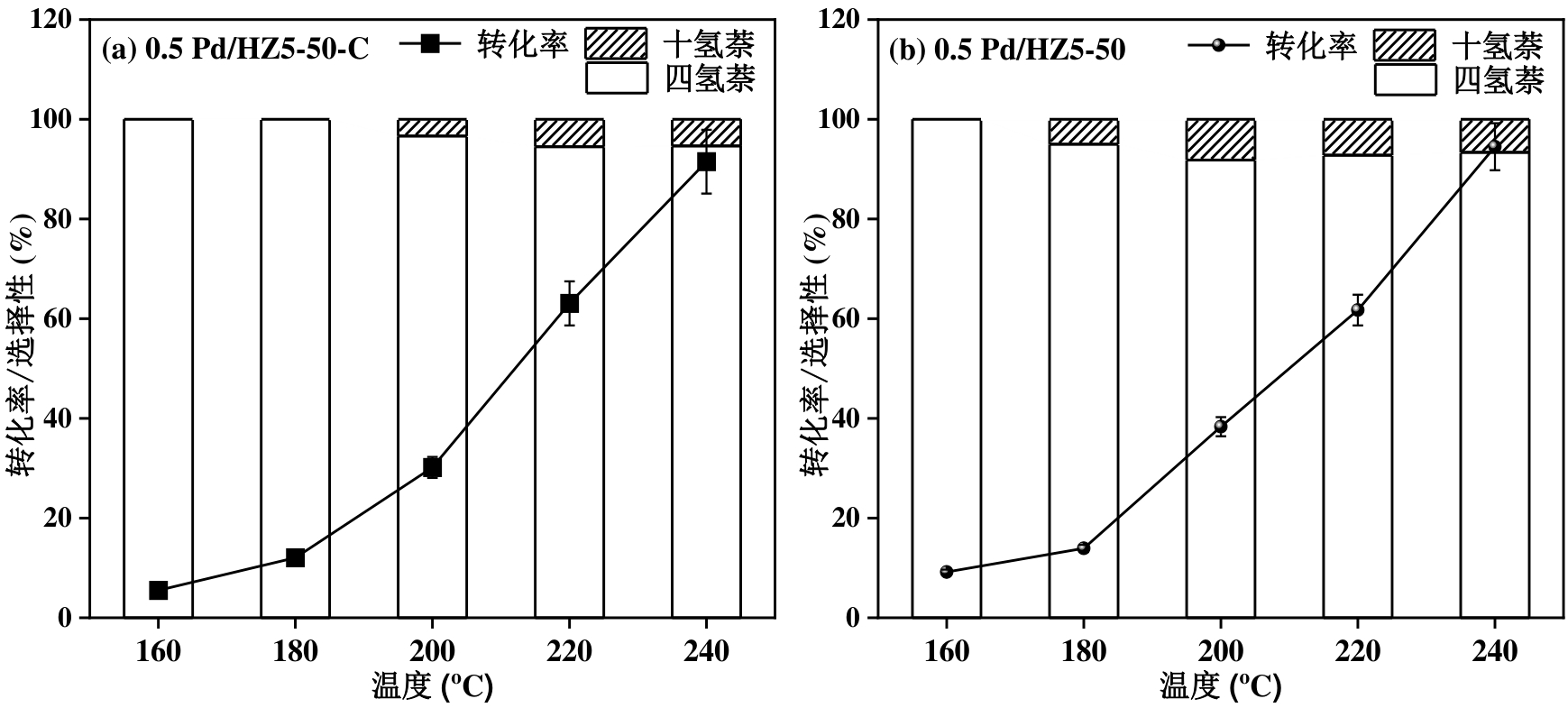
图11 反应温度为160-240 oC下萘加氢反应活性对比:a)0.5 Pd/HZ5-50-C;b)0.5 Pd/HZ5-50。反应条件:100 mg萘,50 mg催化剂,20 mL溶剂,1 h,2 MPa H2(初始)
Figure 11 Comparison of naphthalene hydrogenation activity at a reaction temperature range of 160-240 oC: (a) 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50-C; (b) 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50. Reaction conditions: 100 mg naphthalene, 50 mg catalyst, 20 mL solvent, 1 h, 2 MPa H2 (initial pressure).
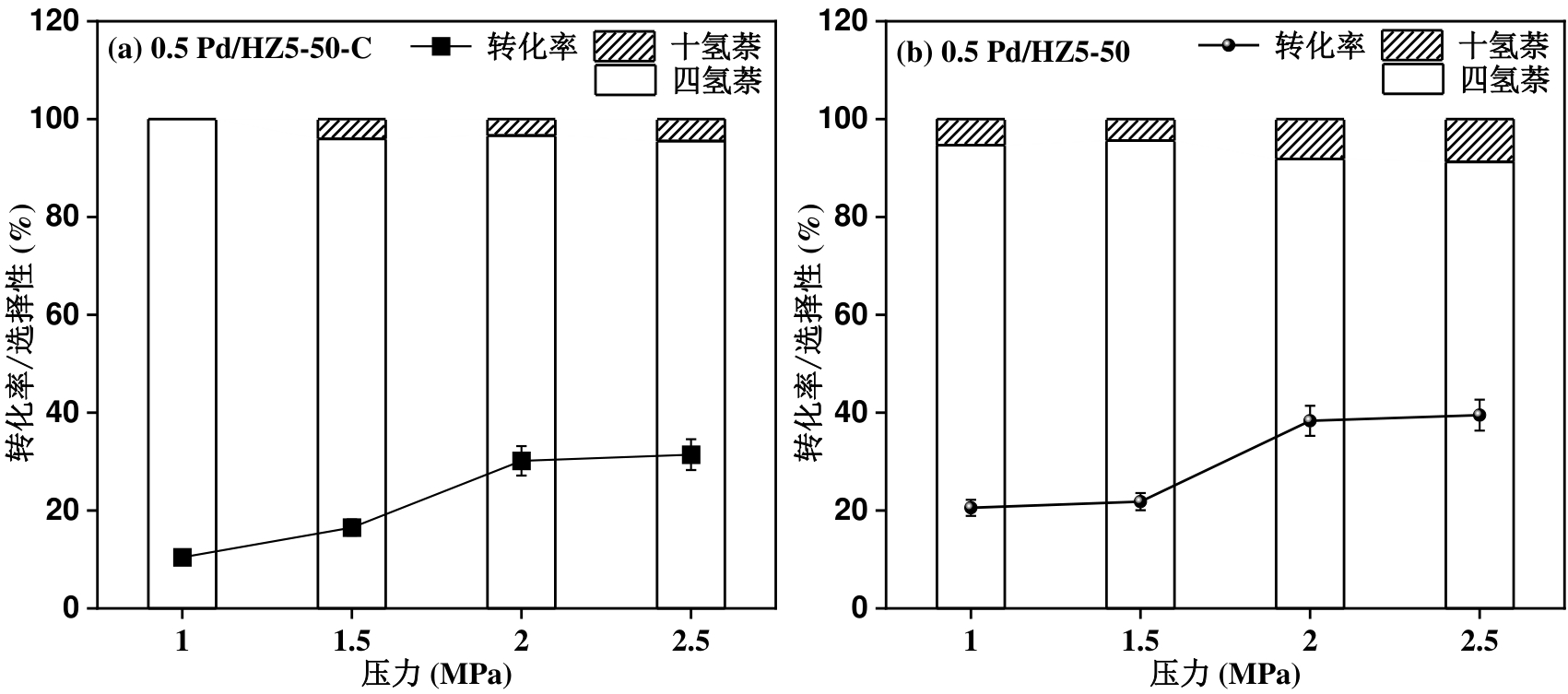
图12 氢气反应初始压力为1.0-2.5 MPa下萘加氢反应活性对比:a)0.5 Pd/HZ5-50-C;b)0.5 Pd/HZ5-50。反应条件:100 mg萘,50 mg催化剂,20 mL溶剂,1 h,200 oC。
Figure 12 Comparison of naphthalene hydrogenation activity at a initial H2 pressure range of 1.0-2.5 MPa: (a) 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50-C; (b) 0.5 Pd/HZ5-50. Reaction conditions: 100 mg naphthalene, 50 mg catalyst, 20 mL solvent, 1 h, 200 oC.
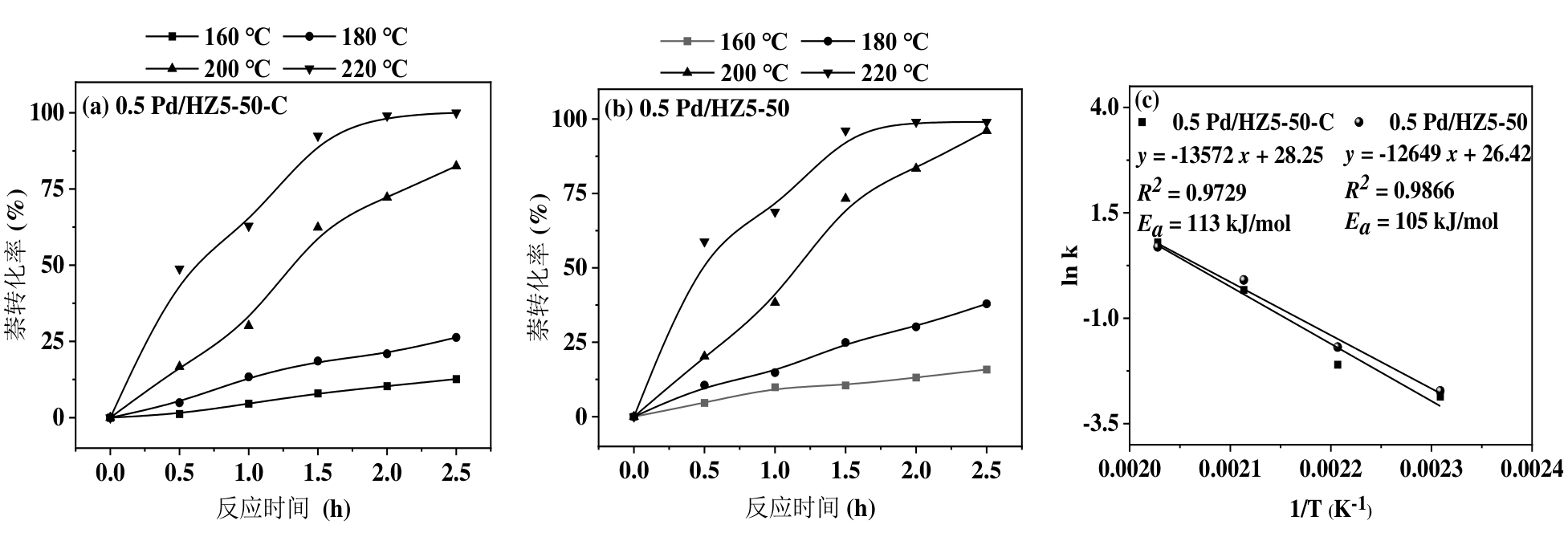
图13 (a)Pd/HZ5-50-C和(b)Pd/HZ5-50催化剂在不同温度下萘转化率随时间变化;(c)反应活化能。反应条件:50 mg催化剂,100 mg萘,20 mL溶剂,0.5-2.5 h,2 MPa H2
Figure 13 Naphthalene hydrogenation activity curves of (a) Pd/HZ5-50-C and (b) Pd/HZ5-50 at different temperatures with a reaction time range of 0.5-2.5 h; (c) activation energy. Reaction conditions: 50 mg catalyst, 100 mg naphthalene, 20 mL solvent, 0.5-2.5 h, 2 MPa H2
| [1] | 周秋成, 席引尚, 马宝岐. 我国煤焦油加氢产业发展现状与展望[J]. 煤化工, 2020, 48(3): 3-8, 49. |
| Zhou Q C, Xi Y S, Ma B Q. Development situation and trend of coal tar hydrogenation industry in China[J]. Coal Chemical Industry, 2020, 48(3): 3-8, 49. | |
| [2] | 薛皓, 李航, 韩旭辉. 煤焦油综合利用现状及发展展望[J]. 现代化工, 2021, 41(S1): 105-109, 113. |
| Xue H, Li H, Han X H. Review on development status and prospect of comprehensive utilization of coal tar[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2021, 41(S1): 105-109, 113. | |
| [3] | Zhang X W, Pan L, Wang L, et al. Review on synthesis and properties of high-energy-density liquid fuels: Hydrocarbons, nanofluids and energetic ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 180: 95-125. |
| [4] | Khan A, Ali S S, Chodimella V P, et al. Catalytic conversion of dicyclopentadiene into high energy density fuel: a brief review[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(5): 1977-1988. |
| [5] | Wang H Y, Gong S Y, Wang L, et al. High pressure pyrolysis mechanism and kinetics of a strained-caged hydrocarbon fuel quadricyclane[J]. Fuel, 2019, 239: 935-945. |
| [6] | Jing J Y, Wang J Z, Liu D C, et al. Naphthalene hydrogenation saturation over Ni2P/Al2O3 catalysts synthesized by thermal decomposition of hypophosphite[J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(48): 31423-31431. |
| [7] | 荆洁颖, 李泽, 赵泽敏, 等. 活性金属Ni d电荷密度对Ni2P/Al2O3催化剂菲加氢性能的影响[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2024, 30(2): 102-113. |
| Jing J Y, Li Z, Zhao Z M, et al. Optimization of active metal Ni d charge density for efficient phenanthrene hydrogenation over Ni2P/Al2O3 catalyst[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2024, 30(2): 102-113. | |
| [8] | Raad Z, Toufaily J, Hamieh T, et al. TiO2-supported Pd as an efficient and stable catalyst for the mild hydrotreatment of tar-type compounds[J]. Nanomaterials, 2021, 11(9): 2380. |
| [9] | Lin S D, Song C S. Noble metal catalysts for low-temperature naphthalene hydrogenation in the presence of benzothiophene[J]. Catalysis Today, 1996, 31(1/2): 93-104. |
| [10] | Liu J J, Zhang H F, Lu N Y, et al. Influence of acidity of mesoporous ZSM-5-supported Pt on naphthalene hydrogenation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(3): 1056-1064. |
| [11] | 张明惠. Pd/HY的构型调控及催化加氢饱和性能研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2022. |
| Zhang M H. Configuration regulation of HY supported Pd for catalytic hydrogenation saturation[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2022. | |
| [12] | Liang Y, Wang L J, Li X K, et al. Ozonation assisted synthesis of well-dispersed Pt on HY zeolite as highly efficient catalyst for deep hydrogenation of naphthalene[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2023, 668: 119490. |
| [13] | Corma A, Martı́nez A, Martı́nez-Soria V. Hydrogenation of aromatics in diesel fuels on Pt/MCM-41 catalysts[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1997, 169(2): 480-489. |
| [14] | Zhao M, Zhao L, Cao J P, et al. Water-involved tandem conversion of aryl ethers to alcohols over metal phosphide catalyst[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 435: 134911. |
| [15] | Sun N, Wang H Y, Luo A, et al. Synthesis and hydrogen isomerization performance of ordered mesoporous nanosheet SAPO-11 molecular sieves[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2022, 309: 122972. |
| [16] | Yang Q, Kong M, Fan Z Y, et al. Aluminum fluoride modified HZSM-5 zeolite with superior performance in synthesis of dimethyl ether from methanol[J]. Energy & fuels, 2012, 26(7): 4475-4480. |
| [17] | Zhang J G, Qian W Z, Kong C Y, et al. Increasing para-xylene selectivity in making aromatics from methanol with a surface-modified Zn/P/ZSM-5 catalyst[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(5): 2982-2988. |
| [18] | Al-Dughaither A S, de Lasa H. HZSM-5 zeolites with different SiO2/Al2O3 ratios. characterization and NH3 desorption kinetics[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(40): 15303-15316. |
| [19] | Lou Y, Ma J, Hu W D, et al. Low-temperature methane combustion over Pd/H-ZSM-5: active Pd sites with specific electronic properties modulated by acidic sites of H-ZSM-5[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(12): 8127-8139. |
| [20] | Parry E P. An infrared study of pyridine adsorbed on acidic solids. Characterization of surface acidity[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1963, 2(5): 371-379. |
| [21] | Vimont A, Lavalley J C, Sahibed-Dine A, et al. Infrared spectroscopic study on the surface properties of gamma-gallium oxide as compared to those of gamma-alumina[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 2005, 109(19): 9656-9664. |
| [22] | Zholobenko V, Freitas C, Jendrlin M, et al. Probing the acid sites of zeolites with pyridine: Quantitative AGIR measurements of the molar absorption coefficients[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2020, 385: 52-60. |
| [23] | 曾伟, 刘甲, 张德谨, 等. Pd-Au/1cTiO2/SiO2催化剂的制备及其烯烃的环氧化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 4999-5006. |
| Zeng W, Liu J, Zhang D J, et al. Preparation of catalyst Pd-Au/1cTiO2/SiO2 and epoxidation of olefins[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(11): 4999-5006. | |
| [24] | Williams M F, Fonfé B, Woltz C, et al. Hydrogenation of tetralin on silica–alumina-supported Pt catalysts II. Influence of the support on catalytic activity[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2007, 251(2): 497-506. |
| [25] | Yashnik S A, Urzhuntsev G A, Stadnichenko A I, et al. Effect of Pd- precursor and support acid properties on the Pd electronic state and the hydrodesulfurization activity of Pd-zeolite catalysts[J]. Catalysis Today, 2019, 323: 257-270. |
| [26] | Spezzati G, Su Y Q, Hofmann J P, et al. Atomically dispersed Pd-O species on CeO(2)(111) as highly active sites for low-temperature CO oxidation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(10): 6887-6891. |
| [27] | Chen C S, Lin J H, Chen H W. Hydrogen adsorption sites studied by carbon monoxide adsorption to explain the hydrogenation activity of benzene on Pd and Pt catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2006, 298: 161-167. |
| [28] | Peter M, Flores Camacho J M, Adamovski S, et al. Trends in the binding strength of surface species on nanoparticles: how does the adsorption energy scale with the particle size?[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(19): 5175-5179. |
| [29] | Gao M Y, Gong Z M, Weng X F, et al. Methane combustion over palladium catalyst within the confined space of MFI zeolite[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2021, 42(10): 1689-1699. |
| [30] | Schmitz A D, Bowers G, Song C S. Shape-selective hydrogenation of naphthalene over zeolite-supported Pt and Pd catalysts[J]. Catalysis Today, 1996, 31(1/2): 45-56. |
| [31] | Zhang M H, Song Q Y, He Z X, et al. Tuning the mesopore-acid-metal balance in Pd/HY for efficient deep hydrogenation saturation of naphthalene[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(48): 20881-20893. |
| [32] | Pawelec B, Mariscal R, Navarro R M, et al. Hydrogenation of aromatics over supported Pt-Pd catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2002, 225(1/2): 223-237. |
| [33] | Borodziński A, Bond G C. Selective hydrogenation of ethyne in ethene-rich streams on palladium catalysts. part 1. effect of changes to the catalyst during reaction[J]. Catalysis Reviews, 2006, 48(2): 91-144. |
| [34] | Kerry Yu K M, Yeung C M Y, Tsang S C. Carbon dioxide fixation into chemicals (methyl formate) at high yields by surface coupling over a Pd/Cu/ZnO nanocatalyst[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(20): 6360-6361. |
| [1] | 刘奕扬, 邢志祥, 刘烨铖, 彭明, 李玉洋, 李云浩, 沈宁舟. 加氢站液氢泄漏扩散特性与安全监测数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4694-4708. |
| [2] | 钱慧慧, 王文婕, 陈文尧, 周兴贵, 张晶, 段学志. 聚丙烯定向转化制芳烃:金属-分子筛协同催化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4838-4849. |
| [3] | 赵维, 邢文乐, 韩朝旭, 袁兴中, 蒋龙波. g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化降解水中有机污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769. |
| [4] | 佟丽丽, 陈英, 艾敏华, 舒玉美, 张香文, 邹吉军, 潘伦. ZnO/WO3异质结光催化环烯烃[2+2]环加成制备高能量密度燃料[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4882-4892. |
| [5] | 王小令, 王绍清, 赵云刚, 常方哲, 穆瑞峰. 基于ReaxFF MD模拟的煤加氢热解有机Ca转化机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4297-4309. |
| [6] | 范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [7] | 杨宁, 李皓男, LIN Xiao, GEORGIADOU Stella, LIN Wen-Feng. 从塑料废弃物到能源催化剂:塑料衍生碳@CoMoO4复合材料在电解水析氢反应中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [8] | 周运桃, 崔丽凤, 张杰, 于富红, 李新刚, 田野. Ga2O3调控CuCeO催化CO2加氢制甲醇的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4042-4051. |
| [9] | 巢欣旖, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 甲醇和乙酸甲酯一步法制丙酸甲酯催化剂的可控制备与性能调控[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4030-4041. |
| [10] | 周媚, 曾浩桀, 蒋火炎, 蒲婷, 曾星星, 刘宝玉. 二次晶化法改性合成MTW分子筛及其在苯和环己烯烷基化反应中的催化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4071-4080. |
| [11] | 赵世颖, 左志帅, 贺梦颖, 安华良, 赵新强, 王延吉. Co-Pt/HAP的制备及其催化1,2-丙二醇氨化反应[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3305-3315. |
| [12] | 陆学瑞, 周帼彦, 方琦, 俞孟正, 张秀成, 涂善东. 固体氧化物燃料电池外重整器积炭效应数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3295-3304. |
| [13] | 李愽龙, 蒋雨希, 任傲天, 秦雯琪, 傅杰, 吕秀阳. TS-1/In-TS-1催化果糖一步法醇解制备乳酸甲酯连续化试验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2678-2686. |
| [14] | 何军, 李勇, 赵楠, 何孝军. 碳负载硒掺杂硫化钴在锂硫电池中的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2995-3008. |
| [15] | 宋粉红, 王文光, 郭亮, 范晶. C元素修饰g-C3N4对TiO2的调控及复合材料光催化产氢性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2983-2994. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号