化工学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (11): 4143-4152.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190931
收稿日期:2019-08-13
修回日期:2019-09-16
出版日期:2019-11-05
发布日期:2019-11-05
通讯作者:
杜占
基金资助:Received:2019-08-13
Revised:2019-09-16
Online:2019-11-05
Published:2019-11-05
Contact:
Zhan DU
摘要:
从热力学角度出发,揭示了还原条件对高温气基还原过程中颗粒表面铁析出行为的影响规律,提出了通过改变还原气氛调控铁析出形貌的操控方法。研究表明在CO中混入H2可以加快铁晶粒的生长速率,同时增加还原初期矿粉表面的铁形核数量,导致矿粉表面新生成的金属铁由晶须状转变为致密状。随着CO-CO2中CO2含量的升高,矿粉表面新生成的金属铁会由“锋利”的晶须状转变为“仙人掌状”,并且表面铁的分布密度会变小。随着还原温度的降低,矿粉表面铁晶须的强度会变弱。
中图分类号:
杜占. 颗粒表面金属铁析出规律的热力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(11): 4143-4152.
Zhan DU. Thermodynamic studies on behavior of newly formed metallic iron on surface of particles[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(11): 4143-4152.
| Composition | Content /%(mass) |
|---|---|
| TFe | 61.13 |
| FeO | 25.43 |
| CaO | 0.83 |
| MgO | 4.32 |
| Al2O3 | 0.84 |
| SiO2 | 6.02 |
| TiO2 | 0.11 |
表1 智利精粉的化学组成
Table 1 Chemical composition of Chilean iron ore
| Composition | Content /%(mass) |
|---|---|
| TFe | 61.13 |
| FeO | 25.43 |
| CaO | 0.83 |
| MgO | 4.32 |
| Al2O3 | 0.84 |
| SiO2 | 6.02 |
| TiO2 | 0.11 |

图2 流化还原系统装置
Fig.2 Experimental apparatus used for fluidized bed reduction1—gas cylinder; 2—shutoff valve; 3—mass flowmeter; 4—fluidized bed; 5—electric resistance furnace; 6—thermocouple; 7—temperature controller; 8—pressure sensor; 9—computer

图4 800℃下矿粉在不同比例CO-H2中还原后的表面铁析出形貌(金属化率约为22%)
Fig.4 Surface morphology of as-reduced samples in CO-H2 mixtures at 800℃(metallization degree is about 22%)
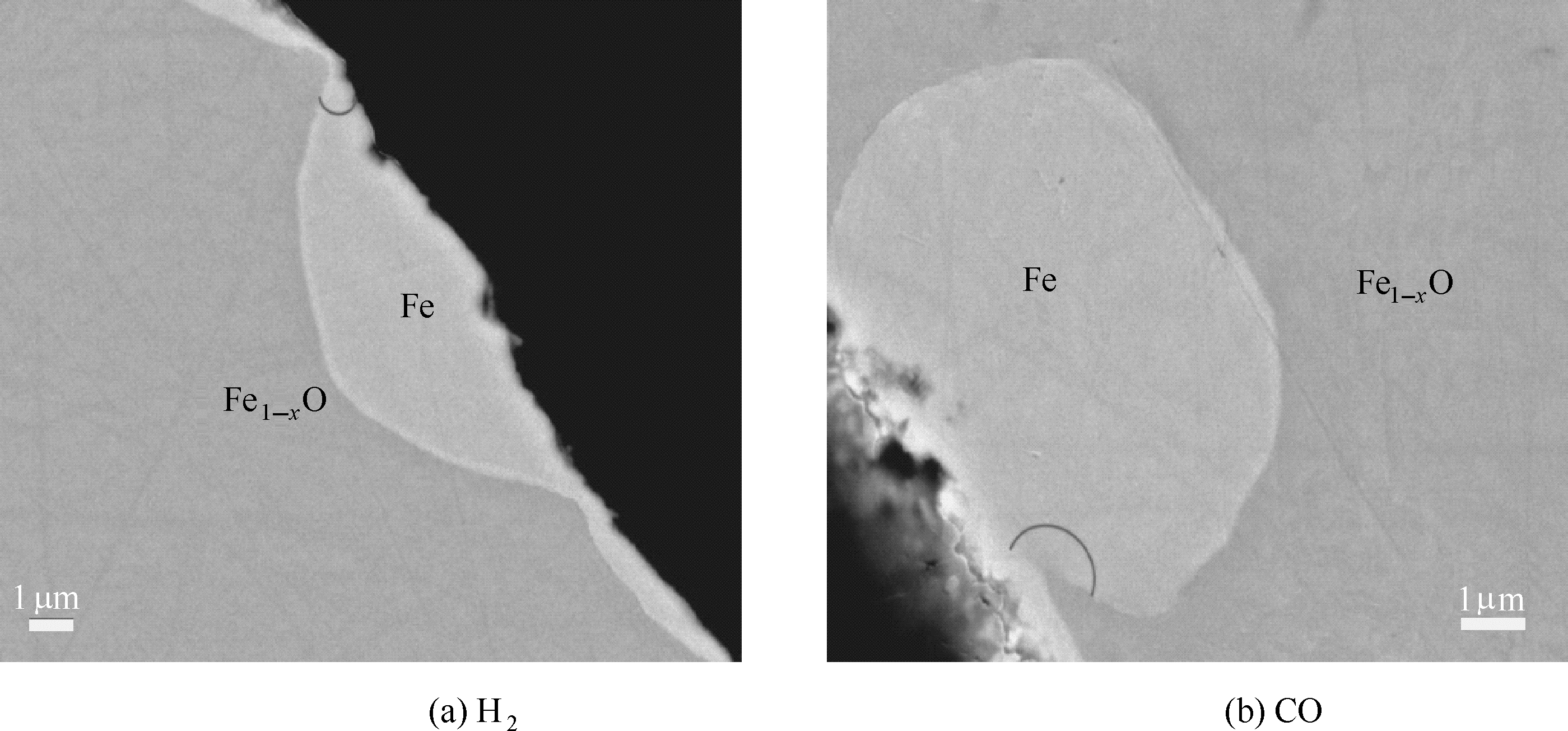
图5 纯H2和纯CO中铁矿粉还原初期的剖面图(金属化率约为5%)
Fig.5 Cross sectional views of as-reduced samples in H2 and CO during initial reduction period(metallization degree is about 5%)
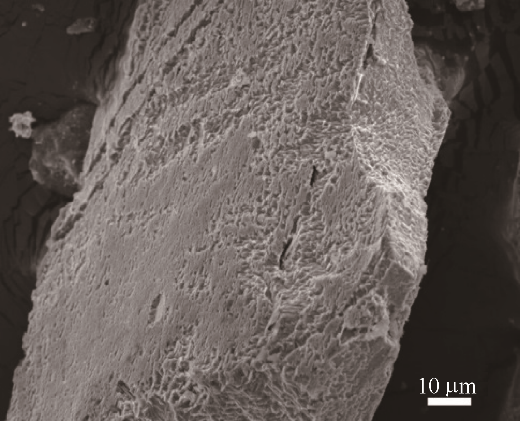

图7 铁矿粉在800℃下H2/(H2+CO)=30%(vol)中预还原5 min,然后再在纯CO中还原至金属化率为22%左右时的表面形貌
Fig.7 Surface morphology of as-reduced sample by pre-reduction in H2/(H2+CO)=30%(vol) for 5 min, metallization degree is about 22%
| CO2 /(CO+CO2)/%(vol) | ΔG/ (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| 10 | -33.8 |
| 20 | -18.3 |
| 30 | -8.7 |
| CO2 Fe/oxide eq=41.1%(vol) | 0 |
表2 800℃下不同比例CO-CO2中的热力学驱动力
Table 2 Thermodynamic driving forces in CO-CO2 mixtures at 800℃
| CO2 /(CO+CO2)/%(vol) | ΔG/ (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| 10 | -33.8 |
| 20 | -18.3 |
| 30 | -8.7 |
| CO2 Fe/oxide eq=41.1%(vol) | 0 |

图9 800℃下矿粉在不同比例CO-CO2中还原后的铁析出形貌(金属化率约为15%)
Fig.9 Surface morphology of as-reduced samples in CO-CO2 mixtures at 800℃(metallization degree is about 15%)
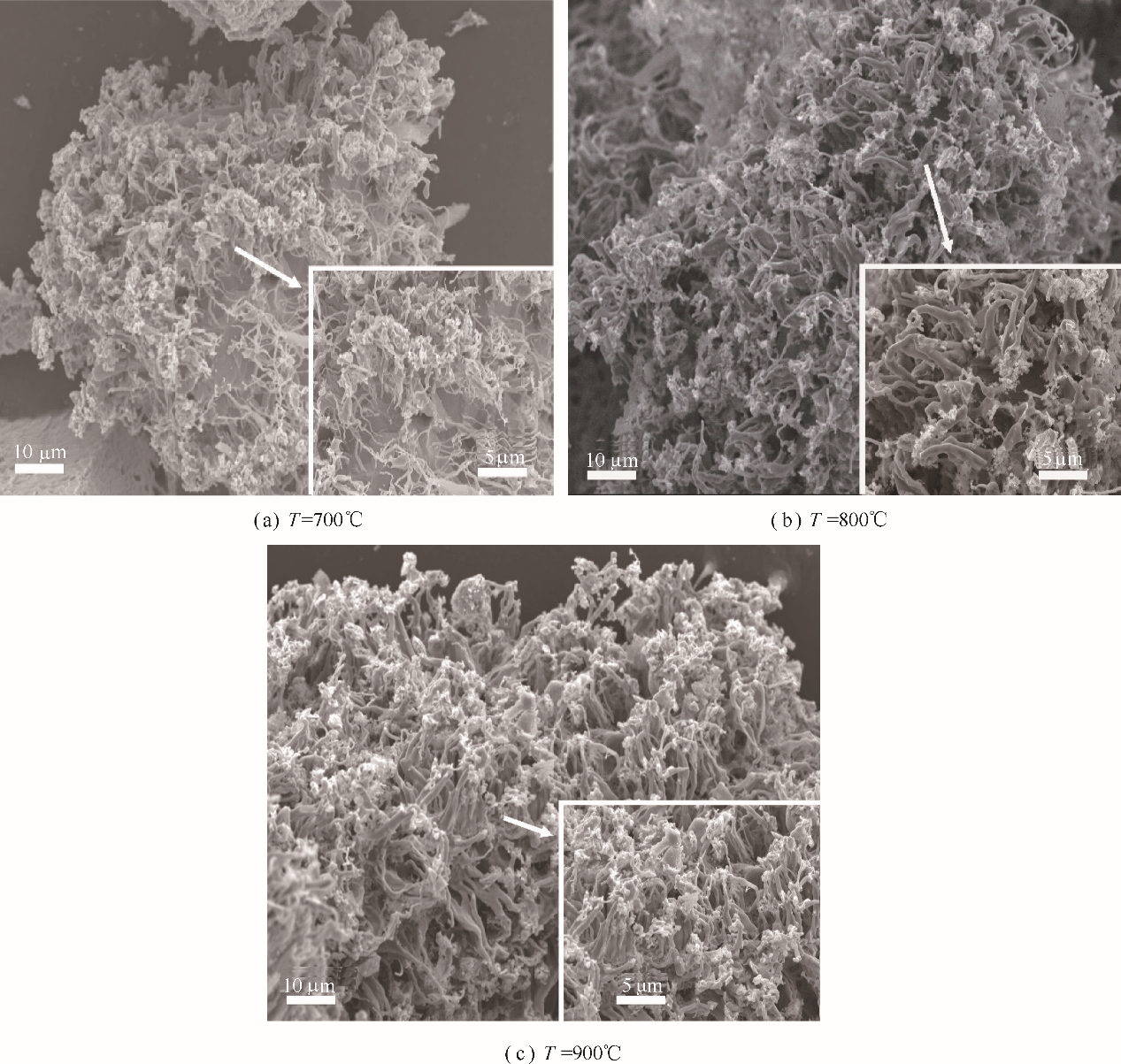
图11 矿粉在纯CO中不同温度下还原后的铁析出形貌(金属化率约为20%)
Fig.11 Surface morphology of as-reduced samples in CO at different temperatures(metallization degree is about 20%)
| 1 | GransdenJ F, SheasbyJ S. Sticking of iron ore during reduction by hydrogen in a fluidized bed[J]. Can. Metall. Quart., 1974, 13(4): 649-657. |
| 2 | HayashiS, SayamaS, IguchiY. Relation between sulfur pressure and sticking of fine iron ores in fluidized bed reduction[J]. ISIJ Int., 1990, 30(9): 722-730. |
| 3 | HayashiS, IguchiY. Factors affecting the sticking of fine iron ores during fluidized bed reduction[J]. ISIJ Int., 1992, 32(9): 962-971. |
| 4 | HayashiS, SawaiS, IguchiY. Influence of coating oxide and sulfur pressure on sticking during fluidized bed reduction of iron ores[J]. ISIJ Int., 1993, 33(10): 1078-1087. |
| 5 | ManzooriA R, AgarwalP K. Agglomeration and defluidization under simulated circulating fluidized-bed combustion conditions[J]. Fuel, 1994, 73(4): 563-568. |
| 6 | MikamiT, KamiyaH, HorioM. The mechanism of defluidization of iron particles in a fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technol., 1996, 89: 231-238. |
| 7 | SevilleJ P K, Silomon-PflugH, KnightP C. Modeling of sintering in high temperature gas fluidization[J]. Powder Technol., 1998, 97: 160-169. |
| 8 | KomatinaM, GudenauH W. The sticking problem during direct reduction of fine iron ore in fluidized bed[J]. Metalurgija, 2004, 10(204): 309-328. |
| 9 | LinC, PengT, WangW. Effect of particle size distribution on agglomeration/defluidization during fluidized bed combustion[J]. Powder Technol., 2011, 207: 290-295. |
| 10 | ShaoJ, GuoZ, TangH. Influence of temperature on sticking behavior of iron powder in fluidized bed[J]. ISIJ Int., 2011, 51(8): 1290-1295. |
| 11 | ZhongY, WangZ, GuoZ, et al. Defluidization behavior of iron powders at elevated temperature: influence of fluidizing gas and particle adhesion[J]. Powder Technol., 2012, 230: 225-231. |
| 12 | ZhuQ, WuR, LiH. Direct reduction of hematite powders in a fluidized bed reactor[J]. Particuology, 2013, 11(3): 294-300. |
| 13 | ZhongY, WangZ, GuoZ, TangQ. Prediction of defluidization behavior of iron powder in a fluidized bed at elevated temperatures: theoretical model and experimental verification[J]. Powder Technol., 2013, 249: 175-180. |
| 14 | LeiC, ZhuQ, LiH. Experimental and theoretical study on the fluidization behaviors of iron powder at high temperature[J]. Chem. Eng. Sci., 2014, 118: 59-69. |
| 15 | SinghM, BjörkmanB. Effect of processing parameters on the swelling behavior of cement-bonded briquettes[J]. ISIJ Int., 2004, 44(1): 59-68. |
| 16 | BarustanM I A, JungS M. Morphology of iron and agglomeration behavior during reduction of iron oxide fines[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2019, 25(4): 1083-1097. |
| 17 | SchillerM. Die Mikromorphologie der eisenphase als fogle der reduktion von eisenoxiden [D]. Germany: RWTH Aachen, 1987. |
| 18 | WangH, SohnH. Effects of reducing gas on swelling and iron whisker formation during the reduction of iron oxide compact[J]. Steel Res. Int., 2012, 83(9): 903-909. |
| 19 | 邵剑华, 郭占成, 唐惠庆. 流态化还原铁精粉黏结过程试验研究[J]. 钢铁, 2011, 46(2): 7-11. |
| ShaoJ H, GuoZ C, TangH Q. Experimental study on sticking process during reduction of iron ore concentrate fines in fluidized bed[J]. Iron & Steel, 2011, 46(2): 7-11. | |
| 20 | 邵剑华, 郭占成, 唐惠庆. 还原气氛对流态化还原铁矿粉黏结失流的影响[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2013, 35(3): 273-281. |
| ShaoJ H, GuoZ C, TangH Q. Influence of reducing atmosphere on the sticking during reduction of iron ore fines in a fluidized bed[J]. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. B., 2013, 35(3): 273-281. | |
| 21 | WangH, SohnH. Effects of firing and reduction conditions on swelling and iron whisker formation during the reduction of iron oxide compact[J]. ISIJ Int., 2011, 51(6): 906-912. |
| 22 | WangH, SohnH. Effect of CaO and SiO2 on swelling and iron whisker formation during reduction of iron oxide compact[J]. Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2011, 38(6): 447-452. |
| 23 | WagnerC. Mechanism of the reduction of oxides and sulphides to metals[J]. J. Metal., 1952, 4(2): 214-216. |
| 24 | NicolleR, RistA. Mechanism of whisker growth in the reduction of wustite[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1979, 10(3): 429-438. |
| 25 | ZhangT, LeiC, ZhuQ. Reduction of fine iron ore via a two-step fluidized bed direct reduction process[J]. Powder Technol., 2014, 254: 1-11. |
| 26 | 黄希祜. 钢铁冶金原理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2013. |
| HuangX G. Principle of Iron and Steel Metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013. | |
| 27 | LuW K. Mechanism of abnormal swelling during the reduction of iron ore pellets[J]. Scand. J. Metall., 1974, 3(2): 49-55. |
| 28 | YamashitaT, NakadaT, NagataK. In-situ observation of Fe0.94O reduction at high temperature with the use of optical microscopy[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2007, 38(2): 185-191. |
| 29 | 程传煊. 表面物理化学[M]. 北京: 科学技术文献出版社, 1995. |
| ChengC X. Physical Chemistry of Surfaces[M]. Beijing: Science and Technology Literature Publishing House, 1995. | |
| 30 | El-GeassyA A, NasrM I, HessienM M. Effect of reducing gas on the volume change during reduction of iron oxide compacts[J]. ISIJ Int., 1996, 36(6): 640-649. |
| 31 | MatthewS P, HayesP C. Microstructural changes occurring during the gaseous reduction of magnetite[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1990, 21(1): 153-172. |
| 32 | BrennerS S. Growth and properties of “whiskers”[J]. Science, 1958, 128(3324): 569-575. |
| 33 | KanekoT. Growth rate of iron whiskers[J]. J. Cryst. Growth, 1978, 44(1): 14-22. |
| [1] | 杨欣, 王文, 徐凯, 马凡华. 高压氢气加注过程中温度特征仿真分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 280-286. |
| [2] | 常明慧, 王林, 苑佳佳, 曹艺飞. 盐溶液蓄能型热泵循环特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 329-337. |
| [3] | 张化福, 童莉葛, 张振涛, 杨俊玲, 王立, 张俊浩. 机械蒸汽压缩蒸发技术研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 8-24. |
| [4] | 胡建波, 刘洪超, 胡齐, 黄美英, 宋先雨, 赵双良. 有机笼跨细胞膜易位行为的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3756-3765. |
| [5] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [6] | 郑玉圆, 葛志伟, 韩翔宇, 王亮, 陈海生. 中高温钙基材料热化学储热的研究进展与展望[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3171-3192. |
| [7] | 张曼铮, 肖猛, 闫沛伟, 苗政, 徐进良, 纪献兵. 危废焚烧处理耦合有机朗肯循环系统工质筛选与热力学优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3502-3512. |
| [8] | 张琦钰, 高利军, 苏宇航, 马晓博, 王翊丞, 张亚婷, 胡超. 碳基催化材料在电化学还原二氧化碳中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [9] | 李盼, 马俊洋, 陈志豪, 王丽, 郭耘. Ru/α-MnO2催化剂形貌对NH3-SCO反应性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2908-2918. |
| [10] | 张谭, 刘光, 李晋平, 孙予罕. Ru基氮还原电催化剂性能调控策略[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [11] | 卫雪岩, 钱勇. 微米级铁粉燃料中低温氧化反应特性及其动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2624-2638. |
| [12] | 张艳梅, 袁涛, 李江, 刘亚洁, 孙占学. 高效SRB混合菌群构建及其在酸胁迫条件下的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2599-2610. |
| [13] | 胡南, 陶德敏, 杨照岚, 王学兵, 张向旭, 刘玉龙, 丁德馨. 铁炭微电解与硫酸盐还原菌耦合修复铀尾矿库渗滤水的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2655-2667. |
| [14] | 姚晓宇, 沈俊, 李健, 李振兴, 康慧芳, 唐博, 董学强, 公茂琼. 流体气液临界参数测量方法研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1847-1861. |
| [15] | 陈科, 杜理, 曾英, 任思颖, 于旭东. 四元体系LiCl+MgCl2+CaCl2+H2O 323.2 K相平衡研究及计算[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1896-1903. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号
