化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (4): 1724-1734.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221589
罗来明1( ), 张劲1, 郭志斌2, 王海宁1, 卢善富1(
), 张劲1, 郭志斌2, 王海宁1, 卢善富1( ), 相艳1
), 相艳1
收稿日期:2022-12-09
修回日期:2023-03-02
出版日期:2023-04-05
发布日期:2023-06-02
通讯作者:
卢善富
作者简介:罗来明(1993—),男,博士研究生,luolaiming2018@126.com
基金资助:
Laiming LUO1( ), Jin ZHANG1, Zhibin GUO2, Haining WANG1, Shanfu LU1(
), Jin ZHANG1, Zhibin GUO2, Haining WANG1, Shanfu LU1( ), Yan XIANG1
), Yan XIANG1
Received:2022-12-09
Revised:2023-03-02
Online:2023-04-05
Published:2023-06-02
Contact:
Shanfu LU
摘要:
以大尺寸单电池(有效工作面积为165 cm2)和多片单电池组装而成的电堆为研究对象,通过数值模拟和实验测试相结合的方法探究了单电池数量对高温聚合物电解质膜燃料电池堆输出性能、单池一致性和热管理的影响。模拟结果显示,当电堆的单池数量从10片增加至60片时,平均单池电压从0.6414 V略微降低至0.6404 V,且单池之间电压极差从1.8 mV增加至6.5 mV;单池间的平均工作温度从431.01 K升高至433.90 K,且每单池自身工作温度的极差从6.95 K增加至10.22 K。表明随着电堆单池数量的增加,电堆的平均单池电压呈轻微下降趋势,且单池间电压极差变大,单池电压一致性有所下降,单池间的温差变大,其单池自身的均温一致性也有所降低,电堆热管理难度增加。在模拟结果的指导下分别组装了30、60和120片单池的高温膜燃料电池堆,在氢/空干气、33 A的恒流放电条件下,测得30、60和120片单池电堆的平均单池电压分别为0.6566、0.6548和0.6552 V,单池极差从24 mV增加到59 mV,与模拟结果显示出良好的一致性,验证了模拟结果的有效性。在氢/空干气计量系数为1.5/2.5的操作条件下,展示出了优异的输出性能,三个电堆在80 A电流放电时的输出功率分别达到1.35、2.64和5.28 kW。研究结果可为千瓦级高温聚合物电解质膜燃料电池堆的设计和组装测试提供理论和实践指导。
中图分类号:
罗来明, 张劲, 郭志斌, 王海宁, 卢善富, 相艳. 1~5 kW高温聚合物电解质膜燃料电池堆的理论模拟与组装测试[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1724-1734.
Laiming LUO, Jin ZHANG, Zhibin GUO, Haining WANG, Shanfu LU, Yan XIANG. Simulation and experiment of high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells stack in the 1—5 kW range[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1724-1734.
| 几何参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 单池数量 | 10~60 |
| 膜电极长度/mm | 176.55 |
| 膜电极宽度/mm | 93.65 |
| 膜电极面积/cm2 | 165 |
| 气体扩散电极厚度/μm | 430 |
| 质子交换膜厚度/μm | 40 |
| 密封圈厚度/mm | 0.9 |
| 石墨双极板厚度/mm | 2.5 |
| 金属端板厚度/mm | 20 |
表1 HT-PEMFCs电堆模型几何参数
Table 1 Geometry parameters of HT-PEMFCs stack model
| 几何参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 单池数量 | 10~60 |
| 膜电极长度/mm | 176.55 |
| 膜电极宽度/mm | 93.65 |
| 膜电极面积/cm2 | 165 |
| 气体扩散电极厚度/μm | 430 |
| 质子交换膜厚度/μm | 40 |
| 密封圈厚度/mm | 0.9 |
| 石墨双极板厚度/mm | 2.5 |
| 金属端板厚度/mm | 20 |

图2 电堆(60片)模型网格划分示意图和三视图(俯视图,左视图和前视图)(单位:m)
Fig.2 Grid schematic diagram and three views (top view, left view and front view) of stack model (60 cells)
| 边界条件和物性参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 氢气摩尔分数 | 1.0 |
| 氧气摩尔分数 | 0.21 |
| 氮气摩尔分数 | 0.79 |
| 氢气/空气(计量比) | 1.5/2.5 |
| 氢空及冷却液进口温度/℃ | 150 |
| 氢空及冷却液出口压力/Pa | 101325 |
| 阳极参考交换电流密度/(A/m2) | 102 |
| 阴极参考交换电流密度/(A/m2) | 10-3 |
| 催化层比表面积/ m-1 | 3×105 |
| 气体扩散层孔隙率 | 0.4 |
| 催化层孔隙率 | 0.3 |
| 气体扩散层渗透率/ m2 | 1.18×10-11 |
| 催化层渗透率/ m2 | 2.36×10-12 |
| 气体扩散电极电导率/(S/m) | 222 |
| 质子交换膜电导率/(S/m) | 7.64 |
| 氢气参考浓度/(mol/m3) | 40.88 |
| 氧气参考浓度/(mol/m3) | 40.88 |
表2 HT-PEMFCs电堆模型边界条件和物性参数
Table 2 Boundary conditions and physical parameters of HT-PEMFCs stack model
| 边界条件和物性参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 氢气摩尔分数 | 1.0 |
| 氧气摩尔分数 | 0.21 |
| 氮气摩尔分数 | 0.79 |
| 氢气/空气(计量比) | 1.5/2.5 |
| 氢空及冷却液进口温度/℃ | 150 |
| 氢空及冷却液出口压力/Pa | 101325 |
| 阳极参考交换电流密度/(A/m2) | 102 |
| 阴极参考交换电流密度/(A/m2) | 10-3 |
| 催化层比表面积/ m-1 | 3×105 |
| 气体扩散层孔隙率 | 0.4 |
| 催化层孔隙率 | 0.3 |
| 气体扩散层渗透率/ m2 | 1.18×10-11 |
| 催化层渗透率/ m2 | 2.36×10-12 |
| 气体扩散电极电导率/(S/m) | 222 |
| 质子交换膜电导率/(S/m) | 7.64 |
| 氢气参考浓度/(mol/m3) | 40.88 |
| 氧气参考浓度/(mol/m3) | 40.88 |
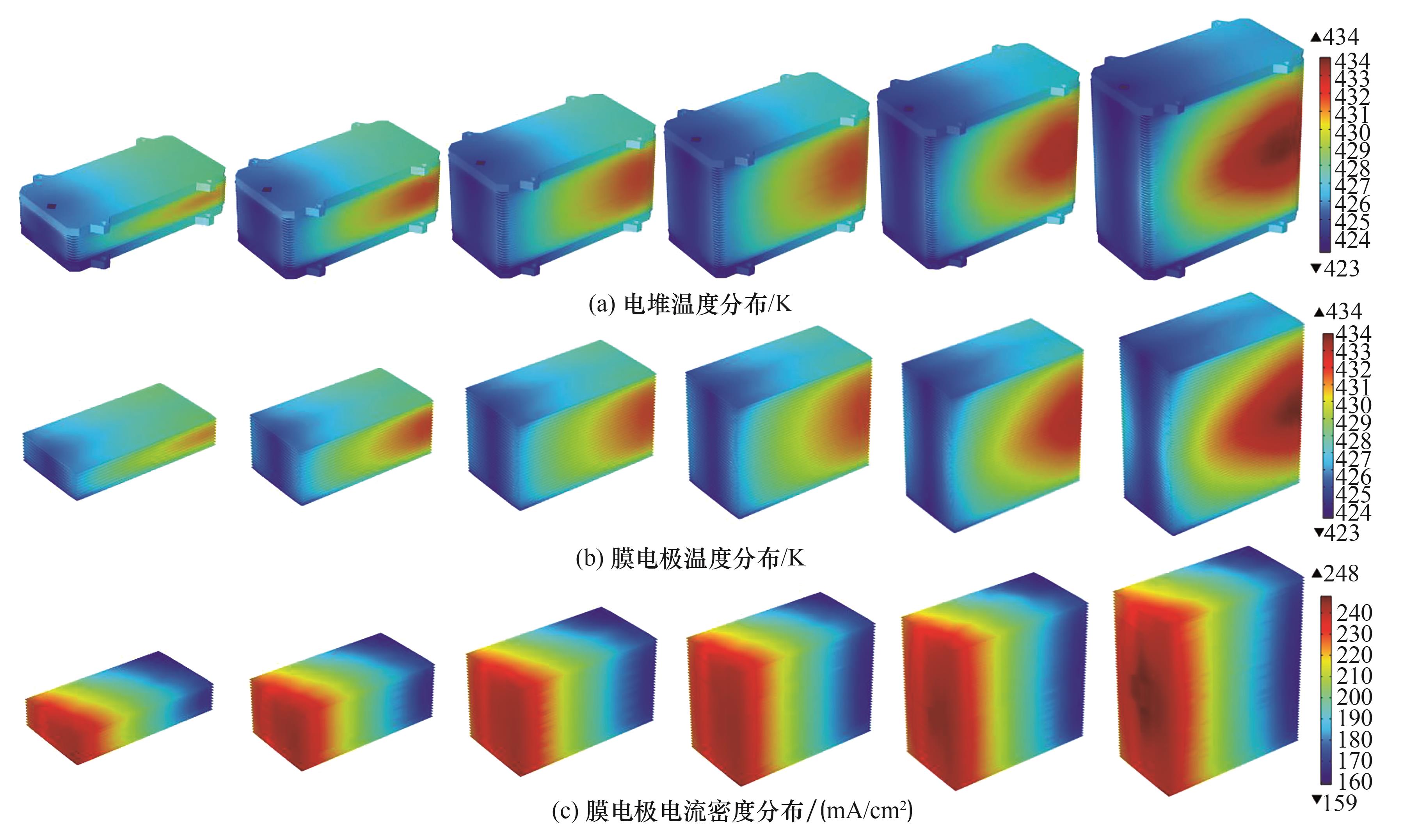
图4 不同单池数量(从左至右10~60片)的电堆温度分布(a)、膜电极温度分布(b)以及膜电极电流密度分布(c)
Fig.4 The stacks temperature distribution (a), MEA temperature distribution (b) and current density distribution on the MEA reaction interface (c) of different single cell numbers (10—60 cells from left to right)
| 电堆单池 数量 | 输出 电压/V | 输出 功率/W | 膜电极 最高温度/K | 膜电极 最低温度/K | 膜电极 温差/K | 氢气流道 压降/Pa | 空气流道 压降/Pa | 冷却液流道 压降/Pa | 空压机和泵的 寄生功耗/W | 净输出 功率/W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 6.41 | 211.66 | 431.01 | 424.06 | 6.95 | 69.07 | 913.30 | 2918.01 | 0.47 | 211.19 |
| 20 | 12.82 | 423.16 | 431.91 | 423.97 | 7.94 | 69.17 | 913.40 | 4021.40 | 0.99 | 422.17 |
| 30 | 19.23 | 634.72 | 431.90 | 423.87 | 8.03 | 69.11 | 913.61 | 5994.63 | 1.61 | 633.11 |
| 40 | 25.64 | 846.15 | 431.91 | 423.80 | 8.11 | 69.18 | 915.38 | 8726.89 | 2.38 | 843.77 |
| 50 | 32.04 | 1057.45 | 432.64 | 423.72 | 8.92 | 69.29 | 915.84 | 12885.26 | 3.41 | 1054.04 |
| 60 | 38.42 | 1267.93 | 433.90 | 423.68 | 10.22 | 69.33 | 917.95 | 19512.85 | 4.92 | 1263.00 |
表3 不同单池数量对电堆模型物理场参数的影响
Table 3 Effect of different single cell numbers on the physical parameters of stacks
| 电堆单池 数量 | 输出 电压/V | 输出 功率/W | 膜电极 最高温度/K | 膜电极 最低温度/K | 膜电极 温差/K | 氢气流道 压降/Pa | 空气流道 压降/Pa | 冷却液流道 压降/Pa | 空压机和泵的 寄生功耗/W | 净输出 功率/W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 6.41 | 211.66 | 431.01 | 424.06 | 6.95 | 69.07 | 913.30 | 2918.01 | 0.47 | 211.19 |
| 20 | 12.82 | 423.16 | 431.91 | 423.97 | 7.94 | 69.17 | 913.40 | 4021.40 | 0.99 | 422.17 |
| 30 | 19.23 | 634.72 | 431.90 | 423.87 | 8.03 | 69.11 | 913.61 | 5994.63 | 1.61 | 633.11 |
| 40 | 25.64 | 846.15 | 431.91 | 423.80 | 8.11 | 69.18 | 915.38 | 8726.89 | 2.38 | 843.77 |
| 50 | 32.04 | 1057.45 | 432.64 | 423.72 | 8.92 | 69.29 | 915.84 | 12885.26 | 3.41 | 1054.04 |
| 60 | 38.42 | 1267.93 | 433.90 | 423.68 | 10.22 | 69.33 | 917.95 | 19512.85 | 4.92 | 1263.00 |
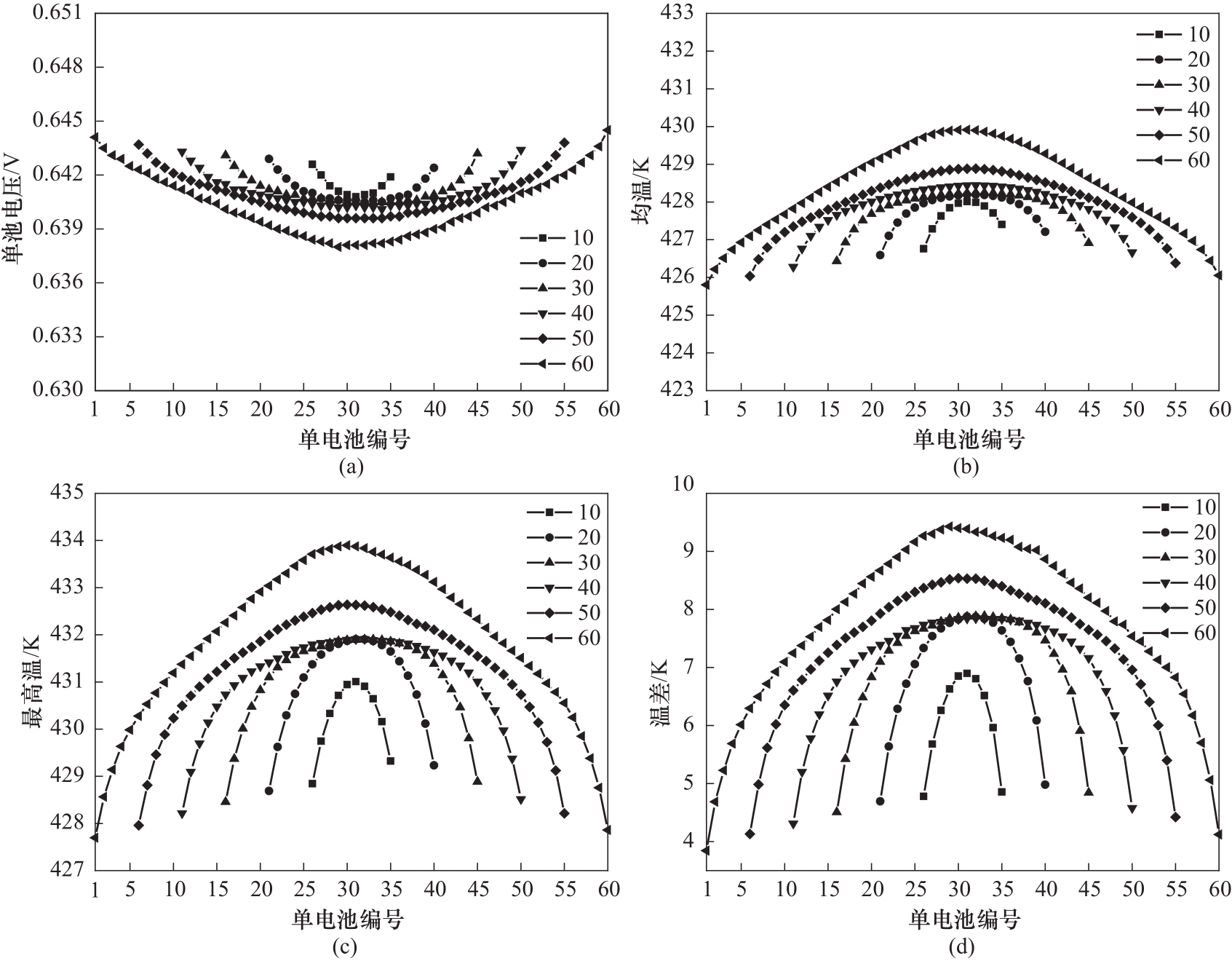
图5 不同单池数量电堆的电压一致性(a),膜电极均温、最高温以及温差一致性[(b)~(d)]
Fig.5 Voltage consistency (a), MEA average temperature, maximum temperature and temperature difference consistency of stacks with different single cell numbers [(b)—(d)]
| 电堆单池数量 | 平均 电压/mV | 标准偏差 | 最高单池 电压/mV | 最低单池 电压/mV | 极差/mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.6414 | 5.93×10-4 | 0.6426 | 0.6408 | 1.8 |
| 20 | 0.6412 | 7.16×10-4 | 0.6429 | 0.6405 | 2.4 |
| 30 | 0.6411 | 7.75×10-4 | 0.6432 | 0.6405 | 2.7 |
| 40 | 0.6410 | 8.89×10-4 | 0.6434 | 0.6401 | 3.3 |
| 50 | 0.6409 | 1.17×10-3 | 0.6438 | 0.6396 | 4.2 |
| 60 | 0.6404 | 1.77×10-3 | 0.6445 | 0.6380 | 6.5 |
表4 不同单池数量对电堆单池电压一致性的影响
Table 4 Effect of different single cell numbers on the voltage consistency of stacks
| 电堆单池数量 | 平均 电压/mV | 标准偏差 | 最高单池 电压/mV | 最低单池 电压/mV | 极差/mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.6414 | 5.93×10-4 | 0.6426 | 0.6408 | 1.8 |
| 20 | 0.6412 | 7.16×10-4 | 0.6429 | 0.6405 | 2.4 |
| 30 | 0.6411 | 7.75×10-4 | 0.6432 | 0.6405 | 2.7 |
| 40 | 0.6410 | 8.89×10-4 | 0.6434 | 0.6401 | 3.3 |
| 50 | 0.6409 | 1.17×10-3 | 0.6438 | 0.6396 | 4.2 |
| 60 | 0.6404 | 1.77×10-3 | 0.6445 | 0.6380 | 6.5 |
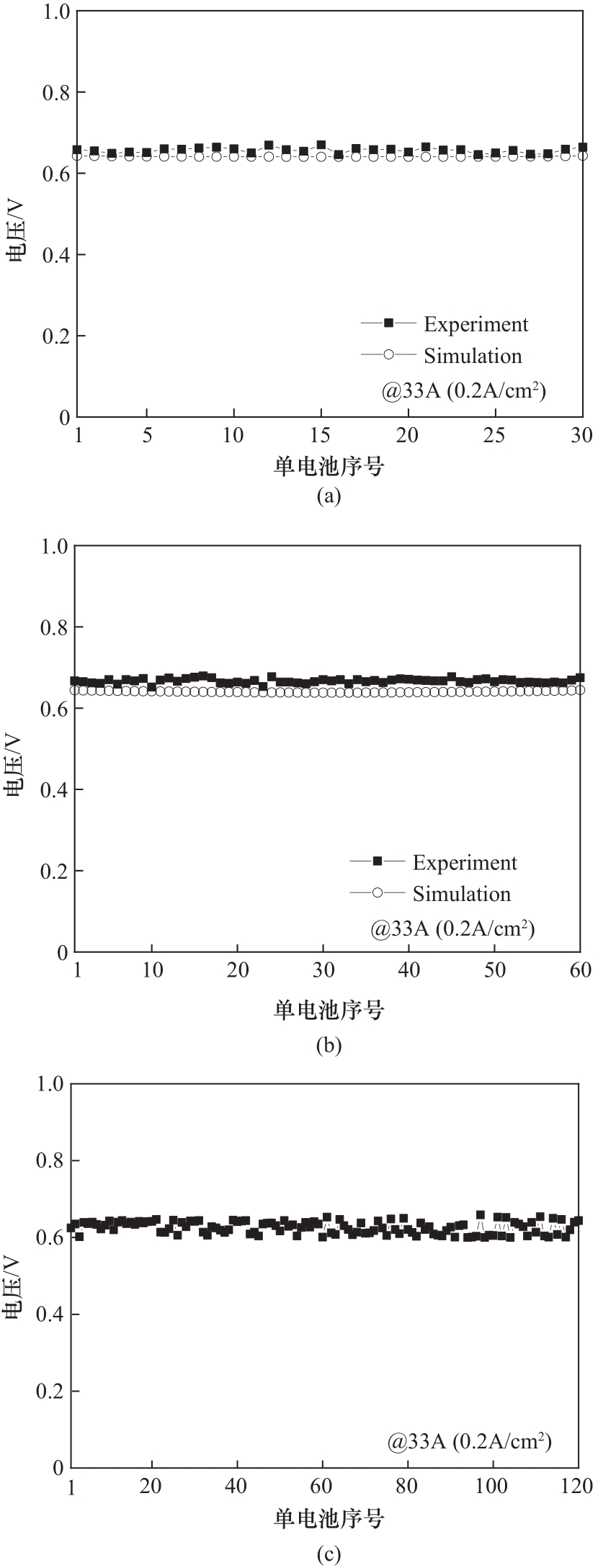
图7 30(a)和60(b)片单池电堆实验和模拟的电压一致性以及120片单池电堆实验测试电压一致性曲线(c)
Fig.7 Experimental and simulation voltage consistency curves for 30 (a) and 60 (b) cells stacks, and experimental voltage consistency curve of 120 cells stack (c)
| 电堆单池 数量 | 平均 电压/mV | 标准 偏差 | 最高单池 电压/mV | 最低单池 电压/mV | 极差/mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | |||||
| 实验 | 0.6566 | 6.51×10-3 | 0.6700 | 0.6460 | 24 |
| 模拟 | 0.6411 | 7.75×10-4 | 0.6432 | 0.6405 | 2.7 |
| 60 | |||||
| 实验 | 0.6548 | 5.48×10-3 | 0.6790 | 0.6520 | 27 |
| 模拟 | 0.6404 | 1.77×10-3 | 0.6445 | 0.6380 | 6.5 |
| 120 | |||||
| 实验 | 0.6552 | 1.62×10-2 | 0.6590 | 0.6000 | 59 |
表5 30和60片单池电堆(实验和模拟)以及120片单池电堆(实验测试)电压一致性参数
Table 5 Voltage consistency parameters of 30 and 60 cells stacks (experiment and simulation), and 120 cells stack (experiment)
| 电堆单池 数量 | 平均 电压/mV | 标准 偏差 | 最高单池 电压/mV | 最低单池 电压/mV | 极差/mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | |||||
| 实验 | 0.6566 | 6.51×10-3 | 0.6700 | 0.6460 | 24 |
| 模拟 | 0.6411 | 7.75×10-4 | 0.6432 | 0.6405 | 2.7 |
| 60 | |||||
| 实验 | 0.6548 | 5.48×10-3 | 0.6790 | 0.6520 | 27 |
| 模拟 | 0.6404 | 1.77×10-3 | 0.6445 | 0.6380 | 6.5 |
| 120 | |||||
| 实验 | 0.6552 | 1.62×10-2 | 0.6590 | 0.6000 | 59 |
| 1 | Asensio F J, San Martín J I, Zamora I, et al. Model for optimal management of the cooling system of a fuel cell-based combined heat and power system for developing optimization control strategies[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 211: 413-430. |
| 2 | Amirfazli A, Asghari S, Koosha M. Mathematical modeling and simulation of thermal management in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell stacks[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 268: 533-545. |
| 3 | 李友才, 许思传, 杨宗田, 等. 燃料电池电堆冷却液加热的实验研究[J]. 电源技术, 2015, 39(7): 1408-1410. |
| Li Y C, Xu S C, Yang Z T, et al. Experiment study of coolant heated on automobile PEMFC[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 39(7): 1408-1410. | |
| 4 | 张巨佳, 张劲, 王海宁, 等. 高温聚合物电解质膜燃料电池膜电极中磷酸分布及调控策略研究进展[J]. 物理化学学报, 2021, 37(9): 172-186. |
| Zhang J J, Zhang J, Wang H N, et al. Advancement in distribution and control strategy of phosphoric acid in membrane electrode assembly of high-temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2021, 37(9): 172-186. | |
| 5 | Zhang J J, Wang H N, Li W, et al. Effect of catalyst layer microstructures on performance and stability for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 505: 230059. |
| 6 | Zhang J J, Bai H J, Yan W R, et al. Enhancing cell performance and durability of high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells by inhibiting the formation of cracks in catalyst layers[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(11): 114501. |
| 7 | Janßen H, Supra J, Lüke L, et al. Development of HT-PEFC stacks in the kW range[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(11): 4705-4713. |
| 8 | 张浩, 杨代军, 李冰, 等. 国产质子交换膜燃料电池电堆研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2012, 33(7): 1248-1252. |
| Zhang H, Yang D J, Li B, et al. Investigation of a home-made PEMFC stack[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2012, 33(7): 1248-1252. | |
| 9 | Huang F X, Qiu D K, Lan S H, et al. Performance evaluation of commercial-size proton exchange membrane fuel cell stacks considering air flow distribution in the manifold[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 203: 112256. |
| 10 | Devrim Y, Devrim H, Eroglu I. Development of 500W PEM fuel cell stack for portable power generators[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(24): 7707-7719. |
| 11 | López-Sabirón A M, Barroso J, Roda V, et al. Design and development of the cooling system of a 2 kW nominal power open-cathode polymer electrolyte fuel cell stack[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(8): 7289-7298. |
| 12 | 倪蕾蕾. 5kW级质子交换膜燃料电池电堆的制备及实验研究[J]. 新型工业化, 2021, 11(2): 229-231. |
| Ni L L. Preparation and experimental study of 5kW proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack[J]. The Journal of New Industrialization, 2021, 11(2): 229-231. | |
| 13 | 陈振兴, 郭树杰, 胡科峰, 等. 燃料电池双极板流场及电堆结构研究现状[J]. 电池工业, 2020, 24(5): 264-268, 280. |
| Chen Z X, Guo S J, Hu K F, et al. Research progress of bipolar plate flow field and stack structure for full cell[J]. Chinese Battery Industry, 2020, 24(5): 264-268, 280. | |
| 14 | 胡翀, 赵袁, RAZA Ali, 等. 基于单层电堆形式的质子交换膜燃料电池仿真模拟研究及优化[J]. 综合智慧能源, 2022, 44(8): 91-96. |
| Hu C, Zhao Y, Ali R, et al. Simulation and optimization for the PEMFC based on single-cell stack structure[J]. Integrated Intelligent Energy, 2022, 44(8): 91-96. | |
| 15 | Zhang G B, Xie X, Xie B, et al. Large-scale multi-phase simulation of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 130: 555-563. |
| 16 | Kvesić M, Reimer U, Froning D, et al. 3D modeling of a 200 cm2 HT-PEFC short stack[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(3): 2430-2439. |
| 17 | 郑文杰, 杨径, 朱林培, 等. 车用燃料电池热管理性能仿真与试验研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2021, 43(3): 381-386. |
| Zheng W J, Yang J, Zhu L P, et al. Simulation and experimental study on thermal management system of vehicle fuel cell[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(3): 381-386. | |
| 18 | Pei H C, Liu Z C, Zhang H N, et al. In situ measurement of temperature distribution in proton exchange membrane fuel cell (Ⅰ): A hydrogen-air stack[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 227: 72-79. |
| 19 | Chen C Y, Huang K P, Yan W M, et al. Development and performance diagnosis of a high power air-cooled PEMFC stack[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(27): 11784-11793. |
| 20 | Wang Y, Sauer D U, Koehne S, et al. Dynamic modeling of high temperature PEM fuel cell start-up process[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(33): 19067-19078. |
| 21 | Andreasen S J, Kær S K. Modelling and evaluation of heating strategies for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell stacks[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33(17): 4655-4664. |
| 22 | Matian M, Marquis A J, Brandon N P. Application of thermal imaging to validate a heat transfer model for polymer electrolyte fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(22): 12308-12316. |
| 23 | Shimpalee S, Ohashi M, van Zee J W, et al. Experimental and numerical studies of portable PEMFC stack[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2009, 54(10): 2899-2911. |
| 24 | Miller M, Bazylak A. A review of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell stack testing[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(2): 601-613. |
| 25 | Scholta J, Messerschmidt M, Jörissen L, et al. Externally cooled high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell stack[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 190(1): 83-85. |
| 26 | 罗来明, 陈思安, 王海宁, 等. 高温聚合物电解质膜燃料电池大尺寸(200 cm2)多蛇形流场模拟与优化[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(9): 4975-4985. |
| Luo L M, Chen S A, Wang H N, et al. Simulation and optimization of large-scale(200 cm2) multiple-serpentine flow field for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(9): 4975-4985. | |
| 27 | 卢善富, 徐鑫, 张劲, 等. 燃料电池用磷酸掺杂高温质子交换膜研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2017, 47(5): 565-572. |
| Lu S F, Xu X, Zhang J, et al. Progress of phosphoric acid doped high temperature proton exchange membrane for fuel cells[J]. Scientia Sinica: Chimica, 2017, 47(5): 565-572. | |
| 28 | 张劲, 郭志斌, 张巨佳, 等. 聚醚砜-聚乙烯吡咯烷酮高温聚合物电解质膜及燃料电池堆性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 589-596. |
| Zhang J, Guo Z B, Zhang J J, et al. Study on performance of polyethersulfone-polyvinylpyrrolidone high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane and fuel cell stack[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 589-596. | |
| 29 | Li W, Wang H N, Zhang J, et al. Advancements of polyvinylpyrrolidone-based polymer electrolyte membranes for electrochemical energy conversion and storage devices[J]. ChemSusChem, 2022, 15(10): e202200071. |
| 30 | Tsukamoto T, Aoki T, Kanesaka H, et al. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of full-scale proton exchange membrane fuel cells at high current densities[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 488: 229412. |
| 31 | Su G Q, Yang D J, Xiao Q F, et al. Effects of vortexes in feed header on air flow distribution of PEMFC stack: CFD simulation and optimization for better uniformity[J]. Renewable Energy, 2021, 173: 498-506. |
| 32 | Harikishan Reddy E, Jayanti S. Thermal management strategies for a 1 kWe stack of a high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2012, 48: 465-475. |
| 33 | 胡祎玮, 夏玉珍, 陆佳宙, 等. 基于计算流体力学的大型质子交换膜燃料电池电堆歧管尺寸优化分析[J]. 汽车技术, 2022(6): 20-26. |
| Hu Y W, Xia Y Z, Lu J Z, et al. Optimization analysis of manifold dimension of large PEMFC stack based on CFD[J]. Automobile Technology, 2022(6): 20-26. | |
| 34 | 石磊, 许思传, 刘泽. 基于人工神经网络的3 kW质子交换膜燃料电池电堆一致性优化[J]. 太阳能学报, 2022, 43(8): 498-503. |
| Shi L, Xu S C, Liu Z. Consistency optimization of 3 kW proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack based on artificial neural network[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2022, 43(8): 498-503. | |
| 35 | 翁元明, 林瑞, 唐文超, 等. 燃料电池堆单片电压一致性研究进展[J]. 电源技术, 2015, 39(1): 199-202. |
| Weng Y M, Lin R, Tang W C, et al. Development of individual cell voltage uniformity of fuel cell stack[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 39(1): 199-202. | |
| 36 | 戴朝华, 史青, 陈维荣, 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池单体电压均衡性研究综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36(5): 1289-1302. |
| Dai C H, Shi Q, Chen W R, et al. A review of the single cell voltage uniformity in proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(5): 1289-1302. | |
| 37 | Amirfazli A, Asghari S, Sarraf M. An investigation into the effect of manifold geometry on uniformity of temperature distribution in a PEMFC stack[J]. Energy, 2018, 145: 141-151. |
| 38 | Salva J A, Iranzo A, Rosa F, et al. Experimental validation of the polarization curve and the temperature distribution in a PEMFC stack using a one dimensional analytical model[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(45): 20615-20632. |
| 39 | Pei H C, Shen J, Cai Y H, et al. Operation characteristics of air-cooled proton exchange membrane fuel cell stacks under ambient pressure[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2014, 63(1): 227-233. |
| 40 | Barreras F, Lozano A, Barroso J, et al. Theoretical model for the optimal design of air cooling systems of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. application to a high-temperature PEMFC[J]. Fuel Cells, 2013, 13(2): 227-237. |
| 41 | Le Ny M, Chadebec O, Cauffet G, et al. A three dimensional electrical model of PEMFC stack[J]. Fuel Cells, 2012, 12(2): 225-238. |
| 42 | Li W, Liu W, Zhang J, et al. Porous proton exchange membrane with high stability and low hydrogen permeability realized by dense double skin layers constructed with amino tris (methylene phosphonic acid)[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33: 2210036. |
| [1] | 陈哲文, 魏俊杰, 张玉明. 超临界水煤气化耦合SOFC发电系统集成及其能量转化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3888-3902. |
| [2] | 李艺彤, 郭航, 陈浩, 叶芳. 催化剂非均匀分布的质子交换膜燃料电池操作条件研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [3] | 闫琳琦, 王振雷. 基于STA-BiLSTM-LightGBM组合模型的多步预测软测量建模[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3407-3418. |
| [4] | 陈朝光, 贾玉香, 汪锰. 以低浓度废酸驱动中和渗析脱盐的模拟与验证[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [5] | 许文烜, 江锦波, 彭新, 门日秀, 刘畅, 彭旭东. 宽速域三种典型型槽油气密封泄漏与成膜特性对比研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1660-1679. |
| [6] | 钱志广, 樊越, 王世学, 岳利可, 王金山, 朱禹. 吹扫条件对PEMFC阻抗弛豫现象和低温启动的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1286-1293. |
| [7] | 郭祥, 乔金硕, 王振华, 孙旺, 孙克宁. 碳燃料固体氧化物燃料电池结构研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 290-302. |
| [8] | 雍加望, 赵倩倩, 冯能莲. 基于非线性动态模型的质子交换膜燃料电池故障诊断[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3983-3993. |
| [9] | 张婉晨, 陈晓阳, 吕秋秋, 钟秦, 朱腾龙. Co掺杂SrTi0.3Fe0.7O3-δ 阳极SOFC在化工副产气燃料下的性能及稳定性[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4079-4086. |
| [10] | 邵健, 冯军宗, 柳凤琦, 姜勇刚, 李良军, 冯坚. 酚醛树脂基炭微球结构调控与功能化制备研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3787-3801. |
| [11] | 张童, 杨扬, 叶丁丁, 陈蓉, 朱恂, 廖强. 催化剂分布对可渗透阳极微流体燃料电池性能特性影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4156-4162. |
| [12] | 方辉煌, 程金星, 罗宇, 陈崇启, 周晨, 江莉龙. 氨电氧化催化剂及其低温直接氨碱性膜燃料电池性能的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3802-3814. |
| [13] | 刘潜, 张香兰, 李志平, 李玉龙, 韩梦醒. 油酚分离过程低共熔溶剂的筛选及萃取性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3915-3928. |
| [14] | 艾承燚, 乔金硕, 王振华, 孙旺, 孙克宁. 原位析出纳米合金的PrBaFe2O6-δ 基阳极构筑及其在固体碳燃料电池中的应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3708-3719. |
| [15] | 黄陆月, 刘畅, 许勇毅, 邢浩若, 王峰, 马双忱. CDI二维浓度传质模型的建立以及实验验证[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2933-2943. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号