• •
收稿日期:2025-11-25
修回日期:2025-12-26
出版日期:2026-01-13
通讯作者:
赵文廷
作者简介:王亚斌(1984—),男,博士,副 教 授,ybw@yau.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yabin WANG1( ), Liangzhu HUANG1, Wenting ZHAO2(
), Liangzhu HUANG1, Wenting ZHAO2( ), Xiuping DING3
), Xiuping DING3
Received:2025-11-25
Revised:2025-12-26
Online:2026-01-13
Contact:
Wenting ZHAO
摘要:
核壳型纳米反应器由内层核芯材料和另一种外壳材料复合而成。当树枝状介孔材料作为其中之一时,基于树枝状结构的核壳型纳米反应器应运而生,包括磁性核@树枝状壳、非磁性核@树枝状壳、树枝状核@介孔壳等多种类型。这些复合体兼备构成材料的物理化学特性,在重金属吸附、催化合成、分子检测、生物酶固定、药物递送等领域具有广泛的应用前景和优势。截至目前,还未出现介绍该类纳米材料的综述文章。因此,本文主要归纳分析树枝状核壳结构纳米反应器的分类,每种类型的结构特征、制备方法及应用领域,分析展望该学科今后的研究重点及发展前景。期望本综述能够给予材料和化学科学家一些参考,加速树枝状核壳结构纳米反应器的蓬勃发展。
中图分类号:
王亚斌, 黄亮珠, 赵文廷, 丁秀萍. 基于树枝状结构的核壳型纳米反应器研究进展[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251319.
Yabin WANG, Liangzhu HUANG, Wenting ZHAO, Xiuping DING. Research progress in core-shell nanoreactors on the basis of dendritic architectures[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251319.
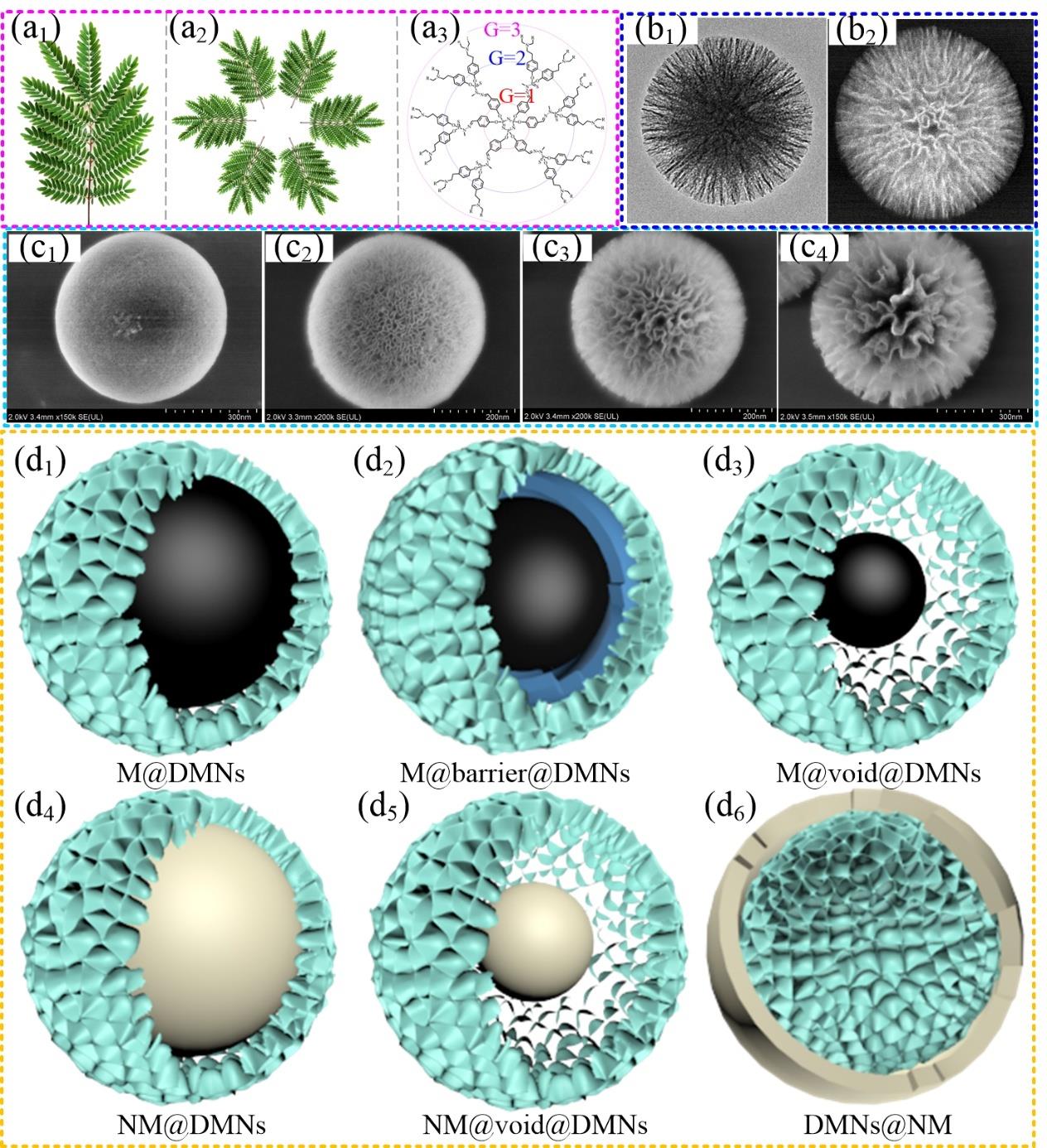
图1 (a) 自然界具有“树枝状”结构的树木分支实物图(a1);(a2) 树木分支实物的环状结构;(a3) 带有功能基团的树枝状大分子示意图;(b) 本文作者课题组制得DMSNs的透射电镜(b1)和次级电子(SE,b2)图像;(c) 本文作者课题组制得具有小孔(c1);中孔(c2);大孔(c3)和极大孔(c4)的DMSNs;(d)树枝状磁性单一材料核壳型M@DMNs(d1);磁性多样材料核壳型M@barrier@DMNs(d2);磁性蛋黄-蛋壳型M@void@DMNs(d3);非磁性核壳型NM@DMNs(d4);非磁性蛋黄-蛋壳型NM@void@DMNs(d5)和非磁性核壳型DMNs@NM(d6)纳米粒子结构模型
Fig.1 (a) A photograph of a tree branch in nature with “dendritic” architecture (a1); the loop of the above tree branches (a2); and a branched organic macromolecule with functional groups (a3); (b) TEM (b1) and secondary electron (SE, b2) images of a single DMSNs synthesized by our team; (c) DMSNs with small (c1); medium (c2); large (c3); and extra-large (c4) pores in our laboratory; (d) Structural models of simple dendritic magnetic core-shell M@DMNs (d1); composite dendritic magnetic core-shell M@barrier@DMNs (d2); dendritic magnetic yolk-shell M@void@DMNs (d3); as well as dendritic non-magnetic core-shell NM@DMNs (d4); non-magnetic yolk-shell NM@void@DMNs (c5); and non-magnetic core-shell DMNs@NM (d6)
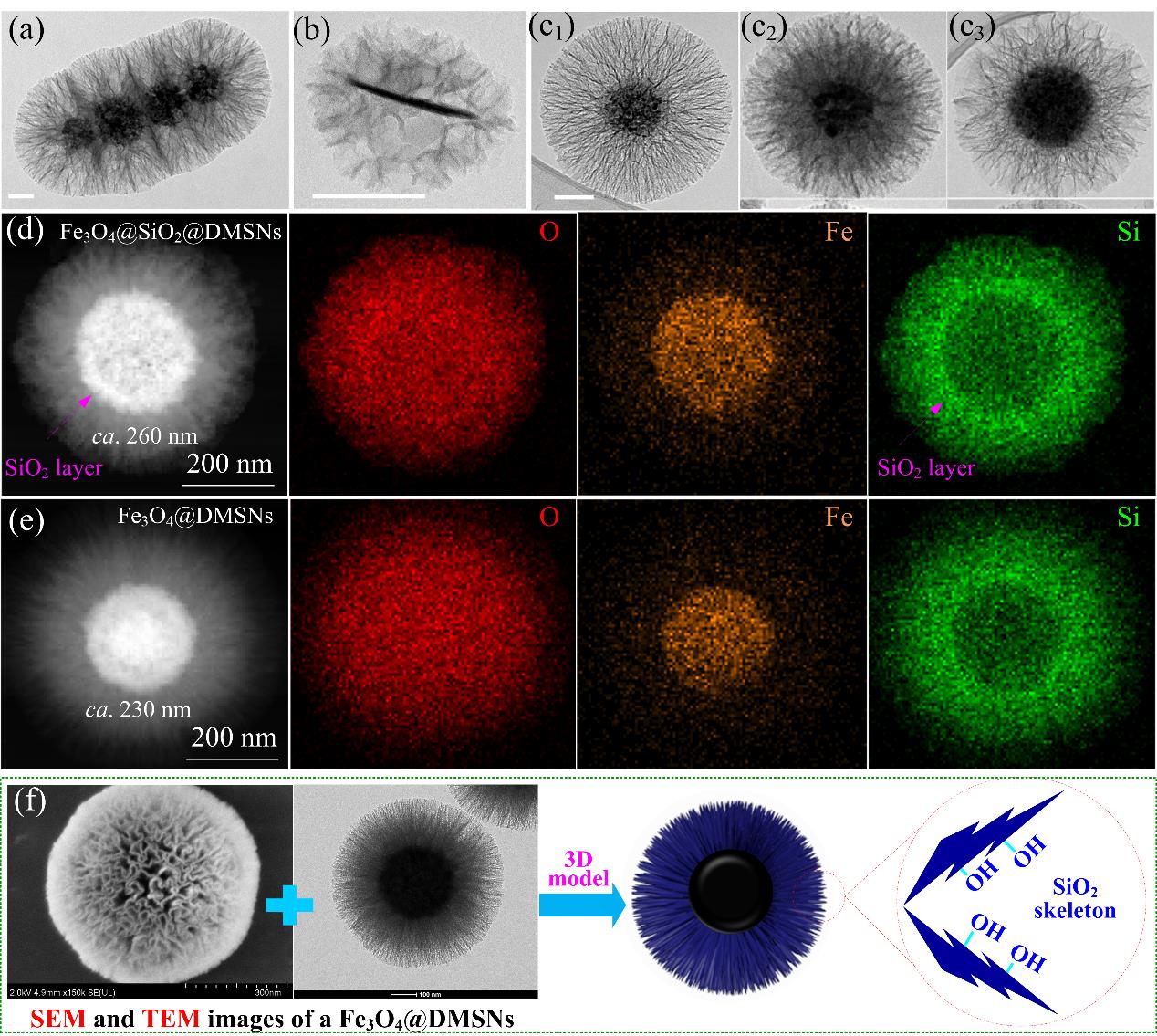
图2 (a-c) 链状(a);盘状(b);球状小孔(c1);球状中孔(c2)和球状大孔(c3)树枝状磁性核壳型纳米反应器的透射电镜图[22];(d) 本文作者课题组制得Fe3O4@SiO2@DMSNs的透射电镜-元素分布图;(e) 本文作者课题组制得Fe3O4@DMSNs的透射电镜-元素分布图;(f) 由作者课题组制得Fe3O4@DMSNs的扫描和透射电镜图像衍生的三维模型示意图
Fig.2 (a) TEM images of magnetic core-shell DMSNs with chainlike (a); disclike (b); and spherical (c) cores; but in forms of small (c1); medium (c2); and large (c3) pores[22]; (d) TEM mapping images of a Fe3O4@SiO2@DMSNs in our laboratory; (e) TEM mapping images of a Fe3O4@DMSNs in our laboratory; (f) A three-dimensional model of a Fe3O4@DMSNs extracted by its SEM and TEM images
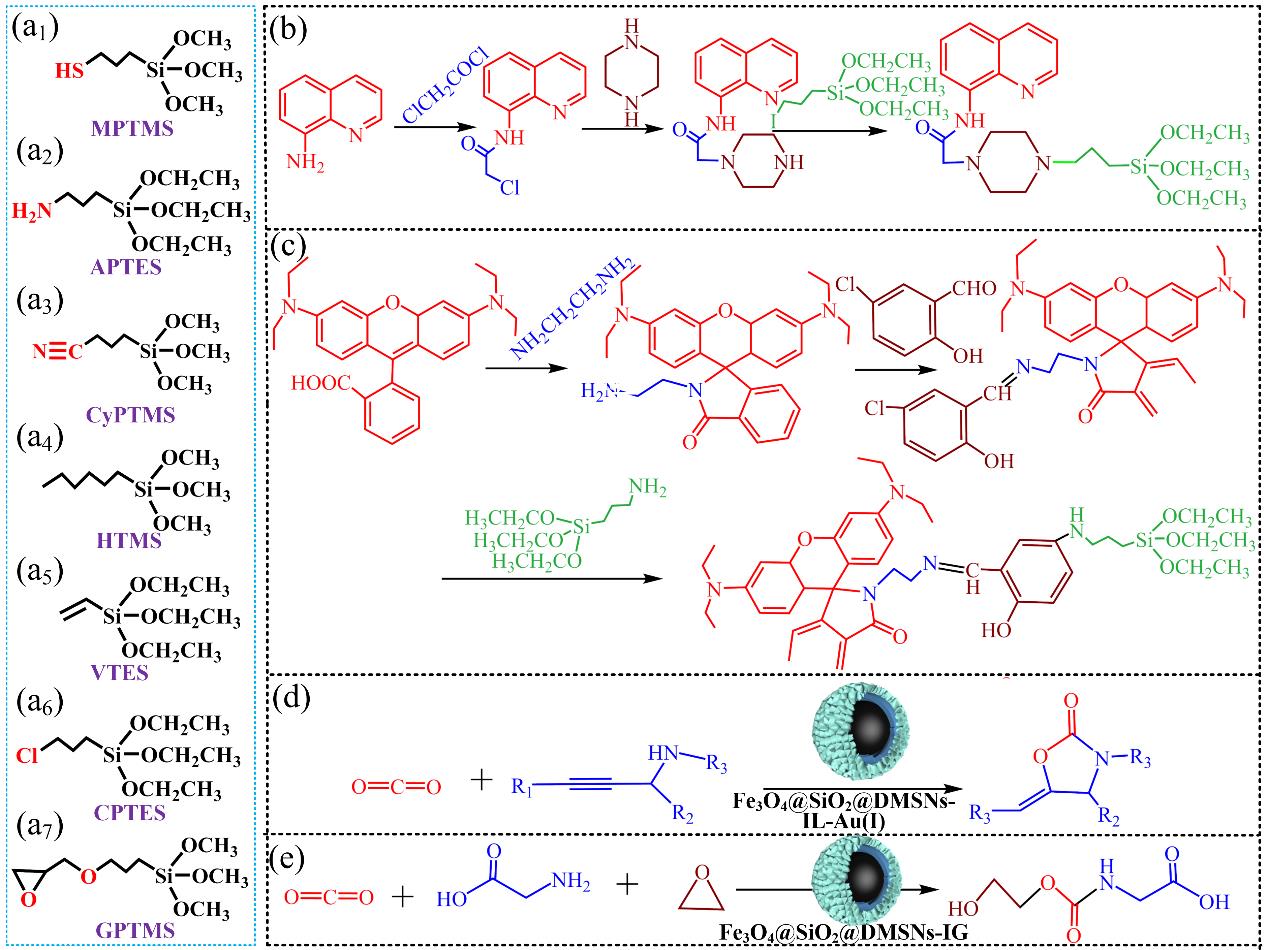
图3 (a) 功能化树枝状磁性核壳型纳米反应器的常用硅烷偶联剂;包括3-巯基丙基三甲氧基硅烷MPTMS(a1);3-氨基丙基三乙氧基硅烷APTES(a2);3-氰基丙基三甲氧基硅烷CyPTMS(a3);正己基三甲氧基硅烷HTMS(a4);乙烯基三乙氧基硅烷VTES(a5);3-氯丙基三乙氧基硅烷CPTES(a6)和3-缩水甘油丙氧基三甲氧基硅烷GPTMS(a7);(b) 含8-氨基喹啉官能团的新型硅烷分子合成路线;(c) 含罗丹明B官能团的新型硅烷分子合成路线;(d) 纳米反应器Fe3O4@SiO2@DMSNs-IL-Au(I)催化系列炔丙胺化合物和二氧化碳生成2-唑烷酮类物质;(e) 纳米反应器Fe3O4@SiO2@DMSNs-IG催化CO2;α-氨基酸和环氧乙烷生成N-[(2-羟乙氧基)羰基]甘氨酸
Fig.3 (a) Normal silane coupling agents for functionalization of dendritic magnetic core-shell nanoreactors; including 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane (a1); 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (a2); 3-cyanopropyltrimethoxysilane (a3); hexyltrimethoxysilane (a4); vinyltriethoxysilane (a5); 3-chloropropyltriethoxysilane (a6); and 3-glycidoxypropyltriethoxysilane (a7); (b) The synthesis route of a novel silane molecule containing 8-aminoquinoline functional group; (c) The synthesis route of a novel silane molecule containing rhodamine B functional group; (d) Synthesis of 2-oxazolidinone with propargylic amines and CO2 catalyzed by Fe3O4@SiO2@DMSNs-IL-Au(I) nanoreactor; (e) Synthesis of N-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)carbonyl]glycine with CO2; α-amino acid, and ethylene oxide catalyzed by Fe3O4@SiO2@DMSNs-IG nanoreactor
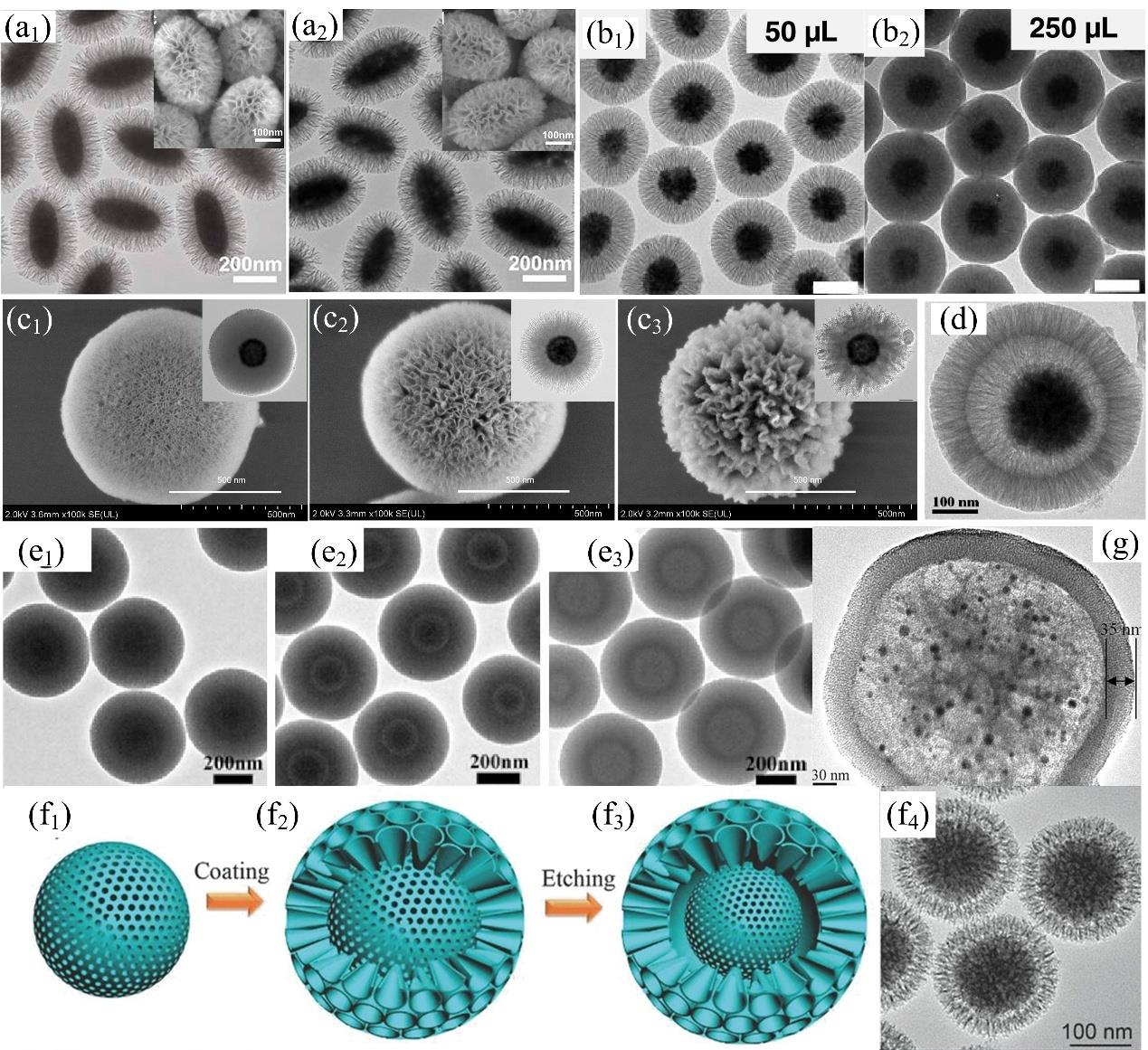
图4 (a) 椭圆形树枝状核壳结构的透射和扫描电镜图;包括Fe2O3@DMSNs(a1)和Fe3O4@DMSNs(a2)[65];(b) 通过调节TEOS添加量制得不同粒径和孔密度SPION@DMSNs的透射电镜图[66];(c) 本文作者课题组制得具有10、25和60 nm孔径Fe3O4@DMSNs-OTES的透射和扫描电镜图;(d) 蛋黄-蛋壳结构Fe3O4@SiO2@void@DMSNs的透射电镜图[17];(e) 一锅自模板界面扩散法制得核壳、蛋黄-蛋壳和空心结构DMSNs的透射电镜图[71];(f) 蛋黄-蛋壳型MONs@void@DMONs的合成示意图及其透射电镜图[73];(g) DMSNs为中心核制备得 (DMSNs-APTES-Au)@void@MSNs的透射电镜图[74]
Fig.4 (a) TEM and inserted SEM images of elliptical magnetic core-shell architectures; being Fe2O3@DMSNs (a1) and Fe3O4@DMSNs (a2) [65]; (b) TEM images of SPION@DMSNs with various diameters and pore densities adjusted by TEOS dosage[66]; (c) TEM and inserted SEM images of superhydrophobic Fe3O4@DMSNs-OTES with 10, 25, and 60 nm pores prepared in our laboratory; (d) TEM image of yolk-shell Fe3O4@SiO2@void@DMSNs[17]; (e) TEM images of core-shell, yolk-shell, and hollow DMSNs prepared by a one-pot self-templated interfacial diffusion method[71]; (f) Schematic illustration of the synthesis process of MONs@void@DMONs and its TEM image[73]; (g) TEM image of a (DMSNs-APTES-Au)@void@MSNs nanoreactor[74]
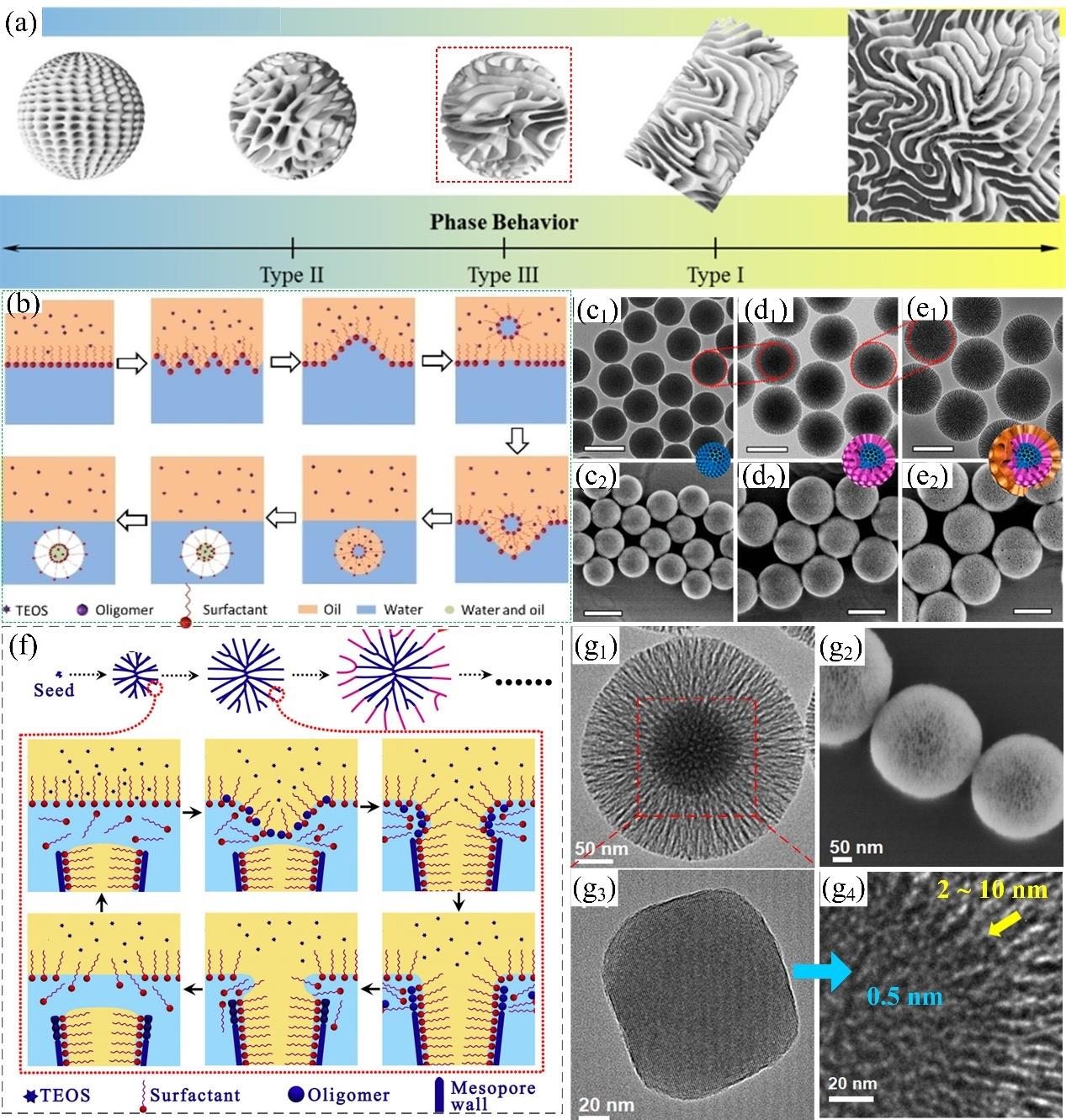
图5 (a) 具有不同相行为和微结构的水-表面活性剂-油三相系统[76];(b) 扰动界面形成SiO2@DMSNs机制示意图[77];(c)DMSNs;(d)DMSNs@DMSNs和(e)DMSNs@DMSNs@DMSNs;纳米颗粒的透射(c1-e1);扫描(c2-e2)电镜图及三维模型图[79];(f) 双相分层法合成DMSNs的界面增长机制[79];(g) ZeoA@DMSNs 的透射(g1)和扫描(g2)电镜图。ZeoA (g3) 以及ZeoA核-DMSNs 壳交汇界面(g4) 的透射电镜图[98]
Fig.5 (a) Water-surfactant-oil ternary systems with various phase behaviors and substructures[76]; (b) Schematic illustration of formation mechanism of SiO2@DMSNs from the disturbed interface[77]; (c-d) TEM (c1-e1); SEM (c2-e2); and inserted 3D model images of DMSNs (c); DMSNs@DMSNs (d); and DMSNs@DMSNs@DMSNs (e)[79]; (f) Synthesis mechanism of DMSNs by interfacial growth from biphase stratification approach[79]; (g) TEM (g1) and SEM (g2) images of ZeoA@DMSNs; TEM images of ZeoA (g3) and the boundary between ZeoA core and DMSNs shell (g4) [98]
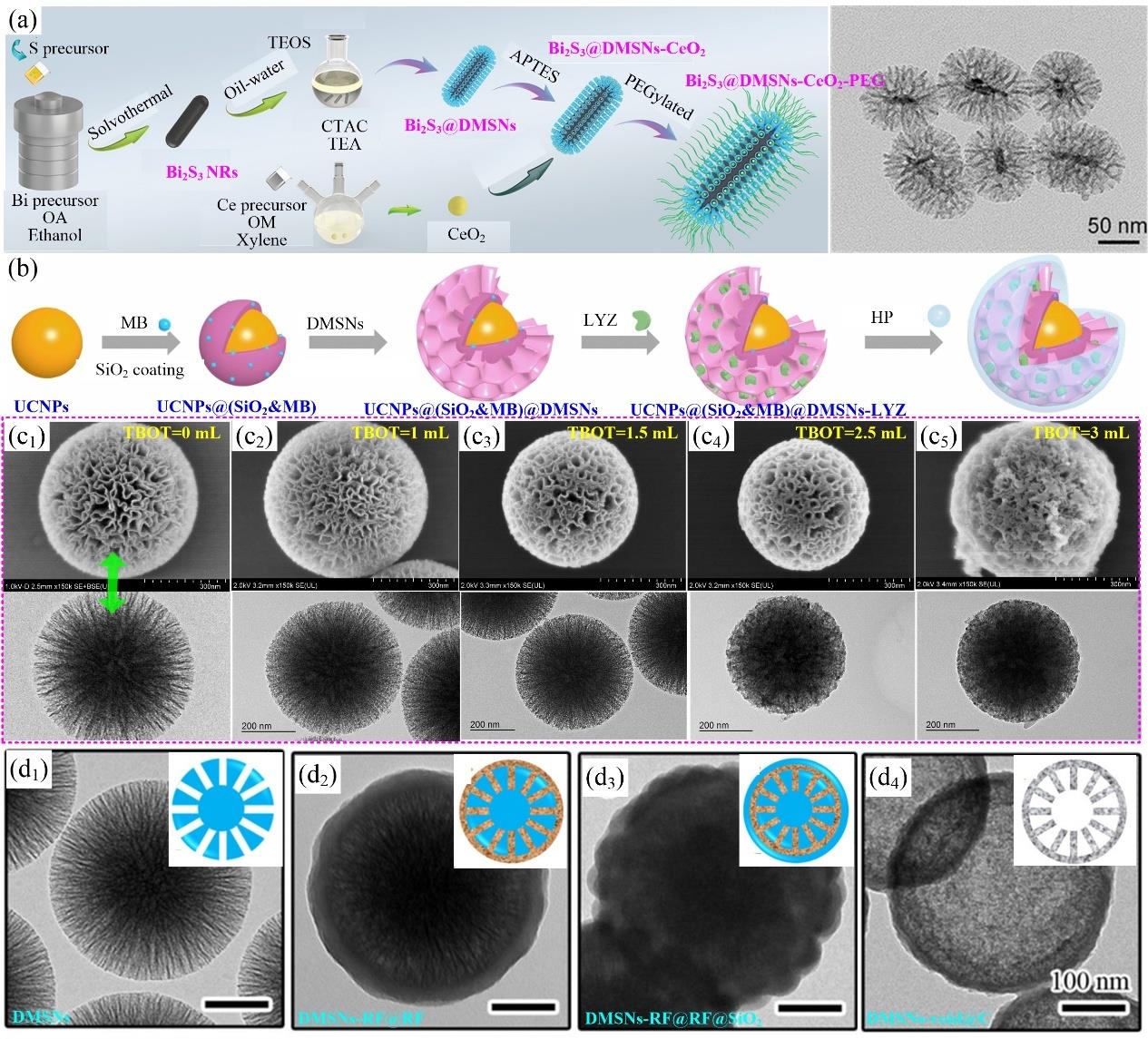
图6 (a) 椭球状Bi2S3@DMSNs-CeO2-PEG合成路线及TEM图[117];(b) 纳米反应器UCNPs@(SiO2&MB)@DMSNs-LYZ@HP的合成过程示意图[125];(c) 本文作者课题组改变TBOT添加量制得系列DMSNs-TiO2复合物的TEM和SEM图;(d) 合成DMSNs-void@C 过程涉及纳米粒子的TEM和示意图;包括DMSNs (d1); DMSNs-RF@RF (d2);DMSNs-RF@RF@SiO2 (d3)和DMSNs-void@C (d4) [130]
Fig.6 (a) Schematic illustration of synthetic procedure for ellipsoidal Bi2S3@DMSNs-CeO2-PEG[117]; (b) Schematic illustration of synthetic route for UCNPs@(SiO2&MB)@DMSNs-LYZ@HP[125]; (c) TEM and SEM images of various DMSNs-TiO2 composites in our laboratory by adjusting TBOT dosage from 0 to 3 mL; (d) TEM and inserted illustration images of involved nanoparticles towards DMSNs-void@C; including DMSNs (d1); DMSNs-RF@RF (d2); DMSNs-RF@RF@SiO2 (d3) and DMSNs-void@C (d4) [130]
| [1] | Kalambate P K, Dhanjai, Huang Z M, et al. Core@shell nanomaterials based sensing devices: a review[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 115: 147-161.[LinkOut] |
| [2] | Gawande M B, Goswami A, Asefa T, et al. Core–shell nanoparticles: synthesis and applications in catalysis and electrocatalysis[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(21): 7540-7590. |
| Gawande M B, Goswami A, Asefa T, et al. Core-shell nanoparticles: synthesis and applications in catalysis and electrocatalysis[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(21): 7540-7590.[LinkOut] | |
| [3] | Ghosh Chaudhuri R, Paria S, Core/Shell Nanoparticles: Classes, Properties, Synthesis Mechanisms, Characterization, and Applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2012, 112(4): 2373-2433. |
| Ghosh Chaudhuri R, Paria S. Core/shell nanoparticles: classes, properties, synthesis mechanisms, characterization, and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2012, 112(4): 2373-2433.[LinkOut] | |
| [4] | Zou Y, Sun Z, Wang Q, et al. Core–Shell Magnetic Particles: Tailored Synthesis and Applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2025, 125(2): 972-1048. |
| Zou Y D, Sun Z K, Wang Q Y, et al. Core-shell magnetic particles: tailored synthesis and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2025, 125(2): 972-1048.[LinkOut] | |
| [5] | Yue Q, Sun J, Kang Y, et al. Advances in the interfacial assembly of mesoporous silica on magnetic particles. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(36): 15804–15817. Yue Q, Sun J G, Kang Y J,et al. Advances in the interfacial assembly of mesoporous silica on magnetite particles[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(37): 15804-15817.[LinkOut] |
| [6] | Shafiee A, Rabiee N, Ahmadi S, et al. Core–Shell Nanophotocatalysts: Review of Materials and Applications. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2022, 5(1): 55–86. Shafiee A, Rabiee N, Ahmadi S,et al. Core-shell nanophotocatalysts: review of materials and applications[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2022, 5(1): 55-86.[LinkOut] |
| [7] | Newkome G R, Moorefield C N, Vögtle F. Dendrimers and Dendrons: Concepts, Syntheses, Applications[M]. In Dendrimers and Dendrons, Wiley‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2001: pp 1-118. |
| Newkome G R, Moorefield C N, Vögtle F. Dendrimers and Dendrons: Concepts, Syntheses, Applications[M]. Wiley, 2001.[LinkOut] | |
| [8] | Fréchet J M J, Tomalia D A. Dendrimers and Other Dendritic Polymers[M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2002: 3-40. |
| Fréchet J M J, Tomalia D A. Dendrimers and Other Dendritic Polymers[M]. Wiley, 2001.[LinkOut] | |
| [9] | Polshettiwar V, Cha D, Zhang X, et al. High‐surface‐area silica nanospheres (KCC-1) with a fibrous morphology[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(50): 9652-9656. |
| Polshettiwar V, Cha D, Zhang X X, et al. High-surface-area silica nanospheres (KCC-1) with a fibrous morphology[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(50): 9652-9656.[LinkOut] | |
| [10] | Xu C, Lei C, Wang Y, et al. Dendritic mesoporous nanoparticles: Structure, synthesis and properties[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61: e202112752. |
| Xu C, Lei C, Wang Y, et al. Dendritic mesoporous nanoparticles: structure, synthesis and properties[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(12): e202112752.[LinkOut] | |
| [11] | Wang Y, Du X, Liu Z, et al. Dendritic fibrous nano-particles (DFNPs): Rising stars of mesoporous materials[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(10): 5111-5152. |
| Wang Y B, Du X, Liu Z, et al. Dendritic fibrous nano-particles (DFNPs): rising stars of mesoporous materials[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(10): 5111-5152.[LinkOut] | |
| [12] | Wang Y, Zhang B, Ding X, et al. Dendritic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles (DMONs): Chemical composition, structural architecture, and promising applications[J]. Nano Today, 2021, 39: 101231. |
| Wang Y B, Zhang B L, Ding X P, et al. Dendritic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles (DMONs): chemical composition, structural architecture, and promising applications[J]. Nano Today, 2021, 39: 101231.[LinkOut] | |
| [13] | Wang Y, Huang L, Li S, et al. The capture and catalytic conversion of CO2 by dendritic mesoporous silica-based nanoparticles[J]. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2024, 7(2): e12593. |
| Wang Y B, Huang L Z, Li S W, et al. The capture and catalytic conversion of CO2 by dendritic mesoporous silica-based nanoparticles[J]. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2024, 7(2): e12593.[LinkOut] | |
| [14] | Maity A, Belgamwar R, Polshettiwar V. Facile synthesis to tune size, textural properties and fiber density of dendritic fibrous nanosilica for applications in catalysis and CO2 capture[J]. Nature protocols, 2019, 14: 2177–2204. |
| Maity A, Belgamwar R, Polshettiwar V. Facile synthesis to tune size, textural properties and fiber density of dendritic fibrous nanosilica for applications in catalysis and CO2 capture[J]. Nature Protocols, 2019, 14(7): 2177-2204.[LinkOut] | |
| [15] | Wang Z, Brown A T, Tan K, et al. Selective Extraction of Thorium from Rare Earth Elements Using Wrinkled Mesoporous Carbon[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140: 14735-14739. |
| Wang Z J, Brown A T, Tan K, et al. Selective extraction of thorium from rare earth elements using wrinkled mesoporous carbon[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(44): 14735-14739.[LinkOut] | |
| [16] | Shao D, Li M, Wang Z, et al. Bioinspired Diselenide-Bridged Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual-Responsive Protein Delivery[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(29): 1801198. |
| Shao D, Li M Q, Wang Z, et al. Bioinspired diselenide-bridged mesoporous silica nanoparticles for dual-responsive protein delivery[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(29): 1801198.[LinkOut] | |
| [17] | Yue Q, Li J, Luo W, et al. An Interface coassembly in biliquid phase: toward core-shell magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres with tunable pore size[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(41): 13282-13289. |
| Yue Q, Li J L, Luo W, et al. An interface coassembly in biliquid phase: toward core-shell magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres with tunable pore size[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(41): 13282-13289.[LinkOut] | |
| [18] | Abbaraju P L, Meka A K, Song H, et al. Asymmetric silica nanoparticles with tunable head–tail structures enhance hemocompatibility and maturation of immune cells[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(18): 6321-6328. |
| Abbaraju P L, Meka A K, Song H, et al. Asymmetric silica nanoparticles with tunable head-tail structures enhance hemocompatibility and maturation of immune cells[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(18): 6321-6328.[LinkOut] | |
| [19] | Xing Y, Pan Q, Du X, et al. Dendritic Janus Nanomotors with Precisely Modulated Coverages and Their Effects on Propulsion[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(10): 10426-10433. |
| Xing Y, Pan Q, Du X, et al. Dendritic Janus nanomotors with precisely modulated coverages and their effects on propulsion[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(10): 10426-10433.[LinkOut] | |
| [20] | Bayal N, Singh B, Singh R, et al. Size and Fiber Density Controlled Synthesis of Fibrous Nanosilica Spheres (KCC-1) [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 24888. |
| Bayal N, Singh B, Singh R, et al. Size and fiber density controlled synthesis of fibrous nanosilica spheres (KCC-1)[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 24888.[LinkOut] | |
| [21] | Yu K, Zhang X, Tong H, et al. Synthesis of fibrous monodisperse core–shell Fe3O4/SiO2/KCC-1[J]. Materials Letters, 2013, 106(9): 151-154. |
| Yu K J, Zhang X B, Tong H W, et al. Synthesis of fibrous monodisperse core-shell Fe3O4/SiO2/KCC-1[J]. Materials Letters, 2013, 106: 151-154.[LinkOut] | |
| [22] | Nemec S, Kralj S. A versatile interfacial coassembly method for fabrication of tunable silica shells with radially aligned dual mesopores on diverse magnetic core nanoparticles[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(1): 1883-1894. |
| Nemec S, Kralj S. A versatile interfacial coassembly method for fabrication of tunable silica shells with radially aligned dual mesopores on diverse magnetic core nanoparticles[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(1): 1883-1894.[LinkOut] | |
| [23] | Emrani S, Ebrahimi M, Zhiani R, et al. Magnetic fibrous silica mesoporous as a selective and efficient system for removal of Cd(II) ions with a focus on optimization by response surface methodology[J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 103(4): 849–867. |
| Emrani S, Ebrahimi M, Zhiani R, et al. Magnetic fibrous silica mesoporous as a selective and efficient system for removal of Cd(II) ions with a focus on optimization by response surface methodology[J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 103(4): 849-867.[LinkOut] | |
| [24] | Salari Goharrizi F, Ebrahimipour S Y, Ebrahimnejad H, et al. Novel magnetic adsorbents based on mesoporous KCC-1 for the removal of heavy metal ions and antibacterial applications[J]. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 2024, 34(11): 5425-5441. |
| Salari Goharrizi F, Ebrahimipour S Y, Ebrahimnejad H, et al. Novel magnetic adsorbents based on mesoporous KCC-1 for the removal of heavy metal ions and antibacterial applications[J]. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 2024, 34(11): 5425-5441.[LinkOut] | |
| [25] | Goharrizi F S, Ebrahimipour S Y, Ebrahimnejad H, et al. Magnetic mesoporous silica functionalized with amine groups for efficient removal of heavy metals and bacterial inhibition[J]. Journal of Cluster Science, 2024, 35(7): 2419-2435. |
| Goharrizi F S, Ebrahimipour S Y, Ebrahimnejad H, et al. Magnetic mesoporous silica functionalized with amine groups for efficient removal of heavy metals and bacterial inhibition[J]. Journal of Cluster Science, 2024, 35(7): 2419-2435.[LinkOut] | |
| [26] | Wang F, Li T, Liao Y, et al. The synthesis of core-shell magnetic dendritic fibrous nano-silica for the fast and selective capture of U(VI) [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 638: 157969. |
| Wang F, Li T T, Liao Y, et al. The synthesis of core-shell magnetic dendritic fibrous nano-silica for the fast and selective capture of U(VI)[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 638: 157969.[LinkOut] | |
| [27] | Wang F, Chen Z, Wu Y, et al. The amidoxime-functionalized magnetic dendritic fibrous nano-silica with a core–shell structure for the efficient capture of U(VI) [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2025, 680: 161491. |
| Wang F, Chen Z, Wu Y, et al. The amidoxime-functionalized magnetic dendritic fibrous nano-silica with a core-shell structure for the efficient capture of U(VI)[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2025, 680: 161491.[LinkOut] | |
| [28] | Lyu J, Zhang F, Li R, et al. Magnetic core supported ethyl acetate microdrops for organic contaminants removal from water[J]. npj Clean Water, 2024, 7(1): 96. |
| Lyu J, Zhang F M, Li R, et al. Magnetic core supported ethyl acetate microdrops for organic contaminants removal from water[J]. npj Clean Water, 2024, 7: 96.[LinkOut] | |
| [29] | Zhang W, Li S, Zhang J, et al. Synthesis and adsorption behavior study of magnetic fibrous mesoporous silica[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019, 282: 15-21. |
| Zhang W, Li S M, Zhang J, et al. Synthesis and adsorption behavior study of magnetic fibrous mesoporous silica[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019, 282: 15-21.[LinkOut] | |
| [30] | Yang J, Shen D, Wei Y, et al. Monodisperse core-shell structured magnetic mesoporous aluminosilicate nanospheres with large dendritic mesochannels[J]. Nano Research, 2015, 8(8): 2503-2514. |
| Yang J P, Shen D K, Wei Y, et al. Monodisperse core-shell structured magnetic mesoporous aluminosilicate nanospheres with large dendritic mesochannels[J]. Nano Research, 2015, 8(8): 2503-2514.[LinkOut] | |
| [31] | Gao J, Kong W, Zhou L, et al. Monodisperse core-shell magnetic organosilica nanoflowers with radial wrinkle for lipase immobilization[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 309: 70-79. |
| Gao J, Kong W X, Zhou L Y, et al. Monodisperse core-shell magnetic organosilica nanoflowers with radial wrinkle for lipase immobilization[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 309: 70-79.[LinkOut] | |
| [32] | Goharrizi F S, Ebrahimipour S Y, Mahani M T, et al. Enhanced stability and activity of diaphorase enzyme immobilized on magnetic mesoporous silica[J]. Journal of Porous Materials, 2025, 32(4): 1607-1625. |
| Goharrizi F S, Ebrahimipour S Y, Mahani M T, et al. Enhanced stability and activity of diaphorase enzyme immobilized on magnetic mesoporous silica[J]. Journal of Porous Materials, 2025, 32(4): 1607-1625.[LinkOut] | |
| [33] | Ali Z, Tian L, Zhang B, et al. Synthesis of paramagnetic dendritic silica nanomaterials with fibrous pore structure (Fe3O4@KCC-1) and their application in immobilization of lipase from Candida rugosa with enhanced catalytic activity and stability[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2017, 41(16): 8222-8231. |
| Ali Z, Tian L, Zhang B L, et al. Synthesis of paramagnetic dendritic silica nanomaterials with fibrous pore structure (Fe3O4@KCC-1) and their application in immobilization of lipase from Candida rugosa with enhanced catalytic activity and stability[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2017, 41(16): 8222-8231.[LinkOut] | |
| [34] | Liu D, Wang X, Jiang Y. Design of enzyme nanoreactor by phase-transitioned lysozyme modified magnetic dendritic silica nanoparticle for efficient catalytic performance at harsh reaction condition[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2023, 292: 116442. |
| Liu D Q, Wang X, Jiang Y C. Design of enzyme nanoreactor by phase-transitioned lysozyme modified magnetic dendritic silica nanoparticle for efficient catalytic performance at harsh reaction condition[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2023, 292: 116442.[LinkOut] | |
| [35] | Asghari E, Saraji M. Preparation of a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer on fibrous silica nanosphere via self-polycondensation for micro solid-phase extraction of chlorpyrifos[J]. Journal of Chromatography B, 2024, 1232: 123961. |
| Asghari E, Saraji M. Preparation of a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer on fibrous silica nanosphere via self-polycondensation for micro solid-phase extraction of chlorpyrifos[J]. Journal of Chromatography B, 2024, 1232: 123961.[LinkOut] | |
| [36] | Sun Z, Li H, Guo D, et al. A multifunctional magnetic core-shell fibrous silica sensing probe for highly sensitive detection and removal of Zn2+ from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2015, 3(18): 4713-4722. |
| Sun Z B, Li H Z, Guo D, et al. A multifunctional magnetic core-shell fibrous silica sensing probe for highly sensitive detection and removal of Zn2+ from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2015, 3(18): 4713-4722.[LinkOut] | |
| [37] | Radhakrishnan K, Panneerselvam P, Ravikumar A. A hybrid magnetic core-shell fibrous silica nanocomposite for a chemosensor-based highly effective fluorescent detection of Cu(II)[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(72): 45824-45833. |
| Radhakrishnan K, Panneerselvam P, Ravikumar A. A hybrid magnetic core-shell fibrous silica nanocomposite for a chemosensor-based highly effective fluorescent detection of Cu(II)[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(72): 45824-45833.[LinkOut] | |
| [38] | Radhakrishnan K, Panneerselvam P, Ravikumar A, et al. Magnetic core-shell fibrous silica functionalized with pyrene derivative for highly sensitive and selective detection of Hg (II) ion[J]. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 2019, 40(9): 1368-1377. |
| Radhakrishnan K, Panneerselvam P, Ravikumar A, et al. Magnetic core-shell fibrous silica functionalized with pyrene derivative for highly sensitive and selective detection of Hg (II) ion[J]. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 2019, 40(9): 1368-1377.[LinkOut] | |
| [39] | Zhao X, Dong J, Zhang Y, et al. Magnetic dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles based integrated platform for rapid and efficient analysis of saccharides[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2024, 1288: 342166. |
| Zhao X L, Dong J C, Zhang Y Q, et al. Magnetic dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles based integrated platform for rapid and efficient analysis of saccharides[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2024, 1288: 342166.[LinkOut] | |
| [40] | Cao G, Gao J, Zhou L, et al. Fabrication of Ni2+-nitrilotriacetic acid functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica nanoflowers for one pot purification and immobilization of His-tagged ω-transaminase[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 128: 116-125. |
| Cao G X, Gao J, Zhou L Y, et al. Fabrication of Ni2+-nitrilotriacetic acid functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica nanoflowers for one pot purification and immobilization of His-tagged ω-transaminase[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 128: 116-125.[LinkOut] | |
| [41] | Hong Y, Zhan Q, Zheng Y, et al., Hydrophilic phytic acid-functionalized magnetic dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres with immobilized Ti4+: A dual-purpose affinity material for highly efficient enrichment of glycopeptides/phosphopeptides[J]. Talanta, 2019, 197: 77-85. |
| Hong Y Y, Zhan Q L, Zheng Y, et al. Hydrophilic phytic acid-functionalized magnetic dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres with immobilized Ti4+: a dual-purpose affinity material for highly efficient enrichment of glycopeptides/phosphopeptides[J]. Talanta, 2019, 197: 77-85.[LinkOut] | |
| [42] | Jin P, Zhu F, Zhou W, et al. Developing magnetic functionalized dendritic fibrous mesoporous silica as advanced adsorbent for quaternary ammonium alkaloids[J]. Microchimica Acta, 2023, 190(12): 481. |
| Jin P, Zhu F C, Zhou W, et al. Developing magnetic functionalized dendritic fibrous mesoporous silica as advanced adsorbent for quaternary ammonium alkaloids[J]. Microchimica Acta, 2023, 190(12): 481.[LinkOut] | |
| [43] | Dong Z, Yu G, Le X. Gold nanoparticle modified magnetic fibrous silica microspheres as a highly efficient and recyclable catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2015, 39(11): 8623-8629. |
| Dong Z P, Yu G Q, Le X. Gold nanoparticle modified magnetic fibrous silica microspheres as a highly efficient and recyclable catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2015, 39(11): 8623-8629.[LinkOut] | |
| [44] | Sun Z, Li H, Cui G, et al. Multifunctional magnetic core–shell dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres decorated with tiny Ag nanoparticles as a highly active heterogeneous catalyst[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 360: 252-262. |
| Sun Z B, Li H Z, Cui G J, et al. Multifunctional magnetic core-shell dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres decorated with tiny Ag nanoparticles as a highly active heterogeneous catalyst[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 360: 252-262.[LinkOut] | |
| [45] | Sadeghzadeh S. M. A green approach for the synthesis of 2-oxazolidinones using gold(I) complex immobilized on KCC-1 as nanocatalyst at room temperature[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2016, 30(10): 835-842. |
| Sadeghzadeh S M. A green approach for the synthesis of 2-oxazolidinones using gold(I) complex immobilized on KCC-1 as nanocatalyst at room temperature[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2016, 30(10): 835-842.[LinkOut] | |
| [46] | Sadeghzadeh S M. A heteropolyacid-based ionic liquid immobilized onto magnetic fibrous nano-silica as robust and recyclable heterogeneous catalysts for the synthesis of tetrahydrodipyrazolopyridines in water[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(79): 75973-75980. |
| Sadeghzadeh S M. A heteropolyacid-based ionic liquid immobilized onto magnetic fibrous nano-silica as robust and recyclable heterogeneous catalysts for the synthesis of tetrahydrodipyrazolopyridines in water[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(79): 75973-75980.[LinkOut] | |
| [47] | Sadeghzadeh S M. Bis(4-pyridylamino)triazine-stabilized magnetite KCC-1: a chemoselective, efficient, green and reusable nanocatalyst for the synthesis of N-substituted 1,4-dihydropyridines[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(101): 99586-99594. |
| Sadeghzadeh S M. Bis(4-pyridylamino)triazine-stabilized magnetite KCC-1: a chemoselective, efficient, green and reusable nanocatalyst for the synthesis of N-substituted 1, 4-dihydropyridines[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(101): 99586-99594.[LinkOut] | |
| [48] | Zhao Y, Tang J J, Motavalizadehkakhky A, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a novel CNT-FeNi3/DFNS/Cu(ii) magnetic nanocomposite for the photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline in wastewater[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(60): 35022-35032. |
| Zhao Y H, Tang J J, Motavalizadehkakhky A, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a novel CNT-FeNi3/DFNS/Cu(II) magnetic nanocomposite for the photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline in wastewater[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(60): 35022-35032.[LinkOut] | |
| [49] | Hassankhani A, Sadeghzadeh S M, Zhiani R. C-C and C-H coupling reactions by Fe3O4/KCC-1/APTPOSS supported palladium-salen-bridged ionic networks as a reusable catalyst[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(16): 8761-8769. |
| Hassankhani A, Sadeghzadeh S M, Zhiani R. C-C and C-H coupling reactions by Fe3O4/KCC-1/APTPOSS supported palladium-salen-bridged ionic networks as a reusable catalyst[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(16): 8761-8769.[LinkOut] | |
| [50] | Saadati S M, Zhiani R, Zahedifar M, et al. Synthesis of tetramethylquinoline-2,4-diamine using FeNi3/KCC-1/APTPOSS-supported copper cyclam and salen complex as a reusable catalyst[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2018, 32(12): e4560. |
| Saadati S M, Zhiani R, Zahedifar M, et al. Synthesis of tetramethylquinoline-2, 4-diamine using FeNi3/KCC-1/APTPOSS-supported copper cyclam and salen complex as a reusable catalyst[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2018, 32(12): e4560.[LinkOut] | |
| [51] | Qiu J, Yu L, Ni J . et al. Palladium–salen-bridged ionic networks immobilized on magnetic dendritic silica fibers for the synthesis of cyclic carbonates by oxidative carboxylation[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 44(4): 1269-1277. |
| Qiu J P, Yu L, Ni J G, et al. Palladium-salen-bridged ionic networks immobilized on magnetic dendritic silica fibers for the synthesis of cyclic carbonates by oxidative carboxylation[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 44(4): 1269-1277.[LinkOut] | |
| [52] | Fei Z Chen F, Zhong M, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a novel ruthenium(ii) trisbipyridine complex magnetic nanocomposite for the selective oxidation of phenols[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(48): 28078-28088. |
| Fei Z X, Chen F, Zhong M Q, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a novel ruthenium(II) trisbipyridine complex magnetic nanocomposite for the selective oxidation of phenols[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(48): 28078-28088.[PubMed] | |
| [53] | Zhiani R, Es-haghi A, Saadati S M, et al. A new class of organocobaloximes based FeNi3/DFNS for reduction of 4-nitrophenol and 2-nitroaniline[J]. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, 2018, 877: 21-31. |
| Zhiani R, Es-haghi A, Saadati S M, et al. A new class of organocobaloximes based FeNi3/DFNS for reduction of 4-nitrophenol and 2-nitroaniline[J]. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, 2018, 877: 21-31.[LinkOut] | |
| [54] | Zhang Q, Wu Y, Wang M, et al. Synthesis and photocatalytic performance of recyclable core-shell mesoporous Fe3O4@Bi2WO6 nanoparticles. Materials Research Bulletin, 2019, 113: 223-230. Zhang Q, Wu Y H, Wang M Z,et al. Synthesis and photocatalytic performance of recyclable core-shell mesoporous Fe3O4@Bi2WO6 nanoparticles[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2019, 113: 223-230.[LinkOut] |
| [55] | Zhiani R, Khoobi M, Sadeghzadeh S M, Synthesis of N-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)carbonyl]glycine from carbon dioxide, ethylene oxide, and α-amino acid by ionic gelation of sodium tripolyphosphate (TPP) and spirulina supported on magnetic KCC-1 in aqueous solution[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 42(12): 10153-10160. |
| Zhiani R, Khoobi M, Sadeghzadeh S M. Synthesis of N-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)carbonyl] glycine from carbon dioxide, ethylene oxide, and α-amino acid by ionic gelation of sodium tripolyphosphate (TPP) and spirulina supported on magnetic KCC-1 in aqueous solution[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 42(12): 10153-10160.[LinkOut] | |
| [56] | Asadi Zeydabadi H, Mehrzad J, Motavalizadehkakhky A, et al. Fixing CO2 into β-Oxopropylcarbamatesin by Palladium NPs Supported on Magnetic Fibrous Silica Ionic Gelation[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2021, 151(2): 582-592. |
| Asadi Zeydabadi H, Mehrzad J, Motavalizadehkakhky A, et al. Fixing CO2 into β-oxopropylcarbamatesin by palladium NPs supported on magnetic fibrous silica ionic gelation[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2021, 151(2): 582-592.[LinkOut] | |
| [57] | Hasanpour Galehban M, Zeynizadeh B, Mousavi H. Diverse and efficient catalytic applications of new cockscomb flower-like Fe3O4@SiO2@KCC-1@MPTMS@CuII mesoporous nanocomposite in the environmentally benign reduction and reductive acetylation of nitroarenes and one-pot synthesis of some coumarin compounds[J]. RSC Advances, 2022, 12(18): 11164-11189. |
| Hasanpour Galehban M, Zeynizadeh B, Mousavi H. Diverse and efficient catalytic applications of new cockscomb flower-like Fe3O4@SiO2@KCC-1@MPTMS@CuII mesoporous nanocomposite in the environmentally benign reduction and reductive acetylation of nitroarenes and one-pot synthesis of some coumarin compounds[J]. RSC Advances, 2022, 12(18): 11164-11189.[LinkOut] | |
| [58] | Galehban M H, Zeynizadeh B, Mousavi H. Introducing Fe3O4@SiO2@KCC-1@MPTMS@CuII catalytic applications for the green one-pot syntheses of 2-aryl (or heteroaryl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-ones and 9-aryl-3,3,6,6-tetramethyl-3,4,5,6,7,9-hexahydro-1H-xanthene-1,8(2H)-diones[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2023, 1271: 134017. |
| Galehban M H, Zeynizadeh B, Mousavi H. Introducing Fe3O4@SiO2@KCC-1@MPTMS@CuII catalytic applications for the green one-pot syntheses of 2-aryl(or heteroaryl)-2, 3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-ones and 9-aryl-3, 3, 6, 6-tetramethyl-3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9-hexahydro-1H-xanthene-1, 8(2H)-diones[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2023, 1271: 134017.[LinkOut] | |
| [59] | Saberi S, Zhiani R, Mehrzad J . et al. Synthesis and characterization of a novel TEMPO@FeNi3/DFNS–laccase magnetic nanocomposite for the reduction of nitro compounds[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(46): 27297-27304. |
| Saberi S, Zhiani R, Mehrzad J, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a novel TEMPO@FeNi3/DFNS-laccase magnetic nanocomposite for the reduction of nitro compounds[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(46): 27297-27304.[LinkOut] | |
| [60] | Seo B, Lee C, Yoo D, et al. A magnetically recoverable photocatalyst prepared by supporting TiO2 nanoparticles on a superparamagnetic iron oxide nanocluster core@fibrous silica shell nanocomposite[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(16): 9587-9595. |
| Seo B, Lee C, Yoo D, et al. A magnetically recoverable photocatalyst prepared by supporting TiO2 nanoparticles on a superparamagnetic iron oxide nanocluster core@fibrous silica shell nanocomposite[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(16): 9587-9595.[LinkOut] | |
| [61] | Wei J, Zou L, Li Y, et al. Synthesis of core–shell-structured mesoporous silica nanospheres with dual-pores for biphasic catalysis[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 43(15): 5833-5838. |
| Wei J, Zou L K, Li Y L, et al. Synthesis of core-shell-structured mesoporous silica nanospheres with dual-pores for biphasic catalysis[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 43(15): 5833-5838.[LinkOut] | |
| [62] | Qiu P, Zhao T, Khim J, et al. Ordered mesoporous carbon-silica frameworks confined magnetic mesoporous TiO2 as an efficient catalyst under acoustic cavitation energy[J]. Journal of Materiomics, 2020, 6(1): 45-53. |
| Qiu P P, Zhao T, Khim J, et al. Ordered mesoporous carbon-silica frameworks confined magnetic mesoporous TiO2 as an efficient catalyst under acoustic cavitation energy[J]. Journal of Materiomics, 2020, 6(1): 45-53.[LinkOut] | |
| [63] | Gu Z, Liu T, Tang J, et al. Mechanism of iron oxide-induced macrophage activation: The impact of composition and the underlying signaling pathway[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(15): 6122-6126. |
| Gu Z Y, Liu T Q, Tang J, et al. Mechanism of iron oxide-induced macrophage activation: the impact of composition and the underlying signaling pathway[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(15): 6122-6126.[PubMed] | |
| [1] | Kalambate P K, Dhanjai, Huang Z, et al. Core@shell nanomaterials based sensing devices: A review[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 115: 147-161. |
| [64] | Tsh A, Lee J H, Lee J J, et al. Mesoporous silica with fibrous morphology: a multifunctional core-shell platform for biomedical applications[J]. Nanotechnology, 2013, 24(34): 345603. |
| Atabaev T S, Lee J H, Lee J J, et al. Mesoporous silica with fibrous morphology: a multifunctional core-shell platform for biomedical applications[J]. Nanotechnology, 2013, 24(34): 345603.[LinkOut] | |
| [65] | Chen J, Lei S, Zeng K, et al. Catalase-imprinted Fe3O4/Fe@fibrous SiO2/polydopamine nanoparticles: An integrated nanoplatform of magnetic targeting, magnetic resonance imaging, and dual-mode cancer therapy[J]. Nano Research, 2017, 10 (7): 2351-2363. |
| Chen J X, Lei S, Zeng K, et al. Catalase-imprinted Fe3O4/Fe@fibrous SiO2/polydopamine nanoparticles: an integrated nanoplatform of magnetic targeting, magnetic resonance imaging, and dual-mode cancer therapy[J]. Nano Research, 2017, 10(7): 2351-2363.[LinkOut] | |
| [66] | Fiedler R, Sivakumaran G, Mallén J, et al. Superparamagnetic core–mesoporous silica shell nanoparticles with tunable extra- and intracellular dissolution rates[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2024, 36(6): 2790-2798. |
| Fiedler R, Sivakumaran G, Mallén J, et al. Superparamagnetic core-mesoporous silica shell nanoparticles with tunable extra- and intracellular dissolution rates[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2024, 36(6): 2790-2798.[LinkOut] | |
| [67] | Alamri H, Al-Shahrani A, Bovero E, et al. Self-cleaning superhydrophobic epoxy coating based on fibrous silica-coated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 513: 349-356. |
| Alamri H, Al-Shahrani A, Bovero E, et al. Self-cleaning superhydrophobic epoxy coating based on fibrous silica-coated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 513: 349-356.[LinkOut] | |
| [68] | Wang Y, Wu P, Wang Y, et al. Controllable pore size of super-hydrophobic magnetic core-shell nanospheres with dendritic architecture and their pore-dependent performances in oil/water separation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 323: 124434. |
| Wang Y B, Wu P, Wang Y N, et al. Controllable pore size of super-hydrophobic magnetic core-shell nanospheres with dendritic architecture and their pore-dependent performances in oil/water separation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 323: 124434.[LinkOut] | |
| [69] | Wang B, Wei Y, Wang Q, et al. Superhydrophobic magnetic core–shell mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles with dendritic architecture for oil–water separation[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2020, 4: 2184-2191 |
| Wang B X, Wei Y Z, Wang Q F, et al. Superhydrophobic magnetic core-shell mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles with dendritic architecture for oil-water separation[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2020, 4(7): 2184-2191.[LinkOut] | |
| [70] | Ali Z, Tian L, Zhang B, et al. Synthesis of fibrous and non-fibrous mesoporous silica magnetic yolk–shell microspheres as recyclable supports for immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2017, 103: 42-52. |
| Ali Z, Tian L, Zhang B L, et al. Synthesis of fibrous and non-fibrous mesoporous silica magnetic yolk-shell microspheres as recyclable supports for immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2017, 103: 42-52.[LinkOut] | |
| [71] | Bian L, Deng W, Xie D, et al. Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Hollow Spheres with One-Pot Self-Templated Interfacial Diffusion Method[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2024, 36(1): 482-491. |
| Bian L, Deng W J, Xie D, et al. Dendritic mesoporous silica hollow spheres with one-pot self-templated interfacial diffusion method[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2024, 36(1): 482-491.[LinkOut] | |
| [72] | Yang Y, Bernardi S, Song H, et al. Anion Assisted Synthesis of Large Pore Hollow Dendritic Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles: Understanding the Composition Gradient[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28(3): 704-707. |
| Yang Y N, Bernardi S, Song H, et al. Anion assisted synthesis of large pore hollow dendritic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles: understanding the composition gradient[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28(3): 704-707.[LinkOut] | |
| [73] | Yang Y, Lu Y, Abbaraju P L, et al. Stepwise Degradable Nanocarriers Enabled Cascade Delivery for Synergistic Cancer Therapy[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(28): 1800706. |
| Yang Y N, Lu Y, Abbaraju P L, et al. Stepwise degradable nanocarriers enabled cascade delivery for synergistic cancer therapy[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(28): 1800706.[LinkOut] | |
| [74] | Du X, Zhao C, Luan Y, et al. Dendritic porous yolk@ordered mesoporous shell structured heterogeneous nanocatalysts with enhanced stability[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(40): 21560-21569. |
| Du X, Zhao C X, Luan Y, et al. Dendritic porous yolk@ordered mesoporous shell structured heterogeneous nanocatalysts with enhanced stability[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(40): 21560-21569.[LinkOut] | |
| [75] | Du X, Zhao C, Li X, et al. Novel yolk-shell polymer/carbon@Au nanocomposites by using dendrimer-like mesoporous silica nanoparticles as hard template[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 700: 83-91. |
| Du X, Zhao C X, Li X Y, et al. Novel yolk-shell polymer/carbon@Au nanocomposites by using dendrimer-like mesoporous silica nanoparticles as hard template[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 700: 83-91.[LinkOut] | |
| [76] | Moon D S, Lee J K. Formation of wrinkled silica mesostructures based on the phase behavior of pseudoternary systems[J]. Langmuir, 2014, 30(51): 15574-15580. |
| Moon D S, Lee J K. Formation of wrinkled silica mesostructures based on the phase behavior of pseudoternary systems[J]. Langmuir, 2014, 30(51): 15574-15580.[LinkOut] | |
| [77] | Qu Q, Li W, Wu Q. Formation Mechanism of Silica Particles with Dendritic Structure[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2019, 4(21): 6656-6661. |
| Qu Q S, Li W Y, Wu Q. Formation mechanism of silica particles with dendritic structure[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2019, 4(21): 6656-6661.[LinkOut] | |
| [78] | Dai Y, Yang D, Yu D, et al. Engineering of monodisperse core–shell up-conversion dendritic mesoporous silica nanocomposites with a tunable pore size[J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(8): 5075-5083. |
| Dai Y, Yang D P, Yu D P, et al. Engineering of monodisperse core-shell up-conversion dendritic mesoporous silica nanocomposites with a tunable pore size[J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(8): 5075-5083.[LinkOut] | |
| [79] | Shen D, Yang J, Li X, et al. Biphase stratification approach to three-dimensional dendritic biodegradable mesoporous silica nanospheres[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(2): 923-932. |
| Shen D K, Yang J P, Li X M, et al. Biphase stratification approach to three-dimensional dendritic biodegradable mesoporous silica nanospheres[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(2): 923-932.[PubMed] | |
| [80] | Firmansyah M L, Jalil A A, Triwahyono S, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Fibrous Silica ZSM-5 for Cumene Hydrocracking[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 2016(6): 5178-5182 |
| Firmansyah M L, Jalil A A, Triwahyono S, et al. Synthesis and characterization of fibrous silica ZSM-5 for cumene hydrocracking[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 6(13): 5178-5182.[LinkOut] | |
| [81] | Abdul Jalil A, Zolkifli A S, Triwahyono S, et al. Altering Dendrimer Structure of Fibrous-Silica-HZSM5 for Enhanced Product Selectivity of Benzene Methylation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(2): 553-562. |
| Abdul Jalil A, Zolkifli A S, Triwahyono S, et al. Altering dendrimer structure of fibrous-silica-HZSM5 for enhanced product selectivity of benzene methylation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(2): 553-562.[LinkOut] | |
| [82] | Rahman A F A, Jalil A A, Siang T J, et al. Mechanistic insight into low temperature toluene production via benzene methylation over mesopore-rich fibrous silica HZSM-5 zeolite[J]. Journal of Porous Materials, 2021, 28(6): 1765-1777. |
| Rahman A F A, Jalil A A, Siang T J, et al. Mechanistic insight into low temperature toluene production via benzene methylation over mesopore-rich fibrous silica HZSM-5 zeolite[J]. Journal of Porous Materials, 2021, 28(6): 1765-1777.[LinkOut] | |
| [83] | Hussain I, Jalil A A, Mamat C R, et al. New insights on the effect of the H2/CO ratio for enhancement of CO methanation over metal-free fibrous silica ZSM-5: Thermodynamic and mechanistic studies[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 199: 112056. |
| Hussain I, Jalil A A, Mamat C R, et al. New insights on the effect of the H2/CO ratio for enhancement of CO methanation over metal-free fibrous silica ZSM-5: thermodynamic and mechanistic studies[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 199: 112056.[LinkOut] | |
| [84] | Teh L P, Triwahyono S, Jalil A A, et al. Fibrous silica mesoporous ZSM-5 for carbon monoxide methanation[J]. Applied Catalysis A General, 2016, 523: 200-208. |
| Teh L P, Triwahyono S, Jalil A A, et al. Fibrous silica mesoporous ZSM-5 for carbon monoxide methanation[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2016, 523: 200-208.[LinkOut] | |
| [85] | Aziz F F A, Jalil A A, Triwahyono S, et al. Controllable structure of fibrous SiO2–ZSM-5 support decorated with TiO2 catalysts for enhanced photodegradation of paracetamol[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 455: 84-95. |
| Aziz F F A, Jalil A A, Triwahyono S, et al. Controllable structure of fibrous SiO2-ZSM-5 support decorated with TiO2 catalysts for enhanced photodegradation of paracetamol[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 455: 84-95.[LinkOut] | |
| [86] | Hambali H U, Jalil A A, Abdulrasheed A A, et al. Fibrous spherical Ni-M/ZSM-5 (M: Mg, Ca, Ta, Ga) catalysts for methane dry reforming: The interplay between surface acidity-basicity and coking resistance[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2020, 44(7): 5696-5712. |
| Hambali H U, Jalil A A, Abdulrasheed A A, et al. Fibrous spherical Ni-M/ZSM-5 (M: Mg, Ca, Ta, Ga) catalysts for methane dry reforming: the interplay between surface acidity-basicity and coking resistance[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2020, 44(7): 5696-5712.[LinkOut] | |
| [87] | Hussain I, Jalil A A, Fatah N A A, et al. A highly competitive system for CO methanation over an active metal-free fibrous silica mordenite via in-situ ESR and FTIR studies[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 211: 112754. |
| Hussain I, Jalil A A, Fatah N A A, et al. A highly competitive system for CO methanation over an active metal-free fibrous silica mordenite via in-situ ESR and FTIR studies[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 211: 112754.[LinkOut] | |
| [88] | Hussain I, Jalil A A, Hassan N S, et al. Fabrication and characterization of highly active fibrous silica-mordenite (FS@SiO2-MOR) cockscomb shaped catalyst for enhanced CO2 methanation[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 228: 115978. |
| Hussain I, Jalil A A, Hassan N S, et al. Fabrication and characterization of highly active fibrous silica-mordenite (FS@SiO2-MOR) cockscomb shaped catalyst for enhanced CO2 methanation[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 228: 115978.[LinkOut] | |
| [89] | Izan S M, Triwahyono S, Jalil A A, et al. Additional Lewis acid sites of protonated fibrous silica@BEA zeolite (HSi@BEA) improving the generation of protonic acid sites in the isomerization of C6 alkane and cycloalkanes[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2019, 570: 228-237. |
| Izan S M, Triwahyono S, Jalil A A, et al. Additional Lewis acid sites of protonated fibrous silica@BEA zeolite (HSi@BEA) improving the generation of protonic acid sites in the isomerization of C6 alkane and cycloalkanes[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2019, 570: 228-237.[LinkOut] | |
| [90] | Ghani N N M, Jalil A A, Triwahyono S, et al. Tailored mesoporosity and acidity of shape-selective fibrous silica beta zeolite for enhanced toluene co-reaction with methanol[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 193: 217-229. |
| Ghani N N M, Jalil A A, Triwahyono S, et al. Tailored mesoporosity and acidity of shape-selective fibrous silica beta zeolite for enhanced toluene co-reaction with methanol[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 193: 217-229.[LinkOut] | |
| [91] | Hussain I, Jalil A A, Hamid M Y S, et al. Substituted natural gas (SNG) production using an environment-friendly, metal-free modified beta zeolite (@BEA) catalyst with a dandelion flower-like structure[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2022, 523: 112140. |
| Hussain I, Jalil A A, Hamid M, et al. Substituted natural gas (SNG) production using an environment-friendly, metal-free modified beta zeolite (@BEA) catalyst with a dandelion flower-like structure[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2022, 523: 112140.[LinkOut] | |
| [92] | Jalil A A, Gambo Y, Ibrahim M, et al. Platinum-promoted fibrous silica Y zeolite with enhanced mass transfer as a highly selective catalyst for n-dodecane hydroisomerization[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2019, 0 (0): 1-16. |
| Jalil A A, Gambo Y, Ibrahim M, et al. Platinum-promoted fibrous silica Y zeolite with enhanced mass transfer as a highly selective catalyst for n-dodecane hydroisomerization[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2019, 43(9): 4201-4216.[LinkOut] | |
| [93] | Triwahyono S, Jalil A A, Izan S M, et al. Isomerization of linear C5–C7 over pt loaded on protonated fibrous silica@Y zeolite (Pt/HSi@Y) [J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2019, 37: 163-171. |
| Triwahyono S, Jalil A A, Izan S M, et al. Isomerization of linear C5-C7 over Pt loaded on protonated fibrous silica@Y zeolite (Pt/HSi@Y)[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2019, 37: 163-171.[LinkOut] | |
| [94] | Chong C C, Bukhari S N, Cheng Y W, et al. Facile synthesis of tunable dendritic fibrous SBA-15 (DFSBA-15) with radial wrinkle structure[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 294: 109872. |
| Chong C C, Bukhari S N, Cheng Y W, et al. Facile synthesis of tunable dendritic fibrous SBA-15 (DFSBA-15) with radial wrinkle structure[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 294: 109872.[LinkOut] | |
| [95] | Chong C C, Setiabudi H D, Jalil A A. Dendritic fibrous SBA-15 supported nickel (Ni/DFSBA-15): A sustainable catalyst for hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(36): 18533-18548. |
| Chong C C, Setiabudi H D, Jalil A A. Dendritic fibrous SBA-15 supported nickel (Ni/DFSBA-15): a sustainable catalyst for hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(36): 18533-18548.[LinkOut] | |
| [96] | Chong C C, Cheng Y W, Setiabudi H D, et al. Dry reforming of methane over Ni/dendritic fibrous SBA-15 (Ni/DFSBA-15): Optimization, mechanism, and regeneration studies[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45 (15): 8507-8525. |
| Chong C C, Cheng Y W, Setiabudi H D, et al. Dry reforming of methane over Ni/dendritic fibrous SBA-15 (Ni/DFSBA-15): optimization, mechanism, and regeneration studies[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(15): 8507-8525.[LinkOut] | |
| [97] | Abubakar Abdulkadir B, Mohd Zaki R S R, Abd Jalil A, et al. Synergistic effects of Fe2O3 supported on dendritic fibrous SBA-15 for superior photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue[J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2025, 185: 108859. |
| Abubakar Abdulkadir B, Mohd Zaki R S R, Abd Jalil A, et al. Synergistic effects of Fe2O3 supported on dendritic fibrous SBA-15 for superior photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue[J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2025, 185: 108859.[LinkOut] | |
| [98] | Hung C T, Duan L, Zhao T, et al. Gradient Hierarchically Porous Structure for Rapid Capillary-Assisted Catalysis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(13): 6091-6099. |
| Hung C T, Duan L L, Zhao T C, et al. Gradient hierarchically porous structure for rapid capillary-assisted catalysis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(13): 6091-6099.[PubMed] | |
| [99] | Peng H, Xu L, Wu H, et al. One-pot synthesis of benzamide over a robust tandem catalyst based on center radially fibrous silica encapsulated TS-1[J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(26): 2709-2711. |
| Peng H G, Xu L, Wu H H, et al. One-pot synthesis of benzamide over a robust tandem catalyst based on center radially fibrous silica encapsulated TS-1[J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(26): 2709-2711.[LinkOut] | |
| [100] | Peng H, Wang D, Xu L, et al. One-pot synthesis of primary amides on bifunctional Rh(OH)x/TS-1@KCC-1 catalysts[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2013, 34(11): 2057–2065. |
| Peng H G, Wang D R, Xu L, et al. One-pot synthesis of primary amides on bifunctional Rh(OH)x/TS-1@KCC-1 catalysts[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2013, 34(11): 2057-2065.[LinkOut] | |
| [101] | Mosaad Awad M, Hussain I, Ahmed Taialla O, et al. Unveiling the catalytic performance of unique core-fibrous shell silica-lanthanum oxide with different nickel loadings for dry reforming of methane[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 311: 118508. |
| Mosaad Awad M, Hussain I, Ahmed Taialla O, et al. Unveiling the catalytic performance of unique core-fibrous shell silica-lanthanum oxide with different nickel loadings for dry reforming of methane[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 311: 118508.[LinkOut] | |
| [102] | Shabir J, Rani S, Sharma M, et al. Synthesis of dendritic fibrous nanosilica over a cubic core (cSiO2@DFNS) with catalytically efficient silver nanoparticles for reduction of nitroarenes and degradation of organic dyes[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(14): 8140-8151. |
| Shabir J, Rani S, Sharma M, et al. Synthesis of dendritic fibrous nanosilica over a cubic core (cSiO2@DFNS) with catalytically efficient silver nanoparticles for reduction of nitroarenes and degradation of organic dyes[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(14): 8140-8151.[LinkOut] | |
| [103] | Qu Q, Min Y, Zhang L, et al. Silica Microspheres with Fibrous Shells: Synthesis and Application in HPLC[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(19): 9631-9638. |
| Qu Q S, Min Y, Zhang L H, et al. Silica microspheres with fibrous shells: synthesis and application in HPLC[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(19): 9631-9638.[LinkOut] | |
| [104] | Qu Q, Si Y, Xuan H, et al. Synthesis of core-shell silica spheres with tunable pore diameters for HPLC[J]. Materials Letters, 2018, 211: 40-42. |
| Qu Q S, Si Y, Xuan H, et al. Synthesis of core-shell silica spheres with tunable pore diameters for HPLC[J]. Materials Letters, 2018, 211: 40-42.[LinkOut] | |
| [105] | Qu Q, Si Y, Xuan H, et al. Dendritic core-shell silica spheres with large pore size for separation of biomolecules[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2018, 1540: 31-37. |
| Qu Q S, Si Y, Xuan H, et al. Dendritic core-shell silica spheres with large pore size for separation of biomolecules[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2018, 1540: 31-37.[LinkOut] | |
| [106] | Qu Q, Xuan H, Zhang K, et al. Core-shell silica particles with dendritic pore channels impregnated with zeolite imidazolate framework-8 for high performance liquid chromatography separation[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2017, 1505: 63-68. |
| Qu Q S, Xuan H, Zhang K H, et al. Core-shell silica particles with dendritic pore channels impregnated with zeolite imidazolate framework-8 for high performance liquid chromatography separation[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2017, 1505: 63-68.[LinkOut] | |
| [107] | Irfan A, Feng W, Liu K, et al. TiO2-modified fibrous core-shell mesoporous material to selectively enrich endogenous phosphopeptides with proteins exclusion prior to CE-MS analysis[J]. Talanta, 2021, 235: 122737. |
| Irfan A, Feng W X, Liu K X, et al. TiO2-modified fibrous core-shell mesoporous material to selectively enrich endogenous phosphopeptides with proteins exclusion prior to CE-MS analysis[J]. Talanta, 2021, 235: 122737.[LinkOut] | |
| [108] | Liu J, Feng W, Tian M, et al. Titanium dioxide-coated core-shell silica microspheres-based solid-phase extraction combined with sheathless capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry for analysis of glyphosate, glufosinate and their metabolites in baby foods[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2021, 1659: 462519. |
| Liu J N, Feng W X, Tian M M, et al. Titanium dioxide-coated core-shell silica microspheres-based solid-phase extraction combined with sheathless capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry for analysis of glyphosate, glufosinate and their metabolites in baby foods[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2021, 1659: 462519.[LinkOut] | |
| [109] | Wang A, Hu L, Liu J, et al. Polyaniline-coated core-shell silica microspheres-based dispersive-solid phase extraction for detection of benzophenone-type UV filters in environmental water samples[J]. Environmental Advances, 2021, 3: 100037. |
| Wang A P, Hu L H, Liu J N, et al. Polyaniline-coated core-shell silica microspheres-based dispersive-solid phase extraction for detection of benzophenone-type UV filters in environmental water samples[J]. Environmental Advances, 2021, 3: 100037.[LinkOut] | |
| [110] | Zhang W, Li S M, Zhang J. Preparation and Chromatographic Features of Fibrous Core–Shell HPLC Packing Material[J]. Chromatographia, 2018, 81(9): 1249-1256. |
| Zhang W, Li S M, Zhang J. Preparation and chromatographic features of fibrous core-shell HPLC packing material[J]. Chromatographia, 2018, 81(9): 1249-1256.[LinkOut] | |
| [111] | Siddiki A K M N A, Lin J, Balkus K J. Encapsulation of ZnO and Ho:ZnO Nanoparticles in the Core of Wrinkled Mesoporous Silica[J]. Langmuir, 2023, 39(36): 12956-12965. |
| Siddiki A K M N A, Lin J, Balkus K J. Encapsulation of ZnO and Ho: ZnO nanoparticles in the core of wrinkled mesoporous silica[J]. Langmuir, 2023, 39(36): 12956-12965.[LinkOut] | |
| [112] | Wang C, Guo T, Tang R, et al. Facile Fabrication of Monodisperse Vinyl Hybrid Core–Shell Silica Microsphere with Short Range Radial Channel in bi-phase System[J]. Small, 2025, 21(8): 2409640. |
| Wang C Y, Guo T T, Tang R Z, et al. Facile fabrication of monodisperse vinyl hybrid core-shell silica microsphere with short range radial channel in bi-phase system[J]. Small, 2025, 21(8): 2409640.[LinkOut] | |
| [113] | Sun J, Zhang P, Yan K, et al. High-performance nanothermometry system with controlled sensitivity based on dual-emission CsPbBr3/CdTe@SiO2 core/shell nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2025, 693: 137607. |
| Sun J N, Zhang P, Yan K, et al. High-performance nanothermometry system with controlled sensitivity based on dual-emission CsPbBr3/CdTe@SiO2 core/shell nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2025, 693: 137607.[LinkOut] | |
| [114] | Liu S, Li W, Dong S, et al. An all-in-one theranostic nanoplatform based on upconversion dendritic mesoporous silica nanocomposites for synergistic chemodynamic/photodynamic/gas therapy[J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(47): 24146-24161. |
| Liu S K, Li W T, Dong S M, et al. An all-in-one theranostic nanoplatform based on upconversion dendritic mesoporous silica nanocomposites for synergistic chemodynamic/photodynamic/gas therapy[J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(47): 24146-24161.[LinkOut] | |
| [115] | Dong Y, Dong S, Wang Z, et al. Multimode Imaging-Guided Photothermal/Chemodynamic Synergistic Therapy Nanoagent with a Tumor Microenvironment Responded Effect[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(47): 52479-52491. |
| Dong Y S, Dong S M, Wang Z, et al. Multimode imaging-guided photothermal/chemodynamic synergistic therapy nanoagent with a tumor microenvironment responded effect[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(47): 52479-52491.[PubMed] | |
| [116] | Xu Y, Liang H, Zeng Q, et al. A bubble-enhanced lanthanide-doped up/down-conversion platform with tumor microenvironment response for dual-modal photoacoustic and near-infrared-II fluorescence imaging[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2024, 659: 149-159. |
| Xu Y N, Liang H R, Zeng Q T, et al. A bubble-enhanced lanthanide-doped up/down-conversion platform with tumor microenvironment response for dual-modal photoacoustic and near-infrared-II fluorescence imaging[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2024, 659: 149-159.[LinkOut] | |
| [117] | Dong S, Dong Y, Jia T, et al. GSH-Depleted Nanozymes with Hyperthermia-Enhanced Dual Enzyme-Mimic Activities for Tumor Nanocatalytic Therapy[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(42): 2002439. |
| Dong S M, Dong Y S, Jia T, et al. GSH-depleted nanozymes with hyperthermia-enhanced dual enzyme-mimic activities for tumor nanocatalytic therapy[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(42): e2002439.[PubMed] | |
| [118] | Abbaraju P L, Yang Y, Yu M, et al. Core–Shell‐structured Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Combined Photodynamic Therapy and Antibody Delivery[J]. Chemistry - An Asian Journal, 2017, 12(13): 1465-1469. |
| Abbaraju P L, Yang Y N, Yu M H, et al. Core-shell-structured dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for combined photodynamic therapy and antibody delivery[J]. Chemistry-An Asian Journal, 2017, 12(13): 1465-1469.[LinkOut] | |
| [119] | Wan M M, Wang Q, Wang R L, et al. Platelet-derived porous nanomotor for thrombus therapy[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(22): eaaz9014. |
| Wan M M, Wang Q, Wang R L, et al. Platelet-derived porous nanomotor for thrombus therapy[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(22): eaaz9014.[PubMed] | |
| [120] | Wan M, Wang Q, Li X, et al. Systematic Research and Evaluation Models of Nanomotors for Cancer Combined Therapy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59: 14458. |
| Wan M M, Wang Q, Li X Y, et al. Systematic research and evaluation models of nanomotors for cancer combined therapy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(34): 14458-14465.[LinkOut] | |
| [121] | Liu S, Zhao Y, Shen M, et al. Hyaluronic acid targeted and pH-responsive multifunctional nanoparticles for chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy of atherosclerosis[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2021, 10: 562. |
| Liu S, Zhao Y, Shen M L, et al. Hyaluronic acid targeted and pH-responsive multifunctional nanoparticles for chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy of atherosclerosis[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2022, 10(4): 562-570.[LinkOut] | |
| [122] | Xu C, Chen F, Valdovinos H F, et al. Bacteria-like mesoporous silica-coated gold nanorods for positron emission tomography and photoacoustic imaging-guided chemo-photothermal combined therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2018, 165: 56-65. |
| Xu C, Chen F, Valdovinos H F, et al. Bacteria-like mesoporous silica-coated gold nanorods for positron emission tomography and photoacoustic imaging-guided chemo-photothermal combined therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2018, 165: 56-65.[LinkOut] | |
| [123] | Wang Z, Fu X, Dai C, et al. NIR II-triggered core-shell upconversion nanocomposites for peroxynitrite-boosted anti-infection against diabetic wound[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 480: 148271. |
| Wang Z K, Fu X Y, Dai C X, et al. NIR II-triggered core-shell upconversion nanocomposites for peroxynitrite-boosted anti-infection against diabetic wound[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 480: 148271.[LinkOut] | |
| [124] | Kashfi-Sadabad R, Gonzalez-Fajardo L, Hargrove D, et al. Engineering Multifunctional Gold Decorated Dendritic Mesoporous Silica/Tantalum Oxide Nanoparticles for Intraperitoneal Tumor-Specific Delivery[J]. Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 2019, 36(4): 1900058. |
| Kashfi-Sadabad R, Gonzalez-Fajardo L, Hargrove D, et al. Engineering multifunctional gold decorated dendritic mesoporous silica/tantalum oxide nanoparticles for intraperitoneal tumor-specific delivery[J]. Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 2019, 36(4): 1900058.[LinkOut] | |
| [125] | Li Z, Lu S, Liu W, et al. Synergistic lysozyme-photodynamic therapy against resistant bacteria based on an intelligent upconversion nanoplatform[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(35): 19201-19206. |
| Li Z, Lu S, Liu W Z, et al. Synergistic lysozyme-photodynamic therapy against resistant bacteria based on an intelligent upconversion nanoplatform[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(35): 19201-19206.[LinkOut] | |
| [126] | Chen Y, Zuo C, Ma X, et al. Solid-silica core/mesoporous-silica shell composite abrasives: synthesis, characterization, and the effect of mesoporous shell structures on CMP[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2018, 29(5): 3817-3828. |
| Chen Y, Zuo C Z, Ma X Y, et al. Solid-silica core/mesoporous-silica shell composite abrasives: synthesis, characterization, and the effect of mesoporous shell structures on CMP[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2018, 29(5): 3817-3828.[LinkOut] | |
| [127] | Chen A, Mu H, Zuo C, et al. Fabrication, characterization, and CMP performance of dendritic mesoporous-silica composite particles with tunable pore sizes[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 770: 335-344. |
| Chen A L, Mu H L, Zuo C Z, et al. Fabrication, characterization, and CMP performance of dendritic mesoporous-silica composite particles with tunable pore sizes[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 770: 335-344.[LinkOut] | |
| [128] | Chen A, Ma X, Cai W, et al. Polystyrene-supported dendritic mesoporous silica hybrid core/shell particles: controlled synthesis and their pore size-dependent polishing behavior[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55(2): 577-590. |
| Chen A L, Ma X Y, Cai W J, et al. Polystyrene-supported dendritic mesoporous silica hybrid core/shell particles: controlled synthesis and their pore size-dependent polishing behavior[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55(2): 577-590.[LinkOut] | |
| [129] | Wang Y, He J, Shi Y, et al. Structure-dependent adsorptive or photocatalytic performances of solid and hollow dendritic mesoporous silica&titania nanospheres[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 305: 110326. |
| Wang Y B, He J, Shi Y M, et al. Structure-dependent adsorptive or photocatalytic performances of solid and hollow dendritic mesoporous silica & titania nanospheres[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 305: 110326.[LinkOut] | |
| [130] | Yu H, Zhang Q, Dahl M, et al. Dual-pore Carbon Shells for Efficient Removal of Humic Acid from Water[J]. Chemistry - A European Journal, 2017, 23: 16249-16256. |
| Yu H X, Zhang Q, Dahl M, et al. Dual-pore carbon shells for efficient removal of humic acid from water[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2017, 23(64): 16249-16256.[LinkOut] | |
| [131] | Jingru Z, Hongtao C, Jiaqi C, et al. Preparation and application of KCC-1@ZIF-8 for the solid extraction of tetracycline with high adsorption capacity[J]. Analytical Methods, 2024, 16(35): 5959-5970. |
| Zhang J R, Chu H T, Chen J Q, et al. Preparation and application of KCC-1@ZIF-8 for the solid extraction of tetracycline with high adsorption capacity[J]. Analytical Methods, 2024, 16(35): 5959-5970.[PubMed] | |
| [132] | Tran N M, Jung S, Yoo H. "Nanospace engineering" by the growth of nano metal-organic framework on dendritic fibrous nanosilica (DFNS) and DFNS/gold hybrids[J]. Nano Research, 2020, 13(3): 775-784. |
| Tran N M, Jung S, Yoo H. "Nanospace engineering" by the growth of nano metal-organic framework on dendritic fibrous nanosilica (DFNS) and DFNS/gold hybrids[J]. Nano Research, 2020, 13(3): 775-784.[LinkOut] | |
| [133] | Zhang S, Wen L, Yang J, et al. Facile Fabrication of Dendritic Mesoporous SiO2@CdTe@SiO2 Fluorescent Nanoparticles for Bioimaging[J]. Particle and Particle Systems Characterization, 2016, 33(5): 261–270. |
| Zhang S H, Wen L, Yang J P, et al. Facile fabrication of dendritic mesoporous SiO2@CdTe@SiO2 fluorescent nanoparticles for bioimaging[J]. Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 2016, 33(5): 261-270.[LinkOut] | |
| [134] | Huang L, Liao T, Wang J, et al. Brilliant Pitaya-Type Silica Colloids with Central–Radial and High‐Density Quantum Dots Incorporation for Ultrasensitive Fluorescence Immunoassays[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(4): 1705380. |
| Huang L, Liao T, Wang J, et al. Brilliant pitaya-type silica colloids with central-radial and high-density quantum dots incorporation for ultrasensitive fluorescence immunoassays[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(4): 1705380.[LinkOut] | |
| [135] | Leng Y, Wang X, Li W, et al. Enabling ultrahigh loading of AIEgens through alkyne-amine click reactions for highly sensitive colorimetric-fluorescent dual-readout lateral flow immunoassay[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2025, 432: 137473. |
| Leng Y K, Wang X L, Li W J, et al. Enabling ultrahigh loading of AIEgens through alkyne-amine click reactions for highly sensitive colorimetric-fluorescent dual-readout lateral flow immunoassay[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2025, 432: 137473.[LinkOut] | |
| [136] | Wu Q, Huang F, Jiang Y, et al. Firefly lantern-inspired AIE-enhanced gold nanocluster microspheres for ultrasensitive detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2025, 422: 136584. |
| Wu Q L, Huang F Y, Jiang Y Y, et al. Firefly lantern-inspired AIE-enhanced gold nanocluster microspheres for ultrasensitive detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2025, 422: 136584.[LinkOut] | |
| [137] | Wang Y, Tao J, Wang Y, et al. Remarkable reduction ability towards p-nitrophenol by a synergistic effect against the aggregation and leaching of palladium nanoparticles in dendritic supported catalysts[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 574: 151702. |
| Wang Y B, Tao J H, Wang Y N, et al. Remarkable reduction ability towards p-nitrophenol by a synergistic effect against the aggregation and leaching of palladium nanoparticles in dendritic supported catalysts[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 574: 151702.[LinkOut] | |
| [138] | Wang Y, He J, Li X, et al. Dendritic mesoporous silica&titania nanospheres (DMSTNs) coupled with amorphous carbon nitride (ACN) for improved visible-light-driven hydrogen production[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 538: 148147. |
| Wang Y B, He J, Li X L, et al. Dendritic mesoporous silica&titania nanospheres (DMSTNs) coupled with amorphous carbon nitride (ACN) for improved visible-light-driven hydrogen production[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 538: 148147.[LinkOut] | |
| [139] | Azizi S, Shadjou N, Soleymani J. CuI/Fe3O4 NPs@Biimidazole IL-KCC-1 as a leach proof nanocatalyst for the synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines in aqueous medium[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2021, 35(1): e6031. |
| Azizi S, Shadjou N, Soleymani J. CuI/Fe3O4 NPs@Biimidazole IL-KCC-1 as a leach proof nanocatalyst for the synthesis of imidazo [1, 2-α] pyridines in aqueous medium[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2021, 35(1): e6031.[LinkOut] | |
| [140] | Yang Y, Lu Y, Abbaraju P L, et al. Multi-shelled dendritic mesoporous organosilica hollow spheres: Roles of composition and architecture in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(29): 8446-8450. |
| Yang Y N, Lu Y, Abbaraju P L, et al. Multi-shelled dendritic mesoporous organosilica hollow spheres: roles of composition and architecture in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(29): 8446-8450.[LinkOut] | |
| [141] | Munaweera I, Trinh M, Hong J, et al. Chemically powered nanomotor as a delivery vehicle for biologically relevant payloads[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2016, 16(9): 9063-9071. |
| Munaweera I, Trinh M, Hong J, et al. Chemically powered nanomotor as a delivery vehicle for biologically relevant payloads[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2016, 16(9): 9063-9071.[LinkOut] |
| [1] | 赵维, 邢文乐, 韩朝旭, 袁兴中, 蒋龙波. g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化降解水中有机污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769. |
| [2] | 吴阿强, 诸葛祥群, 刘通, 王明星, 罗鲲. 纳米普鲁士蓝悬浮电解液对锂氧电池性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4310-4317. |
| [3] | 赵美, 甘雨欣, 赵绍磊, 杨令, 王亭杰. 硅橡胶用纳米二氧化硅表面有机修饰及补强机理研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3125-3136. |
| [4] | 郭铮铮, 赵一丹, 王辅强, 裴璐, 靳彦岭, 任芳, 任鹏刚. 异质结构MoS2/RGO/NiFe2O4复合材料的构筑及电磁波吸收性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3719-3732. |
| [5] | 郭乃胜, 朱小波, 王双, 陈平, 褚召阳, 王志臣. 聚氨酯改性沥青高低温性能及影响因素的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2505-2523. |
| [6] | 张畅, 解强, 沙雨桐, 王炳杰, 梁鼎成, 刘金昌. 低灰低硅竹炭的制备及衍生硬炭的电化学性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3073-3083. |
| [7] | 胡家玮, 王聪, 刘美婧. 一种抑制隧道排水管道中结晶体形成的双层阻垢疏水涂层[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3053-3072. |
| [8] | 石孟琪, 王欢, 王守娟, 席跃宾, 孔凡功. 木质素基炭材料的制备及其在锂硫电池中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1463-1483. |
| [9] | 李远华, 凌思棋, 封科军, 冯颖, 郭于菁, 谢世桓. 基于cMOFs的固定化脂肪酶微反应器的构筑及其扁桃酸催化应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1170-1179. |
| [10] | 肖俊兵, 邹博, 任建地, 刘昌会, 贾传坤. 基于相图分析的氯化物复合熔盐储热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 963-974. |
| [11] | 万俊, 宋佳芮, 范春煌, 魏乐乐, 聂依娜, 刘琳. 高效空穴转移助力光催化碱性甲醇-水溶液制氢[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1064-1075. |
| [12] | 肖俊兵, 钟湘宇, 任建地, 钟芳芳, 刘昌会, 贾传坤. 基于生物碳材料强化的硬脂酸相变材料储热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1312-1322. |
| [13] | 刘彦贝, 王若名, 刘娟, Raza Taimoor, 陆玉正, Raza Rizwan, 朱斌, 李松波, 安胜利, 云斯宁. CeO2@La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ 电解质的制备及半导体离子燃料电池性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1353-1362. |
| [14] | 李文宝, 胡锦鹏, 杜淼, 潘鹏举, 单国荣. 强韧P(SBMA-co-AAc)/SiO2复合水凝胶海洋防污减阻涂层[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 787-796. |
| [15] | 梁晟源, 周如东, 李文凯, 王李军, 李士阔. 金属诱导制备Fe3O4/FeNi/CNT复合材料及其吸波性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 6099-6109. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号