化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (9): 3310-3319.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240306
丁湧1( ), 李文建2, 陈昭宇3, 曹立辉1, 刘轩铭1, 任强强3, 胡松3(
), 李文建2, 陈昭宇3, 曹立辉1, 刘轩铭1, 任强强3, 胡松3( ), 向军3
), 向军3
收稿日期:2024-03-18
修回日期:2024-05-25
出版日期:2024-09-25
发布日期:2024-10-10
通讯作者:
胡松
作者简介:丁湧(1983—),男,硕士,高级工程师,16123129@ceic.com
基金资助:
Yong DING1( ), Wenjian LI2, Zhaoyu CHEN3, Lihui CAO1, Xuanming LIU1, Qiangqiang REN3, Song HU3(
), Wenjian LI2, Zhaoyu CHEN3, Lihui CAO1, Xuanming LIU1, Qiangqiang REN3, Song HU3( ), Jun XIANG3
), Jun XIANG3
Received:2024-03-18
Revised:2024-05-25
Online:2024-09-25
Published:2024-10-10
Contact:
Song HU
摘要:
资源化处理回收废旧晶体硅光伏组件迫在眉睫,而其关键在于乙烯-醋酸乙烯共聚物(EVA)薄膜的处理。面向EVA处理提出了有氧热解方法,展开有氧热解失重特性、动力学及产物特性分析,结果表明:随着氧气浓度的增加,最大失重速率从1.8%(质量分数)/s增加到3.0%(质量分数)/s,EVA在较低温度下热分解更多且速率更快,整体有氧热解活化能呈现出下降的趋势。这是由于氧气的存在促进了氧化反应,加速了有氧热解过程。随着热解终温的升高,焦与油产率呈下降趋势,气产率则随之增加。在2%氧气浓度下,热解终温的提高有利于CH4、C2H6物质富集,有利于油中羧类物质转化为烷烃、烯烃及醇类,使得焦逐渐由非晶质结构朝芳香化与石墨化转变。
中图分类号:
丁湧, 李文建, 陈昭宇, 曹立辉, 刘轩铭, 任强强, 胡松, 向军. 废旧晶体硅光伏组件EVA有氧热解动力学与产物特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3310-3319.
Yong DING, Wenjian LI, Zhaoyu CHEN, Lihui CAO, Xuanming LIU, Qiangqiang REN, Song HU, Jun XIANG. Aerobic pyrolysis kinetic and product characteristics of waste crystalline silicon photovo ltaic modules’ EVA[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3310-3319.
| 工业分析/% | 元素分析/% | 高位 发热量/(MJ/kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | V | FC | A | C | H | N | S | O① | |
| 0.22 | 97.61 | 2.12 | 0.04 | 77.83 | 10.51 | 2.14 | 0.01 | 9.24 | 14.15 |
表1 EVA工业分析和元素分析(质量分数,收到基)
Table 1 Industrial and elemental analysis of EVA (mass fraction, as received basis)
| 工业分析/% | 元素分析/% | 高位 发热量/(MJ/kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | V | FC | A | C | H | N | S | O① | |
| 0.22 | 97.61 | 2.12 | 0.04 | 77.83 | 10.51 | 2.14 | 0.01 | 9.24 | 14.15 |
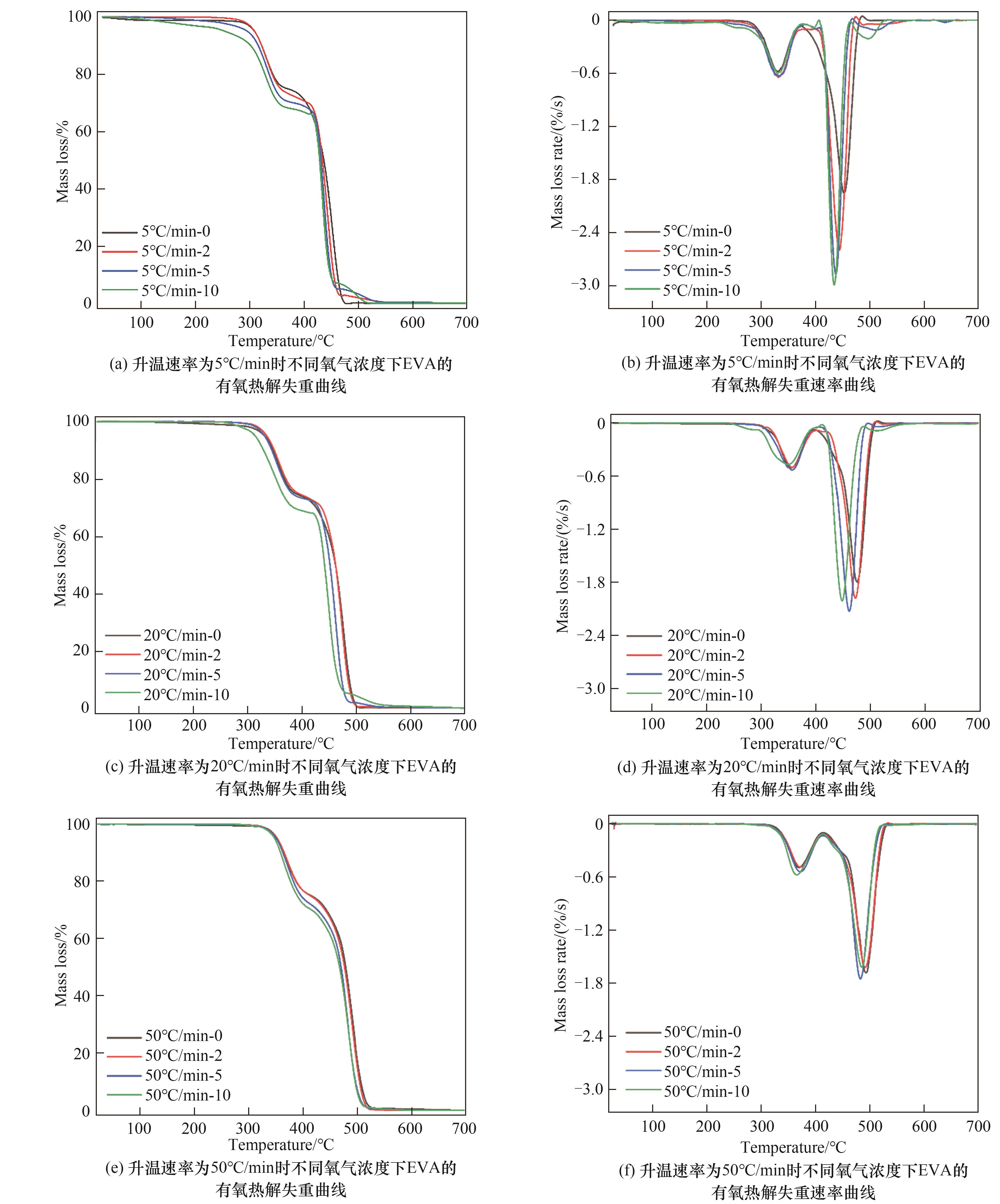
图2 不同升温速率及不同氧气浓度下EVA的有氧热解失重与失重速率曲线
Fig.2 Aerobic pyrolysis mass loss and mass loss rate curves of EVA under different heating rates and oxygen concentrations
| 氧气浓度 | E/(kJ/mol) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α=0.1 | α=0.2 | α=0.3 | α=0.4 | α=0.5 | α=0.6 | α=0.7 | α=0.8 | α=0.9 | ||
| 0 | 46.47 | 50.06 | 80.30 | 80.00 | 85.96 | 89.53 | 91.08 | 92.72 | 91.10 | 78.58 |
| 2% | 45.14 | 47.64 | 85.07 | 89.91 | 82.78 | 80.72 | 80.06 | 79.63 | 79.43 | 74.49 |
| 5% | 39.84 | 45.78 | 44.36 | 104.57 | 91.01 | 86.50 | 84.50 | 83.35 | 82.66 | 73.62 |
| 10% | 30.54 | 42.04 | 38.01 | 110.12 | 85.07 | 77.74 | 74.58 | 73.78 | 78.54 | 67.82 |
表2 不同氧气浓度下EVA有氧热解各转化率下的表观活化能及平均活化能
Table 2 Apparent activation energy and average activation energy of EVA aerobic pyrolysis at different oxygen concentrations
| 氧气浓度 | E/(kJ/mol) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α=0.1 | α=0.2 | α=0.3 | α=0.4 | α=0.5 | α=0.6 | α=0.7 | α=0.8 | α=0.9 | ||
| 0 | 46.47 | 50.06 | 80.30 | 80.00 | 85.96 | 89.53 | 91.08 | 92.72 | 91.10 | 78.58 |
| 2% | 45.14 | 47.64 | 85.07 | 89.91 | 82.78 | 80.72 | 80.06 | 79.63 | 79.43 | 74.49 |
| 5% | 39.84 | 45.78 | 44.36 | 104.57 | 91.01 | 86.50 | 84.50 | 83.35 | 82.66 | 73.62 |
| 10% | 30.54 | 42.04 | 38.01 | 110.12 | 85.07 | 77.74 | 74.58 | 73.78 | 78.54 | 67.82 |
| 1 | Lycourghiotis S. Trends in renewable energy: an overview[J]. Global NEST: the International Journal, 2022, 24(3): 505-525. |
| 2 | Ahmad L, Khordehgah N, Malinauskaite J, et al. Recent advances and applications of solar photovoltaics and thermal technologies[J]. Energy, 2020, 207: 118254. |
| 3 | 水电水利规划设计总院. 中国可再生能源发展报告2022[R]. 北京:水电水利规划设计总院, 2023. |
| Hydroelectric and Water Resources Planning and Design Institute. Development Report on Renewable Energy in China 2022 [R]. Beijing: Hydroelectric and Water Resources Planning and Design Institute, 2023. | |
| 4 | 李淳伟, 胡露, 樊阳波, 等. 光伏组件回收利用现状研究及标准探讨[J]. 中国标准化, 2020, (S1): 163-168. |
| Li C W, Hu L, Fan Y B, et al. Research on the current situation and standard of photovoltaic module recycling[J]. China Standardization, 2020, (S1): 163-168. | |
| 5 | Tammaro M, Salluzzo A, Rimauro J, et al. Experimental investigation to evaluate the potential environmental hazards of photovoltaic panels[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 306: 395-405. |
| 6 | Rong D, Chang N L, Ouyang Z, et al. A techno-economic review of silicon photovoltaic module recycling[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019, 109: 532-550. |
| 7 | 吴智朋, 高德东, 王珊, 等. 废旧晶体硅光伏组件回收技术研究进展[J]. 机械工程学报,2023,59(7):307-329. |
| Wu Z P, Gao D D, Wang S, et al. Research progress on recycling technology of waste crystalline silicon photovoltaic modules[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59(7): 307-329. | |
| 8 | 孔慧玲, 顾卫华, 彭圣娟, 等. 废旧光伏组件回收及高值化利用研究进展[J]. 有色金属 (冶炼部分), 2023, (9): 22-29. |
| Kong H L, Gu W H, Peng S J, et al. Research progress on recycling and high value utilization of waste photovoltaic modules[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2023, (9): 22-29. | |
| 9 | Farrell C C, Osman A I, Doherty R, et al. Technical challenges and opportunities in realising a circular economy for waste photovoltaic modules[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 128: 109911. |
| 10 | Wang X P, Tian X Y, Chen X D, et al. A review of end-of-life crystalline silicon solar photovoltaic panel recycling technology[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2022, 248: 111976. |
| 11 | Pagnanelli F, Moscardini E, Altimari P, et al. Solvent versus thermal treatment for glass recovery from end of life photovoltaic panels: environmental and economic assessment[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 248: 109313. |
| 12 | Tao M, Click N, Ricci L. Commentary on technoeconomic analysis of high-value, crystalline silicon photovoltaic module recycling processes[solar energy materials and solar cells 238 (2022) 111592][J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2022, 239: 111677. |
| 13 | El abdellaoui F, Roethlisberger R P, Ez-Zahraouy H. Oxidative pyrolysis of pellets from lignocellulosic anaerobic digestion residues and wood chips for biochar and syngas production[J]. Fuel, 2023, 350: 128824. |
| 14 | Fu W, Bai X W, Tursun Y, et al. Oxidative pyrolysis of plywood waste: effect of oxygen concentration and other parameters on product yield and composition[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2023, 173: 106068. |
| 15 | Huang R, Ren Q Q, Zhang J L, et al. Adjusting effects of pyrolytic volatiles interaction in char to upgrade oil by swelling waste nylon-tire[J]. Waste Management, 2023, 169: 374-381. |
| 16 | Wang F C Y, The microstructure exploration of thermoplastic copolymers by pyrolysis-gas chromatography[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2004, 71(1): 83-106. |
| 17 | 章蕾, 宋孝辉, 张建庭, 等. 氨甲环酸异构化过程的反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报,2023, 74(10): 4173-4181. |
| Zhang L, Song X H, Zhang J T, et al. Reaction kinetics study of tranexamic acid isomerization process[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(10): 4173-4181. | |
| 18 | Vyazovkin S, Dollimore D. Linear and nonlinear procedures in isoconversional computations of the activation energy of nonisothermal reactions in solids[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 1996, 36(1): 42-45. |
| 19 | 张玉明, 纪德馨, 朱翰文, 等. 微型流化床中萘裂解生成小分子气体的反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(5): 2604-2615. |
| Zhang Y M, Ji D X, Zhu H W, et al. Reaction kinetics of naphthalene cracking into small molecule gas in a micro fluidized bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(5): 2604-2615. | |
| 20 | 赵旭, 卜昌盛, 王昕晔, 等. 铁基载氧体辅助无烟煤焦富氧燃烧动力学分析[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 384-392. |
| Zhao X, Bu C S, Wang X Y, et al. Kinetics investigation on iron-based oxygen carrier aided oxy-fuel combustion of anthracite char[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(1): 384-392. | |
| 21 | 徐智, 郭朝晖, 徐锐, 等. 控氧热解过程中污染稻草生物炭的组分特性及其重金属累积特征[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(2): 1051-1062. |
| Xu Z, Guo Z H, Xu R, et al. Component properties and heavy metal accumulation characteristics of contaminated rice straw biochar during oxygen-controlled pyrolysis[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(2): 1051-1062. | |
| 22 | Cindro N, Car Ž, Petrović Peroković V, et al. Synthesis of aromatic polynitroso compounds: towards functional azodioxy-linked porous polymers[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(11): e21781. |
| 23 | Maurya M R, Kumar A, Costa Pessoa J. Vanadium complexes immobilized on solid supports and their use as catalysts for oxidation and functionalization of alkanes and alkenes[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2011, 255(19/20): 2315-2344. |
| 24 | Fang S W, Yu Z S, Ma X Q, et al. Co-pyrolysis characters between combustible solid waste and paper mill sludge by TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 144: 114-122. |
| 25 | 徐芳, 刘辉, 王擎, 等. 霍林河褐煤化学结构特性的13C NMR与FTIR对比分析[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(11): 4272-4278. |
| Xu F, Liu H, Wang Q, et al. Comparison of Huolinhe lignite structural features by using 13C NMR & FTIR techniques [J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(11): 4272-4278. | |
| 26 | Yadav K, Shah D, Pal S L, et al. Quantitative analysis of functional groups in different metamorphic grade Indian coals using FTIR technique[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2023. |
| 27 | Lin Y, Liao Y F, Yu Z S, et al. A study on co-pyrolysis of bagasse and sewage sludge using TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 151: 190-198. |
| 28 | Lei Z, Yang D, Zhang Y H, et al. Constructions of coal and char molecular models based on the molecular simulation technology[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2017, 45(7): 769-779. |
| 29 | Bu R P, Liu G R, Zhong K, et al. Relationship between the molecular structure and stacking mode: characteristics of the D2 h and D3 h molecules in planar layer-stacked crystals[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2021, 21(12): 6847-6861. |
| 30 | 蔚翠, 何泽召, 刘庆彬, 等. 蓝宝石衬底上PECVD生长石墨烯及其气敏传感器[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(11): 4423-4427. |
| Yu C, He Z Z, Liu Q B, et al. PECVD growth of graphene on sapphire substrate and its gas sensor[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(11): 4423-4427. | |
| 31 | 李津蓉, 戴连奎, 阮华. 基于谱峰分解的拉曼光谱定量分析方法[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(7): 2128-2135. |
| Li J R, Dai L K, Ruan H. Raman spectral quantitative analysis based on peaks-decomposition[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(7): 2128-2135. | |
| 32 | 董莉, 周潇云, 刘景洋, 等. 废光伏组件乙烯-醋酸乙烯酯共聚物热解研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(10): 1211-1215. |
| Dong L, Zhou X Y, Liu J Y, et al. Study on thermal decomposition of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer in waste photovoltaic modules[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2020, 42(10): 1211-1215. | |
| 33 | Preeda P, Ganapathi Raman R, Sakthivel P. Structural, FTIR, FT-Raman, optical and nonlinear optical properties of organic nonlinear optical crystal–3,5-diisopropyl-2-hydroxybenzoic acid[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 2022, 146: 110120. |
| [1] | 徐宏标, 杨亮, 李子栋, 刘道平. 盐水微滴/泡沫铜复合体系中甲烷水合物生成动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3287-3296. |
| [2] | 祝赫, 张仪, 齐娜娜, 张锴. 欧拉-欧拉双流体模型中颗粒黏性对液固散式流态化的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3103-3112. |
| [3] | 唐昊, 胡定华, 李强, 张轩畅, 韩俊杰. 抗加速度双切线弧流道内气泡动力学行为数值与可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3074-3082. |
| [4] | 曾港, 陈林, 杨董, 袁海专, 黄彦平. 矩形通道内超临界CO2局部热流场可视化实验[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2831-2839. |
| [5] | 罗莉, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 氧化铝结构与表面性质调控及其催化甲醇脱水制二甲醚性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2522-2532. |
| [6] | 刘旭升, 李泽洋, 杨宇森, 卫敏. 电催化二氧化碳还原制备气态产物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2385-2408. |
| [7] | 吴邦汉, 林定标, 陆海峰, 郭晓镭, 刘海峰. 竖直管气动物流传输系统管道压降和传送瓶输送特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2465-2473. |
| [8] | 马君霞, 李林涛, 熊伟丽. 基于Tri-training GPR的半监督软测量建模方法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2613-2623. |
| [9] | 杨艳, 郭亚丽, 于硕文, 潘泊年, 沈胜强. 液氨喷射泵热力性能的计算分析[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2134-2142. |
| [10] | 陈彦伶, 袁炳志, 王丽伟, 张宸, 朱涵玉. 非平衡条件下金属氯化物-氨工质对的吸附动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2252-2261. |
| [11] | 霍宗伟, 牛亚宾, 潘艳秋. 油水膜分离中高黏度油滴行为研究和影响因素分析[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2262-2273. |
| [12] | 王文雅, 张玮, 楼小玲, 钟若菲, 陈冰冰, 贠军贤. 纳米纤维素嵌合型晶胶微球的多微管成形与模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2060-2071. |
| [13] | 薛潇, 商敏静, 苏远海. 微反应器内药物连续流合成的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1439-1454. |
| [14] | 范以薇, 刘威, 李盈盈, 王培霞, 张吉松. 有机液体储氢中全氢化乙基咔唑催化脱氢研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1198-1208. |
| [15] | 徐安冉, 刘凯, 王娜, 赵振宇, 李洪, 高鑫. 强吸波催化剂协同微波能强化果糖脱水制5-羟甲基糠醛[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1565-1577. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号