化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (2): 830-842.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221299
姜家豪1( ), 黄笑乐1, 任纪云1, 朱正荣2, 邓磊1(
), 黄笑乐1, 任纪云1, 朱正荣2, 邓磊1( ), 车得福1
), 车得福1
收稿日期:2022-09-27
修回日期:2022-12-07
出版日期:2023-02-05
发布日期:2023-03-21
通讯作者:
邓磊
作者简介:姜家豪(1996—),男,博士研究生,Jiangjh@stu.xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Jiahao JIANG1( ), Xiaole HUANG1, Jiyun REN1, Zhengrong ZHU2, Lei DENG1(
), Xiaole HUANG1, Jiyun REN1, Zhengrong ZHU2, Lei DENG1( ), Defu CHE1
), Defu CHE1
Received:2022-09-27
Revised:2022-12-07
Online:2023-02-05
Published:2023-03-21
Contact:
Lei DENG
摘要:
由木质纤维素类生物质经过热解制得的生物炭能够高效地吸附污水中的重金属离子,将其作为Pb2+吸附剂,具有广阔的应用前景。本文以松木与大豆秸秆为原料,分别在400、600、800℃下制备了生物炭,考察了其理化特性与吸附性能之间的关系,并对各吸附机制的相对贡献进行了定性及定量分析。研究结果表明:大豆秸秆生物炭的吸附性能(最大吸附容量分别为209.35、180.62和226.64 mg∙g-1)远优于松木生物炭的(4.62、12.02和23.47 mg∙g-1)。6种生物炭对Pb2+的吸附过程都符合Langmuir模型和拟二级动力学模型,以化学吸附为主,受物理微观结构的影响较小。阳离子交换在生物炭吸附Pb2+过程中占据重要作用,其中Ca2+的交换能力最强。Pb2+在生物炭表面的矿物沉淀主要为水白铅矿和碳酸铅。矿物质沉淀(贡献占比21.9%~76.8%)和阳离子交换(18.1%~72.5%)是大豆秸秆炭和松木炭对Pb2+的主要吸附机制,其次是π电子相互作用和官能团络合。
中图分类号:
姜家豪, 黄笑乐, 任纪云, 朱正荣, 邓磊, 车得福. 生物炭吸附溶液中Pb2+的定性及定量研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 830-842.
Jiahao JIANG, Xiaole HUANG, Jiyun REN, Zhengrong ZHU, Lei DENG, Defu CHE. Qualitative and quantitative study on Pb2+ adsorption by biochar in solution[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 830-842.
| 生物炭 | 总酸性官能团含量/ (mmol∙g-1) | pH | 灰分/ % | 比表面积/ (m2∙g-1) | 孔容积/ (cm3∙g-1) | 产率/ % | 元素分析/% | C/H | C/N | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | S | |||||||||
| SBC400 | 1.01 | 9.54 | 12.80 | 5.59 | 0.0098 | 33.5 | 67.44 | 2.648 | 1.28 | 0.662 | 25.46 | 52.72 |
| SBC600 | 0.40 | 10.39 | 17.04 | 28.93 | 0.0184 | 25.3 | 70.01 | 1.557 | 1.10 | 0.272 | 44.97 | 63.68 |
| SBC800 | 0.33 | 10.76 | 17.88 | 86.33 | 0.0498 | 23.1 | 70.55 | 1.064 | 1.16 | 0.415 | 66.28 | 60.75 |
| PBC400 | 1.15 | 7.45 | 0.34 | 53.84 | 0.0357 | 28.5 | 80.99 | 2.762 | 0.36 | 0.221 | 29.33 | 226.60 |
| PBC600 | 1.00 | 8.75 | 0.40 | 411.84 | 0.1807 | 19.5 | 88.54 | 1.277 | 0.51 | 0.310 | 69.31 | 173.95 |
| PBC800 | 0.77 | 10.02 | 0.47 | 440.52 | 0.2003 | 15.4 | 89.74 | 0.597 | 0.65 | 0.192 | 150.32 | 138.60 |
表1 生物炭的表征(总酸性官能团、pH、灰分、比表面积、产量、元素分析(干燥基基准))
Table 1 Characterization of biochar (total acidity, pH, ash, surface area, yield, elemental analysis(dry basis))
| 生物炭 | 总酸性官能团含量/ (mmol∙g-1) | pH | 灰分/ % | 比表面积/ (m2∙g-1) | 孔容积/ (cm3∙g-1) | 产率/ % | 元素分析/% | C/H | C/N | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | S | |||||||||
| SBC400 | 1.01 | 9.54 | 12.80 | 5.59 | 0.0098 | 33.5 | 67.44 | 2.648 | 1.28 | 0.662 | 25.46 | 52.72 |
| SBC600 | 0.40 | 10.39 | 17.04 | 28.93 | 0.0184 | 25.3 | 70.01 | 1.557 | 1.10 | 0.272 | 44.97 | 63.68 |
| SBC800 | 0.33 | 10.76 | 17.88 | 86.33 | 0.0498 | 23.1 | 70.55 | 1.064 | 1.16 | 0.415 | 66.28 | 60.75 |
| PBC400 | 1.15 | 7.45 | 0.34 | 53.84 | 0.0357 | 28.5 | 80.99 | 2.762 | 0.36 | 0.221 | 29.33 | 226.60 |
| PBC600 | 1.00 | 8.75 | 0.40 | 411.84 | 0.1807 | 19.5 | 88.54 | 1.277 | 0.51 | 0.310 | 69.31 | 173.95 |
| PBC800 | 0.77 | 10.02 | 0.47 | 440.52 | 0.2003 | 15.4 | 89.74 | 0.597 | 0.65 | 0.192 | 150.32 | 138.60 |
| Char | Q/(mg∙g-1) | Pseudo-first-order model | Pseudo-second-order model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe/(mg∙g-1) | k1/ h-1 | R2 | qe/(mg∙g-1) | k2/(g∙mg-1∙h-1) | R2 | ||
| SBC400 | 206.22 | 195.57 | 0.394 | 0.976 | 218.79 | 0.002 | 0.994 |
| SBC600 | 176.30 | 160.72 | 2.989 | 0.696 | 166.84 | 0.031 | 0.879 |
| SBC800 | 227.24 | 205.65 | 2.699 | 0.583 | 213.94 | 0.021 | 0.861 |
| PBC400 | 4.50 | 3.57 | 2.301 | 0.728 | 3.76 | 0.887 | 0.839 |
| PBC600 | 12.26 | 11.67 | 1.275 | 0.891 | 12.34 | 0.151 | 0.939 |
| PBC800 | 22.60 | 21.55 | 0.930 | 0.876 | 23.01 | 0.057 | 0.933 |
表2 不同生物炭吸附Pb2+的拟一级和拟二级吸附动力学拟合参数
Table 2 Kinetic parameters of the pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order model for Pb2+ adsorption onto different chars
| Char | Q/(mg∙g-1) | Pseudo-first-order model | Pseudo-second-order model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe/(mg∙g-1) | k1/ h-1 | R2 | qe/(mg∙g-1) | k2/(g∙mg-1∙h-1) | R2 | ||
| SBC400 | 206.22 | 195.57 | 0.394 | 0.976 | 218.79 | 0.002 | 0.994 |
| SBC600 | 176.30 | 160.72 | 2.989 | 0.696 | 166.84 | 0.031 | 0.879 |
| SBC800 | 227.24 | 205.65 | 2.699 | 0.583 | 213.94 | 0.021 | 0.861 |
| PBC400 | 4.50 | 3.57 | 2.301 | 0.728 | 3.76 | 0.887 | 0.839 |
| PBC600 | 12.26 | 11.67 | 1.275 | 0.891 | 12.34 | 0.151 | 0.939 |
| PBC800 | 22.60 | 21.55 | 0.930 | 0.876 | 23.01 | 0.057 | 0.933 |
| Char | Q/(mg∙g-1) | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/(mg∙g-1) | KL/(L∙mg-1) | R2 | n | KF/(mg1-n ∙L n ∙g-1) | R2 | ||
| SBC400 | 206.22 | 209.35 | 3.939 | 0.994 | 0.124 | 91.49 | 0.797 |
| SBC600 | 176.30 | 180.62 | 2.029 | 0.999 | 0.122 | 78.99 | 0.771 |
| SBC800 | 227.24 | 226.64 | 2.438 | 0.898 | 0.117 | 100.32 | 0.665 |
| PBC400 | 4.54 | 4.62 | 2.640 | 0.901 | 0.052 | 3.47 | 0.684 |
| PBC600 | 12.26 | 12.02 | 0.907 | 0.930 | 0.107 | 6.52 | 0.809 |
| PBC800 | 22.60 | 23.47 | 1.779 | 0.967 | 0.104 | 12.59 | 0.712 |
表3 不同生物炭吸附Pb2+的Langmuir和Freundlich模型拟合参数
Table 3 Adsorption isotherms parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich model for Pb2+ adsorption onto different chars
| Char | Q/(mg∙g-1) | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/(mg∙g-1) | KL/(L∙mg-1) | R2 | n | KF/(mg1-n ∙L n ∙g-1) | R2 | ||
| SBC400 | 206.22 | 209.35 | 3.939 | 0.994 | 0.124 | 91.49 | 0.797 |
| SBC600 | 176.30 | 180.62 | 2.029 | 0.999 | 0.122 | 78.99 | 0.771 |
| SBC800 | 227.24 | 226.64 | 2.438 | 0.898 | 0.117 | 100.32 | 0.665 |
| PBC400 | 4.54 | 4.62 | 2.640 | 0.901 | 0.052 | 3.47 | 0.684 |
| PBC600 | 12.26 | 12.02 | 0.907 | 0.930 | 0.107 | 6.52 | 0.809 |
| PBC800 | 22.60 | 23.47 | 1.779 | 0.967 | 0.104 | 12.59 | 0.712 |
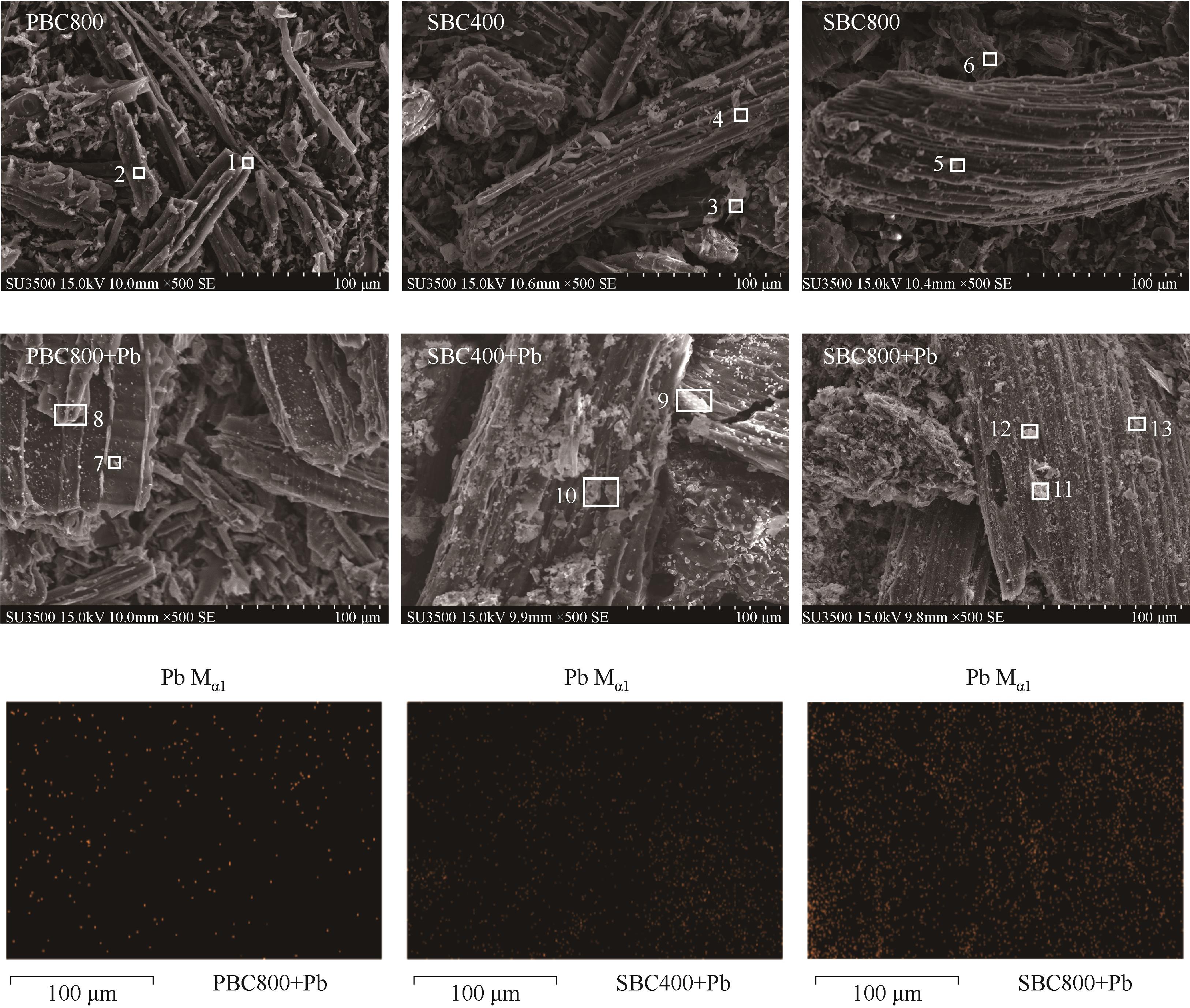
图6 PBC800、SBC400和SBC800吸附前后的微观形貌及吸附后Pb元素分布
Fig.6 Micromorphologies of PBC800, SBC400 and SBC800 before and after adsorption and the Pb distribution after adsorption
| 生物炭 | 区域编号 | EDS扫描的元素分布/% (mass) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Mg | Al | Si | K | Ca | Pb | ||
| PBC800 | 1 | 96.44 | 2.92 | 0.29 | 0.35 | ||||
| 2 | 96.21 | 3.13 | 0.39 | 0.27 | |||||
| SBC400 | 3 | 76.26 | 13.66 | 0.44 | 5.68 | 2.01 | |||
| 4 | 77.84 | 13.07 | 0.94 | 6.59 | 1.23 | ||||
| SBC800 | 5 | 62.38 | 14.80 | 2.01 | 14.26 | 5.03 | |||
| 6 | 64.48 | 20.30 | 1.52 | 5.23 | 6.55 | ||||
| PBC800+Pb | 7 | 95.32 | 3.08 | 0.60 | |||||
| 8 | 97.18 | 2.82 | |||||||
| SBC400+Pb | 9 | 75.90 | 14.06 | 10.04 | |||||
| 10 | 76.85 | 12.87 | 10.28 | ||||||
| SBC800+Pb | 11 | 56.12 | 14.06 | 2.99 | 0.81 | 1.53 | 24.49 | ||
| 12 | 69.49 | 16.10 | 1.82 | 0.75 | 1.86 | 1.22 | 1.10 | 7.67 | |
| 13 | 69.95 | 17.72 | 2.16 | 0.73 | 9.43 | ||||
表4 生物炭表面的EDS扫描结果
Table 4 EDS results of biochar
| 生物炭 | 区域编号 | EDS扫描的元素分布/% (mass) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Mg | Al | Si | K | Ca | Pb | ||
| PBC800 | 1 | 96.44 | 2.92 | 0.29 | 0.35 | ||||
| 2 | 96.21 | 3.13 | 0.39 | 0.27 | |||||
| SBC400 | 3 | 76.26 | 13.66 | 0.44 | 5.68 | 2.01 | |||
| 4 | 77.84 | 13.07 | 0.94 | 6.59 | 1.23 | ||||
| SBC800 | 5 | 62.38 | 14.80 | 2.01 | 14.26 | 5.03 | |||
| 6 | 64.48 | 20.30 | 1.52 | 5.23 | 6.55 | ||||
| PBC800+Pb | 7 | 95.32 | 3.08 | 0.60 | |||||
| 8 | 97.18 | 2.82 | |||||||
| SBC400+Pb | 9 | 75.90 | 14.06 | 10.04 | |||||
| 10 | 76.85 | 12.87 | 10.28 | ||||||
| SBC800+Pb | 11 | 56.12 | 14.06 | 2.99 | 0.81 | 1.53 | 24.49 | ||
| 12 | 69.49 | 16.10 | 1.82 | 0.75 | 1.86 | 1.22 | 1.10 | 7.67 | |
| 13 | 69.95 | 17.72 | 2.16 | 0.73 | 9.43 | ||||
| 1 | 王思远, 杨树俊, 张贺, 等. 土壤中铅污染来源及其危害综述[J]. 农业与技术, 2022, 42(9): 78-81. |
| Wang S Y, Yang S J, Zhang H, et al. Source and harm of lead pollution in soil[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2022, 42(9): 78-81. | |
| 2 | Zhang J Q, Hu X L, Zhang K J, et al. Desorption of calcium-rich crayfish shell biochar for the removal of lead from aqueous solutions[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 554: 417-423. |
| 3 | 刘国成. 生物炭对水体和土壤环境中重金属铅的固持[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014. |
| Liu G C. Immobilization of Pb2+ in contaminated waters and soils by biohcars[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014. | |
| 4 | 吕玉桦. 我国儿童血铅水平现状及对策研究[D]. 衡阳: 南华大学, 2014. |
| Lyu Y H. A study of current situations and countermeasures on blood lead level of children in China[D]. Hengyang: University of South China, 2014. | |
| 5 | 高凤凤. 低维碳基电控离子选择渗透膜的制备及重金属离子分离[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2017. |
| Gao F F. Preparation of low-dimensional carbon-based eletrochemically switched ion permselectivity membrane and separation of heavy metal ion[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2017. | |
| 6 | 杨立鹏. 中和沉淀-Fenton混凝处理蓄电池生产废水工艺及机理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010. |
| Yang L P. Study on the process and mechanism of storage battery wastewater treatment[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010. | |
| 7 | 杨海, 黄新, 林子增, 等. 离子交换法处理重金属废水的研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2019, 48(7): 1675-1680. |
| Yang H, Huang X, Lin Z Z, et al. Research progress in the treatment of heavy metal wastewater by ion exchange[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2019, 48(7): 1675-1680. | |
| 8 | 桂珊, 刘贡钢, 姜珩, 等. 新型多胺羧甲基壳聚糖的合成及对Ni(Ⅱ)的吸附特性[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(5): 1785-1791. |
| Gui S, Liu G G, Jiang H, et al. Synthesis of carboxymethyl polyamines chitosan and its adsorption properties for Ni(Ⅱ)[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(5): 1785-1791. | |
| 9 | 刘凌沁, 黄亚继, 胡华军, 等. 流化床制备玉米秸秆生物炭的Pb2+吸附特性及机理[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 52(4): 666-675. |
| Liu L Q, Huang Y J, Hu H J, et al. Pb2+ adsorption characteristics and mechanism of corn stalk biochar produced by fluidized bed[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 52(4): 666-675. | |
| 10 | 张连科, 刘心宇, 王维大, 等. 油料作物秸秆生物炭对水体中铅离子的吸附特性与机制[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(7): 218-226. |
| Zhang L K, Liu X Y, Wang W D, et al. Characteristics and mechanism of lead adsorption from aqueous solutions by oil crops straw-derived biochar[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(7): 218-226. | |
| 11 | Shen Z T, Zhang Y Y, Jin F, et al. Qualitative and quantitative characterisation of adsorption mechanisms of lead on four biochars[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 609: 1401-1410. |
| 12 | Li H B, Dong X L, Silva E B, et al. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: biochar characteristics and modifications[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 178: 466-478. |
| 13 | Wang L, Wang Y J, Ma F, et al. Mechanisms and reutilization of modified biochar used for removal of heavy metals from wastewater: a review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 668: 1298-1309. |
| 14 | Zhang T, Zhu X X, Shi L N, et al. Efficient removal of lead from solution by celery-derived biochars rich in alkaline minerals[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 235: 185-192. |
| 15 | Ding Y, Liu Y G, Liu S B, et al. Competitive removal of Cd(Ⅱ) and Pb(Ⅱ) by biochars produced from water hyacinths: performance and mechanism[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(7): 5223-5232. |
| 16 | Zhou N, Chen H G, Xi J T, et al. Biochars with excellent Pb(Ⅱ) adsorption property produced from fresh and dehydrated banana peels via hydrothermal carbonization[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 232: 204-210. |
| 17 | Lu H L, Zhang W H, Yang Y X, et al. Relative distribution of Pb2+ sorption mechanisms by sludge-derived biochar[J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(3): 854-862. |
| 18 | Liu L Q, Huang Y J, Meng Y H, et al. Investigating the adsorption behavior and quantitative contribution of Pb2+ adsorption mechanisms on biochars by different feedstocks from a fluidized bed pyrolysis system[J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 187: 109609. |
| 19 | 国家统计局.国家数据[DB/OL]. . |
| National Bureau of Statistics. National data[DB/OL]. . | |
| 20 | Wang Z Y, Liu G C, Zheng H, et al. Investigating the mechanisms of biochar's removal of lead from solution[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 177: 308-317. |
| 21 | Gao L Y, Deng J H, Huang G F, et al. Relative distribution of Cd2+ adsorption mechanisms on biochars derived from rice straw and sewage sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 272: 114-122. |
| 22 | Ma X W, Li F H, Ma M J, et al. Regulation of ash fusibility characteristics for high-ash-fusion-temperature coal by bean straw addition[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(6): 6678-6688. |
| 23 | Huff M D, Kumar S, Lee J W, et al. Comparative analysis of pinewood, peanut shell, and bamboo biomass derived biochars produced via hydrothermal conversion and pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2014, 146: 303-308. |
| 24 | Li J H, Burra K G, Wang Z W, et al. Effect of alkali and alkaline metals on gas formation behavior and kinetics during pyrolysis of pine wood[J]. Fuel, 2021, 290: 120081. |
| 25 | Liu Z G, Zhang F S. Removal of lead from water using biochars prepared from hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 167(1/2/3): 933-939. |
| 26 | 欧阳金波, 陈建, 刘峙嵘, 等. 生物质源多孔碳制备及其对废水中药物吸附研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(12): 5420-5429. |
| Ouyang J B, Chen J, Liu Z R, et al. Research progress on preparation of biomass-derived porous carbon and its adsorption of pharmaceuticals in wastewater[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(12): 5420-5429. | |
| 27 | Hashimoto K, Miura K, Xu J J, et al. Relation between the gasification rate of carbons supporting alkali metal salts and the amount of oxygen trapped by the metal[J]. Fuel, 1986, 65(4): 489-494. |
| 28 | Knudsen J N, Jensen P A, Dam-Johansen K. Transformation and release to the gas phase of Cl, K, and S during combustion of annual biomass[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2004, 18(5): 1385-1399. |
| 29 | Okuno T, Sonoyama N, Hayashi J I, et al. Primary release of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis of pulverized biomass[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2005, 19(5): 2164-2171. |
| 30 | Kołodyńska D, Wnętrzak R, Leahy J J, et al. Kinetic and adsorptive characterization of biochar in metal ions removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 197: 295-305. |
| 31 | Wang X S, Lu Z P, Miao H H, et al. Kinetics of Pb(Ⅱ) adsorption on black carbon derived from wheat residue[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 166(3): 986-993. |
| 32 | Chen X C, Chen G C, Chen L G, et al. Adsorption of copper and zinc by biochars produced from pyrolysis of hardwood and corn straw in aqueous solution[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(19): 8877-8884. |
| 33 | Mohan D, Pittman Jr C U, Bricka M, et al. Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2007, 310(1): 57-73. |
| 34 | Wang R Z, Huang D L, Liu Y G, et al. Investigating the adsorption behavior and the relative distribution of Cd2+ sorption mechanisms on biochars by different feedstock[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 261: 265-271. |
| 35 | 王耀强, 赵怡琳, 李玲慧, 等. 海胆状Fe3O4@TiO2磁性纳米介质对Pb2+的选择吸附特性[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(1): 446-454. |
| Wang Y Q, Zhao Y L, Li L H, et al. Selective adsorption of Pb2+ by sea urchin magnetic nano-Fe3O4@TiO2 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(1): 446-454. | |
| 36 | Cheng M, Zeng G M, Huang D L, et al. Hydroxyl radicals based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for remediation of soils contaminated with organic compounds: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 284: 582-598. |
| 37 | Rwiza M J, Oh S Y, Kim K W, et al. Comparative sorption isotherms and removal studies for Pb(Ⅱ) by physical and thermochemical modification of low-cost agro-wastes from Tanzania[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 195: 135-145. |
| 38 | Ding W C, Dong X L, Ime I M, et al. Pyrolytic temperatures impact lead sorption mechanisms by bagasse biochars[J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 105: 68-74. |
| 39 | Sun J K, Lian F, Liu Z Q, et al. Biochars derived from various crop straws: characterization and Cd(Ⅱ) removal potential[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2014, 106: 226-231. |
| 40 | Li Y F, Liu X, Zhang P Z, et al. Qualitative and quantitative correlation of physicochemical characteristics and lead sorption behaviors of crop residue-derived chars[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 270: 545-553. |
| 41 | Yorita H, Otomo K, Hiramatsu H, et al. Evidence for the cation-π interaction between Cu2+ and tryptophan[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(46): 15266-15267. |
| [1] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [2] | 张建华, 陈萌萌, 孙雅雯, 彭永臻. 部分短程硝化同步除磷耦合Anammox实现生活污水高效脱氮除磷[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2147-2156. |
| [3] | 赵希强, 张健, 孙爽, 王文龙, 毛岩鹏, 孙静, 刘景龙, 宋占龙. 生物质炭改性微球去除化工废水中无机磷的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2158-2173. |
| [4] | 陈冠益, 童图军, 李瑞, 王燕杉, 颜蓓蓓, 李宁, 侯立安. 热解时间对污泥生物炭活化过硫酸盐的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2111-2119. |
| [5] | 高歆婕, 许载周, 彭永臻, 黄雨薇, 丁静, 安泽铭, 汪传新. 污泥双回流-厌氧/好氧/缺氧强化内源反硝化深度脱氮[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5098-5105. |
| [6] | 秦坤, 李佳乐, 王章鸿, 张会岩. 富Ca香菇菌渣基生物炭对含磷废水处理性能的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5263-5274. |
| [7] | 田锐, 王沛力, 吕超, 段雪. 有机-无机复合材料中无机相分散度三维荧光分析[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(6): 3002-3013. |
| [8] | 王龙洋, 蒙西, 乔俊飞. 基于改进集合经验模态分解和深度信念网络的出水总磷预测[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(5): 2745-2753. |
| [9] | 赵杨, 熊伟丽. 基于多策略自适应差分进化算法的污水处理过程多目标优化控制[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 2167-2177. |
| [10] | 陈唐维, 潘志成, 陈滢, 刘敏, 陈婷婷, 钟亚萍. 旋流器分流比对剩余污泥的释碳性能影响[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5761-5769. |
| [11] | 王玉,余广炜,江汝清,林佳佳,汪印. 粒径对餐厨沼渣热解制备生物炭中磷和重金属的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 5344-5353. |
| [12] | 胡智丰,邓时海,张超,李德生,彭帅. 集成式铁基质生物膜反应器自养反硝化深度脱氮[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(7): 3304-3312. |
| [13] | 莫官海, 谢水波, 曾涛涛, 刘迎九, 蔡萍莉. 污泥基生物炭处理酸性含U(Ⅵ)废水的效能与机理[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5): 2352-2362. |
| [14] | 李安玉, 李双莉, 余碧戈, 马爱英, 周鑫兰, 谢建慧, 蒋艳红, 邓华. 镁浸渍生物炭吸附氨氮和磷:制备优化和吸附机理[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1683-1695. |
| [15] | 李伟斌, 宋超, 易贤, 马洪林, 杜雁霞. 动态结冰孔隙结构三维建模方法[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(3): 1009-1017. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号