化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (7): 2670-2679.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240198
胡军勇( ), 胡亚丽, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 张乐炜, 曾俊立, 刘晓奕, 陶源
), 胡亚丽, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 张乐炜, 曾俊立, 刘晓奕, 陶源
收稿日期:2024-02-26
修回日期:2024-04-13
出版日期:2024-07-25
发布日期:2024-08-09
通讯作者:
胡军勇
作者简介:胡军勇(1989—),男,博士,讲师,Hu_Junyong@outlook.com
基金资助:
Junyong HU( ), Yali HU, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Lewei ZHANG, Junli ZENG, Xiaoyi LIU, Yuan TAO
), Yali HU, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Lewei ZHANG, Junli ZENG, Xiaoyi LIU, Yuan TAO
Received:2024-02-26
Revised:2024-04-13
Online:2024-07-25
Published:2024-08-09
Contact:
Junyong HU
摘要:
与单级逆电渗析相比,多级逆电渗析(multi-stage reverse electrodialysis,MSRED)在逆电渗析热机输出功率方面更具有优势,因其可将更多的溶液盐差能转换为电能。为进一步提高MSRED 的输出功率,对比研究了先前开发的LiCl-NH4Cl水溶液(质量摩尔比为2∶8)与传统NaCl水溶液在作为MSRED工作溶液时装置的总净输出功率。结果表明,采用LiCl-NH4Cl水溶液的MSRED能够实现大电流输出,且与等质量摩尔浓度的NaCl水溶液相比,MSRED的总净输出功率最高提升28.6%。另外,无论相关工况参数如何变化,采用LiCl-NH4Cl水溶液的MSRED均能获得比等质量摩尔浓度的NaCl水溶液条件下更高的总净输出功率;同时系统所使用的电堆数量更少,从而可节省设备成本并减小装置体积。
中图分类号:
胡军勇, 胡亚丽, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 张乐炜, 曾俊立, 刘晓奕, 陶源. 基于LiCl-NH4Cl水溶液多级逆电渗析性能的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2670-2679.
Junyong HU, Yali HU, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Lewei ZHANG, Junli ZENG, Xiaoyi LIU, Yuan TAO. Experimental study on the performance of multi-stage reverse electrodialysis based on LiCl-NH4Cl aqueous solution[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2670-2679.
| 试剂 | 纯度 | 生产商 |
|---|---|---|
| 氯化锂 | AR,99.0% | 上海麦克林生化科技 |
| 氯化铵 | AR,99.5% | 上海麦克林生化科技 |
| 氯化钠 | AR,≥ 99.5% | 天津大茂化学试剂厂 |
| 铁氰化钾 | AR,99.5% | 上海阿拉丁生化科技 |
| 亚铁氰化钾 | AR,99.0% | 天津大茂化学试剂厂 |
表1 实验试剂的具体信息
Table 1 Specific information of experimental reagents
| 试剂 | 纯度 | 生产商 |
|---|---|---|
| 氯化锂 | AR,99.0% | 上海麦克林生化科技 |
| 氯化铵 | AR,99.5% | 上海麦克林生化科技 |
| 氯化钠 | AR,≥ 99.5% | 天津大茂化学试剂厂 |
| 铁氰化钾 | AR,99.5% | 上海阿拉丁生化科技 |
| 亚铁氰化钾 | AR,99.0% | 天津大茂化学试剂厂 |
| 型号 | 选择 透过性α/% | 电阻R/(Ω∙cm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fujifilm Type 10 AEM | 1.25 | 94 | 1.7 |
| Fujifilm Type 10 CEM | 1.35 | 98.5 | 2.0 |
表2 IEMs基本参数
Table 2 Basic parameters of Fujifilm IEMs
| 型号 | 选择 透过性α/% | 电阻R/(Ω∙cm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fujifilm Type 10 AEM | 1.25 | 94 | 1.7 |
| Fujifilm Type 10 CEM | 1.35 | 98.5 | 2.0 |
| 型号 | 材料 | 开孔面积/% | 孔隙率ε/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPP32 | PET | 1.50 | 68 | 79.2 |
表3 隔垫的相关参数
Table 3 Relevant parameters of the spacers
| 型号 | 材料 | 开孔面积/% | 孔隙率ε/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPP32 | PET | 1.50 | 68 | 79.2 |
| 实验设备 | 型号 | 测量范围 | 精度 | 生产商 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电子天平 | JJ1523BC | 0~1520 g | ±0.001 g | G&G 测试仪器, 中国 |
| 电化学工作站 | CHI660E | 3 nA~250 mA | 0.2% | 上海辰华仪器有限公司,中国 |
| 电流放大器 | CHI680C | ±2 A | 1 pA | 上海辰华仪器有限公司,中国 |
| 数字万用表 | Keithley 2110 | ±10 V | ±0.012% | 泰克科技有限公司,美国 |
| 恒温水箱 | HH-600 | 室温~100℃ | ±0.5℃ | 智博睿仪器制造有限公司,中国 |
| 压差变送器 | MIK-2051 | 0~350 kPa | ±0.075% | 杭州美控自动化技术有限公司, 中国 |
| 蠕动泵 | DIPump 550-B253 | ≤ 452 ml·min-1 | 0.1 r·min-1 | Kamoer,中国 |
表4 实验设备型号、测量范围及精度
Table 4 Relevant parameters of experimental equipment and instruments
| 实验设备 | 型号 | 测量范围 | 精度 | 生产商 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电子天平 | JJ1523BC | 0~1520 g | ±0.001 g | G&G 测试仪器, 中国 |
| 电化学工作站 | CHI660E | 3 nA~250 mA | 0.2% | 上海辰华仪器有限公司,中国 |
| 电流放大器 | CHI680C | ±2 A | 1 pA | 上海辰华仪器有限公司,中国 |
| 数字万用表 | Keithley 2110 | ±10 V | ±0.012% | 泰克科技有限公司,美国 |
| 恒温水箱 | HH-600 | 室温~100℃ | ±0.5℃ | 智博睿仪器制造有限公司,中国 |
| 压差变送器 | MIK-2051 | 0~350 kPa | ±0.075% | 杭州美控自动化技术有限公司, 中国 |
| 蠕动泵 | DIPump 550-B253 | ≤ 452 ml·min-1 | 0.1 r·min-1 | Kamoer,中国 |
| 电流密度id/(A·m-2) | 浓溶液质量摩尔浓度mHC/(mol·kg-1) | 稀溶液质量摩尔浓度mLC/(mol·kg-1) | 流速v/(cm·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20~80 | 3~5 | 0.01~0.1 | 0.5~2 |
表5 实验参数变化范围
Table 5 Variation range of experimental parameters
| 电流密度id/(A·m-2) | 浓溶液质量摩尔浓度mHC/(mol·kg-1) | 稀溶液质量摩尔浓度mLC/(mol·kg-1) | 流速v/(cm·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20~80 | 3~5 | 0.01~0.1 | 0.5~2 |

图4 不同电流密度下总净输出功率随电堆数量的变化[mHC=4 mol·kg-1,mLC=0.05 mol·kg-1,t =(25±1)℃,v=1.0 cm·s-1]
Fig. 4 Variations of the total net output power with the number of RED stacks under different current densities (id) [mHC=4 mol·kg-1, mLC=0.05 mol·kg-1, t=(25±1)°C, v=1.0 cm·s-1]
电池 单元数 | 工作溶液 | id/(A·m-2) | N | Pnet/W | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | NaCl水溶液 | 60 | 8 | 0.92 | [ |
| 10 | NaCl水溶液 | —① | 22 | 0.34② | [ |
| 10 | LiBr-H2O-CH3CH2OH | —① | 22 | 0.99② | [ |
| 5 | LiCl-NH4Cl水溶液 | 80 | 9 | 1.17 | 本文 |
表6 相关MSRED性能数据对比
Table 6 Comparison of pertinent performance data for MSRED
电池 单元数 | 工作溶液 | id/(A·m-2) | N | Pnet/W | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | NaCl水溶液 | 60 | 8 | 0.92 | [ |
| 10 | NaCl水溶液 | —① | 22 | 0.34② | [ |
| 10 | LiBr-H2O-CH3CH2OH | —① | 22 | 0.99② | [ |
| 5 | LiCl-NH4Cl水溶液 | 80 | 9 | 1.17 | 本文 |

图5 不同进料浓溶液质量摩尔浓度下总净输出功率随电堆数量的变化[mLC=0.05 mol·kg-1,t =(25±1)℃,v=1.0 cm·s-1]
Fig.5 Variations of the total net output power with the number of RED stacks under different molality concentration of HC feed solution [mLC=0.05 mol·kg-1, t=(25±1)℃, v = 1.0 cm·s-1]
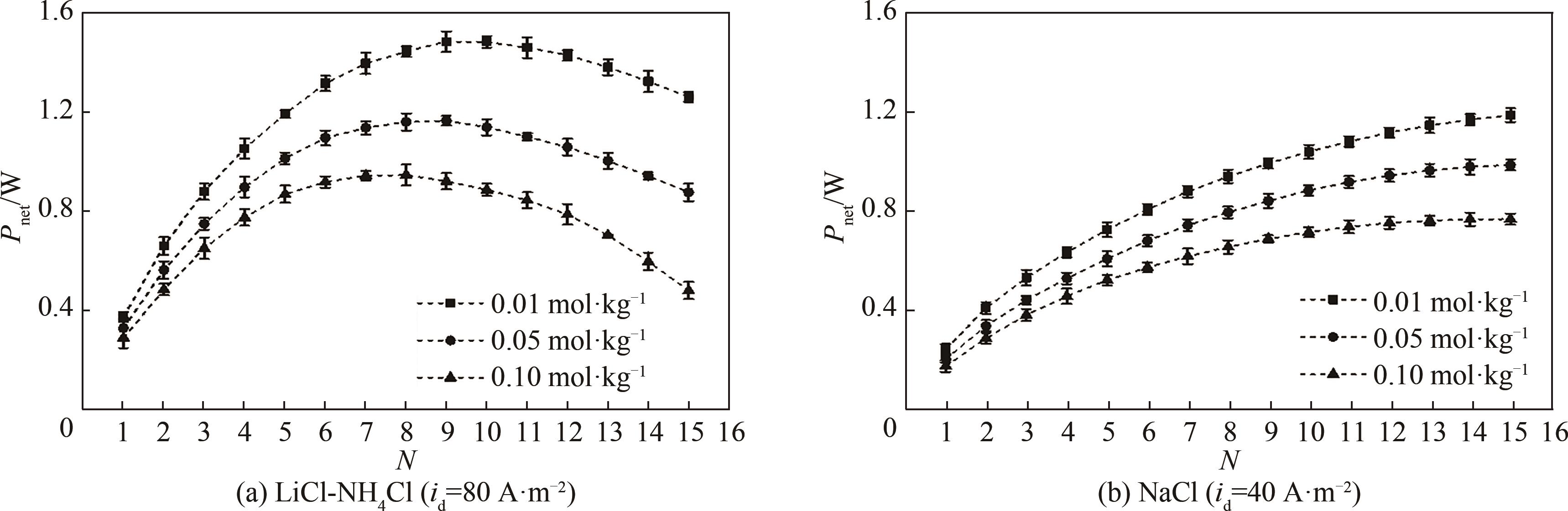
图6 不同进料稀溶液质量摩尔浓度下总净输出功率随电堆数量的变化[mHC=4 mol·kg-1,t=(25±1)℃,v=1.0 cm·s-1]
Fig.6 Variations of the total net output power with the number of RED stacks under different molality concentration of LC feed solution [mHC=4 mol·kg-1, t=(25±1)℃, v=1.0 cm·s-1]

图7 不同进料流速下总净输出功率随电堆数量的变化[mHC=4 mol·kg-1,mLC=0.05 mol·kg-1,t =(25±1)℃]
Fig.7 Variations of the total net output power with the number of RED stacks under different flow velocity [mHC=4 mol·kg-1, mLC=0.05 mol·kg-1, t =(25±1)°C]
| 1 | Kang S B, Li J B, Wang Z H, et al. Salinity gradient energy capture for power production by reverse electrodialysis experiment in thermal desalination plants[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 519: 230806. |
| 2 | Post J W, Goeting C H, Valk J, et al. Towards implementation of reverse electrodialysis for power generation from salinity gradients[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2010, 16(1/2/3): 182-193. |
| 3 | 袁亮. 我国煤炭主体能源安全高质量发展的理论技术思考[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2023, 38(1): 11-22. |
| Yuan L. Theory and technology considerations on high-quality development of coal main energy security in China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2023, 38(1): 11-22. | |
| 4 | 李洪言, 张景谦, 陈健斌, 等. 2021年全球能源转型面临挑战: 基于《BP世界能源统计年鉴(2022)》[J]. 天然气与石油, 2022, 40(6): 129-138. |
| Li H Y, Zhang J Q, Chen J B, et al. Global energy transition faces challenges in 2021—based on the BP Statistical Review of World Energy(2022)[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2022, 40(6): 129-138. | |
| 5 | Xia J B, Eigenberger G, Strathmann H, et al. Acid-base flow battery, based on reverse electrodialysis with Bi-polar membranes: stack experiments[J]. Processes, 2020, 8(1): 99. |
| 6 | 陈霞, 蒋晨啸, 汪耀明, 等. 反向电渗析在新能源及环境保护应用中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(1): 188-202. |
| Chen X, Jiang C X, Wang Y M, et al. Advances in reverse electrodialysis and its applications on renewable energy and environment protection[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(1): 188-202. | |
| 7 | Tamburini A, Tedesco M, Cipollina A, et al. Reverse electrodialysis heat engine for sustainable power production[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 206: 1334-1353. |
| 8 | Tian H L, Wang Y, Pei Y S, et al. Unique applications and improvements of reverse electrodialysis: a review and outlook[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 262: 114482. |
| 9 | Tamburini A, La Barbera G, Cipollina A, et al. CFD prediction of scalar transport in thin channels for reverse electrodialysis[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2015, 55(12): 3424-3445. |
| 10 | Altaee A, Zaragoza G, Drioli E, et al. Evaluation the potential and energy efficiency of dual stage pressure retarded osmosis process[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 199: 359-369. |
| 11 | Kim H, Yang S, Choi J, et al. Optimization of the number of cell pairs to design efficient reverse electrodialysis stack[J]. Desalination, 2021, 497: 114676. |
| 12 | 刘子健, 鹿丁, 白银, 等. 反向电渗析热机发生单元研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(30): 3811-3821. |
| Liu Z J, Lu D, Bai Y, et al. Progress on the regeneration unit of a reverse electrodialysis heat engine[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(30): 3811-3821. | |
| 13 | Simões C, Pintossi D, Saakes M, et al. Electrode segmentation in reverse electrodialysis: improved power and energy efficiency[J]. Desalination, 2020, 492: 114604. |
| 14 | Olkis C, Brandani S, Santori G. Adsorption reverse electrodialysis driven by power plant waste heat to generate electricity and provide cooling[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(2): 1971-1987. |
| 15 | Liu Z J, Lu D, Bai Y, et al. Energy and exergy analysis of heat to salinity gradient power conversion in reverse electrodialysis heat engine[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 252: 115068. |
| 16 | Giacalone F, Olkis C, Santori G, et al. Novel solutions for closed-loop reverse electrodialysis: thermodynamic characterisation and perspective analysis[J]. Energy, 2019, 166: 674-689. |
| 17 | Giacalone F, Catrini P, Tamburini A, et al. Exergy analysis of reverse electrodialysis[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 164: 588-602. |
| 18 | Weiner A M, McGovern R K, Lienhard V J H. A new reverse electrodialysis design strategy which significantly reduces the levelized cost of electricity[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 493: 605-614. |
| 19 | Moreno J, Díez V, Saakes M, et al. Mitigation of the effects of multivalent ion transport in reverse electrodialysis[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 550: 155-162. |
| 20 | Guo Z Y, Ji Z Y, Zhang Y G, et al. Effect of ions (K+, Mg2+, Ca2+ and SO4 2-) and temperature on energy generation performance of reverse electrodialysis stack[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 290: 282-290. |
| 21 | Loeb S. Method and apparatus for generating power utilizing reverse electrodialysis: US4171409[P]. 1979-10-16. |
| 22 | Veerman J, Saakes M, Metz S J, et al. Reverse electrodialysis: a validated process model for design and optimization[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 166(1): 256-268. |
| 23 | Veerman J, Saakes M, Metz S J, et al. Reverse electrodialysis: performance of a stack with 50 cells on the mixing of sea and river water[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2009, 327(1/2): 136-144. |
| 24 | Hu J Y, Xu S M, Wu X, et al. Multi-stage reverse electrodialysis: strategies to harvest salinity gradient energy[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 183: 803-815. |
| 25 | Hu J Y, Xu S M, Wu X, et al. Experimental investigation on the performance of series control multi-stage reverse electrodialysis[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 204: 112284. |
| 26 | Wang Z H, Li J B, Zhang C, et al. Power production from seawater and discharge brine of thermal desalination units by reverse electrodialysis[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 314: 118977. |
| 27 | Daniilidis A, Vermaas D A, Herber R, et al. Experimentally obtainable energy from mixing river water, seawater or brines with reverse electrodialysis[J]. Renewable Energy, 2014, 64: 123-131. |
| 28 | Tedesco M, Brauns E, Cipollina A, et al. Reverse electrodialysis with saline waters and concentrated brines: a laboratory investigation towards technology scale-up[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 492: 9-20. |
| 29 | Wang H, Li J B, Li M Q, et al. Reverse electrodialysis characteristic of the lithium bromide-ethanol-water ternary solution[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 585: 233636. |
| 30 | Micari M, Bevacqua M, Cipollina A, et al. Effect of different aqueous solutions of pure salts and salt mixtures in reverse electrodialysis systems for closed-loop applications[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 551: 315-325. |
| 31 | 胡亚丽, 胡军勇, 马素霞, 等. 逆电渗析热机新型工质开发及电化学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| Hu Y L, Hu J Y, Ma S X, et al. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. | |
| 32 | Vermaas D A, Saakes M, Nijmeijer K. Doubled power density from salinity gradients at reduced intermembrane distance[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2011, 45(16): 7089-7095. |
| 33 | 王一玮. 反向电渗析盐差膜堆系统产电特性及其影响因素研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2022. |
| Wang Y W. Investigation on the power generation performance of a salt-difference stack system by reverse electrodialysis and its influencing factors[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2022. |
| [1] | 张颂红, 赵欣怡, 楼小玲, 沈绍传, 贠军贤. 阳离子交换纳晶胶分离乳过氧化物酶的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2574-2582. |
| [2] | 苏彬, 董浩伟, 罗振敏, 邓军, 王涛, 程方明. 气粉两相体系爆炸动力学特性及机理研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2109-2122. |
| [3] | 赵志星, 姚智豪, 于雪峰, 杨游胜, 曾英, 于旭东. 锂钠镁共存硫酸盐体系多温相图及其应用[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2123-2133. |
| [4] | 许茹枫, 陈煜成, 高丹, 焦静雨, 高栋, 王海彬, 姚善泾, 林东强. 离子交换层析分离单抗电荷异质体的模型辅助过程优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1903-1911. |
| [5] | 王林, 江荣鼎, 张春晓, 李修真, 谈莹莹. 含R1234yf混合工质汽液相平衡的混合规则评估与预测研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 475-483. |
| [6] | 王灵洁, 高海龙, 靳继鹏, 王志浩, 李见波. 海水中的污染物对逆电渗析电堆性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 695-705. |
| [7] | 孙瑞, 田华, 吴子睿, 孙孝存, 舒歌群. 二氧化碳混合工质临界参数计算模型对比研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 439-449. |
| [8] | 吴凡, 彭旭东, 江锦波, 孟祥铠, 梁杨杨. 分子动力学模拟预测天然气密度和黏度的可行性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 450-462. |
| [9] | 常明慧, 王林, 苑佳佳, 曹艺飞. 盐溶液蓄能型热泵循环特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 329-337. |
| [10] | 金正浩, 封立杰, 李舒宏. 氨水溶液交叉型再吸收式热泵的能量及 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. |
| [11] | 赵亚欣, 张雪芹, 王荣柱, 孙国, 姚善泾, 林东强. 流穿模式离子交换层析去除单抗聚集体[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3879-3887. |
| [12] | 高燕, 伍鹏, 尚超, 胡泽君, 陈晓东. 基于双流体喷嘴的磁性琼脂糖微球的制备及其蛋白吸附性能探究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3457-3471. |
| [13] | 程小松, 殷勇高, 车春文. 不同工质在溶液除湿真空再生系统中的性能对比[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3494-3501. |
| [14] | 汪尔奇, 彭书舟, 杨震, 段远源. 含HFO混合体系气液相平衡的理论模型评价[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3216-3225. |
| [15] | 胡亚丽, 胡军勇, 马素霞, 孙禹坤, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 杨奉源. 逆电渗析热机新型工质开发及电化学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号