• •
李雪1( ), 郑爽1, 李楠2, 张睿敏1, 肖永康1, 付嘉宝2
), 郑爽1, 李楠2, 张睿敏1, 肖永康1, 付嘉宝2
收稿日期:2025-10-19
修回日期:2025-11-27
出版日期:2026-01-07
通讯作者:
李雪
作者简介:李雪(1990—),女,博士,讲师,21040801@wit.edu.cn
基金资助:
Xue LI1( ), Shuang ZHENG1, Nan LI2, Ruimin ZHANG1, Yongkang XIAO1, Jiabao FU2
), Shuang ZHENG1, Nan LI2, Ruimin ZHANG1, Yongkang XIAO1, Jiabao FU2
Received:2025-10-19
Revised:2025-11-27
Online:2026-01-07
Contact:
Xue LI
摘要:
颗粒沉积广泛应用于湿法造粒、流化床包衣以及工业除尘中,明确颗粒撞击过程中的黏附机制是准确预测颗粒反弹行为的关键。然而,目前对潮湿环境下微米级颗粒和表面之间碰撞的动力学行为尚未完全明确。本研究通过实验与理论相结合的方法,系统研究了微米级SiO₂颗粒与不锈钢表面在潮湿条件下斜向撞击后的反弹行为;并构建了潮湿环境下微米级颗粒与平板碰撞的动力学模型,得到碰撞过程中颗粒动态变化过程。结果表明当入射角度从0度增加至80度时,法向恢复系数在0.35-0.5范围内波动,而切向恢复系数随入射角增加呈现先减小后增大的变化趋势。通过改进后的EA模型模拟了颗粒的撞击参数,发现随着入射速度增加以及入射角度减小,法向接触位移增大,接触时间缩短;切向位移随相对湿度(RH)的增加而减少,液桥力阻碍相对运动;随着相对湿度的增加,法向和切向接触力增大,碰撞速度减小;通过实验结果对比,发现其能准确预测颗粒的反弹行为,并且与实验结果吻合较好。
中图分类号:
李雪, 郑爽, 李楠, 张睿敏, 肖永康, 付嘉宝. 基于液桥力作用的微米级颗粒斜向撞击平板反弹特性研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251162.
Xue LI, Shuang ZHENG, Nan LI, Ruimin ZHANG, Yongkang XIAO, Jiabao FU. Rebound characteristics of micros-particle oblique impact with planar surfaces based on liquid bridge force[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251162.
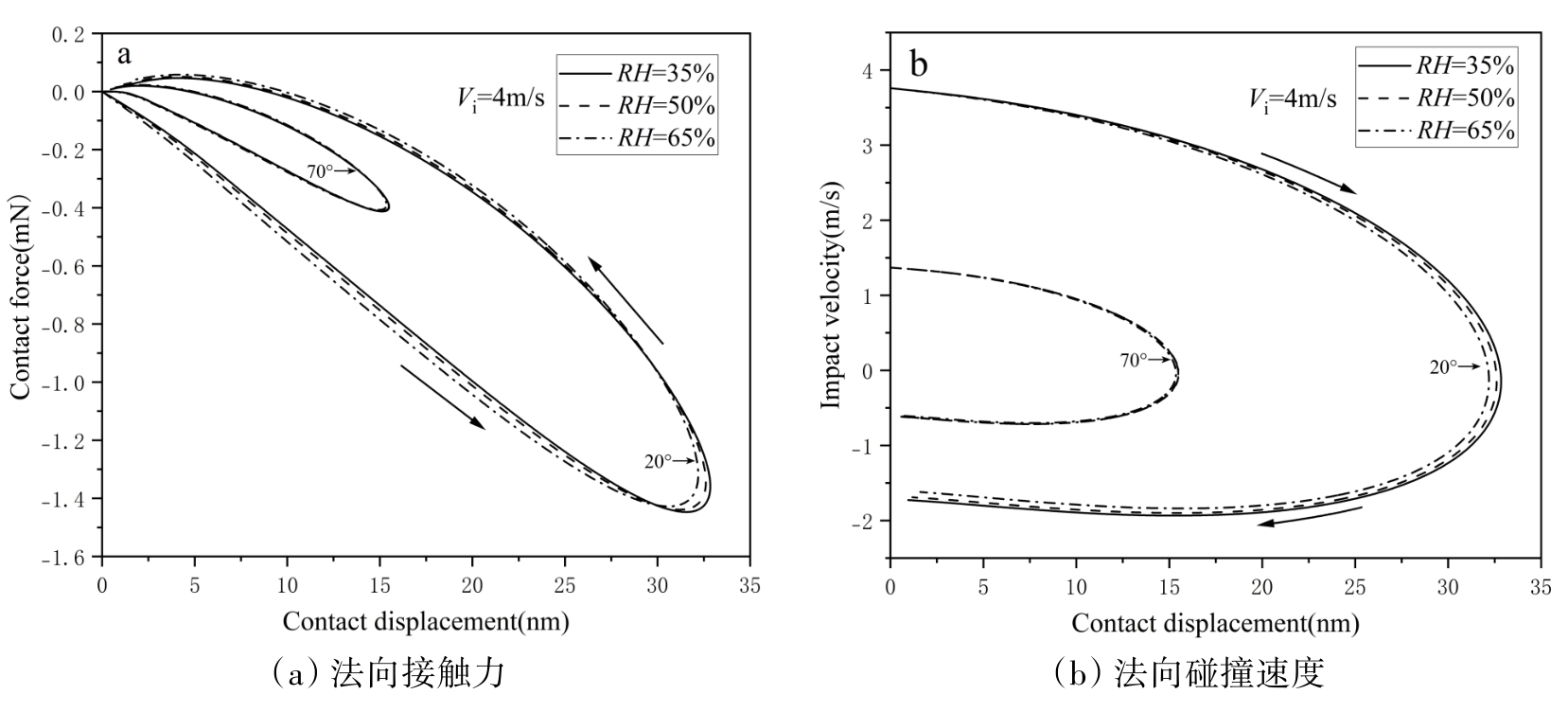
图7 不同法向入射速度下法向接触力和法向碰撞速度随法向接触位移变化
Fig. 7 Variation of normal contact force and normal impact velocity versus normal contact displacement at different normal incident velocities
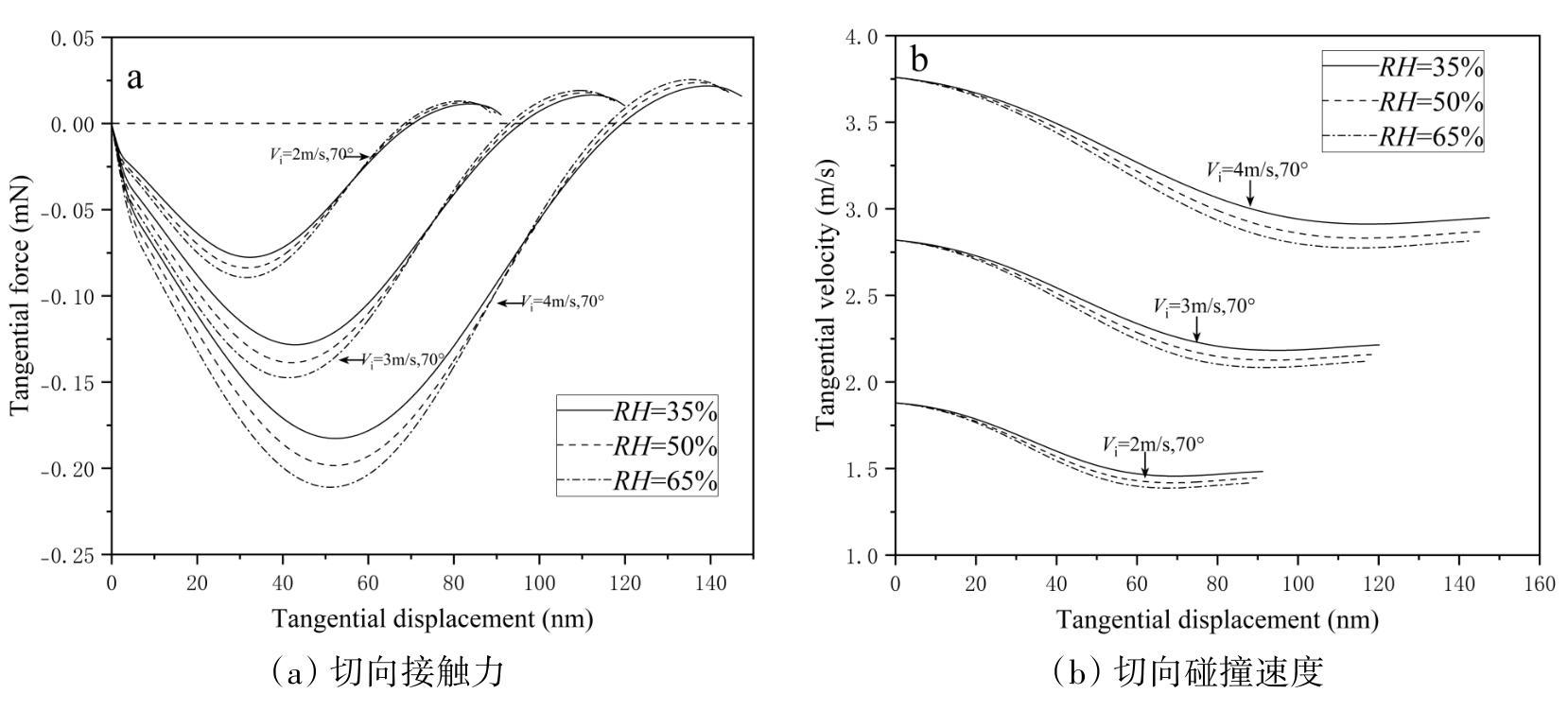
图9 不同切向入射速度下的切向接触力和切向碰撞速度随切向接触位移变化
Fig. 9 Variation of tangential contact force and tangential impact velocity versus tangential displacement at different tangential incident velocities
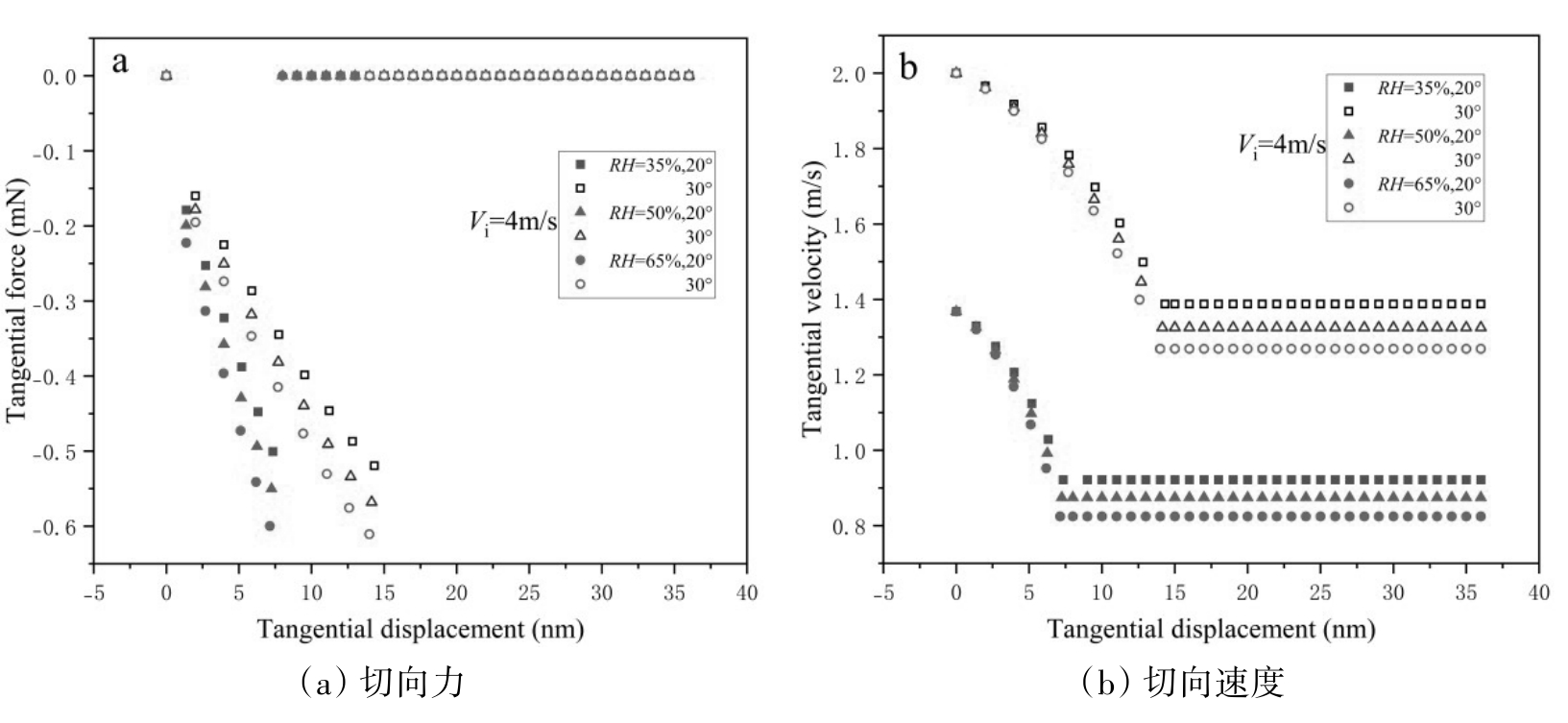
图11 不同速度下的颗粒切向力和切向速度随切向接触位移的变化
Fig. 11 Variation of particle tangential force and tangential velocity versus tangential displacement at different velocities
| [1] | 谢恒来, 吴曼, 赵军, 等. 导向管喷动流化床中废弃印刷线路板的非金属颗粒包覆改性[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(3): 1185-1193. |
| Xie H L, Wu M, Zhao J, et al. Coating modification of non-metal particles of waste printed circuit boards in spout-fluid bed with draft tube[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(3): 1185-1193. | |
| [2] | Wang C, Liu D Y, Ma J L, et al. Characterization of coating shells in a Wurster fluidized bed under different drying conditions and solution viscosities[J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 411: 117914. |
| [3] | 刘道银, 范志恒, 马吉亮, 等. 湿颗粒倾斜碰撞恢复系数的直接数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 4063-4073. |
| Liu D Y, Fan Z H, Ma J L, et al. Direct numerical simulation of restitution coefficient during oblique collision of wet particles[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(10): 4063-4073. | |
| [4] | Kuwabara G, Kono K. Restitution coefficient in a collision between two spheres[J]. Japanese journal of applied physics, 1987, 26(8R): 1230. |
| [5] | Li X, Dunn P F, Brach R M. Experimental and numerical studies of microsphere oblique impact with planar surfaces[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2000, 31(5): 583-594. |
| [6] | Kharaz A H, Gorham D A, Salman A D. An experimental study of the elastic rebound of spheres[J]. Powder Technology, 2001, 120(3): 281-291. |
| [7] | Zarate N V, Harrison A J, Litster J D, et al. Effect of relative humidity on onset of capillary forces for rough surfaces[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2013, 411: 265-272. |
| [8] | Xie J, Zhu Z R, Yang T H, et al. The effect of incident angle on the rebound behavior of micro-particle impacts[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2021, 155: 105778. |
| [9] | Hu S, Yin Q, Zhang Y, et al. Experimental study on the rebound characteristics of oblique collision of ash particles and the influence of ammonium bisulfate[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 2022, 56(11): 1058-1069. |
| [10] | Barnocky G, Davis R H. Elastohydrodynamic collision and rebound of spheres: Experimental verification[J]. The Physics of Fluids, 1988, 31(6): 1324-1329. |
| [11] | Davis R H, Rager D A, Good B T. Elastohydrodynamic rebound of spheres from coated surfaces[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2002, 468: 107-119. |
| [12] | Crüger B, Salikov V, Heinrich S, et al. Coefficient of restitution for particles impacting on wet surfaces: an improved experimental approach[J]. Particuology, 2016, 25: 1-9. |
| [13] | Gollwitzer F, Rehberg I, Kruelle C A, et al. Coefficient of restitution for wet particles[J]. Physical Review. E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2012, 86(1 Pt 1): 011303. |
| [14] | Müller T, Huang K. Influence of the liquid film thickness on the coefficient of restitution for wet particles[J]. Physical Review E, 2016, 93: 042904. |
| [15] | Lin Z, Chi S Z, Ye J H, et al. Effect of liquid layer on the motion of particle during oblique wet collision[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2021, 32(9): 3259-3267. |
| [16] | Li X, Dong M, Li S F, et al. Experimental and theoretical studies of the relationship between dry and humid normal restitution coefficients[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2019, 129: 16-27. |
| [17] | Ma J L, Liu D Y, Chen X P. Experimental study of oblique impact between dry spheres and liquid layers[J]. Physical Review. E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2013, 88(3): 033018. |
| [18] | Hertz H. Miscellaneous Papers[M]. Macmillan, 1896. |
| [19] | Johnson K L, Kendall K, Roberts A D. Surface energy and the contact of elastic solids[J]. Proceedings of the Ryal Sciety of London. A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1971, 324: 301-313. |
| [20] | Derjaguin B V, Muller V M, Toporov Y P. Effect of contact deformations on the adhesion of particles[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1975, 53(2): 314-326. |
| [21] | Brach R M, Dunn P F. Macrodynamics of microparticles[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 1995, 23(1): 51-71. |
| [22] | Cheng W, Brach R M, Dunn P F. Three-dimensional modeling of microsphere contact/impact with smooth flat surfaces[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 2002, 36(11): 1045-1060. |
| [23] | Liu G Q, Li S Q, Yao Q. A JKR-based dynamic model for the impact of micro-particle with a flat surface[J]. Powder Technology, 2011, 207(1/2/3): 215-223. |
| [24] | Xie J, Dong M, Li S F, et al. Dynamic characteristics for the normal impact process of micro-particles with a flat surface[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 2018, 52(2): 222-233. |
| [25] | Dong M, Han J, Li S F, et al. A dynamic model for the normal impact of fly ash particle with a planar surface[J]. Energies, 2013, 6(8): 4288-4307. |
| [26] | Dong M, Li X, Mei Y K, et al. Experimental and theoretical analyses on the effect of physical properties and humidity of fly ash impacting on a flat surface[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2018, 117: 85-99. |
| [27] | 李雪, 东明, 张璜, 等. 潮湿环境下微尺度颗粒撞击平板的动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 1940-1946. |
| Li X, Dong M, Zhang H, et al. Kinetic characteristics of micro-particle impact on a flat surface under humidity conditions[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(5): 1940-1946. | |
| [28] | Kim O V, Dunn P F. A microsphere-surface impact model for implementation in computational fluid dynamics[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2007, 38(5): 532-549. |
| [29] | 邵宏勋, 谢俊, 桂玉双, 等. 基于微米级颗粒临界沉积/剥离标准的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(12): 6141-6156. |
| Shao H X, Xie J, Gui Y S, et al. Research progress of critical deposition/stripping standards based on micron-sized particles[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(12): 6141-6156. | |
| [30] | Rabinovich Y, Adler J, Ata A, et al. Adhesion between nanoscale rough surfaces[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2000, 232(1): 17-24. |
| [31] | Goldman A J, Cox R G, Brenner H. Slow viscous motion of a sphere parallel to a plane wall: otion through a quiescent fluid[J]. Chemical Egineering Sience, 1967, 22(4): 637-651. |
| [32] | Kasper J H, Magnanimo V, de Jong S D M, et al. Effect of viscosity on the avalanche dynamics and flow transition of wet granular matter[J]. Particuology, 2021, 59: 64-75. |
| [33] | Maw N, Barber J R, Fawcett J N. The oblique impact of elastic spheres[J]. Wear, 1976, 38(1): 101-114. |
| [34] | Maw N, Barber J R, Fawcett J N. The role of elastic tangential compliance in oblique impact[J]. Journal of Lubrication Technology, 1981, 103(1): 74-80. |
| [35] | 谢俊. 微尺度颗粒撞击平板表面的动力学特性研究[D]. 大连:大连理工大学, 2017. |
| Xie J. Studies of dynamic characteristics for micro-particle impact on a flat surface[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2017. |
| [1] | 王泽, 胡琼, 陈雅静, 王衍, 耿佳旭, 沈斐然. 液体自冲击密封泄漏特性、密封机理与优化设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4194-4204. |
| [2] | 何晨, 陆明飞, 王令金, 许晓颖, 董鹏博, 赵文涛, 隆武强. 氨-甲醇高压混合气稀燃层流实验与模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4248-4258. |
| [3] | 卢煦旸, 徐强, 康浩鹏, 史健, 曹泽水, 郭烈锦. 化学链制氢系统中磁铁矿氧载体的CO还原特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3286-3294. |
| [4] | 陈曦, 王淑彦, 邵宝力, 丁诺, 谢磊. 基于颗粒动态恢复系数二阶矩模型的液固流化床数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3246-3258. |
| [5] | 王子恒, 李文怀, 周嵬. 图形电极在固体氧化物燃料电池中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3153-3171. |
| [6] | 李家顺, 李旺, 秦祖赠, 苏通明, 谢新玲, 纪红兵. 聚酰亚胺增强木质纤维素纳米纤丝气凝胶制备及其油水分离性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2169-2185. |
| [7] | 刘孟扬, 孙雪剑, 毛文元, 邓晰文, 雷基林. 考虑微观表面分层特征密封环接触特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1156-1169. |
| [8] | 党法璐, 孙志国, 高照, 王刚, 陈政宇, 张霖宙, 连竞存, 刘美佳, 张忠东, 刘超伟. 原油一步法催化裂解制低碳烯烃:实验和反应路径研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 667-685. |
| [9] | 魏攀攀, 刘怿楠, 朱春英, 付涛涛, 高习群, 马友光. 改进的T型微通道内双水相液滴的制备[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 576-583. |
| [10] | 彭子林, 周蕾, 邓庆航, 叶光华, 周兴贵. 包含偏硅酸影响的3D NAND磷酸湿法刻蚀动力学[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 645-653. |
| [11] | 张恒, 魁殿禄, 常虹, 詹志刚. 机械应力对气体扩散层界面传输特性影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 637-644. |
| [12] | 吴雨轩, 常诚, 顾雪萍, 冯连芳, 张才亮. 面向立体异构的丁二烯乳液聚合过程模型化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 879-887. |
| [13] | 邹立, 马砺, 张鹏宇, 魏高明, 郭睿智, 赵钦新. 煅烧电石渣强化生物质气化制氢特性及其反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 6040-6057. |
| [14] | 曹泷, 刘贺, 郭家驹, 张义, 刘文裴, 吴学红. 水平管内分段式多孔镀层R245fa沸腾换热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5806-5815. |
| [15] | 马君霞, 李林涛, 熊伟丽. 基于Tri-training GPR的半监督软测量建模方法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2613-2623. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号