CIESC Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (10): 4052-4061.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190578
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaofeng JIANG( ),Shicheng ZHAO,Zhong XIN(
),Shicheng ZHAO,Zhong XIN( )
)
Received:2019-05-27
Revised:2019-09-10
Online:2019-10-05
Published:2019-10-05
Contact:
Zhong XIN
通讯作者:
辛忠
作者简介:蒋晓峰(1992—),男,博士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Xiaofeng JIANG, Shicheng ZHAO, Zhong XIN. Nucleation effect of carboxylic acid modified alumina nanoparticles on polypropylene[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(10): 4052-4061.
蒋晓峰, 赵世成, 辛忠. 有机羧酸改性氧化铝纳米颗粒在聚丙烯中的成核效果研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(10): 4052-4061.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 样品 | 反应比R/ (mmol/(g Al2O3)) | ΔW/% | 接枝量Y/ (mmol/(g Al2O3)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HA-Al2O3 | 7 | 8.4 | 0.7 |
| SA-Al2O3 | 7 | 14.4 | 0.6 |
| ChA-Al2O3 | 7 | 13.2 | 1.2 |
| BA-Al2O3 | 1 | 6.9 | 0.6 |
Table 1 Overall mass loss and grafting yield of HA-Al2O3, SA-Al2O3, ChA-Al2O3 and BA-Al2O3
| 样品 | 反应比R/ (mmol/(g Al2O3)) | ΔW/% | 接枝量Y/ (mmol/(g Al2O3)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HA-Al2O3 | 7 | 8.4 | 0.7 |
| SA-Al2O3 | 7 | 14.4 | 0.6 |
| ChA-Al2O3 | 7 | 13.2 | 1.2 |
| BA-Al2O3 | 1 | 6.9 | 0.6 |
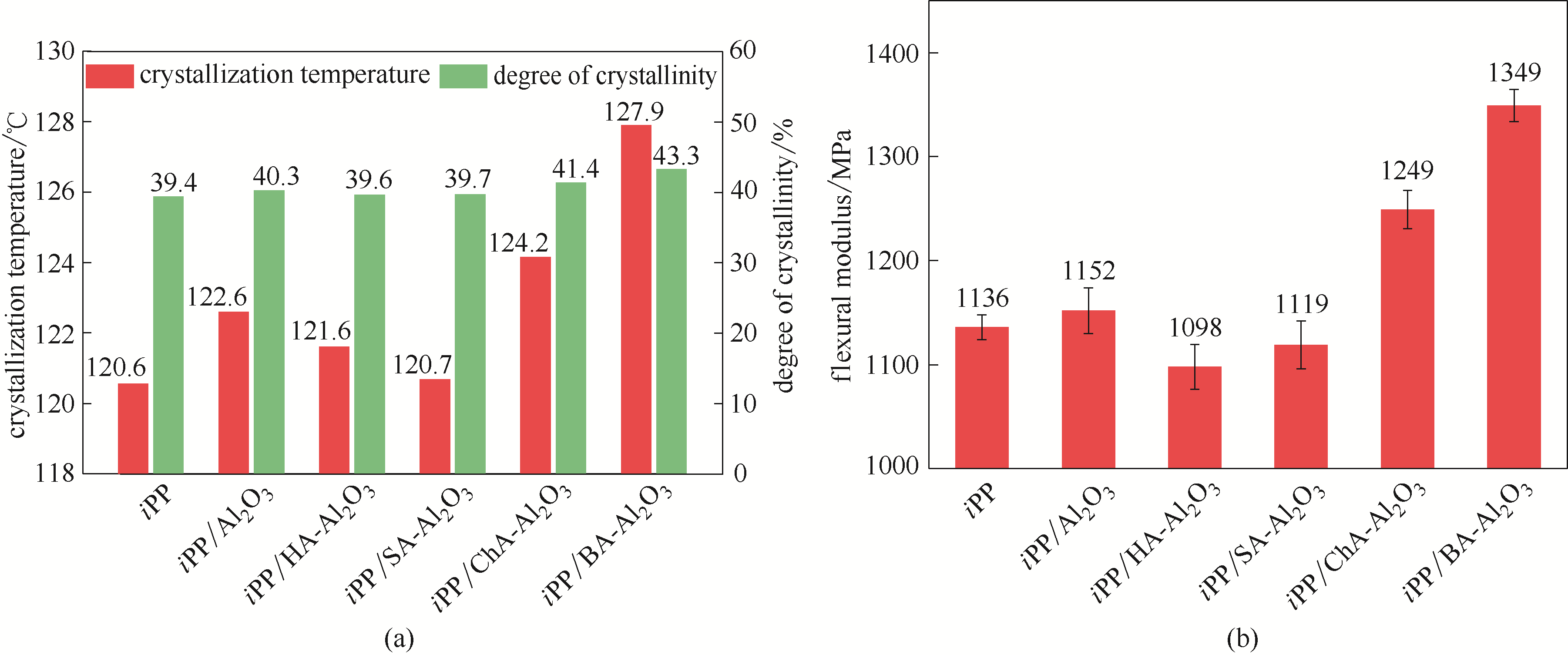
Fig.4 Effect of pristine alumina NPs, functionalized alumina NPs on crystallization temperature and degree of crystallinity (a) and flexural modulus (b) of iPP
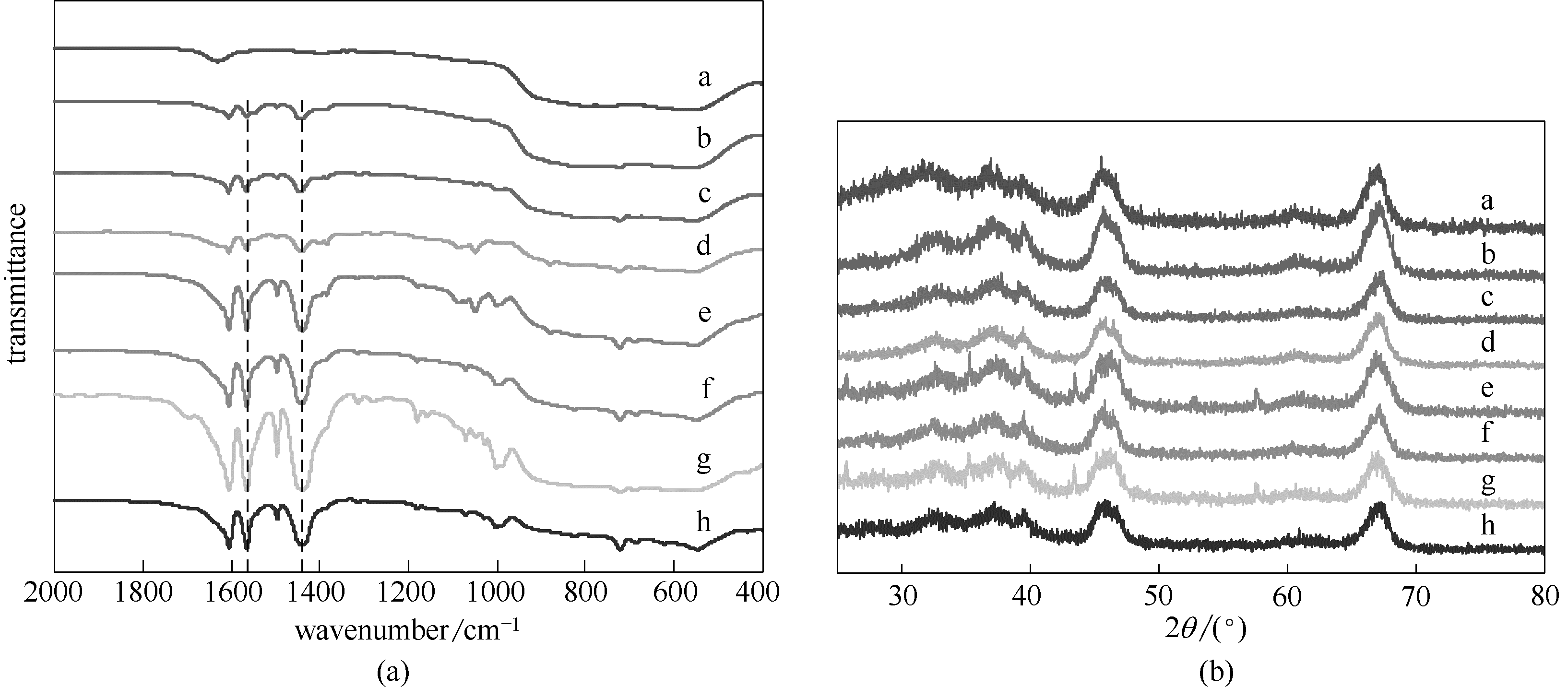
Fig.6 FTIR spectra (a) and XRD patterns (b) of pristine alumina NPs and benzoic acid functionalized alumina NPs BA-Al2O3-xa—Al2O3;b—BA-Al2O3-1;c—BA-Al2O3-2;d—BA-Al2O3-3;e—BA-Al2O3-4;f—BA-Al2O3-5;g—BA-Al2O3-6;h—BA-Al2O3-7
| 样品 | 反应比(R)/ (mmol/(g Al2O3)) | ΔW/% | 接枝量Y/ (mmol/(g Al2O3)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BA-Al2O3-1 | 1 | 6.9 | 0.6 |
| BA-Al2O3-2 | 2 | 10.0 | 0.9 |
| BA-Al2O3-3 | 3 | 13.3 | 1.3 |
| BA-Al2O3-4 | 4 | 20.9 | 2.2 |
| BA-Al2O3-5 | 5 | 23.5 | 2.5 |
| BA-Al2O3-6 | 6 | 28.7 | 3.3 |
| BA-Al2O3-7 | 7 | 30.8 | 3.6 |
Table 2 Overall mass loss and grafting yield of BA-Al2O3-x
| 样品 | 反应比(R)/ (mmol/(g Al2O3)) | ΔW/% | 接枝量Y/ (mmol/(g Al2O3)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BA-Al2O3-1 | 1 | 6.9 | 0.6 |
| BA-Al2O3-2 | 2 | 10.0 | 0.9 |
| BA-Al2O3-3 | 3 | 13.3 | 1.3 |
| BA-Al2O3-4 | 4 | 20.9 | 2.2 |
| BA-Al2O3-5 | 5 | 23.5 | 2.5 |
| BA-Al2O3-6 | 6 | 28.7 | 3.3 |
| BA-Al2O3-7 | 7 | 30.8 | 3.6 |
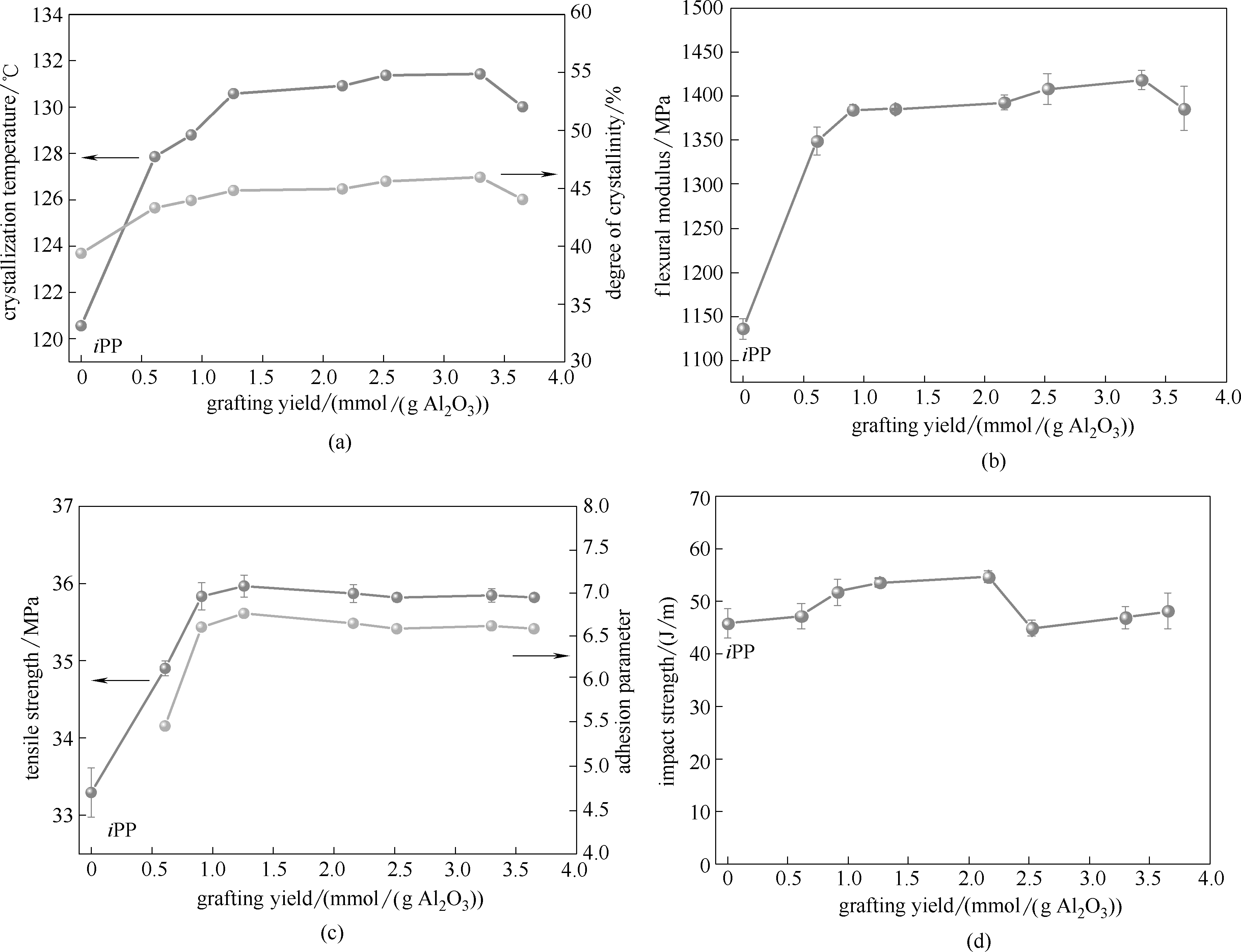
Fig.7 Effect of aromatic group grafting yield of BA-Al2O3-x on crystallization temperature, degree of crystallinity, mechanical properties and adhesion parameter of iPP
| 1 | QinW, XinZ, PanC M, et al. In situ formation of zinc phthalate as a highly dispersed β-nucleating agent for mechanically strengthened isotactic polypropylene[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 358: 1243-1252. |
| 2 | ZhaoS C, QinW, XinZ, et al. In situ generation of a self-dispersed β-nucleating agent with increased nucleation efficiency in isotactic polypropylene[J]. Polymer, 2018, 151: 84-91. |
| 3 | 石尧麒, 辛忠. α/β复合成核剂对等规聚丙烯结晶形态的影响及非等温结晶动力学[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(4): 1274-1286. |
| ShiY Q, XinZ. Crystallization morphologies and non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of isotactic polypropylene modified by α/β compounded nucleating agents[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(4): 1274-1286. | |
| 4 | 周军, 辛忠. 亚苄基缩醛在聚丙烯中溶解性和成核作用[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(3): 941-947. |
| ZhouJ, XinZ. Solubility and nucleation of benzylidene acetals in polypropylene[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(3): 941-947. | |
| 5 | 张跃飞, 辛忠. 取代芳基杂环磷酸金属盐类成核剂在等规聚丙烯中的成核效应[J]. 化工学报, 2006, 57(4): 953-958. |
| ZhangY F, XinZ. Nucleation efficiency of substituted aromatic heterocyclic phosphoric acid metal salts as nucleators for isotactic polypropylene[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering(China), 2006, 57(4): 953-958. | |
| 6 | 张恰, 赵世成, 周帅, 等. 取代芳基磷酸酯钠盐成核剂的晶体结构与聚丙烯附生结晶的过程[J]. 石油化工, 2017, 46(1): 36-43. |
| ZhangQ, ZhaoS C, ZhouS, et al. Single crystal structure of sodium phosphonate ester nucleating agents and their effects on polypropylene epitaxial crystallization[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2017, 46(1): 36-43. | |
| 7 | 周红军, 尹国强, 林轩, 等. PP/PP-g-NH2/纳米SiO2复合材料的非等温结晶[J].化工学报, 2009, 60(4): 1046-1051. |
| ZhouH J, YinG Q, LinX, et al. Nonisothermal crystallization of PP/PP-g-NH2/nano-SiO2 composites [J]. CIESC Journal, 2009, 60(4): 1046-1051. | |
| 8 | BernlandK, TervoortT, SmithP. Phase behavior and optical- and mechanical properties of the binary system isotactic polypropylene and the nucleating/clarifying agent 1,2,3-trideoxy-4,6:5,7-bis--[(4-propylphenyl) methylene]-nonitol[J]. Polymer, 2009, 50(11): 2460-2464. |
| 9 | GuiQ, XinZ, ZhuW, et al. Effects of an organic phosphorus nucleating agent on crystallization behaviors and mechanical properties of poly (propylene)[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2003, 88(2): 297-301. |
| 10 | MathieuC, ThierryA, WittmannJ, et al. “Multiple” nucleation of the (010) contact face of isotactic polypropylene, α phase[J]. Polymer, 2000, 41(19): 7241-7253. |
| 11 | MasirekR, PiorkowskaE. Nucleation of crystallization in isotactic polypropylene and polyoxymethylene with poly(tetrafluoroethylene) particles[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2010, 46(7): 1436-1445. |
| 12 | HanZ, FinaA. Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotubes and their polymer nanocomposites: a review[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2011, 36(7): 914-944. |
| 13 | GongJ, NiuR, WenX, et al. Synergistic effect of carbon fibers and carbon nanotubes on improving thermal stability and flame retardancy of polypropylene: a combination of a physical network and chemical crosslinking[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 5(8): 5484-5493. |
| 14 | SongP, CaoZ, CaiY, et al. Fabrication of exfoliated graphene-based polypropylene nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties[J]. Polymer, 2011, 52(18): 4001-4010. |
| 15 | YangS, LiY, LiangY Y, et al. Graphene oxide induced isotactic polypropylene crystallization: role of structural reduction[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(28): 23930-23941. |
| 16 | ZhaoH, LiR K. Crystallization, mechanical, and fracture behaviors of spherical alumina-filled polypropylene nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics, 2005, 43(24): 3652-3664. |
| 17 | NagendraB, MohanK, GowdEB. Polypropylene/layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanocomposites: influence of LDH particle size on the crystallization behavior of polypropylene[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(23): 12399-12410. |
| 18 | QiuL, GaoY, YanX, et al. Morphology-dependent performance of Mg3AlCO3 layered double hydroxide as a nanofiller for polypropylene nanocomposites[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(64): 51900-51911. |
| 19 | MoniruzzamanM, WineyK I. Polymer nanocomposites containing carbon nanotubes[J]. Macromolecules, 2006, 39(16): 5194-5205. |
| 20 | LiangY Y, XuJ Z, LiuX Y, et al. Role of surface chemical groups on carbon nanotubes in nucleation forpolymer crystallization: Interfacial interaction and steric effect[J]. Polymer, 2013, 54(23): 6479-6488. |
| 21 | NingN, FuS, ZhangW, et al. Realizing the enhancement of interfacial interaction in semicrystalline polymer/filler composites via interfacial crystallization[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2012, 37(10): 1425-1455. |
| 22 | PedrazzoliD, KhumaloV, Karger-KocsisJ, et al. Thermal, viscoelastic and mechanical behavior of polypropylene with synthetic boehmite alumina nanoparticles[J]. Polymer Testing, 2014, 35: 92-100. |
| 23 | EbengouR H. Adsorption as a mechanism for nucleating activity: a thermodynamic explanation[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B Polymer Physics, 2015, 35(9): 1333-1338. |
| 24 | SmithT L, MasilamaniD, LongK B, et al. The mechanism of action of sugar acetals as nucleating agents for polypropylene[J]. Macromolecules, 1994, 27(12): 3147-3155. |
| 25 | ManiM R, ChellaswamyR, MaratheY N, et al. The role of the molecular structure of carboxylate-alumoxanes in the enhanced nucleation of polypropylene[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(49): 10026-10029. |
| 26 | YangR, DingL, ChenW, et al. Chain folding in main-chain liquid crystalline polyester with strong π-π interaction: an efficient β-nucleating agent for isotactic polypropylene[J]. Macromolecules, 2017, 50(4): 1610-1617. |
| 27 | JiangX F, ZhaoS C, MengX, et al. Effect of the metal phenylphosphonates on the nonisothermal crystallization and performance of isotactic polypropylene[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics, 2019, 57(3): 161-173. |
| 28 | LuK, GrossiordN, KoningC E, et al. Carbon nanotube/isotactic polypropylene composites prepared by latex technology: morphology analysis of CNT-induced nucleation[J]. Macromolecules, 2008, 41(21): 8081-8085. |
| 29 | JiangX F, ZhangW X, ZhaoS C, et al. Effect of benzoic acid surface modified alumina nanoparticles on the mechanical properties and crystallization behavior of isotactic polypropylene nanocomposites[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(37): 20790-20800. |
| 30 | MohanR M, RameshC, MaratheY N, et al. The role of the molecular structure of carboxylate-alumoxanes in the enhanced nucleation of polypropylene[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(49): 10026-10029. |
| 31 | AnayaS, SerranoB, HerreroB, et al. γ-Alumina modification with long chain carboxylic acid surface nanocrystals for biocompatible polysulfone nanocomposites[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(16): 14460-14468. |
| 32 | AlexanderS, EastoeJ, LordA M, et al. Branched hydrocarbon low surface energy materials for superhydrophobic nanoparticle derived surfaces[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(1): 660-666. |
| 33 | DerakhshanA A, RajabiL, KarimnezhadH. Morphology and production mechanism of the functionalized carboxylate alumoxane micro and nanostructures[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 225: 156-166. |
| 34 | FuS Y, FengX Q, LaukeB, et al. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate-polymer composites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2008, 39(6): 933-961. |
| 35 | 张以河, 付绍云, 李国耀, 等. 聚合物基纳米复合材料的增强增韧机理[J]. 高技术通讯, 2004, 14(5): 99-105. |
| ZhangY H, FuS Y, LiG Y, et al. Strengthening and toughening mechanisms of polymer based nanocomposites[J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 2004, 14(5): 99-105. | |
| 36 | ZhangQ X, YuZ Z, XieX L, et al. Crystallization and impact energy of polypropylene/CaCO3 nanocomposites with nonionic modifier[J]. Polymer, 2004, 45(17): 5985-5994. |
| [1] | Qi WANG, Bin ZHANG, Xiaoxin ZHANG, Hujian WU, Haitao ZHAN, Tao WANG. Synthesis of isoxepac and 2-ethylanthraquinone catalyzed by chloroaluminate-triethylamine ionic liquid/P2O5 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 245-249. |
| [2] | Rubin ZENG, Zhongjie SHEN, Qinfeng LIANG, Jianliang XU, Zhenghua DAI, Haifeng LIU. Study of the sintering mechanism of Fe2O3 nanoparticles based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [3] | Xingzhi HU, Haoyan ZHANG, Jingkun ZHUANG, Yuqing FAN, Kaiyin ZHANG, Jun XIANG. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of carbon nanofibers embedded with ultra-small CeO2 nanoparticles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [4] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [5] | Ao ZHANG, Yingwu LUO. Low modulus, high elasticity and high peel adhesion acrylate pressure sensitive adhesives [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3079-3092. |
| [6] | Bin LI, Zhenghu XU, Shuang JIANG, Tianyong ZHANG. Clean and efficient synthesis of accelerator CBS by hydrogen peroxide catalytic oxidation method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2919-2925. |
| [7] | Yuming TU, Gaoyan SHAO, Jianjie CHEN, Feng LIU, Shichao TIAN, Zhiyong ZHOU, Zhongqi REN. Advances in the design, synthesis and application of calcium-based catalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2717-2734. |
| [8] | Tan ZHANG, Guang LIU, Jinping LI, Yuhan SUN. Performance regulation strategies of Ru-based nitrogen reduction electrocatalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [9] | Bin CAI, Xiaolin ZHANG, Qian LUO, Jiangtao DANG, Liyuan ZUO, Xinmei LIU. Research progress of conductive thin film materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2308-2321. |
| [10] | Yong LI, Jiaqi GAO, Chao DU, Yali ZHAO, Boqiong LI, Qianqian SHEN, Husheng JIA, Jinbo XUE. Construction of Ni@C@TiO2 core-shell dual-heterojunctions for advanced photo-thermal catalytic hydrogen generation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2458-2467. |
| [11] | Juhui CHEN, Qian ZHANG, Lingfeng SHU, Dan LI, Xin XU, Xiaogang LIU, Chenxi ZHAO, Xifeng CAO. Study on flow characteristics of nanoparticles in a rotating fluidized bed based on DEM method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2374-2381. |
| [12] | Shaoyun CHEN, Dong XU, Long CHEN, Yu ZHANG, Yuanfang ZHANG, Qingliang YOU, Chenglong HU, Jian CHEN. Preparation and adsorption properties of monolayer polyaniline microsphere arrays [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2228-2238. |
| [13] | Jialin DAI, Weidong BI, Yumei YONG, Wenqiang CHEN, Hanyang MO, Bing SUN, Chao YANG. Effect of thermophysical properties on the heat transfer characteristics of solid-liquid phase change for composite PCMs [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1914-1927. |
| [14] | Hao WANG, Siyang TANG, Shan ZHONG, Bin LIANG. An investigation of the enhancing effect of solid particle surface on the CO2 desorption behavior in chemical sorption process with MEA solution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1539-1548. |
| [15] | Ruiqi LIU, Xitong ZHOU, Yue ZHANG, Ying HE, Jing GAO, Li MA. The construction and application of biosensor based on gold nanoparticles loaded SiO2-nanoflowers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1247-1259. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||