• •
付宁1( ), 温凯1(
), 温凯1( ), 宫敬1(
), 宫敬1( ), 戎若飞1, 聂文1, 邱姝娟2, 李政兵3, 李亮4
), 戎若飞1, 聂文1, 邱姝娟2, 李政兵3, 李亮4
收稿日期:2025-12-01
修回日期:2026-01-03
出版日期:2026-01-13
通讯作者:
温凯,宫敬
作者简介:付宁(2000—),女,博士研究生,fning1101@163.com
基金资助:
Ning FU1( ), Kai WEN1(
), Kai WEN1( ), Jing GONG1(
), Jing GONG1( ), Ruofei RONG1, Wen NIE1, Shujuan QIU2, Zhengbing LI3, Liang LI4
), Ruofei RONG1, Wen NIE1, Shujuan QIU2, Zhengbing LI3, Liang LI4
Received:2025-12-01
Revised:2026-01-03
Online:2026-01-13
Contact:
Kai WEN, Jing GONG
摘要:
在“双碳”目标背景下,利用既有成品油管道顺序输送甲醇具有显著的经济与减排优势。然而,甲醇与柴油在常温呈强不相溶特性,在低流速及非稳态工况下易发生重力分层,界面速度差显著放大混油风险。针对这一问题,提出界面滑移诱导混油机理,建立沿程混油与滑移混油分解框架,构建一维双流体-滑移耦合模型,将混油长度分为轴向等效扩散项与滑移对流项,并基于Reynolds数和密度Froude数分析流速变化对掺混机理的影响。结合Ri与K-H判据判据评估地形风险,并提出汽油隔离的三段批序及停输/再启动调控策略,为成品油管道增输甲醇的设计与运行调控提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
付宁, 温凯, 宫敬, 戎若飞, 聂文, 邱姝娟, 李政兵, 李亮. 低流速下甲醇-柴油顺序输送混油机理研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251352.
Ning FU, Kai WEN, Jing GONG, Ruofei RONG, Wen NIE, Shujuan QIU, Zhengbing LI, Liang LI. Investigation of the mixing mechanisms in sequential batch transportation of methanol and diesel at low flow velocity[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251352.
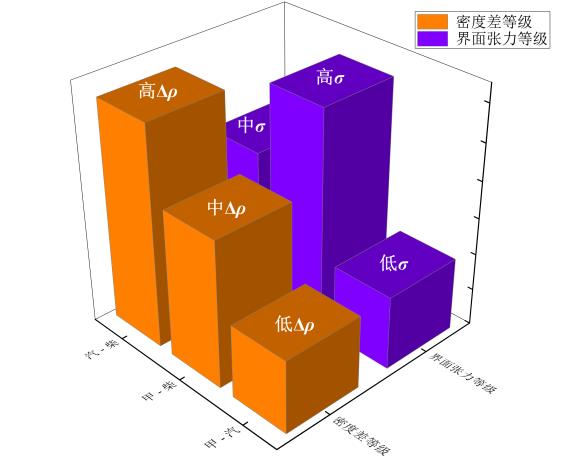
图1 不同体系的典型密度与界面张力等级关系图注:等级划分阈值为∣Δρ∣<20 kg·m-3为低,20~100 kg·m-3为中,>100 kg·m-3为高;∣σ∣<5 mN·m-1为低,5~20 mN·m-1为中,>20 mN·m-1为高。各体系典型值取自本文1.1节给出的物性范围及相关文献量级统计,用于相对位置与机理敏感性说明。
Fig.1 Diagram of the relationship between typical density and interfacial tension grades in different systems
停输时间t (h) | Deff (m2·s-1) | 初始混油带宽度Lmix,0 (m) | 停输阶段沿程混油宽度增量ΔLax (m) | 总混油带宽度为Lmix (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 5.0 | 200 | 624.2 | 824.2 |
| 2 | 5.0 | 200 | 1248.4 | 1448.4 |
| 8 | 5.0 | 200 | 2496.9 | 2696.9 |
表1 停输阶段不同停输时间下沿程混油带宽度算例
Table 1 Calculation examples of axial mixing-band width under different shutdown durations
停输时间t (h) | Deff (m2·s-1) | 初始混油带宽度Lmix,0 (m) | 停输阶段沿程混油宽度增量ΔLax (m) | 总混油带宽度为Lmix (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 5.0 | 200 | 624.2 | 824.2 |
| 2 | 5.0 | 200 | 1248.4 | 1448.4 |
| 8 | 5.0 | 200 | 2496.9 | 2696.9 |
| 工况编号 | 工况类型 | us (m·s-1) | trst (s) | ΔLconv ≈ Lslip (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 中等流量 | 0.10 | 600 | 60 |
| A2 | 中等流量 | 0.10 | 1800 | 180 |
| B1 | 较大流量 | 0.20 | 600 | 120 |
| B2 | 较大流量 | 0.20 | 1800 | 360 |
表2 再启动阶段滑移速度与滑移混油对流延伸量算例
Table 2 Calculation examples of slip velocity and convective extension during the restart phase
| 工况编号 | 工况类型 | us (m·s-1) | trst (s) | ΔLconv ≈ Lslip (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 中等流量 | 0.10 | 600 | 60 |
| A2 | 中等流量 | 0.10 | 1800 | 180 |
| B1 | 较大流量 | 0.20 | 600 | 120 |
| B2 | 较大流量 | 0.20 | 1800 | 360 |
| Ri数范围 | 分层强度等级 |
|---|---|
| Ri < 0.25 | 不稳定分层,速度切变主导,界面容易被破坏 |
| 0.25 ≤ Ri < 1 | 弱分层 |
| 1 ≤ Ri < 10 | 中等分层 |
| Ri ≥ 10 | 强分层,浮力主导,垂向运动受抑制 |
表3 分层强度判断经验区间表
Table 3 Table of Empirical Intervals for Judging Stratification Intensity
| Ri数范围 | 分层强度等级 |
|---|---|
| Ri < 0.25 | 不稳定分层,速度切变主导,界面容易被破坏 |
| 0.25 ≤ Ri < 1 | 弱分层 |
| 1 ≤ Ri < 10 | 中等分层 |
| Ri ≥ 10 | 强分层,浮力主导,垂向运动受抑制 |
倾角θ (°) | 工况 | 滑移速度us (m·s-1) | Richardson数Ri | 界面状态(定性) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | A | 0.020 | 1.04×103 | 强分层,界面稳定 |
| 2 | B | 0.040 | 2.60×102 | 强分层,界面稳定 |
| 5 | A | 0.050 | 1.66×102 | 强分层,界面稳定 |
| 5 | B | 0.100 | 4.14×101 | 强分层,需结合K-H判据进一步判断剪切失稳风险 |
| 10 | A | 0.100 | 4.09×101 | 强分层,需结合K-H判据进一步判断剪切失稳风险 |
| 10 | B | 0.200 | 1.02×101 | 强分层(临界附近),需结合K-H判据进一步判断剪切失稳风险 |
| 15 | A | 0.149 | 1.81×101 | 强分层,界面总体稳定 |
| 15 | B | 0.298 | 4.52 | 中等分层,易出现波状界面,局部掺混风险上升 |
表4 倾角-滑移速度-Ri数算例
Table 4 Calculation Examples of Inclination Angle - Slip Velocity - Ri Number
倾角θ (°) | 工况 | 滑移速度us (m·s-1) | Richardson数Ri | 界面状态(定性) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | A | 0.020 | 1.04×103 | 强分层,界面稳定 |
| 2 | B | 0.040 | 2.60×102 | 强分层,界面稳定 |
| 5 | A | 0.050 | 1.66×102 | 强分层,界面稳定 |
| 5 | B | 0.100 | 4.14×101 | 强分层,需结合K-H判据进一步判断剪切失稳风险 |
| 10 | A | 0.100 | 4.09×101 | 强分层,需结合K-H判据进一步判断剪切失稳风险 |
| 10 | B | 0.200 | 1.02×101 | 强分层(临界附近),需结合K-H判据进一步判断剪切失稳风险 |
| 15 | A | 0.149 | 1.81×101 | 强分层,界面总体稳定 |
| 15 | B | 0.298 | 4.52 | 中等分层,易出现波状界面,局部掺混风险上升 |
| [1] | 王轶辰. 氢能全链条发展前景可期[N]. 经济日报, 2025-08-27(6). |
| Wang Y C. The promising prospect of hydrogen energy full-chain development[N]. Economic Daily, 2025-08-27(6). | |
| [2] | 周天舒, 迟东训, 艾明晔. 双碳背景下可再生能源面临的挑战及对策建议[J]. 宏观经济管理, 2022(7): 59-65. |
| Zhou T S, Chi D X, Ai M Y. Challenges of and countermeasures for renewable energy sources against the background of carbon peaking and carbon neutralization[J]. Macroeconomic Management, 2022(7): 59-65. | |
| [3] | 王梦川, 洪子鑫, 李峰, 等. 绿色甲醇产业发展现状及前景分析[J]. 国际石油经济, 2024, 32(5): 78-84. |
| Wang M C, Hong Z X, Li F, et al. Green methanol industry development status and prospect analysis[J]. International Petroleum Economics, 2024, 32(5): 78-84. | |
| [4] | 赵新月, 刘旭丹. 甲醇全产业链分析: 绿色能源转型与可持续发展前景[J]. 应用化工, 2025, 54(10): 2743-2748. |
| Zhao X Y, Liu X D. Methanol industry chain analysis: Green energy transition and sustainable development prospects[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2025, 54(10): 2743-2748. | |
| [5] | 赵赏鑫. "双碳"目标驱动下甲醇高质量发展路径与储运体系重构[J]. 油气储运, 2025, 44(9): 961-970. |
| Zhao S X. High-quality development path for methanol and reconfiguration of its storage and transportation system driven by the "dual carbon" goals[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2025, 44(9): 961-970. | |
| [6] | 陈光. 节能减排环境下的电力系统规划与重构相关问题研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013. |
| Chen G. Study on relevant issues of power system planning and reconfiguration in the environment of energy saving and emission reduction[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013. | |
| [7] | 任俊嘉, 董嘉琪. "双碳" 目标下大落差成品油管道改输绿色甲醇参数适应性问题的数值分析[J]. 化工设备与管道, 2025, 62(5): 81-91. |
| Ren J J, Dong J Q. Numerical analysis of parameter adaptability for converting green methanol from large-drop refined petroleum products pipelines under the "carbon peaking and carbon neutrality" target[J]. Process Equipment & Piping, 2025, 62(5): 81-91. | |
| [8] | 刘丙泉, 蔡丽韫, 齐鸣, 等. 甲醇单一运输运方式与多式联运经济性对比[J]. 油气储运, 2025, 44(9): 1054-1065. |
| Liu B Q, Cai L Y, Qi M, et al. Comparison of economic efficiency between single-mode and multimodal transportation of methanol[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2025, 44(9): 1054-1065. | |
| [9] | 付广涛, 涂仁福, 蔡丽韫, 等. 考虑成品油储运设施的甲醇区域多式联运系统规划优化[J]. 油气储运, 2025, 44(9): 1066-1079. |
| Fu G T, Tu R F, Cai L Y, et al. Optimization of regional methanol multimodal transport system planning considering refined oil storage and transportation facilities[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2025, 44(9): 1066-1079. | |
| [10] | 黄维和, 刘刚, 陈雷, 等. 中国成品油管道顺序输送混油研究现状与展望[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(5): 122-129. |
| Huang W H, Liu G, Chen L, et al. Current status and prospect of studies on mixed oils in batch transportation of multi-product pipelines in China[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2023, 47(5): 122-129. | |
| [11] | 马荣荣, 王雅倩. 成品油管道顺序输送现状与发展研究[J]. 辽宁化工, 2025, 54(2): 288-291. |
| Ma R R, Wang Y Q. Research status and development direction of product pipeline sequential transportation[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2025, 54(2): 288-291. | |
| [12] | 严大凡. 输油管道设计与管理[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1986: 179-180. |
| Yan D F. Design and management of oil pipeline[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1986: 179-180. | |
| [13] | Taylor G. The dispersion of matter in turbulent flow through a pipe[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1954, 223(1155): 446-468. |
| [14] | 孙健飞, 梁永图. 成品油管道顺序输送混油模型研究进展[J]. 油气储运, 2019, 38(5): 496-502. |
| Sun J F, Liang Y T. Research progress on the mixed oil models for the batch transportation in products pipeline[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2019, 38(5): 496-502. | |
| [15] | Freitas Rachid F B, Carneiro de Araujo J H, Baptista R M. Predicting mixing volumes in serial transport in pipelines[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2002, 124(2): 528-534. |
| [16] | 陈帝武, 史博会, 闫锋, 等. OLGA软件模拟甲醇-柴油顺序输送混油长度适用性分析[J]. 油气储运, 2025, 44(9): 989-997. |
| Chen D W, Shi B H, Yan F, et al. Applicability analysis of mixed oil length simulation using OLGA software for methanol-diesel batch transportation[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2025, 44(9): 989-997. | |
| [17] | 刘翠伟, 艾丽纳, 杜长慧, 等. 甲醇/柴油顺序输送混油规律模拟[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 49(2): 205-213. |
| Liu C W, Ai L N, Du C H, et al. Simulation of mixed oil law of methanol/diesel in sequential transportation[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2025, 49(2): 205-213. | |
| [18] | 黄鑫, 滕霖, 聂超飞, 等. 液氨/甲醇/成品油顺序输送技术研究进展[J]. 油气储运, 2023, 42(12): 1337-1351. |
| Huang X, Teng L, Nie C F, et al. Research progress on batch transportation technology of liquid ammonia/methanol/product oil[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2023, 42(12): 1337-1351. | |
| [19] | 刘翠伟, 杜长慧, 杨飞, 等. 甲醇-柴油顺序输送管道混油变化规律实验研究[J]. 油气储运, 2025, 44(9): 1021-1033. |
| Liu C W, Du C H, Yang F, et al. Experimental study on the variation law of mixed oil in methanol-diesel batch transportation pipelines[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2025, 44(9): 1021-1033. | |
| [20] | 赵赏鑫, 庞贵良, 邱姝娟, 等. 甲醇-成品油混合体系相溶性规律实验[J]. 油气储运, 2024, 43(11): 1239-1248. |
| Zhao S X, Pang G L, Qiu S J, et al. Experimental research on the miscibility law of methanol-product oil blending systems[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2024, 43(11): 1239-1248. | |
| [21] | 杨文, 黄尚圣, 尹鹏博, 等. 甲醇-成品油顺序输送瞬变流动与混油特性[J]. 油气储运, 2025, 44(9): 1034-1044. |
| Yang W, Huang S S, Yin P B, et al. Transient flow and mixed oil characteristics of the methanol-refined oil batch transportation[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2025, 44(9): 1034-1044. | |
| [22] | 宋进舟, 沈亮, 郭祎, 等. 成品油管道顺序输送甲醇混油界面在线检测系统及应用[J]. 油气储运, 2025, 44(9): 1012-1020. |
| Song J Z, Shen L, Guo Y, et al. Online detection system and its application for mixed-oil interfaces in batch transportation of methanol via refined oil pipelines[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2025, 44(9): 1012-1020. | |
| [23] | Lu Y, Tan R, Gao W, et al. Active Control of Natural Gas Pipeline System Based on Box-Jenkins Method[J]. Journal of Pipeline Science and Engineering, 2025: 100265. |
| [24] | 赵赏鑫, 庞贵良, 邱姝娟, 等. 成品油管道增输甲醇的工艺技术探讨[J]. 油气储运, 2025, 44(8): 874-881. |
| Zhao S X, Pang G L, Qiu S J, et al. Technical discussion on incorporating methanol transport in product oil pipelines[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2025, 44(8): 874-881. | |
| [25] | 李嘉宁, 杜胜男, 范开峰, 等. 多起伏大高差油气混输管道停输和再启动瞬态流动规律研究[J]. 辽宁石油化工大学学报, 2022, 42(2): 55-60. |
| Li J N, Du S N, Fan K F, et al. Study on the transient flow law of shutdown and restart of oil and gas mixed pipelines with multiple fluctuations and large height differences[J]. Journal of Liaoning Petrochemical University, 2022, 42(2): 55-60. | |
| [26] | Chen L, Zhao Z C, Wang Y B, et al. Study of methanol-gasoline miscibility based on molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Fuel, 2026, 406: 137251. |
| [27] | 王芳. 脂肪醇聚醚表面活性剂降低CO2驱混相压力研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2016. |
| Wang F. Study on the decrease of miscibility pressure on CO2 flooding by fatty alcohol polyether surfactant[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum (Huadong), 2016. | |
| [28] | Lu Y J, Han J X, Yang M P, et al. Molecular simulation of supercritical CO2 extracting organic matter from coal based on the technology of CO2-ECBM[J]. Energy, 2023, 266: 126393. |
| [29] | Abdulredha M M, Siti Aslina H, Luqman C A. Overview on petroleum emulsions, formation, influence and demulsification treatment techniques[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 13(1): 3403-3428. |
| [30] | Charru F, Hinch E J. 'Phase diagram' of interfacial instabilities in a two-layer Couette flow and mechanism of the long-wave instability[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2000, 414: 195-223. |
| [31] | Govindarajan R. Effect of miscibility on the linear instability of two-fluid channel flow[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2004, 30(10): 1177-1192. |
| [32] | Hickox C E. Instability due to viscosity and density stratification in axisymmetric pipe flow[J]. The Physics of Fluids, 1971, 14(2): 251-262. |
| [33] | 齐雪宇. 油水两相流动掺混及液滴运移特性研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2023. |
| Qi X Y. Investigate on entrainment and droplet transport characteristics of oil-water two-phase flow[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2023. | |
| [34] | Taylor G. The instability of liquid surfaces when accelerated in a direction perpendicular to their planes. I[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1950, 201(1065): 192-196. |
| [35] | Kundu P K, Cohen I M, Dowling D R, et al. Fluid mechanics[M]. Elsevier, 2024. |
| [36] | Hart J, Sonnenwald F, Stovin V, et al. Longitudinal dispersion in unsteady pipe flows[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2021, 147(9): 04021033. |
| [37] | Pérez Guerrero J S, Pontedeiro E M, van Genuchten M T, et al. Analytical solutions of the one-dimensional advection–dispersion solute transport equation subject to time-dependent boundary conditions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 221: 487-491. |
| [38] | 尹晓云, 李静, 申俊, 等. 停输管道再启动过程油水两相流型演变与压降变化特性[J]. 流体机械, 2025, 53(3): 17-25. |
| Yin X Y, Li J, Shen J, et al. Characteristics of oil-water two-phase flow pattern evolution and pressure drop change during restart of shutdown pipeline[J]. Fluid Machinery, 2025, 53(3): 17-25. | |
| [39] | 蒋文明, 杜仕林, 吴君强, 等. 稠油水环发生器结构优化[J]. 油气储运, 2019, 38(8): 937-943. |
| Jiang W M, Du S L, Wu J Q, et al. Structural optimization of core-annular flow generator for the heavy oil transportation[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2019, 38(8): 937-943. | |
| [40] | Ghosh S, Mandal T K, Das G, et al. Review of oil water core annular flow[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2009, 13(8): 1957-1965. |
| [41] | Turner J S, Benton E R. Buoyancy effects in fluids[J]. Physics Today, 1974, 27(3): 52-53. |
| [42] | 钱济国, 杨志伊. 磁液动密封的液-液界面稳定性分析[J]. 流体机械, 2008, 36(12): 21-23, 20. |
| Qian J G, Yang Z Y. Analysis of liquid-liquid interface stability for magnetic liquid dynamic seal[J]. Fluid Machinery, 2008, 36(12): 21-23, 20. |
| [1] | 张彬怡, 孙少东, 姚谦, 蔡文河, 张惠宇, 李成新. 煤制甲醇耦合固体氧化物燃料电池混合系统研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4658-4669. |
| [2] | 周怀荣, 伊嘉伟, 曹阿波, 郭奥雪, 王东亮, 杨勇, 杨思宇. 共电解耦合CO2间接加氢制甲醇工艺集成设计与性能评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4586-4600. |
| [3] | 解勤勤, 翁俊旗, 林振利, 叶光华, 周兴贵. 固定床反应器中甲醇制芳烃工业催化剂结构影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4487-4498. |
| [4] | 田鹏, 张忠林, 任超, 孟国超, 郝晓刚, 刘叶刚, 侯起旺, ABUDULA Abuliti, 官国清. 基于自热再生的一种低温甲醇洗工艺建模与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4601-4612. |
| [5] | 娄岚浩, 杨立鹏, 杨晓光. 锂离子电池电化学机理模型参数辨识研究综述[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4369-4382. |
| [6] | 王梦娇, 胡凯学, 孟祥铠, 江锦波, 彭旭东. 碳化硅表面微织构尺寸和面密度对滑动密封面摩擦学性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4165-4176. |
| [7] | 张淇栋, 艾立强, 马原, 吴胜宝, 王磊, 厉彦忠. 基于一维漂移流模型的低温管路预冷过程两相流动与换热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3842-3852. |
| [8] | 何晨, 陆明飞, 王令金, 许晓颖, 董鹏博, 赵文涛, 隆武强. 氨-甲醇高压混合气稀燃层流实验与模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4248-4258. |
| [9] | 周运桃, 崔丽凤, 张杰, 于富红, 李新刚, 田野. Ga2O3调控CuCeO催化CO2加氢制甲醇的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4042-4051. |
| [10] | 王子恒, 李文怀, 周嵬. 图形电极在固体氧化物燃料电池中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3153-3171. |
| [11] | 郭江悦, 常守金, 胡海涛. 水平管内甲醇流动冷凝数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2580-2588. |
| [12] | 孙睿, 王军锋, 许浩洁, 李步发, 徐雅弦. 喷雾冷却技术及其强化传热机制研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1404-1421. |
| [13] | 徐芳, 张锐, 崔达, 王擎. ReaxFF-MD揭示木质素热解反应机制的分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1253-1263. |
| [14] | 徐桂培, 孙倩, 赖洁文, 卢毅锋, 邸会芳, 黄辉, 王振兵. 电化学双电层电容器失效机理的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 951-962. |
| [15] | 万俊, 宋佳芮, 范春煌, 魏乐乐, 聂依娜, 刘琳. 高效空穴转移助力光催化碱性甲醇-水溶液制氢[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1064-1075. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号