化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (11): 4873-4884.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200785
收稿日期:2020-06-19
修回日期:2020-08-12
出版日期:2020-11-05
发布日期:2020-11-05
通讯作者:
董林
作者简介:汤常金(1984—),男,博士,教授,基金资助:
Changjin TANG1,2( ),Jingfang SUN1,Lin DONG1(
),Jingfang SUN1,Lin DONG1( )
)
Received:2020-06-19
Revised:2020-08-12
Online:2020-11-05
Published:2020-11-05
Contact:
Lin DONG
摘要:
以氨为还原剂的选择性催化还原(SCR)技术是工业脱硝的主流技术。我国已形成在180~420℃(包含低温和中高温)范围内具有良好应用效果的SCR技术及其催化剂体系,但超低温段(< 150℃)仍有待突破。超低温SCR脱硝通常位于“除尘-脱硫”工艺之后,具有烟气组成简单、能耗少、改造成本低等优点,吸引了研究人员的广泛关注。在简要分析不同行业烟气排放特征及治理现状的基础上,总结了150℃以下具有良好SCR活性的催化剂体系(锰基、钒基、铬基和活性炭基),重点对催化剂的抗水、硫、碱金属和硝铵中毒性能进行了探讨,并介绍了该领域最近的一些中试/侧线试验研究进展情况,最后对这一技术的未来发展方向进行了展望。
中图分类号:
汤常金,孙敬方,董林. 超低温(< 150℃)SCR脱硝技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 4873-4884.
Changjin TANG,Jingfang SUN,Lin DONG. Recent progress on elimination of NOx from flue gas via SCR technology under ultra-low temperatures (< 150℃)[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(11): 4873-4884.
| 脱硝工艺 | 脱硝率/% | 还原/氧化剂 | 反应温度/℃ | 催化剂 | 存在的风险 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低氮燃烧 | 30~60 | 无 | 无要求 | 不使用催化剂 | 无 |
| SNCR | 40~70 | NH3或尿素 | 800~1250 | 不使用催化剂 | 氨逃逸 |
| 氧化吸收法 | 50~85 | 氧化剂,碱液 | <100 | 不使用催化剂 | 二次水、臭氧污染等;易产生白烟 |
| 活性焦脱硝 | 50~80 | NH3或尿素 | 130~200 | 活性焦 | 自燃隐患 |
| SCR | 75~90 | NH3或尿素 | 100~500 | 使用催化剂 | 无 |
表1 常用烟气脱硝方法比较
Table 1 The comparison of different technologies for industrial denitration
| 脱硝工艺 | 脱硝率/% | 还原/氧化剂 | 反应温度/℃ | 催化剂 | 存在的风险 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低氮燃烧 | 30~60 | 无 | 无要求 | 不使用催化剂 | 无 |
| SNCR | 40~70 | NH3或尿素 | 800~1250 | 不使用催化剂 | 氨逃逸 |
| 氧化吸收法 | 50~85 | 氧化剂,碱液 | <100 | 不使用催化剂 | 二次水、臭氧污染等;易产生白烟 |
| 活性焦脱硝 | 50~80 | NH3或尿素 | 130~200 | 活性焦 | 自燃隐患 |
| SCR | 75~90 | NH3或尿素 | 100~500 | 使用催化剂 | 无 |
| 行业 | 烟气组成 | 目前使用的 脱硝技术 | NOx排放限值/(mg/m3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOx/(mg/m3) | SOx/(mg/m3) | 粉尘/(mg/m3) | 其他 | |||
| 火电 | 100~1000 | 500~4000 | 30~100 | Hg,Pb等 | SCR | 50 |
| 焦化 | 200~800 | 100~500 | 50~85 | H2S等 | SCR | 150 |
| 钢铁 | 200~310 | 400~1500 | 30~80 | CO,二 英等 英等 | 活性焦、臭氧氧化、SCR | 50 |
| 水泥 | 800~1200 | 30~100 | 80000~120000 | CaO等 | SNCR | 320 |
| 玻璃 | 1200~3000 | 300~3300 | 300~1200 | Na盐,CaO等 | SNCR | 700 |
| 陶瓷 | 200~1100 | 500~3500 | 50~200 | HCl,Pb、Cd等 | SNCR | 180 |
| 垃圾焚烧 | 400~1000 | 200~1200 | 1000~10000 | HCl,二 英等 英等 | SNCR | 300 |
| 燃气锅炉 | 100~400 | 0~20 | — | H2O,CO等 | 低氮燃烧 | 200 |
表2 一些代表性行业的烟气组成、目前使用的脱硝技术与NOx排放限值情况
Table 2 The flue gas composition, adopted denitration technique and emission limit for NOx in some typical industries
| 行业 | 烟气组成 | 目前使用的 脱硝技术 | NOx排放限值/(mg/m3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOx/(mg/m3) | SOx/(mg/m3) | 粉尘/(mg/m3) | 其他 | |||
| 火电 | 100~1000 | 500~4000 | 30~100 | Hg,Pb等 | SCR | 50 |
| 焦化 | 200~800 | 100~500 | 50~85 | H2S等 | SCR | 150 |
| 钢铁 | 200~310 | 400~1500 | 30~80 | CO,二 英等 英等 | 活性焦、臭氧氧化、SCR | 50 |
| 水泥 | 800~1200 | 30~100 | 80000~120000 | CaO等 | SNCR | 320 |
| 玻璃 | 1200~3000 | 300~3300 | 300~1200 | Na盐,CaO等 | SNCR | 700 |
| 陶瓷 | 200~1100 | 500~3500 | 50~200 | HCl,Pb、Cd等 | SNCR | 180 |
| 垃圾焚烧 | 400~1000 | 200~1200 | 1000~10000 | HCl,二 英等 英等 | SNCR | 300 |
| 燃气锅炉 | 100~400 | 0~20 | — | H2O,CO等 | 低氮燃烧 | 200 |
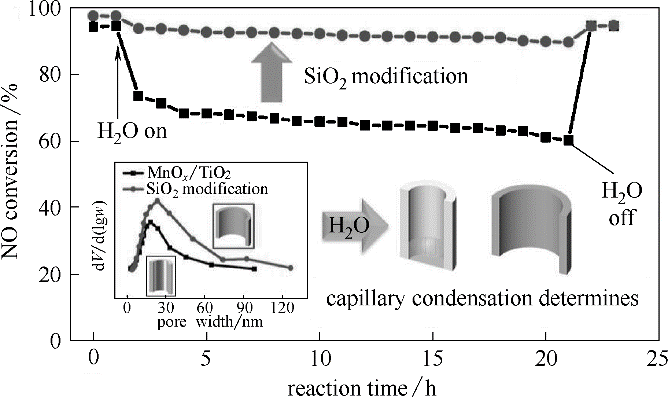
图3 基于毛细作用调控的MnOx/TiO2催化剂抗水性能提高示意图
Fig.3 Schematic illustration of the strategy to improve H2O resistance of MnOx/TiO2 catalyst via controlled capillary condensation

图4 基于牺牲剂策略调控的MnOx-CeO2/TiO2催化剂抗硫性能提升示意图
Fig.4 Schematic illustration of the strategy to improve SO2 resistance of MnOx-CeO2/TiO2 catalyst via adding sacrificial agent

图5 “除尘-脱硫-脱硝”工艺路线示意图(对应超低温脱硝)[102]
Fig.5 Schematic illustration of flue gas treatment via “dedusting-desulfation-denitration” route (corresponding to ultra-low temperature SCR) [102]
| 1 | Huang R J, Zhang Y L, Bozzetti C, et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China[J]. Nature, 2014, 514(7521): 218-222. |
| 2 | Cheng Y, Zheng G, Wei C, et al. Reactive nitrogen chemistry in aerosol water as a source of sulfate during haze events in China[J]. Science Advance, 2017, 2(12): e1601530. |
| 3 | 中国环境监测总站. 中国环境统计年报: 2013—2017[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2014—2018. |
| China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Annual Statistic Report on Environment in China: 2013—2017[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2014—2018. | |
| 4 | 江苏省环境保护厅. 关于开展全省非电行业氮氧化物深度减排的通知[Z]. 2017. |
| Environmental Protection Department of Jiangsu Province. Deployment of NOx emission control from non-electric industries in Jiangsu province [Z]. 2017. | |
| 5 | 王修文, 李露露, 孙敬方, 等. 我国氮氧化物排放控制及脱硝催化剂研究进展[J]. 工业催化, 2019, 27(2): 1-23. |
| Wang X W, Li L L, Sun J F, et al. Analysis of NOx emission and control in China and research progress in denitration catalysts[J]. Industrial Catalysis, 2019, 27(2): 1-23. | |
| 6 | Tang C J, Zhang H L, Dong L. Ceria-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 6(5): 1248-1264. |
| 7 | Yuan H, Sun N, Chen J, et al. Insight into the NH3-assisted selective catalytic reduction of NO on β-MnO2 (110): reaction mechanism, activity descriptor, and evolution from a pristine state to a steady state[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(10): 9269-9279. |
| 8 | Liu C, Shi J W, Gao C, et al. Manganese oxide-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: a review[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2016, 522: 54-69. |
| 9 | Kang M, Yeon T H, Park E D, et al. Novel MnOx catalysts for NO reduction at low temperature with ammonia[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2006, 106(1/2): 77-80. |
| 10 | Kang M, Park E D, Kim J M, et al. Manganese oxide catalysts for NOx reduction with NH3 at low temperatures[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2007, 327(2): 261-269. |
| 11 | 唐晓龙, 郝吉明, 徐文国, 等. 新型MnOx催化剂用于低温NH3选择性催化还原NOx[J]. 催化学报, 2006, 27(10): 843-848. |
| Tang X L, Hao J M, Xu W G, et al. Novel MnOx catalyst for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2006, 27(10): 843-848. | |
| 12 | 戴韵, 李俊华, 彭悦,等. MnO2的晶相结构和表面性质对低温NH3-SCR反应的影响[J]. 物理化学学报, 2012, 28(7):1771-1776. |
| Dai Y, Li J H, Peng Y, et al. Effects of MnO2 crystal structure and surface property on the NH3-SCR reaction at low temperature[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2012, 28(7):1771-1776. | |
| 13 | Gong P J, Xie J L, Fang D, et al. Effects of surface physicochemical properties on NH3-SCR activity of MnO2 catalysts with different crystal structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2017, 38(11): 1925-1934. |
| 14 | Andreoli S, Deorsola F A, Galletti C, et al. Nanostructured MnOx catalysts for low-temperature NOx SCR[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 278: 174-182. |
| 15 | 孙梦婷, 黄碧纯, 马杰文,等. 二氧化锰在低温NH3-SCR催化反应上的形貌效应[J]. 物理化学学报, 2016, 32(6):1501-1510. |
| Sun M T, Huang B C, Ma J W, et al. Morphological effects of manganese dioxide on catalytic reactions for low-temperature NH3-SCR[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2016, 32(6):1501-1510. | |
| 16 | Shi J W, Gao C, Liu C, et al. Porous MnOx for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NOx: the intrinsic relationship between surface physicochemical property and catalytic activity[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2017, 19(6): 194. |
| 17 | Xu T, Wang C, Wu X, et al. Modification of MnCo2Ox catalysts by NbOx for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(99): 97004-97011. |
| 18 | Liu J, Wei Y, Li P Z, et al. Experimental and theoretical investigation of mesoporous MnO2 nanosheets with oxygen vacancies for high-efficiency catalytic deNOx[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(5): 3865-3874. |
| 19 | Zhan S, Zhu D, Qiu M, et al. Highly efficient removal of NO with ordered mesoporous manganese oxide at low temperature[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(37): 29353-29361. |
| 20 | Tian W, Yang H, Fan X, et al. Catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over different-shaped MnO2 at low temperature[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 188(1/2/3): 105-109. |
| 21 | Yao X, Kong T, Yu S, et al. Influence of different supports on the physicochemical properties and denitration performance of the supported Mn-based catalysts for NH3-SCR at low temperature[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 402: 208-217. |
| 22 | Kijlstra W S, Daamen J C M L, van de Graaf J M, et al. Inhibiting and deactivating effects of water on the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide with ammonia over MnOx/Al2O3[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 1996, 7(3/4): 337-357. |
| 23 | Yang G, Zhao H, Luo X, et al. Promotion effect and mechanism of the addition of Mo on the enhanced low temperature SCR of NOx by NH3 over MnOx/γ-Al2O3 catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 245: 743-752. |
| 24 | Qu L, Li C, Zeng G, et al. Support modification for improving the performance of MnOx–CeOy/γ-Al2O3 in selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 242: 76-85. |
| 25 | Zhao W, Li C, Lu P, et al. Iron, lanthanum and manganese oxides loaded on γ-Al2O3 for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperature[J]. Environmental Technology, 2013, 34(1): 81-90. |
| 26 | Wang X, Wu S, Zou W, et al. Fe-Mn/Al2O3 catalysts for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 37(8): 1314-1323. |
| 27 | Smirniotis P G, Sreekanth P M, Peña D A, et al. Manganese oxide catalysts supported on TiO2, Al2O3, and SiO2: a comparison for low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2006, 45(19): 6436-6443. |
| 28 | Jiang B, Liu Y, Wu Z. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO on MnOx/TiO2 prepared by different methods[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 162(2/3): 1249-1254. |
| 29 | Wu Z, Jiang B, Liu Y, et al. Experimental study on a low-temperature SCR catalyst based on MnOx/TiO2 prepared by sol–gel method[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 145(3): 488-494. |
| 30 | 黄海凤, 张峰, 卢晗锋, 等. 制备方法对低温 NH3-SCR 脱硝催化剂MnOx/TiO2结构与性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2010, 61(1): 80-85. |
| Huang H F, Zhang F, Lu H F, et al. Effect of preparation methods on structures and performance of MnOx/TiO2 catalyst for low-temperature NH3-SCR[J]. CIESC Journal, 2010, 61(1): 80-85. | |
| 31 | Li J, Chen J, Ke R, et al. Effects of precursors on the surface Mn species and the activities for NO reduction over MnOx/TiO2 catalysts[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2007, 8(12): 1896-1900. |
| 32 | Deng S, Meng T, Xu B, et al. Advanced MnOx/TiO2 catalyst with preferentially exposed anatase {001} facet for low-temperature SCR of NO[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(9): 5807-5815. |
| 33 | Liu X, Yu Q, Chen H, et al. The promoting effect of S-doping on the NH3-SCR performance of MnOx/TiO2 catalyst[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 508: 144694. |
| 34 | Kim Y J, Kwon H J, Nam I S, et al. High deNOx performance of Mn/TiO2 catalyst by NH3[J]. Catalysis Today, 2010, 151(3/4): 244-250. |
| 35 | Qi G, Yang R T. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over iron and manganese oxides supported on titania[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2003, 44(3): 217-225. |
| 36 | Wu S, Yao X, Zhang L, et al. Improved low temperature NH3-SCR performance of FeMnTiOx mixed oxide with CTAB-assisted synthesis[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(16): 3470-3473. |
| 37 | Wu S, Zhang L, Wang X, et al. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic performance of FeMnTiOx mixed oxides catalyst prepared by a CTAB-assisted process for mid-low temperature NH3-SCR[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2015, 505: 235-242. |
| 38 | Qi G, Yang R T. Performance and kinetics study for low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over MnOx–CeO2 catalyst[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2003, 217(2): 434-441. |
| 39 | Xu L, Li X S, Crocker M, et al. A study of the mechanism of low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3 on MnOx/CeO2[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2013, 378: 82-90. |
| 40 | Andreoli S, Deorsola F A, Pirone R. MnOx/CeO2 catalysts synthesized by solution combustion synthesis for the low-temperature NH3-SCR[J]. Catalysis Today, 2015, 253: 199-206. |
| 41 | Shen B, Wang F, Liu T. Homogeneous MnOx–CeO2 pellets prepared by a one-step hydrolysis process for low-temperature NH3-SCR[J]. Powder Technology, 2014, 253: 152-157. |
| 42 | Yao X, Ma K, Zou W, et al. Influence of preparation methods on the physicochemical properties and catalytic performance of MnOx-CeO2 catalysts for NH3-SCR at low temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2017, 38(1): 146-159. |
| 43 | Liu C, Gao G, Shi J W, et al. MnOx-CeO2 shell-in-shell microspheres for NH3-SCR de-NOx at low temperature[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2016, 86: 36-40. |
| 44 | Li S, Huang B, Yu C. A CeO2-MnOx core-shell catalyst for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NO[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2017, 98: 47-51. |
| 45 | Ma Z, Sheng L, Wang X, et al. Oxide catalysts with ultra-strong resistance to SO2 deactivation for removing nitric oxide at low temperature[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(42): 1903719. |
| 46 | Weiman L, Haidi L, Yunfa C. Mesoporous MnOx-CeO2 composites for NH3-SCR: the effect of preparation methods and a third dopant[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(21): 11912-11921. |
| 47 | Wei Y, Sun Y, Su W, et al. MnO2 doped CeO2 with tailored 3-D channels exhibits excellent performance for NH3-SCR of NO[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(33): 26231-26235. |
| 48 | Gan L, Li K, Yang W, et al. Core-shell-like structured α-MnO2@CeO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO: promoted activity and SO2 tolerance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 391: 123473. |
| 49 | Zhang L, Zhang D, Zhang J, et al. Design of meso-TiO2@MnOx-CeOx/CNTs with a core–shell structure as DeNOx catalysts: promotion of activity, stability and SO2-tolerance[J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(20): 9821-9829. |
| 50 | Ran X, Li M, Wang K, et al. Spatially confined tuning the interfacial synergistic catalysis in mesochannels toward selective catalytic reduction[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(21): 19242-19251. |
| 51 | Li L, Sun B, Sun J, et al. Novel MnOx-CeO2 nanosphere catalyst for low-temperature NH3-SCR[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2017, 100: 98-102. |
| 52 | Ma K, Zou W, Zhang L, et al. Construction of hybrid multi-shell hollow structured CeO2-MnOx materials for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. RSC advances, 2017, 7(10): 5989-5999. |
| 53 | Xiong Y, Tang C, Yao X, et al. Effect of metal ions doping (M= Ti4+, Sn4+) on the catalytic performance of MnOx/CeO2 catalyst for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2015, 495: 206-216. |
| 54 | Zhang L, Shi L, Huang L, et al. Rational design of high-performance deNOx catalysts based on MnxCo3–xO4 nanocages derived from metal-organic frameworks[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2014, 4(6): 1753-1763. |
| 55 | Meng D, Zhan W, Guo Y, et al. A highly effective catalyst of Sm-MnOx for the NH3-SCR of NOx at low temperature: promotional role of Sm and its catalytic performance[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(10): 5973-5983. |
| 56 | Xu Q, Fang Z, Chen Y, et al. Titania–samarium–manganese composite oxide for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(4): 2530-2538. |
| 57 | Wang Z, Guo R, Shi X, et al. The superior performance of CoMnOx catalyst with ball-flowerlike structure for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 381: 122753. |
| 58 | Liu Y, Guo R, Duan C, et al. A highly effective urchin-like MnCrOx catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Fuel, 2020, 271: 117667. |
| 59 | Gao G, Shi J W, Fan Z, et al. MnM2O4 microspheres (M= Co, Cu, Ni) for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: comparative study on catalytic activity and reaction mechanism via in-situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 325: 91-100. |
| 60 | Yan L, Liu Y, Zha K, et al. Scale–activity relationship of MnOx-FeOy nanocage catalysts derived from Prussian blue analogues for low-temperature NO reduction: experimental and DFT studies[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(3): 2581-2593. |
| 61 | Wan Y, Zhao W, Tang Y, et al. Ni-Mn bi-metal oxide catalysts for the low temperature SCR removal of NO with NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2014, 148: 114-122. |
| 62 | Zuo J, Chen Z, Wang F, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over novel Mn-Zr mixed oxide catalysts[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(7): 2647-2655. |
| 63 | Chang H, Li J, Chen X, et al. Effect of Sn on MnOx-CeO2 catalyst for SCR of NOx by ammonia: enhancement of activity and remarkable resistance to SO2[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2012, 27: 54-57. |
| 64 | Inomata Y, Hata S, Mino M, et al. Bulk vanadium oxide versus conventional V2O5/TiO2: NH3-SCR catalysts working at a low temperature below 150℃[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(10): 9327-9331. |
| 65 | Smirniotis P G, Peña D A, Uphade B S. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 by using Mn, Cr, and Cu oxides supported on Hombikat TiO2[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2001, 40(13): 2479-2482. |
| 66 | Li S, Wang X, Tan S, et al. CrO3 supported on sargassum-based activated carbon as low temperature catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Fuel, 2017, 191: 511-517. |
| 67 | Zhang Y, Zhang H, Zhou L, et al. DRIFT study on Cr2O3-SO42-/TiO2 catalyst for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities, 2014, 30(2): 279-283. |
| 68 | Yu S, Xu S, Sun B, et al. Synthesis of CrOx/C catalysts for low temperature NH3-SCR with enhanced regeneration ability in the presence of SO2[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(7): 3858-3868. |
| 69 | Zeng Z, Lu P, Li C, et al. Removal of NO by carbonaceous materials at room temperature: a review[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2012, 2(11): 2188-2199. |
| 70 | 付亚利, 张永发, 李国强,等. 非沥青基煤质氧化活性炭的脱硝特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 7(10): 3727-3732. |
| Fu Y L, Zhang Y F, Li G Q, et al. Denitrification characteristics of non-pitch coal-based oxidized activated carbon[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 7(10): 3727-3732. | |
| 71 | Guo Q, Jing W, Hou Y, et al. On the nature of oxygen groups for NH3-SCR of NO over carbon at low temperatures[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 270: 41-49. |
| 72 | Adapa S, Gaur V, Verma N. Catalytic oxidation of NO by activated carbon fiber (ACF)[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2006, 116(1): 25-37. |
| 73 | Yu S, Jiang N, Zou W, et al. A general and inherent strategy to improve the water tolerance of low temperature NH3-SCR catalysts via trace SiO2 deposition[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2016, 84: 75-79. |
| 74 | Wang H, Huang B, Yu C, et al. Research progress, challenges and perspectives on the sulfur and water resistance of catalysts for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2019, 588: 117207. |
| 75 | Gao C, Shi J W, Fan Z, et al. Sulfur and water resistance of Mn-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx: a review[J]. Catalysts, 2018, 8(1): 11. |
| 76 | Jin R, Liu Y, Wang Y, et al. The role of cerium in the improved SO2 tolerance for NO reduction with NH3 over Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst at low temperature[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2014, 148: 582-588. |
| 77 | Liu H, Fan Z, Sun C, et al. Improved activity and significant SO2 tolerance of samarium modified CeO2-TiO2 catalyst for NO selective catalytic reduction with NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 244: 671-683. |
| 78 | Sun C, Liu H, Chen W, et al. Insights into the Sm/Zr co-doping effects on N2 selectivity and SO2 resistance of a MnOx-TiO2 catalyst for the NH3-SCR reaction[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 347: 27-40. |
| 79 | Wang X, Lan Z, Liu Y, et al. Facile fabrication of hollow tubular mixed oxides for selective catalytic reduction of NOx at low temperature: a combined experimental and theoretical study[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(5): 967-970. |
| 80 | Li H, Zhang D, Maitarad P, et al. In situ synthesis of 3D flower-like NiMnFe mixed oxides as monolith catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(86): 10645-10647. |
| 81 | Wang X, Du X, Liu S, et al. Understanding the deposition and reaction mechanism of ammonium bisulfate on a vanadia SCR catalyst: a combined DFT and experimental study[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 260: 118168. |
| 82 | Chen Y, Li C, Chen J, et al. Self-prevention of well-defined-facet Fe2O3/MoO3 against deposition of ammonium bisulfate in low-temperature NH3-SCR[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(20): 11796-11802. |
| 83 | Ma Z, Sheng L, Wang X, et al. Oxide catalysts with ultrastrong resistance to SO2 deactivation for removing nitric oxide at low temperature [J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(6): 1907806. |
| 84 | Yu J, Guo F, Wang Y, et al. Sulfur poisoning resistant mesoporous Mn-base catalyst for low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3 [J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2010, 95(1/2): 160-168 |
| 85 | Guo K, Fan G, Gu D, et al. Pore size expansion accelerates ammonium bisulfate decomposition for improved sulfur resistance in low-temperature NH3-SCR[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(5): 4900-4907. |
| 86 | Ma K, Guo K, Li L, et al. Cavity size dependent SO2 resistance for NH3-SCR of hollow structured CeO2-TiO2 catalysts[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2019, 128: 105719. |
| 87 | Fan Z, Shi J W, Niu C, et al. The insight into the role of Al2O3 in promoting the SO2 tolerance of MnOx for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 398: 125572. |
| 88 | Huang Z, Gu X, Wen W, et al. A “smart” hollandite deNOx catalyst: self-protection against alkali poisoning[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(2): 660-664. |
| 89 | Li C, Huang Z, Liu X, et al. Rational design of alkali-resistant catalysts for selective NO reduction with NH3[J]. Chemical Communications, 2019, 55(66): 9853-9856. |
| 90 | Liu X, Gao J, Chen Y, et al. Rational design of alkali-resistant NO reduction catalysts using a stable hexagonal V-doped MoO3 support for alkali trapping[J]. ChemCatChem, 2018, 10(18): 3999-4003. |
| 91 | Zheng L, Zhou M, Huang Z, et al. Self-protection mechanism of hexagonal WO3-based deNOx catalysts against alkali poisoning[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(21): 11951-11956. |
| 92 | Hao Z, Shen Z, Li Y, et al. The role of alkali metal in α-MnO2 catalyzed ammonia-selective catalysis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(19): 6351-6356. |
| 93 | Ciardelli C, Nova I, Tronconi E, et al. A “Nitrate Route” for the low temperature “Fast SCR” reaction over a V2O5-WO3/TiO2 commercial catalyst[J]. Chemical Communications, 2004, (23): 2718-2719. |
| 94 | Chen Z, Si Z, Cao L, et al. Decomposition behavior of ammonium nitrate on ceria catalysts and its role in the NH3-SCR reaction[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2017, 7(12): 2531-2541. |
| 95 | van der Grift C J G, Woldhuis A F, Maaskant O L. The shell DENOX system for low temperature NOx removal[J]. Catalysis Today, 1996, 27(1/2): 23-27. |
| 96 | 张霄玲, 鲍佳宁, 余剑, 等. 工业MnOx颗粒催化剂的制备及其低温脱硝应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 5169-5177. |
| Zhang X L, Bao J N, Yu J, et al. The preparation and industrial application of MnOx particle catalyst for low temperature denitration[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020,71(11): 5169-5177. | |
| 97 | 曾红, 刘平乐, 张喻升,等. 表面涂覆型低温脱硝催化剂的开发与中试应用[J]. 过程工程学报, 2017, 17(6): 1208-1216. |
| Zeng H, Liu P L, Zhang Y S, et al. Development and pilot test of surface-coating SCR de-nitration catalyst at low temperature[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2017, 17(6): 1208-1216. | |
| 98 | 皇甫林, 李长明, 王超, 等. 硅系黏结剂对涂覆型蜂窝体催化剂性能的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2020, 20(4): 484-492. |
| Huangfu L, Li C M, Wang C, et al. Effect of silicon-based binder on the performance of coated honeycomb catalyst[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2020, 20(4): 484-492. | |
| 99 | 赵勇刚, 董林, 李奇隽, 等. 低温脱硝催化剂在火电厂锅炉启动期间的中试应用[J]. 工业催化, 2018, 26(4): 64-71. |
| Zhao Y G, Dong L, Li Q J, et al. Pilot-scale application of low temperature deNOx catalyst for start-up of boiler in thermal power plant[J]. Industrial Catalysis, 2018, 26(4): 64-71. | |
| 100 | 王成志, 曹鹏, 颜鑫, 等. 中试规模下蜂窝式Mn-Ce/Al2O3脱硝催化剂的低温性能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(4):75-84. |
| Wang C Z, Cao P, Yan X, et al. Low temperature performance of honeycomb Mn-Ce/Al2O3 de-nitration catalyst in pilot-scale[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2018, 12(4):75-84. | |
| 101 | 唐志雄, 曾环木, 陈雄波, 等. 燃煤烟气低温SCR脱硝中试研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2014, 8(3): 1120-1124. |
| Tang Z X, Zeng H M, Chen X B, et al. Pilot-scale study of selective catalytic reduction of NOx at low temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2014, 8(3): 1120-1124. | |
| 102 | Wang C, Yu F, Zhu M, et al. Microspherical MnO2-CeO2-Al2O3 mixed oxide for monolithic honeycomb catalyst and application in selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 at 50-150℃[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 34: 182-192. |
| 103 | 科技部网站新闻稿. 国家863计划 “固定源烟气处理稀土催化材料的应用与开发” 课题在新疆石河子通过验收[EB/OL]. . |
| News release from website of Ministry of Science and Technology. The National 863 Program “Application and development of rare earth catalytic materials for flue gas treatment from stationary sources” was accepted in Shihezi, Xinjiang [EB/OL]. . |
| [1] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [2] | 张媛媛, 曲江源, 苏欣欣, 杨静, 张锴. 循环流化床燃煤机组SNCR脱硝过程气液传质和反应特性[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2404-2415. |
| [3] | 时国华, 何林珅, 赵玺灵, 张世钢. 余热回收喷淋塔的烟气颗粒物脱除特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1735-1745. |
| [4] | 王佳铭, 阮雪华, 贺高红. 面向不同工业二氧化碳分离体系的膜材料研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3417-3432. |
| [5] | 刘新华, 韩振南, 韩健, 梁斌, 张楠, 胡善伟, 白丁荣, 许光文. 基于热解与燃烧反应重构的低NO x 解耦燃烧原理与技术[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3355-3368. |
| [6] | 何聪, 钟文琪, 周冠文, 陈曦. 高海拔地区水泥生料悬浮炉分解特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2120-2129. |
| [7] | 季超, 刘炜, 漆虹. 基于空冷的疏水陶瓷膜冷凝器用于烟气脱湿过程强化的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2174-2182. |
| [8] | 李雪, 东明, 张璜, 谢俊. 潮湿环境下微尺度颗粒撞击平板的动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 1940-1946. |
| [9] | 刘轩, 苏银皎, 滕阳, 张锴, 王鹏程, 李丽锋, 李圳. 超低排放燃煤机组硒的迁移转化及飞灰对其富集特性[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 923-932. |
| [10] | 白浩隆, 付亮亮, 许光文, 白丁荣. 流化床煤燃烧过程不同气氛下的气态氮释放特征[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 876-886. |
| [11] | 赵旭, 卜昌盛, 王昕晔, 张鑫, 程晓磊, 王乃继, 朴桂林. 铁基载氧体辅助无烟煤焦富氧燃烧动力学分析[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 384-392. |
| [12] | 李泽严, 樊星, 李坚. 非热等离子体强化TiO2催化尿素分解副产物水解性能的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4698-4707. |
| [13] | 马志斌, 张森, 单雪媛, 郭彦霞, 程芳琴. 煤、煤泥和煤矸石燃烧过程锂镓稀土元素的迁移规律[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(6): 3349-3358. |
| [14] | 邱爽, 肖永厚, 刘建辉, 贺高红. 一步法制备高活性NH3-SCR催化剂Cu-SAPO-34:Si含量的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(5): 2578-2585. |
| [15] | 杨林, 孟小谜, 姚露, 赖雨果, 蒋文举. 天然矿物共混活性焦联合低温脱硫脱硝[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 2241-2248. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号