化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (10): 4484-4497.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220507
吴诗德1,2( ), 易峰2, 平丹2(
), 易峰2, 平丹2( ), 张逸飞2, 郝健3, 刘国际1(
), 张逸飞2, 郝健3, 刘国际1( ), 方少明2
), 方少明2
收稿日期:2022-04-07
修回日期:2022-09-28
出版日期:2022-10-05
发布日期:2022-11-02
通讯作者:
平丹,刘国际
作者简介:吴诗德(1979—),男,博士研究生,副教授,wushide@zzuli.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shide WU1,2( ), Feng YI2, Dan PING2(
), Feng YI2, Dan PING2( ), Yifei ZHANG2, Jian HAO3, Guoji LIU1(
), Yifei ZHANG2, Jian HAO3, Guoji LIU1( ), Shaoming FANG2
), Shaoming FANG2
Received:2022-04-07
Revised:2022-09-28
Online:2022-10-05
Published:2022-11-02
Contact:
Dan PING, Guoji LIU
摘要:
二氧化碳(CO2)的资源化利用是实现“碳达峰,碳中和”的重要手段。在众多CO2转化技术当中,电催化CO2还原反应因反应条件温和、工艺过程简单等优点,被认为是极具应用前景的减碳技术之一,其关键在于高效、高稳定性电催化剂的开发。过渡金属-氮-碳(M-N-C)材料是电还原CO2生成CO的有效催化剂,针对其高温热解制备过程中活性金属原子容易聚集且氮原子流失严重,进而使得活性位密度降低,催化性能下降等问题,本文提出以双氰胺(DCDA)为碳源和氮源,以乙酰丙酮镍(Ni(acac)2)为金属源,以氯化铵(NH4Cl)为第二氮源和造孔剂,采用简单的NH4Cl辅助热解-酸刻蚀的方法制备得到镍-氮-碳纳米管(Ni-N-CNTs)电还原CO2催化剂,并详细考察NH4Cl添加量对催化剂结构和催化性能的影响。表征结果表明:NH4Cl的加入有利于催化剂纳米管状形貌和多级孔结构的生成,同时有利于催化剂中Ni-Nx (1.6%,摩尔分数)和pyridinic-N (1.75%,摩尔分数)物种含量的增加。一系列性能测试结果表明:催化剂的活性中心为Ni-Nx,同时pyridinic-N的存在也有利于催化性能的提高,当前体中NH4Cl加入量与氮源和金属源总质量比为1∶1时,所得Ni-N-CNTs-1催化剂催化性能最好,在电压为-0.65 V (vs RHE)时,CO法拉第效率最高达92%,此时CO部分电流密度为8 mA·cm-2。此外,该催化剂还表现出良好的催化稳定性,连续恒电位电解12 h,催化性能基本不变。该催化剂制备工艺简单,制备条件可控,研究结果可为高效M-N-C电还原CO2催化剂的设计和制备提供一种切实有效的研究思路和方法。
中图分类号:
吴诗德, 易峰, 平丹, 张逸飞, 郝健, 刘国际, 方少明. NH4Cl辅助热解制备镍-氮-碳纳米管催化剂及其电还原CO2性能[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4484-4497.
Shide WU, Feng YI, Dan PING, Yifei ZHANG, Jian HAO, Guoji LIU, Shaoming FANG. NH4Cl assisted preparation of Ni-N-CNTs catalyst and its performance for electrochemical CO2 reduction[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4484-4497.
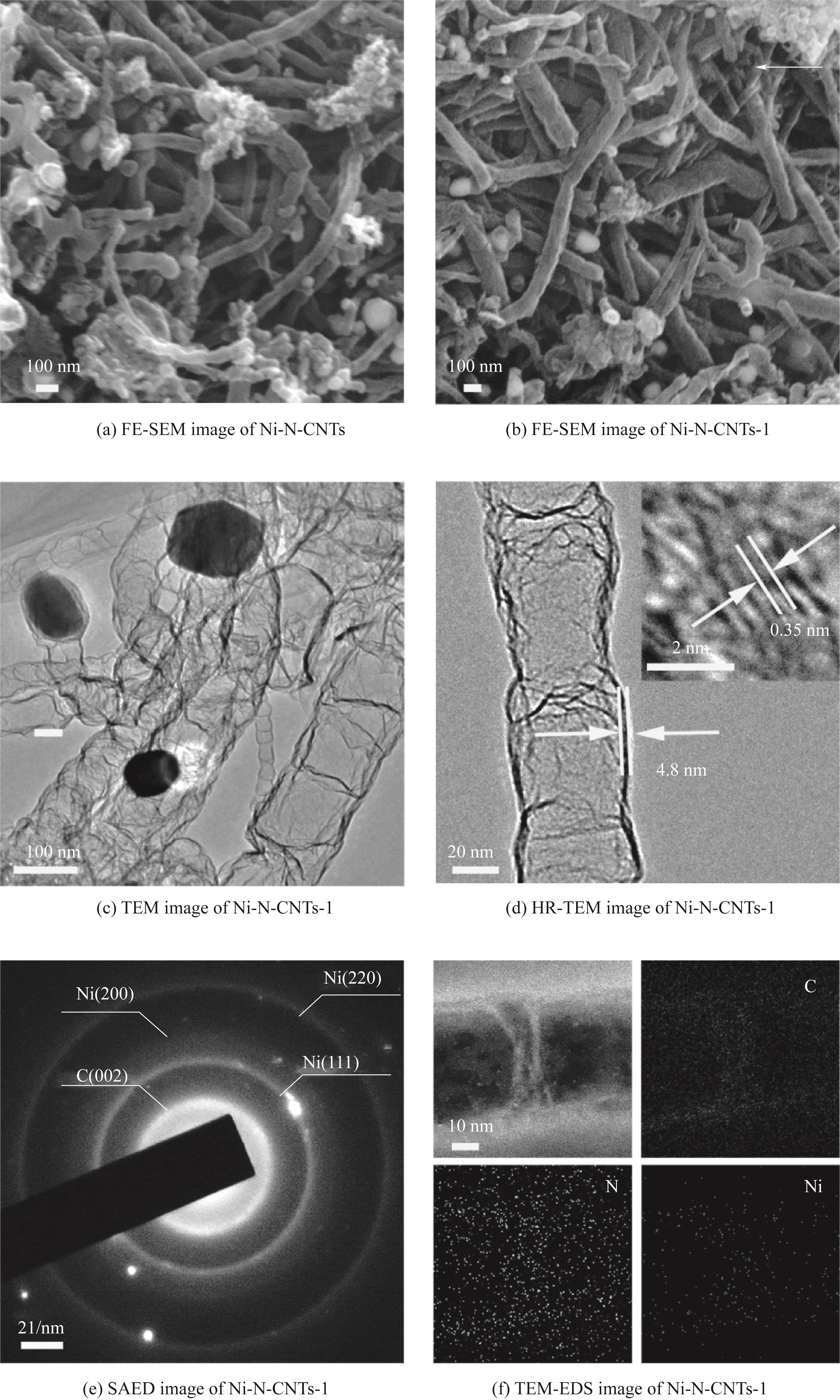
图4 Ni-N-CNTs催化剂的FE-SEM图,Ni-N-CNTs-1催化剂的FE-SEM图、TEM图、HR-TEM图、SAED图和TEM-EDS图
Fig.4 The FE-SEM image of the Ni-N-CNTs catalyst, and the FE-SEM, TEM, HR-TEM, SAED and TEM-EDS mapping images of the Ni-N-CNTs-1 catalyst
| 样品 | 比表面积/ (m2·g-1) | 孔隙体积/ (cm3·g-1) | 孔隙直径/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-N-CNTs | 448.24 | 0.97 | 8.35 |
| Ni-N-CNTs-1/3 | 320.10 | 0.58 | 6.79 |
| Ni-N-CNTs-1 | 333.48 | 1.00 | 11.07 |
| Ni-N-CNTs-3 | 272.88 | 0.24 | 4.05 |
表1 所制备催化剂的比表面积和孔结构特性
Table1 The specific surface areas and textural properties of prepared catalysts
| 样品 | 比表面积/ (m2·g-1) | 孔隙体积/ (cm3·g-1) | 孔隙直径/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-N-CNTs | 448.24 | 0.97 | 8.35 |
| Ni-N-CNTs-1/3 | 320.10 | 0.58 | 6.79 |
| Ni-N-CNTs-1 | 333.48 | 1.00 | 11.07 |
| Ni-N-CNTs-3 | 272.88 | 0.24 | 4.05 |
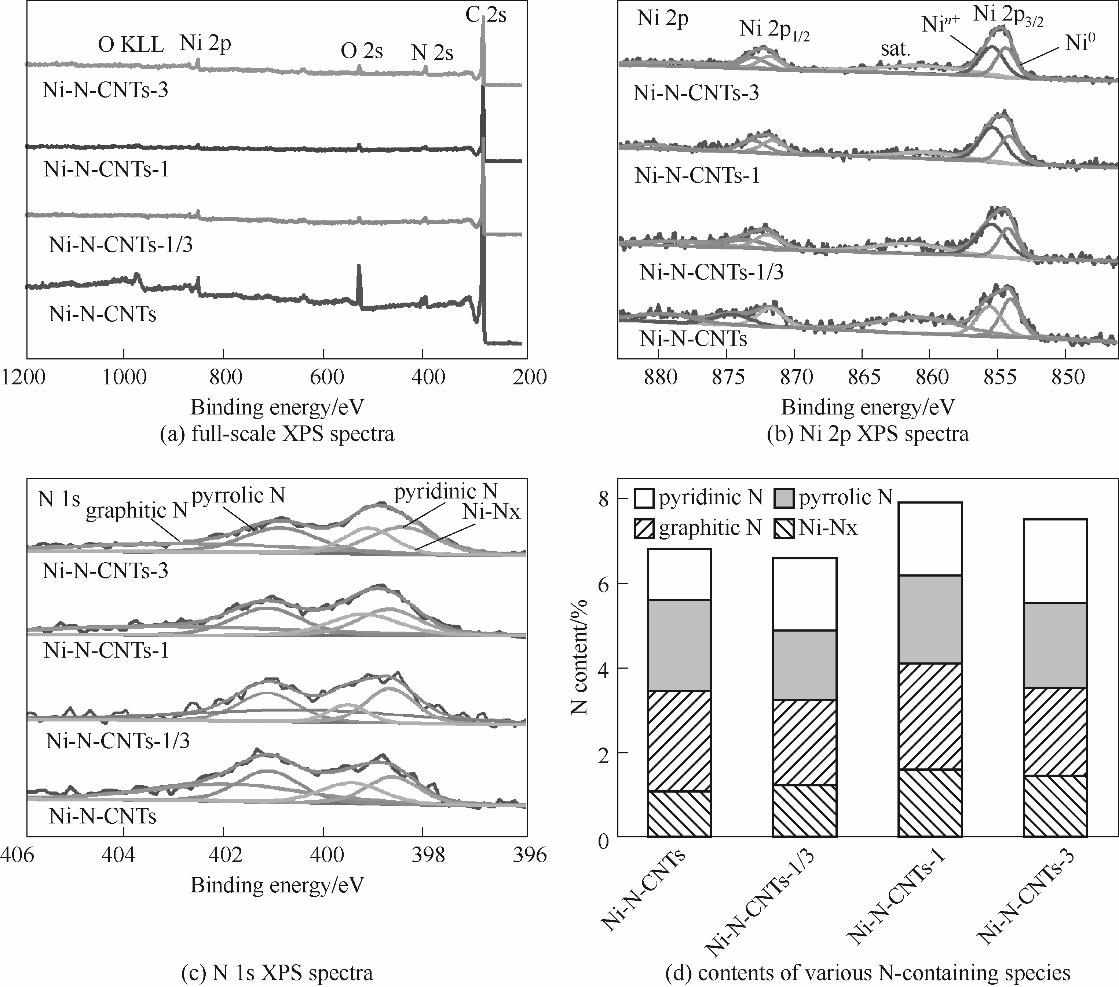
图6 所制备催化剂的 XPS总谱图、Ni 2p的XPS谱图、 N 1s的XPS谱图和各类含氮物种的含量对比
Fig.6 The full-scale XPS spectra, Ni 2p XPS spectra, N 1s XPS spectra, and the contents of various N-containing species of prepared catalysts
| 样品 | XPS | Ni(ICP-OES)/% (mass) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/%(mol(mass)) | N/%(mol(mass)) | Ni/%(mol(mass)) | N/%(mol) | Ni n+/Ni0 | |||||
| Ni-Nx | Graphitic-N | Pyrrolic-N | Pyridinic-N | ||||||
| Ni-N-CNTs | 84.36(77.99) | 6.17(6.65) | 1.12(5.06) | 1.09 | 2.31 | 2.23 | 1.15 | 0.97 | 18.12 |
| Ni-N-CNTs-1/3 | 87.32(82.56) | 6.5(7.08) | 0.87(3.97) | 1.18 | 2.06 | 1.65 | 1.65 | 1.42 | 13.82 |
| Ni-N-CNTs-1 | 87.44(81.58) | 7.86(8.56) | 1.21(5.11) | 1.60 | 2.46 | 2.06 | 1.75 | 1.59 | 16.1 |
| Ni-N-CNTs-3 | 87.19(81.04) | 7.45(8.08) | 1.08(4.91) | 1.43 | 2.03 | 2.00 | 2.01 | 1.22 | 10.8 |
表2 所制备催化剂中各物种的定量分析结果
Table 2 Summary contents of various species in the prepared catalysts
| 样品 | XPS | Ni(ICP-OES)/% (mass) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/%(mol(mass)) | N/%(mol(mass)) | Ni/%(mol(mass)) | N/%(mol) | Ni n+/Ni0 | |||||
| Ni-Nx | Graphitic-N | Pyrrolic-N | Pyridinic-N | ||||||
| Ni-N-CNTs | 84.36(77.99) | 6.17(6.65) | 1.12(5.06) | 1.09 | 2.31 | 2.23 | 1.15 | 0.97 | 18.12 |
| Ni-N-CNTs-1/3 | 87.32(82.56) | 6.5(7.08) | 0.87(3.97) | 1.18 | 2.06 | 1.65 | 1.65 | 1.42 | 13.82 |
| Ni-N-CNTs-1 | 87.44(81.58) | 7.86(8.56) | 1.21(5.11) | 1.60 | 2.46 | 2.06 | 1.75 | 1.59 | 16.1 |
| Ni-N-CNTs-3 | 87.19(81.04) | 7.45(8.08) | 1.08(4.91) | 1.43 | 2.03 | 2.00 | 2.01 | 1.22 | 10.8 |

图7 所制备催化剂的LSV图、FECO和jCO以及Ni-N-CNTs-1催化剂在-0.65 V(vs RHE)下的稳定性测试结果和稳定性测试前后的LSV图
Fig.7 The LSV curves, FECO and jCO of prepared catalysts, the stability test of Ni-N-CNTs-1 at -0.65 V(vs RHE)and the LSV curves of Ni-N-CNT-1 before and after the stability test
| Electrocatalyst | Cathode material | Electrolyte(pH) | FECO/% | Potential (vs RHE)/V | (mA·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meso NC-Fe | glassy carbon | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (7.2) | 85.0 | -0.73 | 3.7 | [ |
| SA-Ni@NC | glassy carbon | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (7.2) | 86.2 | -0.60 | 1.78 | [ |
| NiSA-N-CNTs | carbon paper | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (7.2) | 92 | -0.70 | 23.5 | [ |
| Ni SAs/N-C | carbon paper | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (7.2) | 70.3 | -1.00 | 7.37 | [ |
| Fe-N/O-C (MZ) | carbon paper | 0.1 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (6.8) | 95.5 | -0.57 | 5.6 | [ |
| FeMn-N-C | glassy carbon plate | 0.1 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (6.8) | 84.0 | -0.51 | 1.8 | [ |
| CATpyr/CNT | glassy carbon plate | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3(7.2) | 93 | -0.59 | 0.24 | [ |
| CoPc@HCS-9 | carbon fiber paper | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (7.2) | 88 | -0.87 | 6.5 | [ |
| Ni-N-CNTs-1 | glassy carbon | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (7.2) | 92.0 | -0.65 | 8.0 | this work |
表3 文献报道的CO2RR催化剂的性能比较
Table 3 Performance comparison of CO2RR catalysts reported in recent years
| Electrocatalyst | Cathode material | Electrolyte(pH) | FECO/% | Potential (vs RHE)/V | (mA·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meso NC-Fe | glassy carbon | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (7.2) | 85.0 | -0.73 | 3.7 | [ |
| SA-Ni@NC | glassy carbon | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (7.2) | 86.2 | -0.60 | 1.78 | [ |
| NiSA-N-CNTs | carbon paper | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (7.2) | 92 | -0.70 | 23.5 | [ |
| Ni SAs/N-C | carbon paper | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (7.2) | 70.3 | -1.00 | 7.37 | [ |
| Fe-N/O-C (MZ) | carbon paper | 0.1 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (6.8) | 95.5 | -0.57 | 5.6 | [ |
| FeMn-N-C | glassy carbon plate | 0.1 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (6.8) | 84.0 | -0.51 | 1.8 | [ |
| CATpyr/CNT | glassy carbon plate | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3(7.2) | 93 | -0.59 | 0.24 | [ |
| CoPc@HCS-9 | carbon fiber paper | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (7.2) | 88 | -0.87 | 6.5 | [ |
| Ni-N-CNTs-1 | glassy carbon | 0.5 mol·L-1 KHCO3 (7.2) | 92.0 | -0.65 | 8.0 | this work |

图8 所制备催化剂在不同扫速下的CV曲线图、在-0.07 V (vs RHE)时电流密度差与扫速关系及Tafel曲线
Fig.8 CV curves of prepared catalysts at different scan rates, the capacitive current (Δj) against the scan rate at -0.07 V (vs RHE) and the Tafel plots

图9 Ni-N-CNTs-1,Ni-N-CNTs-1-12h,Ni-N-CNTs-1-24h和Ni NPs/N-CNTs-1样品的XRD谱图和性能对比
Fig.9 XRD patterns and performances of Ni-N-CNTs-1, Ni-N-CNTs-1-12h, Ni-N-CNTs-1-24h and Ni NPs/N-CNTs-1 samples

图10 Ni-N-CNTs-1催化剂经KSCN处理前后和经2 mol·L-1 H3PO4溶液浸泡不同时间后的FECO和jCO,所制备催化剂上Ni-Nx和pyridinic-N含量与FECO的对应关系以及CO2RR生成CO可能的机理
Fig.10 The catalytic performance of Ni-N-CNTs-1 electrocatalyst with or without KSCN treatment, and after soaking in 2 mol·L-1 H3PO4 for different time, the relationship between the contents of Ni-Nx and pyridinic-N with FECO, and the proposed mechanism for CO2RR to CO on prepared electrocatalysts
| 1 | Zhang X L, Guo S X, Gandionco K A, et al. Electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction: from fundamental principles to catalyst design[J]. Materials Today Advances, 2020, 7: 100074. |
| 2 | 任静, 谭玲, 赵宇飞, 等. 超薄二维材料光/电催化CO2还原的最新进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 398-424. |
| Ren J, Tan L, Zhao Y F, et al. Latest development of ultrathin two-dimensional materials for photocatalytic and electrocatalytic CO2 reduction[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 398-424. | |
| 3 | Kim J, Song J T, Ryoo H, et al. Morphology-controlled Au nanostructures for efficient and selective electrochemical CO2 reduction[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(12): 5119-5128. |
| 4 | Chen D, Yao Q, Cui P L, et al. Tailoring the selectivity of bimetallic copper-palladium nanoalloys for electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018, 1(2): 883-890. |
| 5 | Xie H, Wan Y Y, Wang X M, et al. Boosting Pd-catalysis for electrochemical CO2 reduction to CO on Bi-Pd single atom alloy nanodendrites[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 289: 119783. |
| 6 | Luo W, Zhang Q, Zhang J, et al. Electrochemical reconstruction of ZnO for selective reduction of CO2 to CO[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 273: 119060. |
| 7 | Li Z, He D, Yan X, et al. Size-dependent nickel-based electrocatalysts for selective CO2 reduction[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 2020, 59(42): 18572-18577. |
| 8 | Lu P L, Zhang J X, He H X, et al. Iron/nickel nano-alloy encapsulated in nitrogen-doped carbon framework for CO2 electrochemical conversion with prominent CO selectivity[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 449: 227496. |
| 9 | Fan Q, Hou P F, Choi C, et al. Activation of Ni particles into single Ni-N atoms for efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2 [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(5): 1903068. |
| 10 | Ping D, Huang S G, Wu S D, et al. LDHs-based bifunctional electrocatalyst for effective tunable syngas generation via CO2 reduction[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(56): 23653-23660. |
| 11 | Jia C, Tan X, Zhao Y, et al. Sulfur-dopant-promoted electroreduction of CO2 over coordinatively unsaturated Ni-N2 moieties[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(43): 23342-23348. |
| 12 | Lin L, Li H B, Wang Y, et al. Temperature-dependent CO2 electroreduction over Fe-N-C and Ni-N-C single-atom catalysts[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(51): 26582-26586. |
| 13 | Jiang P F, Jiang K Y, Tranca D N, et al. Rational control of topological defects in porous carbon for high-efficiency carbon dioxide conversion[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2021, 8(7): 2100051. |
| 14 | Xiong W F, Li H F, Wang H M, et al. Hollow mesoporous carbon sphere loaded Ni-N4 single-atom: support structure study for CO2 electrocatalytic reduction catalyst[J]. Small, 2020, 16(41): 2003943. |
| 15 | 董灵玉, 葛睿, 原亚飞, 等. 多孔炭基二氧化碳电催化材料研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(6): 2492-2509. |
| Dong L Y, Ge R, Yuan Y F, et al. Recent advances in porous carbon-based carbon dioxide electrocatalytic materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(6): 2492-2509. | |
| 16 | Sheng J, Li Y. Applications of carbon nanotubes in oxygen electrocatalytic reactions[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(18): 20455-20462. |
| 17 | Zhang C, Chen G Y, Zhang R X, et al. Charge modulation of CNTs-based conductive network for oxygen reduction reaction and microwave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2021, 178(35): 310-319. |
| 18 | Hou P X, Zhang F, Zhang L L, et al. Synthesis of carbon nanotubes by floating catalyst chemical vapor deposition and their applications[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(11): 2270066. |
| 19 | Lu P L, Yang Y J, Yao J N, et al. Facile synthesis of single-nickel-atomic dispersed N-doped carbon framework for efficient electrochemical CO2 reduction[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 241: 113-119. |
| 20 | Shen S J, Han C, Wang B, et al. Self-supported nickel single atoms overwhelming the concomitant nickel nanoparticles enable efficient and selective CO2 electroreduction[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2021, 8(20): 2101542. |
| 21 | Gao C B, LYu F L, Yin Y D. Encapsulated metal nanoparticles for catalysis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(2): 834-881. |
| 22 | Niu Y J, Zhang C H, Wang Y Y, et al. Confining chainmail-bearing Ni nanoparticles in N-doped carbon nanotubes for robust and efficient electroreduction of CO2 [J]. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(4): 1140-1154. |
| 23 | Hu C, Mu Y, Bai S L, et al. Polyvinyl pyrrolidone mediated fabrication of Fe, N-codoped porous carbon sheets for efficient electrocatalytic CO2 reduction[J]. Carbon, 2019, 153: 609-616. |
| 24 | Guo Y, Yang H J, Zhou X, et al. Electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO with 100% faradaic efficiency by using pyrolyzed zeolitic imidazolate frameworks supported on carbon nanotube networks[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(47): 24867-24873. |
| 25 | Zhu Z Z, Li Z, Wei X X, et al. Achieving efficient electroreduction of CO2 to CO in a wide potential window by encapsulating Ni nanoparticles in N-doped carbon nanotubes[J]. Carbon, 2021, 185: 9-16. |
| 26 | Ding C M, Feng C C, Mei Y H, et al. Carbon nitride embedded with transition metals for selective electrocatalytic CO2 reduction[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 268: 118391. |
| 27 | Zhao X Y, Huang S H, Chen Z Y, et al. Carbon nanosheets supporting Ni-N3S single-atom sites for efficient electrocatalytic CO2 reduction[J]. Carbon, 2021, 178: 488-496. |
| 28 | Wu S D, Lv X N, Ping D, et al. Highly exposed atomic Fe-N active sites within carbon nanorods towards electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 340: 135930. |
| 29 | Liang S Y, Jiang Q, Wang Q, et al. Revealing the real role of nickel decorated nitrogen doped carbon catalysts for electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(36): 2101477. |
| 30 | Li P B, Qi X Q, Zhao L, et al. Hierarchical 3D porous carbon with facilely accessible Fe-N4 single-atom sites for Zn-air batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(11): 5925-5929. |
| 31 | Lu Y, Wang H J, Yu P F, et al. Isolated Ni single atoms in nitrogen doped ultrathin porous carbon templated from porous g-C3N4 for high-performance CO2 reduction[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 77:105158. |
| 32 | Wu S D, Yi F, Ping D, et al. Constructing single-atomic nickel sites in carbon nanotubes for efficient CO2 electroreduction[J]. Carbon, 2022, 196: 1-9. |
| 33 | Wu W, Zhang W, Long Y, et al. MOF-derived Fe-N-C with interconnected mesoporous structure for halonitrobenzenes hydrogenation: role of dicyandiamide on the growth of active sites and pore structure[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2021, 328: 111472. |
| 34 | Liu Y Z, Li C H, Loubidi M, et al. Increasing exposure of atomically dispersed Ni sites via constructing hierarchically porous supports for enhanced electrochemical CO2 reduction[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 426: 131414. |
| 35 | Han S G, Ma D D, Zhou S H, et al. Fluorine-tuned single-atom catalysts with dense surface Ni-N4 sites on ultrathin carbon nanosheets for efficient CO2 electroreduction[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 283: 119591. |
| 36 | Sun X H, Wang R M, Ould-Chikh S, et al. Structure-activity relationships in metal organic framework derived mesoporous nitrogen-doped carbon containing atomically dispersed iron sites for CO2 electrochemical reduction[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 378: 320-330. |
| 37 | Zhang C, Fu Z H, Zhao Q, et al. Single-atom-Ni-decorated, nitrogen-doped carbon layers for efficient electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2020, 116: 106758. |
| 38 | Cheng Y, Zhao S Y, Johannessen B, et al. Atomically dispersed transition metals on carbon nanotubes with ultrahigh loading for selective electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(13): 1706287. |
| 39 | Zhao C M, Dai X Y, Yao T, et al. Ionic exchange of metal-organic frameworks to access single nickel sites for efficient electroreduction of CO2 [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(24) : 8078-8081. |
| 40 | Wang X S, Pan Y Y, Ning H, et al. Hierarchically micro- and meso-porous Fe-N4O-doped carbon as robust electrocatalyst for CO2 reduction[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 266: 118630. |
| 41 | Varela A S, Ranjbar S N, Steinberg J, et al. Metal-doped nitrogenated carbon as an efficient catalyst for direct CO2 electroreduction to CO and hydrocarbons[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(37): 10758-10762. |
| 42 | Maurin A, Robert M. Noncovalent immobilization of a molecular iron-based electrocatalyst on carbon electrodes for selective, efficient CO2-to-CO conversion in water[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(8): 2492-2495. |
| 43 | Gong S H, Wang W B, Xiao X X, et al. Elucidating influence of the existence formation of anchored cobalt phthalocyanine on electrocatalytic CO2-to-CO conversion[J]. Nano Energy, 2021, 84: 105904. |
| 44 | Miao Z C, Meng J, Liang M F, et al. In-situ CVD synthesis of Ni@N-CNTs/carbon paper electrode for electro-reduction of CO2 [J]. Carbon, 2021, 172: 324-333. |
| 45 | Tan D X, Cui C N, Shi J B, et al. Nitrogen-carbon layer coated nickel nanoparticles for efficient electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide[J]. Nano Research, 2019, 12(5): 1167-1172. |
| 46 | Zhang S Y, Yang Y Y, Zheng Y Q, et al. Ag-doped Co3O4 catalyst derived from heterometallic MOF for syngas production by electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 in water[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2018, 263: 44-51. |
| 47 | Wang X Y, Feng S H, Lu W C, et al. A new strategy for accelerating dynamic proton transfer of electrochemical CO2 reduction at high current densities[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(50): 2104243. |
| 48 | Liu S, Yang H B, Huang X, et al. Identifying active sites of nitrogen-doped carbon materials for the CO2 reduction reaction[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(21):1800499. |
| 49 | Ma C, Hou P F, Wang X P, et al. Carbon nanotubes with rich pyridinic nitrogen for gas phase CO2 electroreduction[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 250: 347-354. |
| 50 | Lu Q, Chen C, Di Q, et al. Dual role of pyridinic-N doping in carbon-coated Ni nanoparticles for highly efficient electrochemical CO2 reduction to CO over a wide potential range[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(2): 1364-1374. |
| [1] | 吴雷, 刘姣, 李长聪, 周军, 叶干, 刘田田, 朱瑞玉, 张秋利, 宋永辉. 低阶粉煤催化微波热解制备含碳纳米管的高附加值改性兰炭末[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3956-3967. |
| [2] | 杨峥豪, 何臻, 常玉龙, 靳紫恒, 江霞. 生物质快速热解下行式流化床反应器研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2249-2263. |
| [3] | 衣思敏, 马亚丽, 刘伟强, 张金帅, 岳岩, 郑强, 贾松岩, 李雪. 微晶菱镁矿蒸氨及水化动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1578-1586. |
| [4] | 陈瑞哲, 程磊磊, 顾菁, 袁浩然, 陈勇. 纤维增强树脂复合材料化学回收技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 981-994. |
| [5] | 张娜, 潘鹤林, 牛波, 张亚运, 龙东辉. 酚醛树脂热裂解反应机理的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 843-860. |
| [6] | 郝泽光, 张乾, 高增林, 张宏文, 彭泽宇, 杨凯, 梁丽彤, 黄伟. 生物质与催化裂化油浆共热解协同作用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4070-4078. |
| [7] | 邵健, 冯军宗, 柳凤琦, 姜勇刚, 李良军, 冯坚. 酚醛树脂基炭微球结构调控与功能化制备研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3787-3801. |
| [8] | 陈晨, 杨倩, 陈云, 张睿, 刘冬. 不同氧浓度下煤挥发分燃烧的化学动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4133-4146. |
| [9] | 肖皓宇, 杨海平, 张雄, 陈应泉, 王贤华, 陈汉平. 塑料催化热解制备高附加值产品的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3461-3471. |
| [10] | 唐恺鸿, 何晓峰, 徐桂秋, 于洋, 刘啸凤, 葛铁军, 张爱玲. 酚醛泡沫的燃烧行为及阻燃研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3483-3500. |
| [11] | 陈永安, 周安宁, 李云龙, 石智伟, 贺新福, 焦卫红. 磁性MgFe2O4及其核壳催化剂制备与煤热解性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3026-3037. |
| [12] | 陈玉弓, 陈昊, 黄耀松. 基于分子反应动力学模拟的六甲基二硅氧烷热解机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2844-2857. |
| [13] | 郑默, 李晓霞. ReaxFF MD模拟揭示的煤热解挥发分自由基反应的竞争与协调[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2732-2741. |
| [14] | 陈冠益, 童图军, 李瑞, 王燕杉, 颜蓓蓓, 李宁, 侯立安. 热解时间对污泥生物炭活化过硫酸盐的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2111-2119. |
| [15] | 赵希强, 张健, 孙爽, 王文龙, 毛岩鹏, 孙静, 刘景龙, 宋占龙. 生物质炭改性微球去除化工废水中无机磷的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2158-2173. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号