化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (12): 5672-5680.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200604
收稿日期:2020-05-18
修回日期:2020-08-31
出版日期:2020-12-05
发布日期:2020-12-05
通讯作者:
黄明忠
作者简介:赵立杰(1972—),女,博士,教授,基金资助:
ZHAO Lijie( ),WANG Jia,HUANG Mingzhong(
),WANG Jia,HUANG Mingzhong( ),WANG Guogang
),WANG Guogang
Received:2020-05-18
Revised:2020-08-31
Online:2020-12-05
Published:2020-12-05
Contact:
HUANG Mingzhong
摘要:
准确、可靠地测量污水处理厂的出水水质指标是成功控制和优化污水处理厂的关键。由于现有的离线化验方法存在操作繁复、测量滞后的问题,难以实现水质的实时控制。为了提高估计的准确性和可靠性,提出了一种偏最小二乘的随机配置网络方法(PLS-SCN)。为了克服输入数据高维度和多重共线性导致的预测风险,将偏最小二乘(PLS)方法嵌入到随机配置网络(SCN)框架中,以代替经典的普通最小二乘(OLS)方法。PLS-SCN方法从隐含层输出中提取影响水质指标的主要潜在变量,通过正交投影运算来增强泛化性能。某城市污水处理厂水质指标仿真结果表明,PLS-SCN网络具有良好的输入输出关系,性能优于传统SCN和PLS方法,能够快速、可靠地估计污水水质的质量。
中图分类号:
赵立杰,王佳,黄明忠,王国刚. 基于偏最小二乘随机配置网络的污水水质指标估计[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(12): 5672-5680.
ZHAO Lijie,WANG Jia,HUANG Mingzhong,WANG Guogang. Estimation of effluent quality index based on partial least squares stochastic configuration networks[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(12): 5672-5680.
水质 指标 | 训练 | 测试 | L | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCN | PLS-SCN | SCN | PLS-SCN | SCN | PLS-SCN | ||
| BOD | 10 | 3.59 | 3.59 | 3.44 | 3.44 | 10 | 10 |
| 30 | 2.76 | 2.94 | 3.33 | 3.30 | 30 | 30 | |
| 50 | 2.16 | 2.77 | 3.79 | 3.36 | 50 | 50 | |
| 70 | 1.73 | 2.72 | 3.96 | 3.21 | 70 | 70 | |
| 90 | 1.40 | 2.64 | 3.92 | 3.31 | 90 | 90 | |
| 110 | 1.16 | 2.62 | 4.34 | 3.18 | 110 | 110 | |
| 130 | 0.96 | 2.59 | 4.48 | 3.18 | 130 | 130 | |
| 150 | 0.81 | 2.61 | 4.78 | 3.15 | 150 | 150 | |
| 170 | 0.67 | 2.63 | 5.25 | 3.19 | 170 | 170 | |
| 190 | 0.53 | 2.59 | 6.03 | 3.20 | 190 | 190 | |
| NH | 10 | 3.57 | 3.66 | 3.25 | 3.33 | 10 | 10 |
| 30 | 2.53 | 2.69 | 2.80 | 2.81 | 30 | 30 | |
| 50 | 1.94 | 2.49 | 2.62 | 2.70 | 50 | 50 | |
| 70 | 1.60 | 2.43 | 2.82 | 2.65 | 70 | 70 | |
| 90 | 1.34 | 2.40 | 2.80 | 2.55 | 90 | 90 | |
| 110 | 1.12 | 2.35 | 3.51 | 2.49 | 110 | 110 | |
| 130 | 0.99 | 2.33 | 3.59 | 2.60 | 130 | 130 | |
| 150 | 0.85 | 2.34 | 3.82 | 2.53 | 150 | 150 | |
| 170 | 0.74 | 2.28 | 4.55 | 2.50 | 170 | 170 | |
| 190 | 0.64 | 2.35 | 5.37 | 2.47 | 189 | 190 | |
| COD | 10 | 10.00 | 10.02 | 12.55 | 12.58 | 10 | 10 |
| 30 | 7.86 | 8.23 | 12.16 | 12.19 | 30 | 30 | |
| 50 | 6.54 | 7.60 | 12.80 | 12.34 | 50 | 50 | |
| 70 | 5.60 | 7.47 | 14.10 | 12.21 | 70 | 70 | |
| 90 | 4.73 | 7.34 | 14.77 | 11.97 | 90 | 90 | |
| 110 | 3.97 | 7.31 | 16.10 | 11.88 | 110 | 110 | |
| 130 | 3.40 | 7.29 | 18.02 | 11.84 | 130 | 130 | |
| 150 | 2.85 | 7.20 | 18.98 | 11.83 | 150 | 150 | |
| 170 | 2.39 | 7.15 | 20.50 | 11.93 | 170 | 170 | |
| 190 | 2.00 | 7.17 | 24.20 | 11.69 | 190 | 190 | |
| SVI | 10 | 8.92 | 9.01 | 7.43 | 7.38 | 10 | 10 |
| 30 | 5.47 | 5.92 | 6.73 | 6.62 | 30 | 30 | |
| 50 | 4.02 | 5.45 | 7.17 | 6.58 | 50 | 50 | |
| 70 | 3.28 | 5.19 | 7.64 | 6.35 | 70 | 70 | |
| 90 | 2.63 | 5.10 | 7.71 | 6.14 | 90 | 90 | |
| 110 | 2.40 | 5.11 | 8.10 | 6.07 | 98 | 110 | |
| 130 | 2.40 | 5.03 | 8.31 | 5.99 | 98 | 130 | |
| 150 | 2.40 | 5.02 | 8.23 | 6.09 | 98 | 150 | |
| 170 | 2.40 | 4.98 | 8.47 | 5.95 | 99 | 170 | |
| 190 | 2.40 | 5.12 | 8.29 | 5.89 | 100 | 190 | |
表1 水质指标PLS-SCN模型和SCN模型均方根误差对比
Table 1 RMSE comparison of effluent quality indexes for PLS-SCN and SCN model
水质 指标 | 训练 | 测试 | L | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCN | PLS-SCN | SCN | PLS-SCN | SCN | PLS-SCN | ||
| BOD | 10 | 3.59 | 3.59 | 3.44 | 3.44 | 10 | 10 |
| 30 | 2.76 | 2.94 | 3.33 | 3.30 | 30 | 30 | |
| 50 | 2.16 | 2.77 | 3.79 | 3.36 | 50 | 50 | |
| 70 | 1.73 | 2.72 | 3.96 | 3.21 | 70 | 70 | |
| 90 | 1.40 | 2.64 | 3.92 | 3.31 | 90 | 90 | |
| 110 | 1.16 | 2.62 | 4.34 | 3.18 | 110 | 110 | |
| 130 | 0.96 | 2.59 | 4.48 | 3.18 | 130 | 130 | |
| 150 | 0.81 | 2.61 | 4.78 | 3.15 | 150 | 150 | |
| 170 | 0.67 | 2.63 | 5.25 | 3.19 | 170 | 170 | |
| 190 | 0.53 | 2.59 | 6.03 | 3.20 | 190 | 190 | |
| NH | 10 | 3.57 | 3.66 | 3.25 | 3.33 | 10 | 10 |
| 30 | 2.53 | 2.69 | 2.80 | 2.81 | 30 | 30 | |
| 50 | 1.94 | 2.49 | 2.62 | 2.70 | 50 | 50 | |
| 70 | 1.60 | 2.43 | 2.82 | 2.65 | 70 | 70 | |
| 90 | 1.34 | 2.40 | 2.80 | 2.55 | 90 | 90 | |
| 110 | 1.12 | 2.35 | 3.51 | 2.49 | 110 | 110 | |
| 130 | 0.99 | 2.33 | 3.59 | 2.60 | 130 | 130 | |
| 150 | 0.85 | 2.34 | 3.82 | 2.53 | 150 | 150 | |
| 170 | 0.74 | 2.28 | 4.55 | 2.50 | 170 | 170 | |
| 190 | 0.64 | 2.35 | 5.37 | 2.47 | 189 | 190 | |
| COD | 10 | 10.00 | 10.02 | 12.55 | 12.58 | 10 | 10 |
| 30 | 7.86 | 8.23 | 12.16 | 12.19 | 30 | 30 | |
| 50 | 6.54 | 7.60 | 12.80 | 12.34 | 50 | 50 | |
| 70 | 5.60 | 7.47 | 14.10 | 12.21 | 70 | 70 | |
| 90 | 4.73 | 7.34 | 14.77 | 11.97 | 90 | 90 | |
| 110 | 3.97 | 7.31 | 16.10 | 11.88 | 110 | 110 | |
| 130 | 3.40 | 7.29 | 18.02 | 11.84 | 130 | 130 | |
| 150 | 2.85 | 7.20 | 18.98 | 11.83 | 150 | 150 | |
| 170 | 2.39 | 7.15 | 20.50 | 11.93 | 170 | 170 | |
| 190 | 2.00 | 7.17 | 24.20 | 11.69 | 190 | 190 | |
| SVI | 10 | 8.92 | 9.01 | 7.43 | 7.38 | 10 | 10 |
| 30 | 5.47 | 5.92 | 6.73 | 6.62 | 30 | 30 | |
| 50 | 4.02 | 5.45 | 7.17 | 6.58 | 50 | 50 | |
| 70 | 3.28 | 5.19 | 7.64 | 6.35 | 70 | 70 | |
| 90 | 2.63 | 5.10 | 7.71 | 6.14 | 90 | 90 | |
| 110 | 2.40 | 5.11 | 8.10 | 6.07 | 98 | 110 | |
| 130 | 2.40 | 5.03 | 8.31 | 5.99 | 98 | 130 | |
| 150 | 2.40 | 5.02 | 8.23 | 6.09 | 98 | 150 | |
| 170 | 2.40 | 4.98 | 8.47 | 5.95 | 99 | 170 | |
| 190 | 2.40 | 5.12 | 8.29 | 5.89 | 100 | 190 | |
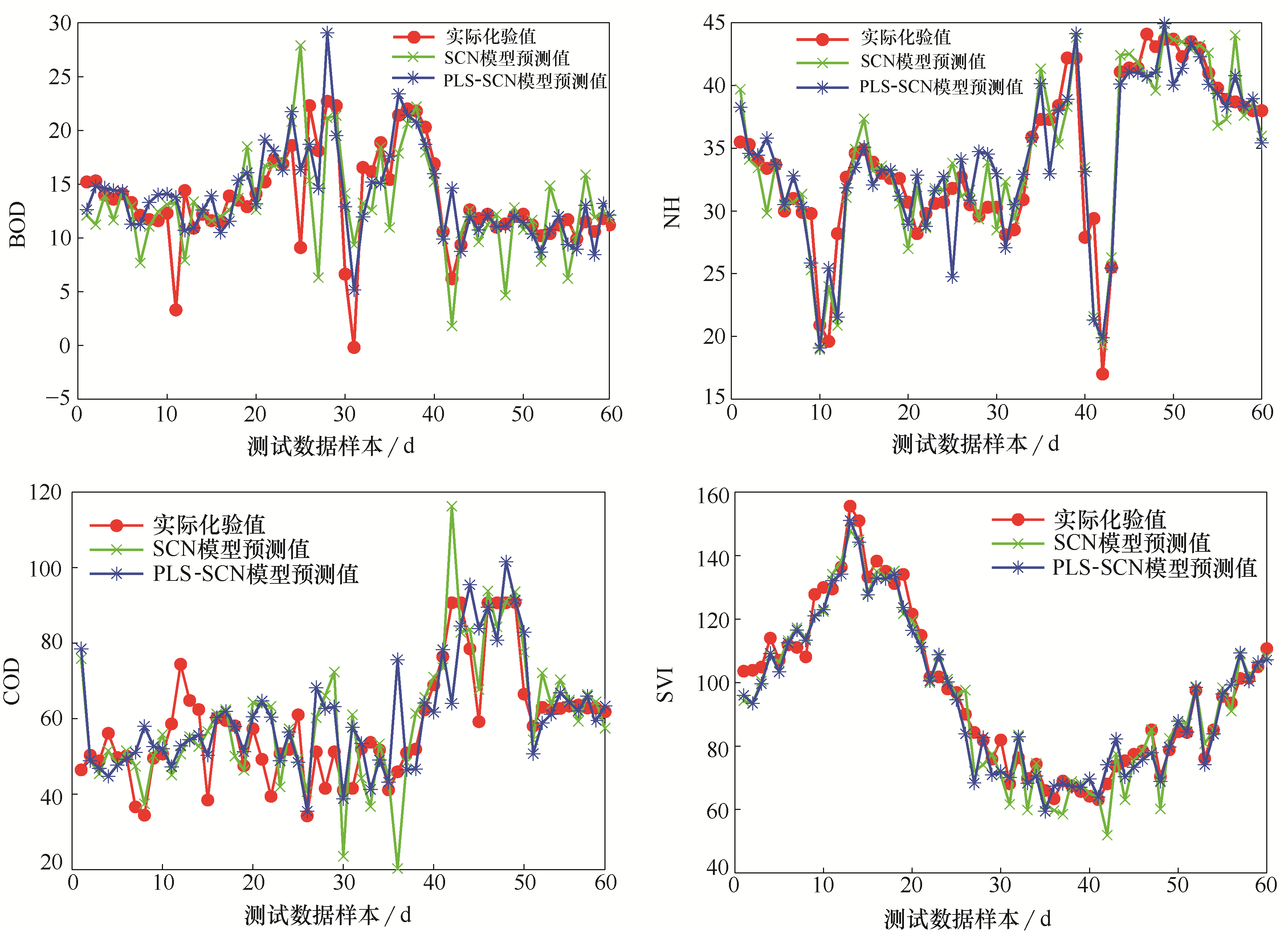
图6 水质指标预测对比ORP1 —— 缺氧池氧化还原电位,mVORP2 —— 好氧池氧化还原电位,mVQair —— 曝气池曝气流量,m3?d-1Qi —— 进水流量,m3?d-1Qr —— 回流污泥流量,m3?d-1SV —— 生化池污泥体积,mg?L-1SVI —— 生化池污泥体积指数,ml?g-1Zb,pH —— 生化池pHZe,BOD —— 出水BOD5浓度,mg?L-1Ze,COD —— 出水COD浓度,mg?L-1Ze,NH —— 出水氨氮浓度,mg?L-1Ze,SS —— 出水SS浓度,mg?L-1Zi,COD —— 进水COD浓度,mg?L-1Zi,NH —— 进水氨氮浓度,mg?L-1Zi,pH —— 进水pHZi,SS —— 进水SS浓度,mg?L-1Zp,COD —— 配水计量槽COD浓度,mg?L-1Zp,SS —— 配水计量槽悬浮物浓度,mg?L-1
Fig.6 Prediction comparison of effluent quality index
| 建模方法 | RMSE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOD | NH | COD | SVI | |
| PLS | 3.36 | 3.48 | 12.90 | 6.67 |
| PLS-ELM | 3.10 | 2.69 | 11.31 | 6.07 |
| SVR | 3.43 | 3.52 | 13.26 | 6.37 |
| PLS-NN | 3.12 | 3.13 | 11.40 | 7.62 |
| PLS-SCN | 3.15 | 2.47 | 11.69 | 5.89 |
表2 不同建模方法水质指标测试性能均方根误差对比
Table 2 Comparison of root mean square error of water quality index test performance of different modeling methods
| 建模方法 | RMSE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOD | NH | COD | SVI | |
| PLS | 3.36 | 3.48 | 12.90 | 6.67 |
| PLS-ELM | 3.10 | 2.69 | 11.31 | 6.07 |
| SVR | 3.43 | 3.52 | 13.26 | 6.37 |
| PLS-NN | 3.12 | 3.13 | 11.40 | 7.62 |
| PLS-SCN | 3.15 | 2.47 | 11.69 | 5.89 |
| 2 | 余杰, 田宁宁, 王凯军, 等. 中国城市污水处理厂污泥处理、处置问题探讨分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2007, 1(1): 82-86. |
| Yu J, Tian N N, Wang K J, et al. Analysis and discussion of sludge disposal and treatment of sewage treatment plants in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2007, 1(1): 82-86. | |
| 3 | Kabouris J C. Modeling, instrumentation, automation, and optimization of wastewater treatment facilities[J]. Water Environment Research, 1999, 70(4): 772-827. |
| 4 | 乌尔松. 污水处理系统的建模、诊断和控制[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2004. |
| Urson. Modeling, Diagnosis and Control of Sewage Treatment System[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2004. | |
| 5 | Zhao L J, Yuan D C, Tang J, et al. Nonlinear robust PLS modeling of wastewater effluent quality indices[J]. Journal of Software, 2011, 6(6): 1067-1074. |
| 6 | 乔俊飞, 李瑞祥, 柴伟, 等. 基于PSO-ESN神经网络的污水BOD预测[J]. 控制工程, 2016, 23(4): 463-467. |
| Qiao J F, Li R X, Chai W, et al. Prediction of BOD based on PSO-ESN neural network [J]. Control Engineering, 2016, 23(4): 463-467. | |
| 7 | Han H G, Liu Z, Ge L M, et al. Prediction of sludge bulking using the knowledge-leverage-based fuzzy neural network[J]. Water Science & Technology, 2018, 77(3/4): 617-627. |
| 8 | 赵立杰, 柴天佑, 黄肖玲. 城市污水处理过程综合自动化系统及其应用[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2005, 11(1): 138-144. |
| Zhao L J, Chai T Y, Huang X L. Integrated automation system of municipal wastewater treatment plant and its applications[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing System, 2005, 11(1): 138-144. | |
| 9 | Mogens H, Willi G, Takahashi M, et al. Activated sludge model No. 2d, ASM2d[J]. Water Science & Technology, 1999, 39(1): 165-182. |
| 1 | Du X J, Hao X H, Li H J, et al. Study on modeling and simulation of wastewater biochemical treatment activated sludge process[J]. Asian Journal of Chemistry, 2011, 23(10): 4457-4460. |
| 10 | 黄道平, 刘乙奇, 李艳. 软测量在污水处理过程中的研究与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2011, 62(1): 1-9. |
| Huang D P, Liu Y Q, Li Y. Soft sensor research and its application in wastewater treatment[J]. CIESC Journal, 2011, 62(1): 1-9. | |
| 11 | Sharmin R, Sundararaj U, Shah S, et al. Inferential sensors for estimation of polymer quality parameters: industrial application of a PLS-based soft sensor for a LDPE plant[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2006, 61(19): 6372-6384. |
| 12 | Duerrenmatt D J, Gujer W. Data-driven modeling approaches to support wastewater treatment plant operation[J]. Environmental Modeling & Software, 2012, 30: 47-56. |
| 13 | Zhao L J, Chai T Y. Wastewater BOD forecasting model for optimal operation using robust time-delay neural network[J]. Letter Notes in Computer Science, 2005, 3498: 1028-1033. |
| 14 | Woo S H, Jeon C O, Yun Y S, et al. On-line estimation of key process variables based on kernel partial least squares in an industrial cokes wastewater treatment plant[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161(1): 538-544. |
| 15 | Lee D S, Jeon C O, Park J M, et al. Hybrid neural network modeling of a full-scale industrial wastewater treatment process[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 2010, 78(6): 670-682. |
| 16 | Tomida S, Hanai T, Honda H, et al. Construction of COD simulation model for activated sludge process by recursive fuzzy neural network[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 1999, 88(2): 215-220. |
| 17 | Fang F, Ni B J, Li W W, et al. A simulation-based integrated approach to optimize the biological nutrient removal process in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 174(2/3): 635-643. |
| 18 | Zhao L J, Wang D H, Chai T Y. Estimation of effluent quality using PLS-based extreme learning machines[J]. Neural Computing & Applications, 2013, 22(3/4): 509-519. |
| 19 | Wang D H, Li M. Stochastic configuration networks: fundamentals and algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(10): 3466-3479. |
| 20 | 赵立杰. 生物脱氮污水处理过程建模和优化控制若干问题研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2006. |
| Zhao L J. Research on the issues of the modeling and optimization control for wastewater treatment plant with biological nitrogen removal[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2006. | |
| 21 | 高晓波. 分段进水AO生物脱氮工艺优化运行研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2013. |
| Gao X B. Study on the optimal operation of the step feeding AO nitrogen removal process[D]. Xian: Changan University, 2013. | |
| 22 | 赵立杰, 袁德成, 柴天佑. 基于多分类概率极限学习机的污水处理过程操作工况识别[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(10): 3173-3182. |
| Zhao L J, Yuan D C, Chai T Y. Identification of wastewater operational conditions based on multi-classification probabilistic extreme learning machine[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(10): 3173-3182. | |
| 23 | Cao Z P, Li J, Zhang H. Influence of solid retention time on sludge characteristics and effluent quality in immersed membrane bioreactor [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(24): 3942-3950. |
| 24 | Doederer K, Gernjak W, Weinberg H S, et al. Factors affecting the formation of disinfection by-products during chlorination and chloramination of secondary effluent for the production of high quality recycled water[J]. Water Research, 2014, 48: 218-228. |
| 25 | 丛秋梅, 苑明哲, 王宏. 基于稳定Hammerstein模型的在线软测量建模方法及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(4): 1378-1387. |
| Cong Q M, Yuan M Z, Wang H. On-line soft sensor based on stable Hammerstein model and its applications[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(4): 1378-1387. | |
| 26 | Wang D H, Li M. Robust stochastic configuration networks with kernel density estimation for uncertain data regression[J]. Information Sciences, 2017, 412/413: 210-222. |
| 27 | Wang D H, Cui C H. Stochastic configuration networks ensemble with heterogeneous features for large-scale data analytics[J]. Information Sciences, 2017, 417: 55-71. |
| 28 | Barker M, Rayens W. Partial least squares for discrimination[J]. Journal of Chemometrics, 2003, 17(3): 166-173. |
| 29 | Geladi P, Kowalski B R. Partial least-squares regression: a tutorial[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1986, 185: 1-17. |
| 30 | Sijmen D J. SIMPLS: an alternative approach to partial least squares regression[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 1993, 18(3): 251-263. |
| [1] | 温凯杰, 郭力, 夏诏杰, 陈建华. 一种耦合CFD与深度学习的气固快速模拟方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3775-3785. |
| [2] | 诸程瑛, 王振雷. 基于改进深度强化学习的乙烯裂解炉操作优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3429-3437. |
| [3] | 闫琳琦, 王振雷. 基于STA-BiLSTM-LightGBM组合模型的多步预测软测量建模[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3407-3418. |
| [4] | 尹刚, 李伊惠, 何飞, 曹文琦, 王民, 颜非亚, 向禹, 卢剑, 罗斌, 卢润廷. 基于KPCA和SVM的铝电解槽漏槽事故预警方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3419-3428. |
| [5] | 徐野, 黄文君, 米俊芃, 申川川, 金建祥. 多源信息融合的离心式压缩机喘振诊断方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2979-2987. |
| [6] | 郭雨莹, 敬加强, 黄婉妮, 张平, 孙杰, 朱宇, 冯君炫, 陆洪江. 稠油管道水润滑减阻及压降预测模型修正[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2898-2907. |
| [7] | 于源, 陈薇薇, 付俊杰, 刘家祥, 焦志伟. 几何相似涡流空气分级机环形区流场变化规律研究及预测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2363-2373. |
| [8] | 陈朝光, 贾玉香, 汪锰. 以低浓度废酸驱动中和渗析脱盐的模拟与验证[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [9] | 高学金, 姚玉卓, 韩华云, 齐咏生. 基于注意力动态卷积自编码器的发酵过程故障监测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2503-2521. |
| [10] | 李艳辉, 丁邵明, 白周央, 张一楠, 于智红, 邢利梅, 高鹏飞, 王永贞. 非常规服役超临界锅炉的微纳尺度腐蚀动力学模型建立及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2436-2446. |
| [11] | 黄磊, 孔令学, 白进, 李怀柱, 郭振兴, 白宗庆, 李平, 李文. 油页岩添加对准东高钠煤灰熔融行为影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2123-2135. |
| [12] | 贠程, 王倩琳, 陈锋, 张鑫, 窦站, 颜廷俊. 基于社团结构的化工过程风险演化路径深度挖掘[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1639-1650. |
| [13] | 罗来明, 张劲, 郭志斌, 王海宁, 卢善富, 相艳. 1~5 kW高温聚合物电解质膜燃料电池堆的理论模拟与组装测试[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1724-1734. |
| [14] | 张中秋, 李宏光, 石逸林. 基于人工预测调控策略的复杂化工过程多任务学习方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1195-1204. |
| [15] | 张江淮, 赵众. 碳三加氢装置鲁棒最小协方差约束控制及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1216-1227. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号