化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (12): 4403-4412.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240554
李云昊1,2( ), 徐纯刚1,2(
), 徐纯刚1,2( ), 李小森1,2, 陈朝阳1,2
), 李小森1,2, 陈朝阳1,2
收稿日期:2024-05-26
修回日期:2024-08-19
出版日期:2024-12-25
发布日期:2025-01-03
通讯作者:
徐纯刚
作者简介:李云昊(2000—),男,硕士研究生,liyh1@ms.giec.ac.cn
基金资助:
Yunhao LI1,2( ), Chungang XU1,2(
), Chungang XU1,2( ), Xiaosen LI1,2, Zhaoyang CHEN1,2
), Xiaosen LI1,2, Zhaoyang CHEN1,2
Received:2024-05-26
Revised:2024-08-19
Online:2024-12-25
Published:2025-01-03
Contact:
Chungang XU
摘要:
系统探讨了CO2水合物在海水环境中的热力学和动力学,特别关注盐度对水合物形成和稳定性的影响。通过综合分析现有文献,讨论了海水的温度、压力、盐度等因素对CO2水合物的形成和稳定性的影响。阐述了几种常见的盐水体系下CO2水合物的相平衡条件模型,总结了海水环境CO2水合物形成速率与稳定性的影响,归纳出不同盐离子对CO2水合物形成的抑制作用。最后,对近年来海水CO2水合物封存进行评估与总结,指出目前主要问题在于海水海泥体系中CO2水合物研究还不够充分,未来研究方向应主要围绕海泥作为多孔介质可以替代水合物形成促进剂展开,以期为CO2水合物海洋封存技术的工业化应用和CO2水合物的研究提供参考。
中图分类号:
李云昊, 徐纯刚, 李小森, 陈朝阳. 海洋CO2水合物封存基础性研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(12): 4403-4412.
Yunhao LI, Chungang XU, Xiaosen LI, Zhaoyang CHEN. Basic research progress on marine CO2 hydrate sequestration[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(12): 4403-4412.
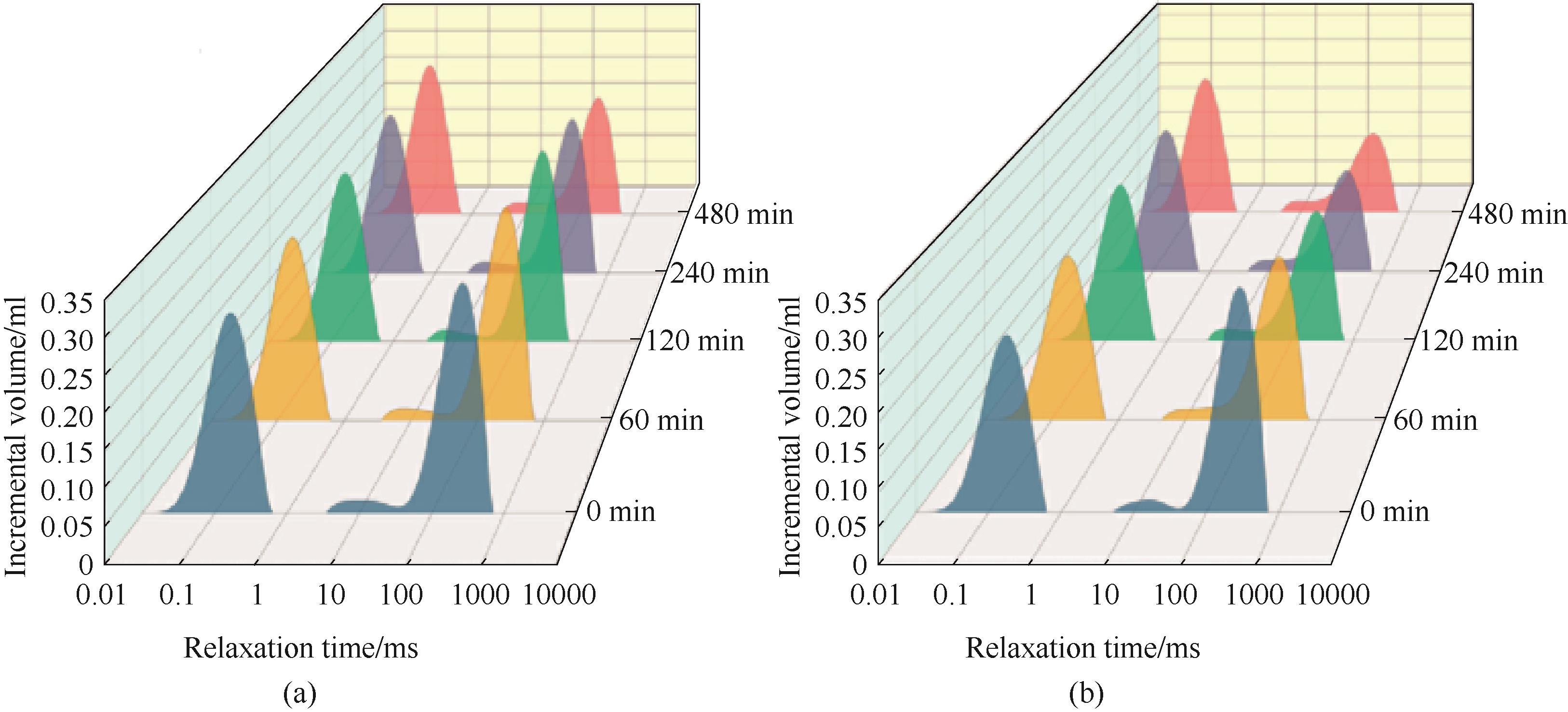
图4 3%(质量分数)NaCl-0.5%(质量分数)CSOM溶液中水合物弛豫时间变化(a)和3%(质量分数) CaCl2-0.5%(质量分数)溶液中水合物弛豫时间变化(b)[54]
Fig.4 Changes of hydrate relaxation time in 3%(mass) NaCl-0.5%(mass) CSOM solution (a) and 3%(mass) CaCl2-0.5%(mass) solution (b)[54]
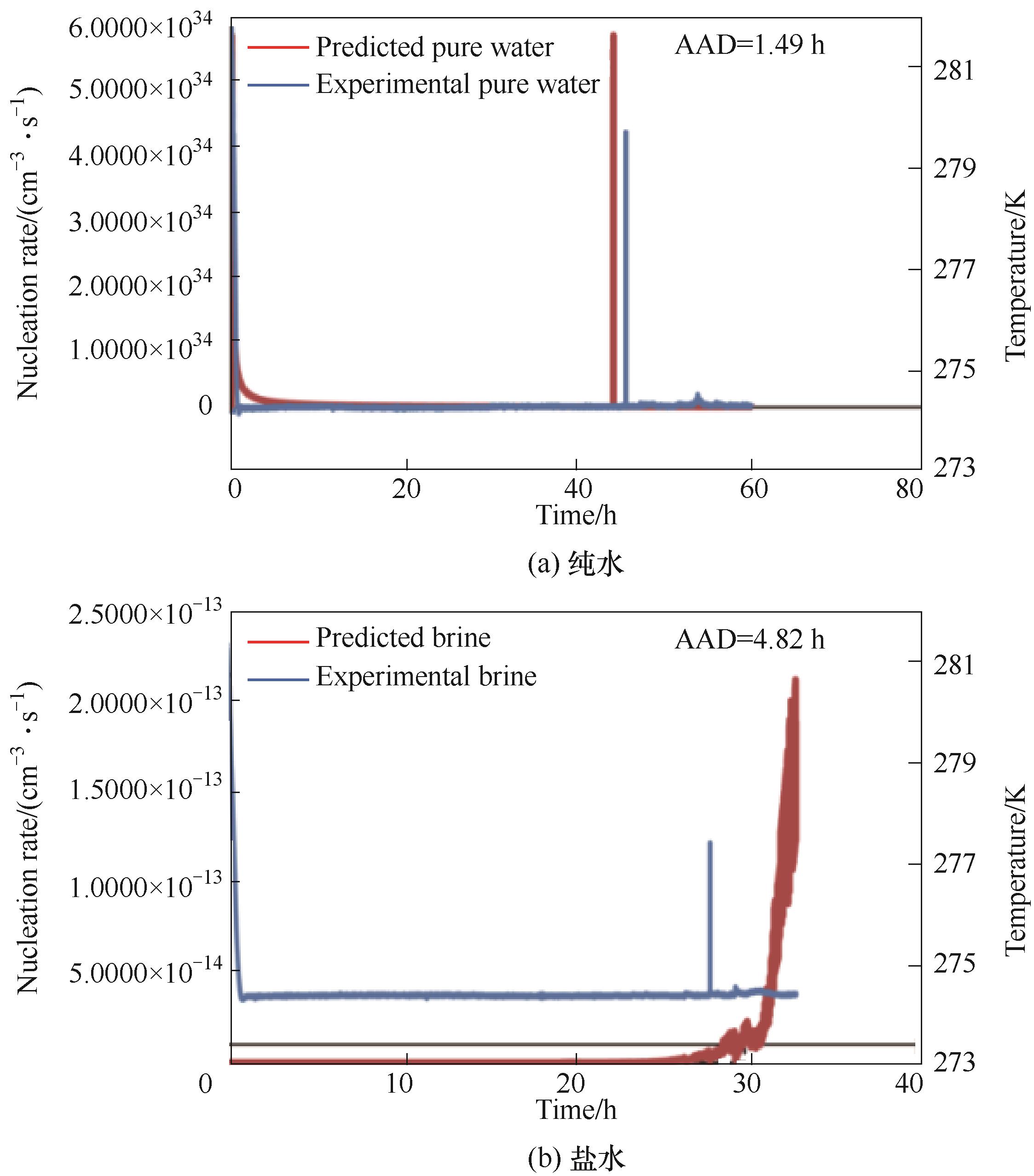
图5 预测不同体系的CO2水合物成核速率和实验温度随时间的变化[56]
Fig.5 Predict nucleation rate of CO2 hydrates in different systems and variation of experimental temperature over time[56]
| System | Introduction time/h | CO2 gas consumed /mol | CO2 gas uptake/ (mol·mmol-1) | Hydrate formation rate /(mmol·h-1) | Cgh/% | Cwh/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-methionine | 100 | 0.6568 | 90.89 | 2.173 | 93.29 | 53.99 |
| L-isoleucine | 112 | 0.2623 | 36.30 | 0.376 | 38.27 | 21.56 |
| L-threonine | 16.6 | 0.4587 | 56.41 | 5.427 | 70.54 | 33.84 |
| SDS | 150 | 0.5349 | 66.69 | 1.422 | 80.75 | 40.01 |
| brine | 28 | 0.4270 | 57.11 | 7.494 | 68.38 | 34.26 |
表1 在3.3%(质量分数)的石英砂-盐水溶液中(4 MPa, 274.15 K),在0.2%(质量分数)的L-蛋氨酸、L-异亮氨酸、L-苏氨酸和SDS下测量的CO2水合物形成动力学数据[57]
Table 1 Measured CO2 hydrate formation kinetic data at 0.2%(mass) of L-meth, L-iso, L-threo, and SDS in 3.3%(mass) brine solution at 4 MPa and 274.15 K in quartz sand[57]
| System | Introduction time/h | CO2 gas consumed /mol | CO2 gas uptake/ (mol·mmol-1) | Hydrate formation rate /(mmol·h-1) | Cgh/% | Cwh/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-methionine | 100 | 0.6568 | 90.89 | 2.173 | 93.29 | 53.99 |
| L-isoleucine | 112 | 0.2623 | 36.30 | 0.376 | 38.27 | 21.56 |
| L-threonine | 16.6 | 0.4587 | 56.41 | 5.427 | 70.54 | 33.84 |
| SDS | 150 | 0.5349 | 66.69 | 1.422 | 80.75 | 40.01 |
| brine | 28 | 0.4270 | 57.11 | 7.494 | 68.38 | 34.26 |
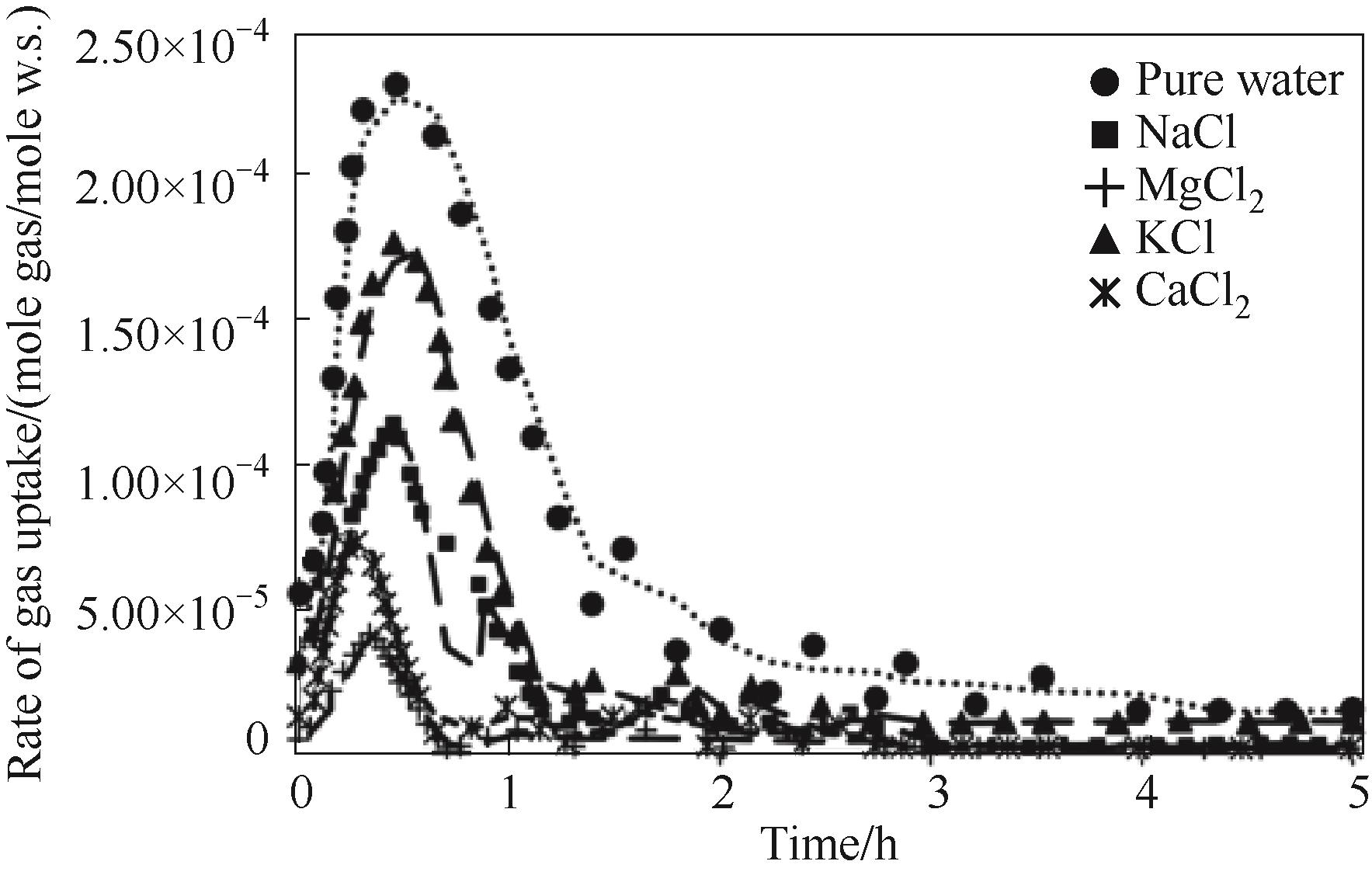
图6 恒定浓度为1000 mg/L时不同水溶液中水合物形成过程中的气体吸收速率[65]
Fig.6 Gas absorption rates during hydrate formation in different aqueous solutions at a constant concentration of 1000 mg/L[65]
| 1 | Amstrup S C, Deweaver E T, Douglas D C, et al. Greenhouse gas mitigation can reduce sea-ice loss and increase polar bear persistence[J]. Nature, 2010, 468(7326): 955-958. |
| 2 | Stainforth D A, Aina T, Christensen C, et al. Uncertainty in predictions of the climate response to rising levels of greenhouse gases[J]. Nature, 2005, 433(7024): 403-406. |
| 3 | Ajayi T, Gomes J S, Bera A. A review of CO2 storage in geological formations emphasizing modeling, monitoring and capacity estimation approaches[J]. Petroleum Science, 2019, 16(5): 1028-1063. |
| 4 | Orr J C, Fabry V J, Aumont O, et al. Anthropogenic ocean acidification over the twenty-first century and its impact on calcifying organisms[J]. Nature, 2005, 437(7059): 681-686. |
| 5 | Ricke K L, Orr J C, Schneider K, et al. Risks to coral reefs from ocean carbonate chemistry changes in recent earth system model projections[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2013, 8(3): 034003. |
| 6 | Siegel D A, DeVries T, Doney S C, et al. Assessing the sequestration time scales of some ocean-based carbon dioxide reduction strategies[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2021, 16(10): 104003. |
| 7 | Kumar Y, Sangwai J S. A perspective on the effect of physicochemical parameters, macroscopic environment, additives, and economics to harness the large-scale hydrate-based CO2 sequestration potential in oceans[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2023, 11(30): 10950-10979. |
| 8 | Zulqarnain M, Mohd Yusoff M H, Keong L K, et al. Recent development of integrating CO2 hydrogenation into methanol with ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) as potential source of green energy[J]. Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 2023, 16(1): 2152740. |
| 9 | Sun X, Shang A R, Wu P, et al. A review of CO2 marine geological sequestration[J]. Processes, 2023, 11(7): 2206. |
| 10 | Chong Z R, Yang S H B, Babu P, et al. Review of natural gas hydrates as an energy resource: Prospects and challenges[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 162: 1633-1652. |
| 11 | Englezos P. Clathrate hydrates[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1993, 32(7): 1251-1274. |
| 12 | Zheng J J, Chong Z R, Qureshi M F, et al. Carbon dioxide sequestration via gas hydrates: a potential pathway toward decarbonization[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34(9): 10529-10546. |
| 13 | Nesterov A N, Reshetnikov A M. New combination of thermodynamic and kinetic promoters to enhance carbon dioxide hydrate formation under static conditions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 378: 122165. |
| 14 | Qureshi M F, Khandelwal H, Usadi A, et al. CO2 hydrate stability in oceanic sediments under brine conditions[J]. Energy, 2022, 256: 124625. |
| 15 | Park S, Koh D Y, Kang H, et al. Effect of molecular nitrogen on multiple hydrogen occupancy in clathrate hydrates[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(35):20203-20208. |
| 16 | Zatsepina O Y, Buffett B A. Phase equilibrium of gas hydrate: implications for the formation of hydrate in the deep sea floor[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1997, 24(13): 1567-1570. |
| 17 | Duan Z H, Sun R. An improved model calculating CO2 solubility in pure water and aqueous NaCl solutions from 273 to 533 K and from 0 to 2000 bar[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 193(3/4): 257-271. |
| 18 | House K Z, Schrag D P, Harvey C F, et al. Permanent carbon dioxide storage in deep-sea sediments[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(33): 12291-12295. |
| 19 | Chong Z R, Koh J W, Linga P. Effect of KCl and MgCl2 on the kinetics of methane hydrate formation and dissociation in sandy sediments[J]. Energy, 2017, 137: 518-529. |
| 20 | Jacobson L C, Hujo W, Molinero V. Amorphous precursors in the nucleation of clathrate hydrates[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(33): 11806-11811. |
| 21 | Khurana M, Yin Z Y, Linga P. A review of clathrate hydrate nucleation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(12): 11176-11203. |
| 22 | Ke W, Svartaas T M, Chen D Y. A review of gas hydrate nucleation theories and growth models[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2019, 61: 169-196. |
| 23 | Liang R D, Xu H J, Shen Y N, et al. Nucleation and dissociation of methane clathrate embryo at the gas-water interface[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(47): 23410-23415. |
| 24 | Kiran B S, Prasad P S R. Storage of methane gas in the form of clathrates in the presence of natural bioadditives[J]. ACS Omega, 2018, 3(12): 18984-18989. |
| 25 | Fakharian H, Ganji H, Naderifar A. Desalination of high salinity produced water using natural gas hydrate[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2017, 72: 157-162. |
| 26 | Chong Z R, Chan A H M, Babu P, et al. Effect of NaCl on methane hydrate formation and dissociation in porous media[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 27: 178-189. |
| 27 | Tse C W, Bishnoi P R. Prediction of carbon dioxide gas hydrate formation conditions in aqueous electrolyte solutions[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1994, 72(1): 119-124. |
| 28 | van der Waals J H, Platteeuw J C. Clathrate Solutions[M]. NYSE: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.,2007. |
| 29 | Lee J, Kim K S, Seo Y. Thermodynamic, structural, and kinetic studies of cyclopentane + CO2 hydrates: applications for desalination and CO2 capture[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 375: 121974. |
| 30 | Mok J, Choi W, Kim S, et al. NaCl-induced enhancement of thermodynamic and kinetic CO2 selectivity in CO2 + N2 hydrate formation and its significance for CO2 sequestration[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 451: 138633. |
| 31 | Serikkali A, Van H N, Pham T K, et al. Phase equilibrium and dissociation enthalpies of CO2/cyclopentane hydrates in presence of salts for water treatment and CO2 capture: new experimental data and modeling[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2022, 556: 113410. |
| 32 | Zeng S Y, Yin Z Y, Ren J J, et al. Effect of MgCl2 on CO2 sequestration as hydrates in marine environment: a thermodynamic and kinetic investigation with morphology insights[J]. Energy, 2024, 286: 129616. |
| 33 | Naullage P M, Bertolazzo A A, Molinero V. How do surfactants control the agglomeration of clathrate hydrates?[J]. ACS Central Science, 2019, 5(3): 428-439. |
| 34 | Lv X F, Lu D Y, Liu Y, et al. Study on methane hydrate formation in gas-water systems with a new compound promoter[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(57): 33506-33518. |
| 35 | Wang F, Liu G Q, Meng H L, et al. Improved methane hydrate formation and dissociation with nanosphere-based fixed surfactants as promoters[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2016, 4(4): 2107-2113. |
| 36 | Kumar A, Bhattacharjee G, Kulkarni B D, et al. Role of surfactants in promoting gas hydrate formation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(49): 12217-12232. |
| 37 | Sa J H, Sum A K. Promoting gas hydrate formation with ice-nucleating additives for hydrate-based applications[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 251: 113352. |
| 38 | Zhong Y, Rogers R E. Surfactant effects on gas hydrate formation[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2000, 55(19): 4175-4187. |
| 39 | Heydari A, Peyvandi K. Study of biosurfactant effects on methane recovery from gas hydrate by CO2 replacement and depressurization[J]. Fuel, 2020, 272: 117681. |
| 40 | Hayama H, Mitarai M, Mori H, et al. Surfactant effects on crystal growth dynamics and crystal morphology of methane hydrate formed at gas/liquid interface[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2016, 16(10): 6084-6088. |
| 41 | Dicharry C, Diaz J, Torré J P, et al. Influence of the carbon chain length of a sulfate-based surfactant on the formation of CO2, CH4 and CO2-CH4 gas hydrates[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 152: 736-745. |
| 42 | Okutani K, Kuwabara Y, Mori Y H. Surfactant effects on hydrate formation in an unstirred gas/liquid system: an experimental study using methane and sodium alkyl sulfates[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2008, 63(1): 183-194. |
| 43 | Tian L Q, Wu G Z. Cyclodextrins as promoter or inhibitor for methane hydrate formation?[J]. Fuel, 2020, 264: 116828. |
| 44 | Wang F, Jia Z Z, Luo S J, et al. Effects of different anionic surfactants on methane hydrate formation[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2015, 137: 896-903. |
| 45 | Kwon Y A, Park J M, Jeong K E, et al. Synthesis of anionic multichain type surfactant and its effect on methane gas hydrate formation[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2011, 17(1): 120-124. |
| 46 | Kumar A, Sakpal T, Linga P, et al. Influence of contact medium and surfactants on carbon dioxide clathrate hydrate kinetics[J]. Fuel, 2013, 105: 664-671. |
| 47 | Molokitina N S, Nesterov A N, Podenko L S, et al. Carbon dioxide hydrate formation with SDS: further insights into mechanism of gas hydrate growth in the presence of surfactant[J]. Fuel, 2019, 235: 1400-1411. |
| 48 | Naeiji P, Varaminian F. Kinetic study of carbon dioxide hydrate formation by thermal analysis in the presence of two surfactants: sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and lauryl alcohol ethoxylate (LAE)[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 254: 120-129. |
| 49 | Du J W, Li H J, Wang L G. Effects of ionic surfactants on methane hydrate formation kinetics in a static system[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2014, 25(4): 1227-1233. |
| 50 | Darbouret M, Cournil M, Herri J M. Rheological study of TBAB hydrate slurries as secondary two-phase refrigerants[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2005, 28(5): 663-671. |
| 51 | David F, Vokhmin V, Ionova G. Water characteristics depend on the ionic environment. Thermodynamics and modelisation of the aquo ions[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2001, 90(1/2/3): 45-62. |
| 52 | Dichicco M C, Laurita S, Paternoster M, et al. Serpentinite carbonation for CO2 sequestration in the southern Apennines: preliminary study[J]. Energy Procedia, 2015, 76: 477-486. |
| 53 | Emerson W W, Chi C L. Exchangeable calcium, magnesium and sodium and the dispersion of illites in water(Ⅱ): Dispersion of illites in water[J]. Soil Research, 1977, 15(3): 255. |
| 54 | Liu Y Z, Qi H P, Liang H Y, et al. Influence mechanism of interfacial organic matter and salt system on carbon dioxide hydrate nucleation in porous media[J]. Energy, 2024, 290: 130179. |
| 55 | Farhang F, Nguyen A V, Hampton M A. Influence of sodium halides on the kinetics of CO2 hydrate formation[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(2): 1220-1229. |
| 56 | Rehman A N, Pendyala R, Lal B. Effect of brine on the kinetics of carbon dioxide hydrate formation and dissociation in porous media[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021, 47: 1366-1370. |
| 57 | Rehman A N, Bavoh C B, Khan M Y, et al. Amino acid-assisted effect on hydrate-based CO2 storage in porous media with brine[J]. RSC Advances, 2024, 14(13): 9339-9350. |
| 58 | Claussen W F. A second water structure for inert gas hydrates[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1951, 19(11): 1425-1426. |
| 59 | Asadi F, Ejtemaei M, Birkett G, et al. The link between the kinetics of gas hydrate formation and surface ion distribution in the low salt concentration regime[J]. Fuel, 2019, 240: 309-316. |
| 60 | Karamoddin M, Varaminian F. Performance of hydrate inhibitors in tetrahydrofuran hydrate formation by using measurement of electrical conductivity[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2014, 20(5): 3815-3820. |
| 61 | Yang S H B, Babu P, Chua S F S, et al. Carbon dioxide hydrate kinetics in porous media with and without salts[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 162: 1131-1140. |
| 62 | Li F, Chen Z J, Dong H S, et al. Promotion effect of graphite on cyclopentane hydrate based desalination[J]. Desalination, 2018, 445: 197-203. |
| 63 | Moeini H, Bonyadi M, Esmaeilzadeh F, et al. Experimental study of sodium chloride aqueous solution effect on the kinetic parameters of carbon dioxide hydrate formation in the presence/absence of magnetic field[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2018, 50: 231-239. |
| 64 | Ling Z, Shi C R, Li F, et al. Desalination and Li+ enrichment via formation of cyclopentane hydrate[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 231: 115921. |
| 65 | Maniavi Falahieh M, Bonyadi M, Lashanizadegan A. A new hybrid desalination method based on the CO2 gas hydrate and capacitive deionization processes[J]. Desalination, 2021, 502: 114932. |
| 66 | Sun Z G, Wang R Z, Ma R S, et al. Natural gas storage in hydrates with the presence of promoters[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2003, 44(17): 2733-2742. |
| 67 | Riesco N, Trusler J P M. Novel optical flow cell for measurements of fluid phase behaviour[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2005, 228: 233-238. |
| 68 | Babu P, Kumar R, Linga P. Pre-combustion capture of carbon dioxide in a fixed bed reactor using the clathrate hydrate process[J]. Energy, 2013, 50: 364-373. |
| 69 | Arjang S, Manteghian M, Mohammadi A. Effect of synthesized silver nanoparticles in promoting methane hydrate formation at 4.7MPa and 5.7MPa[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2013, 91(6): 1050-1054. |
| 70 | da Silva Lirio C F, Pessoa F L P, Uller A M C. Storage capacity of carbon dioxide hydrates in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and tetrahydrofuran (THF)[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 96: 118-123. |
| [1] | 赵焕娟, 包颖昕, 于康, 刘婧, 钱新明. 多元组分爆轰不稳定性定量实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 339-348. |
| [2] | 卢昕悦, 陈锐莹, 姜夏雪, 梁海瑞, 高歌, 叶正芳. 耦合LNG冷能的液态空气储能系统和液态CO2储能系统对比分析[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3297-3309. |
| [3] | 徐宏标, 杨亮, 李子栋, 刘道平. 盐水微滴/泡沫铜复合体系中甲烷水合物生成动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3287-3296. |
| [4] | 祝赫, 张仪, 齐娜娜, 张锴. 欧拉-欧拉双流体模型中颗粒黏性对液固散式流态化的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3103-3112. |
| [5] | 丁湧, 李文建, 陈昭宇, 曹立辉, 刘轩铭, 任强强, 胡松, 向军. 废旧晶体硅光伏组件EVA有氧热解动力学与产物特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3310-3319. |
| [6] | 唐昊, 胡定华, 李强, 张轩畅, 韩俊杰. 抗加速度双切线弧流道内气泡动力学行为数值与可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3074-3082. |
| [7] | 陈巨辉, 苏潼, 李丹, 陈立伟, 吕文生, 孟凡奇. 翅形扰流片作用下的微通道换热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3122-3132. |
| [8] | 曾港, 陈林, 杨董, 袁海专, 黄彦平. 矩形通道内超临界CO2局部热流场可视化实验[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2831-2839. |
| [9] | 杨明军, 巩广军, 郑嘉男, 宋永臣. 泥质低渗水合物降压开采特性与模型研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2909-2916. |
| [10] | 杨明军, 宋维, 张磊, 凌铮, 陈兵兵, 宋永臣. CO2-海水水合物生成强化方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2939-2948. |
| [11] | 罗莉, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 氧化铝结构与表面性质调控及其催化甲醇脱水制二甲醚性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2522-2532. |
| [12] | 吴邦汉, 林定标, 陆海峰, 郭晓镭, 刘海峰. 竖直管气动物流传输系统管道压降和传送瓶输送特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2465-2473. |
| [13] | 马君霞, 李林涛, 熊伟丽. 基于Tri-training GPR的半监督软测量建模方法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2613-2623. |
| [14] | 李新泽, 张双星, 杨洪海, 杜文静. 基于电池冷却用新型脉动热管性能的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2222-2232. |
| [15] | 陈彦伶, 袁炳志, 王丽伟, 张宸, 朱涵玉. 非平衡条件下金属氯化物-氨工质对的吸附动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2252-2261. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号