化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (8): 4318-4330.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250077
周奕彤1,2( ), 周明熙1(
), 周明熙1( ), 刘若晨1, 叶爽1, 黄伟光1,2
), 刘若晨1, 叶爽1, 黄伟光1,2
收稿日期:2025-01-17
修回日期:2025-04-14
出版日期:2025-08-25
发布日期:2025-09-17
通讯作者:
周明熙
作者简介:周奕彤(2001—),女,硕士研究生,zhouyt2023@shanghaitech.edu.cn
Yitong ZHOU1,2( ), Mingxi ZHOU1(
), Mingxi ZHOU1( ), Ruochen LIU1, Shuang YE1, Weiguang HUANG1,2
), Ruochen LIU1, Shuang YE1, Weiguang HUANG1,2
Received:2025-01-17
Revised:2025-04-14
Online:2025-08-25
Published:2025-09-17
Contact:
Mingxi ZHOU
摘要:
直接还原铁-电弧炉(direct reduced iron-electric arc furnace,DRI-EAF)是钢铁工业减碳的一种短流程炼钢工艺,其大规模绿氢冶金应用须关注可再生能源利用率、时序源荷交互、经济可行性等。本研究建立了光伏与电网协同驱动的氢基DRI-EAF工艺模型,基于典型地理区域的技术经济参数,评估了该工艺的能耗、碳排放及经济效益。结果表明,新疆乌鲁木齐2500 MW光伏电站规模可实现可再生能源渗透率90.26%,相比于纯电网运行、高炉-转炉工艺和天然气DRI-EAF工艺,分别减少碳排放84.54%、81.35%和68.28%。100 MW光伏电站规模下,以上海为代表的高电价地区难以回收投资成本,地区电网电价是影响可再生能源氢基DRI-EAF工艺经济性的关键因素之一。制氢成本一定时,碳价由90 CNY/t上涨到1614 CNY/t,新疆乌鲁木齐2500 MW光伏电站回收期由8.28年降低至3.45年。
中图分类号:
周奕彤, 周明熙, 刘若晨, 叶爽, 黄伟光. 光伏与电网协同驱动氢基直接还原铁炼钢的技术经济分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4318-4330.
Yitong ZHOU, Mingxi ZHOU, Ruochen LIU, Shuang YE, Weiguang HUANG. Technical and economic analysis on hydrogen based direct reduction steelmaking co-driven by photovoltaic and power grid[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4318-4330.
| 项目 | 数值 | |
|---|---|---|
单晶硅 光伏组件 | 转换效率/% | 20.64 |
| 峰值功率/W | 580.0 | |
| 开路电压/V | 40.9 | |
| 短路电流/A | 18.2 | |
| 工作电压/V | 33.8 | |
| 工作电流/A | 17.2 | |
组串式 逆变器 | 最大输入电压/V | 1500 |
| 额定输入电压/V | 1080 | |
| 最小MPPT电压/V | 600 | |
| 最大MPPT电压/V | 1500 | |
| 额定输出电压/V | 800 | |
| 转换效率/% | 98.43 | |
表1 光伏与逆变器关键组件参数
Table 1 Key component parameters of PV and inverters
| 项目 | 数值 | |
|---|---|---|
单晶硅 光伏组件 | 转换效率/% | 20.64 |
| 峰值功率/W | 580.0 | |
| 开路电压/V | 40.9 | |
| 短路电流/A | 18.2 | |
| 工作电压/V | 33.8 | |
| 工作电流/A | 17.2 | |
组串式 逆变器 | 最大输入电压/V | 1500 |
| 额定输入电压/V | 1080 | |
| 最小MPPT电压/V | 600 | |
| 最大MPPT电压/V | 1500 | |
| 额定输出电压/V | 800 | |
| 转换效率/% | 98.43 | |
| 地区 | 地理位置 | 太阳能年均DNI/(W/m2) | 电力二氧化碳排放因子[ | 电网电力 可再生能源 占比/%[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
新疆 乌鲁木齐 | 43.82°N 87.61°E | 221.65 | 0.6231 | 22.5 |
广东 湛江 | 21.28°N 110.35°E | 127.86 | 0.4403 | 28.1 |
河北 张家口 | 40.82°N 114.87°E | 240.02 | 0.7252 | 24.4 |
| 上海 | 31.24°N 121.47°E | 127.48 | 0.5849 | 30.3 |
表2 不同地理位置太阳能年均法向直接辐射量、电力二氧化碳排放因子与电网可再生能源占比
Table 2 Annual average direct normal irradiance (DNI) of solar energy, CO2 emission factor of electricity and the proportion of renewable energy in the grid in different geographical locations
| 地区 | 地理位置 | 太阳能年均DNI/(W/m2) | 电力二氧化碳排放因子[ | 电网电力 可再生能源 占比/%[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
新疆 乌鲁木齐 | 43.82°N 87.61°E | 221.65 | 0.6231 | 22.5 |
广东 湛江 | 21.28°N 110.35°E | 127.86 | 0.4403 | 28.1 |
河北 张家口 | 40.82°N 114.87°E | 240.02 | 0.7252 | 24.4 |
| 上海 | 31.24°N 121.47°E | 127.48 | 0.5849 | 30.3 |
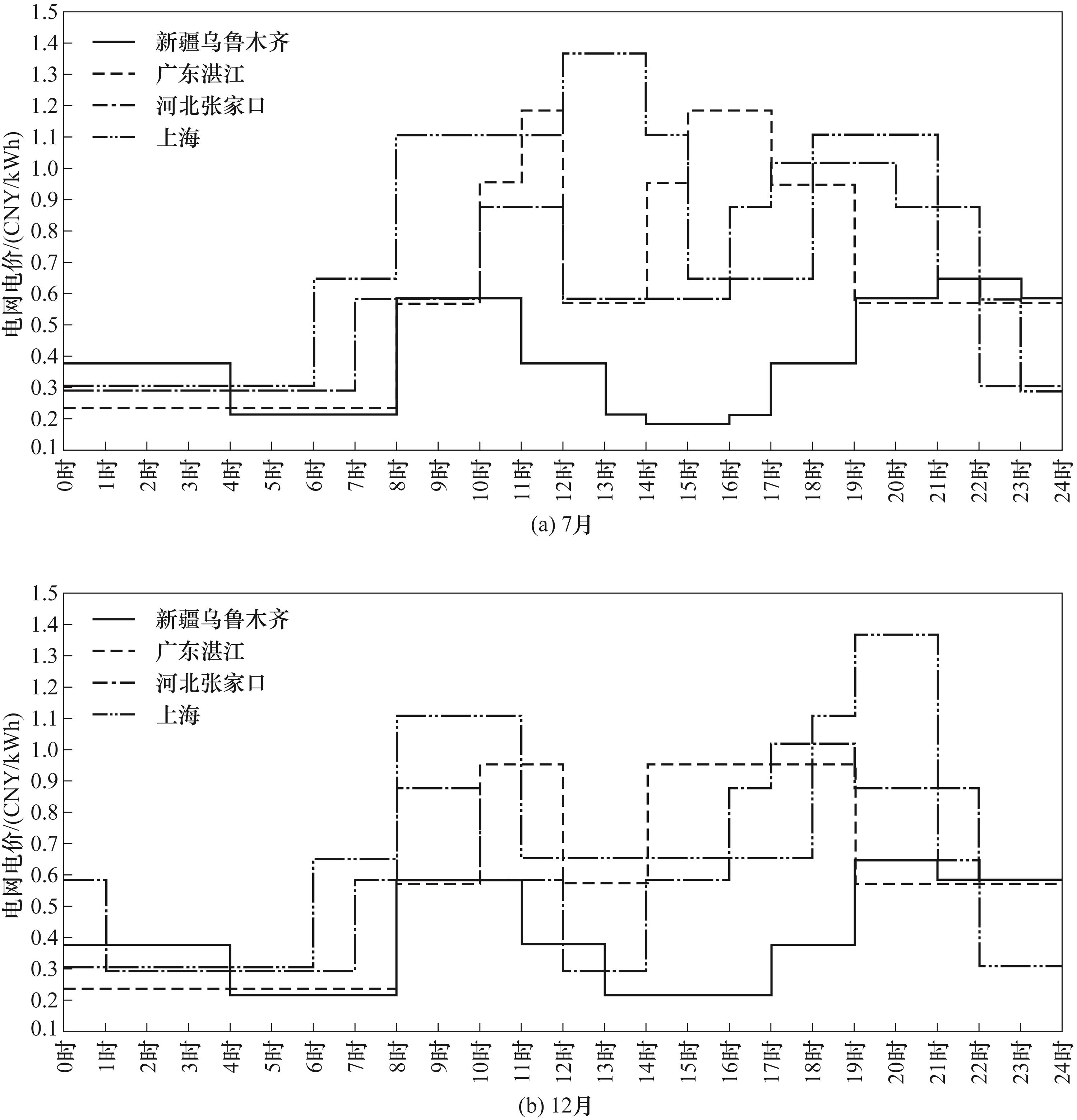
图2 新疆乌鲁木齐、广东湛江、河北张家口、上海四地7月与12月24 h工商业峰谷平电价
Fig.2 24 h industrial and commercial electricity prices in July and December in Urumqi, Xinjiang; Zhanjiang, Guangdong; Zhangjiakou, Hebei and Shanghai
| 参数 | 输入值 |
|---|---|
| 电解槽额定容量/MW | 20[ |
| 电解槽模块数量/套 | 34 |
| 电解槽制氢电耗/(kWh/ | 50 |
| 电解槽设计容量冗余度/% | 50[ |
| 氢气电加热效率/% | 60[ |
表3 电解槽单元参数
Table 3 Parameters of the electrolyser
| 参数 | 输入值 |
|---|---|
| 电解槽额定容量/MW | 20[ |
| 电解槽模块数量/套 | 34 |
| 电解槽制氢电耗/(kWh/ | 50 |
| 电解槽设计容量冗余度/% | 50[ |
| 氢气电加热效率/% | 60[ |
| 参数 | 输入值 |
|---|---|
| 地下储氢容量/m3 | 32000[ |
| 压缩机/膨胀机额定容量/MW | 1.7[ |
| 压缩机/膨胀机模块数量 | 1~120 |
| 压缩机/膨胀机电效率/% | 70 |
表4 储氢单元参数
Table 4 Parameters of the hydrogen storage
| 参数 | 输入值 |
|---|---|
| 地下储氢容量/m3 | 32000[ |
| 压缩机/膨胀机额定容量/MW | 1.7[ |
| 压缩机/膨胀机模块数量 | 1~120 |
| 压缩机/膨胀机电效率/% | 70 |
| 参数 | 输入值 |
|---|---|
| DRI金属化率/% | 94[ |
| 铁矿石电加热效率/% | 85[ |
| 铁矿石杂质SiO2的质量分数/% | 3[ |
| 铁矿石杂质Al2O3的质量分数/% | 2[ |
| 电弧炉电效率/% | 60[ |
| 电弧炉石灰消耗量/(kg/tLS) | 50[ |
| 电弧炉焦炭消耗量/(kg/tLS) | 20[ |
| 电弧炉石墨电极消耗量/(kg/tLS) | 3[ |
表5 DRI-EAF单元参数
Table 5 Parameters of DRI-EAF
| 参数 | 输入值 |
|---|---|
| DRI金属化率/% | 94[ |
| 铁矿石电加热效率/% | 85[ |
| 铁矿石杂质SiO2的质量分数/% | 3[ |
| 铁矿石杂质Al2O3的质量分数/% | 2[ |
| 电弧炉电效率/% | 60[ |
| 电弧炉石灰消耗量/(kg/tLS) | 50[ |
| 电弧炉焦炭消耗量/(kg/tLS) | 20[ |
| 电弧炉石墨电极消耗量/(kg/tLS) | 3[ |
| 参数 | 输入值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 工厂年产能/t | 1×106 | |
| 换热器效率/% | 60[ | |
| 竖炉氢气过量供应与需求量比率 | 1.5[ | |
| 铁矿石价格①/(CNY/t) | 851[ | |
| 工商业用水价格/(CNY/t) | 4.74[ | |
| 焦炭价格②/(CNY/t) | 2004 | |
| 石灰价格③/(CNY/t) | 782[ | |
| 光伏电站 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 3400[ |
| 运营成本/% | 3[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 30[ | |
| 电解槽 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 2136[ |
| 运营成本/% | 3[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 压缩机 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 8546[ |
| 运营成本/% | 4[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 地下储氢 | 建设成本/(CNY/m3) | 359[ |
| 运营成本/% | 2[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 30[ | |
| 膨胀机 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 4409[ |
| 运营成本④/% | 4 | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 竖炉 | 建设成本/(CNY/tDRI) | 1780[ |
| 运营成本/% | 3[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 电弧炉 | 建设成本/(CNY/tLS) | 1638[ |
| 运营成本/% | 2[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 劳动力成本/(CNY/(人·a)) | 9.76万[ | |
| 粗钢售价⑤/(CNY/t) | 4629[ | |
| 碳市场碳价⑥/(CNY/t) | 90 | |
| 税率⑦/% | 25 | |
| 折现率/% | 7[ | |
| 残值率⑧/% | 5 | |
表6 氢基DRI-EAF工厂技术与经济参数
Table 6 Technical and economic parameters of hydrogen-based DRI-EAF plant
| 参数 | 输入值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 工厂年产能/t | 1×106 | |
| 换热器效率/% | 60[ | |
| 竖炉氢气过量供应与需求量比率 | 1.5[ | |
| 铁矿石价格①/(CNY/t) | 851[ | |
| 工商业用水价格/(CNY/t) | 4.74[ | |
| 焦炭价格②/(CNY/t) | 2004 | |
| 石灰价格③/(CNY/t) | 782[ | |
| 光伏电站 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 3400[ |
| 运营成本/% | 3[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 30[ | |
| 电解槽 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 2136[ |
| 运营成本/% | 3[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 压缩机 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 8546[ |
| 运营成本/% | 4[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 地下储氢 | 建设成本/(CNY/m3) | 359[ |
| 运营成本/% | 2[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 30[ | |
| 膨胀机 | 建设成本/(CNY/kW) | 4409[ |
| 运营成本④/% | 4 | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 竖炉 | 建设成本/(CNY/tDRI) | 1780[ |
| 运营成本/% | 3[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 电弧炉 | 建设成本/(CNY/tLS) | 1638[ |
| 运营成本/% | 2[ | |
| 使用寿命/a | 20[ | |
| 劳动力成本/(CNY/(人·a)) | 9.76万[ | |
| 粗钢售价⑤/(CNY/t) | 4629[ | |
| 碳市场碳价⑥/(CNY/t) | 90 | |
| 税率⑦/% | 25 | |
| 折现率/% | 7[ | |
| 残值率⑧/% | 5 | |
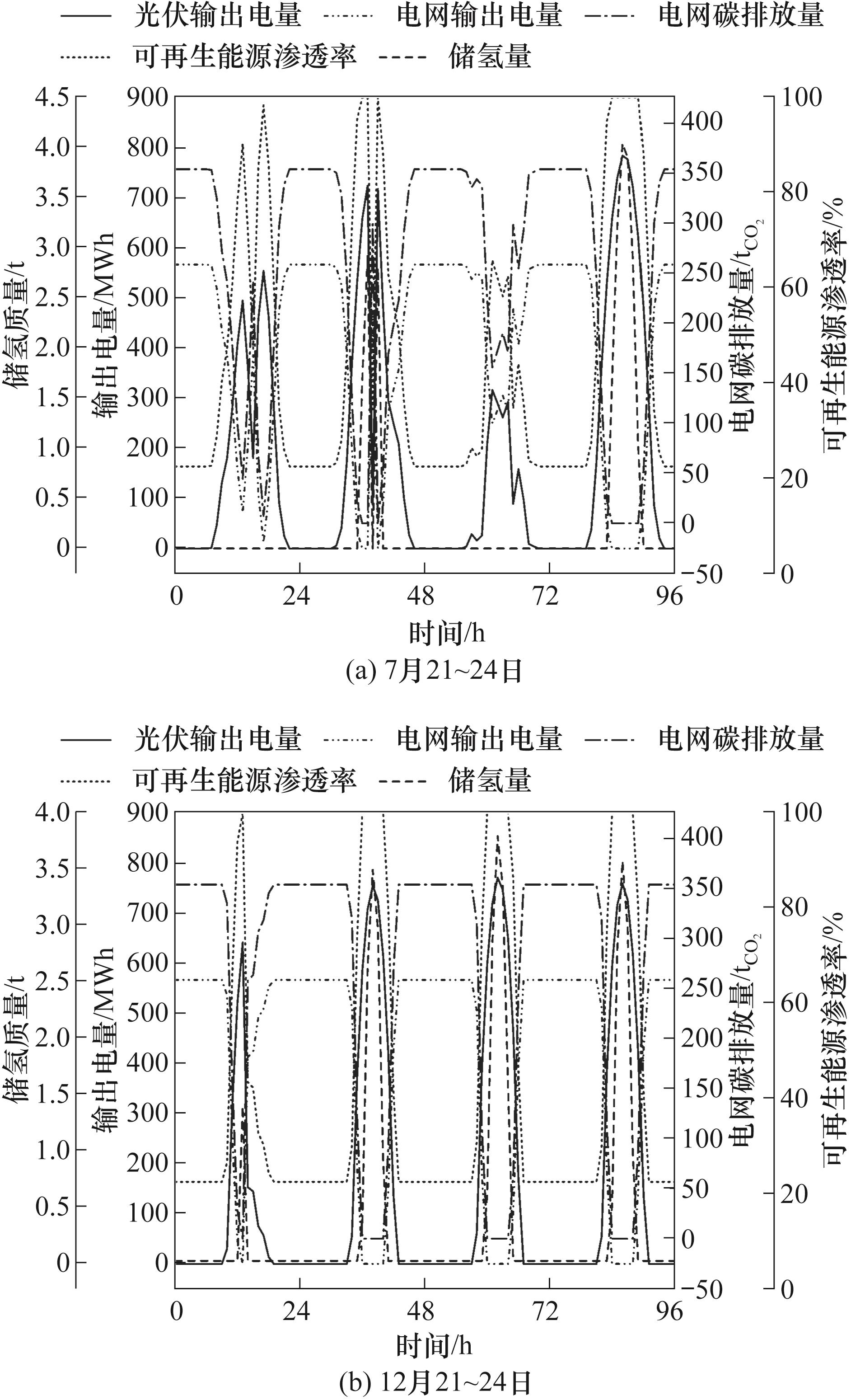
图4 新疆乌鲁木齐1000 MW光伏规模下小时光伏电站产电量、电网输出电量与碳排放量、多余可再生能源储氢量和可再生能源渗透率
Fig.4 Hourly PV power generation, grid output power and carbon emissions, excess renewable energy hydrogen storage capacity and renewable energy share ratio of the 1000 MW PV power station in Urumqi, Xinjiang
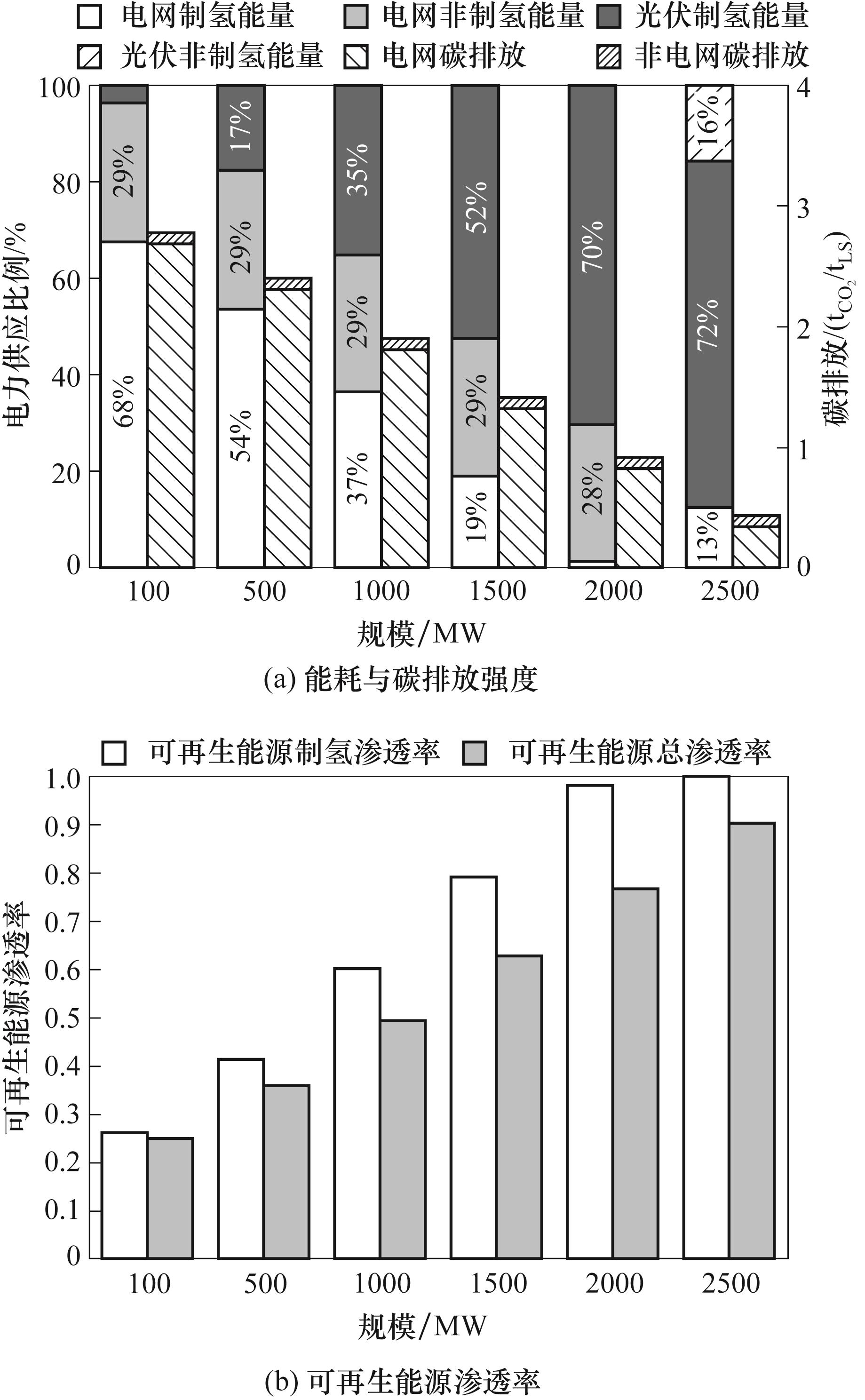
图5 新疆乌鲁木齐不同光伏电站建设规模条件下的DRI-EAF工厂的能耗、碳排放强度与可再生能源渗透率
Fig.5 Energy consumption, carbon emission intensity, and renewable energy share ratio of the DRI-EAF plant under different scales of the PV power station in Urumqi, Xinjiang
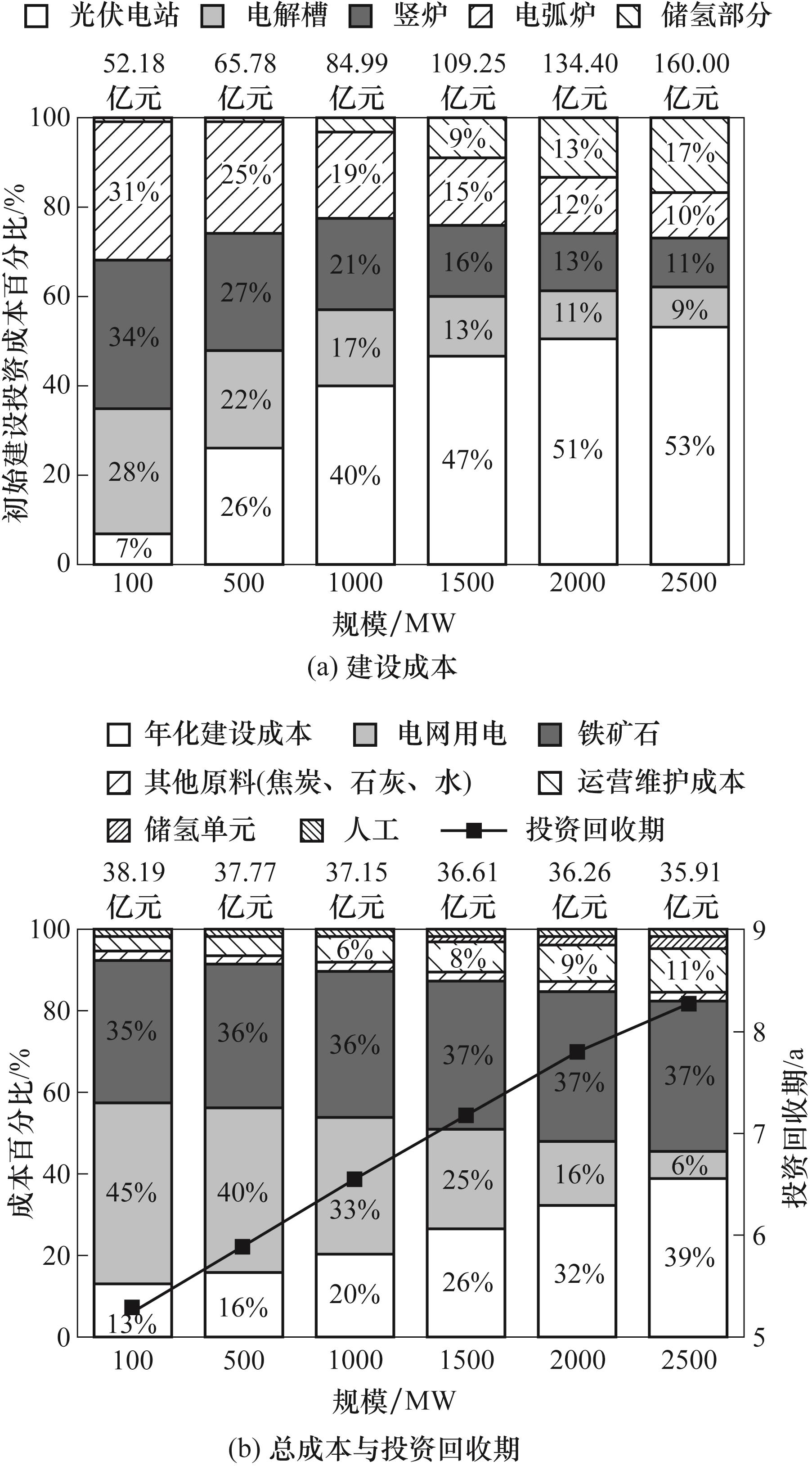
图6 新疆乌鲁木齐不同光伏电站建设规模条件下的DRI-EAF工厂的建设成本、总成本与投资回收期
Fig.6 Construction cost, total cost and payback period of the DRI-EAF plant under different scales of the PV power station in Urumqi, Xinjiang
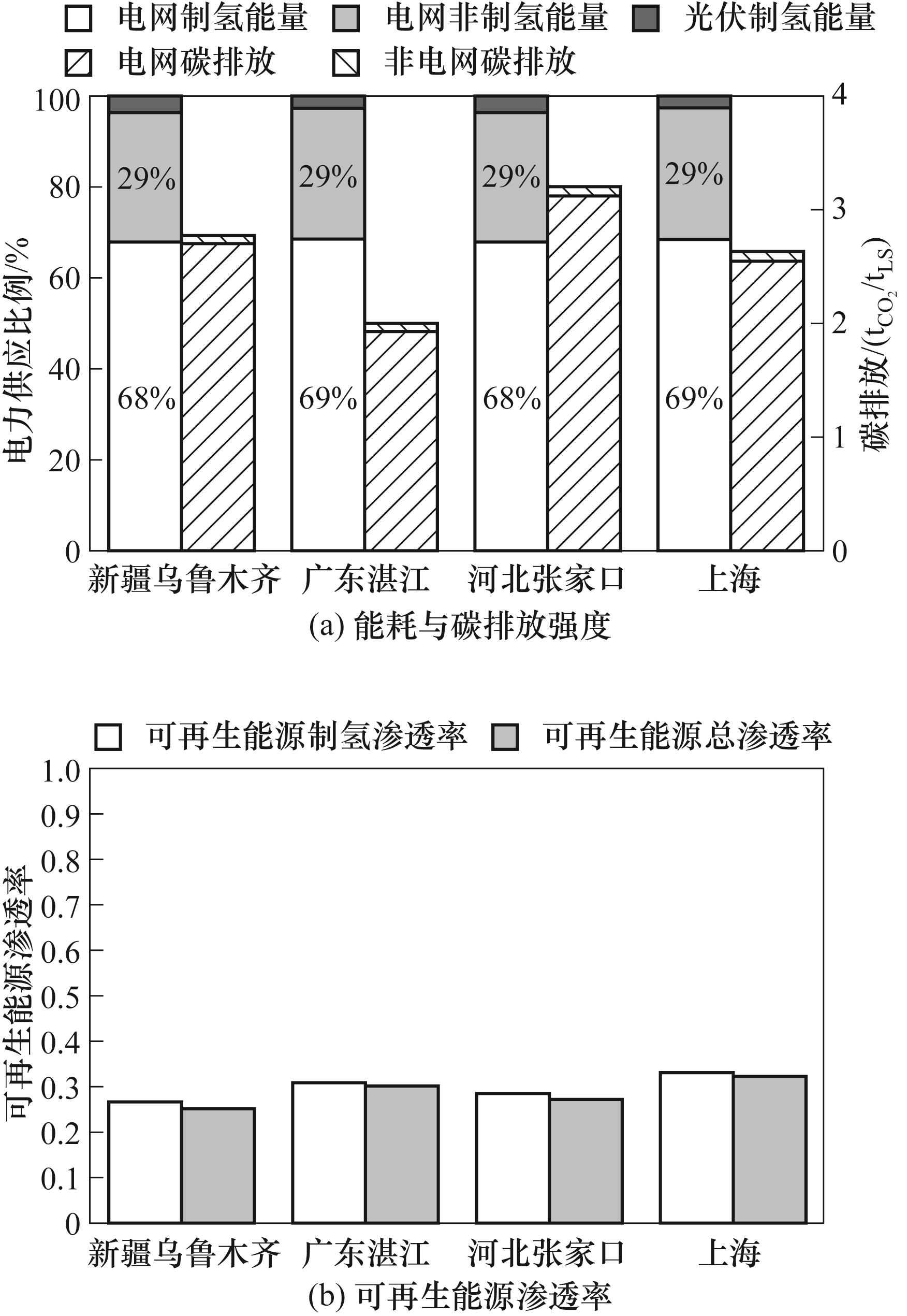
图7 各地理区域100 MW光伏电站规模条件下的DRI-EAF工厂的能耗、碳排放强度与可再生能源渗透率
Fig.7 Energy consumption, carbon emission intensity and renewable energy share ratio of the DRI-EAF plant with 100 MW PV power station at different locations
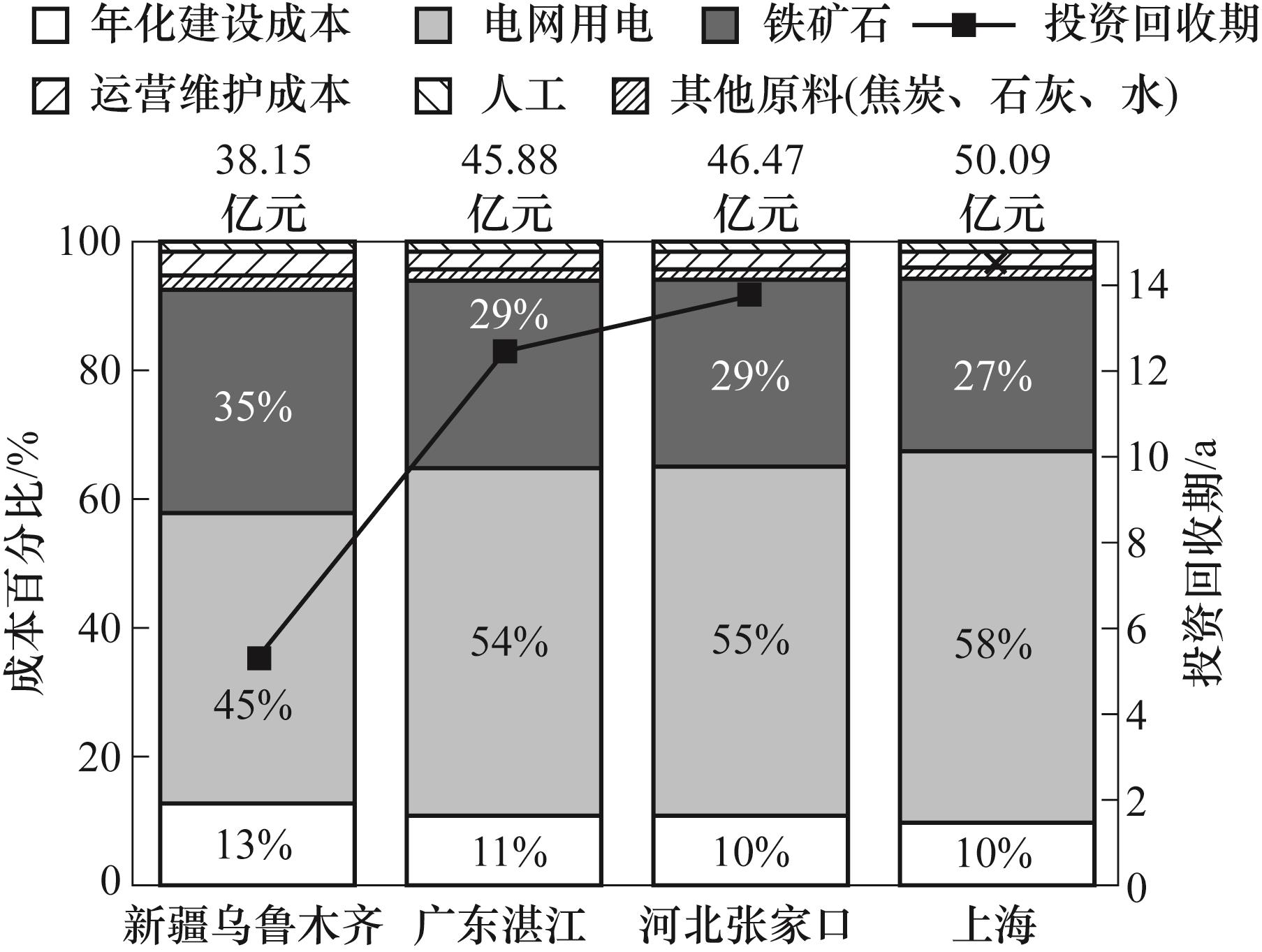
图8 各地理区域100 MW光伏电站规模条件下的DRI-EAF工厂的总成本与投资回收期
Fig.8 Total cost and payback period of the DRI-EAF plant with 100 MW PV power station at different locations
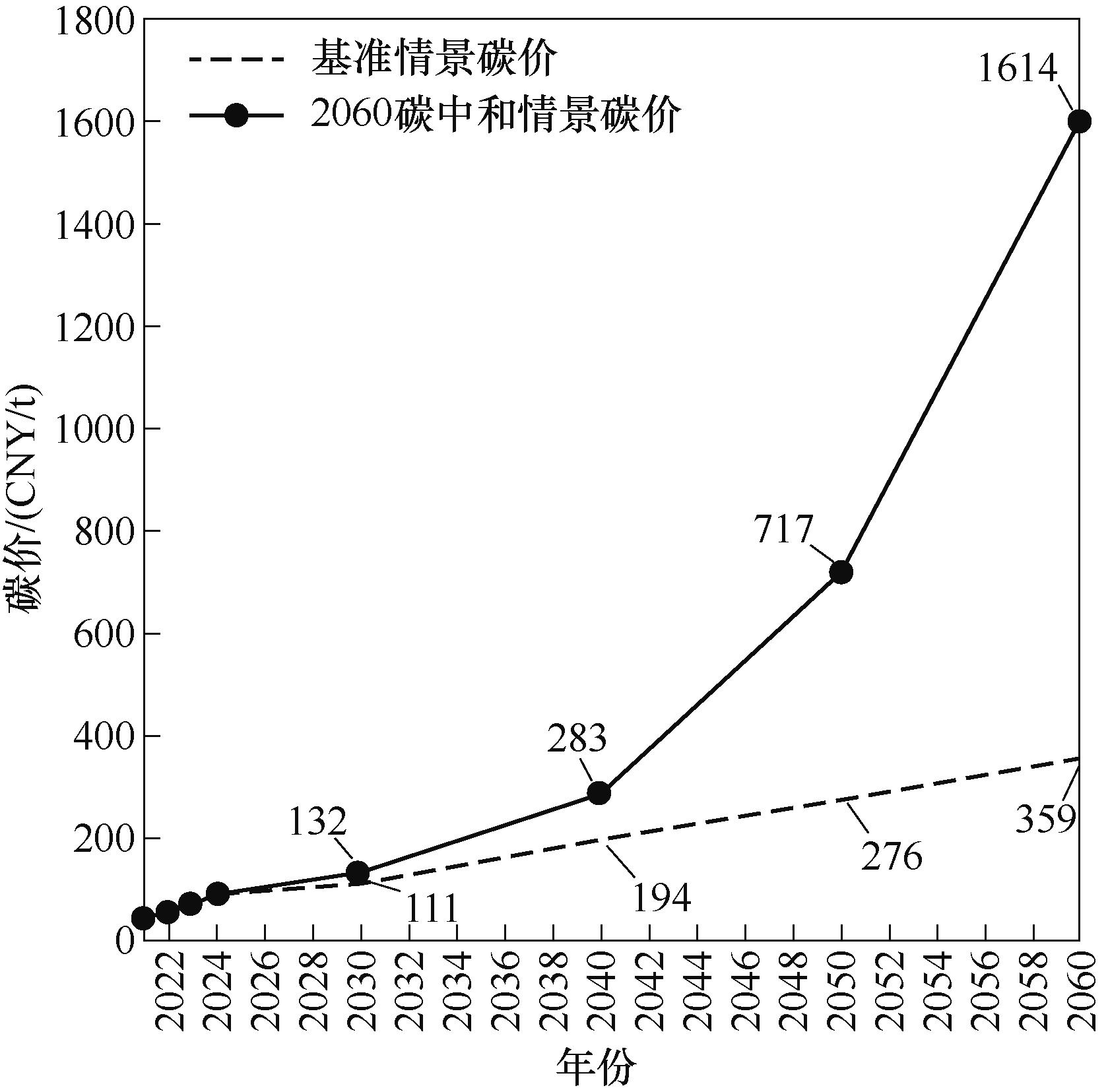
图9 全国碳市场2021—2024年历史碳价、2030—2060年预测碳价[40]
Fig.9 History carbon price of the China carbon market during 2021 to 2024, and the predicted carbon price from 2030 to 2060[40]
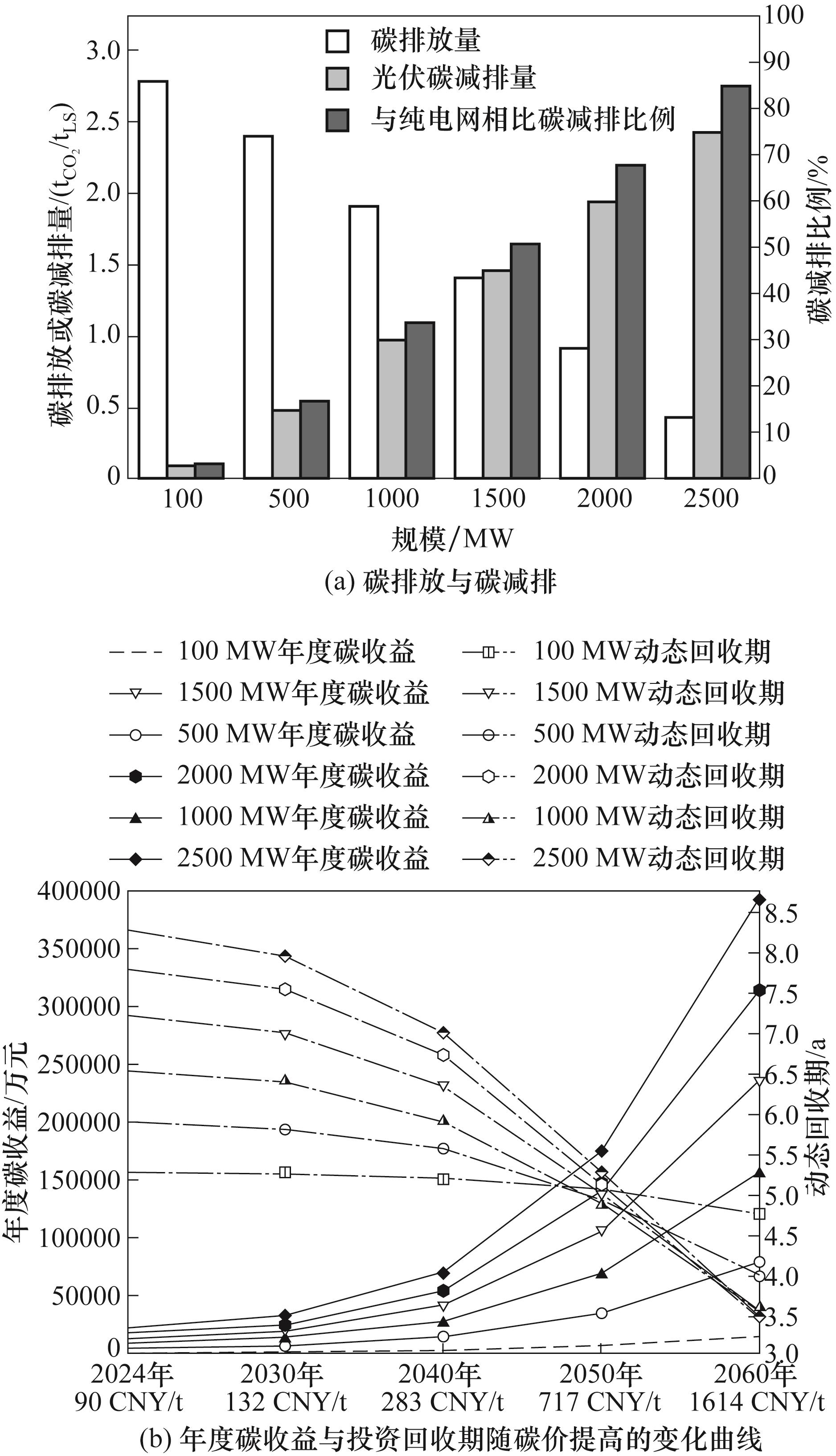
图10 新疆乌鲁木齐不同光伏电站建设规模条件下的DRI-EAF工厂的碳减排强度与碳价的影响
Fig.10 Carbon emission reduction intensity and effects of carbon price of the DRI-EAF plant under different scales of the PV power station in Urumqi, Xinjiang
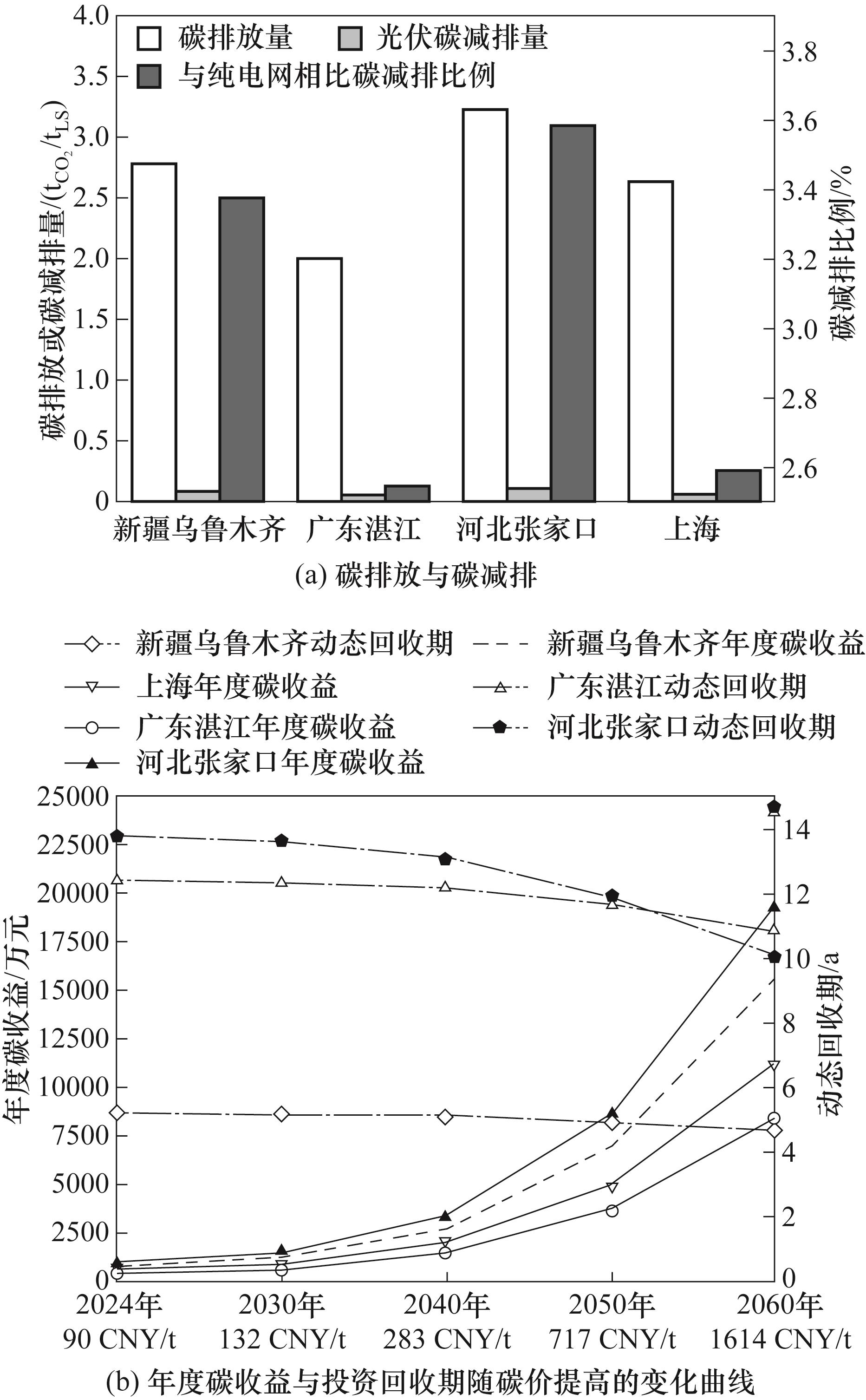
图11 各地理区域100 MW光伏电站规模条件下的DRI-EAF工厂的碳减排强度与碳价的影响
Fig.11 Carbon emission reduction intensity and effects of carbon price of the DRI-EAF plant with 100 MW PV power station at different locations
| [1] | International Energy Agency. Iron and steel technology roadmap[R]. Paris: IEA, 2020. |
| [2] | Zhang J S, Shen J L, Xu L S, et al. The CO2 emission reduction path towards carbon neutrality in the Chinese steel industry: a review[J]. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 2023, 99: 107017. |
| [3] | Perpiñán J, Peña B, Bailera M, et al. Integration of carbon capture technologies in blast furnace based steel making: a comprehensive and systematic review[J]. Fuel, 2023, 336: 127074. |
| [4] | World Steel Association. Sustainability indicators 2023 report[R]. Brussels: WSA, 2023. |
| [5] | Wang Y X, Liu J, Tang X L, et al. Decarbonization pathways of C h i n a ' s iron and steel industry toward carbon neutrality[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2023, 194: 106994. |
| [6] | Seker M, Memmedov A, Huseyinov R, et al. Power quality measurement and analysis in electric arc furnace for Turkish electricity transmission system[J]. Elektronika Ir Elektrotechnika, 2017, 23(6): 25-33. |
| [7] | Fan Z Y, Friedmann S J. Low-carbon production of iron and steel: technology options, economic assessment, and policy[J]. Joule, 2021, 5(4): 829-862. |
| [8] | Kodgire P. Hydrogen — imminent clean and green energy: hydrogen production technologies life cycle assessment review[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2025, 193: 483-500. |
| [9] | Hasnain S M W U, Farooqi A S, Ayodele B V, et al. Advancements in Ni and Co-based catalysts for sustainable syngas production via Bi-reforming of methane: a review of recent advances[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 434: 139904. |
| [10] | Shen J L, Zhang Q, Tian S S, et al. The role of hydrogen in iron and steel production: development trends, decarbonization potentials, and economic impacts[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 92: 1409-1422. |
| [11] | Lan C C, Hao Y J, Shao J N, et al. Effect of H2 on blast furnace ironmaking: a review[J]. Metals, 2022, 12(11): 1864. |
| [12] | Rechberger K, Spanlang A, Conde A S, et al. Green hydrogen-based direct reduction for low-carbon steelmaking[J]. Steel Research International, 2020, 91(11): 2000110. |
| [13] | Müller N, Herz G, Reichelt E, et al. Assessment of fossil-free steelmaking based on direct reduction applying high-temperature electrolysis[J]. Cleaner Engineering and Technology, 2021, 4: 100158. |
| [14] | Elsheikh H, Eveloy V. Assessment of variable solar- and grid electricity-driven power-to-hydrogen integration with direct iron ore reduction for low-carbon steel making[J]. Fuel, 2022, 324: 124758. |
| [15] | 李峰, 储满生, 唐珏, 等. 中国氢冶金工艺现状、挑战及发展对策[J]. 前瞻科技, 2024, 3(4): 44-57. |
| Li F, Chu M S, Tang J, et al. Current status, challenges, and development strategies of hydrogen metallurgy technologies in China[J]. Science and Technology Foresight, 2024, 3(4): 44-57. | |
| [16] | Bhaskar A, Assadi M, Nikpey Somehsaraei H. Decarbonization of the iron and steel industry with direct reduction of iron ore with green hydrogen[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(3): 758. |
| [17] | Jacobasch E, Herz G, Rix C, et al. Economic evaluation of low-carbon steelmaking via coupling of electrolysis and direct reduction[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 328: 129502. |
| [18] | Vogl V, Max Å, Nilsson L J. Assessment of hydrogen direct reduction for fossil-free steelmaking[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 203: 736-745. |
| [19] | Home-System Advisor Model[Z]. [2025-01-07]. . |
| [20] | 生态环境部. 关于发布2022年电力二氧化碳排放因子的公告[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Announcement on the release of 2022 electricity carbon dioxide emission factors[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . | |
| [21] | 国家能源局. 国家能源局关于印发2023年度全国可再生能源电力发展监测评价结果的通知[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . |
| National Energy Administration. Notice of the national energy administration on issuing the monitoring and evaluation results of national renewable energy power development in 2023[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . | |
| [22] | Bhaskar A. HDRI-EAF-Technoeconomic-model[CP/OL]. Zenodo, 2020[2025-01-07]. . |
| [23] | Bade S O, Taiwo K, Ndulue U F, et al. A review of underground hydrogen storage systems: current status, modeling approaches, challenges, and future prospective[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 80: 449-474. |
| [24] | Daraei M, Campana P E, Thorin E. Power-to-hydrogen storage integrated with rooftop photovoltaic systems and combined heat and power plants[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 276: 115499. |
| [25] | Germeshuizen L M, Blom P W E. A techno-economic evaluation of the use of hydrogen in a steel production process, utilizing nuclear process heat[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(25): 10671-10682. |
| [26] | Pfeifer H, Kirschen M. Thermodynamic analysis of EAF energy efficiency and comparison with a statistical model of electric energy demand[R]. Venice: Associazione Italiana di Metallurgia, 2002. |
| [27] | 百川盈孚. 2023年中国铁矿石市场报告[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . |
| Bainfo. 2023 China iron ore market report[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . | |
| [28] | 乌鲁木齐市人民政府. 乌鲁木齐市城市供水价格标准及依据[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . |
| Urumqi Municipal People's Government. Price standards and basis for urban water supply in Urumqi city[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . | |
| [29] | Yang L Z, Hu H, Wang M X, et al. Comparative life cycle assessment and techno-economic analysis of electric arc furnace steelmaking processes integrated with solar energy system[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 425: 138868. |
| [30] | 中国光伏行业协会. 中国光伏产业发展路线图(2023—2024年)[EB/OL]. [2025-01-06]. . |
| China Photovoltaic Industry Association. Roadmap for the development of China's photovoltaic industry (2023—2024)[EB/OL]. [2025-01-06]. . | |
| [31] | Sheng K L, Wang X J, Si F Y, et al. Rational capacity investment for renewable hydrogen-based steelmaking systems: a multi-stage expansion planning strategy[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 372: 123746. |
| [32] | International Energy Agency. Global hydrogen review 2022[R]. Paris: OECD, 2022. |
| [33] | Tebibel H. Dual-objective optimization of solar driven alkaline electrolyzer system for on-site hydrogen production and storage: current and future scenarios[J]. Renewable Energy, 2024, 237: 121784. |
| [34] | Jindal A, Shrimali G, Tiwary N. At scale adoption of green hydrogen in Indian industry: costs, subsidies and policies[J]. Energy for Sustainable Development, 2024, 83, 101549. |
| [35] | Chen Y Z, Hill D, Billings B, et al. Hydrogen underground storage for grid electricity storage: an optimization study on techno-economic analysis[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 322: 119115. |
| [36] | Singer G, Köll R, Aichhorn L, et al. Utilizing hydrogen pressure energy by expansion machines — PEM fuel cells in mobile and other potential applications[J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 343: 121056. |
| [37] | Eveloy V, Kannan P, Romeo L M. Comparative energy, emissions and economic assessment of low-carbon iron and steel making processes using imported liquid organic hydrogen carrier options[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 89: 1321-1341. |
| [38] | 我的钢铁网. Mysteel年报:2023年国内钢铁市场回顾与2024年展望[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . |
| Mysteel. Mysteel annual report: review of domestic steel market in 2023 and outlook for 2024[EB/OL]. [2025-01-07]. . | |
| [39] | Bhaskar A, Assadi M, Somehsaraei H N. Can methane pyrolysis based hydrogen production lead to the decarbonisation of iron and steel industry?[J]. Energy Conversion and Management: X, 2021, 10: 100079. |
| [40] | Qi S Z, Cheng S H, Tan X J, et al. Predicting China's carbon price based on a multi-scale integrated model[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 324: 119784. |
| [1] | 范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [2] | 杨宁, 李皓男, LIN Xiao, GEORGIADOU Stella, LIN Wen-Feng. 从塑料废弃物到能源催化剂:塑料衍生碳@CoMoO4复合材料在电解水析氢反应中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [3] | 王御风, 罗小雪, 范鸿亮, 吴白婧, 李存璞, 魏子栋. 耦合电解水制氢的绿色有机电合成——电极界面调控策略综述[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3753-3771. |
| [4] | 陈佳祥, 周伟, 张学伟, 王丽杰, 黄玉明, 于洋, 孙苗婷, 李宛静, 袁骏舒, 张宏博, 孟晓晓, 高继慧, 赵广播. 脉冲电压下二维PEMWE模型的制氢特性仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3521-3530. |
| [5] | 吴天灏, 叶霆威, 林延, 黄振. 生物质化学链气化原位补氢制H2/CO可控合成气[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3498-3508. |
| [6] | 廖鹏伟, 刘庆辉, 潘安, 王嘉岳, 符小贵, 杨思宇, 余皓. 考虑不确定性的风电制氢系统:多时间尺度运行策略[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2743-2754. |
| [7] | 宋粉红, 王文光, 郭亮, 范晶. C元素修饰g-C3N4对TiO2的调控及复合材料光催化产氢性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2983-2994. |
| [8] | 赵鹏飞, 戚若玫, 郭新锋, 方虎, 徐庐飞, 李潇, 林今. 千标方级碱性水电解制氢系统氧中氢杂质分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1765-1778. |
| [9] | 陶智能, 邱彤, 王保国. 阴离子交换膜电解水制氢稳态建模[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1711-1721. |
| [10] | 李京润, 杨思宇, 刘庆辉, 潘安, 王嘉岳, 符小贵, 余皓. 大规模风电耦合火电制氢多情景下不同运行策略分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1191-1206. |
| [11] | 万俊, 宋佳芮, 范春煌, 魏乐乐, 聂依娜, 刘琳. 高效空穴转移助力光催化碱性甲醇-水溶液制氢[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1064-1075. |
| [12] | 钟晓航, 许卫, 张文, 许莉, 王宇新. 碱性水电解制氢中铁杂质的影响研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 519-531. |
| [13] | 白谨豪, 管小平, 杨宁. 压滤式水电解槽乳突板内的流动特性分析与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 584-595. |
| [14] | 张珂, 任维杰, 王梦娜, 范凯锋, 常丽萍, 李佳斌, 马涛, 田晋平. Bunsen反应产物在微通道中的液-液两相混合特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 623-636. |
| [15] | 殷梦凡, 王倩, 郑涛, 姬奎, 王绍贵, 郭辉, 林志强, 张睿, 孙晖, 刘海燕, 刘植昌, 徐春明, 孟祥海, 王月平. 可再生能源电解水制氢-低温低压合成氨万吨级工业示范流程设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 825-834. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号