CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (1): 170-191.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221071
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xun JIAO1( ), Cheng TONG1, Cunpu LI1,2(
), Cheng TONG1, Cunpu LI1,2( ), Zidong WEI1,2(
), Zidong WEI1,2( )
)
Received:2022-08-01
Revised:2022-12-12
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
Cunpu LI, Zidong WEI
焦巡1( ), 童成1, 李存璞1,2(
), 童成1, 李存璞1,2( ), 魏子栋1,2(
), 魏子栋1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
李存璞,魏子栋
作者简介:焦巡(1995—),女,博士研究生,20211801052@cqu.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xun JIAO, Cheng TONG, Cunpu LI, Zidong WEI. Kinetic regulation strategies in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 170-191.
焦巡, 童成, 李存璞, 魏子栋. 锂硫电池的动力学调控策略[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 170-191.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
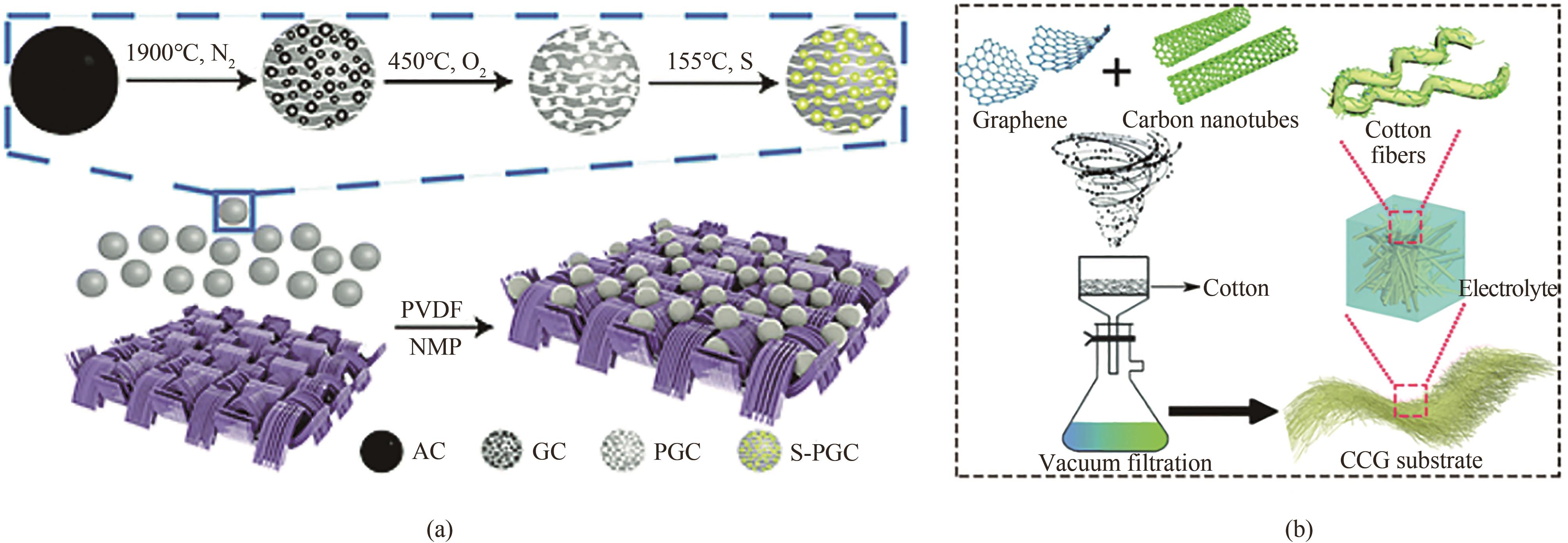
Fig.2 (a) Schematic illustration of the procedure for fabricating S-PGC-CFF cathode and the microstructures of each component[46]; (b) Schematic of the CCG substrate preparation and its corresponding configurations[48]
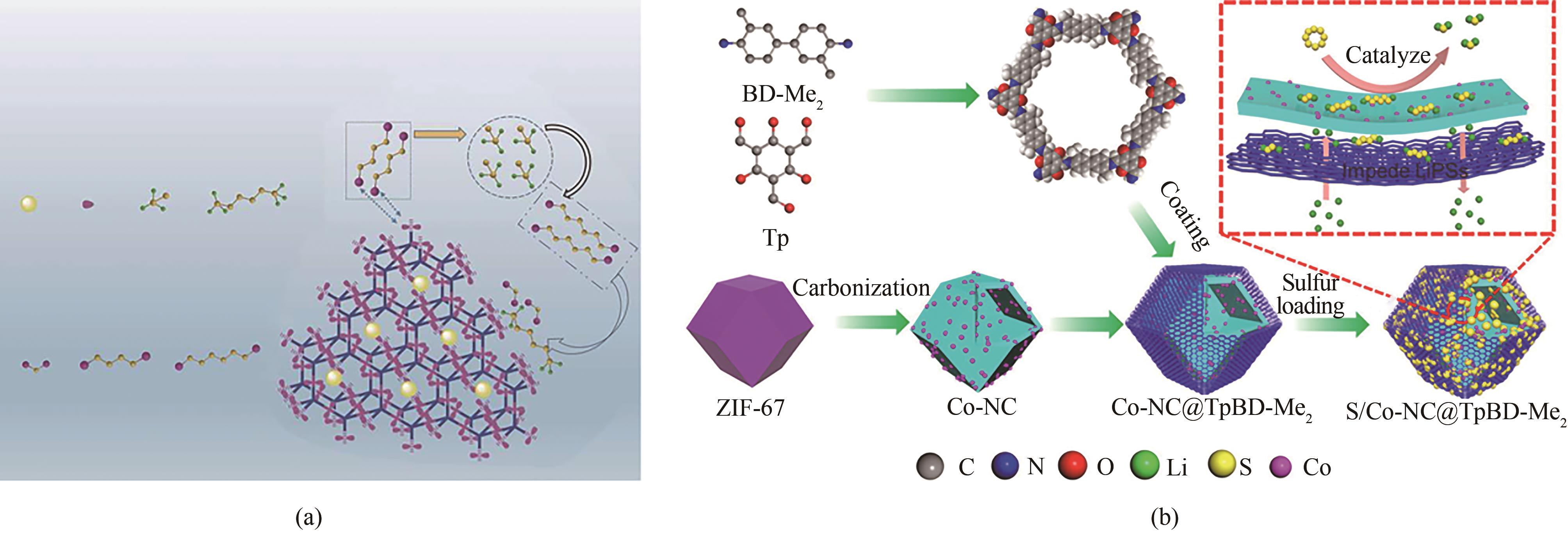
Fig.4 (a) Schematic illustration of the interactions between polysulfides and hydroxyl groups[57]; (b) Preparation procedure of Co-NC@TpBD-Me2 cathode and its working mechanism as sulfur cathode[58]
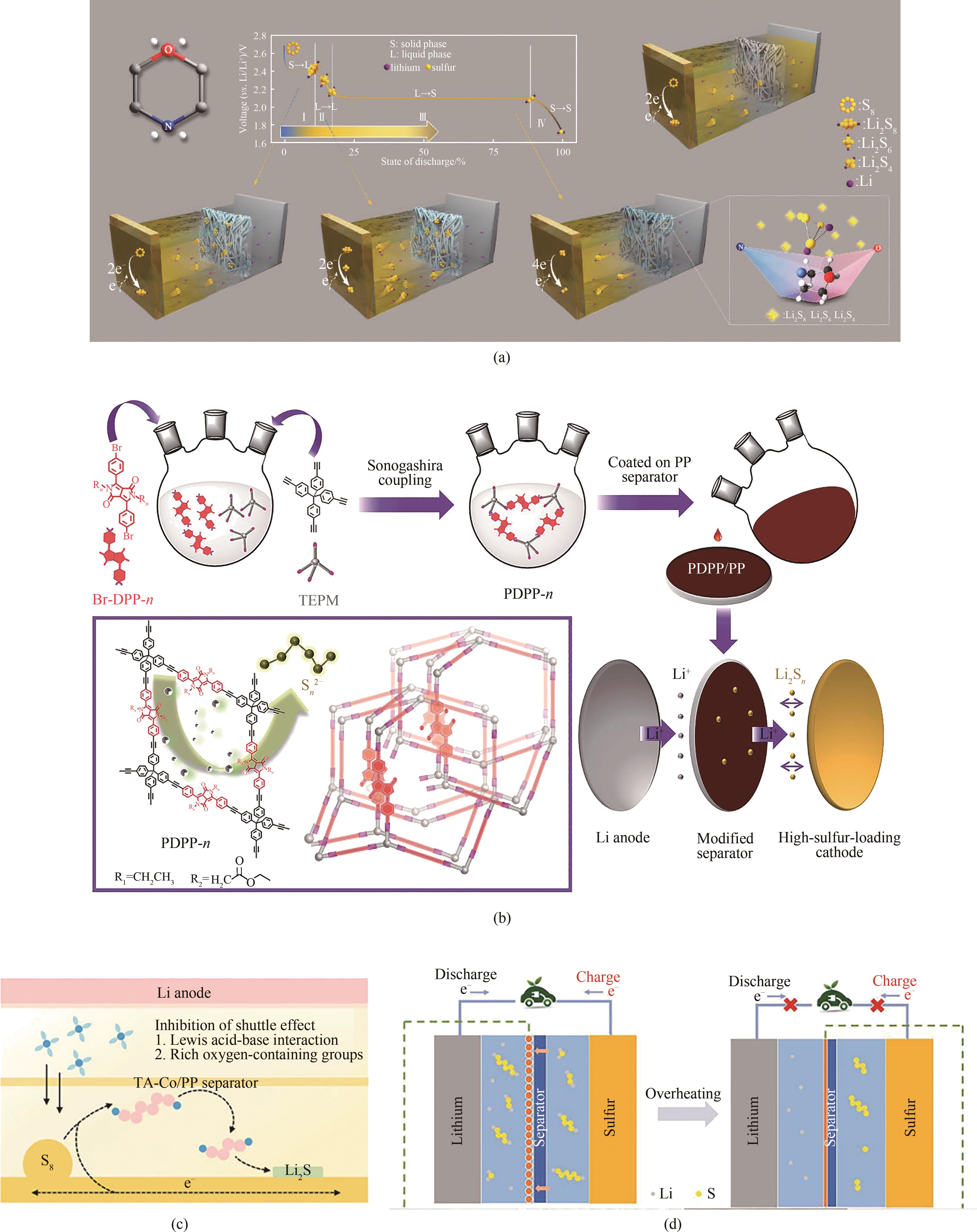
Fig.5 (a) Chemical structure of MP and PP-C-St-MP diaphragm for reversible clinching effect[62]; (b) Schematic diagram of PDPP modified separator and its effect in Li-S battery[63]; (c) Schematic diagram of TA-Co separator in Li-S battery[64]; (d) Schematic illustration of the Li-S battery with EVA microspheres-coated separators[65]
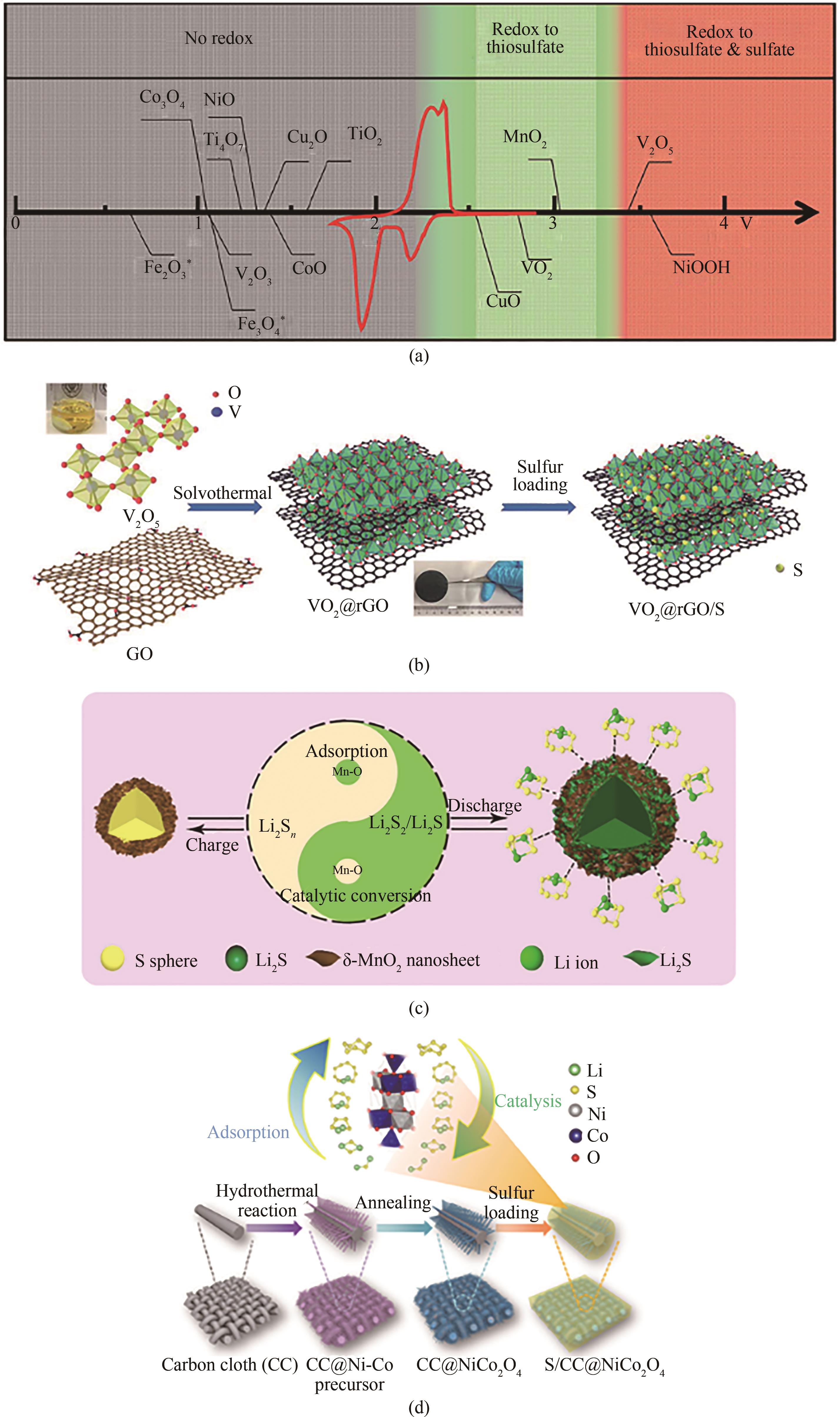
Fig.6 (a) Chemical reactivity of different metal oxides with LiPSs as a function of redox potential versus Li/Li+, superimposed with a typical Li-S cyclic voltammetry curve (shown in red)[69]; (b) Schematic of the fabrication processes of VO2@rGO/S product[70]; (c) Catalytic conversion mechanism of ultrathin δ-MnO2 nanosheets in the core-shell structure[72]; (d) Schematic of the synthesis steps for the S/CC@NiCo2O4 composite, the NiCo2O4 nanofiber arrays can effectively adsorb and catalyze the conversion reaction of LiPSs[73]
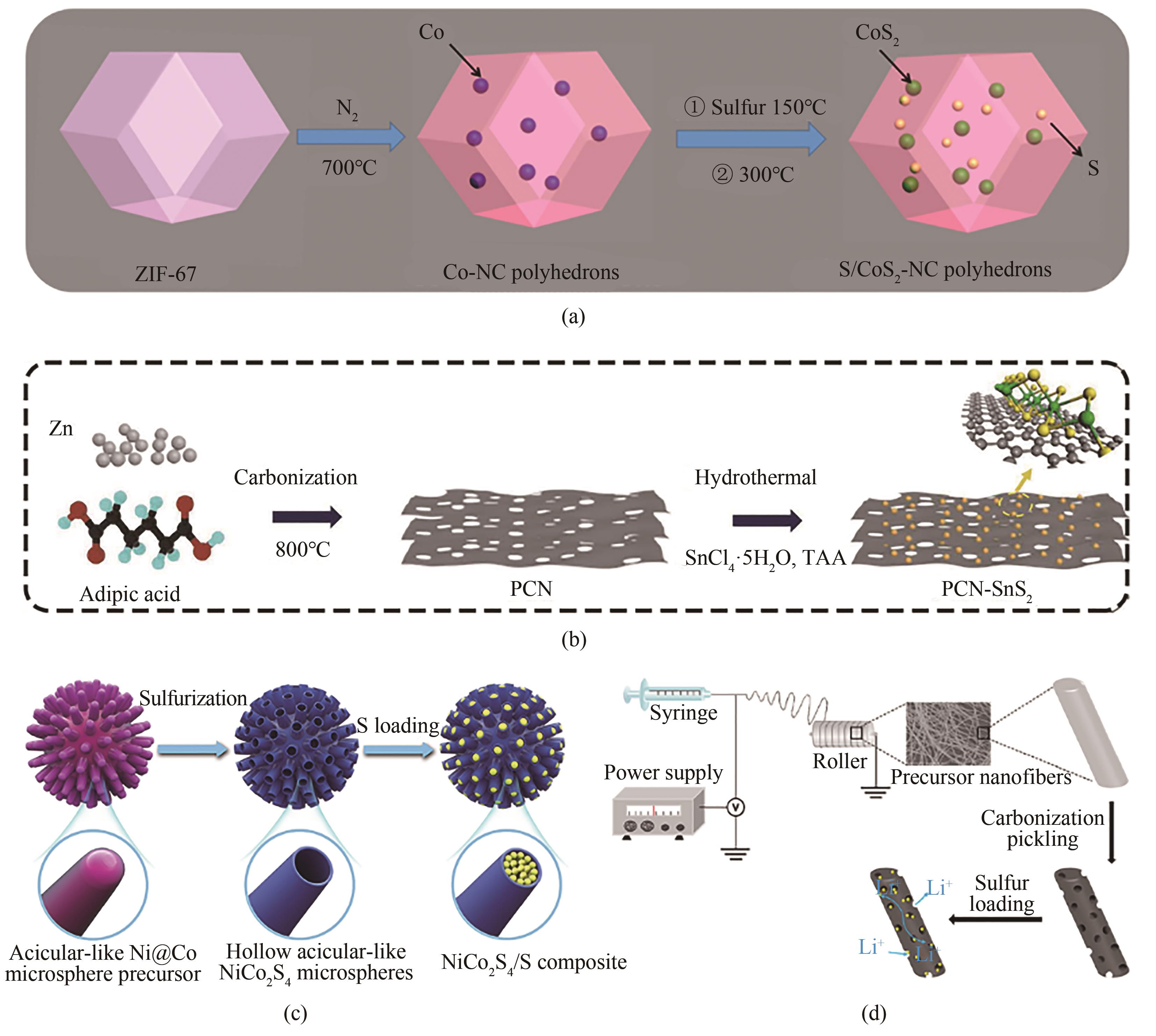
Fig.7 (a) Schematic illustration of the synthesis process of S/CoS2-NC composites[74]; (b) Schematic illustration of the preparation of PCN-SnS2 composites[75]; (c) Schematic illustration of the synthetic processes of NiCo2S4/S composite[76]; (d) Preparation of MoS2@CNF and S@MoS2@CNF composite[77]
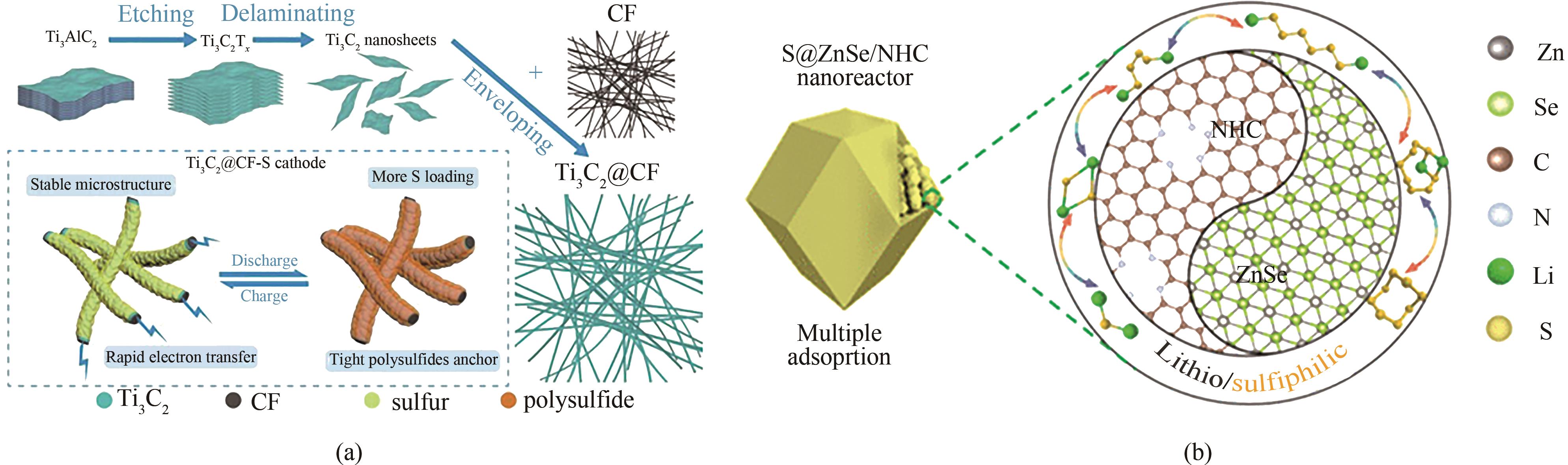
Fig.9 (a) Schematic illustration of Ti3C2@CF preparation and as a multifunctional cathode material to ameliorate the performance of Li-S batteries[80]; (b) Schematic diagram of the effect of S@ZnSe/NHC cathode on Li-S batteries[81]

Fig.10 (a)—(c) The role of perovskite promoter on LiPSs suppression and Li2S regulation in a working Li-S battery and the crystal structure of Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3-δ PrNP[82]; (d) Schematic illustration of the Li2S nucleation and growth on routine conductive surface (left) and on conductive and catalytic nanotriple-phase interface with uniformly distributed nucleation sites (right)[83]; (e) Schematic illustration of polysulfide redox reaction and Li2S nucleation[83]
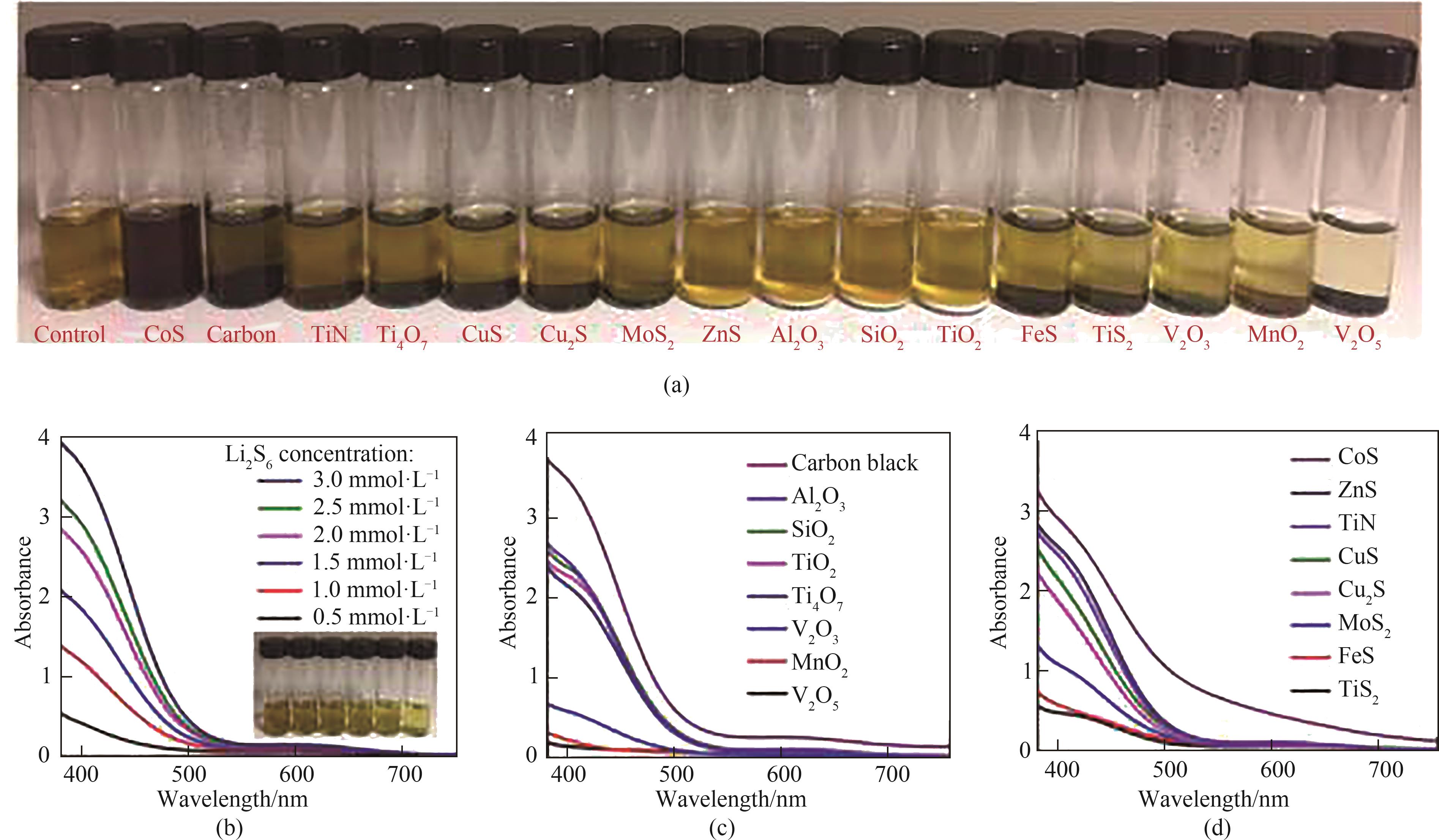
Fig.11 Li2S6 polysulfide adsorption test: (a) Optical photos of candidate materials; (b) UV-Vis data of varying concentrations of Li2S6 in DOL/DME solution without candidate materials; (c), (d) UV-Vis data of candidate materials added in 3.0 mmol·L-1 Li2S6[84]

Fig.13 Dimensionless transient profiles of MoO2 (a), α-MoC (b) and MoO2/α-MoC (c) at 2.09 V; SEM images of MoO2, α-MoC and, MoO2/α-MoC electrodes after discharged to maximum current [(d)—(f)] and after Li2S deposition [(g)—(i)][89]

Fig.14 (a) Liquid-phase LiPSs are strongly adsorbed by Co9S8 and therefore cannot be transferred to MoS2 to accomplish fast conversion; (b) Sulfur vacancies can harmonize the chemisorption of components to uniformly adsorb LiPSs; (c)—(e) CV curves within the voltage range of 1.6—2.8 V at different sweep rates of CMG-L, CMG-M and CMG-H; (f) The NTR values of CMG-L, CMG-M and CMG-H at different sweep rates; (g) Long cycle performances of CMG-L, CMG-M and CMG-H at 0.5 C[91]
| 1 | Armand M, Tarascon J M. Building better batteries[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 652-657. |
| 2 | Palacín M R, de Guibert A. Why do batteries fail?[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6273): 1253292. |
| 3 | Olabi A G, Onumaegbu C, Wilberforce T, et al. Critical review of energy storage systems[J]. Energy, 2021, 214: 118987. |
| 4 | Manthiram A. An outlook on lithium ion battery technology[J]. ACS Central Science, 2017, 3(10): 1063-1069. |
| 5 | Yoshino A. The birth of the lithium-ion battery[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(24): 5798-5800. |
| 6 | Manthiram A, Fu Y, Su Y S. Challenges and prospects of lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2013, 46(5): 1125-1134. |
| 7 | Manthiram A, Chung S H, Zu C. Lithium-sulfur batteries: progress and prospects[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(12): 1980-2006. |
| 8 | Kim J, Lee D J, Jung H G, et al. An advanced lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2013, 23(8): 1076-1080. |
| 9 | Li T, Bai X, Gulzar U, et al. A comprehensive understanding of lithium-sulfur battery technology[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(32): 1901730. |
| 10 | Evers S, Nazar L F. New approaches for high energy density lithium-sulfur battery cathodes[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2013, 46(5): 1135-1143. |
| 11 | Li G R, Wang S, Zhang Y N, et al. Revisiting the role of polysulfides in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(22): 1705590. |
| 12 | Kim S J, Kim K, Park J, et al. Role and potential of metal sulfide catalysts in lithium-sulfur battery applications[J]. ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(10): 2373-2387. |
| 13 | Hu Y, Chen W, Lei T Y, et al. Strategies toward high-loading lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(17): 2000082. |
| 14 | Nazar L F, Cuisinier M, Pang Q. Lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. MRS Bulletin, 2014, 39(5): 436-442. |
| 15 | Fang R P, Zhao S Y, Sun Z H, et al. More reliable lithium-sulfur batteries: status, solutions and prospects[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(48): 1606823. |
| 16 | Seh Z W, Sun Y, Zhang Q, et al. Designing high-energy lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016, 45(20): 5605-5634. |
| 17 | Kolosnitsyn V S, Karaseva E V. Lithium-sulfur batteries: problems and solutions[J]. Russian Journal of Electrochemistry, 2008, 44(5): 506-509. |
| 18 | Yang X F, Li X, Adair K, et al. Structural design of lithium-sulfur batteries: from fundamental research to practical application[J]. Electrochemical Energy Reviews, 2018, 1(3): 239-293. |
| 19 | Bhargav A, He J, Gupta A, et al. Lithium-sulfur batteries: attaining the critical metrics[J]. Joule, 2020, 4(2): 285-291. |
| 20 | Yan J, Liu X, Li B. Capacity fade analysis of sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2016, 3(12): 1600101. |
| 21 | 李存璞, 王建川, 魏子栋. 电化学反应器隔膜材料的分子设计与介尺度策略[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(10): 4490-4501. |
| Li C P, Wang J C, Wei Z D. Mesoscopic strategies and molecular design of diaphragm for electrochemical reactors[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(10): 4490-4501. | |
| 22 | Chen Y, Wang T Y, Tian H J, et al. Advances in lithium-sulfur batteries: from academic research to commercial viability[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(29): 2003666. |
| 23 | Zheng C, Niu S, Lv W, et al. Propelling polysulfides transformation for high-rate and long-life lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 33: 306-312. |
| 24 | Li G, Chen Z, Lu J. Lithium-sulfur batteries for commercial applications[J]. Chem, 2018, 4(1): 3-7. |
| 25 | Peng H J, Huang J Q, Cheng X B, et al. Review on high-loading and high-energy lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(24): 1700260. |
| 26 | Zhao M, Li B Q, Chen X, et al. Redox comediation with organopolysulfides in working lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chem, 2020, 6(12): 3297-3311. |
| 27 | Liang X, Hart C, Pang Q, et al. A highly efficient polysulfide mediator for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nature communications, 2015, 6(1): 1-8. |
| 28 | Huang L, Li J J, Liu B, et al. Electrode design for lithium-sulfur batteries: problems and solutions[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(22): 1910375. |
| 29 | 高希雅, 邓子华, 李存璞, 等. 锂硫电池中的催化应用[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(9): 5073-5087. |
| Gao X Y, Deng Z H, Li C P, et al. Catalytic application in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(9): 5073-5087. | |
| 30 | Liu D H, Zhang C, Zhou G M, et al. Catalytic effects in lithium-sulfur batteries: promoted sulfur transformation and reduced shuttle effect[J]. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(1): 1700270. |
| 31 | Peres-Benito J F. Iron (Ⅲ)-hydrogen peroxide reaction: kinetic evidence of a hydroxyl-mediated chain mechanism[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2004, 108(22): 4853-4858. |
| 32 | Manthiram A, Fu Y, Chung S H, et al. Rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(23): 11751-11787. |
| 33 | Huang S, Wang Z, Lim Y V, et al. Recent advances in heterostructure engineering for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(10): 2003689. |
| 34 | Dong Q, Shen R P, Li C P, et al. Construction of soft base tongs on separator to grasp polysulfides from shuttling in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Small, 2018, 14(52): 1804277. |
| 35 | Wang H L, Yang Y, Liang Y Y, et al. Graphene-wrapped sulfur particles as a rechargeable lithium-sulfur battery cathode material with high capacity and cycling stability[J]. Nano Letters, 2011, 11(7): 2644-2647. |
| 36 | Xu G Y, Ding B, Pan J, et al. High performance lithium-sulfur batteries: advances and challenges[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(32): 12662-12676. |
| 37 | Wang P, Xi B J, Huang M, et al. Emerging catalysts to promote kinetics of lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(7): 2002893. |
| 38 | Lin Z, Liu Z C, Fu W J, et al. Lithium polysulfidophosphates: a family of lithium-conducting sulfur-rich compounds for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(29): 7460-7463. |
| 39 | Zhang X, Xie H, Kim C S, et al. Advances in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Materials Science and Engineering R: Reports, 2017, 121: 1-29. |
| 40 | Hou T Z, Xu W T, Chen X, et al. Lithium bond chemistry in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 129(28): 8290-8294. |
| 41 | Yin Y X, Xin S, Guo Y G, et al. Lithium-sulfur batteries: electrochemistry, materials, and prospects[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(50): 13186-13200. |
| 42 | Fan X J, Sun W W, Meng F C, et al. Advanced chemical strategies for lithium-sulfur batteries: a review[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2018, 3(1): 2-19. |
| 43 | Cao J, Chen C, Zhao Q, et al. A flexible nanostructured paper of a reduced graphene oxide-sulfur composite for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries with unconventional configurations[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(43): 9629-9636. |
| 44 | Zhou G, Paek E, Hwang G S, et al. Long-life Li/polysulphide batteries with high sulphur loading enabled by lightweight three-dimensional nitrogen/sulphur-codoped graphene sponge[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 1-11. |
| 45 | Li Z, Zhang J T, Chen Y M, et al. Pie-like electrode design for high-energy density lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 1-8. |
| 46 | Chen H, Hong H F, Zhang X, et al. Integration of porous graphitic carbon and carbon fiber framework for ultrahigh sulfur-loading lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2022, 51(8): 3357-3365. |
| 47 | Cao D X, Jiao Y C, Cai Q F, et al. Stable lithium-sulfur full cells enabled by dual functional and interconnected mesocarbon arrays[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(7): 3289-3297. |
| 48 | Wu Y, Wang C, Yang Z W, et al. Designing conductive networks of hybrid carbon enables stable and long-lifespan cotton-fiber-based lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(55): 34955-34962. |
| 49 | Shen Z H, Jin X, Tian J M, et al. Cation-doped ZnS catalysts for polysulfide conversion in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2022, 5(6): 555-563. |
| 50 | Yang S, Xiao R, Hu T Z, et al. Ni2P electrocatalysts decorated hollow carbon spheres as bi-functional mediator against shuttle effect and Li dendrite for Li-S batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2021, 90: 106584. |
| 51 | Xiao R, Yu T, Yang S, et al. Electronic structure adjustment of lithium sulfide by a single-atom copper catalyst toward high-rate lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 51: 890-899. |
| 52 | Yan B, Li Y, Gao L, et al. Confining ZnS/SnS2 ultrathin heterostructured nanosheets in hollow N-doped carbon nanocubes as novel sulfur host for advanced Li-S batteries[J]. Small, 2022, 18(24): e2107727. |
| 53 | Yan L, Zhang Z X, Yu F, et al. Rational design of NiCo2S4@MoS2 ball-in-ball heterostructure nanospheres for advanced lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 383: 138268. |
| 54 | Han P, Chung S H, Manthiram A. Pyrrolic-type nitrogen-doped hierarchical macro/mesoporous carbon as a bifunctional host for high-performance thick cathodes for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Small, 2019, 15(16): 1900690. |
| 55 | Cheng D D, Zhao Y L, An T, et al. 3D interconnected crumpled porous carbon sheets modified with high-level nitrogen doping for high performance lithium sulfur batteries[J]. Carbon, 2019, 154: 58-66. |
| 56 | Liu J, Wei A X, Pan G X, et al. Atomic layer deposition-assisted construction of binder-free Ni@N-doped carbon nanospheres films as advanced host for sulfur cathode[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2019, 11(1): 1-14. |
| 57 | Li Z, Zhou H Y, Zhao F L, et al. Three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks as host materials for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 2020, 38(5): 550-557. |
| 58 | Du B W, Luo Y H, Yang Y Q, et al. COFs-confined multifunctional sulfur-host design towards high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 442: 135823. |
| 59 | Zhu F L, Tao Y L, Bao H F, et al. Ferroelectric metal-organic framework as a host material for sulfur to alleviate the shuttle effect of lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2020, 26(61): 13779-13782. |
| 60 | Fan X L, Liu Y Q, Tan J Y, et al. An ultrathin and highly efficient interlayer for lithium-sulfur batteries with high sulfur loading and lean electrolyte[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(14): 7653-7659. |
| 61 | Xiao R, Yang S, Yu T, et al. A janus separator for inhibiting shuttle effect and lithium dendrite in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Batteries & Supercaps, 2022, 5(4): e202100389. |
| 62 | Dong Q, Wang T, Gan R Y, et al. Balancing the seesaw: investigation of a separator to grasp polysulfides with diatomic chemisorption[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(18): 20596-20604. |
| 63 | Xu J, Bi S M, Tang W Q, et al. Duplex trapping and charge transfer with polysulfides by a diketopyrrolopyrrole-based organic framework for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(30): 18100-18108. |
| 64 | Yang L W, Wang Y, Li Q, et al. Inhibition of the shuttle effect of lithium-sulfur batteries via a tannic acid-metal one-step in situ chemical film-forming modified separator[J]. Nanoscale, 2021, 13(9): 5058-5068. |
| 65 | Wei Z Z, Zhang N X, Feng T, et al. A copolymer microspheres-coated separator to enhance thermal stability of lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 430: 132678. |
| 66 | Wang P, Zhang Z A, Hong B, et al. Multifunctional porous VN nanowires interlayer as polysulfides barrier for high performance lithium sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2019, 832: 475-479. |
| 67 | Song N, Xi B J, Wang P, et al. Immobilizing VN ultrafine nanocrystals on N-doped carbon nanosheets enable multiple effects for high-rate lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nano Research, 2022, 15(2): 1424-1432. |
| 68 | Xu J, Yang L K, Cao S F, et al. Sandwiched cathodes assembled from CoS2-modified carbon clothes for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2021, 8(16): 2101019. |
| 69 | Liang X, Kwok C Y, Lodi-Marzano F, et al. Tuning transition metal oxide-sulfur interactions for long life lithium sulfur batteries: the "Goldilocks" principle[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(6): 1501636. |
| 70 | Li S, Cen Y, Xiang Q, et al. Vanadium dioxide-reduced graphene oxide binary host as an efficient polysulfide plague for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(4): 1658-1668. |
| 71 | Patil S B, Kim H J, Lim H K, et al. Exfoliated 2D lepidocrocite titanium oxide nanosheets for high sulfur content cathodes with highly stable Li-S battery performance[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(2): 412-419. |
| 72 | Li Q, Ma Z P, Li J J, et al. Core-shell-structured sulfur cathode: ultrathin δ-MnO2 nanosheets as the catalytic conversion shell for lithium polysulfides in high sulfur content lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(31): 35049-35057. |
| 73 | Chen S J, Zhang J X, Wang Z Y, et al. Electrocatalytic NiCo2O4 nanofiber arrays on carbon cloth for flexible and high-loading lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(12): 5285-5292. |
| 74 | Zhou J, Lin N, long Cai W, et al. Synthesis of S/CoS2 nanoparticles-embedded N-doped carbon polyhedrons from polyhedrons ZIF-67 and their properties in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 218: 243-251. |
| 75 | Zhou N, Dong W D, Zhang Y J, et al. Embedding tin disulfide nanoparticles in two-dimensional porous carbon nanosheet interlayers for fast-charging lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Science China Materials, 2021, 64(11): 2697-2709. |
| 76 | Li S, Xu P, Aslam M K, et al. Propelling polysulfide conversion for high-loading lithium-sulfur batteries through highly sulfiphilic NiCo2S4 nanotubes[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 27: 51-60. |
| 77 | Wang H X, Wei D, Zheng J C, et al. Electrospinning MoS2-decorated porous carbon nanofibers for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3(12): 11893-11899. |
| 78 | Mosavati N, Salley S O, Ng K Y S. Characterization and electrochemical activities of nanostructured transition metal nitrides as cathode materials for lithium sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 340: 210-216. |
| 79 | Li C C, Shi J J, Zhu L, et al. Titanium nitride hollow nanospheres with strong lithium polysulfide chemisorption as sulfur hosts for advanced lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nano Research, 2018, 11(8): 4302-4312. |
| 80 | Gan R Y, Yang N, Dong Q, et al. Enveloping ultrathin Ti3C2 nanosheets on carbon fibers: a high-density sulfur loaded lithium-sulfur battery cathode with remarkable cycling stability[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(15): 7253-7260. |
| 81 | Yang D W, Zhang C Q, Biendicho J J, et al. ZnSe/N-doped carbon nanoreactor with multiple adsorption sites for stable lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(11): 15492-15504. |
| 82 | Kong L, Chen X, Li B Q, et al. A bifunctional perovskite promoter for polysulfide regulation toward stable lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(2): 1705219. |
| 83 | Yuan H, Peng H J, Li B Q, et al. Conductive and catalytic triple-phase interfaces enabling uniform nucleation in high-rate lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(1): 1802768. |
| 84 | Wu D S, Shi F, Zhou G, et al. Quantitative investigation of polysulfide adsorption capability of candidate materials for Li-S batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 13: 241-246. |
| 85 | Li J B, Qu Y R, Chen C Y, et al. Theoretical investigation on lithium polysulfide adsorption and conversion for high-performance Li-S batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2021, 13(1): 15-35. |
| 86 | Zhu Y J, Wang C S. Galvanostatic intermittent titration technique for phase-transformation electrodes[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(6): 2830-2841. |
| 87 | Dees D W, Kawauchi S, Abraham D P, et al. Analysis of the galvanostatic intermittent titration technique (GITT) as applied to a lithium-ion porous electrode[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 189(1): 263-268. |
| 88 | Yang B, Jiang H R, Zhou Y C, et al. Critical role of anion donicity in Li2S deposition and sulfur utilization in Li-S batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(29): 25940-25948. |
| 89 | Cai D Q, Yang J L, Liu T, et al. Interfaces-dominated Li2S nucleation behavior enabled by heterostructure catalyst for fast kinetics Li-S batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2021, 89: 106452. |
| 90 | Yang J L, Cai D Q, Hao X G, et al. Rich heterointerfaces enabling rapid polysulfides conversion and regulated Li2S deposition for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(7): 11491-11500. |
| 91 | Xu R, Tang H A, Zhou Y Y, et al. Enhanced catalysis of LiS3· radical-to-polysulfide interconversion via increased sulfur vacancies in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Science, 2022, 13(21): 6224-6232. |
| [1] | Cheng CHENG, Zhongdi DUAN, Haoran SUN, Haitao HU, Hongxiang XUE. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of surface microstructure effect on crystallization fouling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [2] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [3] | Bingchun SHENG, Jianguo YU, Sen LIN. Study on lithium resource separation from underground brine with high concentration of sodium by aluminum-based lithium adsorbent [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3375-3385. |
| [4] | Ruihang ZHANG, Pan CAO, Feng YANG, Kun LI, Peng XIAO, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Changyu SUN, Guangjin CHEN. Analysis of key parameters affecting product purity of natural gas ethane recovery process via ZIF-8 nanofluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [5] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [6] | Yan GAO, Peng WU, Chao SHANG, Zejun HU, Xiaodong CHEN. Preparation of magnetic agarose microspheres based on a two-fluid nozzle and their protein adsorption properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3457-3471. |
| [7] | Linzheng WANG, Yubing LU, Ruizhi ZHANG, Yonghao LUO. Analysis on thermal oxidation characteristics of VOCs based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [8] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [9] | Ji CHEN, Ze HONG, Zhao LEI, Qiang LING, Zhigang ZHAO, Chenhui PENG, Ping CUI. Study on coke dissolution loss reaction and its mechanism based on molecular dynamics simulations [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2935-2946. |
| [10] | Yaxin CHEN, Hang YUAN, Guanzhang LIU, Lei MAO, Chun YANG, Ruifang ZHANG, Guangya ZHANG. Advances in enzyme self-immobilization mediated by protein nanocages [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [11] | Xiaoling TANG, Jiarui WANG, Xuanye ZHU, Renchao ZHENG. Biosynthesis of chiral epichlorohydrin by halohydrin dehalogenase based on Pickering emulsion system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2926-2934. |
| [12] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [13] | Yuanhao QU, Wenyi DENG, Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU. Study on electro-osmotic dewatering of sludge assisted by activated carbon/graphite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [14] | Jie WANG, Xiaolin QIU, Ye ZHAO, Xinyang LIU, Zhongqiang HAN, Yong XU, Wenhan JIANG. Preparation and properties of polyelectrolyte electrostatic deposition modified PHBV antioxidant films [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [15] | Tan ZHANG, Guang LIU, Jinping LI, Yuhan SUN. Performance regulation strategies of Ru-based nitrogen reduction electrocatalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||