• •
收稿日期:2025-10-09
修回日期:2025-11-09
出版日期:2025-11-14
通讯作者:
李翔南
作者简介:安敏(1990—),女,博士研究生,讲师,anmin@zzu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Min AN1( ), Yun XI3, Hongkang YAO2, Xiangnan LI1(
), Yun XI3, Hongkang YAO2, Xiangnan LI1( )
)
Received:2025-10-09
Revised:2025-11-09
Online:2025-11-14
Contact:
Xiangnan LI
摘要:
相较于气液鼓泡塔,气液固浆态床内颗粒的引入会使得反应器的流动及传递过程发生显著变化。广泛应用于气液鼓泡塔流动行为预测的多流体模型和群平衡模型,在模拟浆态床时准确性缺失,其原因在于浆态床内颗粒-湍流-气泡的多尺度耦合机制更为复杂,但尚未得到深入研究。以颗粒-湍流、气泡-湍流和颗粒-气泡的两两相互作用作为主要内容,综述了基于直接数值/大涡模拟或小尺度实验的颗粒-湍流-气泡的底层微介观耦合机制的研究进展。重点关注了颗粒和气泡对湍流场能谱结构和湍流特征参量的影响机制,探讨了湍流特性与介尺度的颗粒团聚物及气泡聚并/破碎行为的关联,论述了颗粒对气泡动力学的影响,最后提出了主要结论和未来研究建议。
中图分类号:
安敏, 西芸, 姚宏康, 李翔南. 气液固浆态床中颗粒-湍流涡-气泡的多尺度耦合机制[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251110.
Min AN, Yun XI, Hongkang YAO, Xiangnan LI. Multiscale coupling mechanisms of particle-turbulence eddy-bubble in gas-liquid-solid slurry bubble columns[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251110.
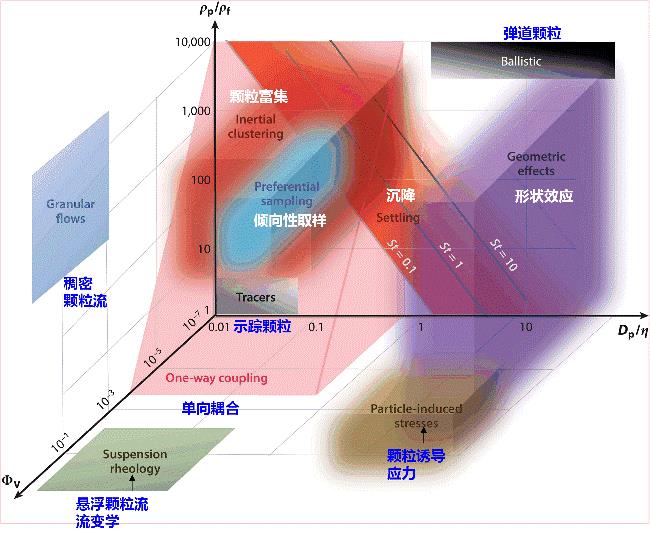
图2 球形颗粒湍流输送系统的控制机制的三维示意图 [26](坐标轴分别为颗粒直径与最小湍流涡尺度比值Dp/η,颗粒与流体密度的比值ρp/ρf,以及固相体积分数Φv)
Fig.2 Three-dimensional view of the different regimes characterizing the transport of spherical particles in turbulence [26](The phase space is defined by the particle size compared to the smallest turbulence scales Dp/η, the particle-to-fluid density ratio ρp/ρf, and the solid-phase volume fraction Φv)
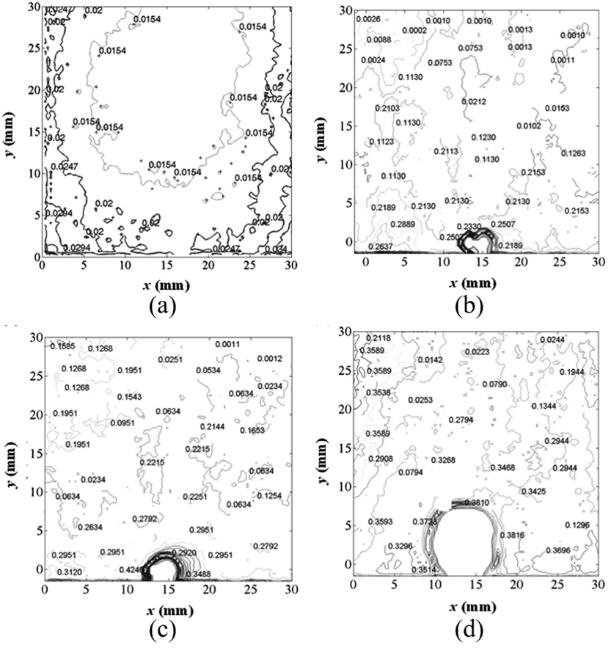
图4 基于速度梯度计算的能量耗散率云图(Reg=10800)[37]注:(a) 单相流;(b)单相流和1 mm固定颗粒;(c)单相流和3 mm固定颗粒;(d)单相流和8 mm固定颗粒
Fig.4 Specific energy dissipation rate contours computed using velocity gradient method for Reg=10,800[37] (a) fluid (b) fluid and 1 mm particle (c) fluid and 3 mm particle and (d) fluid and 8 mm particle
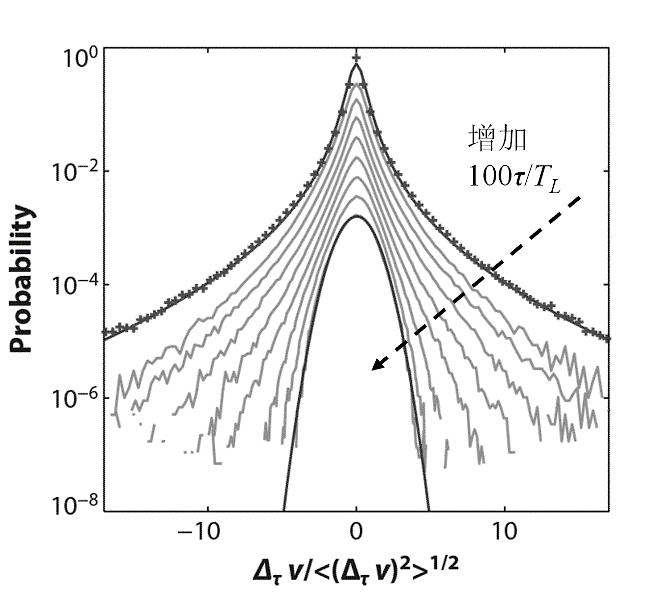
图6 不同时间间隔的示踪粒子速度增量的概率密度分布[47]注:(时间间隔分别为100τ/TL =1.3;2.7;5.4;11.2;22.4;44;89.3;174)
Fig.6 Probability distribution function of velocity increment calculated for time lags[47](for time lags 100τ/TL =1.3;2.7;5.4;11.2;22.4;44;89.3;174)
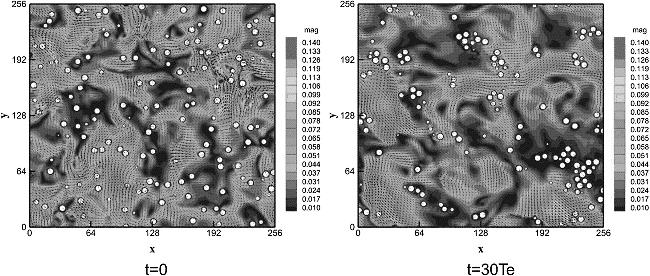
图7 速度幅值云图和颗粒分布图[30](t=0起始时刻颗粒均匀分布;t=30Te当计算时间为30个涡流周期时计算停止)
Fig.7 Contours of fluid velocity magnitude and particle position[30](at the start of simulation with particle evenly inserted and at the end of simulation when t equals 30 times eddy turnover time)
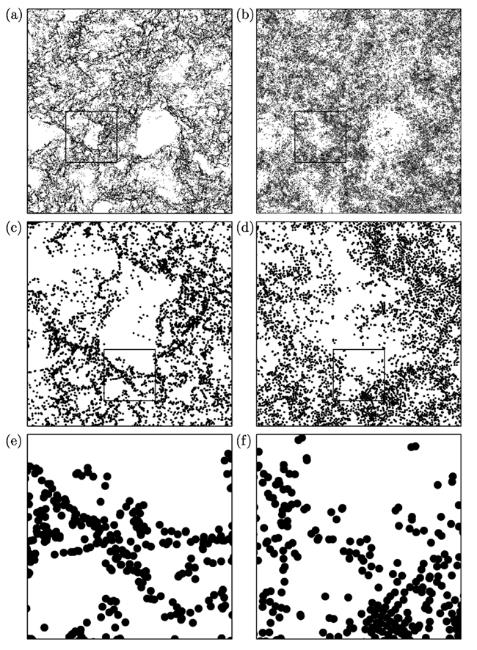
图8 惯性颗粒(a、c、e)和零加速点(b、d、f)的空间分布[55](a和b中绘图区域的边长约为7倍的积分长度,相当于200倍的Kolmogorov尺度;c和d中绘图区域是a和b中框选区域的4倍;e和f中绘图区域是c和d中中框选区域的4倍)
Fig.8 Spatial distribution of inertial particles (a, c, and e) and zero-acceleration points (b, d, and f)[55]((a and b) The side length of plots is about 7 integral scales corresponding to 200 Kolmogorov scale. (c and d) The four-times magnification of squared region in (a and b). (e and f) The four-times magnification of squared region in (c and d))
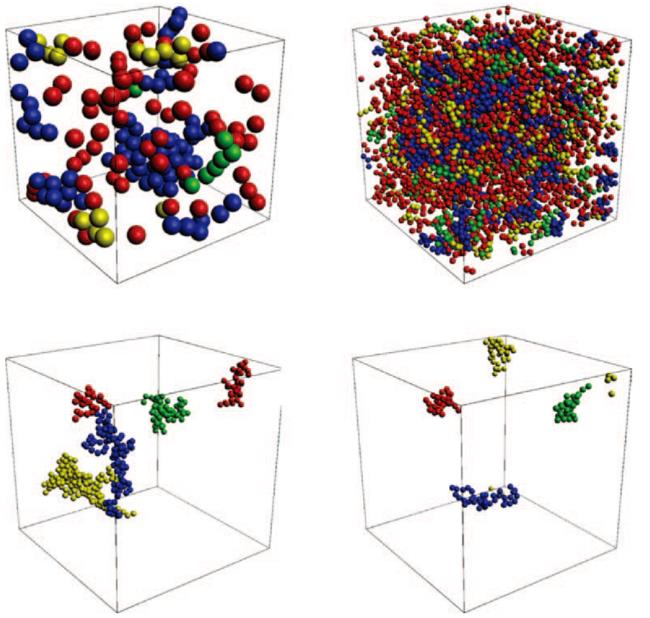
图9 一个立方体区域内的颗粒团聚物的单独展示[56](颗粒颜色由其所属的团聚物尺寸决定:红色:nagg<4;黄色:4≤nagg<7;绿色:7≤nagg<10;蓝色:nagg≥10)
Fig.9 Single realizations of aggregates in cubic domains[56](primary spheres colored by the size of the aggregate they are part of (red: nagg<4; yellow: 4≤nagg <7; green: 7≤nagg<10; blue: nagg≥10))
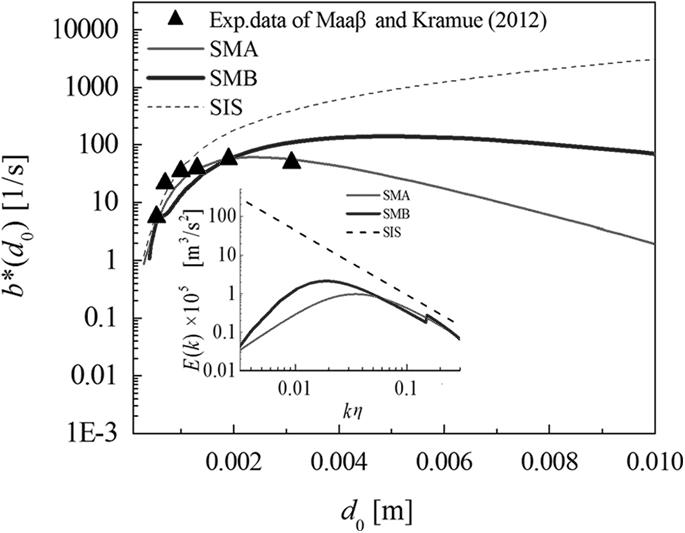
图12 基于不同能谱结构的气泡破碎频率[79]注:(SMA:谱模型A (Pope model[80]); SMB: 谱模型 B (Hinze model[81]); SIS: 惯性子区谱模型)
Fig.12 Breakage frequencies predicted by different energyspectrum models[79](SMA: Spectrum model A (Pope model[80]); SMB: Spectrum model B (Hinze model[81]); SIS: Spectrum of inertia subrange)
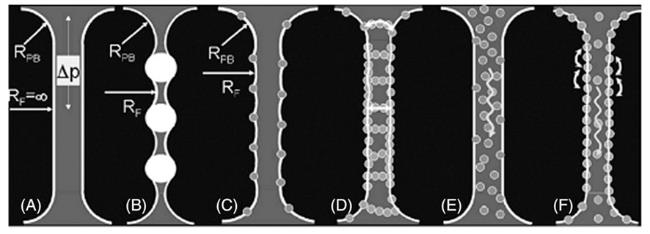
图13 不同的颗粒与气泡界面作用方式[91](A:干净的气液界面;B:连接颗粒发挥稳定气液界面作用;C:轻吸附颗粒通过改变界面曲率影响毛细管力; D:连接的悬浮颗粒群传递‘离散’力; E: 非吸附颗粒改变液膜黏度; F:强吸附颗粒形成阻力边界层)
Fig.13 various interaction mechanisms of particles and bubbles at the bubble interface[91] (A: clean bubble interfilm; B: stabilisation from bridging particles; C: weakly adsorbing particles reducing capillary flow through meniscus alterations in curvature; D: bridging flocs transmitting mechanical ‘disjoining’ force; E: non-adsorbing particles altering viscosity; F: strongly adsorbing particles creating steric barrier)
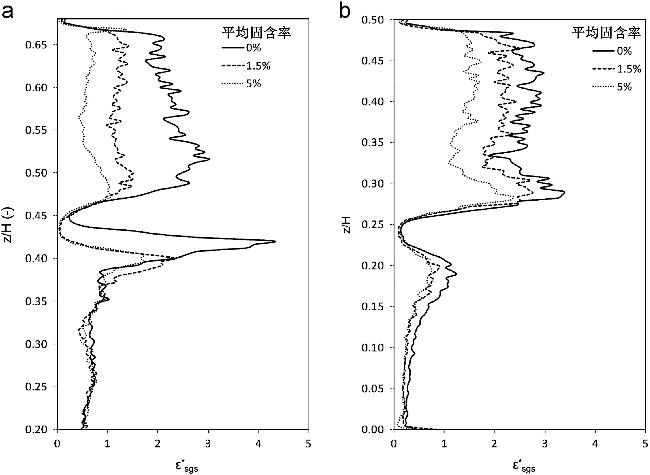
图16 εsgs*的轴向分布[34]:(a)搅拌桨向上的布局中r/R=0.55径向位置处;(b)搅拌桨向下的布局中r/R=0.65径向位置处
Fig.16 Vertical distribution of εsgs* for: (a) the impeller operated in (U) configuration at a radial position of r/R=0.55; (b) the (D) the impeller operated in configuration at a radial position of r/R=0.65[34]
| [1] | Vazirizadeh A, Bouchard J, Chen Y. Effect of particles on bubble size distribution and gas hold-up in column flotation[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2016, 157: 163-173. |
| [2] | Li X M, Yang N. Modeling the light distribution in airlift photobioreactors under simultaneous external and internal illumination using the two-flux model[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 88: 16-22. |
| [3] | 孙启文. 煤炭间接液化[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2012. |
| Sun Q W. Indirect liquefaction of coal[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2012. | |
| [4] | Paul T, Sinharoy A, Pakshirajan K, et al. Lipid-rich bacterial biomass production using refinery wastewater in a bubble column bioreactor for bio-oil conversion by hydrothermal liquefaction[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2020, 37: 101462. |
| [5] | Saxena S C. Bubble column reactors and Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Catalysis Reviews, 1995, 37(2): 227-309. |
| [6] | Aguirre A, Neria d'Angelo M F. The role of vapor-liquid equilibria during the Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: A modeling study[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 233: 116394. |
| [7] | Liu H, Liu B, Lin L C, et al. A hybrid absorption–adsorption method to efficiently capture carbon[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 5147. |
| [8] | Liu Q, Liang X F, Luo X J, et al. A PBM-CFD model with optimized PBM-customized drag equations for chemisorption of CO2 in a bubble column[J]. International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering, 2018, 16(5): 20170174. |
| [9] | Zhang H H, Guo Z S, Wang Y L, et al. Effect of particles on hydrodynamics and mass transfer in a slurry bubble column: Correlation of experimental data[J]. AIChE Journal, 2023, 69(3): e17843. |
| [10] | Tyagi P, Buwa V V. Dense gas–liquid–solid flow in a slurry bubble column: Measurements of dynamic characteristics, gas volume fraction and bubble size distribution[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 173: 346-362. |
| [11] | Feng W, Wen J P, Fan J H, et al. Local hydrodynamics of gas–liquid-nanoparticles three-phase fluidization[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2005, 60(24): 6887-6898. |
| [12] | Yang H, Chen A Q, Geng S J, et al. Influences of fluid physical properties, solid particles, and operating conditions on the hydrodynamics in slurry reactors[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022, 44: 51-71. |
| [13] | Yang G Q, Du B, Fan L S. Bubble formation and dynamics in gas–liquid–solid fluidization: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(1-2): 2-27. |
| [14] | Wang T F, Wang J F, Jin Y. Slurry reactors for gas-to-liquid processes: a review[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2007, 46(18): 5824-5847. |
| [15] | An M, Gao J Q, Wang T K, et al. Particle effects on the hydrodynamics in slurry bubble column reactors: A review from multiscale mechanisms[J]. Particuology, 2024, 91: 176-189. |
| [16] | Yang N. Mesoscale transport phenomena and mechanisms in gas–liquid reaction systems[M]//Mesoscale Modeling in Chemical Engineering Part I. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2015: 245-280. |
| [17] | Tanaka T, Eaton J K. Sub-Kolmogorov resolution partical image velocimetry measurements of particle-laden forced turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2010, 643: 177-206. |
| [18] | Liao Y X, Lucas D. A literature review of theoretical models for drop and bubble breakup in turbulent dispersions[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(15): 3389-3406. |
| [19] | Liao Y X, Lucas D. A literature review on mechanisms and models for the coalescence process of fluid particles[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2010, 65(10): 2851-2864. |
| [20] | Guan X P, Yang N, Li Z Q, et al. Experimental investigation of flow development in large-scale bubble columns in the churn-turbulent regime[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(11): 3125-3130. |
| [21] | Shen X K, Zhang H H, Jia Z Y, et al. Numerical simulations of particle concentration and size effects in a slurry bubble column with a CFD-PBM coupled model[J]. AIChE Journal, 2024, 70(11): e18518. |
| [22] | 王则力. 多相流全尺度直接数值模拟方法及应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2010. |
| Wang Z L. Fully resolved direct numerical simulation technique and its application in multiphase flows[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2010. | |
| [23] | Wood A M, Hwang W, Eaton J K. Preferential concentration of particles in homogeneous and isotropic turbulence[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2005, 31(10/11): 1220-1230. |
| [24] | Risso F. Agitation, mixing, and transfers induced by bubbles[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2018, 50: 25-48. |
| [25] | Horozov T S. Foams and foam films stabilised by solid particles[J]. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2008, 13(3): 134-140. |
| [26] | Brandt L, Coletti F. Particle-laden turbulence: progress and perspectives[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2022, 54: 159-189. |
| [27] | Squires K D, Eaton J K. Effect of selective modification of turbulence on two-equation models for particle-laden turbulent flows[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 1994, 116(4): 778-784. |
| [28] | Solsvik J, Jakobsen H A. A review of the statistical turbulence theory required extending the population balance closure models to the entire spectrum of turbulence[J]. AIChE Journal, 2016, 62(5): 1795-1820. |
| [29] | 柳朝晖, 贺铸, 李瑞霞, 等. 各向同性湍流中颗粒引起湍流变动的直接模拟[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2006, 27(S1): 221-224. |
| Liu Z H, He Z, Li R X, et al. Direct numerical simulation of turbulence modulation by small particles in isotropic turbulence[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2006, 27(S1): 221-224. | |
| [30] | Wang G C, Wan D D, Peng C, et al. LBM study of aggregation of monosized spherical particles in homogeneous isotropic turbulence[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 201: 201-211. |
| [31] | Zhang H H, Li W J, Sun P J, et al. Particle-resolved direct numerical simulation of particle-laden turbulent channel flow[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2025, 37(4): 043336. |
| [32] | 中国科学院. 中国学科发展战略-流体动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014. |
| Chinese Academy of Sciences. The development strategy of Chinese disciplines, fluid dynamics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014. | |
| [33] | Luo K, Luo M B, Fan J R. On turbulence modulation by finite-size particles in dilute gas-solid internal flows[J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 301: 1259-1263. |
| [34] | Gabriele A, Tsoligkas A N, Kings I N, et al. Use of PIV to measure turbulence modulation in a high throughput stirred vessel with the addition of high Stokes number particles for both up- and down-pumping configurations[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(23): 5862-5874. |
| [35] | Graham D I. Turbulence attenuation by small particles in simple shear flows[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2000, 122(1): 134-137. |
| [36] | Eaton J K. Two-way coupled turbulence simulations of gas-particle flows using point-particle tracking[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2009, 35(9): 792-800. |
| [37] | Hoque M M, Mitra S, Sathe M J, et al. Experimental investigation on modulation of homogeneous and isotropic turbulence in the presence of single particle using time-resolved PIV[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 153: 308-329. |
| [38] | Balachandar S, Eaton J K. Turbulent dispersed multiphase flow[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2010, 42: 111-133. |
| [39] | Gore R A, Crowe C T. Effect of particle size on modulating turbulent intensity[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1989, 15(2): 279-285. |
| [40] | Tanaka T, Eaton J K. Classification of turbulence modification by dispersed spheres using a novel dimensionless number[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 101(11): 114502. |
| [41] | Saito I, Watanabe T, Gotoh T. A new time scale for turbulence modulation by particles[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 880: R6. |
| [42] | Rao A, Curtis J S, Hancock B C, et al. Numerical simulation of dilute turbulent gas-particle flow with turbulence modulation[J]. AIChE Journal, 2012, 58(5): 1381-1396. |
| [43] | Squires K D, Eaton J K. Particle response and turbulence modification in isotropic turbulence[J]. Physics of Fluids A: Fluid Dynamics, 1990, 2(7): 1191-1203. |
| [44] | Squires K D, Eaton J K. Measurements of particle dispersion obtained from direct numerical simulations of isotropic turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1991, 226: 1-35. |
| [45] | Squires K D, Eaton J K. Preferential concentration of particles by turbulence[J]. Physics of Fluids A: Fluid Dynamics, 1991, 3(5): 1169-1178. |
| [46] | Porta A L, Voth G A, Crawford A M, et al. Fluid particle accelerations in fully developed turbulence[J]. Nature, 2001, 409(6823): 1017-1019. |
| [47] | Toschi F, Bodenschatz E. Lagrangian properties of particles in turbulence[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2009, 41: 375-404. |
| [48] | Frisch U. Turbulence: The legacy of A. N. Kolmogorov[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1996. |
| [49] | Xu H T, Ouellette N T, Bodenschatz E. Evolution of geometric structures in intense turbulence[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2008, 10(1): 013012. |
| [50] | Yang T S, Shy S S. Two-way interaction between solid particles and homogeneous air turbulence: particle settling rate and turbulence modification measurements[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2005, 526: 171-216. |
| [51] | Eaton J K, Fessler J R. Preferential concentration of particles by turbulence[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1994, 20: 169-209. |
| [52] | Bec J, Biferale L, Boffetta G, et al. Acceleration statistics of heavy particles in turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2006, 550: 349-358. |
| [53] | Goto S, Vassilicos J C. Sweep-stick mechanism of heavy particle clustering in fluid turbulence[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100(5): 054503. |
| [54] | Coleman S W, Vassilicos J C. A unified sweep-stick mechanism to explain particle clustering in two- and three-dimensional homogeneous, isotropic turbulence[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2009, 21(11): 113301. |
| [55] | Goto S, Vassilicos J C. Self-similar clustering of inertial particles and zero-acceleration points in fully developed two-dimensional turbulence[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2006, 18(11): 115103. |
| [56] | Derksen J J. Direct numerical simulations of aggregation of monosized spherical particles in homogeneous isotropic turbulence[J]. AIChE Journal, 2012, 58(8): 2589-2600. |
| [57] | Liu J H, Liu M Y, Hu Z D. Fractal structure in gas–liquid–solid circulating fluidized beds with low solid holdups of macroporous resin particles[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(33): 11404-11413. |
| [58] | Monchaux R, Bourgoin M, Cartellier A. Analyzing preferential concentration and clustering of inertial particles in turbulence[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2012, 40: 1-18. |
| [59] | Innocenti A, Jaccod A, Popinet S, et al. Direct numerical simulation of bubble-induced turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2021, 918: A23. |
| [60] | Roghair I, Mercado J M, Van Sint Annaland M, et al. Energy spectra and bubble velocity distributions in pseudo-turbulence: Numerical simulations vs. experiments[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2011, 37(9): 1093-1098. |
| [61] | Prakash V N, Mercado J M, van Wijngaarden L, et al. Energy spectra in turbulent bubbly flows[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2016, 791: 174-190. |
| [62] | Feng J Y, Bolotnov I A. Evaluation of bubble-induced turbulence using direct numerical simulation[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2017, 93: 92-107. |
| [63] | Rzehak R, Krepper E. CFD modeling of bubble-induced turbulence[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2013, 55: 138-155. |
| [64] | Hosokawa S, Tomiyama A. Turbulence modification in gas–liquid and solid–liquid dispersed two-phase pipe flows[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2004, 25(3): 489-498. |
| [65] | Sato Y, Sekoguchi K. Liquid velocity distribution in two-phase bubble flow[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1975, 2(1): 79-95. |
| [66] | Troshko A A, Hassan Y A. A two-equation turbulence model of turbulent bubbly flows[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2001, 27(11): 1965-2000. |
| [67] | Shu S L, El Bahraoui N, Bertrand F, et al. A bubble-induced turbulence model for gas-liquid bubbly flows in airlift columns, pipes and bubble columns[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 227: 115945. |
| [68] | Shi W B, Yang X G, Sommerfeld M, et al. Modelling of mass transfer for gas-liquid two-phase flow in bubble column reactor with a bubble breakage model considering bubble-induced turbulence[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 371: 470-485. |
| [69] | Pfleger D, Becker S. Modelling and simulation of the dynamic flow behaviour in a bubble column[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2001, 56(4): 1737-1747. |
| [70] | Liao Y X, Ma T, Krepper E, et al. Application of a novel model for bubble-induced turbulence to bubbly flows in containers and vertical pipes[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 202: 55-69. |
| [71] | Jiao Y P, Wang L M, Chen J H. A mesoscale bubble-induced turbulence model and simulation of gas–liquid flows[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2023, 35: 013314. |
| [72] | Ma T, Santarelli C, Ziegenhein T, et al. Direct numerical simulation–based Reynolds-averaged closure for bubble-induced turbulence[J]. Physical Review Fluids, 2017, 2(3): 034301. |
| [73] | Luo H A. Coalescence, breakup and liquid circulation in bubble column reactors [D]. Trondheim:The University of Trondheim, 1993. |
| [74] | Prince M J, Blanch H W. Bubble coalescence and break-up in air-sparged bubble columns[J]. AIChE Journal, 1990, 36(10): 1485-1499. |
| [75] | Wang T F, Wang J F, Jin Y. Population balance model for Gas-Liquid flows: influence of bubble coalescence and breakup models[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2005, 44(19): 7540-7549. |
| [76] | 王铁峰. 气液(浆)反应器流体力学行为的实验研究和数值模拟[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2004. |
| Wang T F. Experimental study and numerical simulation on the hydrodynamics in gas-liquid (slurry) reactors[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2004. | |
| [77] | Chen P, Sanyal J, Duduković M P. Numerical simulation of bubble columns flows: effect of different breakup and coalescence closures[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2005, 60(4): 1085-1101. |
| [78] | Gong S G, Han L C, Luo H A. A novel multiscale theoretical model for droplet coalescence induced by turbulence in the framework of entire energy spectrum[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 176: 377-399. |
| [79] | Han L C, Gong S G, Li Y Q, et al. Influence of energy spectrum distribution on drop breakage in turbulent flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 117: 55-70. |
| [80] | Pope S B. Turbulent Flows[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2000. |
| [81] | Hinze J O. Turbulence[M]. New York; Tokyo: McGraw-Hill, 1975 |
| [82] | Solsvik J. Turbulence modeling in the wide energy spectrum: Explicit formulas for Reynolds number dependent energy spectrum parameters[J]. European Journal of Mechanics - B/Fluids, 2017, 61: 170-176. |
| [83] | Solsvik J, Jakobsen H A. Development of fluid particle breakup and coalescence closure models for the complete energy spectrum of isotropic turbulence[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(5): 1449-1460. |
| [84] | 施炜斌, 龙姗姗, 杨晓钢, 等. 计及气泡诱导与剪切湍流的气泡破碎、湍流相间扩散及传质模型[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2573-2588. |
| Shi W B, Long S S, Yang X G, et al. Bubble breakage, turbulence dispersion and mass transfer model considering the joint effects of bubble-induced turbulence and shear turbulence[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2573-2588. | |
| [85] | Yang N, Chen J H, Zhao H, et al. Explorations on the multi-scale flow structure and stability condition in bubble columns[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(24): 6978-6991. |
| [86] | Yang N, Chen J H, Ge W, et al. A conceptual model for analyzing the stability condition and regime transition in bubble columns[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2010, 65(1): 517-526. |
| [87] | 李静海. 颗粒流体两相流多尺度方法和能量最小模型[D]. 北京: 中国科学院化工冶金研究所, 1987. |
| Li J H. Multi-scale modeling and method of energy minimizationfor particle-fluid two-phase flow[D]. Beijing: Institute of Chemical Metallurgy, Academia Sinica, 1987. | |
| [88] | 赵辉. 气液(浆)反应器的多尺度模拟[D]. 北京: 中国科学院过程工程研究所, 2006. |
| Zhao H. Multi-scale simulation of gas-liquid (slurry) reactor[D]. Beijing: Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2006. | |
| [89] | Chen Y M, Fan L S. Bubble breakage mechanisms due to collision with a particle in liquid medium[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1989, 44(1): 117-132. |
| [90] | 毛成. 浮选柱内矿物浮选过程相间传输行为的数值模拟研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2014. |
| Mao C. Numerical simulation research of interphase transport behavior in froth flotation column[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2014. | |
| [91] | Hunter T N, Pugh R J, Franks G V, et al. The role of particles in stabilising foams and emulsions[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2008, 137(2): 57-81. |
| [92] | Mena P C, Ruzicka M C, Rocha F A, et al. Effect of solids on homogeneous–heterogeneous flow regime transition in bubble columns[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2005, 60(22): 6013-6026. |
| [93] | Rabha S, Schubert M, Hampel U. Hydrodynamic studies in slurry bubble columns: experimental and numerical study[J]. Chemie Ingenieur Technik, 2013, 85(7): 1092-1098. |
| [94] | Hooshyar N, van Ommen J R, Hamersma P J, et al. Dynamics of single rising bubbles in neutrally buoyant liquid-solid suspensions[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 110(24): 244501. |
| [95] | Tsuchiya K, Furumoto A, Fan L S, et al. Suspension viscosity and bubble rise velocity in liquid-solid fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1997, 52(18): 3053-3066. |
| [96] | Lakhdissi E M, Soleimani I, Guy C, et al. Simultaneous effect of particle size and solid concentration on the hydrodynamics of slurry bubble column reactors[J]. AIChE Journal, 2020, 66(2): e16813. |
| [97] | Prakash R, Majumder S K, Singh A. Particle-laden bubble size and its distribution in microstructured bubbling bed in the presence and absence of a surface active agent[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(8): 3499-3522. |
| [98] | Ojima S, Hayashi K, Tomiyama A. Effects of hydrophilic particles on bubbly flow in slurry bubble column[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2014, 58: 154-167. |
| [99] | Ojima S, Sasaki S, Hayashi K, et al. Effects of particle diameter on bubble coalescence in a slurry bubble column[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 2015, 48(3): 181-189. |
| [100] | Sethumadhavan G, Bindal S, Nikolov A, et al. Stability of thin liquid films containing polydisperse particles[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2002, 204(1-3): 51-62. |
| [101] | An M, Guan X P, Yang N. Modeling the effects of solid particles in CFD-PBM simulation of slurry bubble columns[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 223: 115743. |
| [102] | Gandhi B, Prakash A, Bergougnou M A. Hydrodynamic behavior of slurry bubble column at high solids concentrations[J]. Powder Technology, 1999, 103(2): 80-94. |
| [103] | Bhatia V K, Epstein N. Three phase fluidization: a generalized wake model[M]. Toulouse: Angelino H, 1974. |
| [104] | Fan L S, Tsuchiya K. Bubble Wake Dynamics in Liquids and Liquid–Solid Suspensions[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1990 |
| [105] | Zhang W, Chen X L, Pan W T, et al. Numerical simulation of wake structure and particle entrainment behavior during a single bubble ascent in liquid-solid system[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 253: 117573. |
| [106] | Banisi S, Finch J A, Laplante A R, et al. Effect of solid particles on gas holdup in flotation columns: II. investigation of mechanisms of gas holdup reduction in presence of solids[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1995, 50(14): 2335-2342. |
| [1] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [2] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| [3] | 贾志勇, 沈宪琨, 蓝晓程, 王铁峰. 气体密度对高压流态化影响的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4383-4397. |
| [4] | 邹家庆, 张肇钰, 张建国, 张博宇, 刘定胜, 毛庆, 王挺, 李建军. 碱水制氢电解槽极板通道中气泡的生成及演化性质[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4786-4799. |
| [5] | 张帅, 徐嘉宇, 华蕾娜, 葛蔚. 气固系统的CG-DPM与MP-PIC耦合模拟方法[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4412-4424. |
| [6] | 梁晓江, 陈薇薇, 罗佳南, 费浩天, 叶雪蕾, 李文豪, 聂勇. 电分散管式填充床中荷电气泡的分散特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3915-3931. |
| [7] | 王泽, 胡琼, 陈雅静, 王衍, 耿佳旭, 沈斐然. 液体自冲击密封泄漏特性、密封机理与优化设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4194-4204. |
| [8] | 常心泉, 张克学, 王军, 夏国栋. 自由分子区内不规则颗粒的热泳力计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3944-3953. |
| [9] | 朱紫橙, 焦云鹏, 刘梦溪, 陈建华. 三相流化床内分布器与挡板效应的模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3873-3884. |
| [10] | 张伟, 武齐永, 孙华中, 胡适, 朱小龙, 孔帅. 微米尺度液滴与尘粒作用后反弹行为特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3990-4003. |
| [11] | 胡晓红, 徐璇, 陈厚涛, 凡凤仙, 苏明旭. 烟气中细颗粒声凝并的随机模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3964-3975. |
| [12] | 王树宇, 薛志亮, 朱静, 付鑫, 周永刚, 胡一鸣, 黄群星. 废弃全钢胎颗粒热解过程中质量和形态变化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3459-3467. |
| [13] | 郭铮铮, 赵一丹, 王辅强, 裴璐, 靳彦岭, 任芳, 任鹏刚. 异质结构MoS2/RGO/NiFe2O4复合材料的构筑及电磁波吸收性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3719-3732. |
| [14] | 徐鹏国, 孟子衡, 朱干宇, 李会泉, 王晨晔, 孙振华, 田国才. 粗碳酸锂CO2微气泡深度碳化工艺与动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3325-3338. |
| [15] | 陈曦, 王淑彦, 邵宝力, 丁诺, 谢磊. 基于颗粒动态恢复系数二阶矩模型的液固流化床数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3246-3258. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号