• •
收稿日期:2025-11-13
修回日期:2026-01-07
出版日期:2026-01-08
通讯作者:
段远源
作者简介:卿康(2001—),男,博士研究生,qk23@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn
基金资助:
Kang QING1( ), Erqi WANG1, Zhen YANG1, Yuanyuan DUAN1,2(
), Erqi WANG1, Zhen YANG1, Yuanyuan DUAN1,2( )
)
Received:2025-11-13
Revised:2026-01-07
Online:2026-01-08
Contact:
Yuanyuan DUAN
摘要:
饱和密度是流体物质在气液相平衡时的重要热物性参数,在热力循环及化工过程中被广泛应用,但实验数据往往有限且离散,因此建立能够准确关联数据并能够可靠外推的饱和密度方程具有重要意义。基于饱和密度与饱和蒸气压的热力学特征相似性,此前提出的饱和蒸气压方程可推广至饱和密度,并以32种物质为对象与Zhang方程和Wagner型方程比较分析后证明,在关联性能上,新方程与Zhang方程和Wagner型方程偏差量级相当,足以在测量不确定度范围内关联实验数据;而在外推性能上,新方程总体优于Zhang方程和Wagner型方程,外推趋势更为稳定准确。如在外推拟合中将新方程部分参数固定后,外推趋势稳定性及准确性可进一步提升。
中图分类号:
卿康, 汪尔奇, 杨震, 段远源. 饱和气液相密度关联外推的新通用对比态方程[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251266.
Kang QING, Erqi WANG, Zhen YANG, Yuanyuan DUAN. New universal corresponding state equation for correlation and extrapolation of saturated vapor-liquid density[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251266.
| 物质 | Tc / K | ρc / kg/m3 | ρr′ | ρr′′ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Tr范围 | 1/ρr′范围 | uave(ρr′) | N | Tr范围 | ρr′′范围 | uave(ρr′′) | |||
| 氖(Neon) | 44.4 | 486.31 | 36 | 0.555~1.0 | 0.39~0.984 | 0.062 | 51 | 0.567~1.0 | 0.011~0.884 | 0.015 |
| 氩(Argon) | 150.687 | 535.60 | 234 | 0.557~1.0 | 0.377~0.999 | 0.108 | 100 | 0.557~1.0 | 0.008~0.99 | 0.056 |
| 氪(Krypton) | 209.48 | 909.21 | 75 | 0.553~1.0 | 0.371~0.947 | 0.016 | 17 | 0.601~0.999 | 0.015~0.888 | 0.001 |
| 氙(Xenon) | 289.733 | 1102.86 | 94 | 0.557~1.0 | 0.37~0.998 | 0.005 | 43 | 0.712~1.0 | 0.053~0.99 | 0.048 |
| 甲烷(Methane) | 190.564 | 162.66 | 348 | 0.466~1.0 | 0.358~0.939 | 0.006 | 102 | 0.478~1.0 | 0.002~0.955 | 0.001 |
| 氧气(Oxygen) | 154.581 | 436.14 | 317 | 0.352~1.0 | 0.333~0.945 | 0.059 | 194 | 0.352~1.0 | 0.0~0.945 | 0.015 |
| 氮气(Nitrogen) | 126.192 | 313.30 | 270 | 0.496~1.0 | 0.359~0.898 | 0.019 | 56 | 0.513~1.0 | 0.003~0.888 | 0.001 |
| 一氧化碳(Carbon monoxide) | 132.86 | 303.91 | 57 | 0.513~0.995 | 0.359~0.72 | 0.003 | 56 | 0.513~0.998 | 0.003~0.837 | 0.001 |
| 乙烯(Ethene) | 282.35 | 214.24 | 221 | 0.368~1.0 | 0.327~0.916 | 0.010 | 81 | 0.561~1.0 | 0.005~0.928 | 0.003 |
| 乙烯(Ethylene) | 282.35 | 214.24 | 221 | 0.368~1.0 | 0.327~0.916 | 0.010 | 81 | 0.561~1.0 | 0.005~0.928 | 0.003 |
| 乙烷(Ethane) | 305.322 | 206.18 | 437 | 0.291~1.0 | 0.316~0.993 | 0.058 | 126 | 0.605~1.0 | 0.01~0.965 | 0.007 |
| 丙烯(Propylene) | 364.211 | 229.63 | 135 | 0.256~1.0 | 0.302~0.849 | 0.038 | 50 | 0.632~1.0 | 0.012~0.839 | 0.001 |
| 丙烷(Propane) | 369.89 | 220.48 | 385 | 0.234~1.0 | 0.301~0.984 | 0.010 | 99 | 0.622~1.0 | 0.01~0.9 | 0.003 |
| 异丁烷(Isobutane) | 407.81 | 225.50 | 262 | 0.282~1.0 | 0.305~0.983 | 0.012 | 53 | 0.638~1.0 | 0.012~1.0 | 0.011 |
| 新戊烷(Neopentane) | 433.74 | 235.93 | 94 | 0.592~0.999 | 0.374~0.851 | 0.037 | 44 | 0.791~0.999 | 0.074~0.795 | 0.001 |
| 正丁烷(n-Butane) | 425.125 | 228.00 | 359 | 0.209~1.0 | 0.293~0.887 | 0.005 | 125 | 0.317~1.0 | 0.0~0.874 | 0.001 |
| 苯(Benzene) | 562.02 | 304.71 | 548 | 0.486~0.999 | 0.338~0.911 | 0.042 | 140 | 0.513~0.999 | 0.001~0.88 | 0.007 |
| 六氟化硫(Sulfur hexafluoride) | 318.7232 | 742.30 | 64 | 0.703~1.0 | 0.403~0.988 | 0.003 | 56 | 0.703~1.0 | 0.027~1.0 | 0.001 |
| 二氧化碳(Carbon dioxide) | 304.1282 | 467.60 | 170 | 0.714~1.0 | 0.397~0.93 | 0.025 | 133 | 0.714~1.0 | 0.03~0.915 | 0.011 |
2,3-二甲基丁烷 (2,3-Dimethylbutane) | 500.6 | 241.29 | 69 | 0.546~0.999 | 0.355~0.813 | 0.009 | 55 | 0.645~0.999 | 0.011~0.767 | 0.003 |
| 正戊烷(n-Pentane) | 469.7 | 231.60 | 250 | 0.317~1.0 | 0.306~0.923 | 0.020 | 79 | 0.645~1.0 | 0.011~0.925 | 0.008 |
| 二氧化硫(Sulfur dioxide) | 430.64 | 517.51 | 66 | 0.518~1.0 | 0.332~0.872 | 0.006 | 38 | 0.651~0.999 | 0.012~0.884 | 0.000 |
| 三氟甲烷(Trifluoromethane) | 299 | 522.40 | 194 | 0.417~1.0 | 0.311~0.994 | 0.006 | 50 | 0.793~1.0 | 0.066~0.909 | 0.001 |
| 甲苯(Toluene) | 591.75 | 291.99 | 278 | 0.313~0.994 | 0.305~0.706 | 0.029 | 39 | 0.504~1.0 | 0.0~0.92 | 0.002 |
1,1-二氟乙烷 (1,1-Difluoroethane) | 386.43 | 368.33 | 129 | 0.406~1.0 | 0.31~0.985 | 0.015 | 70 | 0.705~1.0 | 0.017~0.982 | 0.005 |
| 二氟甲烷(Difluoromethane) | 351.25 | 424.80 | 184 | 0.395~1.0 | 0.299~0.911 | 0.012 | 69 | 0.72~1.0 | 0.027~0.877 | 0.009 |
| 正己烷(n-Hexane) | 507.82 | 233.19 | 97 | 0.361~0.999 | 0.31~0.809 | 0.013 | 21 | 0.656~0.999 | 0.011~0.775 | 0.007 |
| 异辛烷(Isooctane) | 544 | 242.16 | 111 | 0.428~1.0 | 0.327~0.997 | 0.011 | 42 | 0.535~0.997 | 0.001~0.722 | 0.003 |
| 丙酮(Acetone) | 508.1 | 272.97 | 128 | 0.361~0.998 | 0.3~0.834 | 0.049 | 30 | 0.537~0.997 | 0.001~0.741 | 0.010 |
| 正庚烷(n-Heptane) | 540.2 | 233.47 | 195 | 0.342~1.0 | 0.302~0.949 | 0.018 | 52 | 0.635~1.0 | 0.006~0.994 | 0.014 |
| 正辛烷(n-Octane) | 568.74 | 232.00 | 124 | 0.427~1.0 | 0.312~0.999 | 0.011 | 71 | 0.691~1.0 | 0.014~0.97 | 0.003 |
| 甲醇(Methanol) | 513.38 | 281.50 | 258 | 0.4~0.999 | 0.322~0.997 | 0.016 | 45 | 0.581~0.999 | 0.001~0.976 | 0.007 |
表2 所研究物质的临界温度(Tc)、临界密度(ρc)及实验数据信息(数量(N)、对比温度(Tr)范围、对比密度(ρr′或ρr′′)范围及其平均不确定度(uave(ρr′或ρr′′)))
Table 2 The critical temperature (Tc), critical density (ρc) and information on experimental data (number (N), reduced temperature (Tr) range, reduced density (ρr′ or ρr′′) range and average uncertainty of reduced density uave(ρr′ or ρr′′)) of the studied substance
| 物质 | Tc / K | ρc / kg/m3 | ρr′ | ρr′′ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Tr范围 | 1/ρr′范围 | uave(ρr′) | N | Tr范围 | ρr′′范围 | uave(ρr′′) | |||
| 氖(Neon) | 44.4 | 486.31 | 36 | 0.555~1.0 | 0.39~0.984 | 0.062 | 51 | 0.567~1.0 | 0.011~0.884 | 0.015 |
| 氩(Argon) | 150.687 | 535.60 | 234 | 0.557~1.0 | 0.377~0.999 | 0.108 | 100 | 0.557~1.0 | 0.008~0.99 | 0.056 |
| 氪(Krypton) | 209.48 | 909.21 | 75 | 0.553~1.0 | 0.371~0.947 | 0.016 | 17 | 0.601~0.999 | 0.015~0.888 | 0.001 |
| 氙(Xenon) | 289.733 | 1102.86 | 94 | 0.557~1.0 | 0.37~0.998 | 0.005 | 43 | 0.712~1.0 | 0.053~0.99 | 0.048 |
| 甲烷(Methane) | 190.564 | 162.66 | 348 | 0.466~1.0 | 0.358~0.939 | 0.006 | 102 | 0.478~1.0 | 0.002~0.955 | 0.001 |
| 氧气(Oxygen) | 154.581 | 436.14 | 317 | 0.352~1.0 | 0.333~0.945 | 0.059 | 194 | 0.352~1.0 | 0.0~0.945 | 0.015 |
| 氮气(Nitrogen) | 126.192 | 313.30 | 270 | 0.496~1.0 | 0.359~0.898 | 0.019 | 56 | 0.513~1.0 | 0.003~0.888 | 0.001 |
| 一氧化碳(Carbon monoxide) | 132.86 | 303.91 | 57 | 0.513~0.995 | 0.359~0.72 | 0.003 | 56 | 0.513~0.998 | 0.003~0.837 | 0.001 |
| 乙烯(Ethene) | 282.35 | 214.24 | 221 | 0.368~1.0 | 0.327~0.916 | 0.010 | 81 | 0.561~1.0 | 0.005~0.928 | 0.003 |
| 乙烯(Ethylene) | 282.35 | 214.24 | 221 | 0.368~1.0 | 0.327~0.916 | 0.010 | 81 | 0.561~1.0 | 0.005~0.928 | 0.003 |
| 乙烷(Ethane) | 305.322 | 206.18 | 437 | 0.291~1.0 | 0.316~0.993 | 0.058 | 126 | 0.605~1.0 | 0.01~0.965 | 0.007 |
| 丙烯(Propylene) | 364.211 | 229.63 | 135 | 0.256~1.0 | 0.302~0.849 | 0.038 | 50 | 0.632~1.0 | 0.012~0.839 | 0.001 |
| 丙烷(Propane) | 369.89 | 220.48 | 385 | 0.234~1.0 | 0.301~0.984 | 0.010 | 99 | 0.622~1.0 | 0.01~0.9 | 0.003 |
| 异丁烷(Isobutane) | 407.81 | 225.50 | 262 | 0.282~1.0 | 0.305~0.983 | 0.012 | 53 | 0.638~1.0 | 0.012~1.0 | 0.011 |
| 新戊烷(Neopentane) | 433.74 | 235.93 | 94 | 0.592~0.999 | 0.374~0.851 | 0.037 | 44 | 0.791~0.999 | 0.074~0.795 | 0.001 |
| 正丁烷(n-Butane) | 425.125 | 228.00 | 359 | 0.209~1.0 | 0.293~0.887 | 0.005 | 125 | 0.317~1.0 | 0.0~0.874 | 0.001 |
| 苯(Benzene) | 562.02 | 304.71 | 548 | 0.486~0.999 | 0.338~0.911 | 0.042 | 140 | 0.513~0.999 | 0.001~0.88 | 0.007 |
| 六氟化硫(Sulfur hexafluoride) | 318.7232 | 742.30 | 64 | 0.703~1.0 | 0.403~0.988 | 0.003 | 56 | 0.703~1.0 | 0.027~1.0 | 0.001 |
| 二氧化碳(Carbon dioxide) | 304.1282 | 467.60 | 170 | 0.714~1.0 | 0.397~0.93 | 0.025 | 133 | 0.714~1.0 | 0.03~0.915 | 0.011 |
2,3-二甲基丁烷 (2,3-Dimethylbutane) | 500.6 | 241.29 | 69 | 0.546~0.999 | 0.355~0.813 | 0.009 | 55 | 0.645~0.999 | 0.011~0.767 | 0.003 |
| 正戊烷(n-Pentane) | 469.7 | 231.60 | 250 | 0.317~1.0 | 0.306~0.923 | 0.020 | 79 | 0.645~1.0 | 0.011~0.925 | 0.008 |
| 二氧化硫(Sulfur dioxide) | 430.64 | 517.51 | 66 | 0.518~1.0 | 0.332~0.872 | 0.006 | 38 | 0.651~0.999 | 0.012~0.884 | 0.000 |
| 三氟甲烷(Trifluoromethane) | 299 | 522.40 | 194 | 0.417~1.0 | 0.311~0.994 | 0.006 | 50 | 0.793~1.0 | 0.066~0.909 | 0.001 |
| 甲苯(Toluene) | 591.75 | 291.99 | 278 | 0.313~0.994 | 0.305~0.706 | 0.029 | 39 | 0.504~1.0 | 0.0~0.92 | 0.002 |
1,1-二氟乙烷 (1,1-Difluoroethane) | 386.43 | 368.33 | 129 | 0.406~1.0 | 0.31~0.985 | 0.015 | 70 | 0.705~1.0 | 0.017~0.982 | 0.005 |
| 二氟甲烷(Difluoromethane) | 351.25 | 424.80 | 184 | 0.395~1.0 | 0.299~0.911 | 0.012 | 69 | 0.72~1.0 | 0.027~0.877 | 0.009 |
| 正己烷(n-Hexane) | 507.82 | 233.19 | 97 | 0.361~0.999 | 0.31~0.809 | 0.013 | 21 | 0.656~0.999 | 0.011~0.775 | 0.007 |
| 异辛烷(Isooctane) | 544 | 242.16 | 111 | 0.428~1.0 | 0.327~0.997 | 0.011 | 42 | 0.535~0.997 | 0.001~0.722 | 0.003 |
| 丙酮(Acetone) | 508.1 | 272.97 | 128 | 0.361~0.998 | 0.3~0.834 | 0.049 | 30 | 0.537~0.997 | 0.001~0.741 | 0.010 |
| 正庚烷(n-Heptane) | 540.2 | 233.47 | 195 | 0.342~1.0 | 0.302~0.949 | 0.018 | 52 | 0.635~1.0 | 0.006~0.994 | 0.014 |
| 正辛烷(n-Octane) | 568.74 | 232.00 | 124 | 0.427~1.0 | 0.312~0.999 | 0.011 | 71 | 0.691~1.0 | 0.014~0.97 | 0.003 |
| 甲醇(Methanol) | 513.38 | 281.50 | 258 | 0.4~0.999 | 0.322~0.997 | 0.016 | 45 | 0.581~0.999 | 0.001~0.976 | 0.007 |
| 拟合数据范围 | 相态 | 100·OAAD① | 100·OMAD② | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang | Wagner | 式(10)和式(11) | (固定参数)③ | Zhang | Wagner | 式(10)和式(11) | (固定参数)③ | ||
关联 Ttr < Tr ≤ 1 | 饱和液相 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.93 | - | 8.11 | 8.43 | 8.73 | - |
| 饱和气相 | 0.78 | 0.63 | 0.72 | - | 5.63 | 5.08 | 4.99 | - | |
向临界点方向外推 Ttr < Tr ≤ 0.7 | 饱和液相 | 11.71 (30) | 6.24 (31) | 5.34 (31) | 1.34 (32) | 29.94 (27) | 18.18 (31) | 15.48 (31) | 9.15 (32) |
| 饱和气相 | 2.33 (32) | 32.24 (28) | 5.30 (32) | 1.88 (32) | 10.37 (32) | 56.84 (21) | 19.67 (32) | 7.03 (32) | |
向三相点与临界点方向同时外推 0.8 < Tr ≤ 0.9 | 饱和液相 | 3.55 (32) | 41.47 (24) | 5.46 (32) | 1.78 (32) | 15.12 (32) | 70.19 (15) | 27.52 (32) | 9.56 (32) |
| 饱和气相 | 1.69 (32) | 24.29 (26) | 3.51 (32) | 1.08 (32) | 9.33 (32) | 39.00 (26) | 16.43 (32) | 6.83 (32) | |
向三相点方向外推 0.9 < Tr ≤ 1 | 饱和液相 | 12.49 (32) | 87.33 (7) | 29.25 (31) | 5.73 (32) | 33.20 (32) | 95.57 (3) | 62.05 (22) | 15.13 (32) |
| 饱和气相 | 5.02 (32) | 24.15 (26) | 1.67 (32) | 0.89 (32) | 21.38 (31) | 38.63 (22) | 8.15 (31) | 5.25 (32) | |
表3 各方程关联及外推性能比较
Table 3 Comparison of correlation and extrapolation performance of various equations
| 拟合数据范围 | 相态 | 100·OAAD① | 100·OMAD② | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang | Wagner | 式(10)和式(11) | (固定参数)③ | Zhang | Wagner | 式(10)和式(11) | (固定参数)③ | ||
关联 Ttr < Tr ≤ 1 | 饱和液相 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.93 | - | 8.11 | 8.43 | 8.73 | - |
| 饱和气相 | 0.78 | 0.63 | 0.72 | - | 5.63 | 5.08 | 4.99 | - | |
向临界点方向外推 Ttr < Tr ≤ 0.7 | 饱和液相 | 11.71 (30) | 6.24 (31) | 5.34 (31) | 1.34 (32) | 29.94 (27) | 18.18 (31) | 15.48 (31) | 9.15 (32) |
| 饱和气相 | 2.33 (32) | 32.24 (28) | 5.30 (32) | 1.88 (32) | 10.37 (32) | 56.84 (21) | 19.67 (32) | 7.03 (32) | |
向三相点与临界点方向同时外推 0.8 < Tr ≤ 0.9 | 饱和液相 | 3.55 (32) | 41.47 (24) | 5.46 (32) | 1.78 (32) | 15.12 (32) | 70.19 (15) | 27.52 (32) | 9.56 (32) |
| 饱和气相 | 1.69 (32) | 24.29 (26) | 3.51 (32) | 1.08 (32) | 9.33 (32) | 39.00 (26) | 16.43 (32) | 6.83 (32) | |
向三相点方向外推 0.9 < Tr ≤ 1 | 饱和液相 | 12.49 (32) | 87.33 (7) | 29.25 (31) | 5.73 (32) | 33.20 (32) | 95.57 (3) | 62.05 (22) | 15.13 (32) |
| 饱和气相 | 5.02 (32) | 24.15 (26) | 1.67 (32) | 0.89 (32) | 21.38 (31) | 38.63 (22) | 8.15 (31) | 5.25 (32) | |
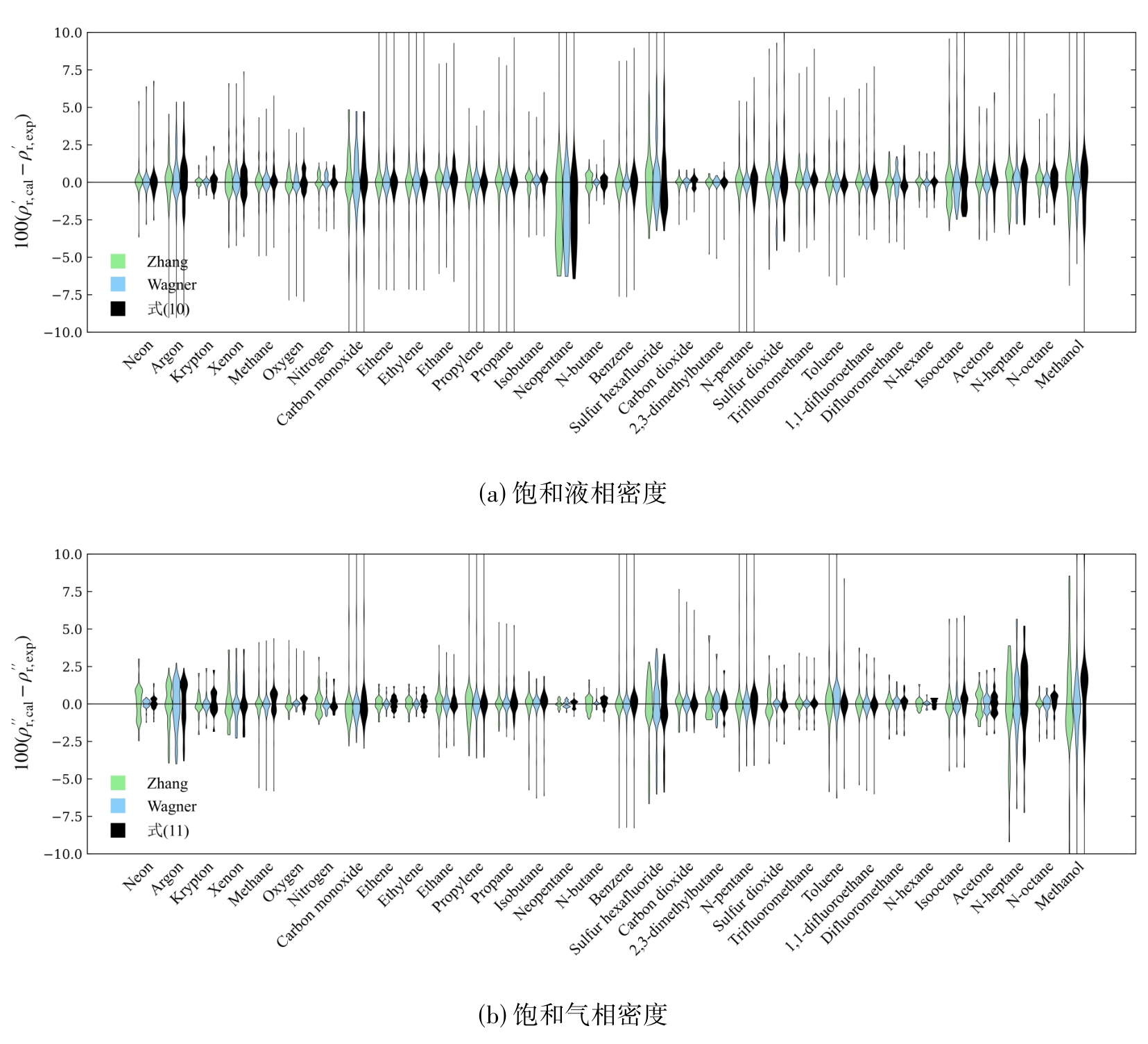
图3 式(10)和(11)、Zhang方程和Wagner型方程对实验数据的关联偏差比较
Fig. 3 Comparison of correlation bias between Eq. (10) and (11), Zhang equation and Wagner equation on experimental data
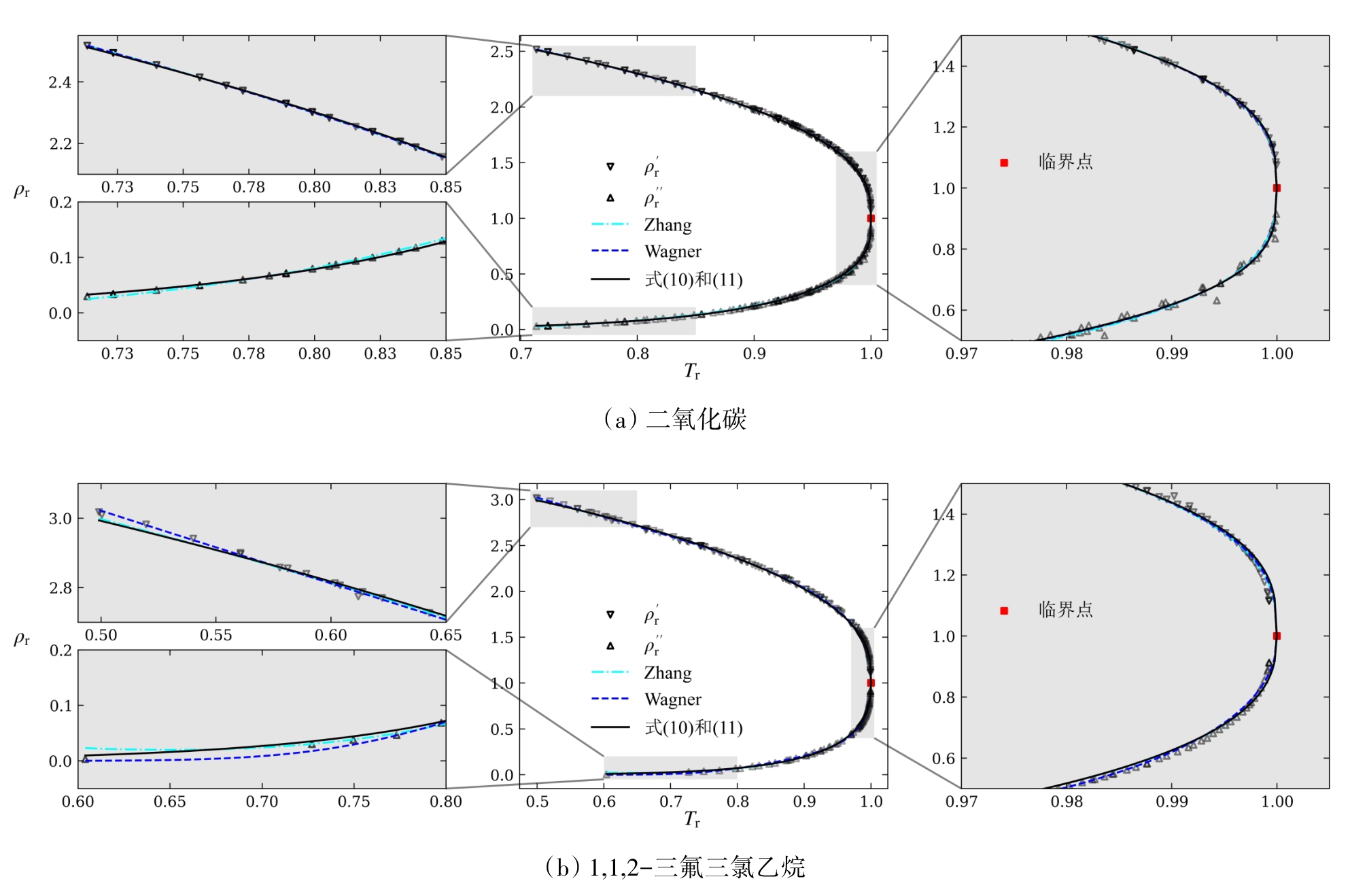
图4 以二氧化碳和1,1,2-三氟三氯乙烷为例的各方程关联效果比较
Fig. 4 Comparison of correlation effect of various equations using carbon dioxide and 1,1,2-trifluorotrichloroethane as examples
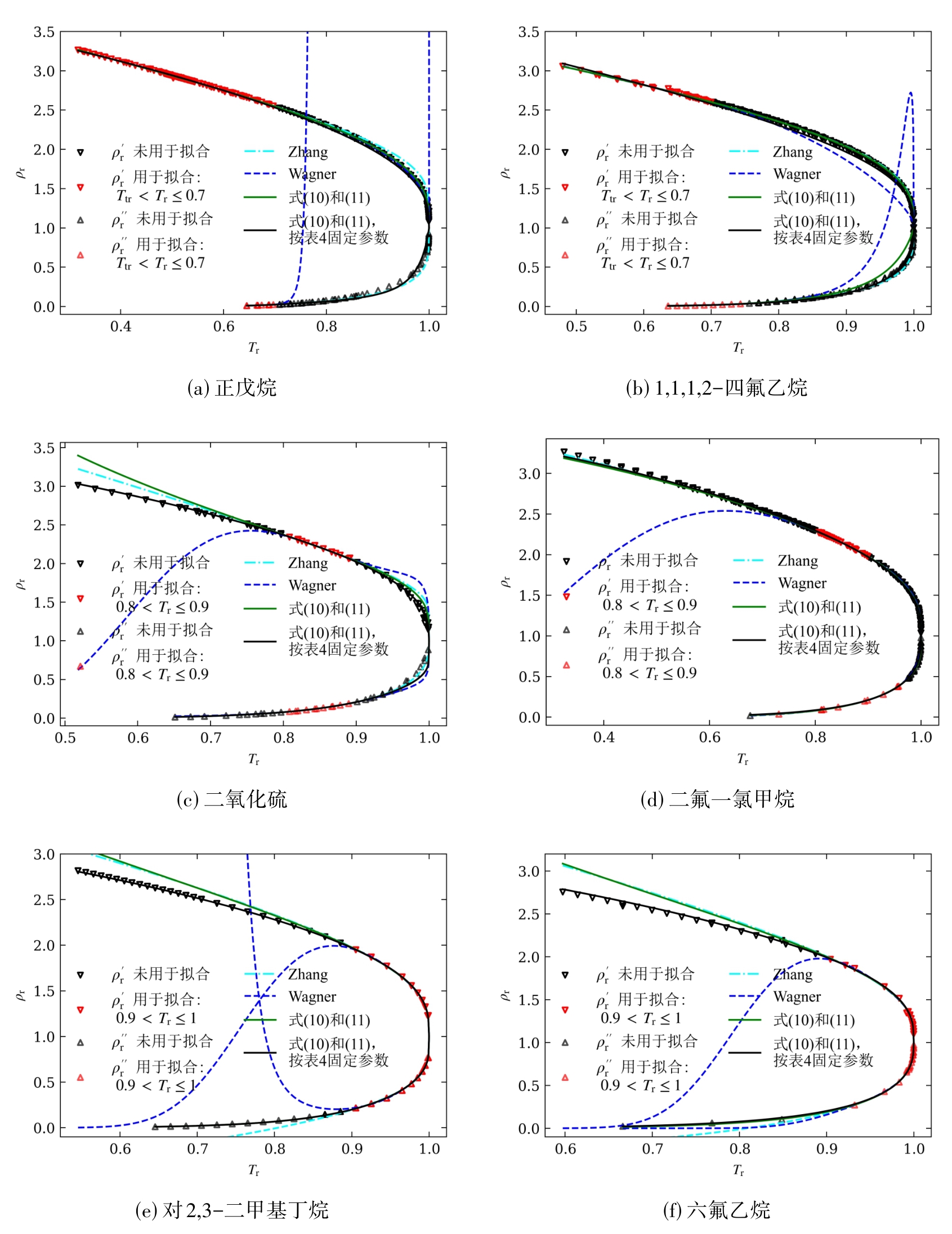
图5 以正戊烷、1,1,1,2-四氟乙烷、二氧化硫、二氟一氯甲烷、2,3-二甲基丁烷和六氟乙烷为例的各方程外推效果比较
Fig. 5 Comparison of extrapolation effects for various equations, using n-pentane, 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane, sulfur dioxide, difluorochloromethane, 2,3-dimethylbutane, and hexafluoroethane as examples
| 式(10) | 式(11) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 拟合初始值设定① | a0′ = 0.04, b0′ = 0.30, c0′ = 1.34 | a0′′ = 5.23, b0′′ = 0.36, c0′′ = 2.44 | |
外推时 固定参数设定② | 向临界点方向外推 | b′ = 0.30, c′ = 1.34 | b′′ = 0.36, c′′ = 2.44 |
| 向三相点与临界点方向同时外推 | a′ = 0.04, b′ = 0.30 | a′′ = 5.23, b′′ = 0.36 | |
| 向三相点方向外推 | a′ = 0.04 | a′′ = 5.23 | |
表4 式(10)和(11)在不同方向外推时固定参数设定
Table 4 Fixed parameter settings when Eq. (10) and (11) are extrapolated in different directions
| 式(10) | 式(11) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 拟合初始值设定① | a0′ = 0.04, b0′ = 0.30, c0′ = 1.34 | a0′′ = 5.23, b0′′ = 0.36, c0′′ = 2.44 | |
外推时 固定参数设定② | 向临界点方向外推 | b′ = 0.30, c′ = 1.34 | b′′ = 0.36, c′′ = 2.44 |
| 向三相点与临界点方向同时外推 | a′ = 0.04, b′ = 0.30 | a′′ = 5.23, b′′ = 0.36 | |
| 向三相点方向外推 | a′ = 0.04 | a′′ = 5.23 | |
| [1] | Li J, Ge Z, Duan Y Y, et al. Parametric optimization and thermodynamic performance comparison of single-pressure and dual-pressure evaporation organic Rankine cycles[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 217: 409-421. |
| [2] | Li J, Peng X Y, Yang Z, et al. Design, improvements and applications of dual-pressure evaporation organic Rankine cycles: a review[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 311: 118609. |
| [3] | Yang F F, Yang F B, Chu Q F, et al. Thermodynamic performance limits of the organic Rankine cycle: Working fluid parameterization based on corresponding states modeling[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 217: 113011. |
| [4] | Li S H, Xu L, Liu H T, et al. Vapor pressure measurements and correlation for cis-1, 1, 1, 4, 4, 4-hexafluoro-2-butene (HFO-1336mzz(Z))[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2020, 65(9): 4223-4229. |
| [5] | An B L, Duan Y Y, Tan L S, et al. Vapor pressure of HFE 7100[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2015, 60(4): 1206-1210. |
| [6] | Gmehling J, Kleiber M, Kolbe B, et al. Chemical Thermodynamics for Process Simulation[M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2019. |
| [7] | Bergman T L, Lavine A, Incropera F P, et al. Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer[M]. 7th ed. Hoboken, N.J.: John Wiley & Sons, 2011. |
| [8] | Zhao Y X, Dong X Q, Zhong Q, et al. Modeling vapor liquid phase equilibrium for C x H y + C x H y F z using Peng–Robinson and perturbed-chain SAFT[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(25): 7384-7389. |
| [9] | 徐英杰, 李鹏, 高赞军, 等. 饱和液体密度测量装置的研制与可靠性验证[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2013, 34(1): 14-18. |
| Xu Y J, Li P, Gao Z J, et al. Development and stability verification of a measuring installation of saturation liquid density[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2013, 34(1): 14-18. | |
| [10] | Soave G. Equilibrium constants from a modified Redlich-Kwong equation of state[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1972, 27(6): 1197-1203. |
| [11] | Peng D Y, Robinson D B. A new two-constant equation of state[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals, 1976, 15(1): 59-64. |
| [12] | Span R, Wagner W. A new equation of state for carbon dioxide covering the fluid region from the triple-point temperature to 1100 K at pressures up to 800 MPa[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1996, 25(6): 1509-1596. |
| [13] | 孙佳惠, 王潇然, 赵文英, 等. 立方型与PC-SAFT EoS对纯组分热力学性质预测能力的评价[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 50(6): 810-816. |
| Sun J H, Wang X R, Zhao W Y, et al. Evaluation of the predictive capability of cubic and PC-SAFT EoS for the thermodynamic properties of pure components[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology, 2024, 50(6): 810-816. | |
| [14] | Kud A, Coquelet C, Maixner S. A new semi-empirical model for saturated vapor density of pure compounds[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2020, 65(2): 577-590. |
| [15] | Rowlinson J S, Widom B. Molecular theory of capillarity[M]. Courier Corporation, 2013. |
| [16] | Cailletet L, Mathias E. Recherches sur les densités des gaz liquéfiés et de leurs vapeurs saturées[J]. Journal de Physique Théorique et Appliquée, 1886, 5(1): 549-564. |
| [17] | Cailletet, Mathias. Recherches sur la densité de l'acide sulfureux à l'état de liquide et de vapeur saturée[J]. Journal de Physique Théorique et Appliquée, 1887, 6(1): 414-426. |
| [18] | Campbell S W, Thodos G. Saturated liquid densities of polar and nonpolar pure substances[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals, 1984, 23(4): 500-510. |
| [19] | Zhang H Y, Gao B, Li H Y, et al. Saturated liquid density equation for pure refrigerants including CFCs, HCFCs, HFCs, HCs, HFOs, HFEs, PFAs and ISs based on the scaling law and the law of rectilinear diameter[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2018, 87: 65-77. |
| [20] | Kleinrahm R, Wagner W. Measurement and correlation of the equilibrium liquid and vapour densities and the vapour pressure along the coexistence curve of methane[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 1986, 18(8): 739-760. |
| [21] | Wagner W. New vapour pressure measurements for argon and nitrogen and a new method for establishing rational vapour pressure equations[J]. Cryogenics, 1973, 13(8): 470-482. |
| [22] | Barile R G, Thodos G. Saturated vapor and liquid densities of pure substances[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1965, 43(3): 137-142. |
| [23] | Ambrose D, Walton J. Vapour pressures up to their critical temperatures of normal alkanes and 1-alkanols[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1989, 61(8): 1395-1403. |
| [24] | Wu J T, Liu Z G. An accurate vapor pressure equation with good extrapolation characteristics[J]. International Journal of Thermophysics, 2005, 26(3): 767-784. |
| [25] | 卿康, 汪尔奇, 杨震, 等. 可准确外推的三参数饱和蒸气压新方程[J]. 计量学报, 2025, 46(4): 482-490. |
| Qing K, Wang E Q, Yang Z, et al. A new three parameters vapor pressure equation with high-precision fitting and accurate extrapolation ability for the entire region[J]. Acta Metrologica Sinica, 2025, 46(4): 482-490. | |
| [26] | Velasco S, White J A, Srinivasan K, et al. Waring and riedel functions for the liquid–vapor coexistence curve[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(7): 3197-3202. |
| [27] | Diky V, Muzny C D, Smolyanitsky A Y, et al. ThermoData Engine (TDE) Version 10.1 (Pure Compounds, Binary Mixtures, Ternary Mixtures, and Chemical Reactions): NIST Standard Reference Database 103b. 2016. |
| [28] | Funke M, Kleinrahm R, Wagner W. Measurement and correlation of the (p, ρ, T) relation of ethane II. Saturated-liquid and saturated-vapour densities and vapour pressures along the entire coexistence curve[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2002, 34(12): 2017-2039. |
| [29] | Wagner W, Pruss A. International equations for the saturation properties of ordinary water substance. revised according to the international temperature scale of 1990. addendum to J. phys. chem. ref. data 16, 893 (1987)[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1993, 22(3): 783-787. |
| [30] | Garbow B S, Hillstrom K E, More J J. Implementation guide for MINPACK-1. [Package of Fortran subprograms for solution of systems of nonlinear equations][R]. Argonne National Lab., 1980. |
| [31] | Forero G L A, Velásquez J J A. Wagner liquid–vapour pressure equation constants from a simple methodology[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2011, 43(8): 1235-1251. |
| [32] | McGarry J. Correlation and prediction of the vapor pressures of pure liquids over large pressure ranges[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 1983, 22(2): 313-322. |
| [1] | 刘豪, 王林, 丁昊, 耿嘉怡. R1150+R1234ze(E)二元体系223.15~253.15 K汽液相平衡研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 1-8. |
| [2] | 臧子晴, 李修真, 谈莹莹, 刘晓庆. 分凝器对两级分离自复叠制冷循环特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [3] | 郭纪超, 徐肖肖, 孙云龙. 基于植物工厂中的CO2浓度气流模拟及优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 237-245. |
| [4] | 马爱华, 赵帅, 王林, 常明慧. 太阳能吸收制冷循环动态特性仿真方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 318-325. |
| [5] | 吴成云, 孙浩然. 民用飞机空调系统性能仿真与燃油代偿损失研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 351-359. |
| [6] | 李卫, 陈浩, 柯钢, 黄孝胜, 李成娇, 郭航, 叶芳. 高原环境适应性试验室模拟平台新风系统仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 360-369. |
| [7] | 密晓光, 孙国刚, 程昊, 张晓慧. 印刷电路板式天然气冷却器性能仿真模型和验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 426-434. |
| [8] | 黄灏, 王文, 李沛昀. 三角转子膨胀机串联运行特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 435-443. |
| [9] | 张文锋, 郭玮, 张新玉, 曹昊敏, 丁国良. 铝管铝翅片换热器模型开发及软件实现[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 84-92. |
| [10] | 王偲凡, 栗一帆, 陈江波, 周桓. 碳酸盐型卤水Li+, Na+, K+, CO |
| [11] | 王一飞, 李玉星, 欧阳欣, 赵雪峰, 孟岚, 胡其会, 殷布泽, 郭雅琦. 基于裂尖减压特性的CO2管道断裂扩展数值计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4683-4693. |
| [12] | 刘奕扬, 邢志祥, 刘烨铖, 彭明, 李玉洋, 李云浩, 沈宁舟. 加氢站液氢泄漏扩散特性与安全监测数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4694-4708. |
| [13] | 赵婧, 董书辰, 李高洋, 黄友科, 石浩森, 缪舒文, 谭辰妍, 朱唐琦, 李永帅, 潘慧, 凌昊. 基于电化学模型的电池性能模拟与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4922-4932. |
| [14] | 娄岚浩, 杨立鹏, 杨晓光. 锂离子电池电化学机理模型参数辨识研究综述[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4369-4382. |
| [15] | 周轶磊, 李智, 彭鑫. 基于代理模型的连续重整反应过程自优化控制结构设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4499-4511. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号