化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (5): 2233-2241.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220060
肖习羽1,2( ),李青松2,4(
),李青松2,4( ),吴俊文1,3(
),吴俊文1,3( ),李国新2,陈国元2
),李国新2,陈国元2
收稿日期:2022-01-12
修回日期:2022-03-26
出版日期:2022-05-05
发布日期:2022-05-24
通讯作者:
李青松,吴俊文
作者简介:肖习羽(1995—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Xiyu XIAO1,2( ),Qingsong LI2,4(
),Qingsong LI2,4( ),Junwen WU1,3(
),Junwen WU1,3( ),Guoxin LI2,Guoyuan CHEN2
),Guoxin LI2,Guoyuan CHEN2
Received:2022-01-12
Revised:2022-03-26
Online:2022-05-05
Published:2022-05-24
Contact:
Qingsong LI,Junwen WU
摘要:
采用VUV/UV/NaClO与UV/NaClO工艺降解百里香酚(Tml),以协同因子(R)为评价指标,探究了NaClO浓度和pH对Tml去除及协同效应的影响;以硝基苯(NB)和苯甲酸(BA)为探针化合物,确定了不同工艺中HO·和Cl·的稳态浓度及其与Tml的二级反应速率常数;并对比了两种工艺中不同物质对Tml降解的贡献。结果表明,VUV/UV/NaClO与UV/NaClO工艺降解Tml均符合拟一级反应动力学,其一级动力学常数kVUV/UV/Cl和kUV/Cl分别为0.0113 s-1和0.00479 s-1,且均与NaClO浓度呈正相关;VUV/UV/NaClO和UV/NaClO工艺对Tml的降解具有显著的协同效应,相应的协同因子(RVUV/UV/Cl、RUV/Cl)随NaClO的浓度的增加及溶液pH的增大均先增加再降低;当NaClO浓度为0.3 mg·L-1和pH=7时,RVUV/UV/Cl和RUV/Cl达到最大值,分别为1.9和2.1,对应的协同增效为90%和110%。VUV/UV/NaClO和UV/NaClO工艺中HO·的贡献率分别为42.7%和37.6%,Cl·的贡献率分别为42.4%和28.5%。两种工艺中HO·和Cl·均为主要贡献物质。
中图分类号:
肖习羽, 李青松, 吴俊文, 李国新, 陈国元. VUV/UV/NaClO工艺降解百里香酚协同效应及活性物质贡献[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2233-2241.
Xiyu XIAO, Qingsong LI, Junwen WU, Guoxin LI, Guoyuan CHEN. Synergistic effect of thymol degradation by VUV/UV/NaClO technique and its major contributor of active species[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(5): 2233-2241.
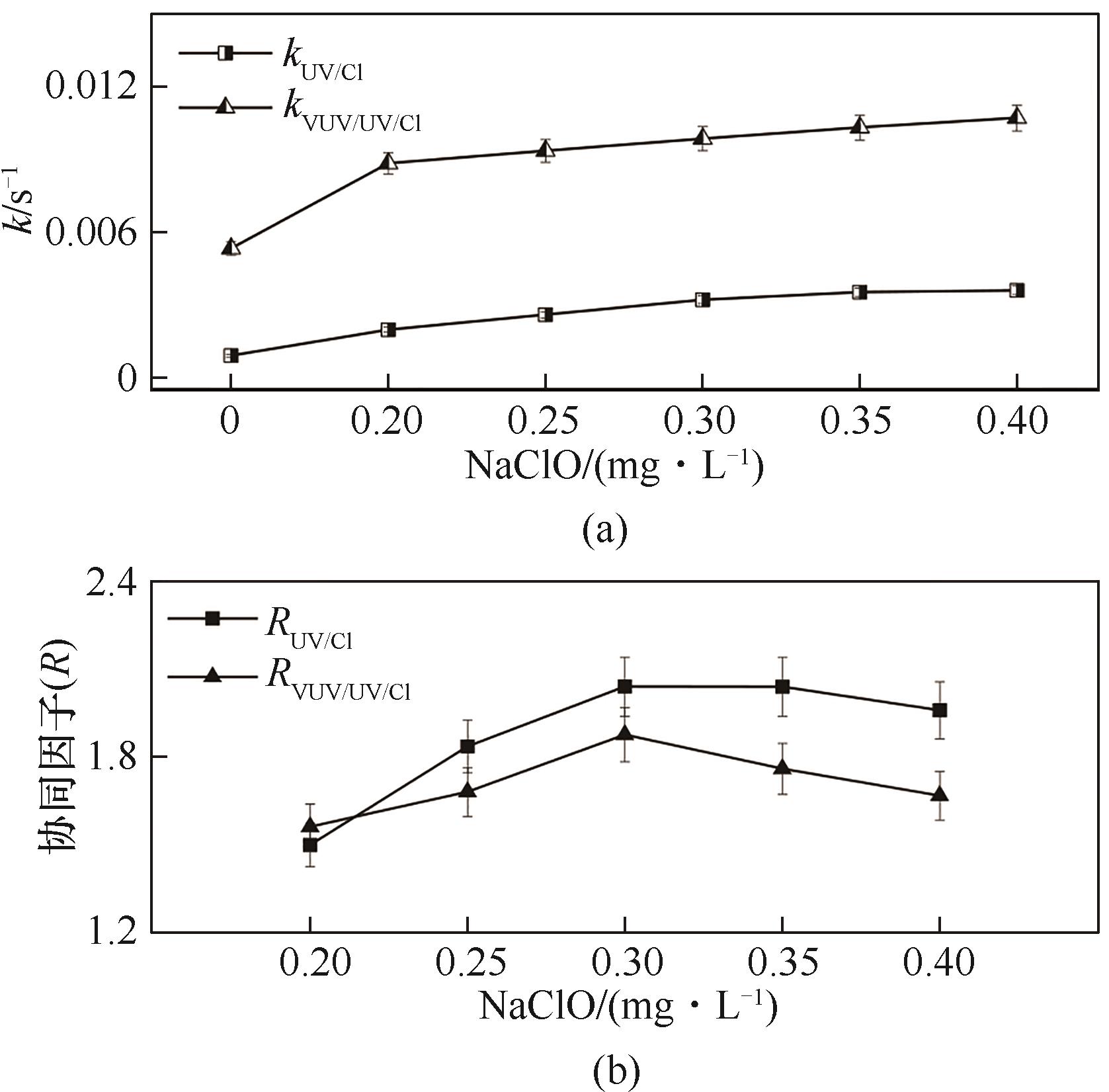
图2 NaClO对VUV/UV/NaClO和UV/NaClO降解Tml的k (a)和协同因子R (b)的影响([Tml]0=3.33 μmol·L-1, pH=7.0(±0.2))
Fig.2 Effect of NaClO concentration on the k (a) and R (b) during the Tml degradation by VUV/UV/NaClO and UV/NaClO
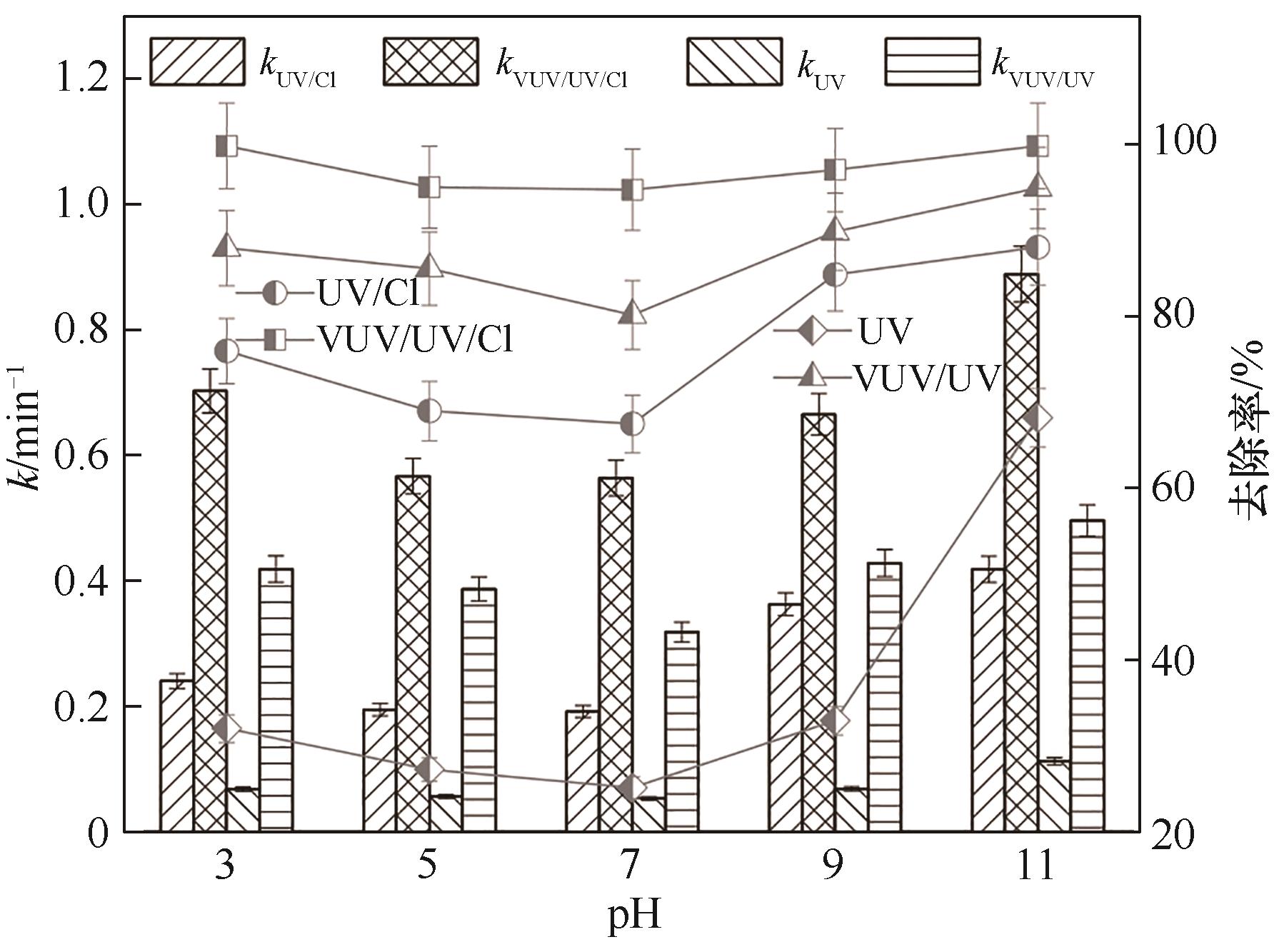
图3 pH对4种工艺降解Tml的k和去除率的影响([Tml]0=3.33 μmol·L-1, [NaClO]0=0.3 mg·L-1)
Fig.3 Effect of pH on the k and removal rate during the Tml degradation by four processes

图4 pH对VUV/UV/NaClO和UV/NaClO降解Tml k (a)和协同因子R (b)的影响([Tml]0=3.33 μmol·L–1, [NaClO]0=0.3 mg·L–1)
Fig.4 Effect of pH on the k (a) and R (b) during the Tml degradation by VUV/UV/NaClO and UV/NaClO
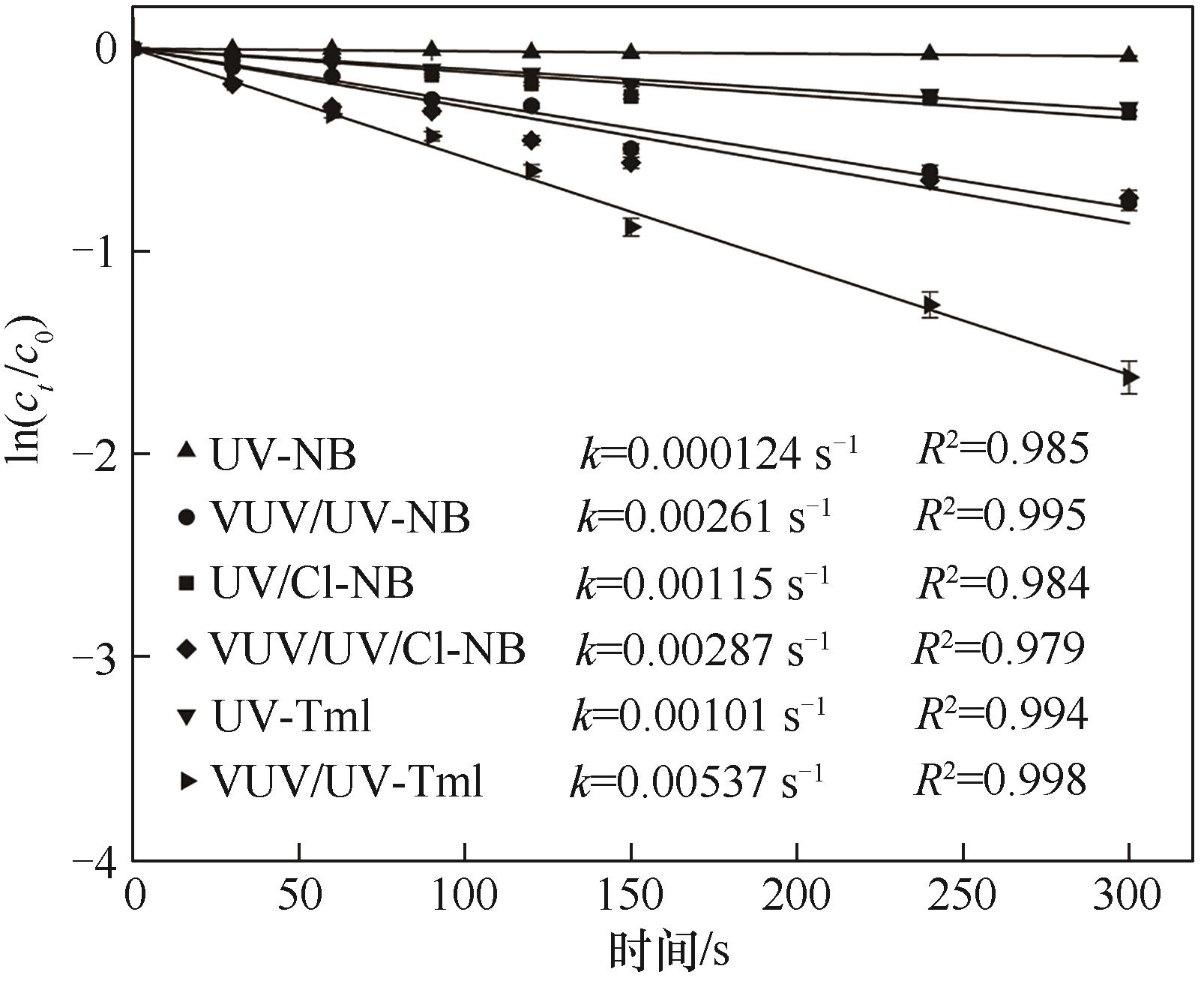
图5 不同工艺对NB和Tml的降解([NB]0=1.22 μmol·L-1, [Tml]0=3.33 μmol·L-1, [NaClO]0=0.3 mg·L-1, pH=7.0(±0.2))
Fig.5 Degradation of NB and Tml in different processes
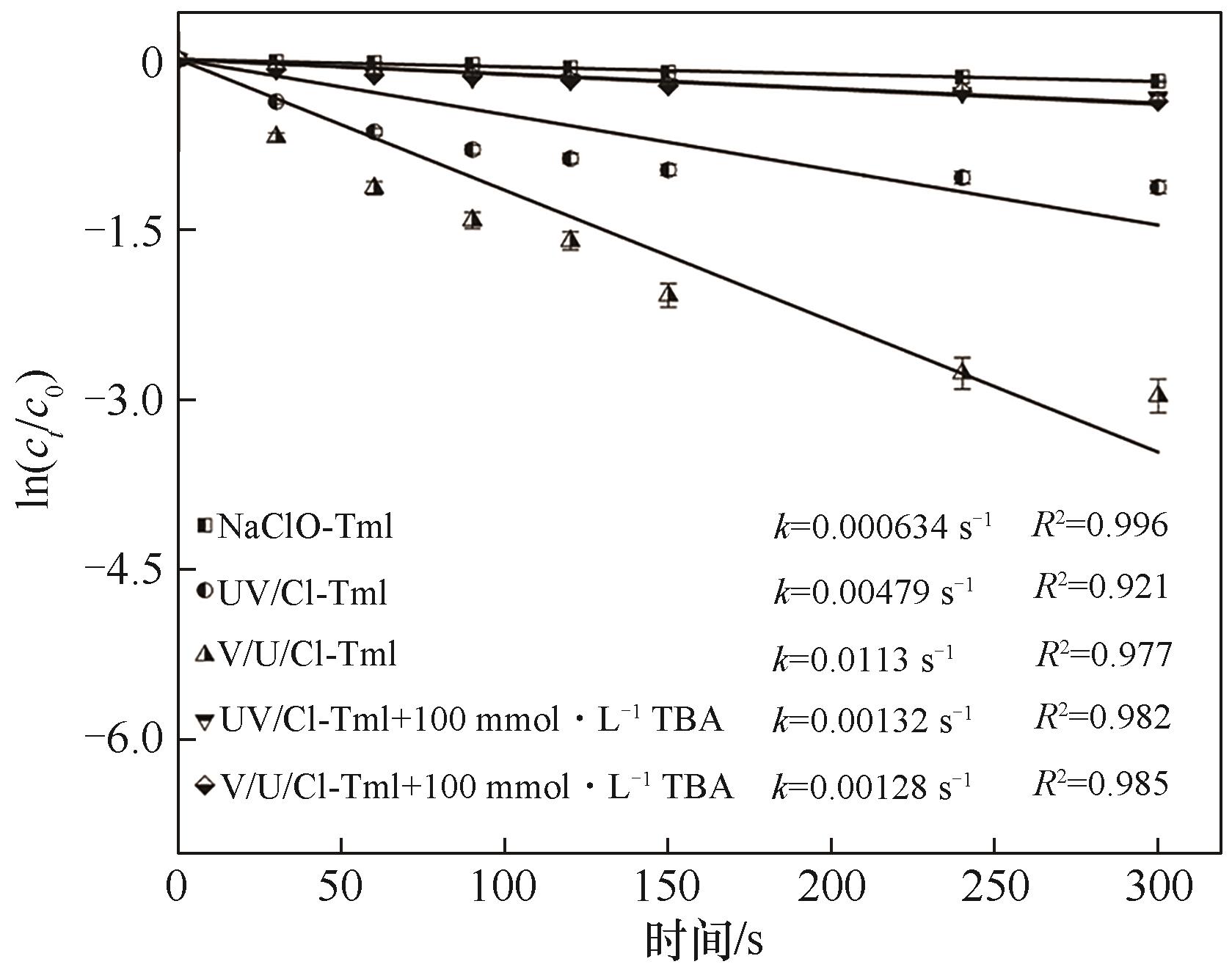
图7 VUV/UV/NaClO、UV/NaClO和NaClO对Tml的降解动力学([Tml]0=3.33 μmol·L–1, [NaClO]0=0.3 mg·L–1, pH=7.0(±0.2))
Fig.7 Kinetics of Tml degradation in VUV/UV/NaClO, UV/NaClO and NaClO

图8 VUV/UV/NaClO和UV/NaClO工艺中不同物质对Tml的降解的贡献([Tml]0=3.33 μmol·L-1, [NaClO]0=0.3 mg·L-1, pH=7.0(±0.2))
Fig.8 Contribution of different species to Tml degradation in VUV/UV/NaClO and UV/NaClO processes
| 1 | Sui Q, Cao X Q, Lu S G, et al. Occurrence, sources and fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the groundwater: a review[J]. Emerging Contaminants, 2015, 1(1): 14-24. |
| 2 | Schwab B W, Hayes E P, Fiori J M, et al. Human pharmaceuticals in US surface waters: a human health risk assessment[J]. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2005, 42(3): 296-312. |
| 3 | Ebele A J, Abou-Elwafa Abdallah M, Harrad S. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the freshwater aquatic environment[J]. Emerging Contaminants, 2017, 3(1): 1-16. |
| 4 | 张静, 冯岗, 袁旭超, 等. 百里香酚抑菌活性初探[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(21): 277-280. |
| Zhang J, Feng G, Yuan X C, et al. Preliminary study on the antifungal activity of thymol[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 25(21): 277-280. | |
| 5 | Nakada N, Kiri K, Shinohara H, et al. Evaluation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products as water-soluble molecular markers of sewage[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(17): 6347-6353. |
| 6 | 梅雪冰, 隋倩, 张紫薇, 等. 不同特征污染源中指示性药物和个人护理品识别与筛选[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(3): 1173-1180. |
| Mei X B, Sui Q, Zhang Z W, et al. Identification of indicator pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) in different emission sources[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(3): 1173-1180. | |
| 7 | Esplugas S, Giménez J, Contreras S, et al. Comparison of different advanced oxidation processes for phenol degradation[J]. Water Research, 2002, 36(4): 1034-1042. |
| 8 | Couto C F, Lange L C, Amaral M C S. Occurrence, fate and removal of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) in water and wastewater treatment plants—a review[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2019, 32: 100927. |
| 9 | 闫子娇, 张有林, 于月英. 百里香挥发油成分分析及急性毒理学实验研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2011, 32(2): 144-146. |
| Yan Z J, Zhang Y L, Yu Y Y. Study of composition and emergency toxicology test of thymus[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2011, 32(2): 144-146. | |
| 10 | 张有林, 张润光, 钟玉. 百里香精油的化学成分、抑菌作用、抗氧化活性及毒理学特性[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(9): 1888-1897. |
| Zhang Y L, Zhang R G, Zhong Y. Chemical component, antimicrobial effect, antioxidation activity and toxicological character of thyme essential oil[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(9): 1888-1897. | |
| 11 | Bianchi C L, Pirola C, Ragaini V, et al. Mechanism and efficiency of atrazine degradation under combined oxidation processes[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2006, 64(1/2): 131-138. |
| 12 | Huang N, Wang T, Wang W L, et al. UV/chlorine as an advanced oxidation process for the degradation of benzalkonium chloride: synergistic effect, transformation products and toxicity evaluation[J]. Water Research, 2017, 114: 246-253. |
| 13 | Li S M, Ao X W, Li C, et al. Insight into PPCP degradation by UV/NH2Cl and comparison with UV/NaClO: kinetics, reaction mechanism, and DBP formation[J]. Water Research, 2020, 182: 115967. |
| 14 | Liu Z, Xu B, Zhang T Y, et al. Formation of disinfection by-products in a UV-activated mixed chlorine/chloramine system[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 407: 124373. |
| 15 | Gao Z C, Lin Y L, Xu B, et al. Effect of UV wavelength on humic acid degradation and disinfection by-product formation during the UV/chlorine process[J]. Water Research, 2019, 154: 199-209. |
| 16 | Juang L C, Tseng D H, Lee J F. Photolytic mechanism of monochlorobenzene in an aqueous UV/H2O2 system[J]. Chemosphere, 1998, 36(6): 1187-1199. |
| 17 | Yuan F, Hu C, Hu X X, et al. Degradation of selected pharmaceuticals in aqueous solution with UV and UV/H2O2 [J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(6): 1766-1774. |
| 18 | Yi Q Y, Ji J H, Shen B, et al. Singlet oxygen triggered by superoxide radicals in a molybdenum cocatalytic fenton reaction with enhanced REDOX activity in the environment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(16): 9725-9733. |
| 19 | Zoschke K, Börnick H, Worch E. Vacuum-UV radiation at 185 nm in water treatment—a review[J]. Water Research, 2014, 52: 131-145. |
| 20 | 褚宏怡, 鲁金凤, 寇方航, 等. 过硫酸盐高级氧化技术的活化方法研究进展[J]. 供水技术, 2017, 11(4): 24-28. |
| Chu H Y, Lu J F, Kou F H, et al. Research progress of the activation methods based on persulfate advanced oxidation technology[J]. Water Technology, 2017, 11(4): 24-28. | |
| 21 | Lee Y, von Gunten U. Oxidative transformation of micropollutants during municipal wastewater treatment: comparison of kinetic aspects of selective (chlorine, chlorine dioxide, ferrate Ⅵ, and ozone) and non-selective oxidants (hydroxyl radical)[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(2): 555-566. |
| 22 | Fang J Y, Fu Y, Shang C. The roles of reactive species in micropollutant degradation in the UV/free chlorine system[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(3): 1859-1868. |
| 23 | Dong H Y, Qiang Z M, Hu J, et al. Degradation of chloramphenicol by UV/chlorine treatment: kinetics, mechanism and enhanced formation of halonitromethanes[J]. Water Research, 2017, 121: 178-185. |
| 24 | Gonzalez M G, Oliveros E, Wörner M, et al. Vacuum-ultraviolet photolysis of aqueous reaction systems[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C: Photochemistry Reviews, 2004, 5(3): 225-246. |
| 25 | Buchanan W, Roddick F, Porter N, et al. Fractionation of UV and VUV pretreated natural organic matter from drinking water[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(12): 4647-4654. |
| 26 | Chen J, Zhang P Y, Liu J. Photodegradation of perfluorooctanoic acid by 185 nm vacuum ultraviolet light[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2007, 19(4): 387-390. |
| 27 | Kim I, Tanaka H. Photodegradation characteristics of PPCPs in water with UV treatment[J]. Environment International, 2009, 35(5): 793-802. |
| 28 | Li W Z, Lu S G, Chen N, et al. Photo-degradation of clofibric acid by ultraviolet light irradiation at 185 nm[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2009, 60(11): 2983-2989. |
| 29 | Imoberdorf G, Mohseni M. Degradation of natural organic matter in surface water using vacuum-UV irradiation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(1): 240-246. |
| 30 | Li M K, Hao M Y, Yang L X, et al. Trace organic pollutant removal by VUV/UV/chlorine process: feasibility investigation for drinking water treatment on a mini-fluidic VUV/UV photoreaction system and a pilot photoreactor[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(13): 7426-7433. |
| 31 | Xiang Y Y, Fang J Y, Shang C. Kinetics and pathways of ibuprofen degradation by the UV/chlorine advanced oxidation process[J]. Water Research, 2016, 90: 301-308. |
| 32 | Guo K H, Wu Z H, Shang C, et al. Radical chemistry and structural relationships of PPCP degradation by UV/chlorine treatment in simulated drinking water[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(18): 10431-10439. |
| 33 | Bu L J, Zhou S Q, Zhu S M, et al. Insight into carbamazepine degradation by UV/monochloramine: reaction mechanism, oxidation products, and DBPs formation[J]. Water Research, 2018, 146: 288-297. |
| 34 | Yang L X, Zhang Z H. Degradation of six typical pesticides in water by VUV/UV/chlorine process: evaluation of the synergistic effect[J]. Water Research, 2019, 161: 439-447. |
| 35 | Watts M J, Linden K G. Chlorine photolysis and subsequent OH radical production during UV treatment of chlorinated water[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(13): 2871-2878. |
| 36 | Li M K, Qiang Z M, Hou P, et al. VUV/UV/chlorine as an enhanced advanced oxidation process for organic pollutant removal from water: assessment with a novel mini-fluidic VUV/UV photoreaction system (MVPS)[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(11): 5849-5856. |
| 37 | Cai W W, Peng T, Zhang J N, et al. Degradation of climbazole by UV/chlorine process: kinetics, transformation pathway and toxicity evaluation[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 219: 243-249. |
| 38 | Yang L X, Li M K, Li W T, et al. A green method to determine VUV (185 nm) fluence rate based on hydrogen peroxide production in aqueous solution[J]. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2018, 94(4): 821-824. |
| 39 | Deborde M, von Gunten U. Reactions of chlorine with inorganic and organic compounds during water treatment—kinetics and mechanisms: a critical review[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(1/2): 13-51. |
| 40 | Wang D, Bolton J R, Hofmann R. Medium pressure UV combined with chlorine advanced oxidation for trichloroethylene destruction in a model water[J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(15): 4677-4686. |
| 41 | Collivignarelli C, Sorlini S. AOPs with ozone and UV radiation in drinking water: contaminants removal and effects on disinfection byproducts formation[J]. Water Science and Technology: a Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 2004, 49(4): 51-56. |
| 42 | 李博强, 马晓雁, 李青松, 等. UV-LED/NaClO工艺对水中对乙酰氨基酚的降解[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(11): 4681-4688. |
| Li B Q, Ma X Y, Li Q S, et al. Degradation of acetaminophen in aqueous by UV-LED/NaClO process[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(11): 4681-4688. | |
| 43 | Han M Q, Mohseni M. Impact of organic and inorganic carbon on the formation of nitrite during the VUV photolysis of nitrate containing water[J]. Water Research, 2020, 168: 115169. |
| 44 | Chen B Y, Huang Y X, Zhang Q, et al. Formation of nitrite and hydrogen peroxide in water during the vacuum ultraviolet irradiation process: impacts of pH, dissolved oxygen, and nitrate concentration[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(3): 1682-1689. |
| 45 | Dao Y H, Tran H N, Tran-Lam T T, et al. Degradation of paracetamol by an UV/chlorine advanced oxidation process: influencing factors, factorial design, and intermediates identification[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2018, 15(12): 2637. |
| 46 | Kutschera K, Börnick H, Worch E. Photoinitiated oxidation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol by irradiation with 254 nm and 185 nm UV light[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(8): 2224-2232. |
| 47 | Kong Q Q, Lei X, Zhang X R, et al. The role of chlorine oxide radical (ClO•) in the degradation of polychoro-1, 3-butadienes in UV/chlorine treatment: kinetics and mechanisms[J]. Water Research, 2020, 183: 116056. |
| 48 | Yang B, Kookana R S, Williams M, et al. Removal of carbamazepine in aqueous solutions through solar photolysis of free available chlorine[J]. Water Research, 2016, 100: 413-420. |
| [1] | 李锦潼, 邱顺, 孙文寿. 煤浆法烟气脱硫中草酸和紫外线强化煤砷浸出过程[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3522-3532. |
| [2] | 何晓崐, 刘锐, 薛园, 左然. MOCVD生长AlN单晶薄膜的气相和表面化学反应综述[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2800-2813. |
| [3] | 龙臻, 王谨航, 任俊杰, 何勇, 周雪冰, 梁德青. 离子液体协同PVCap抑制天然气水合物生成实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2639-2646. |
| [4] | 张兰河, 赖青燚, 王铁铮, 关潇卓, 张明爽, 程欣, 徐小惠, 贾艳萍. H2O2对SBR脱氮效率和污泥性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2186-2196. |
| [5] | 李瑞康, 何盈盈, 卢维鹏, 王园园, 丁皓东, 骆勇名. 电化学强化钴基阴极活化过一硫酸盐的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [6] | 杨庆云, 李青松, 陈泽铭, 邓靖, 李玉瑛, 杨帆, 陈国元, 李国新. UV/PMS、UV/PDS、UV/SPC工艺降解尼泊金甲酯[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1322-1331. |
| [7] | 章承浩, 罗京, 张吉松. 微反应器内基于氮氧自由基催化剂连续氧气/空气氧化反应的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 511-524. |
| [8] | 李雨萧, 王青月, Ho Lim Khak, 李晓辉, Erlita Mastan, 彭博, 王文俊. 自由基聚合反应动力学常数测定技术[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 559-570. |
| [9] | 靳文章, 张玉玲, 贾晓宇. 电化学高级氧化对HEDP的降解效能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4062-4069. |
| [10] | 邓靖, 杨庆云, 陈民杰, 李青松, 杨帆, 陈国元, 李国新. UV-LED/NaClO工艺降解尼泊金甲酯:不同活性物种的作用[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4113-4121. |
| [11] | 郑默, 李晓霞. ReaxFF MD模拟揭示的煤热解挥发分自由基反应的竞争与协调[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2732-2741. |
| [12] | 张红锐, 张田, 隆曦孜, 李先宁. 光催化与微生物燃料电池耦合对Cu-EDTA的降解特性[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2149-2157. |
| [13] | 余彬彬, 蒋新生, 禹进, 蔡运雄, 李玉玺, 何东海, 于佳佳. 全氟己酮抑制航空煤油燃烧实验及化学动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1834-1844. |
| [14] | 李春晖, 何辉, 何明键, 张萌, 高杨, 矫彩山. 离子液体萃取硝酸中Ce(Ⅳ)的动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1606-1614. |
| [15] | 许超群, 俞娟, 范一民, 王基夫, 储富祥. 原子转移自由基聚合法接枝改性纳米纤维素及其功能化应用[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(3): 1022-1043. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号