化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (6): 2995-3008.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241336
收稿日期:2024-11-22
修回日期:2025-01-19
出版日期:2025-06-25
发布日期:2025-07-09
通讯作者:
何孝军
作者简介:何军(1995—),男,博士研究生,junsshe@163.com
基金资助:
Jun HE1( ), Yong LI1, Nan ZHAO2, Xiaojun HE1(
), Yong LI1, Nan ZHAO2, Xiaojun HE1( )
)
Received:2024-11-22
Revised:2025-01-19
Online:2025-06-25
Published:2025-07-09
Contact:
Xiaojun HE
摘要:
阴离子掺杂诱导空位工程可以有效调节过渡金属硫化物的电子结构,从而提高其对锂硫电池中多硫化锂(LiPSs)的吸附及硫的利用率。以羰基化煤沥青基多孔碳(DCC)为Co纳米粒子的载体,经过一步高温硫化、硒化,将Co纳米粒子转化为具有S空位的Se掺杂CoS2(CoSe x S y @DCC)催化剂。制备的CoSe5S2@DCC具有丰富的孔结构和S空位,可有效地提高其对LiPSs的吸附能力,并加速了硫转化的反应动力学。电化学测试结果表明,负载S后的CoSe5S2@DCC/S正极具有较好的倍率性能(在0.1 C下其比容量为1120 mAh·g-1;在5 C下比容量为488.5 mAh·g-1)、循环稳定性(在5 C的电流密度下,经2000次循环后可维持400.3 mAh·g-1的比容量,库仑效率接近100%)和快的离子扩散性能。这一工作对利用阴离子掺杂诱导空位工程以提高锂硫电池用催化剂催化活性的研究具有重要的参考价值。
中图分类号:
何军, 李勇, 赵楠, 何孝军. 碳负载硒掺杂硫化钴在锂硫电池中的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2995-3008.
Jun HE, Yong LI, Nan ZHAO, Xiaojun HE. Study on the properties of carbon with Se doping cobalt sulfide in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2995-3008.
| 样品 | 含量(Mad)/%(质量分数) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | S | |
| DCTP | 77.84 | 3.42 | 17.34 | 0.82 | 0.58 |
表1 DCTP的元素含量
Table 1 Element content of DCTP
| 样品 | 含量(Mad)/%(质量分数) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | S | |
| DCTP | 77.84 | 3.42 | 17.34 | 0.82 | 0.58 |
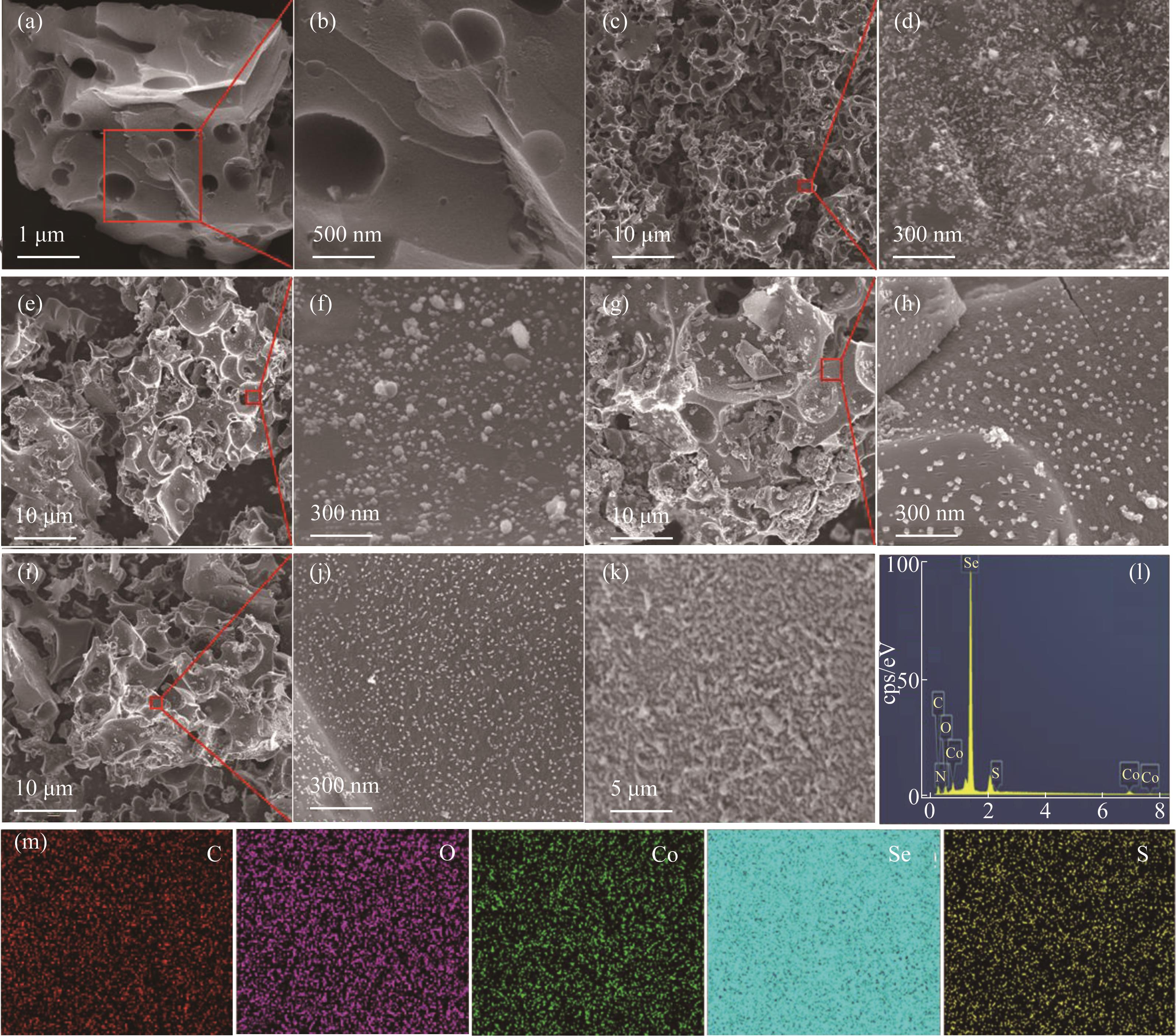
图2 DCC [(a)、(b)], Co@DCC [(c)、(d)], CoSe@DCC [(e)、(f)], CoSe5S2@DCC [(g)、(h)]和CoSe2S5@DCC [(i)、(j)]的FESEM图;CoSe5S2@DCC的FESEM图及其对应的EDS映射[(k)~(m)]
Fig.2 FESEM images of DCC [(a),(b)], Co@DCC [(c),(d)], CoSe@DCC [(e),(f)], CoSe5S2@DCC [(g),(h)], and CoSe2S5@DCC [(i),(j)] CoSe5S2@DCC and the corresponding EDS mapping[(k)—(m)]
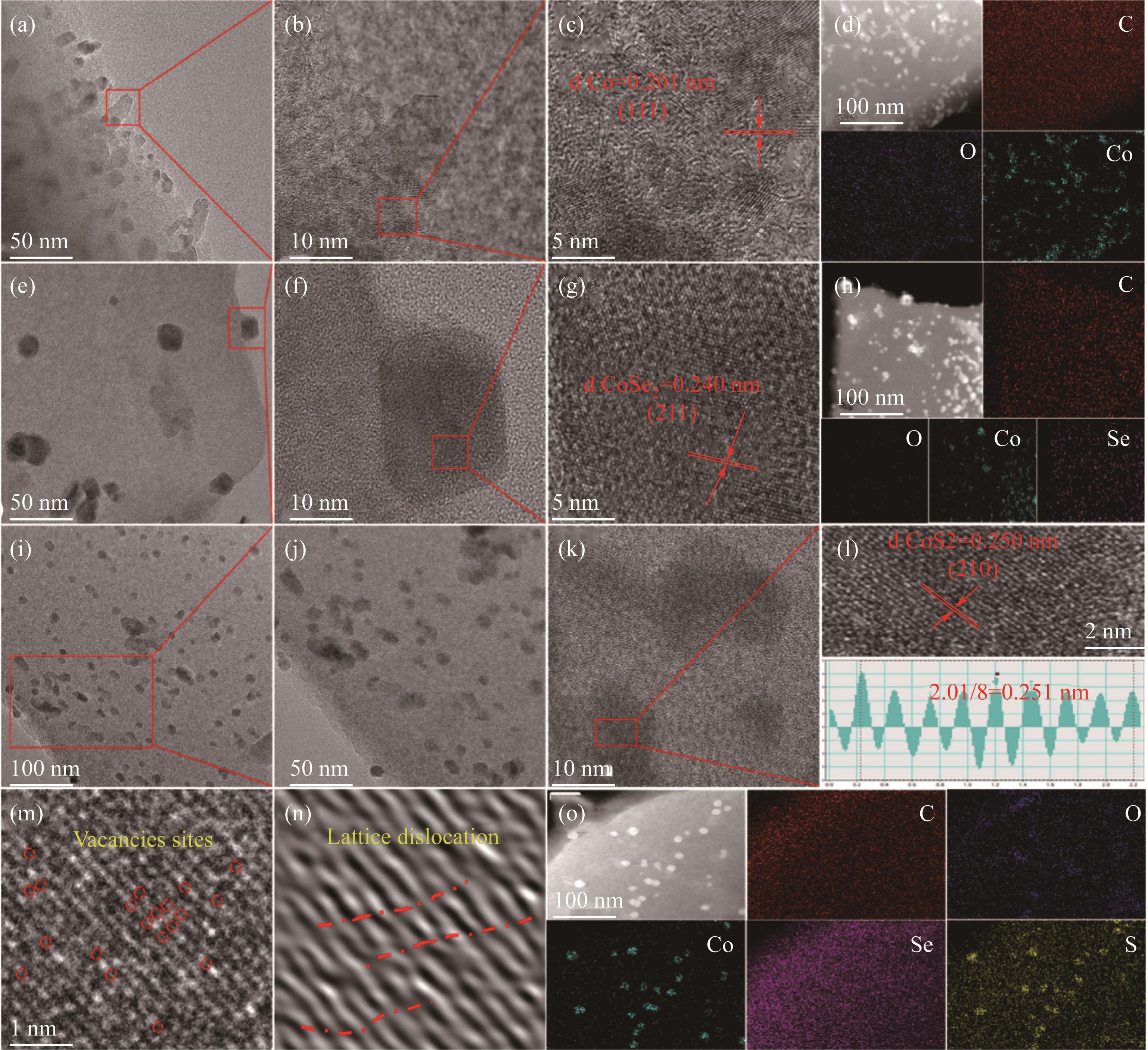
图3 Co@DCC的TEM和HRTEM图[(a)~(c)];Co@DCC和相应的EDS mapping图(d);CoSe@DCC的TEM和HRTEM图[(e)~(g)];CoSe@DCC和相应的EDS mapping图(h);CoSe5S2@DCC的TEM和HRTEM [(i)~(l)];空位(m)和晶体畸变图(n);CoSe5S2@DCC和相应的EDS mapping图(o)
Fig.3 TEM and HRTEM images of Co@DCC [(a)~(c)]; Co@DCC and the corresponding EDS mapping (d); TEM and HRTEM images of CoSe@DCC [(e)~(g)]; CoSe@DCC and the corresponding EDS mapping (h); TEM and HRTEM images of CoSe5S2@DCC [(i)~(l)]; Vacancy sites (m); Lattice distortion (n); CoSe5S2@DCC and the corresponding EDS mapping (o)

图4 DCC、Co@DCC、CoSe@DCC、CoSe5S2@DCC和CoSe2S5@DCC的XRD谱图(a)、Raman谱图(b)、N2吸脱附等温线(c)、孔径分布曲线(d)、XPS谱图(e);CoSe5S2@DCC的C 1s(f)、Co 2p(g)、Se 3d(h)和S 2p(i)高分辨光谱
Fig.4 XRD patterns (a), Raman spectra (b), Nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms (c), pore size distribution curves (d) and XPS spectra (e) of DCC, Co@DCC, CoSe@DCC, CoSe5S2@DCC, and CoSe2S5@DCC; High resolution XPS spectra of C 1s(f), Co 2p (g), Se 3d (h), and S 2p (i) for CoSe5S2@DCC
| Samples | Dap /Å | SBET/ (m2·g-1) | Smic/ (m2·g-1) | Vt/ (cm3·g-1) | Vmic/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCC | 25.26 | 2817.56 | 857.18 | 1.54 | 0.44 |
| Co@DCC | 17.12 | 1252.67 | 1074.4 | 0.53 | 0.42 |
| CoSe3@DCC | 22.16 | 205.84 | 21.26 | 0.111 | 0.004 |
| CoSe5S2@DCC | 20.98 | 449.03 | 67.88 | 0.232 | 0.022 |
| CoSe2S5@DCC | 19.66 | 1575.1 | 754.0 | 0.765 | 0.3 |
表2 DCC、Co@DCC、CoSe@DCC、CoSe5S2@DCC和CoSe2S5@DCC的比表面积及孔结构参数
Table 2 Specific surface area and pore structure parameters of DCC, Co@DCC, CoSe@DCC, CoSe5S2 @DCC, and CoSe2S5@DCC
| Samples | Dap /Å | SBET/ (m2·g-1) | Smic/ (m2·g-1) | Vt/ (cm3·g-1) | Vmic/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCC | 25.26 | 2817.56 | 857.18 | 1.54 | 0.44 |
| Co@DCC | 17.12 | 1252.67 | 1074.4 | 0.53 | 0.42 |
| CoSe3@DCC | 22.16 | 205.84 | 21.26 | 0.111 | 0.004 |
| CoSe5S2@DCC | 20.98 | 449.03 | 67.88 | 0.232 | 0.022 |
| CoSe2S5@DCC | 19.66 | 1575.1 | 754.0 | 0.765 | 0.3 |
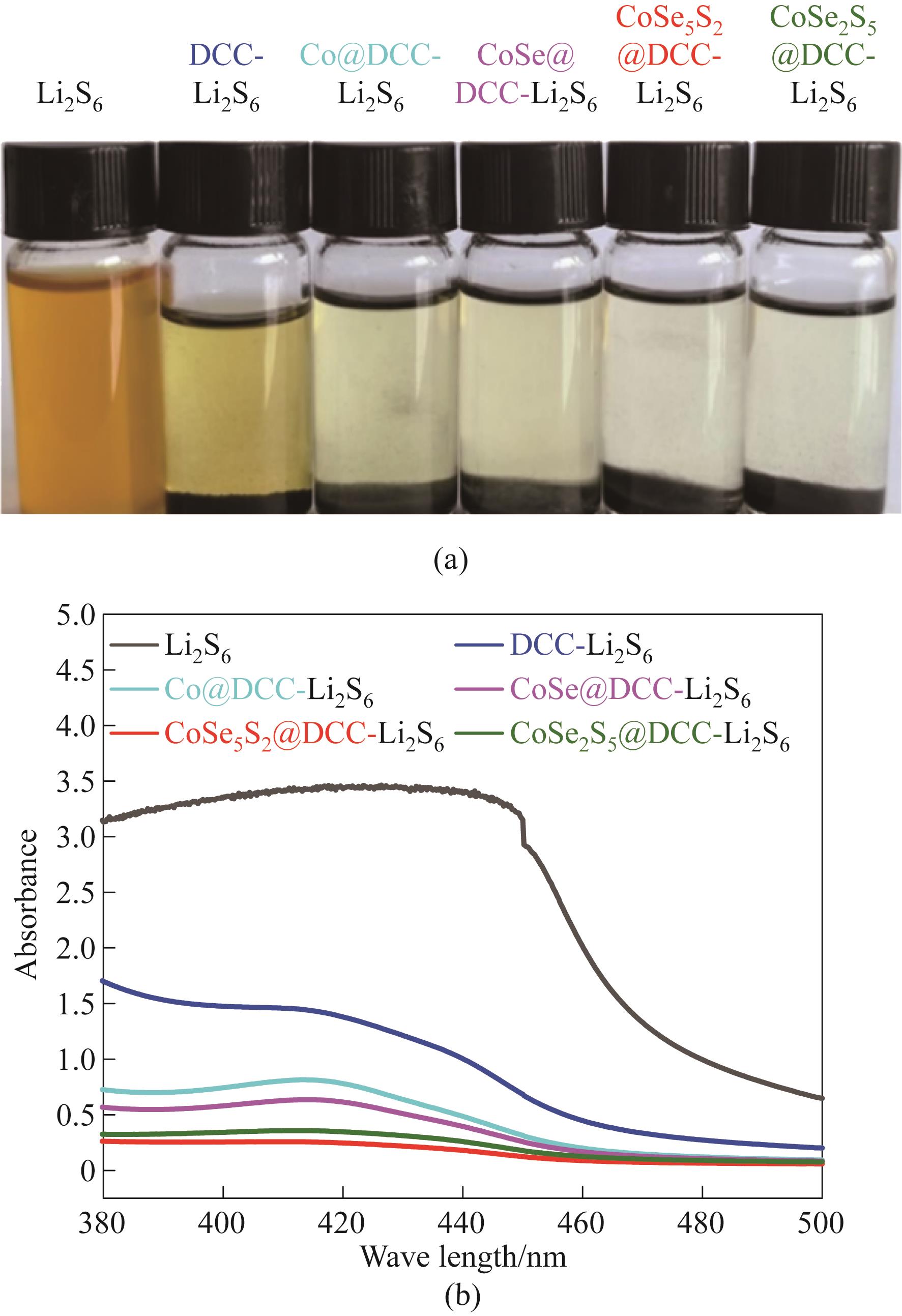
图5 不同样品在Li2S6溶液中吸附并静置12 h后的照片(a)和上清液的紫外可见吸收光谱(b)
Fig.5 Photographs of various samples after adsorption and settling in Li2S6 solution after 12 h (a) and UV-vis spectrum of supnatant (b)
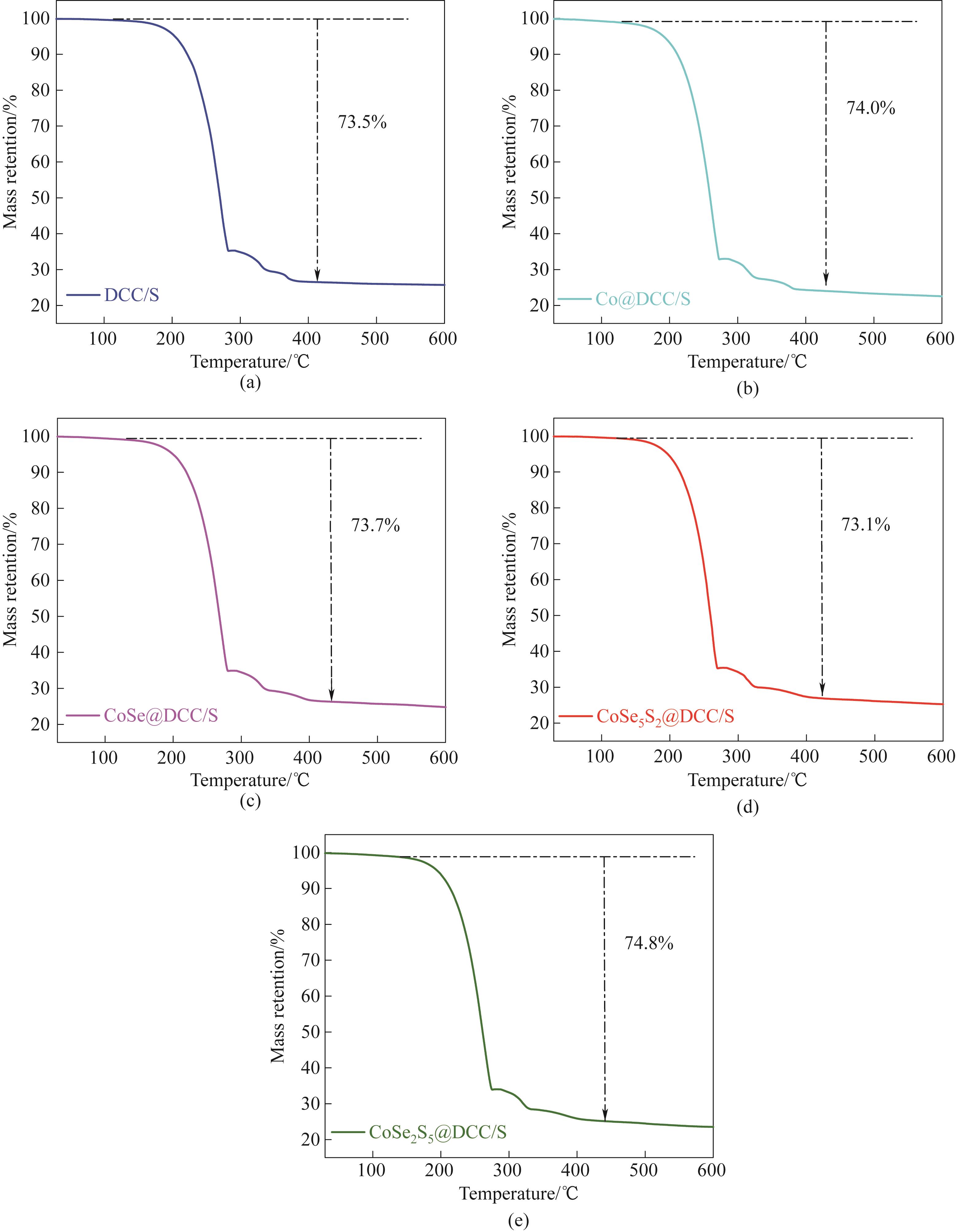
图6 DCC (a)、Co@DCC/S (b)、CoSe@DCC/S (c)、CoSe5S2@DCC/S (d)和CoSe2S5@DCC/S (e)的TGA曲线
Fig.6 TGA curves of DCC/S (a), Co@DCC/S (b), CoSe@DCC/S (c), CoSe5S2@DCC/S (d), and CoSe2S5@DCC/S (e)
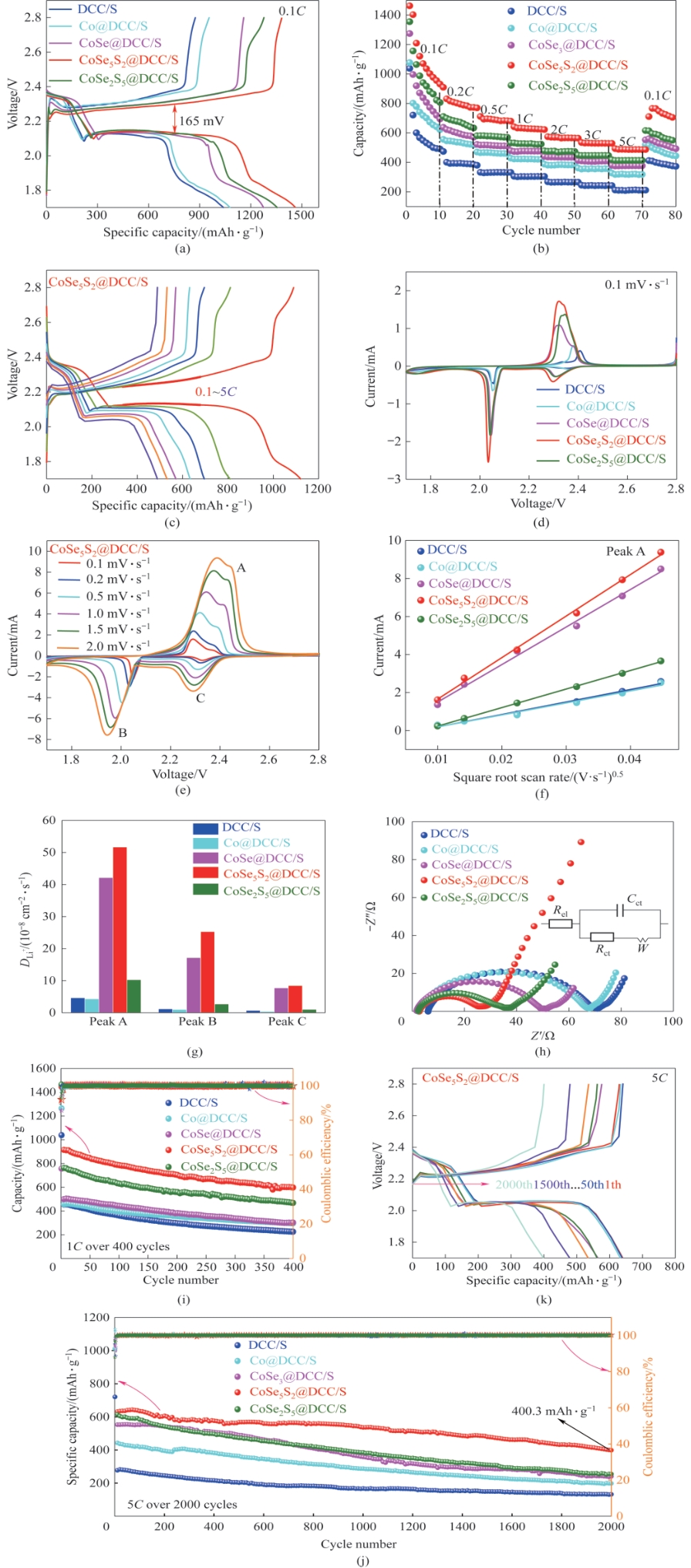
图7 0.1C下DCC/S、Co@DCC/S、CoSe@DCC/S、CoSe5S2@DCC/S、CoSe2S5@DCC/S基电池的GCD曲线(a);各电极电池在0.1~5C下的倍率性能比较(b);CoSe5S2@DCC/S电池在0.1~5C下的GCD曲线(c);0.1 mV·s-1时DCC/S、Co@DCC/S、CoSe@DCC/S、CoSe5S2@DCC/S、CoSe2S5@DCC/S的初始CV曲线(d);基于CoSe5S2@DCC/S电池在0.1~2 mV·s-1下的CV曲线(e);氧化峰A:不同正极的峰值电流与扫描速率的平方根的关系(f);根据Randles-Sevcik方程从CV氧化还原峰计算Li+扩散系数(g);各正极的Nyquist图(h);1C时的循环稳定性(i);5C时的长周期循环测试(j);CoSe5S2@DCC/S电池在5C下第1、50、100、300、500、1000、1500、2000次循环的GCD曲线(k)
Fig.7 GCD curves of DCC/S, Co@DCC/S, CoSe@DCC/S, CoSe5S2@DCC/S, and CoSe2S5@DCC/S cells at 0.1C (a); Rate performance comparison at 0.1 to 5C of all cells (b); GCD curves of the CoSe5S2@DCC/S cell at 0.1—5C (c); The initial CV curves of DCC/S, Co@DCC/S, CoSe@DCC/S, CoSe5S2@DCC/S, and CoSe2S5@DCC/S at 0.1 mV·s-1 (d); CV curves of cells based on CoSe5S2@DCC/S electrodes at 0.1—2 mV·s-1 (e); Oxidation A peak: current vs. square root of scan rate for different cathodes (f); Li+ diffusion coefficient calculated from the CV redox peaks according to the Randles-Sevcik equation (g); Nyquist plot for each cathode (h); Cycle stability at 1C (i); Long cycle test at 5C (j); GCD curves of the CoSe5S2@DCC/S cell at the cycle of 1, 50, 100, 300, 500, 1000, 1500, and 2000 at 5C (k)
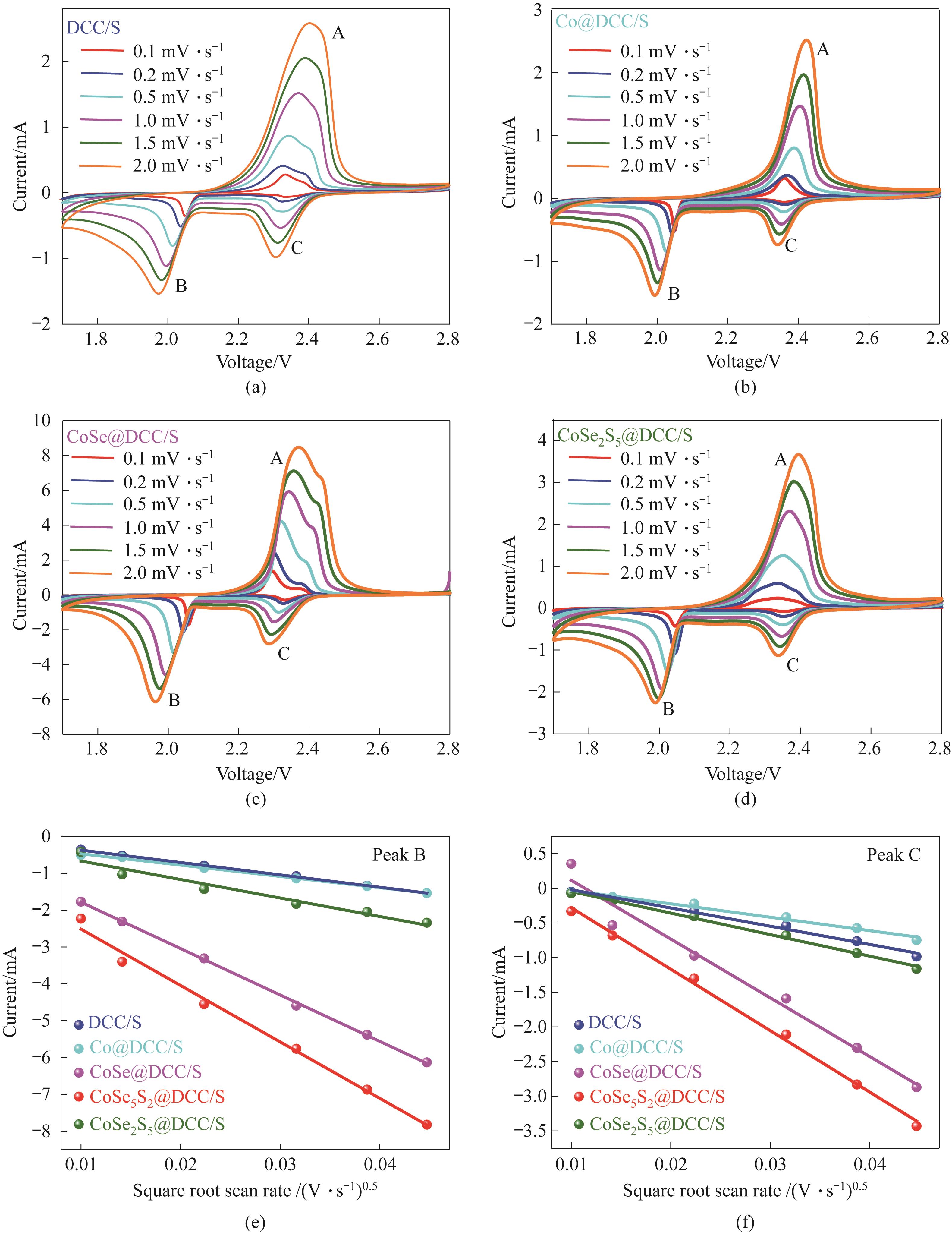
图8 DCC/S (a)、Co@DCC/S (b)、CoSe@DCC/S (c)和CoSe2S5@DCC/S (d)基电池在0.1~2 mV·s-1扫描速率下的CV曲线;还原峰B:不同正极的峰值电流与扫描速率的平方根的关系(e);还原峰C:不同正极的峰值电流与扫描速率的平方根的关系(f)
Fig.8 CV curves of cells based on DCC/S (a), Co@DCC/S (b), CoSe@DCC/S (c), and CoSe2S5@DCC/S (d) electrodes at scan rates in the range 0.1—2 mV·s-1; Reduction B peak: current vs square root of scan rate for different cathodes (e); Reduction C peak: current vs square root of scan rate for different cathodes (f)
| [1] | Guo Y, Niu Q, Pei F, et al. Interface engineering toward stable lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(4): 1330-1367. |
| [2] | Ma T, Deng J J, Lin Y X, et al. Li-rich organosulfur cathode with boosted kinetics for high-energy lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2024, 7(4): e12704. |
| [3] | Xu Y H, Yuan W C, Geng C N, et al. High-entropy catalysis accelerating stepwise sulfur redox reactions for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(31): 2402497. |
| [4] | Zhang Y D, Zhang H W, Lei J, et al. Design double layered anode for stably introducing lithium source to achieve sulfur-carbon full batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2025, 35(11): 2417124. |
| [5] | Song Y W, Shen L, Yao N, et al. Anion-involved solvation structure of lithium polysulfides in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(19): e202400343. |
| [6] | Zhang W, Zhu J W, Ye Y D, et al. Suppressing shuttle effect via cobalt phthalocyanine mediated dissociation of lithium polysulfides for enhanced Li-S battery performance[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(40): 2403888. |
| [7] | Li J P, Cong J L, Ji H J, et al. Tuning the solubility of polysulfides for constructing practical lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2024, 95: 611-617. |
| [8] | Bi C X, Yao N, Li X Y, et al. Unveiling the reaction mystery between lithium polysulfides and lithium metal anode in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(41): 2411197. |
| [9] | Huang C, Yu J, Zhang C Y, et al. Electronic spin alignment within homologous NiS2/NiSe2 heterostructures to promote sulfur redox kinetics in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(25): 2400810. |
| [10] | Zhao M, Peng H J, Li B Q, et al. Kinetic promoters for sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2024, 57(4): 545-557. |
| [11] | Chen R X, Zhou Y C, Li X D. Nanocarbon-enabled mitigation of sulfur expansion in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 68: 103353. |
| [12] | Zhou F Y, Meng Y H, Wang T, et al. Strutted graphene foam loading sulfur for high-rate long-lifetime Li-S batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2024, 127: 109755. |
| [13] | Cai S B, Ma R L, Ke W, et al. Flower-like covalent organic frameworks as host materials for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 491: 151979. |
| [14] | Zhao Y, Lu H C, Kong X R, et al. Graphitic carbon nitride stabilized the lithium anode/sulfide electrolyte interface for all-solid-state lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 489: 150887. |
| [15] | Dong W, Wu Z M, Zhu X Y, et al. Synergistic pyridinic N/pyrrolic N configurations in rGO/CNT composite sulfur hosts for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 488: 150872. |
| [16] | Yang H T, Wang L, Geng C N, et al. Catalytic solid-state sulfur conversion confined in micropores toward superhigh coulombic efficiency lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(21): 2400249. |
| [17] | Li Z, Liang G Y, Wang T L, et al. Sulfur nanosheets deposited on reduced graphene oxide enable excellent cycling life for lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Carbon, 2024, 229: 119512. |
| [18] | Lin H, Guo Z L, Zhang Q C, et al. Coupled Ni-Co dual-atom catalyst for guiding sulfur and lithium evolutions in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Small, 2024, 20(46): 2404983. |
| [19] | Zhao X H, Xu Y J, Qiu T, et al. Enhanced Li bonds enable bidirectional sulfur catalysis by a molecular Co-N4 catalyst for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 72: 103728. |
| [20] | Zuo Y Z, Jiao X C, Huang Z, et al. Surface electron reconstruction of catalyst through alloying strategy for accelerating sulfur conversion in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(44): 2405853. |
| [21] | Lv S, Ma X K, Ke S W, et al. Metal-coordinated covalent organic frameworks as advanced bifunctional hosts for both sulfur cathodes and lithium anodes in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(13): 9385-9394. |
| [22] | Liu J L, Zhang L M, Wu H J. Anion-doping-induced vacancy engineering of cobalt sulfoselenide for boosting electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(26): 2200544. |
| [23] | Peng L, Bai Y, Li H, et al. Boosting bidirectional sulfur conversion enabled by introducing boron-doped atoms and phosphorus vacancies in Ni2P for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2025, 100: 760-769. |
| [24] | Wang C, Liu R Q, Liu W X, et al. Porous carbon cloth@CoSe2 as kinetics-enhanced and high-loading integrated sulfur host for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(25): 2316221. |
| [25] | Wang M K, Hu X Y, Su H, et al. Modulating ionic conduction and accelerating sulfur conversion kinetics through oxygen vacancy engineering for high-performance solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(44): 2407549. |
| [26] | Han F C, Yan D Z, Guan X G, et al. Self-assembled 3D CoSe-based sulfur host enables high-efficient and durable electrocatalytic conversion of polysulfides for flexible lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 71: 103652. |
| [27] | Luo R J, Zhao J Z, Zheng M, et al. Built-in electric field within CoSe2-FeSe2 heterostructure for enhanced sulfur reduction reaction in Li-S batteries[J]. Small, 2024, 20(49): 2406415. |
| [28] | Xu C, Jiang X L, Huang M G, et al. A multi-functional CoN-Mo2N heterostructure nanorods for high performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 488: 151132. |
| [29] | Ding Y, Li X, Chen Y M, et al. Hit two birds with one stone: a bi-functional selenium-substituted organosulfur polymer additive for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 482: 148803. |
| [30] | Dong H H, Ji Y, Wang L, et al. Bimetallic coupling strategy modulating electronic construction to accelerate sulfur redox reaction kinetics for high-energy flexible Li-S batteries[J]. Small, 2024, 20(49): 2406565. |
| [31] | Li X, Yu J Q, Li W Z, et al. Non-metal iodine single-atom catalysts anchored on N-doped graphene for high-performance lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 505(1): 159355. |
| [32] | Zhang Y, Yu T, Xiao R, et al. The role of long-range interactions between high-entropy single-atoms in catalyzing sulfur conversion reactions[J]. Advanced Materials, 2025, 37(10): 2413653. |
| [33] | Wang D W, Gwalani B, Wierzbicki D, et al. Overcoming the conversion reaction limitation at three-phase interfaces using mixed conductors towards energy-dense solid-state Li-S batteries[J]. Nature Materials, 2025, 24: 243-251. |
| [34] | Liu J, Zhou Y H, Xiao Z X, et al. Tailoring molecular structures for enhanced anchoring of polysulfides in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 484: 149596. |
| [35] | Yin Y, Tan P C, Chen Q D, et al. A grain-boundary-rich cobalt selenide hollow multi-shelled structure as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2024, 12(40): 27400-27408. |
| [1] | 吴馨, 龚建英, 李祥宇, 王宇涛, 杨小龙, 蒋震. 超声波激励疏水表面液滴运动的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 133-139. |
| [2] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [3] | 裴星亮, 叶翠平, 裴赢丽, 李文英. 碱改性MIL-53(Cr)选择性吸附分离二甲苯异构体[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 258-267. |
| [4] | 吴梓航, 徐震原, 游锦方, 潘权稳, 王如竹. 基于吸附式储冷技术的深井钻探设备冷却系统[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 309-317. |
| [5] | 黄国瑞, 赵耀, 谢明熹, 陈尔健, 代彦军. 一种新型数据中心余热回收系统实验与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 409-417. |
| [6] | 麦棹铭, 武颖韬, 王维, 穆海宝, 黄佐华, 汤成龙. 正十二烷-甲烷双燃料非线性着火特性及稀释气体效应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3115-3124. |
| [7] | 彭新艳, 刘云鸿, 陈凌宇, 韦跃兰, 陈淑琴, 胡柱东. 小分子外交联法制备超高交联聚苯乙烯血液灌流吸附剂[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3093-3103. |
| [8] | 刘峰, 韩春硕, 张益, 刘彦成, 郁林军, 申家伟, 高晓泉, 杨凯. 高温高盐环境下单烃链和双烃链表面活性剂对油水界面性质影响的微观机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2939-2957. |
| [9] | 赵清萍, 张敏, 赵辉, 王刚, 邱永福. 乙烯氢甲酯化合成丙酸甲酯的氢键作用机制及反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2701-2713. |
| [10] | 杨盛华, 孙阳杰, 薛晓君, 米杰, 王建成, 冯宇. 缺陷型金属氧化物脱除气体污染物研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2469-2482. |
| [11] | 郭彭涛, 王婷, 薛波, 应允攀, 刘大欢. 用于CH4/N2分离的多吸附位点超微孔MOF[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2304-2312. |
| [12] | 唐磊, 王振菲, 李聪利, 杨佳辉, 郑浩, 石琪, 董晋湘. Co-MOF-74和Mg-MOF-74的CO工作吸附容量及操作条件[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2279-2293. |
| [13] | 李艳, 雷美丽, 李鑫钢. 基于分离性能的顺序式模拟移动床结构调控策略[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2219-2229. |
| [14] | 巴雅琪, 吴涛, 邸安頔, 陆安慧. 多孔炭材料用于低碳烃分离的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2136-2157. |
| [15] | 谈朋, 李雪梅, 刘晓勤, 孙林兵. 基于柔性MOFs的磁响应复合材料及其丙烯吸附性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2230-2240. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号