CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (7): 3038-3050.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230354
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuanhao QU( ), Wenyi DENG(
), Wenyi DENG( ), Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU
), Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU
Received:2023-04-10
Revised:2023-06-10
Online:2023-08-31
Published:2023-07-05
Contact:
Wenyi DENG
通讯作者:
邓文义
作者简介:屈园浩(1997—),男,硕士研究生,15503949225@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yuanhao QU, Wenyi DENG, Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU. Study on electro-osmotic dewatering of sludge assisted by activated carbon/graphite[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050.
屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 含水率/%(质量) | pH | 电导率/(μS/cm) | 灰分(干基)/%(质量) | 挥发分(干基)/%(质量) | 固定碳(干基)/%(质量) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80.0±0.5 | 7.2±0.1 | 1175±50 | 45.9±0.5 | 47.8±0.5 | 6.3±0.5 |
Table 1 Basic properties of sludge
| 含水率/%(质量) | pH | 电导率/(μS/cm) | 灰分(干基)/%(质量) | 挥发分(干基)/%(质量) | 固定碳(干基)/%(质量) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80.0±0.5 | 7.2±0.1 | 1175±50 | 45.9±0.5 | 47.8±0.5 | 6.3±0.5 |
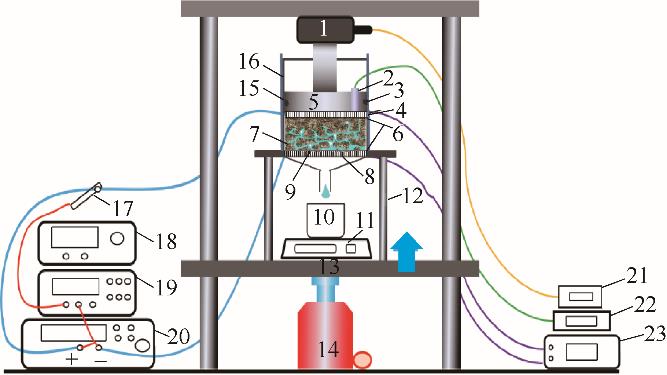
Fig.1 Electro-osmotic dewatering device1—pressure sensor; 2—thermocouple; 3—sealing apron; 4—ruthenium iridium titanium anode plate; 5—piston; 6—filter cloth; 7—sludge sample; 8—bottom filter plate; 9—stainless steel cathode mesh; 10—beaker; 11—electronic balance; 12—bracket; 13—base; 14—jack; 15—insulating sleeve; 16—metal sleeve; 17—current probe; 18—signal generator; 19—oscilloscope; 20—power amplifier; 21—digital display of pressure value; 22—digital display of temperature; 23—voltmeter
| 粒径/mm | 含水率/%(质量) |
|---|---|
| <0.056 | 41.8±0.2 |
| 0.056~0.1 | 41.0±0.2 |
| 0.1~0.335 | 41.3±0.2 |
| 0.335~0.5 | 42.0±0.2 |
| 0.5~0.8 | 42.5±0.2 |
| 0.8~1 | 42.1±0.2 |
Table 2 The results of pre-experiments
| 粒径/mm | 含水率/%(质量) |
|---|---|
| <0.056 | 41.8±0.2 |
| 0.056~0.1 | 41.0±0.2 |
| 0.1~0.335 | 41.3±0.2 |
| 0.335~0.5 | 42.0±0.2 |
| 0.5~0.8 | 42.5±0.2 |
| 0.8~1 | 42.1±0.2 |
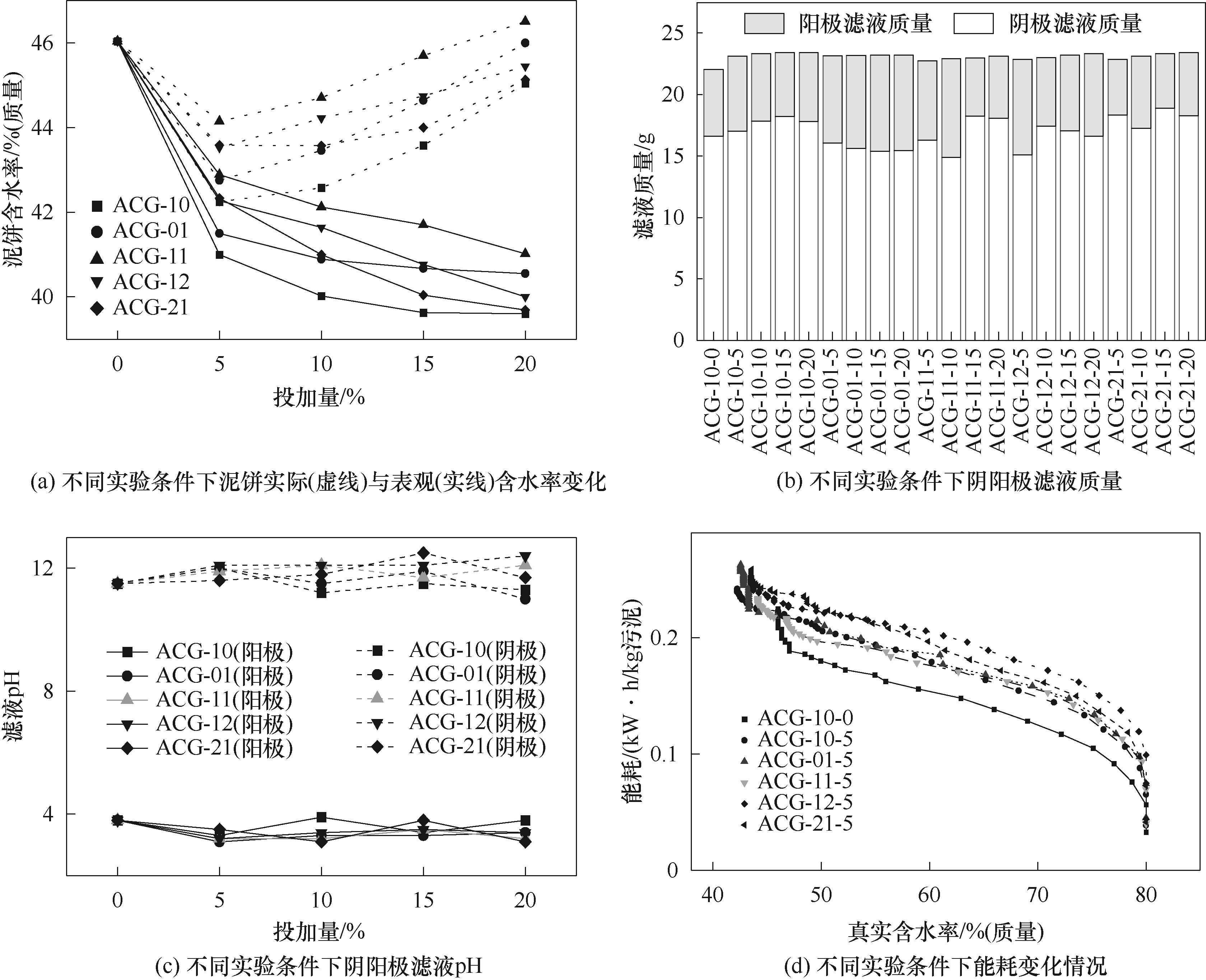
Fig.2 Water content of sewage sludge (a), filtrate content of cathode and anode (b) and pH of filtrate (c) from electro-osmotic dewatering with different percentage of additives, and energy consumption change curve (d)
| 1 | 戴晓虎. 我国污泥处理处置现状及发展趋势[J]. 科学, 2020, 72(6): 30-34, 4. |
| Dai X H. Applications and perspectives of sludge treatment and disposal in China[J]. Science, 2020, 72(6): 30-34, 4. | |
| 2 | Kacprzak M, Neczaj E, Fijałkowski K, et al. Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development [J]. Environmental Research, 2017, 156: 39-46. |
| 3 | Yang G, Zhang G M, Wang H C. Current state of sludge production, management, treatment and disposal in China[J]. Water Research, 2015, 78: 60-73. |
| 4 | Grobelak A, Czerwińska K, Murtaś A. General considerations on sludge disposal, industrial and municipal sludge[M]//Industrial and Municipal Sludge. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019: 135-153. |
| 5 | Qian X, Zhou X Q, Wu J D, et al. Electro-dewatering of sewage sludge: influence of combined action of constant current and constant voltage on performance and energy consumption[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 667: 751-760. |
| 6 | Mahmoud A, Olivier J, Vaxelaire J, et al. Electrical field: a historical review of its application and contributions in wastewater sludge dewatering[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(8): 2381-2407. |
| 7 | Rao B Q, Wang G Q, Xu P. Recent advances in sludge dewatering and drying technology[J]. Drying Technology, 2022, 40(15): 3049-3063. |
| 8 | Wei Y J, Zhou X Q, Zhou L, et al. Electro-dewatering of sewage sludge: effect of near-anode sludge modification with different dosages of calcium oxide[J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 186: 109487. |
| 9 | 王晗. 电渗法在污泥脱水领域应用的影响因素[J]. 中国环保产业, 2022(11): 37-39, 42. |
| Wang H. Factors influencing the application of electroosmosis in the field of sludge dewatering[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry, 2022 (11): 37-39, 42. | |
| 10 | 同帜, 王瑞露, 曹秉帝, 等. 炭材料调理改善活性污泥脱水性能的影响机制[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(7): 2094-2105. |
| Tong Z, Wang R L, Cao B D, et al. Mechanism of carbon conditioning for improving dewatering performance of activated sludge[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2018, 12(7): 2094-2105. | |
| 11 | Mahmoud A, Hoadley A F A, Conrardy J B, et al. Influence of process operating parameters on dryness level and energy saving during wastewater sludge electro-dewatering[J]. Water Research, 2016, 103: 109-123. |
| 12 | Deng W Y, Lai Z C, Hu M H, et al. Effects of frequency and duty cycle of pulsating direct current on the electro-dewatering performance of sewage sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 243: 125372. |
| 13 | Liu C Y, Zhou X Q, Zhou L, et al. Enhancement of sludge electro-dewatering by anthracite powder modification[J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 201: 111510. |
| 14 | Cao B D, Wang R L, Zhang W J, et al. Carbon-based materials reinforced waste activated sludge electro-dewatering for synchronous fuel treatment[J]. Water Research, 2019, 149: 533-542. |
| 15 | Dong Y T, Yuan H P, Ge D D, et al. A novel conditioning approach for amelioration of sludge dewaterability using activated carbon strengthening electrochemical oxidation and realized mechanism[J]. Water Research, 2022, 220: 118704. |
| 16 | 国家质量监督检验检疫总局,国家标准化管理委员会. 煤的工业分析方法: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Proximate analysis of coal: [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. | |
| 17 | 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 纳米技术 碳纳米管粉体电阻率 四探针法: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021. |
| State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Nanotechnology—Resistivity of carbon nanotube powder—Four probe method: [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2021. | |
| 18 | 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 高绝缘电阻测量仪(高阻计)检定规程: [S]. 北京: 中国计量出版社, 2004. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Verification Regulation of High Insulation Resistance Meters: [S]. Beijing: China Metrology Publishing House, 2004. | |
| 19 | 中华人民共和国建设部. 城市污水处理厂污泥检验方法: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. |
| Ministry of Construction of the People's Republic of China. Determination method for municipal sludge in wastewater treatment plant: [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006. | |
| 20 | Cao B D, Zhang W J, Du Y J, et al. Compartmentalization of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) solubilization and cake microstructure in relation to wastewater sludge dewatering behavior assisted by horizontal electric field: effect of operating conditions[J]. Water Research, 2018, 130: 363-375. |
| 21 | Citeau M, Larue O, Vorobiev E. Influence of salt, pH and polyelectrolyte on the pressure electro-dewatering of sewage sludge[J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(6): 2167-2180. |
| 22 | Clayton S A, Scholes O N, Hoadley A F A, et al. Dewatering of biomaterials by mechanical thermal expression[J]. Drying Technology, 2006, 24(7): 819-834. |
| 23 | Lv H, Liu D G, Zhang Y L, et al. Effects of temperature variation on wastewater sludge electro-dewatering[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 214: 873-880. |
| 24 | Weber K, Stahl W. Influence of an electric field on filtration in a filter press[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology: Industrial Chemistry-Plant Equipment-Process Engineering-Biotechnology, 2003, 26(1): 44-48. |
| 25 | Weber K, Stahl W. Improvement of filtration kinetics by pressure electrofiltration[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2002, 26(1): 69-80. |
| 26 | Bergins C, Berger S, Strauß K. Dewatering of fossil fuels and suspensions of ultrafine particles by mechanical/thermal dewatering[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 1999, 22(11): 923-927. |
| 27 | Navab-Daneshmand T, Beton R, Hill R J, et al. Impact of Joule heating and pH on biosolids electro-dewatering[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(9): 5417-5424. |
| 28 | Hu S G, Hu J P, Sun Y F, et al. Simultaneous heavy metal removal and sludge deep dewatering with Fe (Ⅱ) assisted electrooxidation technology [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 405: 124072. |
| 29 | 王瑞露, 刘相汝, 曹秉帝, 等. 炭材料强化污泥电脱水效果及同步燃料化处理[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(11): 4120-4129. |
| Wang R L, Liu X R, Cao B D, et al. Carbon material reinforced sludge electric-dewatering synchronous fuel treatment[J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(11): 4120-4129. | |
| 30 | Rao B Q, Su J G, Xu J, et al. Coupling mechanism and parameter optimization of sewage sludge dewatering jointly assisted by electric field and mechanical pressure[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 817: 152939. |
| 31 | Li Y L, Liu L, Li X R, et al. Influence of alternating electric field on deep dewatering of municipal sludge and changes of extracellular polymeric substance during dewatering[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 842: 156839. |
| 32 | 李亚林, 刘蕾, 张毅, 等. 电渗透/Fe-过硫酸盐氧化协同强化污泥深度脱水[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(9): 4013-4019. |
| Li Y L, Liu L, Zhang Y, et al. Coordination of electro-osmotic and Fe-persulfate oxidation process on sewage sludge deep-dewatering[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(9): 4013-4019. | |
| 33 | Barton W A, Miller S A, Veal C J. The electrodewatering of sewage sludges[J]. Drying Technology, 1999, 17(3): 498-522. |
| [1] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [2] | Chen HAN, Youmin SITU, Bin ZHU, Jianliang XU, Xiaolei GUO, Haifeng LIU. Study of reaction and flow characteristics in multi-nozzle pulverized coal gasifier with co-processing of wastewater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| [3] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [4] | Manzheng ZHANG, Meng XIAO, Peiwei YAN, Zheng MIAO, Jinliang XU, Xianbing JI. Working fluid screening and thermodynamic optimization of hazardous waste incineration coupled organic Rankine cycle system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3502-3512. |
| [5] | Longyi LYU, Wenbo JI, Muda HAN, Weiguang LI, Wenfang GAO, Xiaoyang LIU, Li SUN, Pengfei WANG, Zhijun REN, Guangming ZHANG. Enhanced anaerobic removal of halogenated organic pollutants by iron-based conductive materials: research progress and future perspectives [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3193-3202. |
| [6] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [7] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [8] | Tan ZHANG, Guang LIU, Jinping LI, Yuhan SUN. Performance regulation strategies of Ru-based nitrogen reduction electrocatalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [9] | Zhaoguang CHEN, Yuxiang JIA, Meng WANG. Modeling neutralization dialysis desalination driven by low concentration waste acid and its validation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [10] | Zhen LI, Bo ZHANG, Liwei WANG. Development and properties of PEG-EG solid-solid phase change materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2680-2688. |
| [11] | Ruikang LI, Yingying HE, Weipeng LU, Yuanyuan WANG, Haodong DING, Yongming LUO. Study on the electrochemical enhanced cobalt-based cathode to activate peroxymonosulfate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [12] | Xu GUO, Yongzheng ZHANG, Houbing XIA, Na YANG, Zhenzhen ZHU, Jingyao QI. Research progress in the removal of water pollutants by carbon-based materials via electrooxidation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1862-1874. |
| [13] | Zheng ZHANG, Yongping HE, Haidong SUN, Rongzi ZHANG, Zhengping SUN, Jinlan CHEN, Yixuan ZHENG, Xiao DU, Xiaogang HAO. Electrochemically switched ion exchange device with serpentine flow field for selective extraction of lithium [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2022-2033. |
| [14] | Chengze WANG, Kaili GU, Jinhua ZHANG, Jianxuan SHI, Yiwei LIU, Jinxiang LI. Sulfidation couples with aging to enhance the reactivity of zerovalent iron toward Cr(Ⅵ) in water [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2197-2206. |
| [15] | Han HU, Liang YANG, Chunxiao LI, Daoping LIU. Kinetics of methane storage in the natural tobacco leaching filtrate in the hydrate form [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1313-1321. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||