化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (1): 348-362.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240492
贾艳萍( ), 马艳菊, 管文昕, 杨彬, 张健, 张兰河(
), 马艳菊, 管文昕, 杨彬, 张健, 张兰河( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-06
修回日期:2024-07-04
出版日期:2025-01-25
发布日期:2025-02-08
通讯作者:
张兰河
作者简介:贾艳萍(1973—),女,博士,教授,jiayanping1111@sina.com
基金资助:
Yanping JIA( ), Yanju MA, Wenxin GUAN, Bin YANG, Jian ZHANG, Lanhe ZHANG(
), Yanju MA, Wenxin GUAN, Bin YANG, Jian ZHANG, Lanhe ZHANG( )
)
Received:2024-05-06
Revised:2024-07-04
Online:2025-01-25
Published:2025-02-08
Contact:
Lanhe ZHANG
摘要:
染料废水具有色度大、成分复杂、生物毒性强和难降解的特点。Fe0/H2O2体系氧化能力强、反应快速高效、成本低廉,可有效去除染料废水中的难降解污染物。采用Fe0/H2O2工艺处理染料废水,利用响应面法优化工艺运行条件,通过电子顺磁共振波谱仪(EPR)检测活性自由基,采用傅里叶变换红外光谱(FT-IR)和紫外-可见光谱(UV-Vis)分析染料废水处理前后有机物成分的变化,考察染料废水中结晶紫、藏红T、TOC、COD和色度的去除率变化,探究染料废水的降解动力学和降解机理。结果表明:在初始pH为3、Fe0浓度为0.3 g/L、H2O2投加量为20 ml/L的条件下,利用响应面法预测结晶紫去除率为97.94%,与实测值仅相差0.36%(<2%);藏红T去除率为77.31%,与实测值仅相差1.3%(<2%)。由动力学分析可知:结晶紫、藏红T、COD和色度的降解过程符合BMG动力学模型,相关系数大于0.98,结晶紫的初始降解速率最快。由EPR分析可知:·OH为Fe0/H2O2降解染料废水的主要活性物种;通过FT-IR和UV-Vis检测分析可知:Fe0/H2O2工艺对结晶紫和藏红T的去除效果最好,染料分子被氧化成分子量小的中间体或小分子物质;由气相色谱-质谱(GC-MS)分析可知:结晶紫与藏红T分子结构被
中图分类号:
贾艳萍, 马艳菊, 管文昕, 杨彬, 张健, 张兰河. 响应面法优化Fe0/H2O2体系降解染料废水的工艺条件及机理[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 348-362.
Yanping JIA, Yanju MA, Wenxin GUAN, Bin YANG, Jian ZHANG, Lanhe ZHANG. Process conditions optimization and degradation mechanism of dye wastewater by Fe0/H2O2 system using response surface methodology[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 348-362.
| 编码 | 因素 | 单位 | 水平 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| A | 初始pH | — | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| B | Fe0浓度 | mg/L | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| C | H2O2投加量 | ml/L | 15 | 20 | 25 |
表1 响应面实验因素和水平设计
Table 1 Experimental factors and level design for response surface
| 编码 | 因素 | 单位 | 水平 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| A | 初始pH | — | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| B | Fe0浓度 | mg/L | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| C | H2O2投加量 | ml/L | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| 序号 | 变量取值 | 结晶紫 去除率/% | 藏红T 去除率/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | |||
| 1 | -1 | -1 | 0 | 94.96 | 57.45 |
| 2 | 1 | -1 | 0 | 95.83 | 66.28 |
| 3 | -1 | 1 | 0 | 96.95 | 48.35 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 91.03 | 67.84 |
| 5 | -1 | 0 | -1 | 96.85 | 52.83 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 94.75 | 59.75 |
| 7 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 96.56 | 51.63 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 94.19 | 67.68 |
| 9 | 0 | -1 | -1 | 92.05 | 62.84 |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | -1 | 95.10 | 60.18 |
| 11 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 96.31 | 72.11 |
| 12 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 91.95 | 64.81 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 98.07 | 78.14 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 98.34 | 78.57 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 97.92 | 77.85 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 97.86 | 76.85 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 97.50 | 75.15 |
表2 响应面实验组设计及实验结果
Table 2 Experiment design and experimental results of response surface test group
| 序号 | 变量取值 | 结晶紫 去除率/% | 藏红T 去除率/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | |||
| 1 | -1 | -1 | 0 | 94.96 | 57.45 |
| 2 | 1 | -1 | 0 | 95.83 | 66.28 |
| 3 | -1 | 1 | 0 | 96.95 | 48.35 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 91.03 | 67.84 |
| 5 | -1 | 0 | -1 | 96.85 | 52.83 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 94.75 | 59.75 |
| 7 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 96.56 | 51.63 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 94.19 | 67.68 |
| 9 | 0 | -1 | -1 | 92.05 | 62.84 |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | -1 | 95.10 | 60.18 |
| 11 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 96.31 | 72.11 |
| 12 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 91.95 | 64.81 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 98.07 | 78.14 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 98.34 | 78.57 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 97.92 | 77.85 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 97.86 | 76.85 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 97.50 | 75.15 |
| 变差来源 | 平方和 | 自由度 | 均方和 | F值 | P值 | 显著性 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 | 81.51 | 9 | 9.06 | 53.69 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| A | 11.33 | 1 | 11.33 | 67.16 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| B | 2.12 | 1 | 2.12 | 12.58 | 0.0094 | 显著 | |
| C | 0.0085 | 1 | 0.0085 | 0.0501 | 0.8293 | 不显著 | |
| AB | 11.53 | 1 | 11.53 | 68.33 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| AC | 0.0182 | 1 | 0.0182 | 0.1080 | 0.7520 | 不显著 | |
| BC | 13.73 | 1 | 13.73 | 81.38 | <0.0001 | 显著 | |
| A2 | 2.40 | 1 | 2.40 | 14.24 | 0.0070 | 显著 | |
| B2 | 26.11 | 1 | 26.11 | 154.79 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| C2 | 10.72 | 1 | 10.72 | 63.52 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| 残差 | 1.18 | 7 | 0.1687 | ||||
| 失拟项 | 0.8035 | 3 | 0.2678 | 2.84 | 0.1696 | 不显著 | |
| 误差 | 0.3773 | 4 | 0.0943 | ||||
| 合计 | 82.69 | 16 | |||||
| 标准偏差 | 0.4107 | 相关系数 | 0.9857 | ||||
| 平均值 | 95.66 | 校正决定系数 | 0.9674 | ||||
| 变异系数 | 0.4293 | 预测相关系数 | 0.8374 | ||||
| 信噪比 | 21.1047 | ||||||
表3 结晶紫去除率模型方差分析
Table 3 Variance analysis of crystal violet removal efficiency model
| 变差来源 | 平方和 | 自由度 | 均方和 | F值 | P值 | 显著性 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 | 81.51 | 9 | 9.06 | 53.69 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| A | 11.33 | 1 | 11.33 | 67.16 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| B | 2.12 | 1 | 2.12 | 12.58 | 0.0094 | 显著 | |
| C | 0.0085 | 1 | 0.0085 | 0.0501 | 0.8293 | 不显著 | |
| AB | 11.53 | 1 | 11.53 | 68.33 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| AC | 0.0182 | 1 | 0.0182 | 0.1080 | 0.7520 | 不显著 | |
| BC | 13.73 | 1 | 13.73 | 81.38 | <0.0001 | 显著 | |
| A2 | 2.40 | 1 | 2.40 | 14.24 | 0.0070 | 显著 | |
| B2 | 26.11 | 1 | 26.11 | 154.79 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| C2 | 10.72 | 1 | 10.72 | 63.52 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| 残差 | 1.18 | 7 | 0.1687 | ||||
| 失拟项 | 0.8035 | 3 | 0.2678 | 2.84 | 0.1696 | 不显著 | |
| 误差 | 0.3773 | 4 | 0.0943 | ||||
| 合计 | 82.69 | 16 | |||||
| 标准偏差 | 0.4107 | 相关系数 | 0.9857 | ||||
| 平均值 | 95.66 | 校正决定系数 | 0.9674 | ||||
| 变异系数 | 0.4293 | 预测相关系数 | 0.8374 | ||||
| 信噪比 | 21.1047 | ||||||
| 变差来源 | 平方和 | 自由度 | 均方和 | F值 | P值 | 显著性 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 | 1520.80 | 9 | 168.98 | 65.06 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| A | 328.83 | 1 | 328.83 | 126.60 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| B | 38.28 | 1 | 38.28 | 14.74 | 0.0064 | 显著 | |
| C | 53.20 | 1 | 53.20 | 20.48 | 0.0027 | 显著 | |
| AB | 28.41 | 1 | 28.41 | 10.94 | 0.0130 | 显著 | |
| AC | 20.84 | 1 | 20.84 | 8.02 | 0.0253 | 显著 | |
| BC | 5.38 | 1 | 5.38 | 2.07 | 0.1932 | 不显著 | |
| A2 | 623.85 | 1 | 623.85 | 240.19 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| B2 | 112.10 | 1 | 112.10 | 43.16 | 0.0003 | 显著 | |
| C2 | 216.29 | 1 | 216.29 | 83.28 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| 残差 | 18.18 | 7 | 2.60 | ||||
| 失拟项 | 10.74 | 3 | 3.58 | 1.92 | 0.2675 | 不显著 | |
| 误差 | 7.45 | 4 | 1.86 | ||||
| 合计 | 1538.98 | 16 | |||||
| 标准偏差 | 1.61 | 相关系数 | 0.9882 | ||||
| 平均值 | 65.78 | 校正决定系数 | 0.9730 | ||||
| 变异系数 | 2.45 | 预测相关系数 | 0.8808 | ||||
| 信噪比 | 23.1347 | ||||||
表4 藏红T去除率模型方差分析
Table 4 Variance analysis of saffron T removal efficiency model
| 变差来源 | 平方和 | 自由度 | 均方和 | F值 | P值 | 显著性 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 | 1520.80 | 9 | 168.98 | 65.06 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| A | 328.83 | 1 | 328.83 | 126.60 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| B | 38.28 | 1 | 38.28 | 14.74 | 0.0064 | 显著 | |
| C | 53.20 | 1 | 53.20 | 20.48 | 0.0027 | 显著 | |
| AB | 28.41 | 1 | 28.41 | 10.94 | 0.0130 | 显著 | |
| AC | 20.84 | 1 | 20.84 | 8.02 | 0.0253 | 显著 | |
| BC | 5.38 | 1 | 5.38 | 2.07 | 0.1932 | 不显著 | |
| A2 | 623.85 | 1 | 623.85 | 240.19 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| B2 | 112.10 | 1 | 112.10 | 43.16 | 0.0003 | 显著 | |
| C2 | 216.29 | 1 | 216.29 | 83.28 | <0.0001 | 极显著 | |
| 残差 | 18.18 | 7 | 2.60 | ||||
| 失拟项 | 10.74 | 3 | 3.58 | 1.92 | 0.2675 | 不显著 | |
| 误差 | 7.45 | 4 | 1.86 | ||||
| 合计 | 1538.98 | 16 | |||||
| 标准偏差 | 1.61 | 相关系数 | 0.9882 | ||||
| 平均值 | 65.78 | 校正决定系数 | 0.9730 | ||||
| 变异系数 | 2.45 | 预测相关系数 | 0.8808 | ||||
| 信噪比 | 23.1347 | ||||||
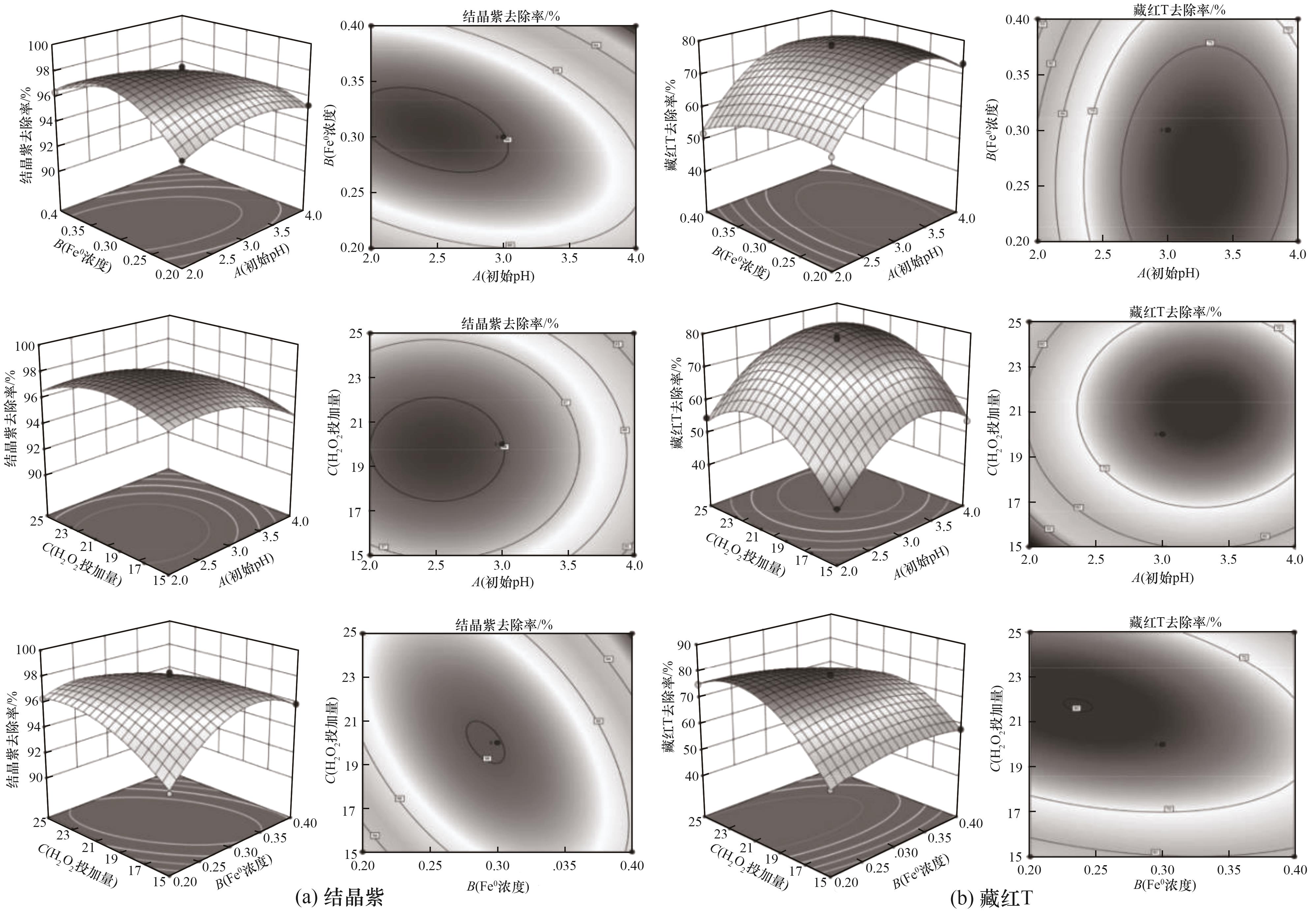
图6 不同因素对结晶紫和藏红T去除率影响的响应面三维图和等高线图
Fig.6 Three-dimensional graph and contour map of response surface affected by different factors on removal efficiency of crystal violet and saffron T
| 污染物 | 一级动力学方程 | 二级动力学方程 | BMG动力学方程 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min-1 | k2/(mg/(L·min)) | (1/m)/min-1 | 1/b | ||||
| 结晶紫 | 0.00754 | 0.98256 | 0.00303 | 0.93845 | 0.27635 | 0.9851 | 0.99977 |
| 藏红T | 0.00318 | 0.96553 | 4.62×10-5 | 0.98636 | 0.00638 | 0.7637 | 0.99290 |
表5 不同污染物降解动力学的拟合结果
Table 5 Fitting results of degradation kinetic of different pollutants
| 污染物 | 一级动力学方程 | 二级动力学方程 | BMG动力学方程 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min-1 | k2/(mg/(L·min)) | (1/m)/min-1 | 1/b | ||||
| 结晶紫 | 0.00754 | 0.98256 | 0.00303 | 0.93845 | 0.27635 | 0.9851 | 0.99977 |
| 藏红T | 0.00318 | 0.96553 | 4.62×10-5 | 0.98636 | 0.00638 | 0.7637 | 0.99290 |
| 产物 | 保留时间/min | m/z | 分子式 | 分子结构 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.815 | 94 | C6H6O | 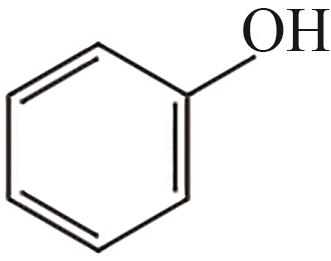 |
| 2 | 4.330 | 93 | C6H7N | 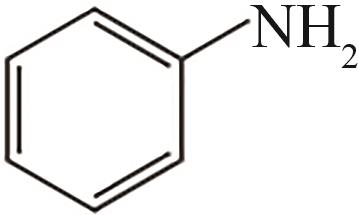 |
| 3 | 5.771 | 287 | C18H15N4 | 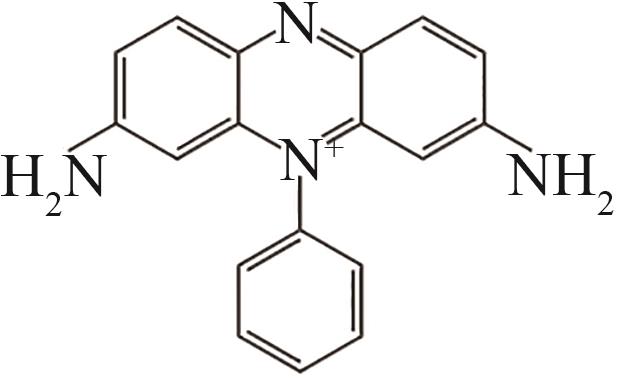 |
| 4 | 6.033 | 166 | C6H14O5 | 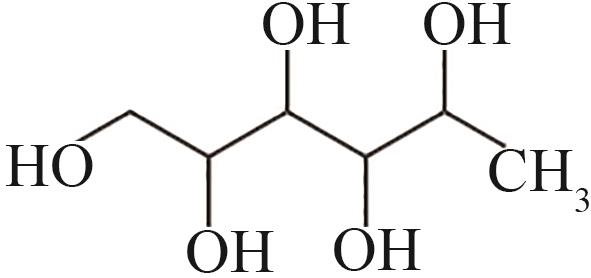 |
| 5 | 7.360 | 142.5 | C6H7ClN2 | 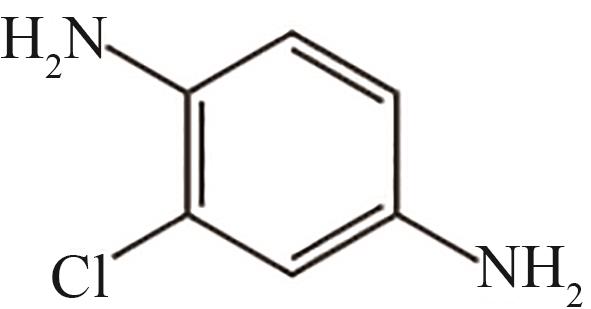 |
| 6 | 9.615 | 165 | C9H11O2N | 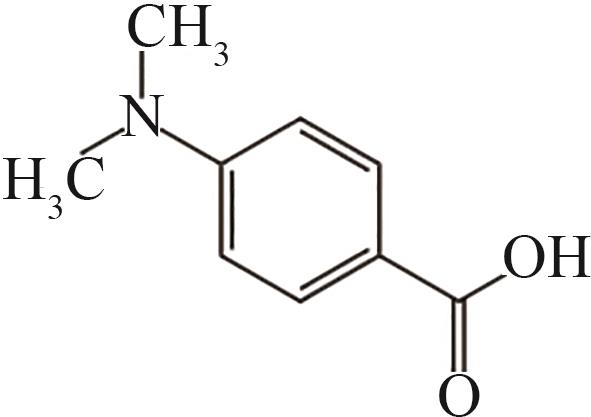 |
| 7 | 11.350 | 184 | C12H12N2 | 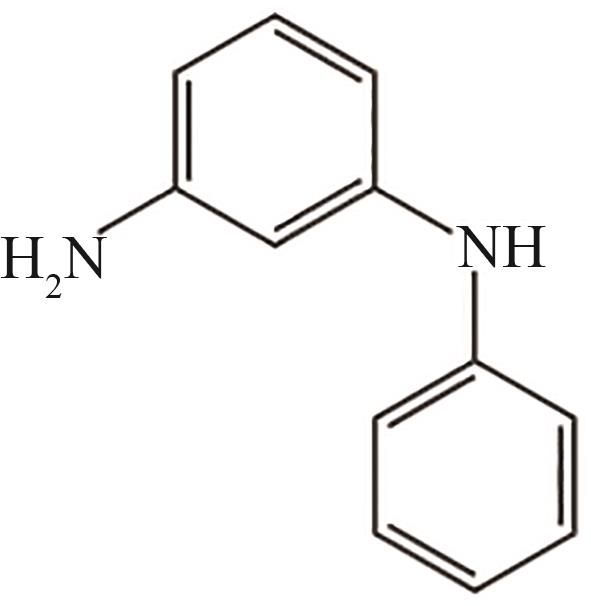 |
| 8 | 13.540 | 137 | C8H11ON | 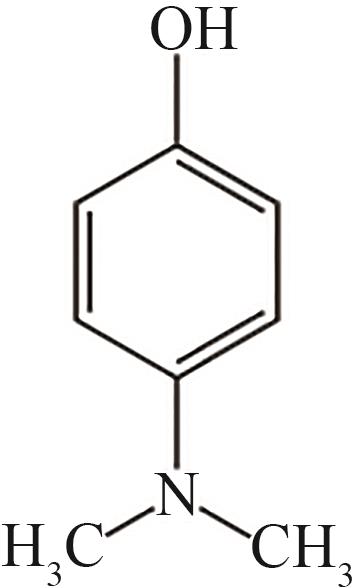 |
| 9 | 14.556 | 134.5 | C6H11OCl | 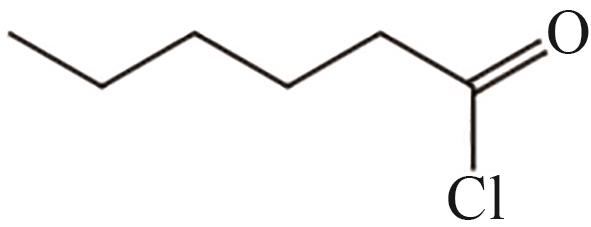 |
| 10 | 15.627 | 112.5 | C6H5Cl | 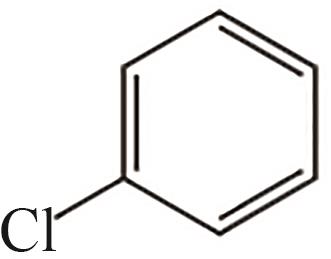 |
| 11 | 16.055 | 137 | C7H7O2N | 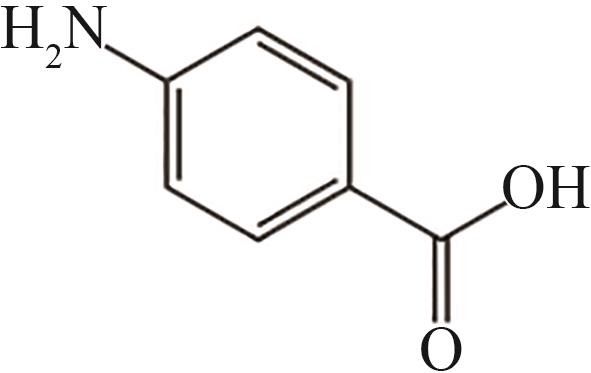 |
| 12 | 17.645 | 109 | C6H7ON | 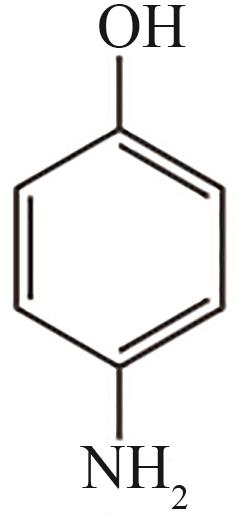 |
| 13 | 21.830 | 121 | C8H11N | 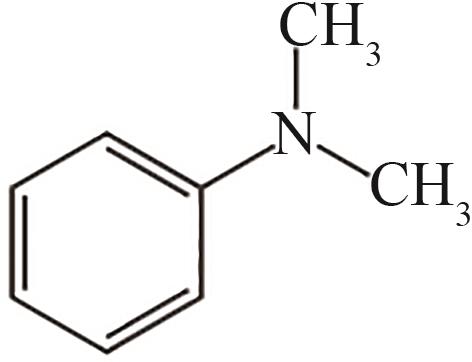 |
| 14 | 22.048 | 268 | C17H20ON2 | 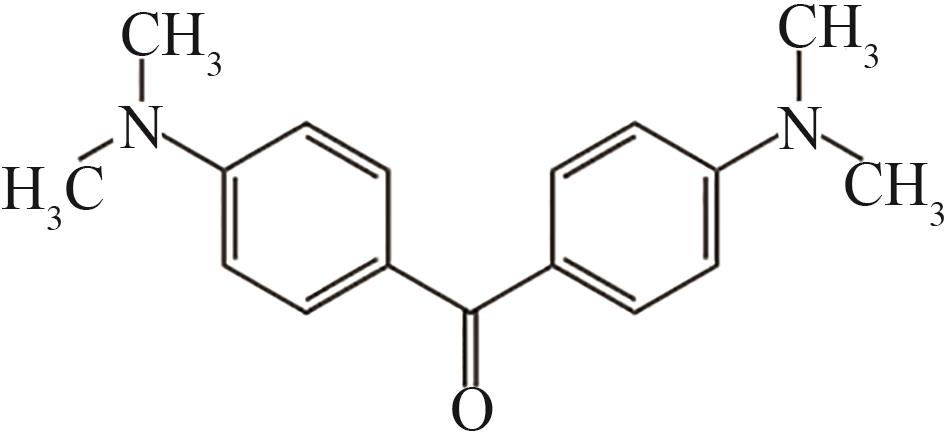 |
| 15 | 27.895 | 72 | C3H4O2 | 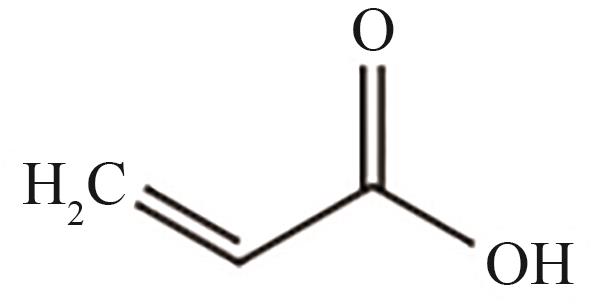 |
表6 结晶紫与藏红T降解过程的中间产物
Table 6 Intermediate products in degradation process of crystal violet and saffron T
| 产物 | 保留时间/min | m/z | 分子式 | 分子结构 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.815 | 94 | C6H6O |  |
| 2 | 4.330 | 93 | C6H7N |  |
| 3 | 5.771 | 287 | C18H15N4 |  |
| 4 | 6.033 | 166 | C6H14O5 |  |
| 5 | 7.360 | 142.5 | C6H7ClN2 |  |
| 6 | 9.615 | 165 | C9H11O2N |  |
| 7 | 11.350 | 184 | C12H12N2 |  |
| 8 | 13.540 | 137 | C8H11ON |  |
| 9 | 14.556 | 134.5 | C6H11OCl |  |
| 10 | 15.627 | 112.5 | C6H5Cl |  |
| 11 | 16.055 | 137 | C7H7O2N |  |
| 12 | 17.645 | 109 | C6H7ON |  |
| 13 | 21.830 | 121 | C8H11N |  |
| 14 | 22.048 | 268 | C17H20ON2 |  |
| 15 | 27.895 | 72 | C3H4O2 |  |
| 1 | 赵韬. 染料废水处理技术及实施要点分析[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2018, 36(4): 98-100. |
| Zhao T. Wastewater treatment technology and analysis of implementation points[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2018, 36(4): 98-100. | |
| 2 | 任南琪, 周显娇, 郭婉茜, 等. 染料废水处理技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(1): 84-94. |
| Ren N Q, Zhou X J, Guo W Q, et al. A review on treatment methods of dye wastewater[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(1): 84-94. | |
| 3 | Nashy E, Alashkar T, Masaoud R, et al. Integration of Fenton oxidation with nano-graphene oxide to eliminate the hazardous effect of chromated/dyed tannery effluents[J]. Egyptian Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 64(2): 649-660. |
| 4 | Meriç S, Selçuk H, Belgiorno V. Acute toxicity removal in textile finishing wastewater by Fenton’s oxidation, ozone and coagulation-flocculation processes[J]. Water Research, 2005, 39(6): 1147-1153. |
| 5 | Yao Y, Li K, Chen S, et al. Decolorization of Rhodamine B in a thin-film photoelectrocatalytic (PEC) reactor with slant-placed TiO2 nanotubes electrode[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 187: 29-35. |
| 6 | García-Montaño J, Torrades F, García-Hortal J A, et al. Combining photo-Fenton process with aerobic sequencing batch reactor for commercial hetero-bireactive dye removal[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2006, 67(1/2): 86-92. |
| 7 | Mondal P, Mukherji S, Garg A. Performance of treatment schemes comprising chromium-hydrogen peroxide-based advanced oxidation process for textile wastewater[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29(58): 88089-88100. |
| 8 | 厉鹏远, 邱立平, 孙绍芳, 等. 强化传统芬顿/类芬顿氧化效能的研究进展[J].中国给水排水, 2021, 37(10): 34-40. |
| Li P Y, Qiu L P, Sun S F, et al. Research progress on enhancing the oxidation efficiency of traditional Fenton/Fenton-like process[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2021, 37(10): 34-40. | |
| 9 | 张潇逸, 何青春, 蒋进元, 等. 类芬顿处理技术研究进展综述[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2015, 40(6): 58-61. |
| Zhang X Y, He Q C, Jiang J Y, et al. Study progress of class-Fenton treatment technology[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2015, 40(6): 58-61. | |
| 10 | 王丽苹, 李平, 木合塔尔·吐尔洪, 等. Fe0/H2O2类芬顿法提高污泥脱水性能及机理分析[J]. 现代化工, 2018, 38(12): 119-123. |
| Wang L P, Li P, Tuerhong M, et al. Improving dewaterability of waste activated sludge by Fe0/H2O2 Fenton-like process and its mechanism[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2018, 38(12): 119-123. | |
| 11 | Martins R C, Lopes D V, Quina M J, et al. Treatment improvement of urban landfill leachates by Fenton-like process using ZVI[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 192: 219-225. |
| 12 | Teixeira A P C, Tristão J C, Araujo M H, et al. Iron: a versatile element to produce materials for environmental applications[J]. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 2012, 23(9): 1579-1593. |
| 13 | 邹亚辰, 贾小宁, 冉浪, 等. 零价铁类芬顿法处理含低浓度重金属离子有机废水[J]. 化学反应工程与工艺, 2021, 37(2): 167-174. |
| Zou Y C, Jia X N, Ran L, et al. Study on the treatment of organic wastewater containing low concentration heavy metal ions by zero-valent iron Fenton-like process[J]. Chemical Reaction Engineering and Technology, 2021, 37(2): 167-174. | |
| 14 | 王彦斌, 赵红颖, 赵国华, 等. 基于铁化合物的异相Fenton催化氧化技术[J]. 化学进展, 2013, 25(8): 1246-1259. |
| Wang Y B, Zhao H Y, Zhao G H, et al. Iron compound-based heterogeneous Fenton catalytic oxidation technology[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2013, 25(8): 1246-1259. | |
| 15 | 兰明, 杨晶, 严松, 等. 零价铁Fenton技术处理含聚乙烯醇的印染退浆废水[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2016, 38(5): 82-86. |
| Lan M, Yang J, Yan S, et al. Treatment of polyvinyl alcohol containing desizing wastewater by zero-valent iron Fenton technology[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2016, 38(5): 82-86. | |
| 16 | 张乐观, 方冰, 朱泮民. Fe0价铁催化Fenton法降解酸性橙Ⅱ的研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2010, 36(12): 35-38. |
| Zhang L G, Fang B, Zhu P M. Study on the degradation of dye acid orange Ⅱ in Fenton process catalyzed by Fe0 [J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2010, 36(12): 35-38. | |
| 17 | Fu F L, Wang Q, Tang B. Effective degradation of C.I. Acid Red 73 by advanced Fenton process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 174(1/2/3): 17-22. |
| 18 | Chang M C, Shu H Y, Yu H H. An integrated technique using zero-valent iron and UV/H2O2 sequential process for complete decolorization and mineralization of C.I. Acid Black 24 wastewater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 138(3): 574-581. |
| 19 | Zhang S, Wang D, Zhou L, et al. Intensified internal electrolysis for degradation of methylene blue as model compound induced by a novel hybrid material: multi-walled carbon nanotubes immobilized on zero-valent iron plates (Fe0-CNTs)[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 217: 99-107. |
| 20 | Feng J Y, Hu X J, Yue P L. Effect of initial solution pH on the degradation of Orange Ⅱ using clay-based Fe nanocomposites as heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst[J]. Water Research, 2006, 40(4): 641-646. |
| 21 | Wang Y, Gao Y W, Chen L, et al. Goethite as an efficient heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for the degradation of methyl orange[J]. Catalysis Today, 2015, 252: 107-112. |
| 22 | 廖琳, 黄宏星, 叶俊炜, 等. Fe(0)/H2O2协同降解亚甲基蓝的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(10): 1547-1550. |
| Liao L, Huang H X, Ye J W, et al. Degradation of methylene blue by Fe(0)/H2O2 [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 20(10): 1547-1550. | |
| 23 | 林光辉, 吴锦华, 李平, 等. 零价铁与双氧水异相Fenton降解活性艳橙X-GN[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(3): 913-917. |
| Lin G H, Wu J H, Li P, et al. Effective degradation of reactive brilliant orange X-GN by heterogeneous Fenton reaction using zero-valent iron and H2O2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 7(3): 913-917. | |
| 24 | Lei P X, Chen C C, Yang J, et al. Degradation of dye pollutants by immobilized polyoxometalate with H2O2 under visible-light irradiation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(21): 8466-8474. |
| 25 | Hu S H, Yao H R, Wang K F, et al. Intensify removal of nitrobenzene from aqueous solution using nano-zero valent iron/granular activated carbon composite as Fenton-like catalyst[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2015, 226(5): 155. |
| 26 | Xiong Y, Karlsson H T. An experimental investigation of chemical oxygen demand removal from the wastewater containing oxalic acid using three-phase three-dimensional electrode reactor[J]. Advances in Environmental Research, 2002, 7(1): 139-145. |
| 27 | 贾艳萍, 丁雪, 刚健, 等. Mn强化Fe/C微电解工艺条件优化及降解油墨废水机理[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2183-2193. |
| Jia Y P, Ding X, Gang J, et al. Optimization of process conditions for Mn enhanced Fe/C microelectrolysis and degradation mechanism of ink wastewater[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(5): 2183-2193. | |
| 28 | Körbahti B K, Rauf M A. Response surface methodology (RSM) analysis of photoinduced decoloration of toludine blue[J].Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 136(1): 25-30. |
| 29 | 贾艳萍, 单晓倩, 宋祥飞, 等. 响应面法优化餐饮废水混凝工艺研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4931-4940. |
| Jia Y P, Shan X Q, Song X F, et al. Optimization of coagulation process of catering wastewater by response surface methodology[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(9): 4931-4940. | |
| 30 | 胡甜甜, 赵地顺, 武宇, 等. 醚基功能化离子液体催化合成乙酸正丁酯[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(1): 136-145. |
| Hu T T, Zhao D S, Wu Y, et al. Synthesis of n-butyl acetate by ether-functionalized ionic liquid[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(1): 136-145. | |
| 31 | Zhang W X. Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: an overview[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2003, 5(3): 323-332. |
| 32 | Sun Y P, Li X Q, Cao J S, et al. Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2006, 120(1/2/3): 47-56. |
| 33 | Bergendahl J A, Thies T P. Fenton’s oxidation of MTBE with zero-valent iron[J]. Water Research, 2004, 38(2): 327-334. |
| 34 | Gallard H, De Laat J. Kinetic modelling of Fe(Ⅲ)/H2O2 oxidation reactions in dilute aqueous solution using atrazine as a model organic compound[J]. Water Research, 2000, 34(12): 3107-3116. |
| 35 | Tunç S, Duman O, Gürkan T. Monitoring the decolorization of Acid Orange 8 and Acid Red 44 from aqueous solution using Fenton’s reagents by online spectrophotometric method: effect of operation parameters and kinetic study[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(4): 1414-1425. |
| 36 | Behnajady M A, Modirshahla N, Ghanbary F. A kinetic model for the decolorization of C.I. Acid Yellow 23 by Fenton process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 148(1/2): 98-102. |
| 37 | 张全碧, 羊依金, 郭旭晶. 芬顿氧化法对利福平制药废水中溶解性有机物的催化降解[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2217-2227. |
| Zhang Q B, Yang Y J, Guo X J. Catalytic degradation of dissolved organic matter in rifampicin pharmaceutical wastewater by Fenton oxidation process[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2217-2227. | |
| 38 | Lin Y M, Li D Z, Hu J H, et al. Highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants by PANI-modified TiO2 composite[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(9): 5764-5772. |
| 39 | Xiao M S, Zhang Y G. Electro-catalytic oxidation of phenacetin with a three-dimensional reactor: degradation pathway and removal mechanism[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 152: 17-22. |
| 40 | 贾艳萍, 张真, 佟泽为, 等. 铁碳微电解处理印染废水的效能及机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1791-1801. |
| Jia Y P, Zhang Z, Tong Z W, et al. Study on efficiency and mechanism of iron-carbon microelectrolysis treatment of dyeing wastewater[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(4): 1791-1801. | |
| 41 | 沈拥军, 王云丽, 姜明吉, 等. 响应面法优化NaClO2/UV降解藏红T及动力学研究[J]. 南通大学学报 (自然科学版), 2018, 17(1): 15-22, 2. |
| Shen Y J, Wang Y L, Jiang M J, et al. Kinetics study and optimization of NaClO2/UV treated Safranine T based response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Nantong University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 17(1): 15-22, 2. | |
| 42 | 刘柏辰. 电化学高级氧化技术降解水溶液中藏红T的研究[D]. 天津: 河北工业大学, 2020. |
| Liu B C. Study on the degradation of Safranine T in aqueous solution by electrochemical advanced oxidation technology[D]. Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology, 2020. | |
| 43 | 汤世麟. Fe2O3/硅藻土复合材料的制备及其催化降解结晶紫的研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2019. |
| Tang S L. Preparation of Fe2O3/diatomite composite material and its study on catalytic degradation of crystal violet in water[D]. Changsha: Changsha University of Science & Technology, 2019. | |
| 44 | 王犇, 孙燕, 李爱英, 等. 三维电解法联合臭氧电催化氧化处理结晶紫模拟染料废水[J]. 化学与生物工程, 2022, 39(5): 36-42. |
| Wang B, Sun Y, Li A Y, et al. Treatment of crystal violet simulated dye wastewater by three-dimensional electrolysis combined with ozone electrocatalytic oxidation[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 2022, 39(5): 36-42. | |
| 45 | Liu B C, Ren B L, Xia Y, et al. Electrochemical degradation of Safranine T in aqueous solution by Ti/PbO2 electrodes[J]. Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 98(1): 7-14. |
| [1] | 郭珊, 田雨, 徐永滨, 王朋, 刘治明. 废旧电池再资源化制备高性能中熵合金催化剂及其性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 231-240. |
| [2] | 赵焕娟, 包颖昕, 于康, 刘婧, 钱新明. 多元组分爆轰不稳定性定量实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 339-348. |
| [3] | 徐宏标, 杨亮, 李子栋, 刘道平. 盐水微滴/泡沫铜复合体系中甲烷水合物生成动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3287-3296. |
| [4] | 胡术刚, 田国庆, 刘文娟, 徐广飞, 刘华清, 张建, 王艳龙. 纳米零价铁的制备及氧化还原技术的应用进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3041-3055. |
| [5] | 祝赫, 张仪, 齐娜娜, 张锴. 欧拉-欧拉双流体模型中颗粒黏性对液固散式流态化的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3103-3112. |
| [6] | 丁湧, 李文建, 陈昭宇, 曹立辉, 刘轩铭, 任强强, 胡松, 向军. 废旧晶体硅光伏组件EVA有氧热解动力学与产物特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3310-3319. |
| [7] | 唐昊, 胡定华, 李强, 张轩畅, 韩俊杰. 抗加速度双切线弧流道内气泡动力学行为数值与可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3074-3082. |
| [8] | 张佳颖, 王聪, 王雅君. CNT-Co/Bi2O3催化剂光催化协同过硫酸盐活化高效降解四环素[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3163-3175. |
| [9] | 曾港, 陈林, 杨董, 袁海专, 黄彦平. 矩形通道内超临界CO2局部热流场可视化实验[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2831-2839. |
| [10] | 吴邦汉, 林定标, 陆海峰, 郭晓镭, 刘海峰. 竖直管气动物流传输系统管道压降和传送瓶输送特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2465-2473. |
| [11] | 马君霞, 李林涛, 熊伟丽. 基于Tri-training GPR的半监督软测量建模方法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2613-2623. |
| [12] | 罗莉, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 氧化铝结构与表面性质调控及其催化甲醇脱水制二甲醚性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2522-2532. |
| [13] | 陈彦伶, 袁炳志, 王丽伟, 张宸, 朱涵玉. 非平衡条件下金属氯化物-氨工质对的吸附动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2252-2261. |
| [14] | 霍宗伟, 牛亚宾, 潘艳秋. 油水膜分离中高黏度油滴行为研究和影响因素分析[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2262-2273. |
| [15] | 杨艳, 郭亚丽, 于硕文, 潘泊年, 沈胜强. 液氨喷射泵热力性能的计算分析[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2134-2142. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号